Membrane Dynamics
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary terms related to Membrane Dynamics in human physiology.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Intracellular fluid(ICF)
Fluid within cells, making up 2/3 of total body water volume.
Extracellular fluid/Interstitial (ECF)
All fluid outside of cells, consisting of interstitial fluid and plasma.
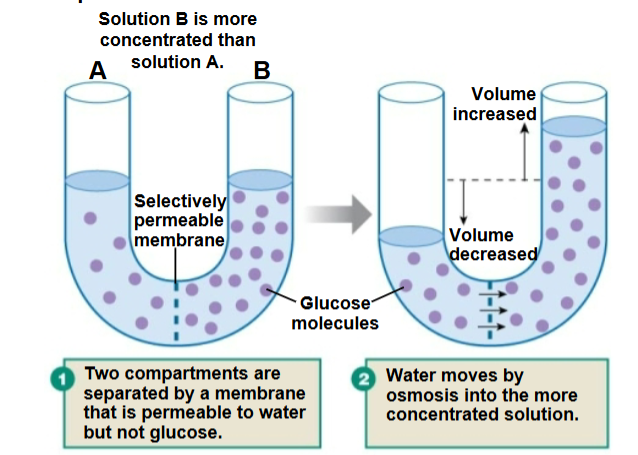
Osmosis
Movement of water across a membrane in response to a solute concentration gradient. (where there is more concentration, water follows)
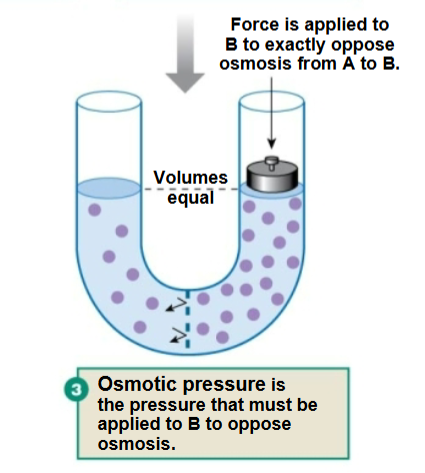
Osmotic pressure
The exact amount of pressure needed to stop water from moving across a membrane via osmosis.

Osmolarity
A measure of solute concentration in a solution, typically expressed as osmoles of solute per liter of solution.

Molarity
A measure of solute concentration defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution.

Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (Chemical gradient) until equilibrium is reached.
Rapid over short distances
Directly related to temperature
inversely related to molecular weight and size
in an open system or across a partition
Equilibrium
Net movement until concentration is equal
Fick's Law of Diffusion
Describes the factors affecting the rate of diffusion, such as concentration gradient and membrane permeability.
Facilitated diffusion
The process of passive transport of molecules across a cell membrane via a carrier protein.
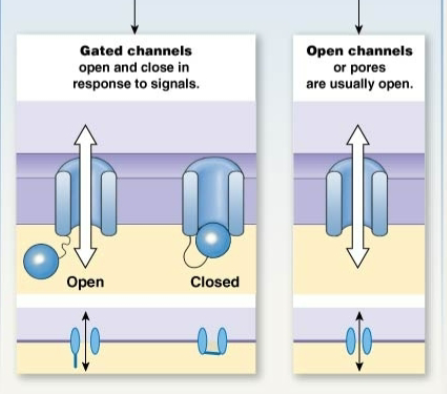
Channels
Water channels: Water only
Ion Channel: Only allows ions through
Open Channel: always open
Gated Channel: Closed
Chemically gated channel, ligan comes and opens.
Voltage-gated channel electicity opens.
mechanically gated channels sound closes quiet opens.
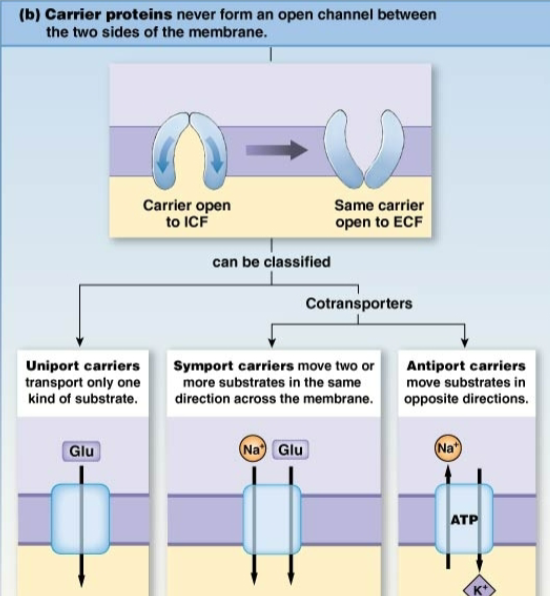
Carrier-mediated transport
Channels without doors for specific molecules across a cell membrane using carrier proteins.
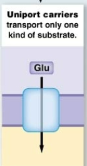
Uniport carriers
Transport only one kind of substrate
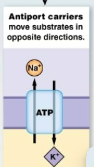
Antiport Carrier
Transport two or more substrates in opposite directions across the membrane.
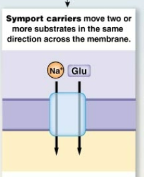
Symport carriers
Move two or more substrates in the same direction accross the membrame
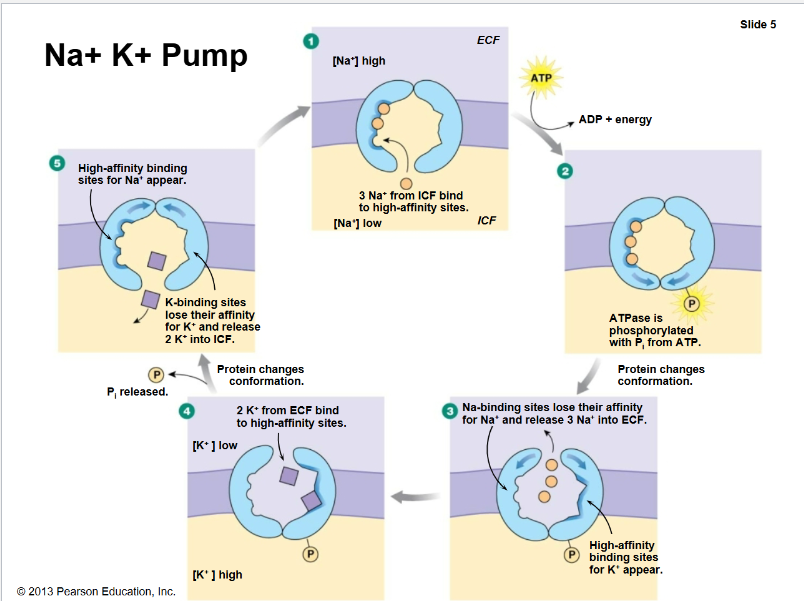
Na+-K+-ATPase
An enzyme that pumps sodium ions out of cells and potassium ions into cells, using ATP. (Pumping against the concentration gradient)
3 sodium 2 potassium ratio
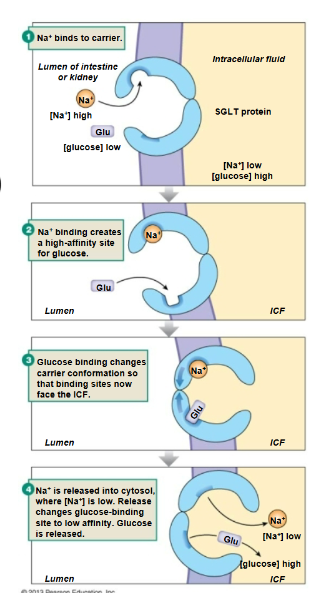
Sodium-glucose transporter (SGLT)
A secondary active transporter that moves glucose into cells alongside sodium ions.
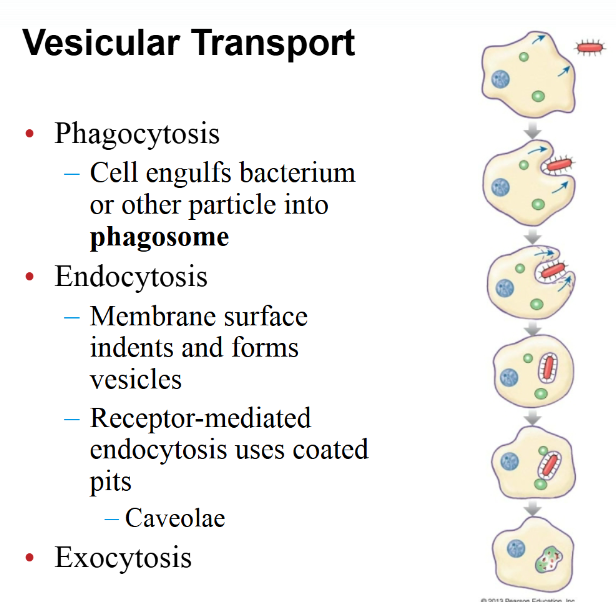
Vesicular transport
Moving large amounts of materials in or out of a cell using small sacs called vesicles
Phagocytosis: Germs bacteria
Endocytosis: Digestive system
Exocytosis: Molecules exiting cells
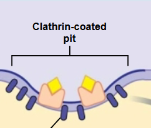
Clathrin
A protein that plays a key role in the formation of vesicles for endocytosis by coating the pits on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane.
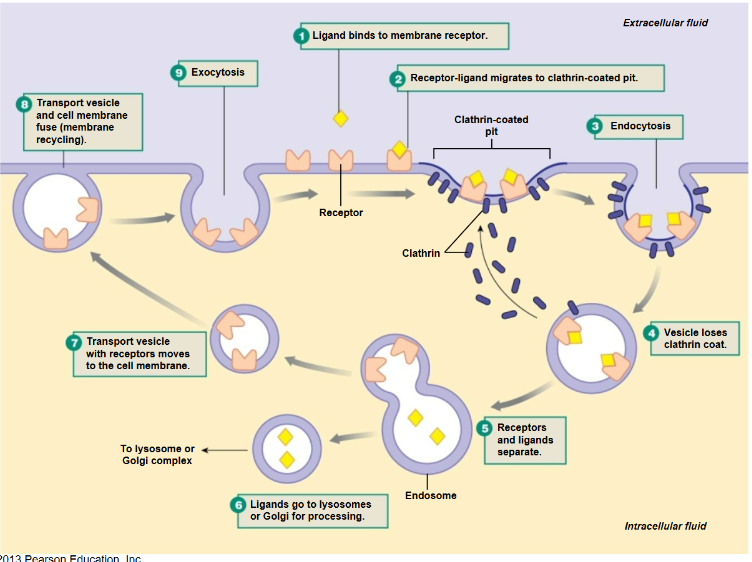
Receptor mediated cytosis
A form of endocytosis that involves the uptake of specific molecules based on their interaction with receptors on the cell surface.
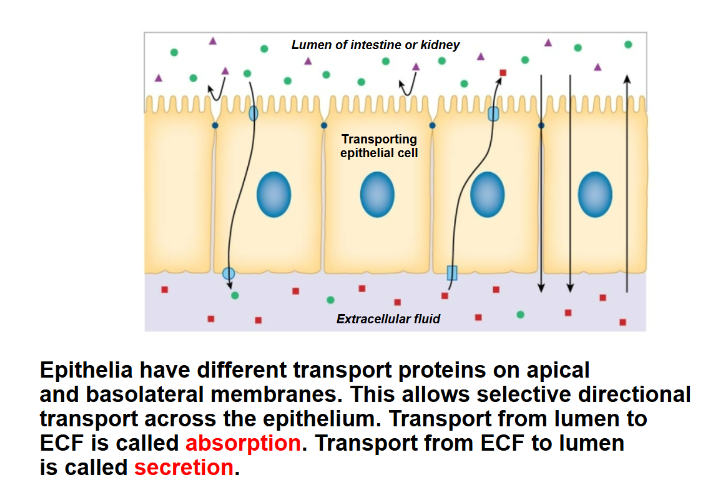
Absorption
Movement of substances across the membrane into a cell/ blood.
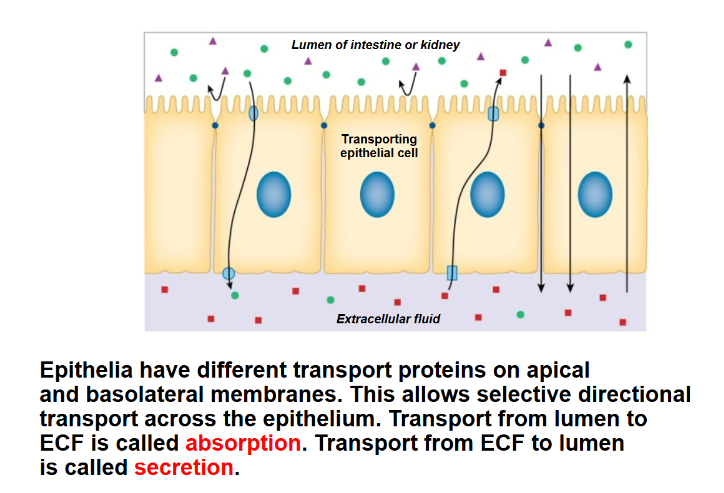
Secretion
Moving substances out of the cell, typically by vesicle fusion with the plasma membrane.
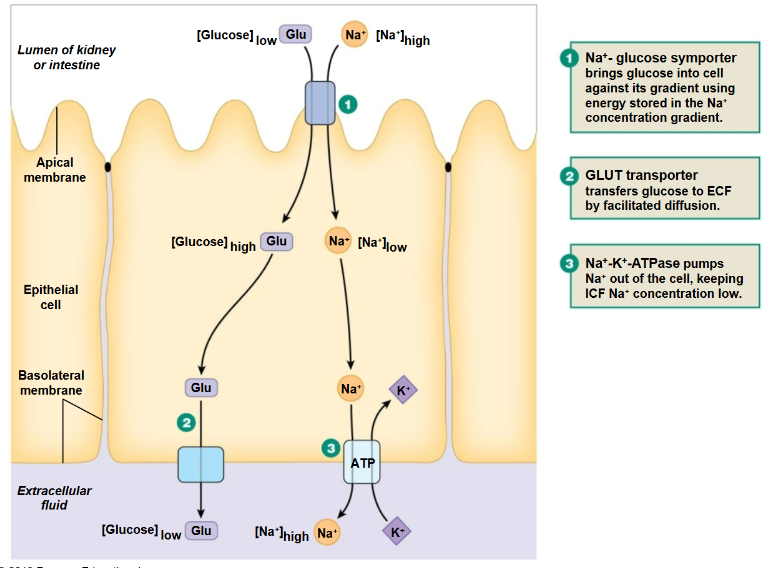
Na+ Glucose symporter
A transport protein that simultaneously moves sodium ions and glucose molecules into the cell, leveraging the sodium gradient to facilitate glucose uptake.
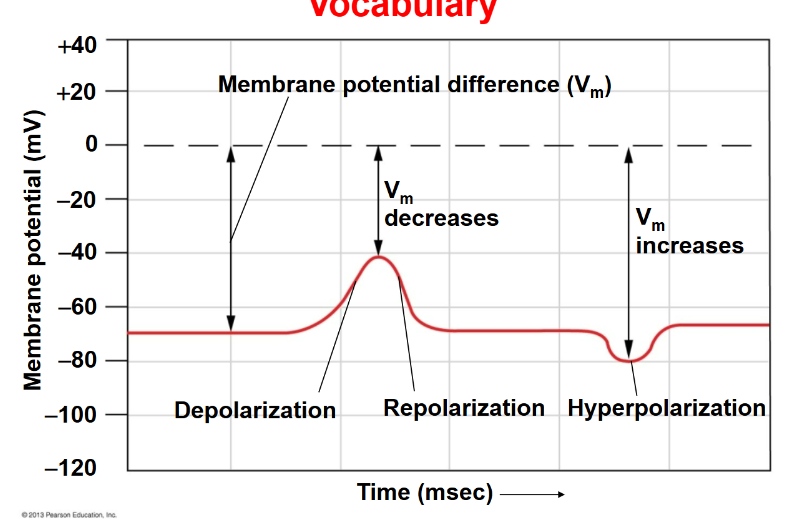
Membrane potential difference (Vm)
The difference in electric potential across a cell membrane.
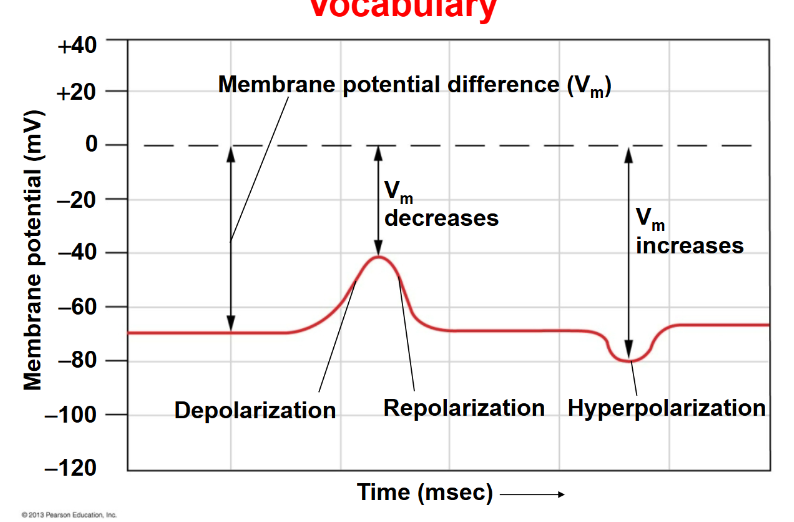
Hyperpolarization
An increase in the membrane potential, making the inside of the cell more negative.
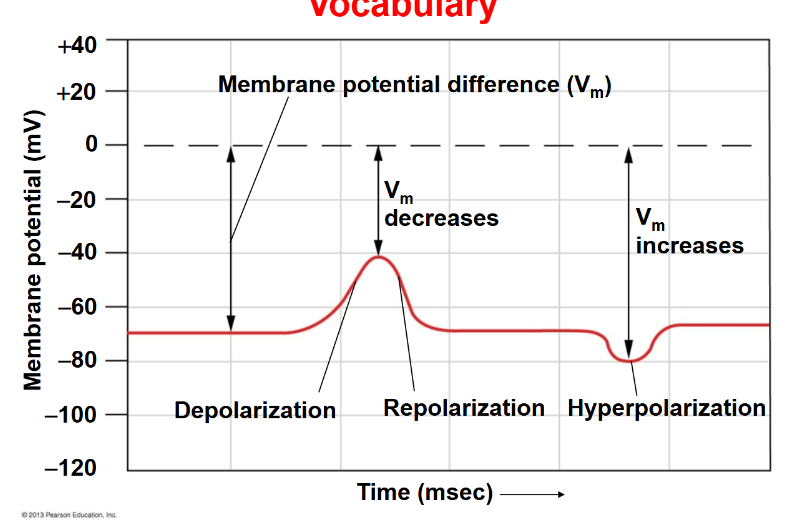
Depolarization
The voltage is going up
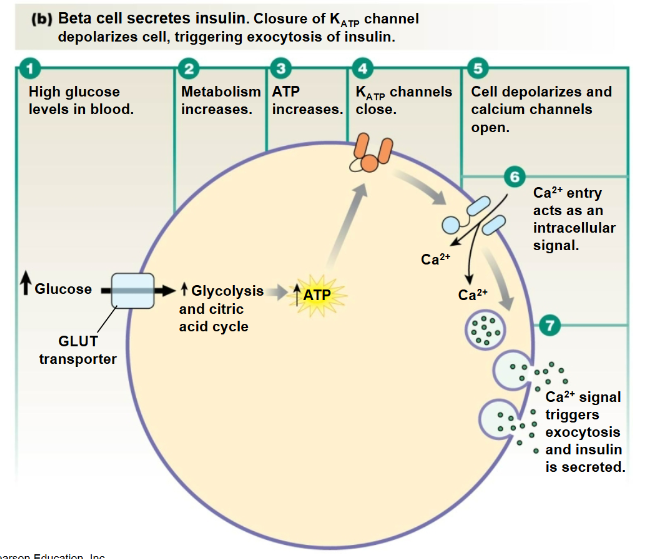
Insulin Secretion
The release of insulin from pancreatic beta cells in response to glucose levels, facilitating glucose uptake by cells.
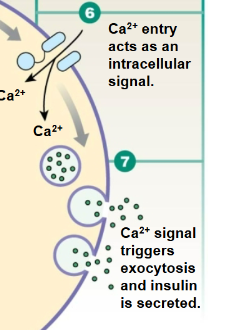
Exocytosis
The process by which a cell expels materials in vesicles that fuse with the plasma membrane. (Ca 2+ is required for secretion)
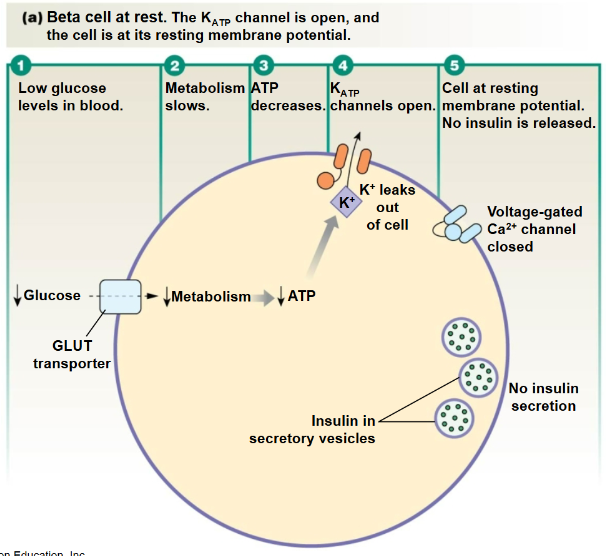
Low Glucose
levels inhibit insulin secretion, preventing excessive blood sugar regulation.
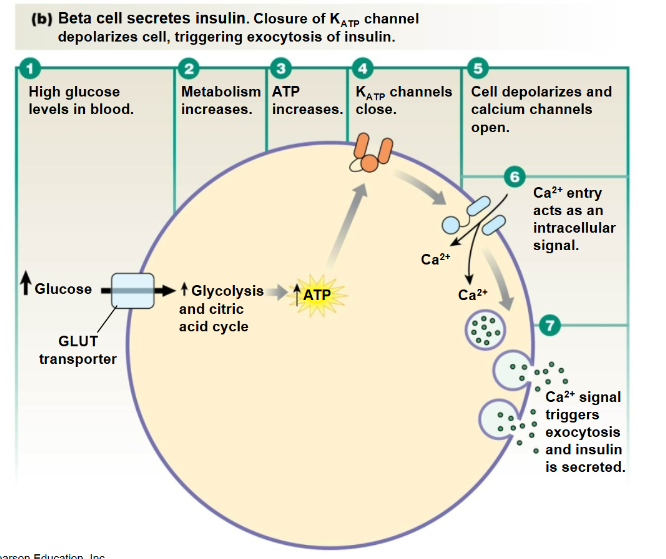
High Glucose
The condition that stimulates insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells, facilitating the uptake of glucose by tissues and lowering blood sugar levels.