Nyeta Histopath Prelim-Midterm
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
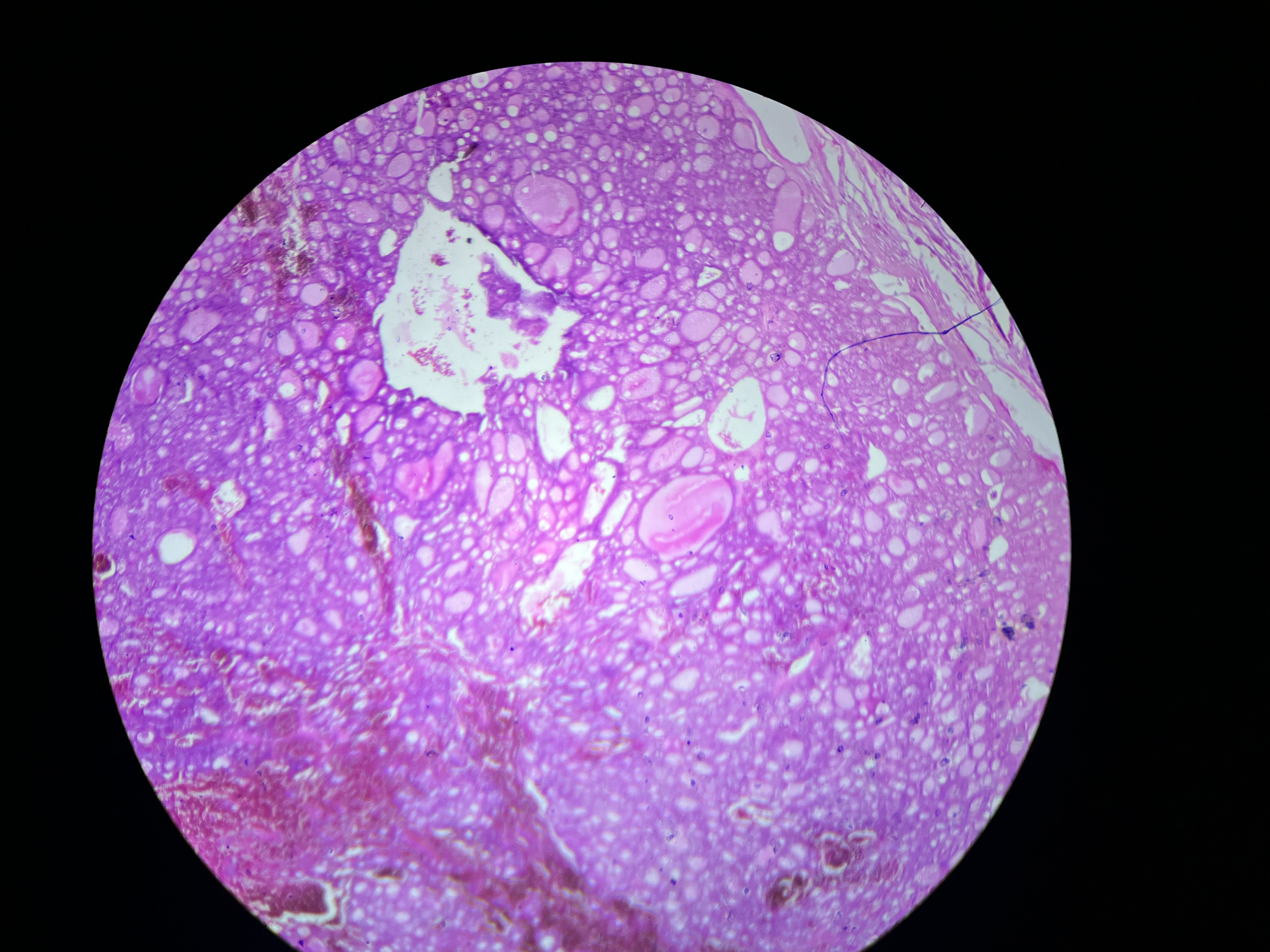
Lipoma, Breast
A benign tumor composed of fatty tissue that occurs in the breast.
Histomorphologic findings: Typically include a well-circumscribed mass composed of mature adipocytes (fat cells) with a fibrous capsule, and no signs of malignancy.
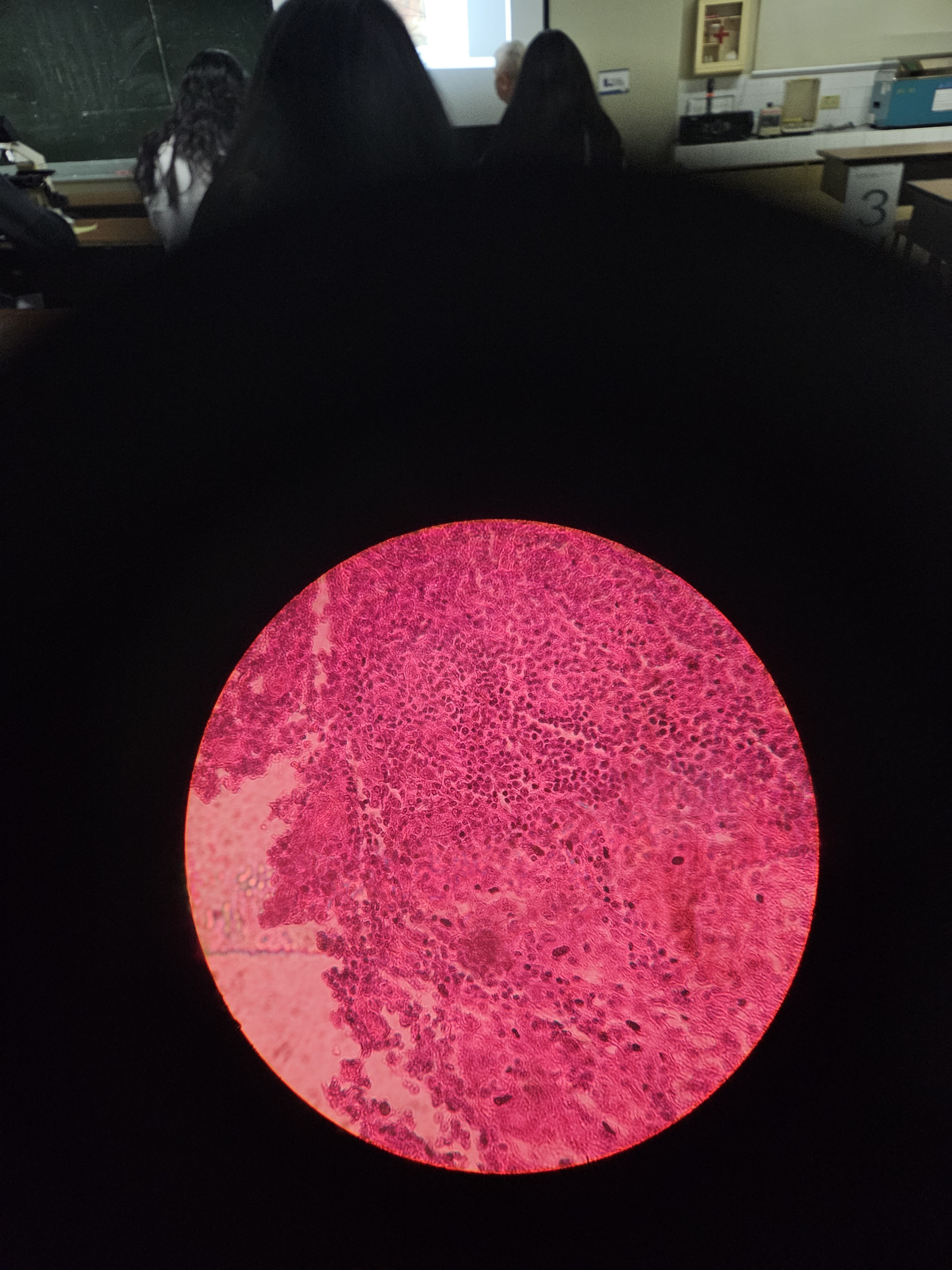
Follicular adenoma, thyroid
A benign tumor of the thyroid gland is characterized by the proliferation of follicular cells, associated with increased levels of thyroglobulin due to the active follicular cell proliferation.
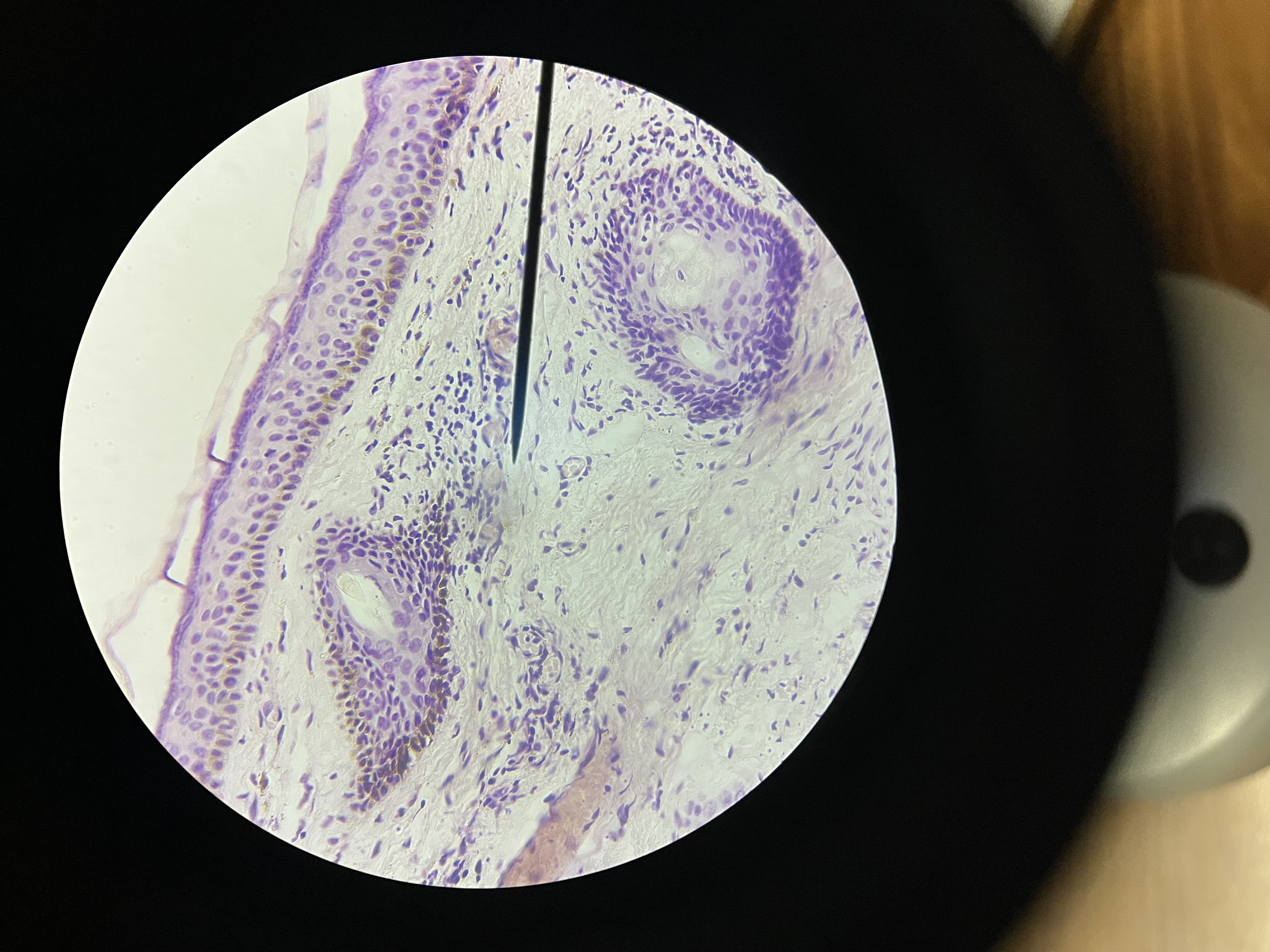
Basal cell carcinoma skin
type of skin cancer that is considered malignant in nature; however, it is typically non-aggressive and rarely metastasizes,considered reversible
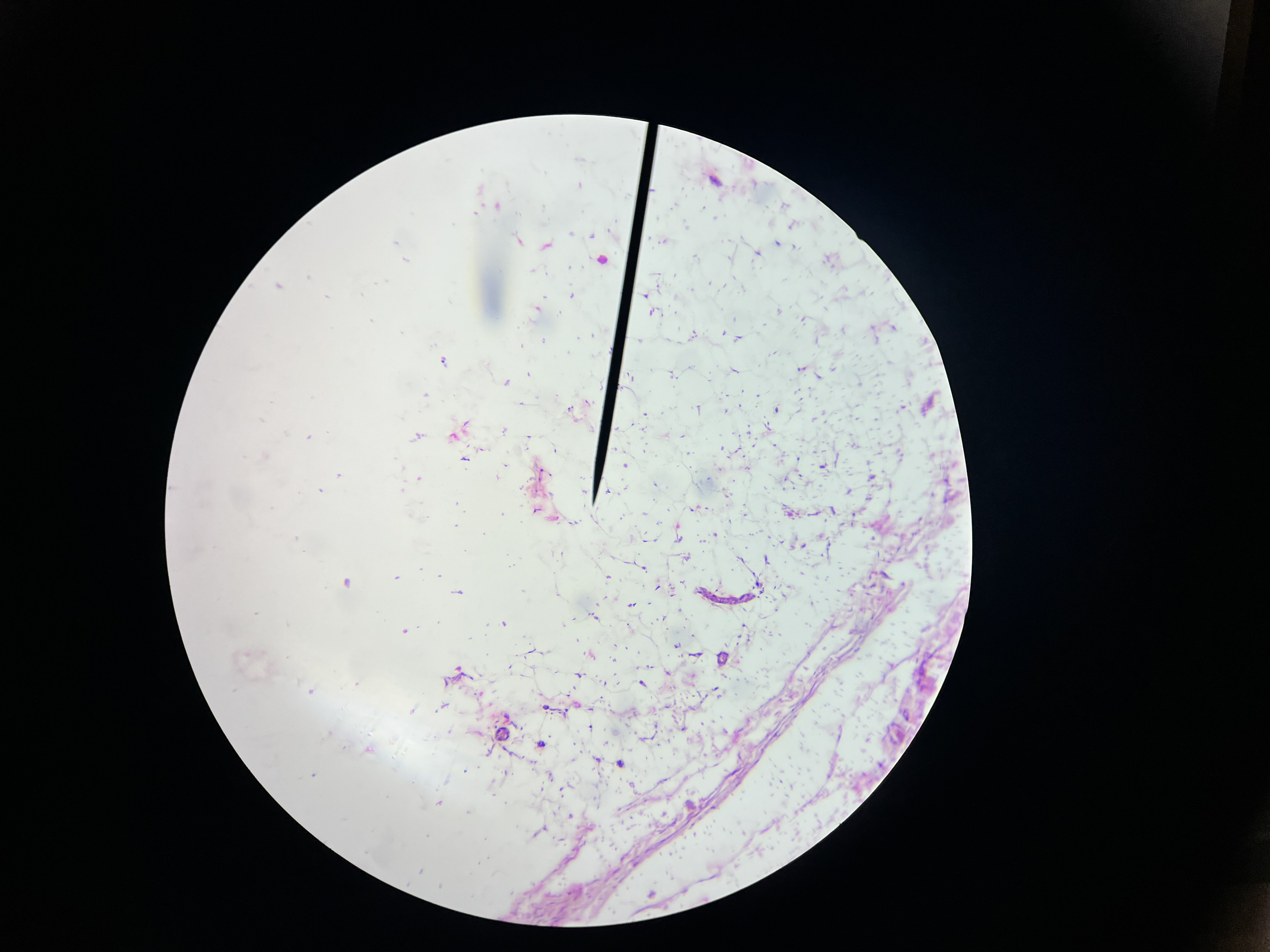
Adenocarcinoma, colon
A malignant tumor that arises from glandular tissue in the colon, increased nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio,and often associated with mutations in the APC gene. It is the most common type of colorectal cancer.
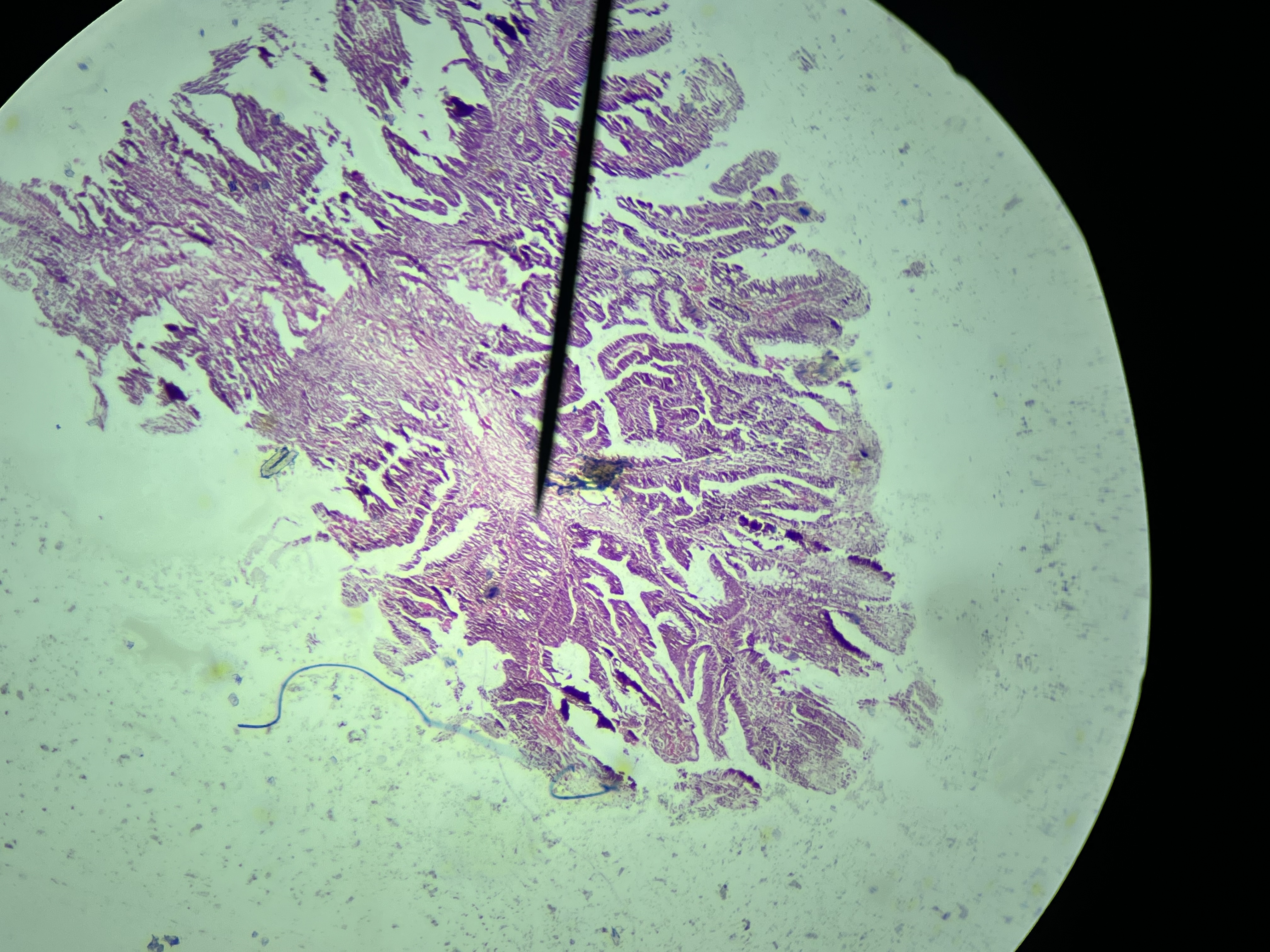
Emphysema Lungs
A chronic lung condition characterized by the destruction of alveoli, leading to reduced elastic recoil and airflow obstruction. Generally considered irreversible, as the damage to lung tissue is permanent
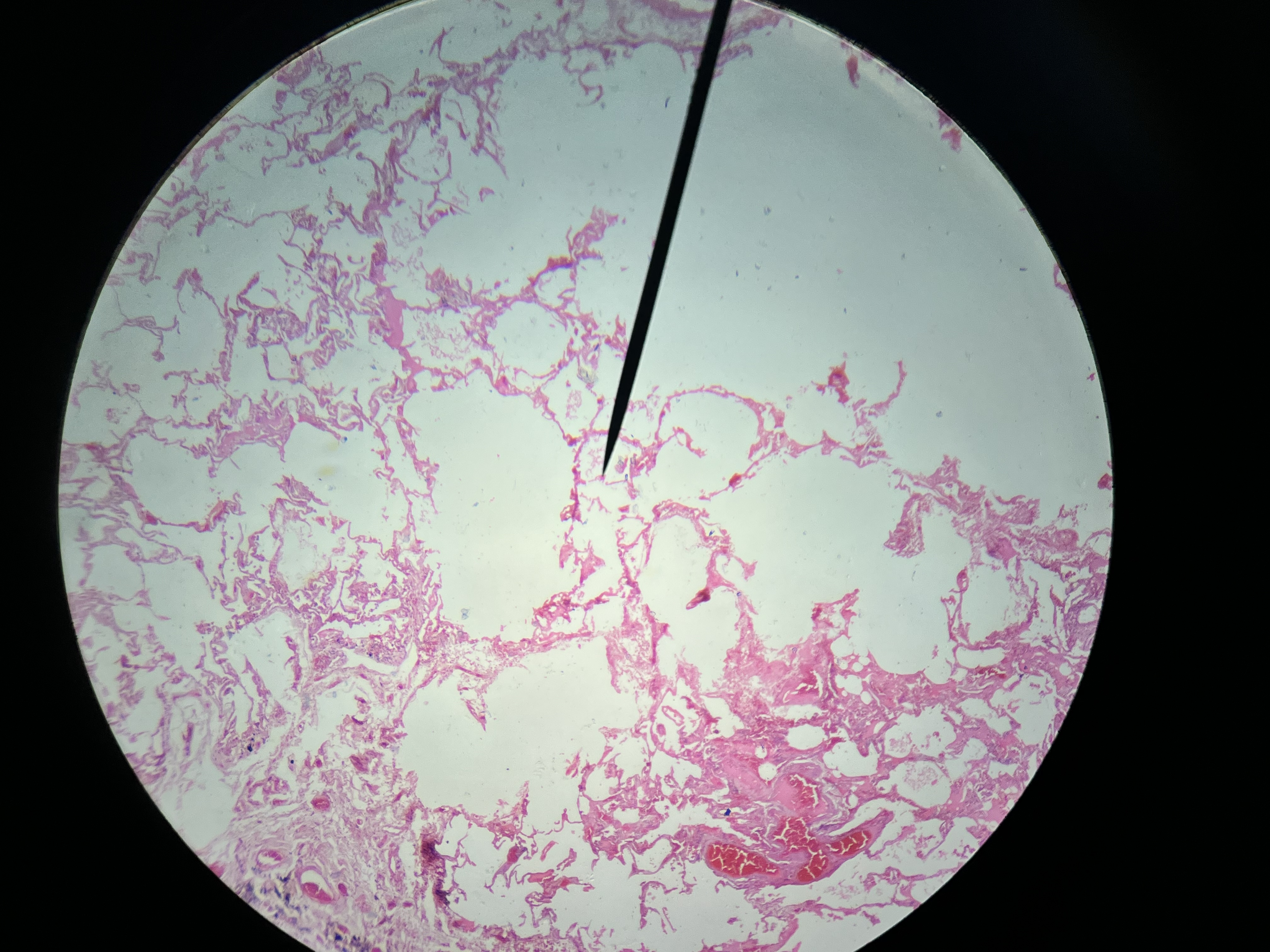
Emphysema, Lungs
Symptoms are Dyspnea, Cachexia, Tachypnea
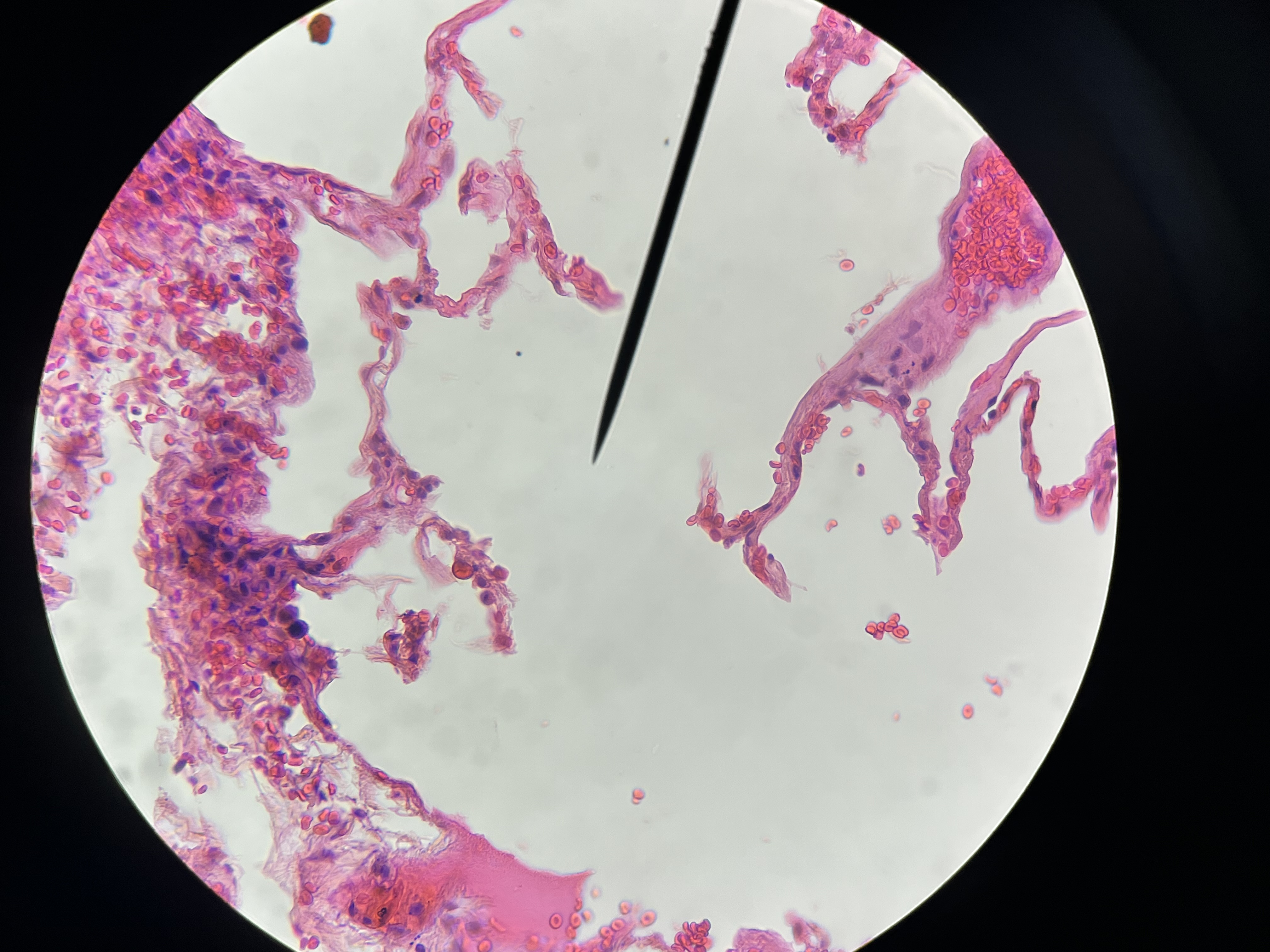
Atherosclerosis, Aorta
Histomorphologic findings: typically include the presence of atherosclerotic plaques characterized by a fibrous cap and a necrotic core, with accumulation of lipids.
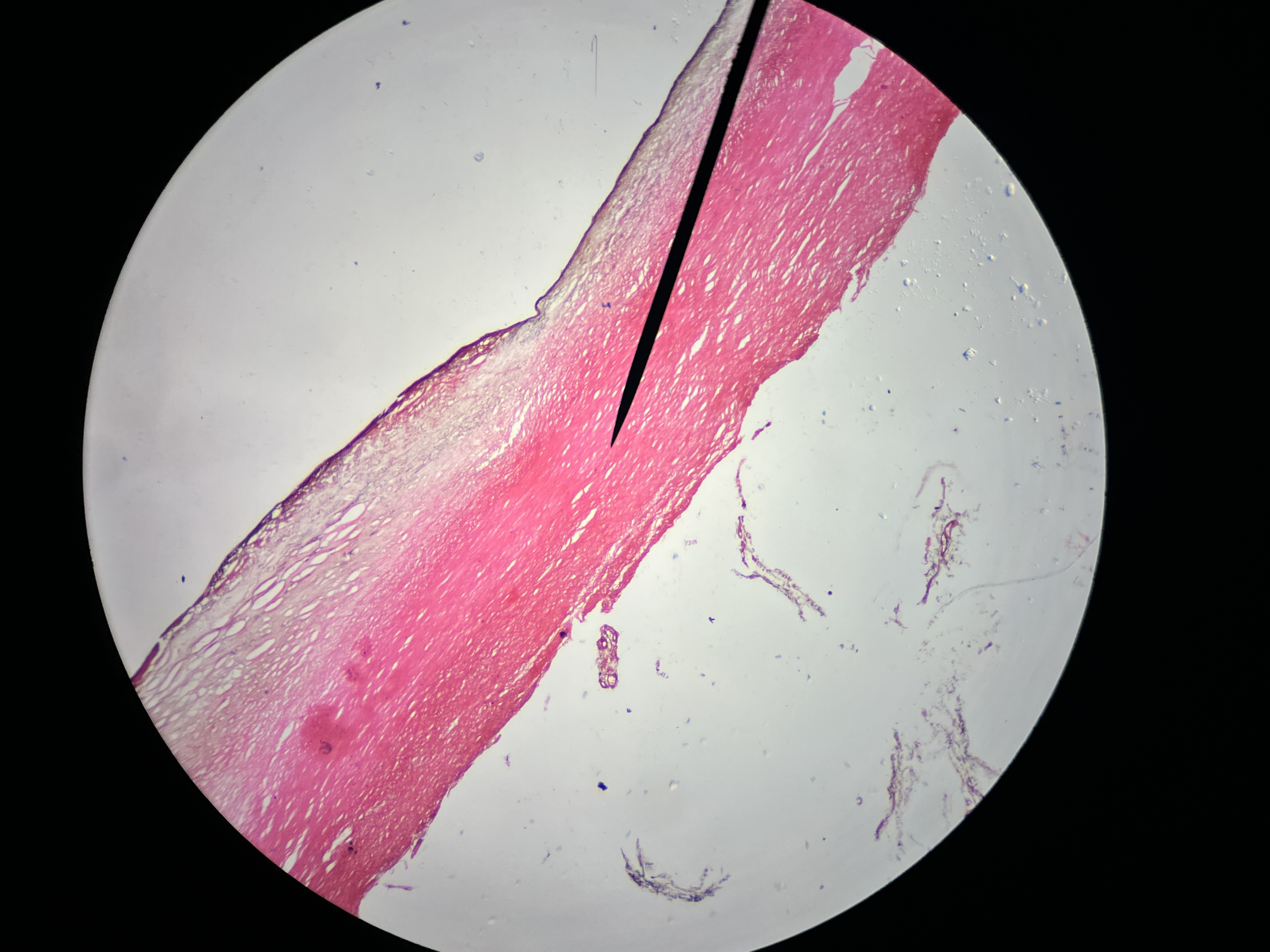
Atherosclerosis, Aorta
characterized by a fibrous cap and a necrotic core, with accumulation of lipids.
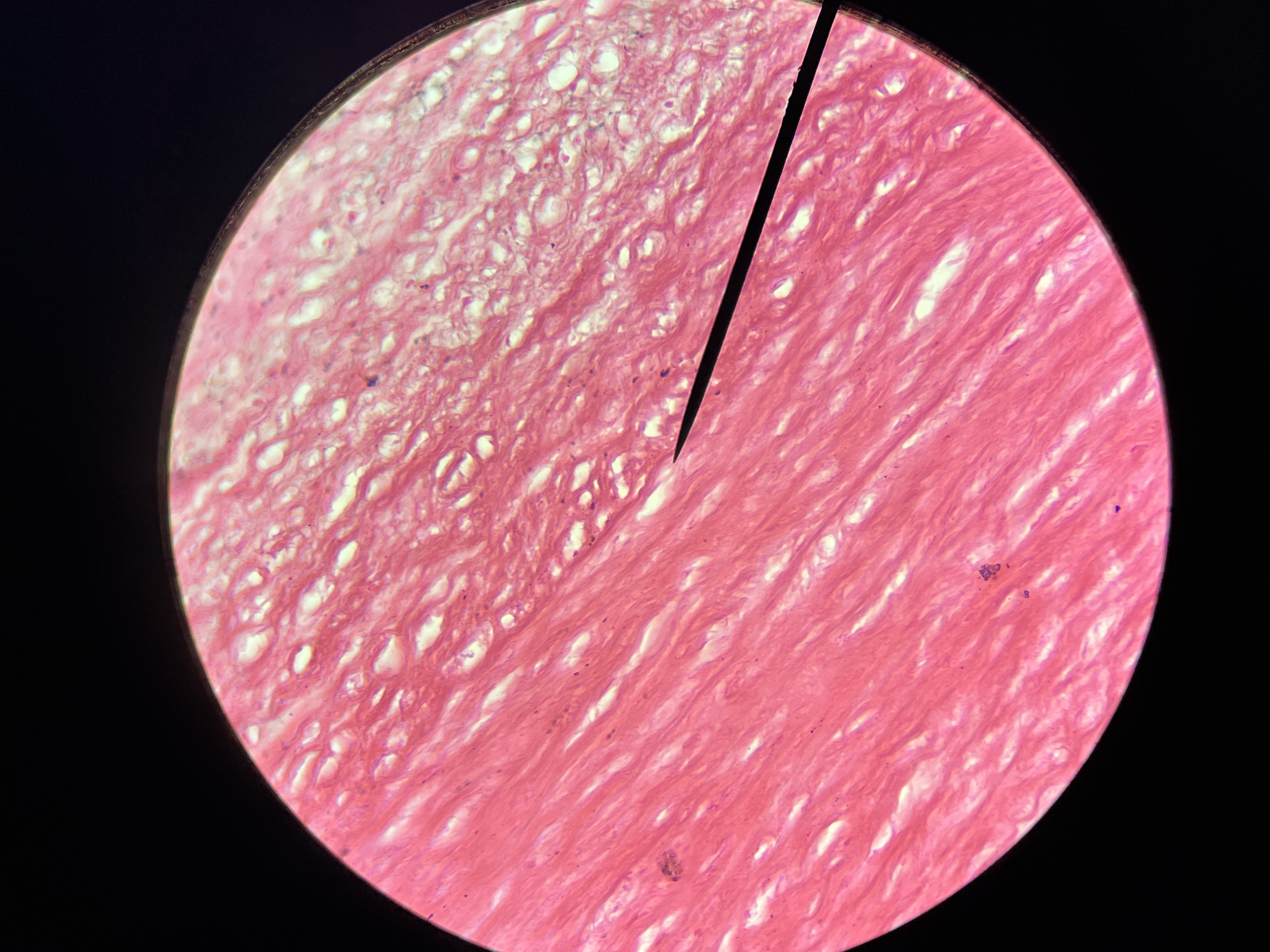
Fatty change, liver
A reversible condition where excess fat accumulates in liver cells, often associated with alcohol consumption or metabolic disorders.
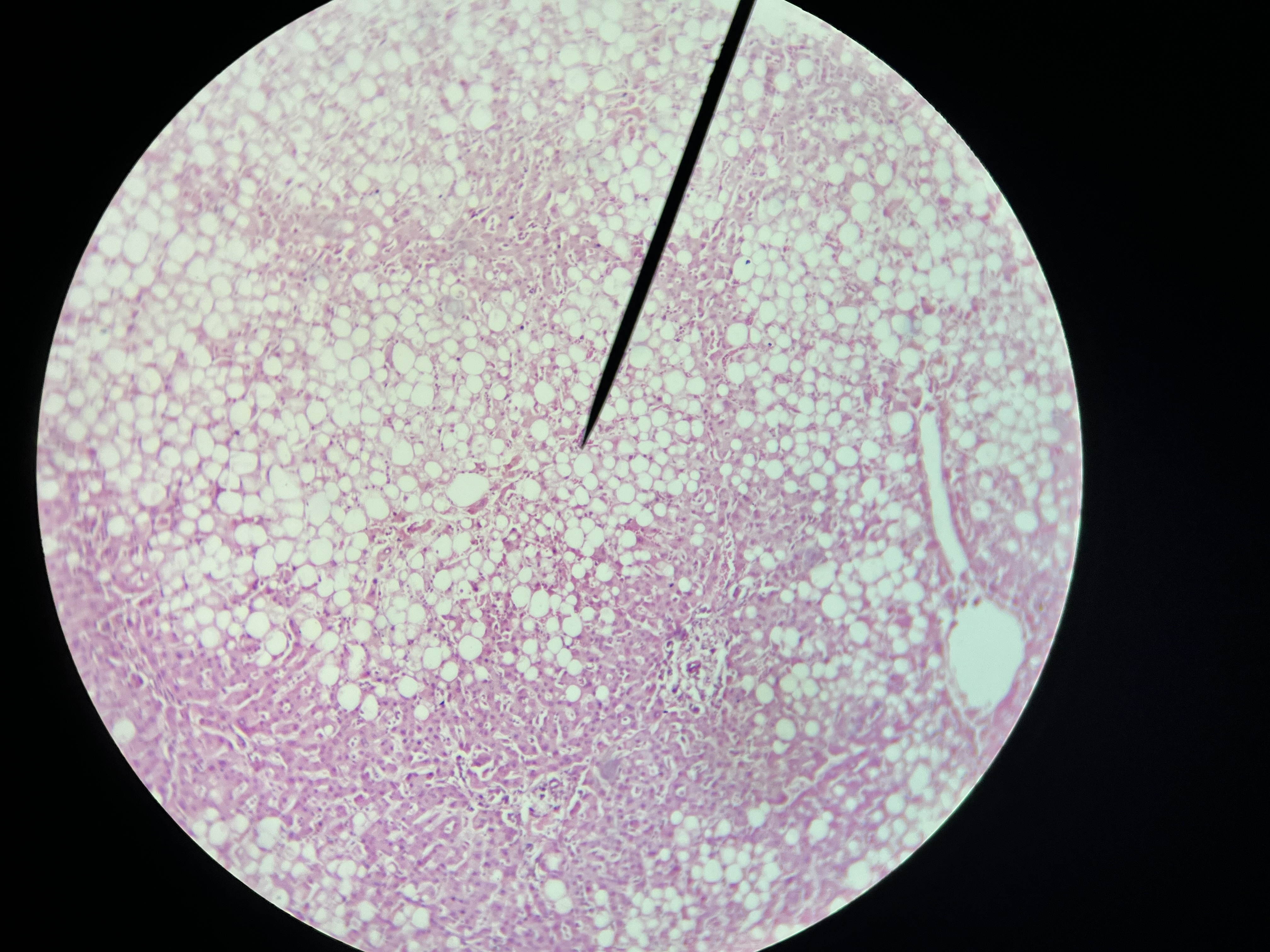
Fatty change, liver
Histomorphologic findings include the accumulation of fat within hepatocytes, which can present as macrovesicular or microvesicular steatosis.
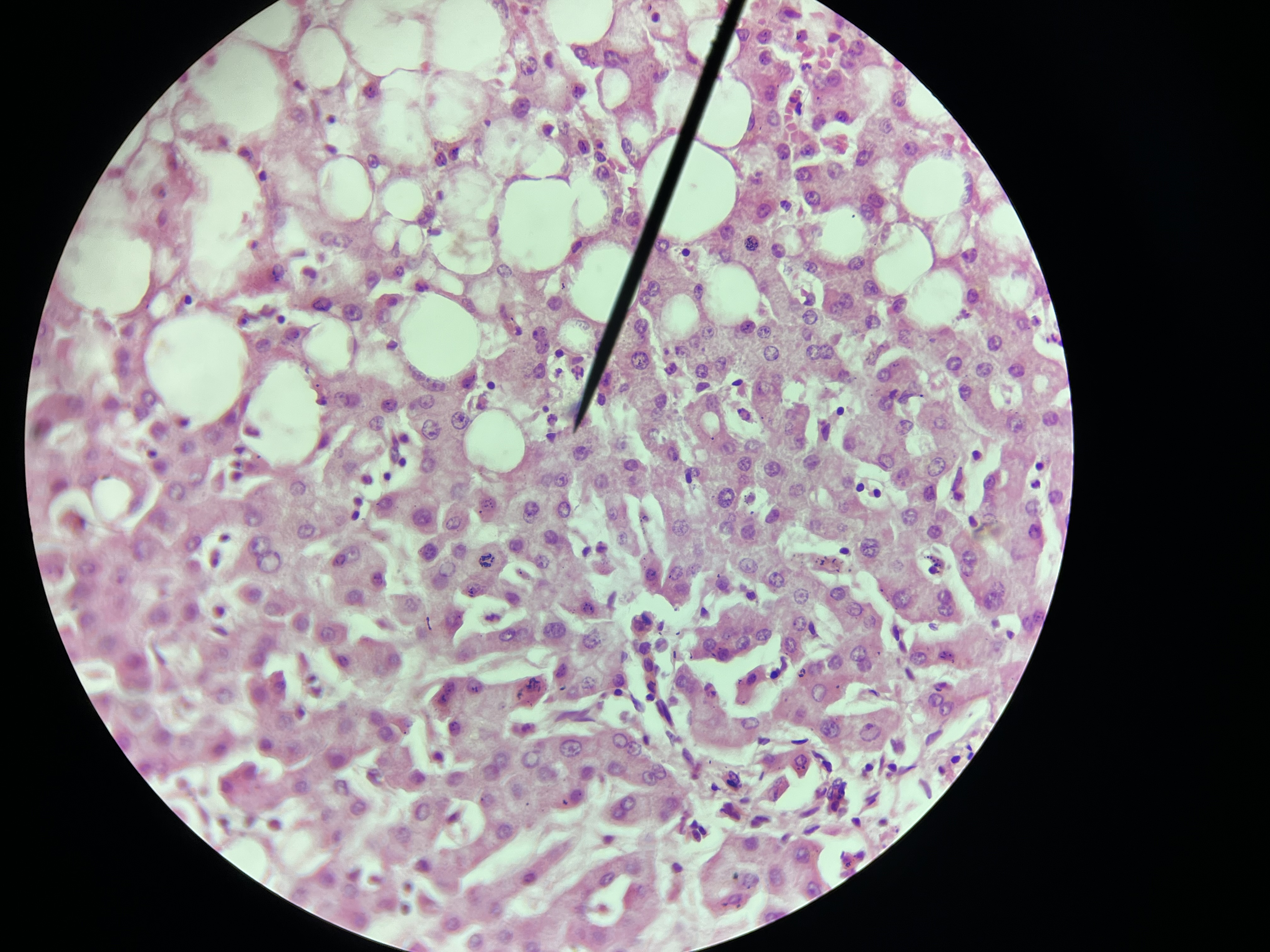
Hashimoto thyroiditis
An autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the thyroid gland, leading to hypothyroidism and often characterized by thyroid enlargement.
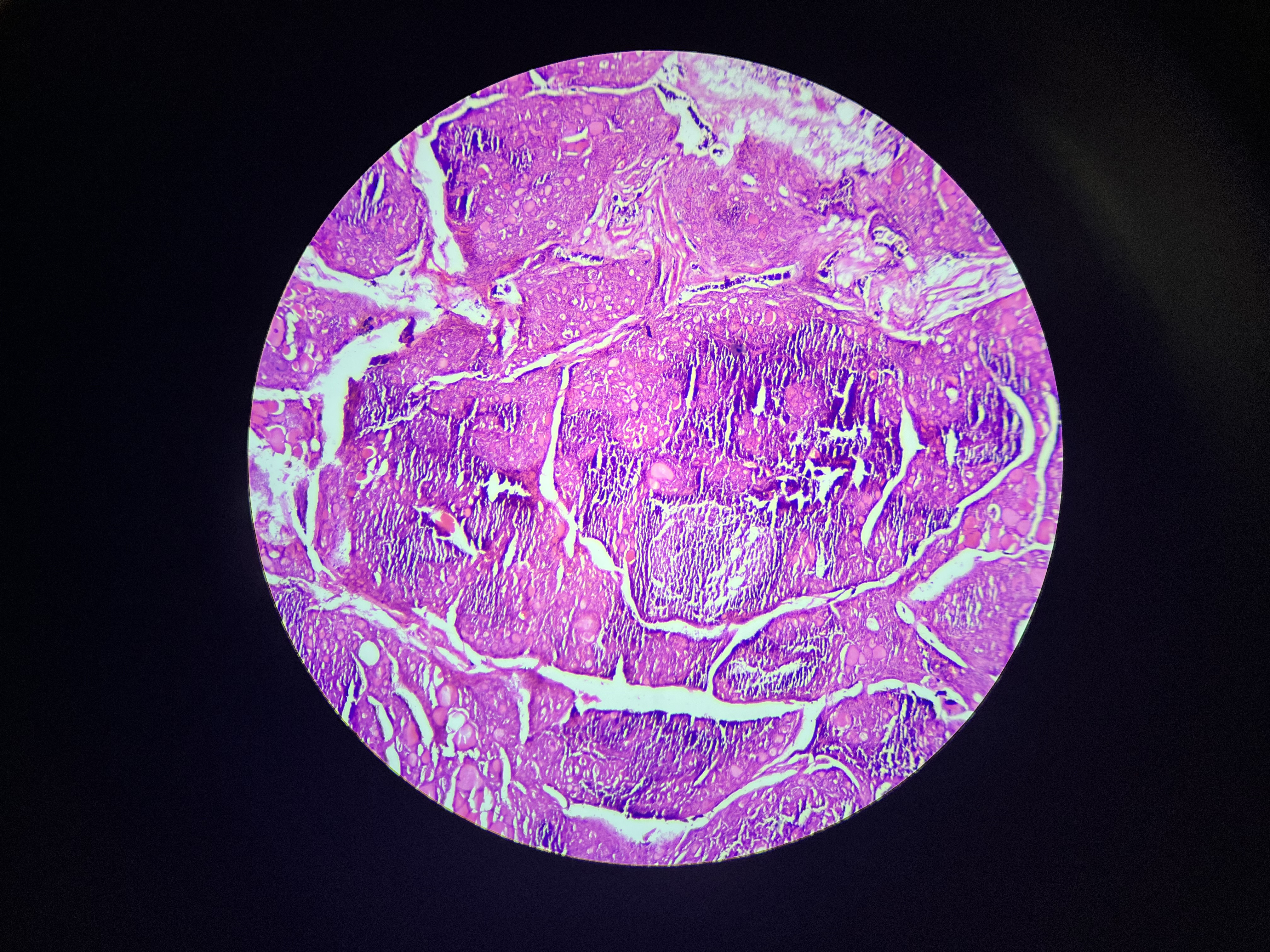
Hashimoto thyroiditis
Histomorphologic findings include significant lymphocytic infiltration of the thyroid gland, characterized by the presence of germinal centers, which are areas of active B-cell proliferation.
The infiltrate often leads to destruction of the thyroid follicles, causing a reduction in hormone production. Patients often present with thyroid enlargement (goiter), fatigue, weight gain, and sensitivity to cold due to decreased metabolic rate.
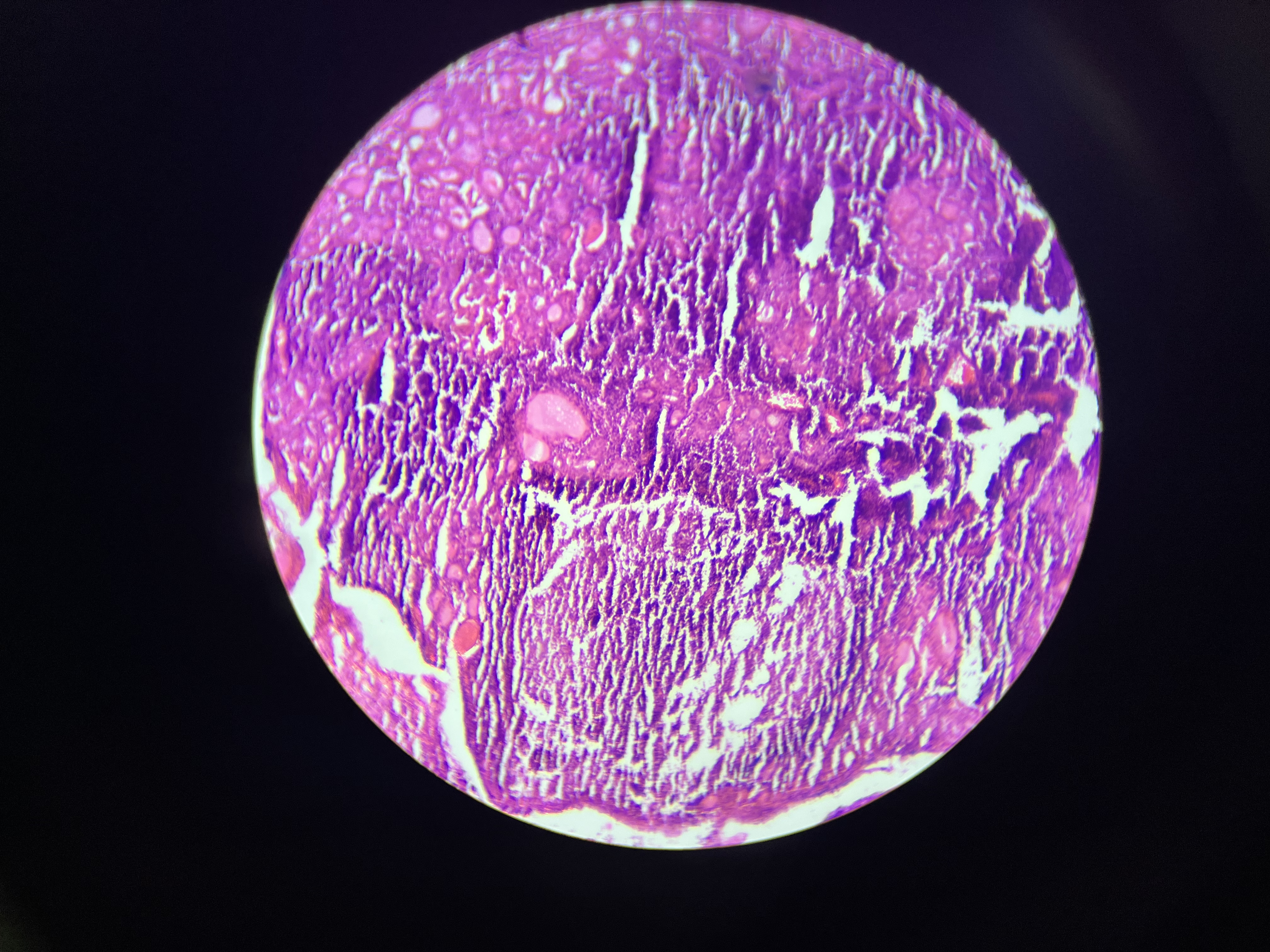
Parathyroid adenoma
A benign tumor of the parathyroid gland that results in increased secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH), leading to hypercalcemia and associated symptoms such as weakness, fatigue, and kidney stones.
Parathyroid adenoma
Histomorphologic finding: Oxyphil cells, Proliferating chief cells.
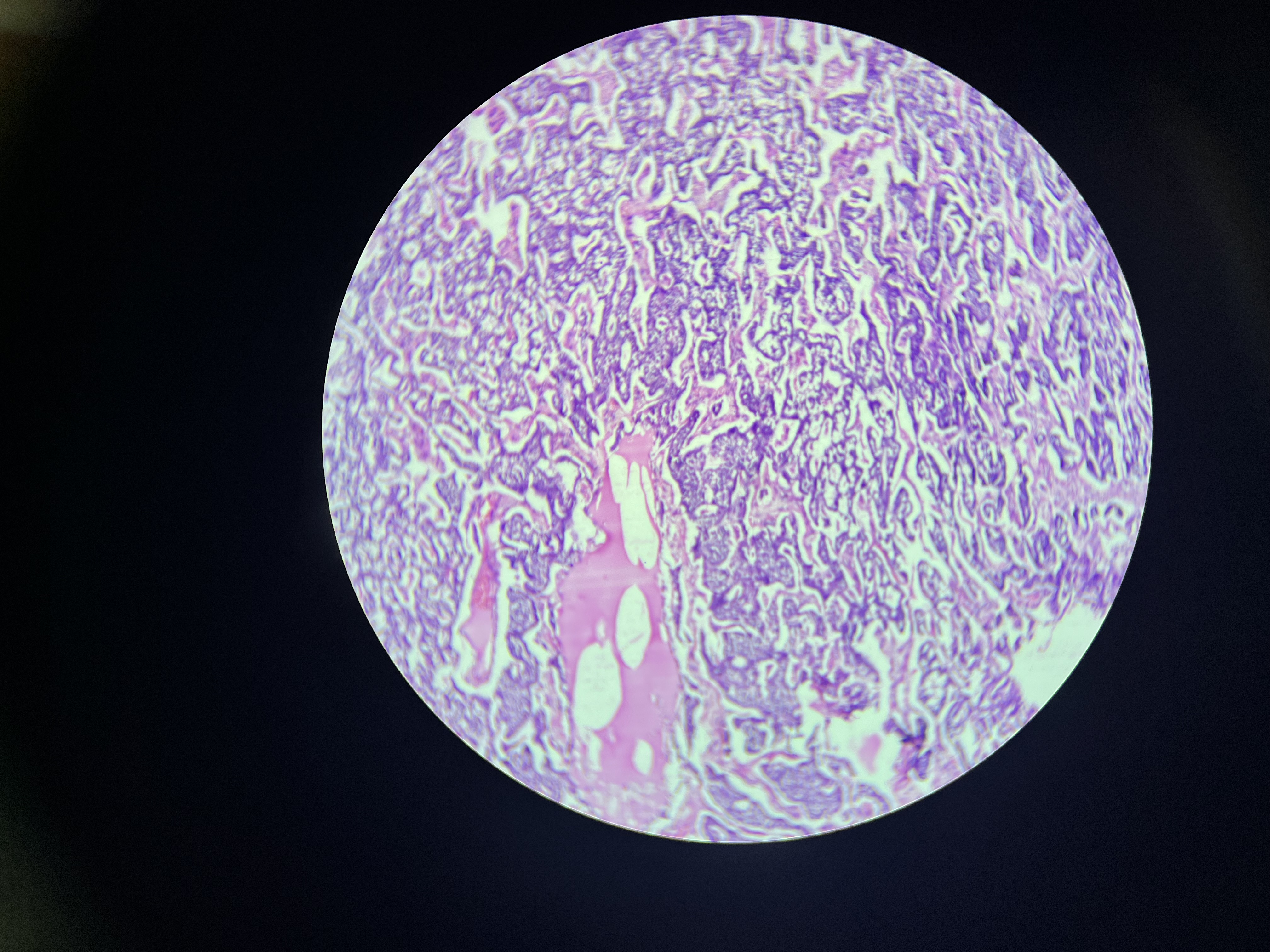
Adrenal hemorrhage
A severe form of adrenal hemorrhage typically associated with infection, most commonly Neisseria meningitidis, leading to adrenal gland failure and often causing shock due to the rapid loss of adrenal hormones.
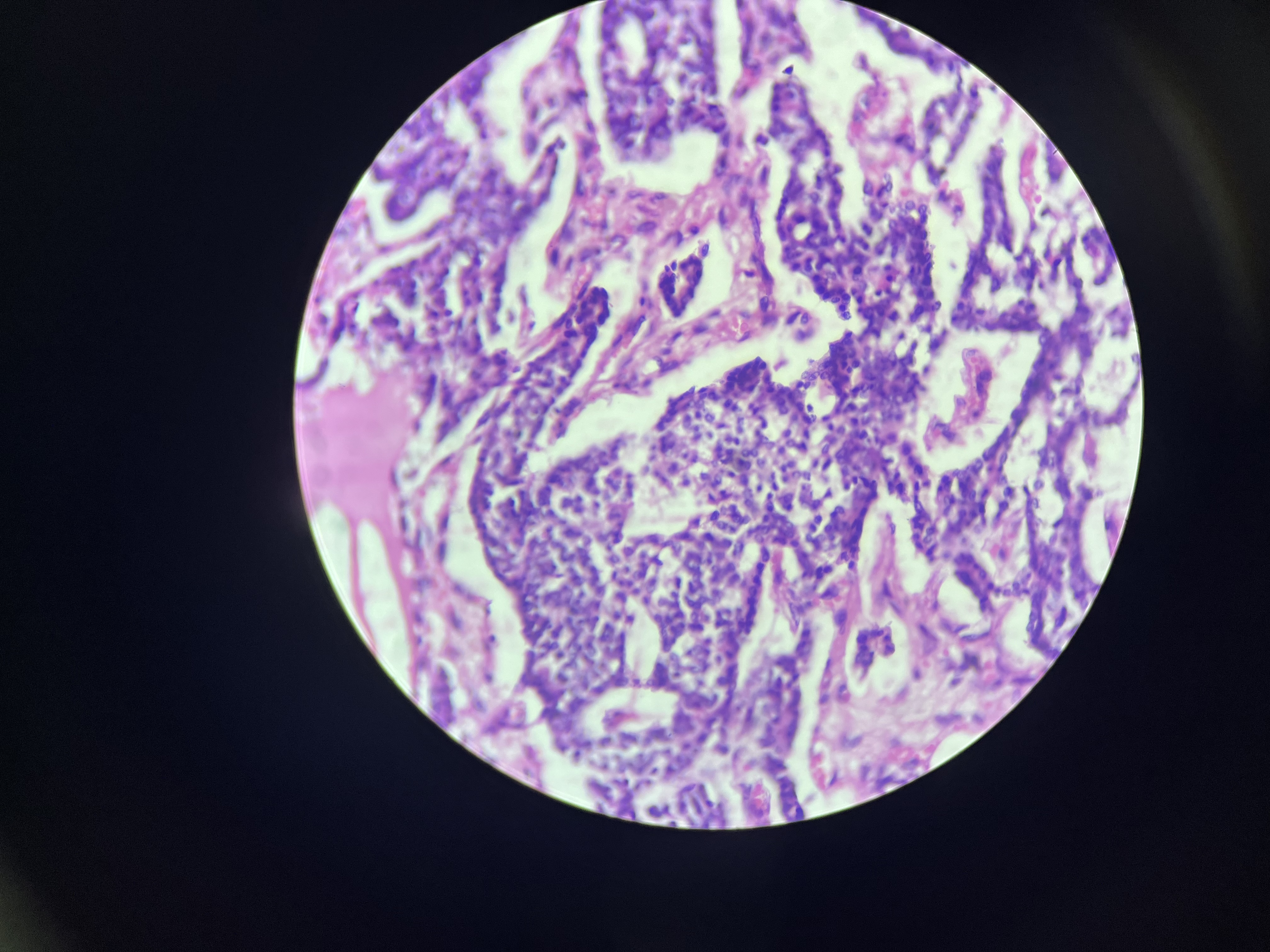
Diabetic Nephropathy
A progressive kidney disease caused by diabetes, characterized by damage to the kidney’s filtering system. This condition is considered chronic.
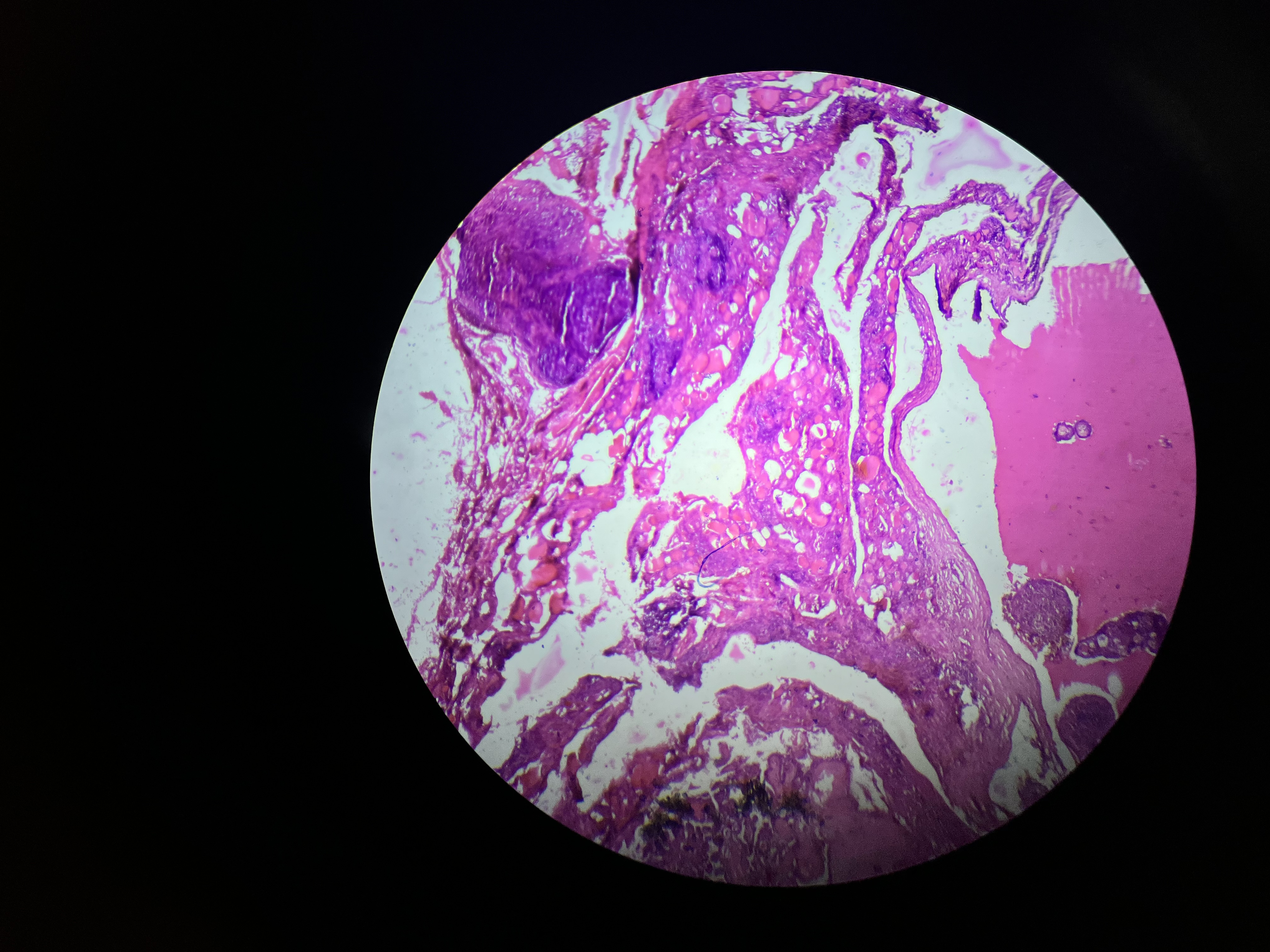
Papillary Carcinoma, Thyroid
The most common type of thyroid cancer, characterized by follicular cell origin and often presenting as a slow-growing mass.
It typically has a good prognosis and may exhibit features such as psammoma bodies and nuclear atypia.
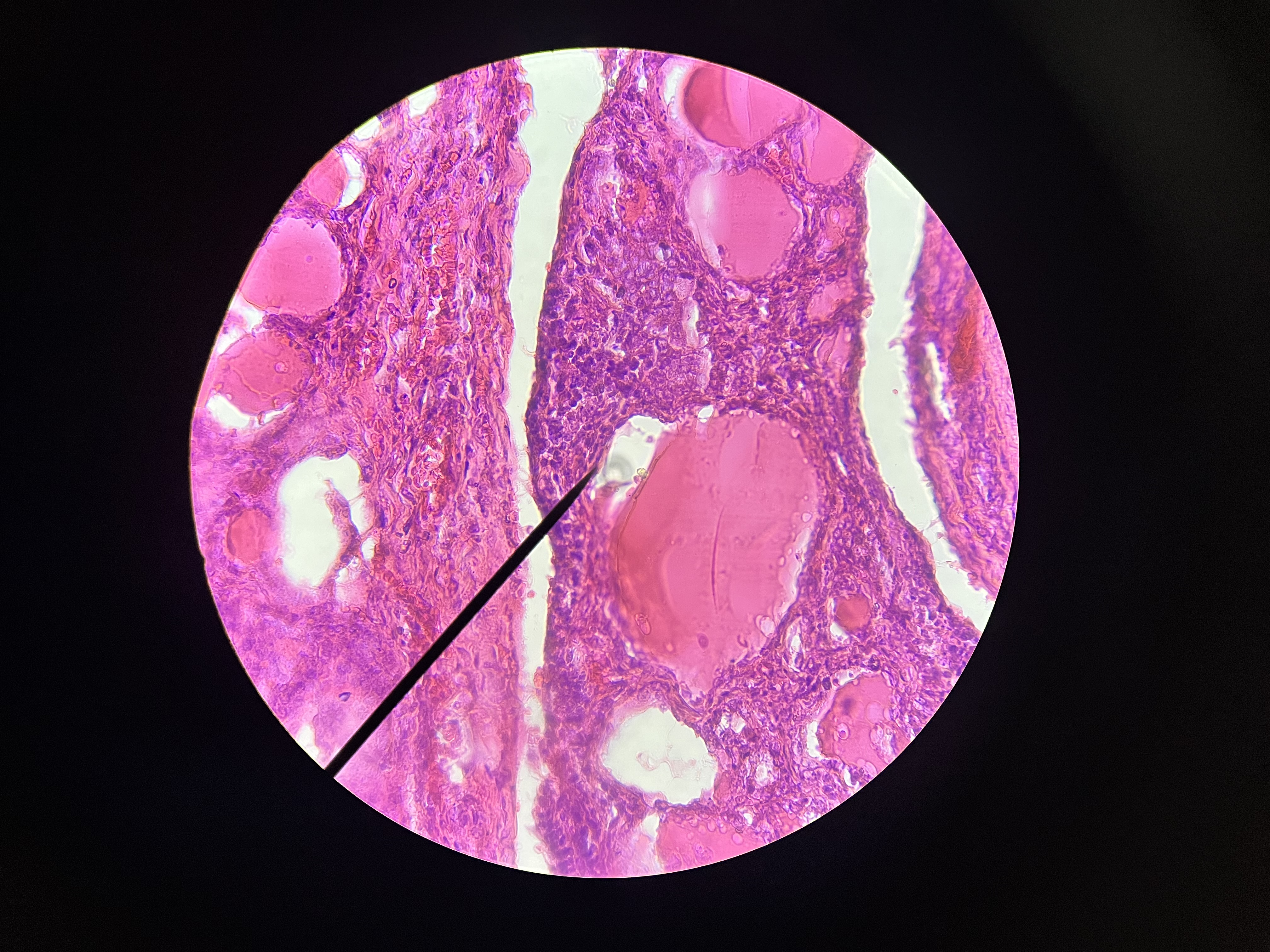
Papillary Carcinoma, thyroid
Known for its histomorphologic feature as the “Orphan Annie eye”
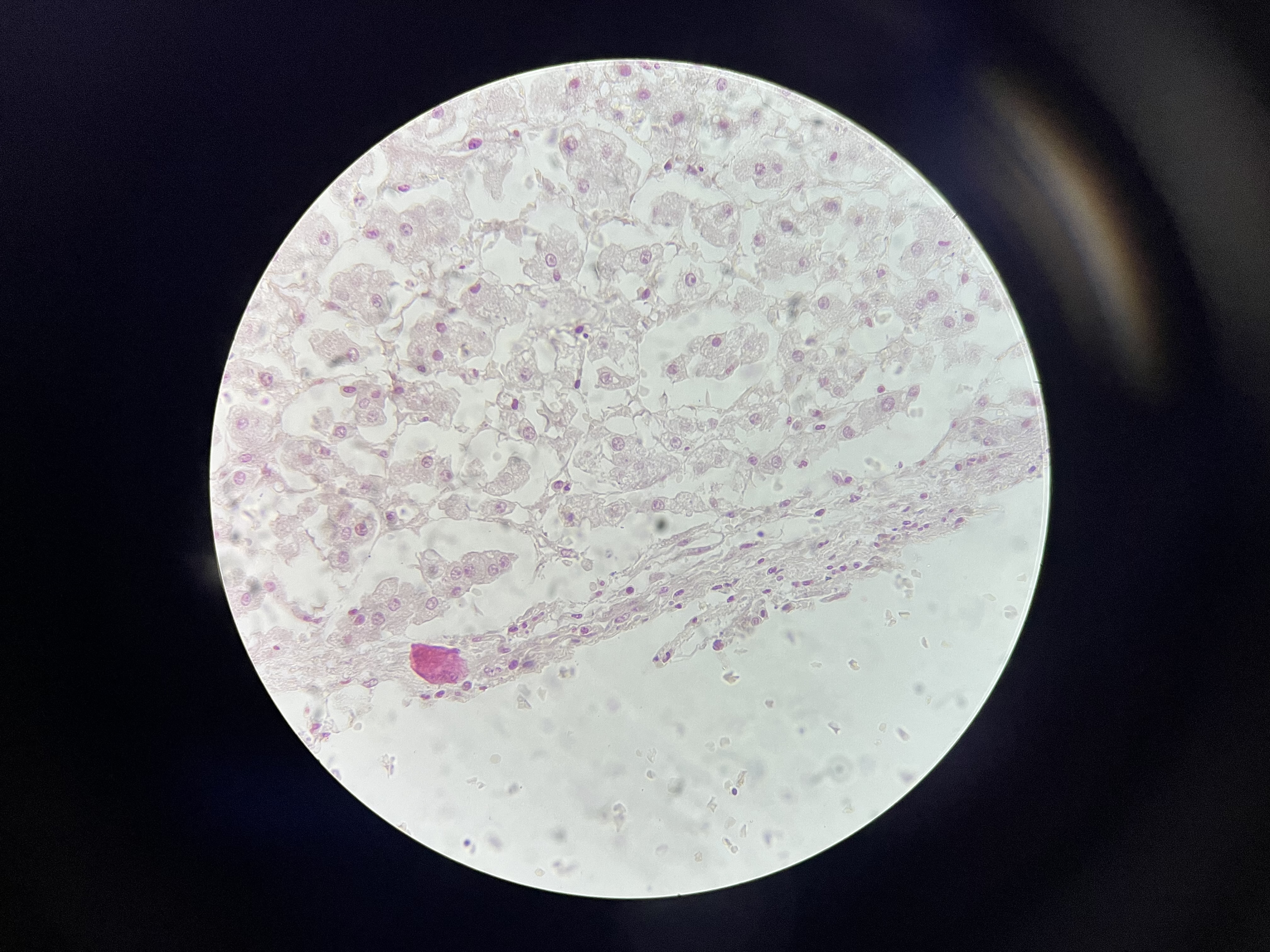
Adrenal Hemorrhage
Characterized by the presence of blood within the adrenal glands, often resulting in necrosis and infarction of adrenal tissue due to sudden vascular compromise.
Cirrhosis liver
include widespread fibrosis, formation of regenerative nodules, and distortion of the normal liver architecture. There may also be associated features of portal hypertension and necrosis of liver cells.
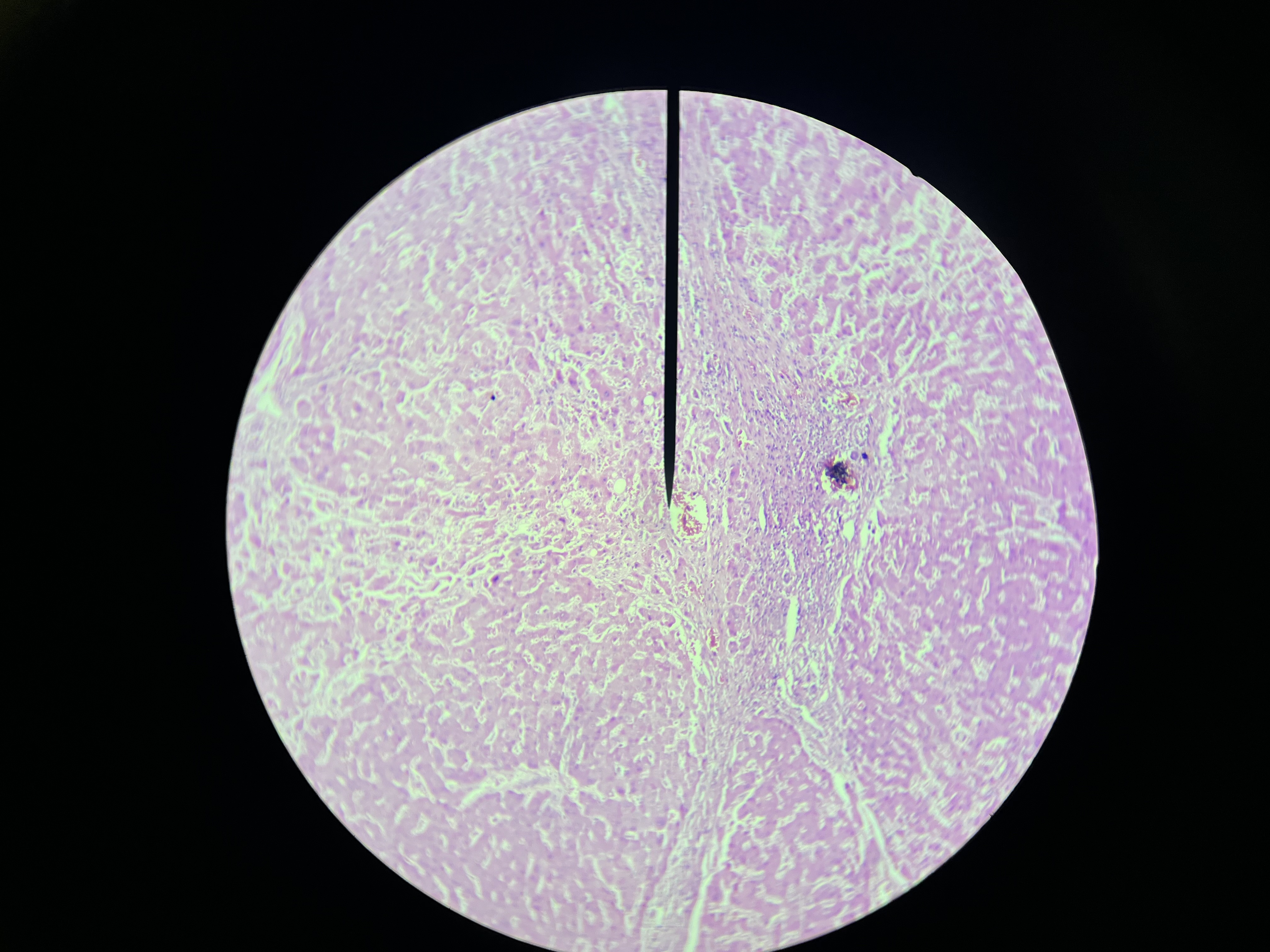
Lobar Pneumonia, lungs
A type of pneumonia characterized by the consolidation of lung tissue in one or more lobes, leading to symptoms such as cough, fever, and difficulty breathing.
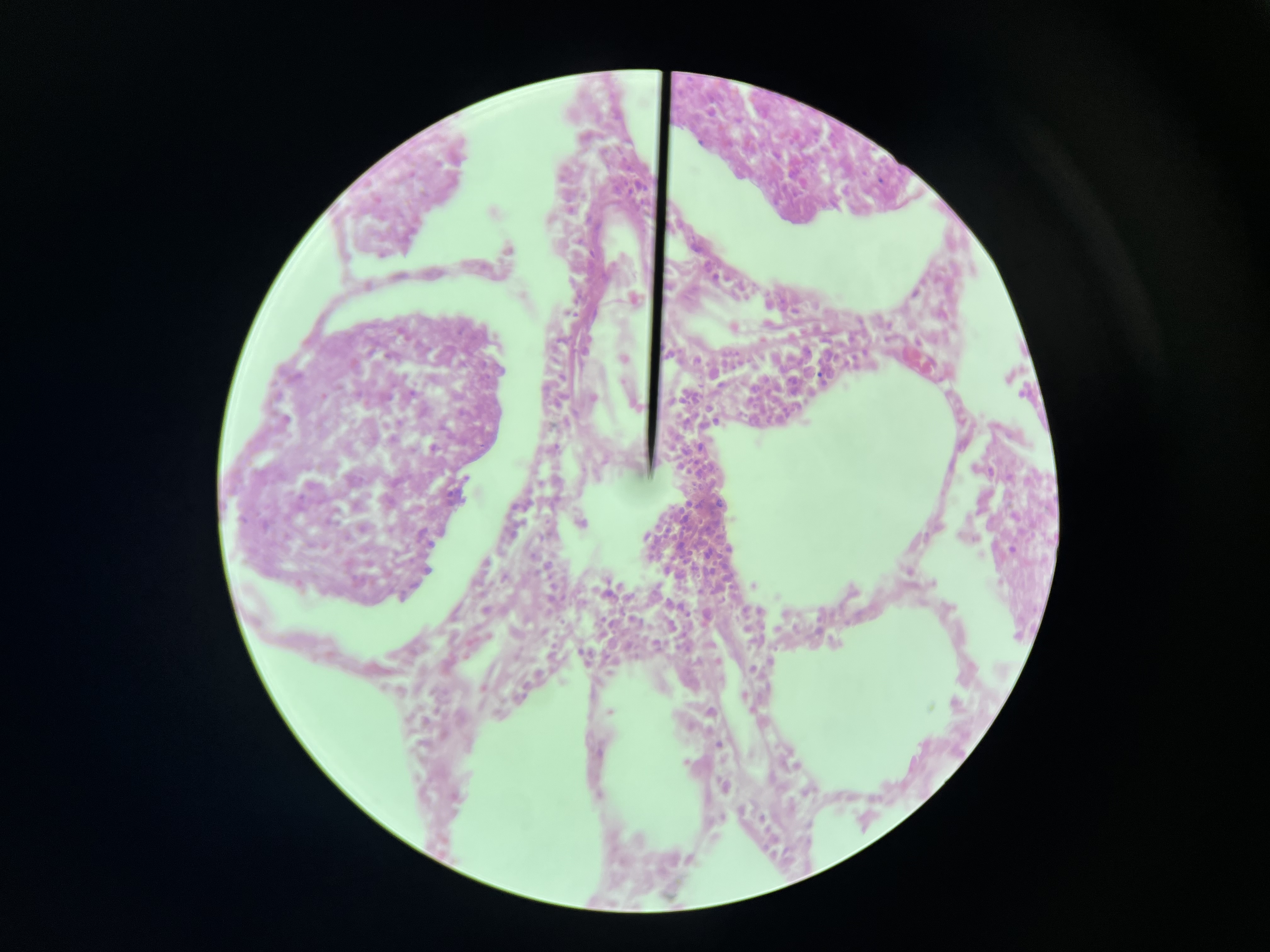
Lobar Pneumonia, lungs
an infection that affects a large and continuous area of the lobe of a lung, often characterized by consolidation of lung tissue and symptoms such as cough, fever, and difficulty breathing.
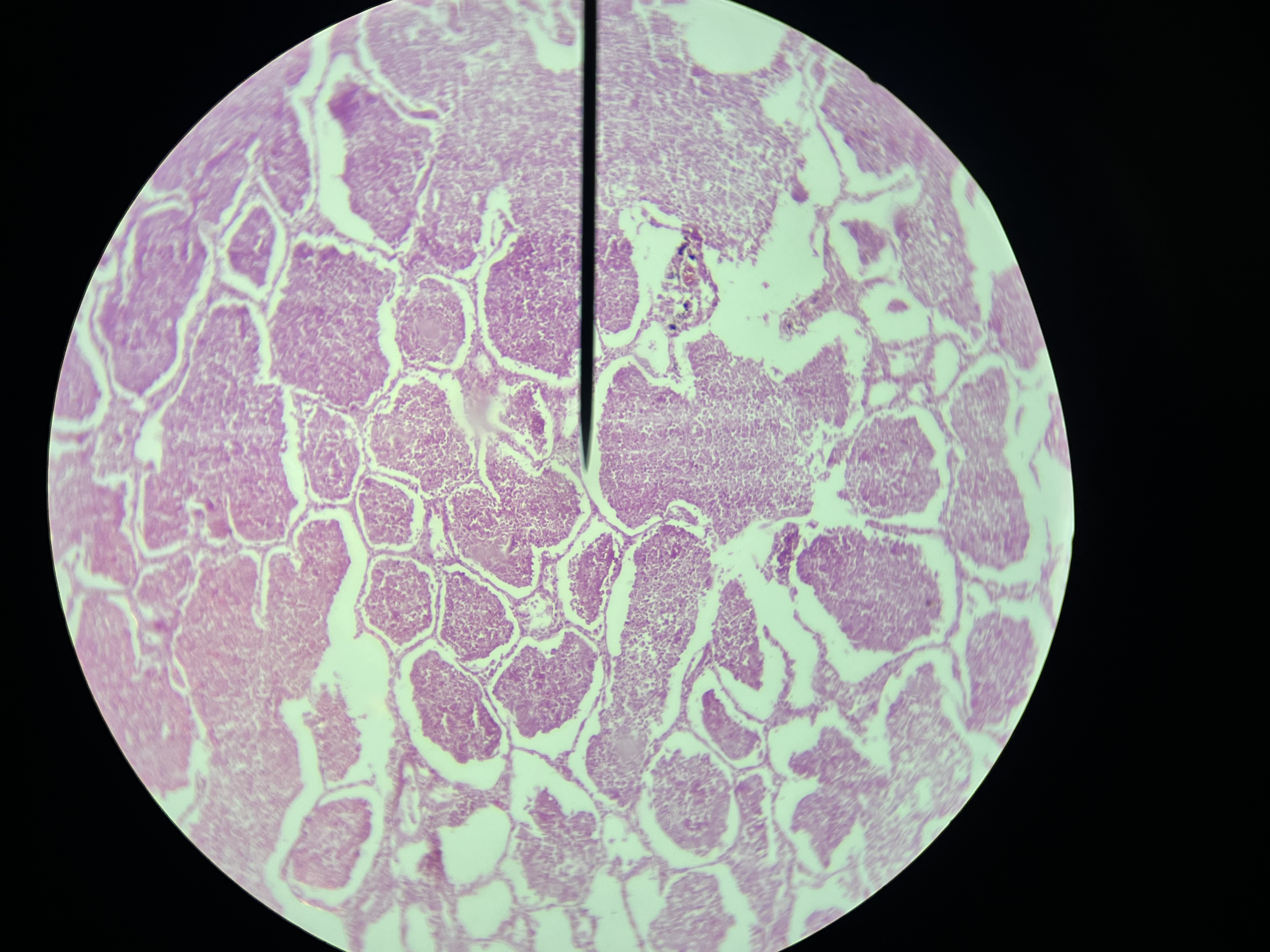
Cirrhosis liver
A chronic liver disease marked by scarring, liver cell degeneration, and impaired liver function.
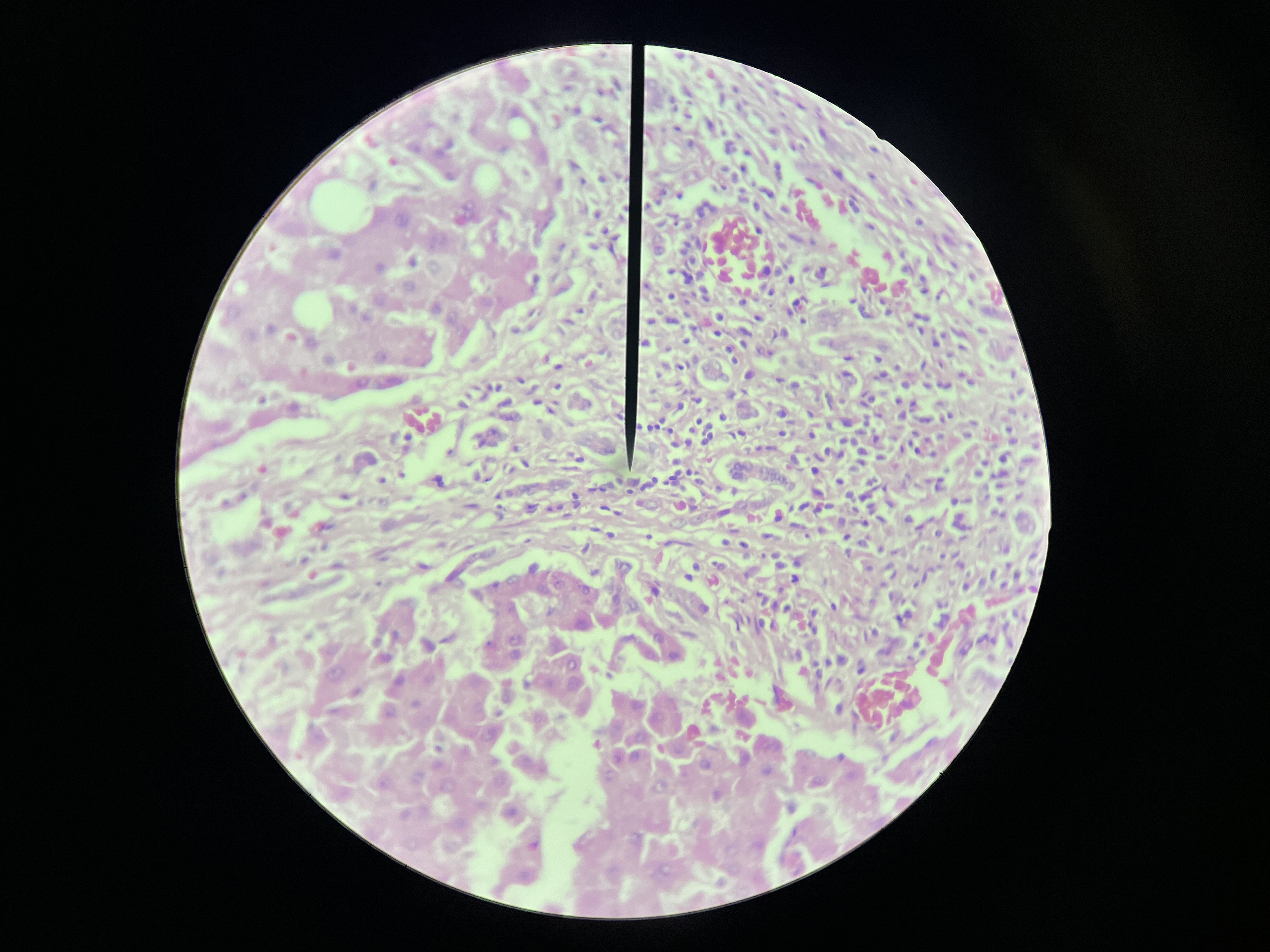
Molluscum Contagiosum, Skin
A viral skin infection caused by the Molluscum contagiosum virus, characterized by small, raised, painless bumps on the skin that can spread through direct contact.
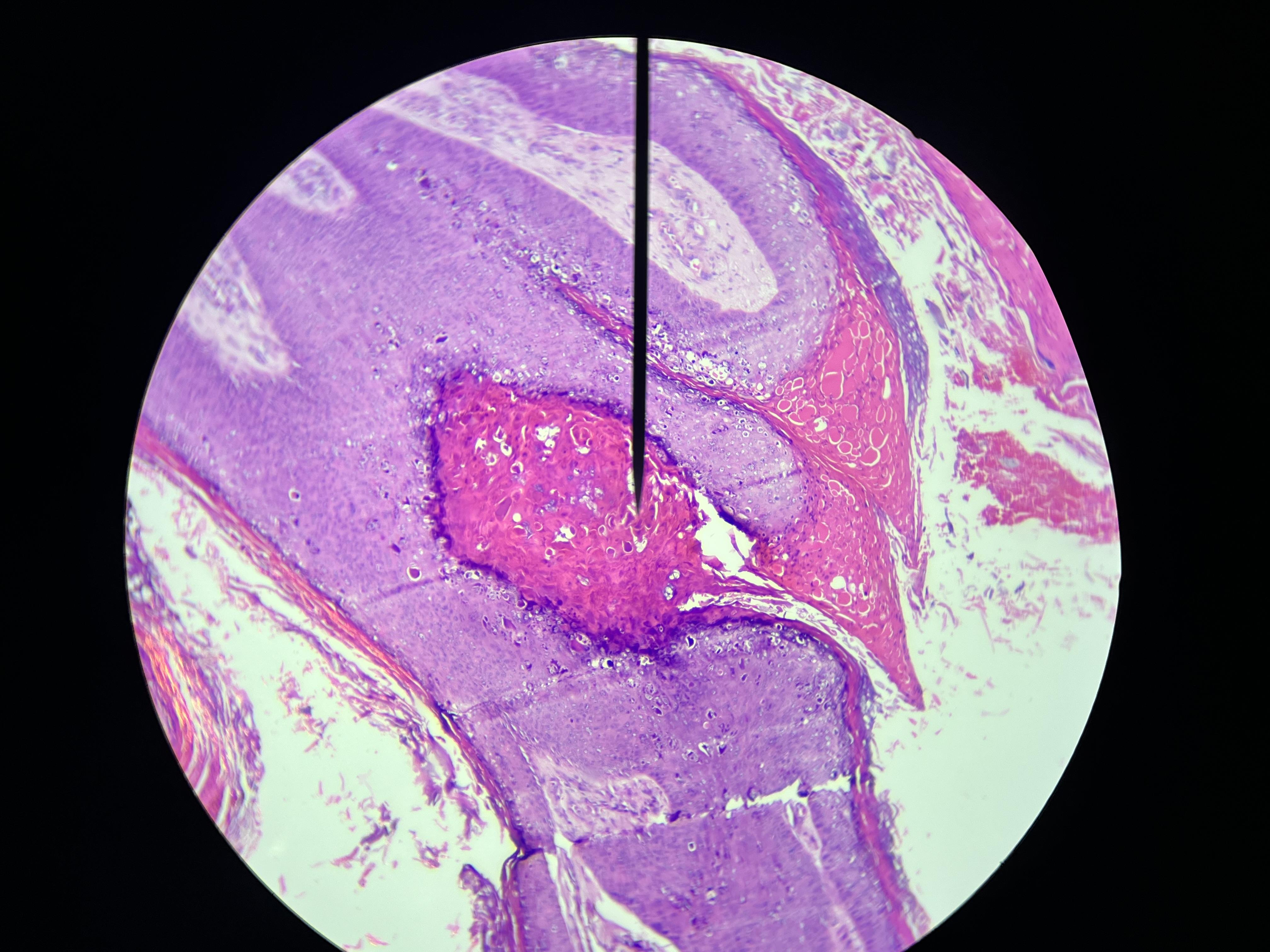
Molluscum Contagiosum, Skin
presence of molluscum bodies within the epidermis, characterized by large eosinophilic cytoplasmic inclusions in the keratinocytes.
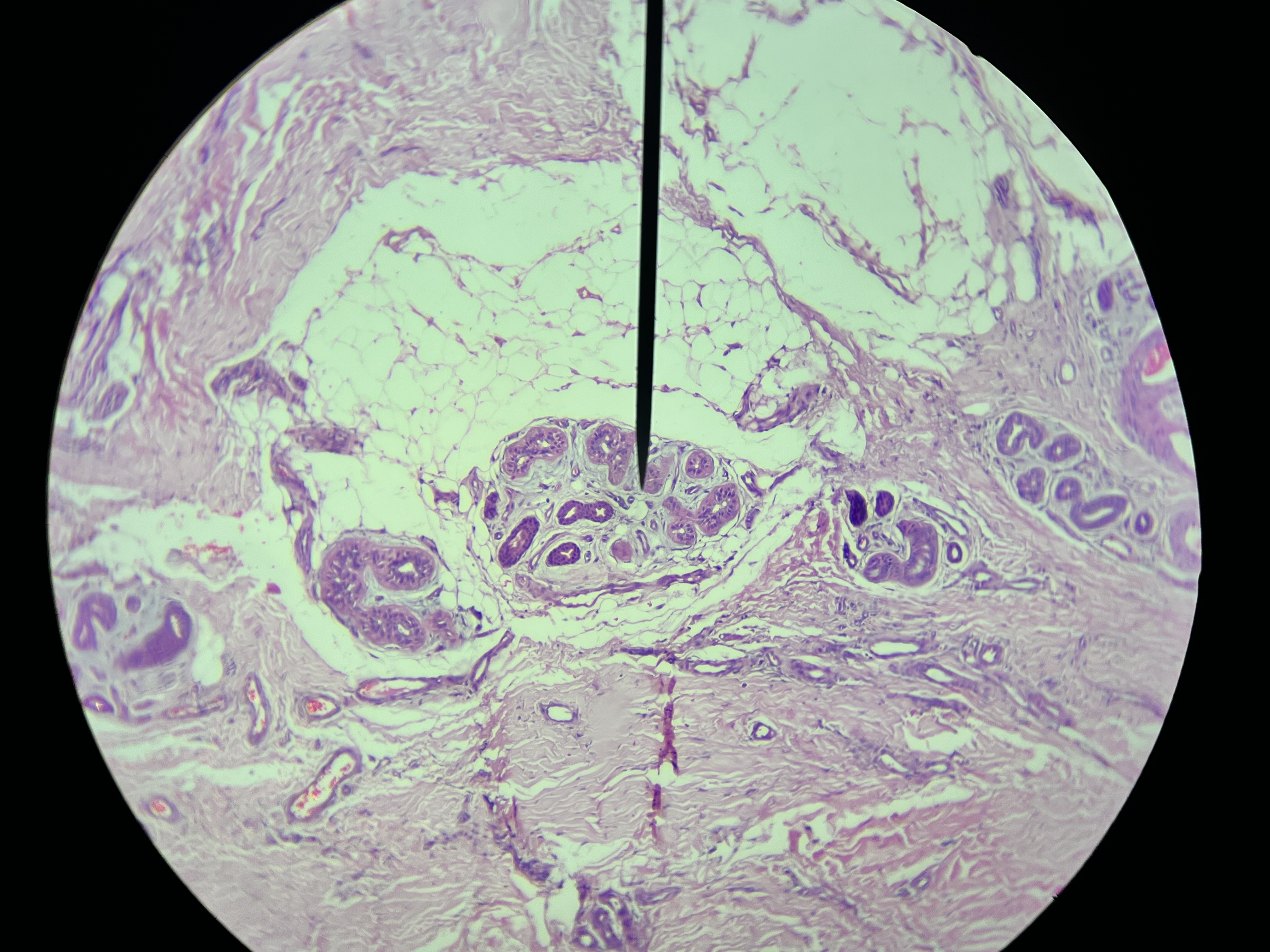
Molluscum Contagiosum, Skin
The virus originates from the Poxviridae family, and its transmission can occur through skin-to-skin contact or by sharing personal items such as towels or clothing.
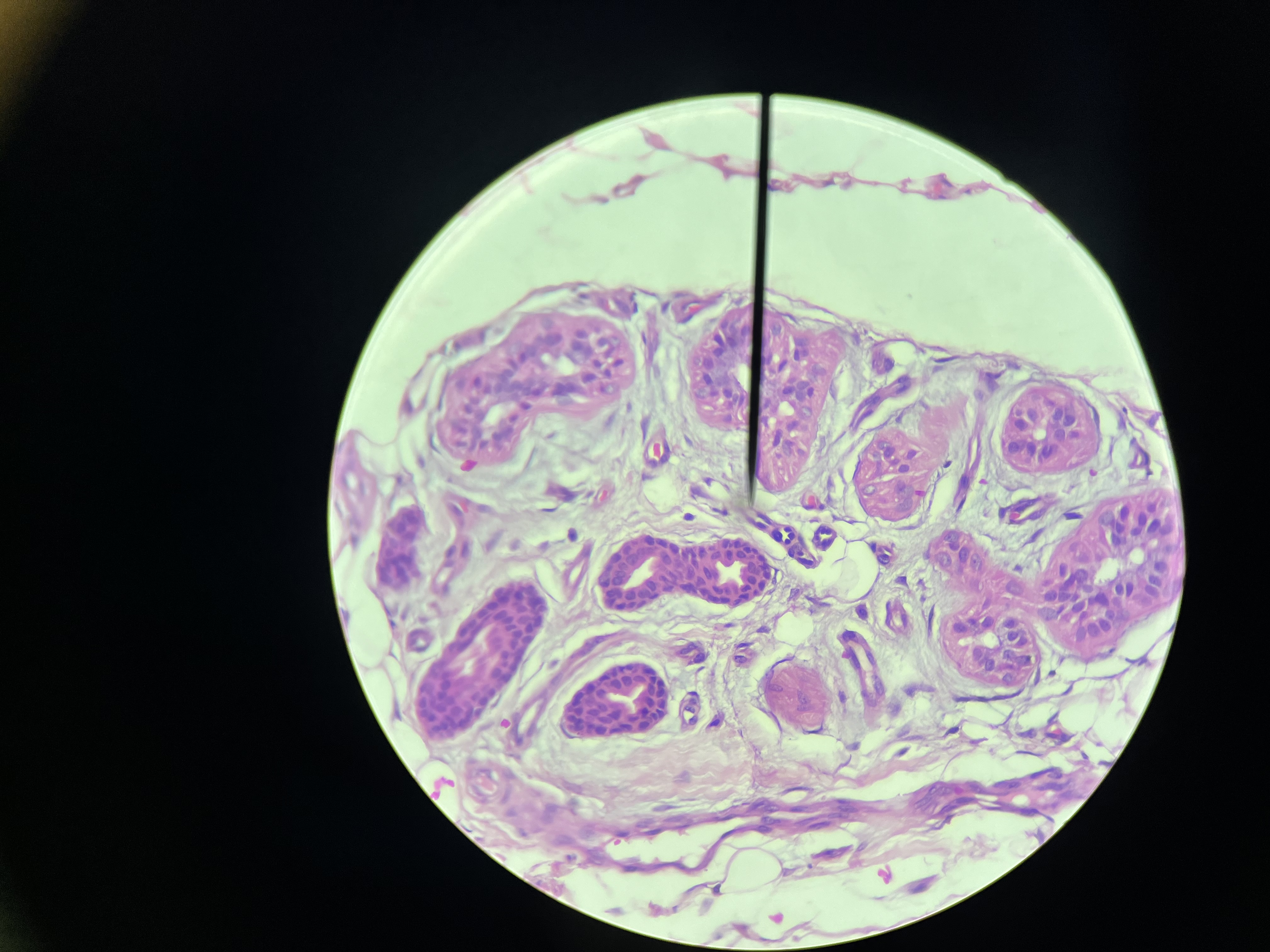
Molluscum Contagiosum, Skin
A contagious viral infection that causes benign, raised lesions on the skin, primarily affecting children and sexually active adults.
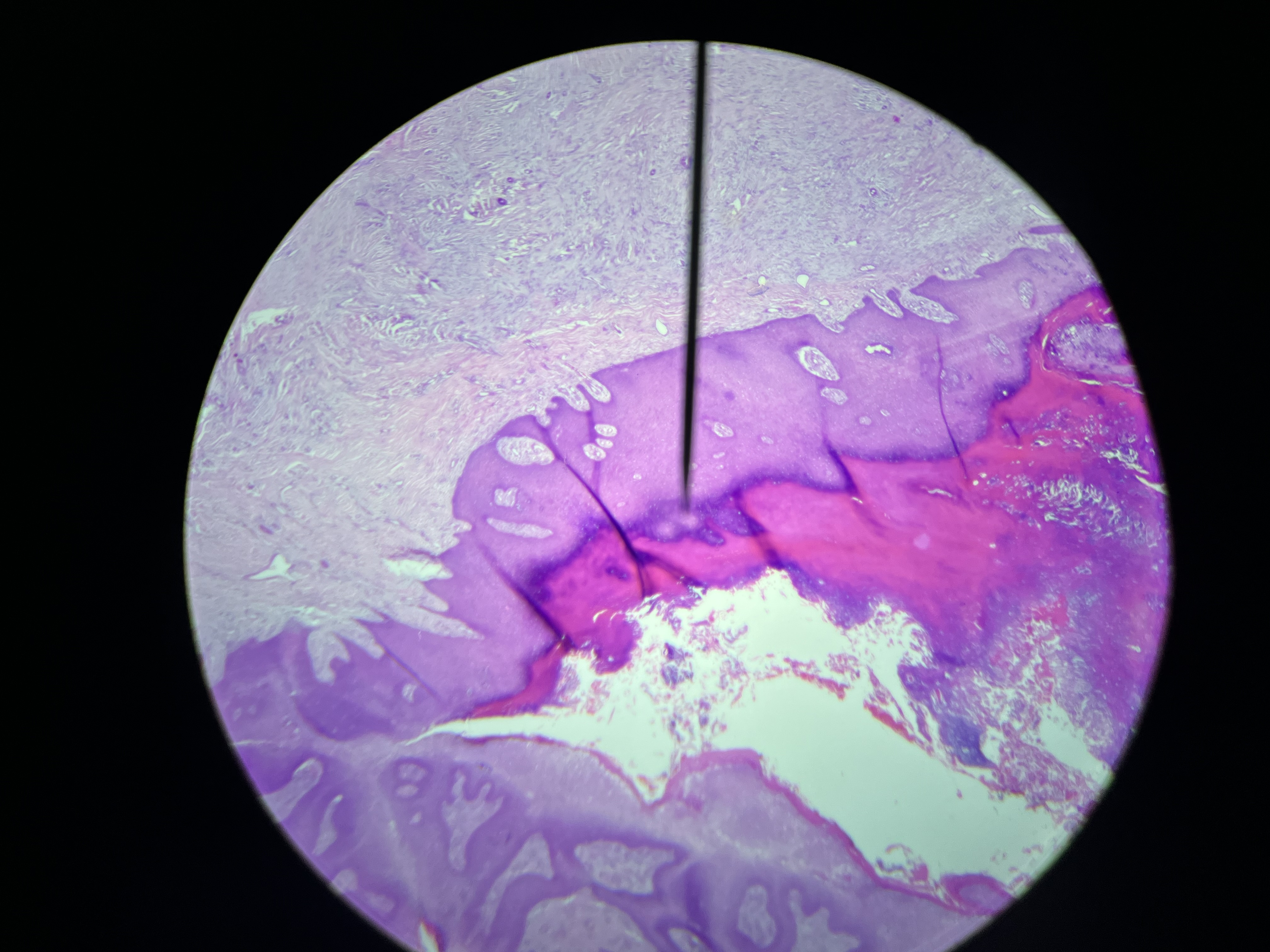
Liver Schistosomiasis
A parasitic infection caused by trematodes of the Schistosoma genus, leading to liver damage and portal hypertension.
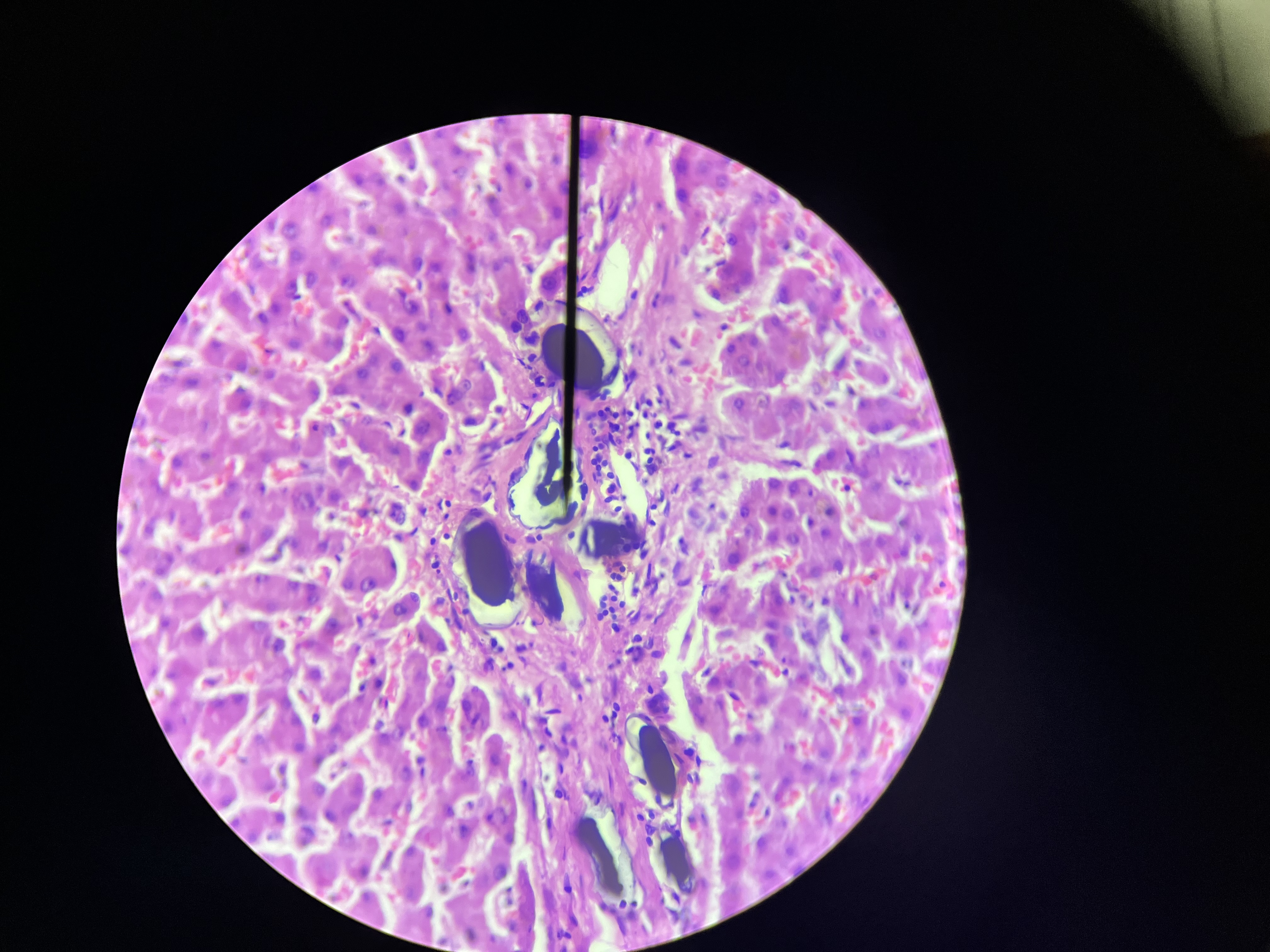
Molluscum Contagiosum, Skin
A viral skin infection characterized by small, raised, painless bumps on the skin. It is commonly seen in children and can resolve spontaneously.
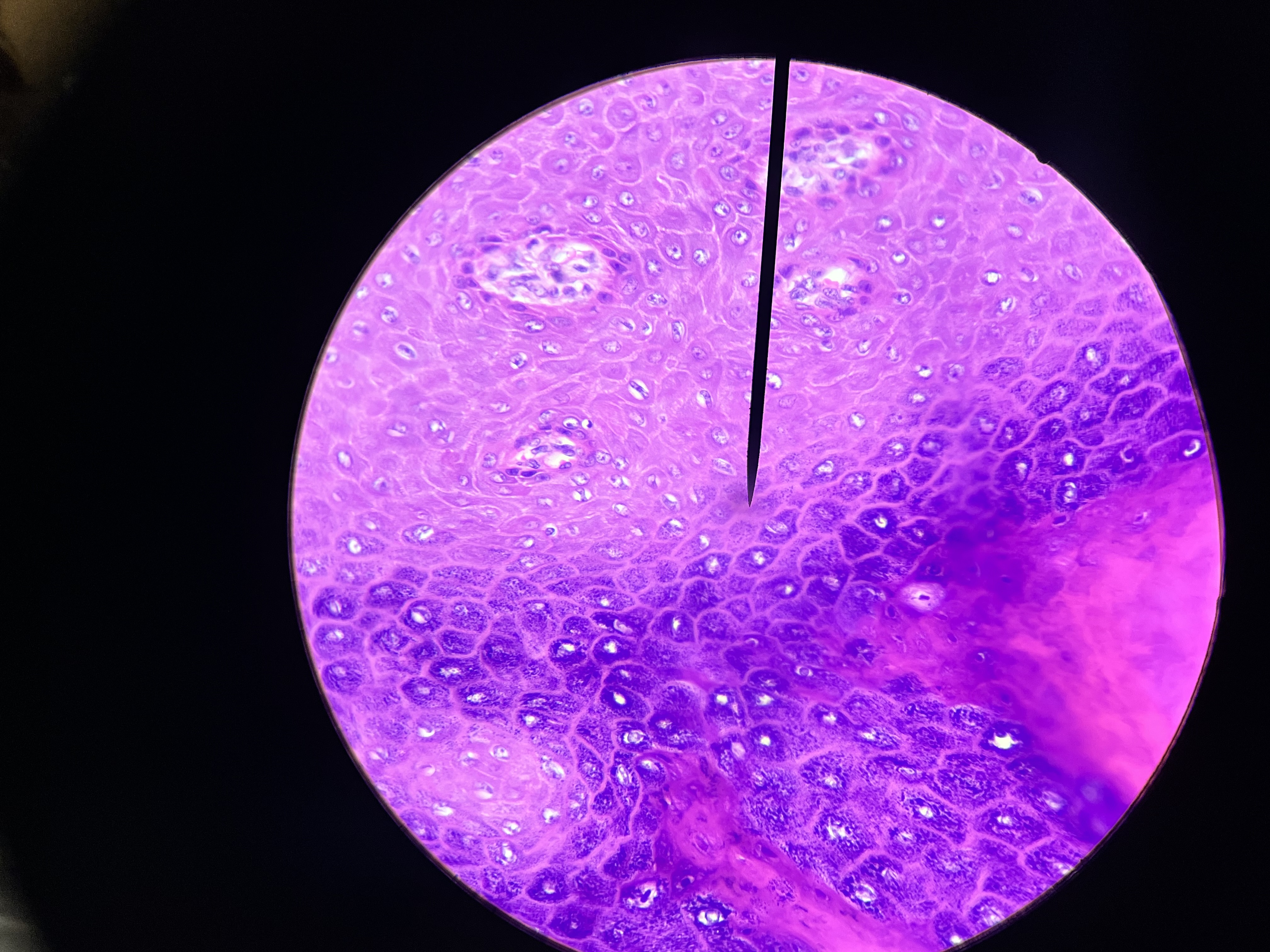
Liver Schistosomiasis
A parasitic disease caused by Schistosoma species, characterized by liver inflammation, fibrosis, and potential complications such as portal hypertension.
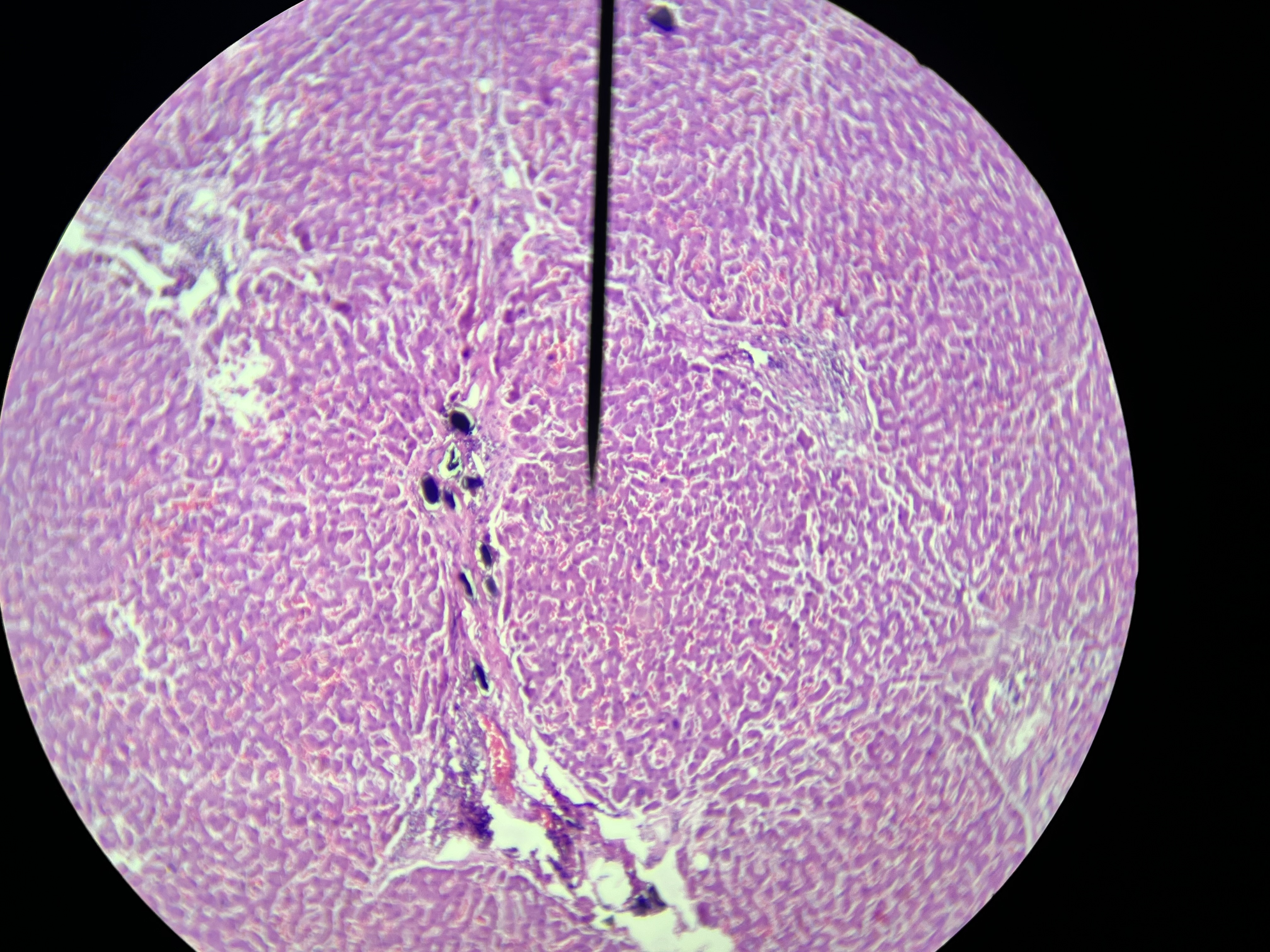
Breast, Lipoma
What is the diagnosis?
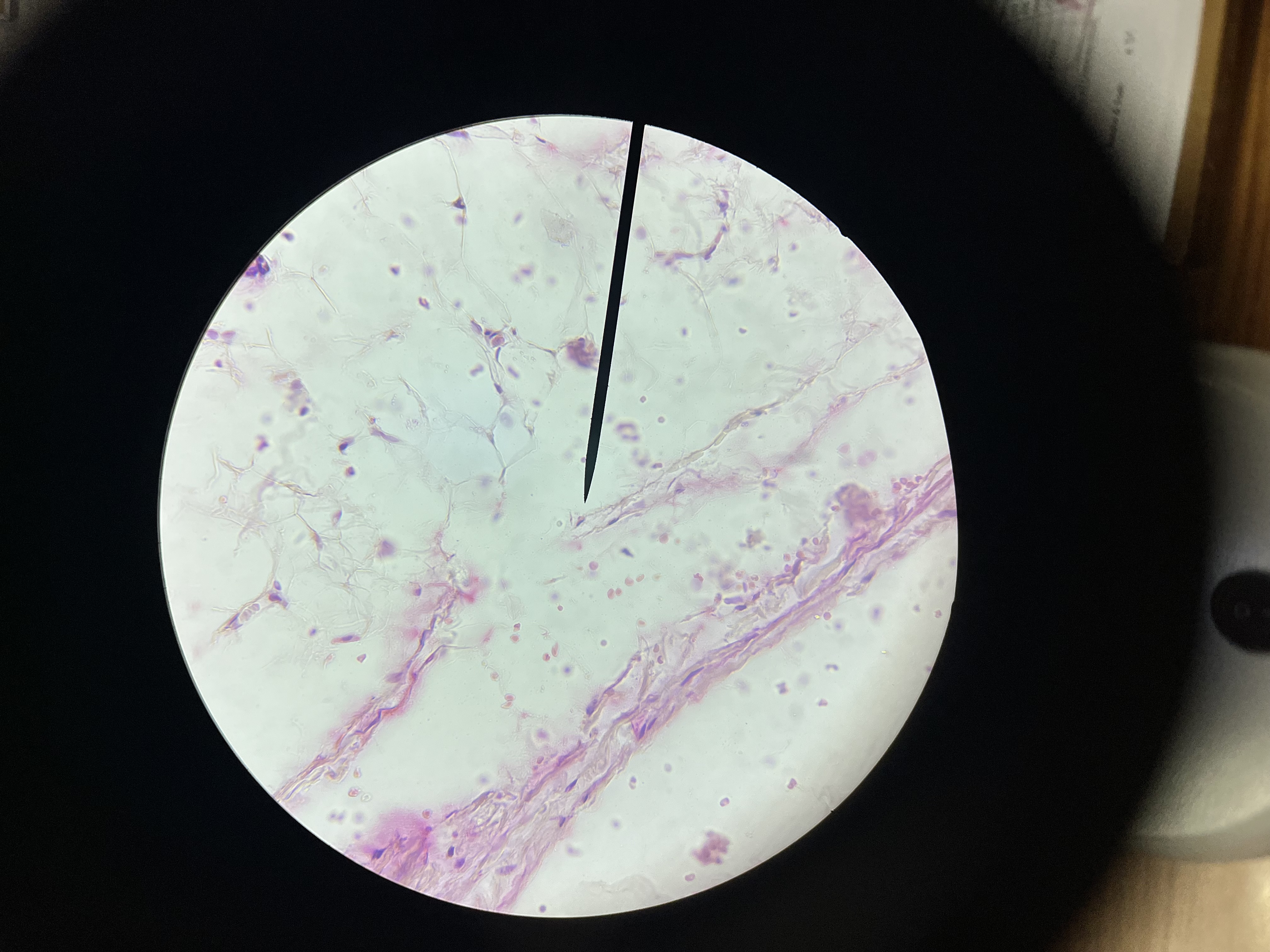
Thyroid Follicular adeoma
What is the diagnosis?
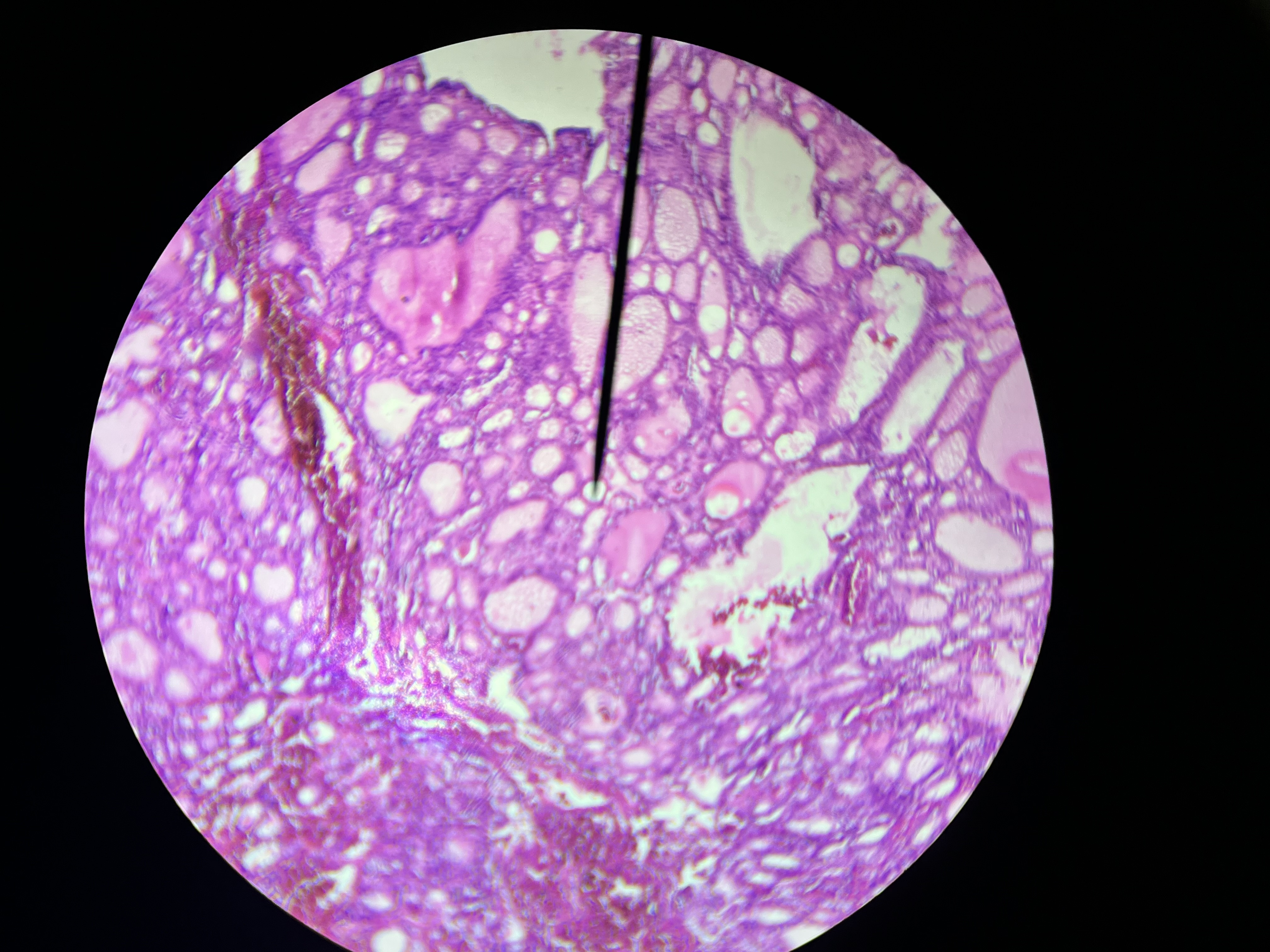
Skin, basal cell carcinoma
What is the diagnosis?
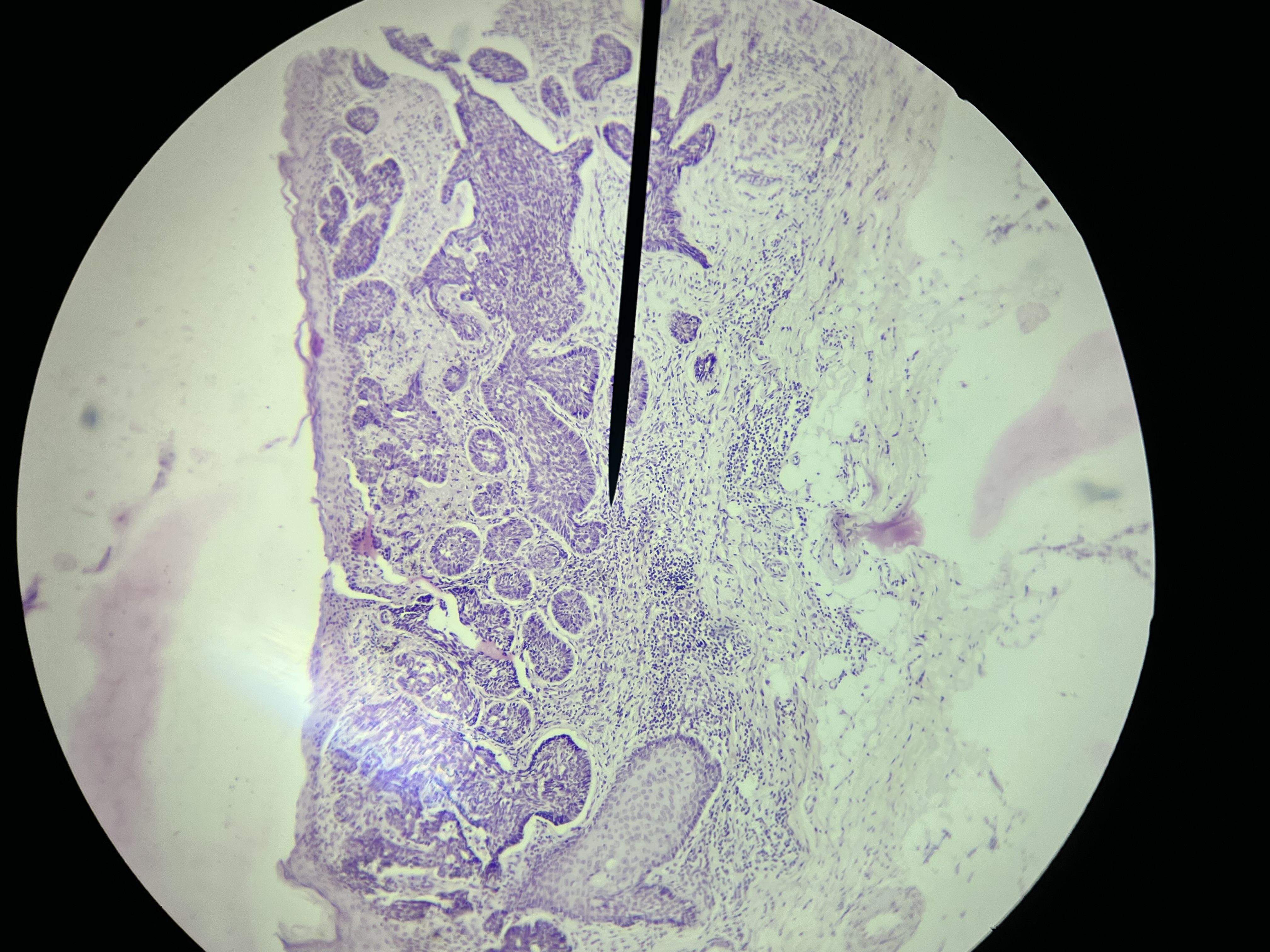
Basal cell carcinoma
What is the diagnosis?
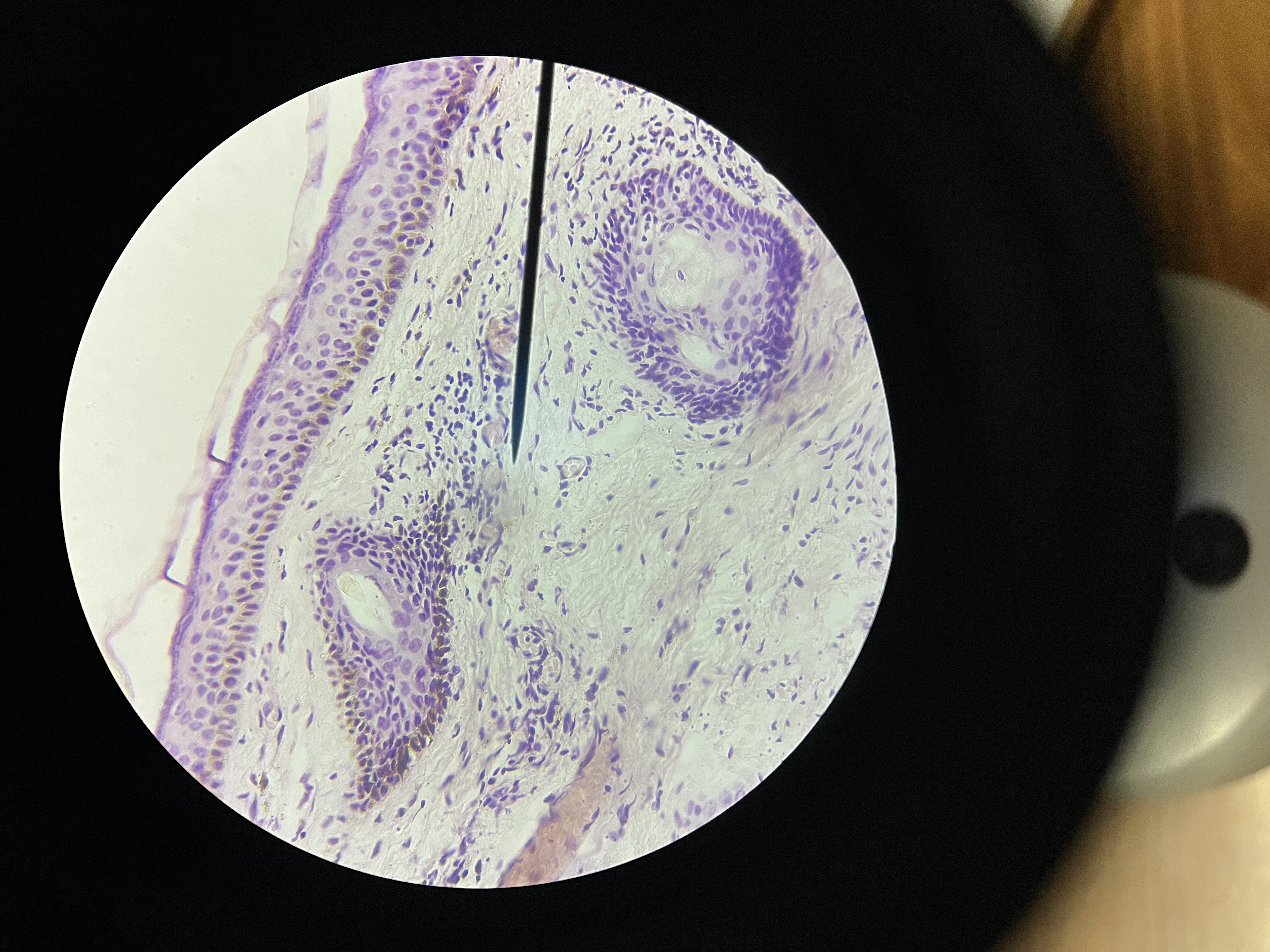
Adenocarcinoma, colon
What is the diagnosis?
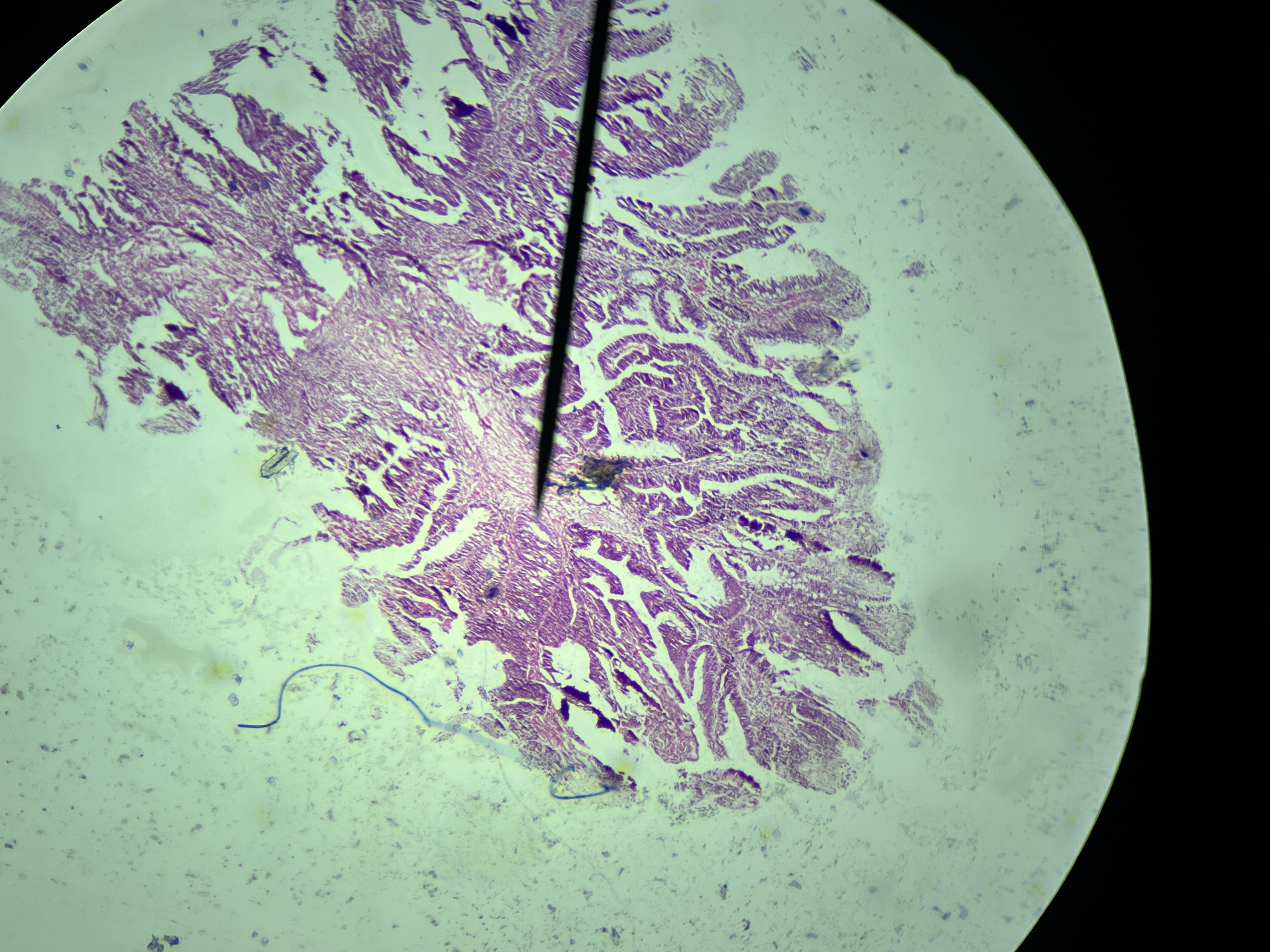
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma, Metastatic to the Lymph Node
What is the diagnosis?