Cardiac Physiology: Anatomy and Function of the Heart
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What are the two main circulatory systems in the body?
Systemic and pulmonary circulations.
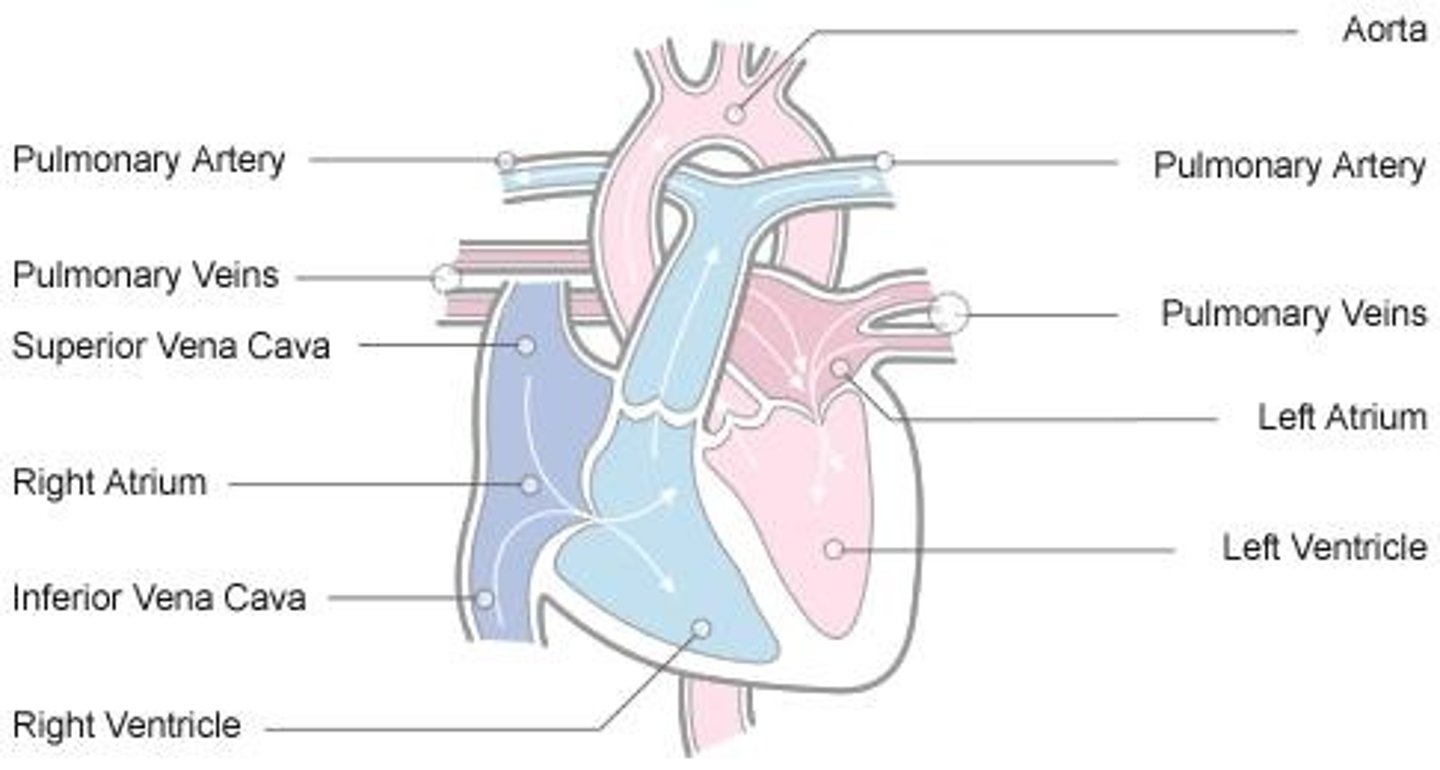
What is the main function of the heart in the circulatory system?
To pump oxygenated blood into systemic circulation and deoxygenated blood into pulmonary circulation.
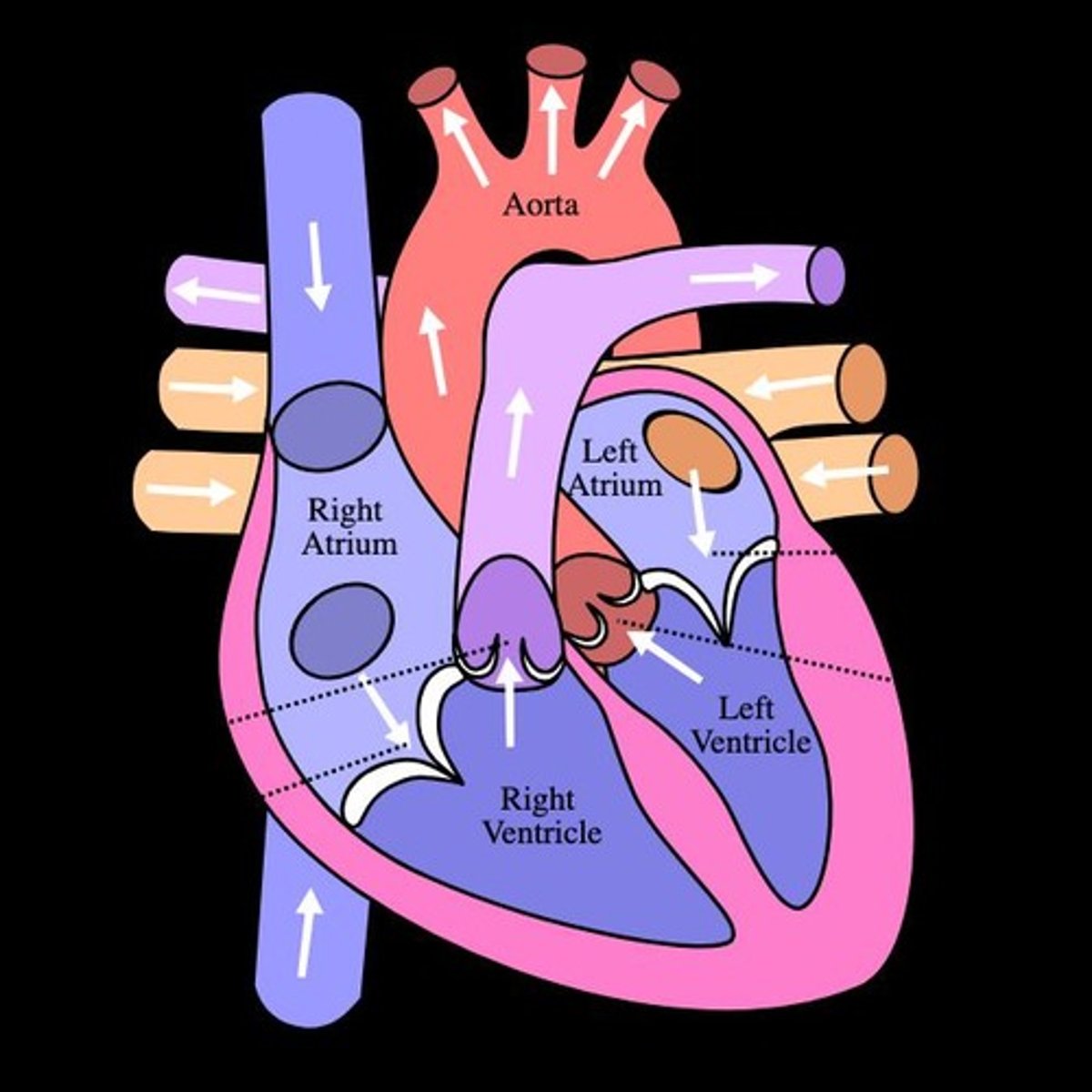
What are the two main divisions of the cardiovascular system?
The heart and the blood vessels.
What are the two types of circulation in the circulatory system?
Systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation.
Describe systemic circulation.
Blood is pumped from the left ventricle around the body and returns to the heart through the right ventricle.
Describe pulmonary circulation.
Blood is pumped from the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery to the lungs for oxygenation.
What is the approximate size of the human heart?
About the size of a fist.
Where is the heart located in the body?
Superior surface of the diaphragm, left of the midline, anterior to the vertebral column, and posterior to the sternum.
How many chambers does the heart have, and what are they?
The heart has 4 chambers: 2 atria (left and right) and 2 ventricles (left and right).
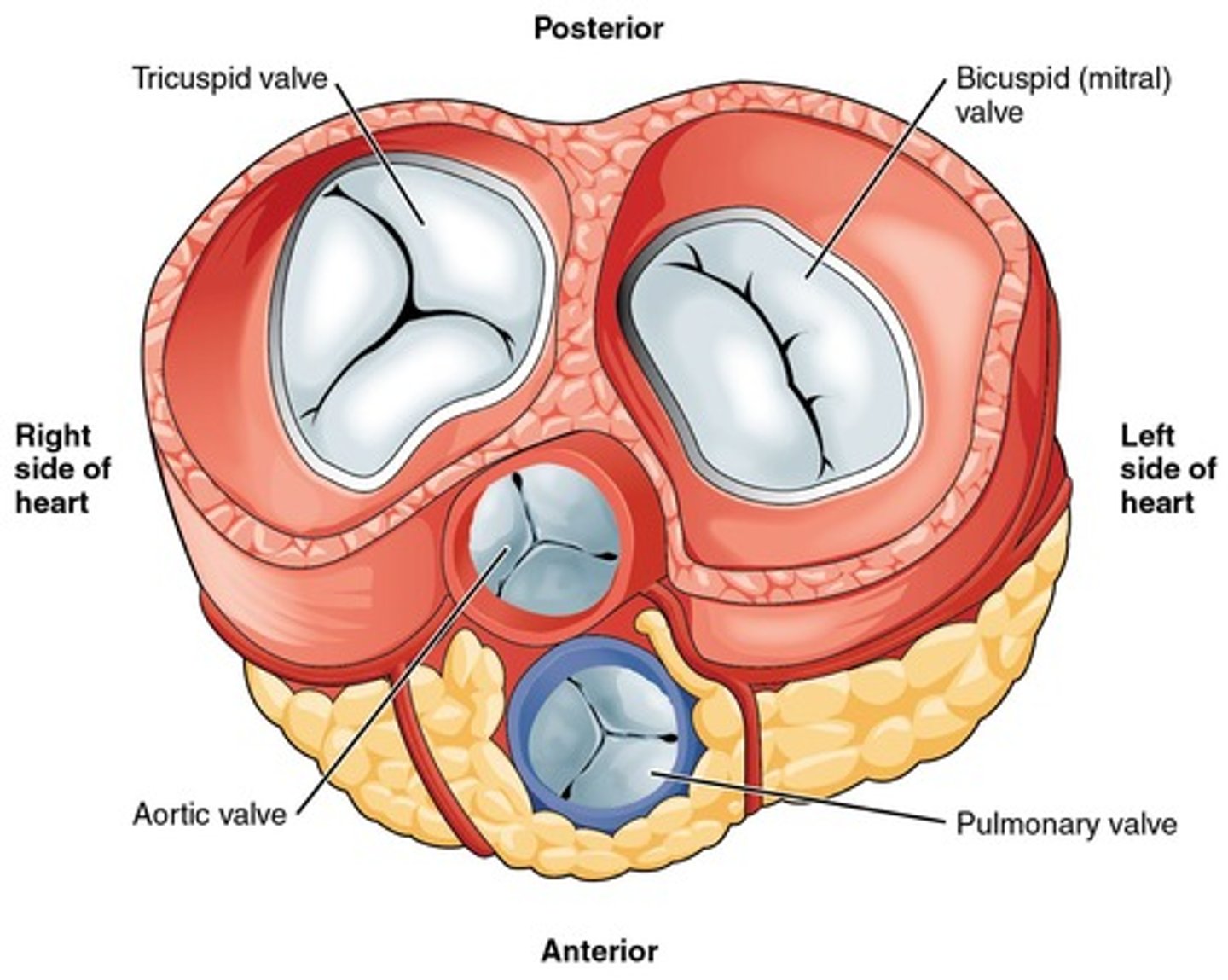
Which ventricle has a thicker wall and why?
The left ventricle has a thicker wall because it needs to pump blood into systemic circulation.
What is the function of the heart valves?
To aid the unidirectional flow of blood.
What are the receiving chambers of the heart?
The atria.
What blood vessels return blood to the right atrium?
Superior and inferior venae cavae.
What blood vessels return blood to the left atrium?
Pulmonary veins.
What is the function of the right ventricle?
To pump deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary artery.
What is the function of the left ventricle?
To pump oxygenated blood into the aorta.
What are the layers of the heart wall?
Epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium.
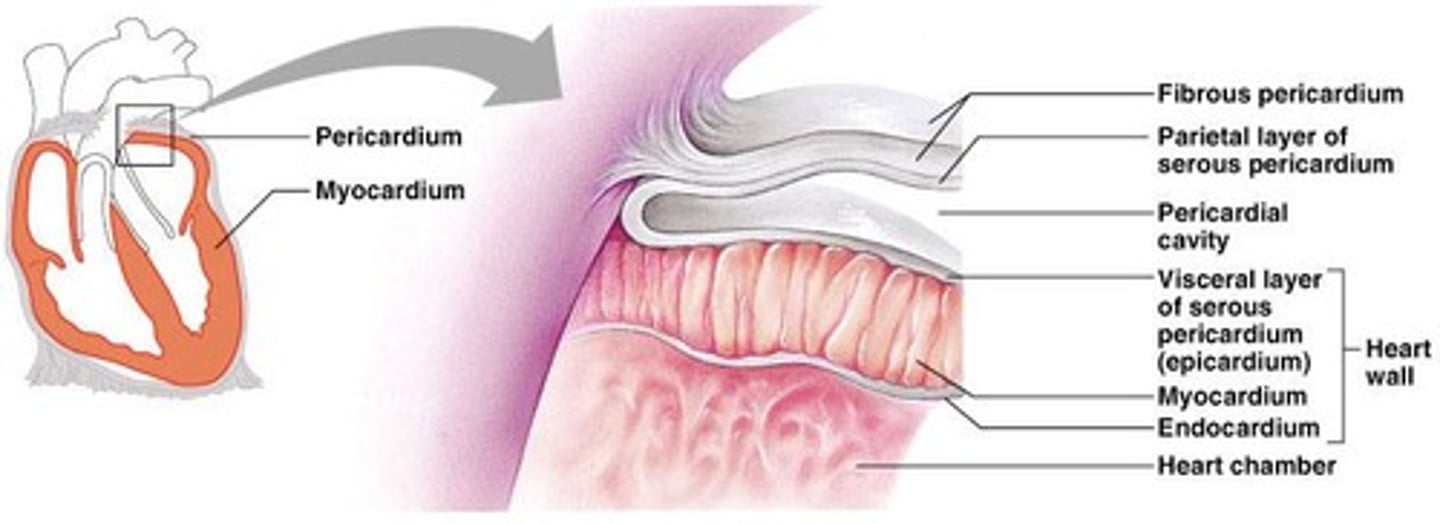
What is the pericardium?
A double-walled sac around the heart composed of a fibrous pericardium and a serous pericardium.
What are the major vessels returning blood to the heart from the anterior view?
Superior and inferior venae cavae, right and left pulmonary veins.
What vessels convey blood away from the heart?
Pulmonary trunk (splitting into right and left pulmonary arteries) and the ascending aorta.
What arteries supply the heart?
Right and left coronary arteries, marginal artery, circumflex artery, and anterior interventricular artery.
What veins drain the heart?
Small cardiac vein, anterior cardiac vein, great cardiac vein, posterior vein to left ventricle, coronary sinus, and middle cardiac vein.
When does most blood flow through the coronary arteries occur?
When the heart is relaxed.
What is the weight of the heart in an adult?
Approximately 300 grams.
What is myocardial ischemia?
A condition caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, often due to atherosclerosis.
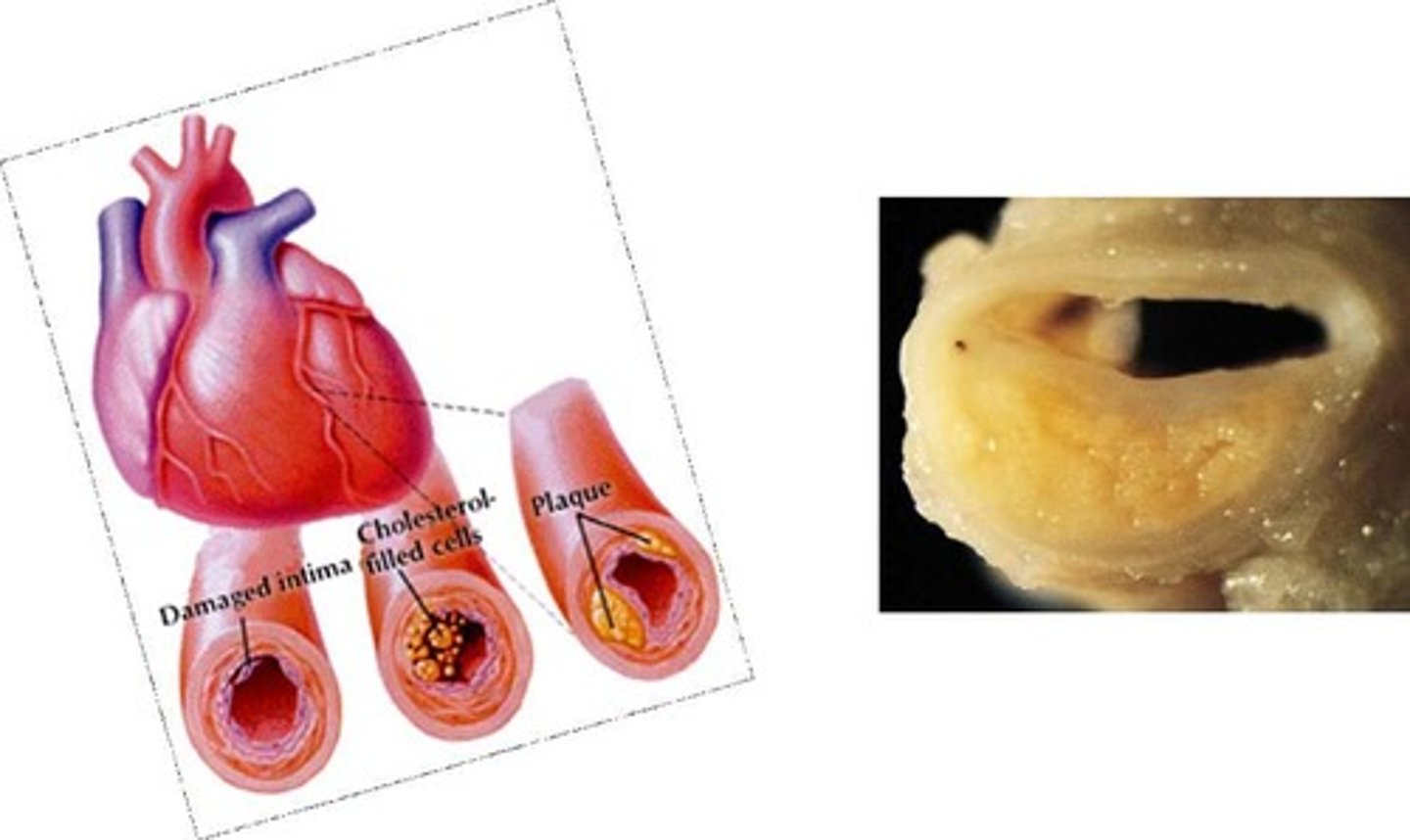
What is atherosclerosis?
A disease characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries, which can lead to myocardial ischemia.
What are the characteristics of cardiac muscle contraction?
Cardiac muscle is stimulated by nerves, is self-excitable, contracts as a unit, and has a long absolute refractory period of 250 ms.
What is the function of pacemaker cells in the heart?
Pacemaker cells, such as those in the sinoatrial (SA) node, regulate the heart's rhythm by generating action potentials.
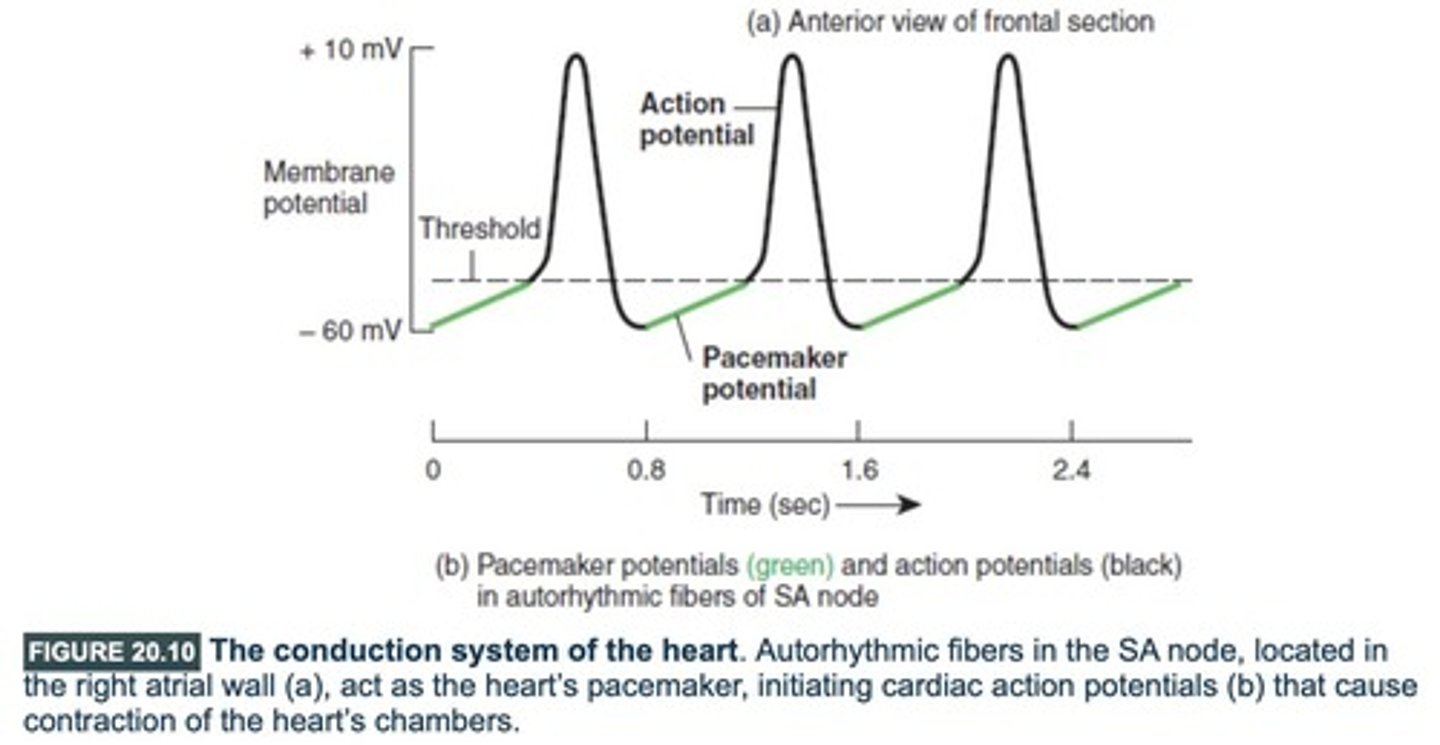
What is the pathway of conduction for an action potential in the heart?
The action potential originates in the SA node, propagates to the AV node, travels down the Bundle of His, and spreads through the left and right bundle branches and Purkinje fibers.
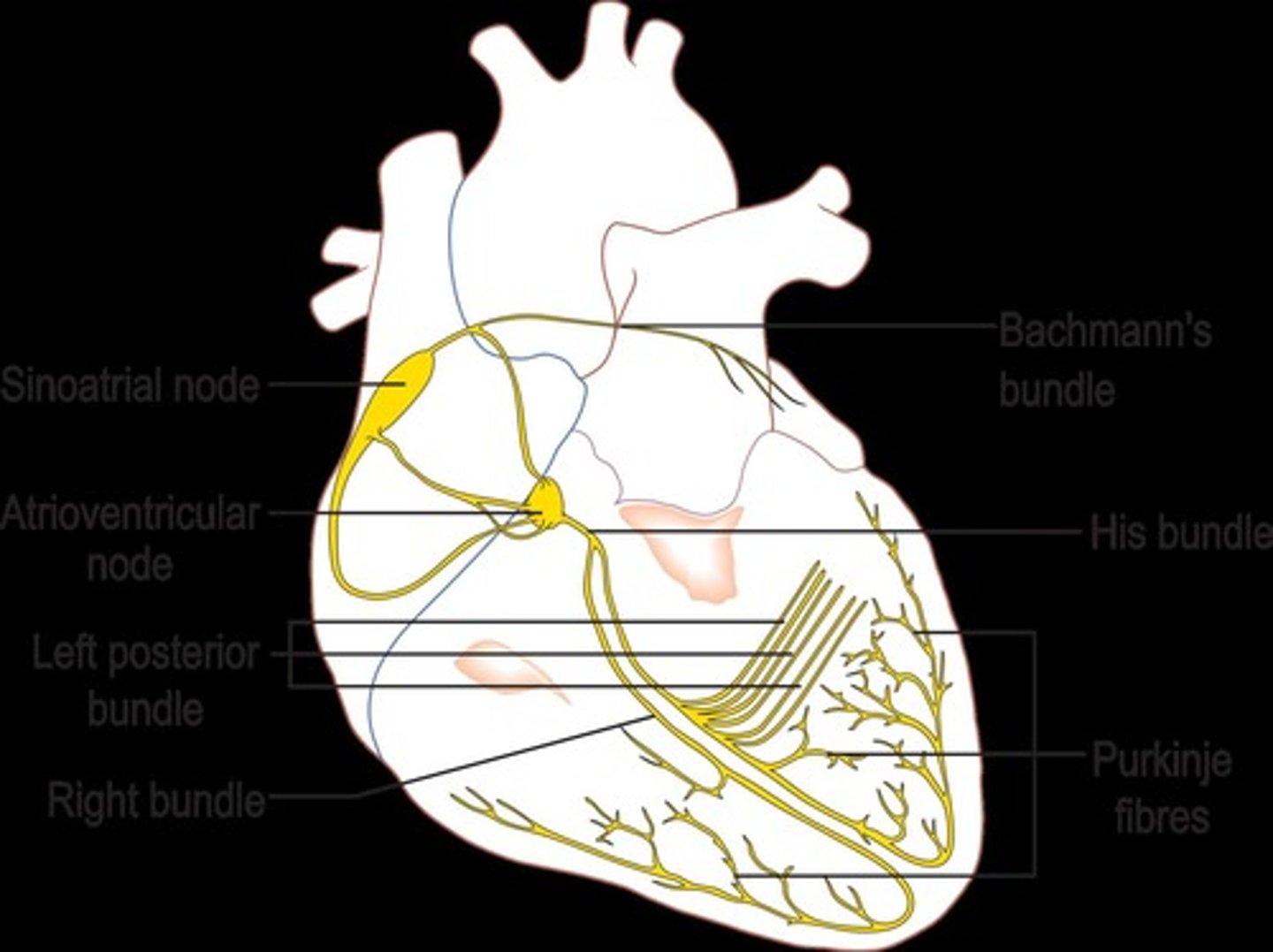
What role does the sinoatrial (SA) node play in the heart?
The SA node serves as the natural pacemaker of the heart, initiating action potentials that regulate heart rate.
What happens at the atrioventricular (AV) node during action potential conduction?
The action potential is delayed at the AV node, allowing the atria to contract before the ventricles.
What is the significance of the long absolute refractory period in cardiac muscle?
It prevents tetanus (sustained contraction), allowing the heart to relax and fill with blood between beats.
What ions are involved in the cardiac action potential?
Sodium (Na+), calcium (Ca2+), and potassium (K+) ions are involved in the phases of depolarization and repolarization.
How does the autonomic nervous system influence heart rate?
The sympathetic nervous system increases heart rate, while the parasympathetic nervous system decreases it.
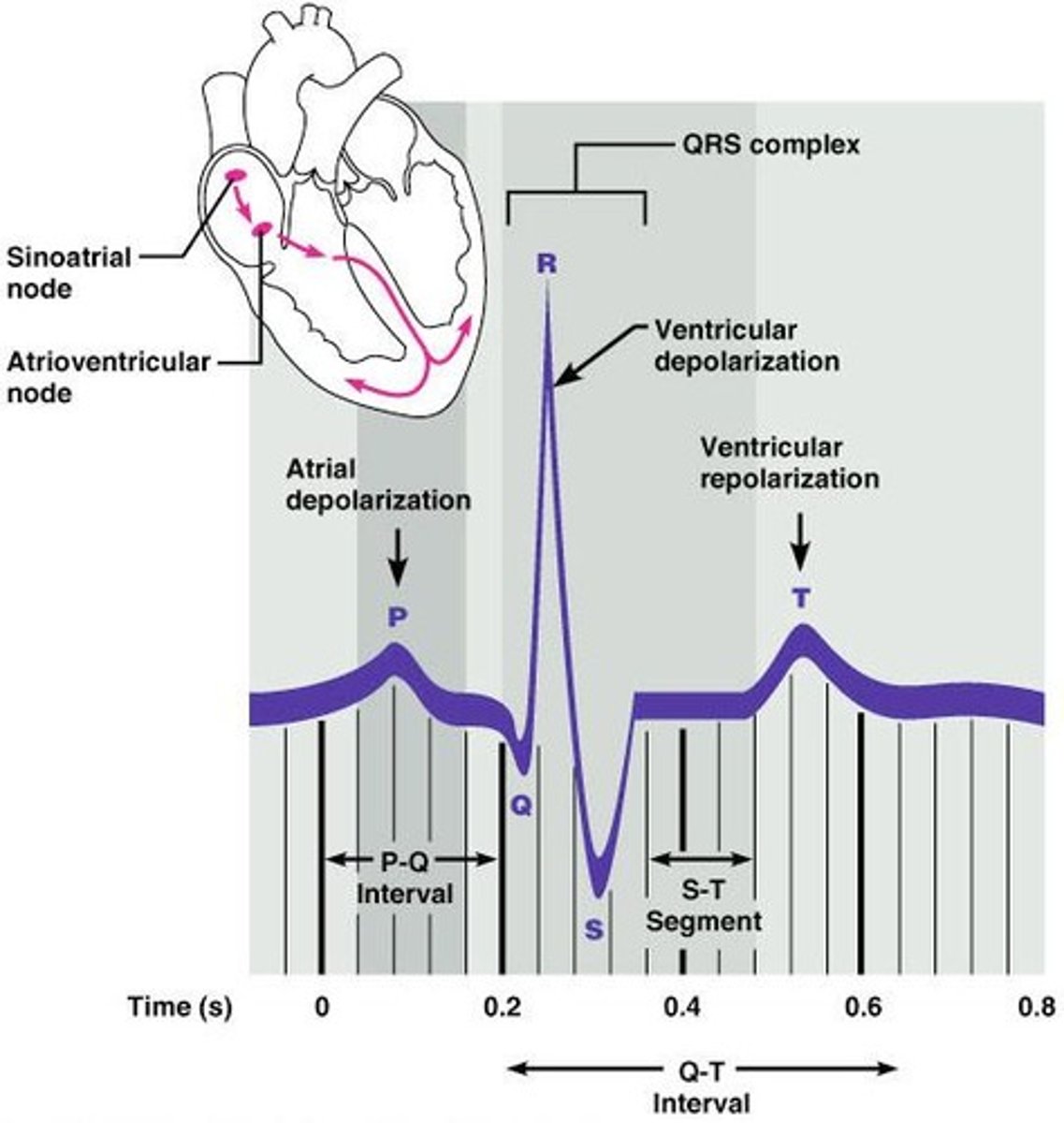
What is the electrocardiogram (ECG)?
An ECG is a recording of the overall electrical activity of the heart over time, reflecting the conduction of action potentials.
What is the role of Purkinje fibers in the heart?
Purkinje fibers rapidly disperse the action potential throughout the ventricular myocardium, ensuring coordinated contraction.
What is the typical rate of action potentials generated by the heart?
The heart typically generates about 75-80 action potentials per minute.
What is the consequence of the rapid cell-to-cell spread of impulses through gap junctions in the heart?
It allows for nearly simultaneous depolarization of the ventricular myocardium.
What is the role of the sympathetic cardioacceleratory center?
It stimulates the heart to increase its rate and force of contraction.
What is the role of the parasympathetic cardioinhibitory center?
It inhibits heart activity, decreasing heart rate.
What is the significance of the refractory period in cardiac muscle contraction?
It ensures that the heart muscle has time to relax and fill with blood before the next contraction.
What are the components of the cardiac conduction system?
The components include the SA node, AV node, Bundle of His, left and right bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers.
What happens during the rapid depolarization phase of the cardiac action potential?
Sodium channels open, allowing Na+ ions to flow into the cell, causing a rapid increase in membrane potential.
What occurs during the repolarization phase of the cardiac action potential?
Calcium channels close and potassium channels open, leading to K+ outflow and restoration of the resting membrane potential.
How does the heart's conduction system regulate heart rhythm?
It coordinates the timing of contractions between the atria and ventricles, ensuring efficient blood flow.
What is the purpose of the electrocardiogram (ECG)?
To record the electrical activity of the heart.
What does the P wave on an ECG represent?
Atrial depolarization.
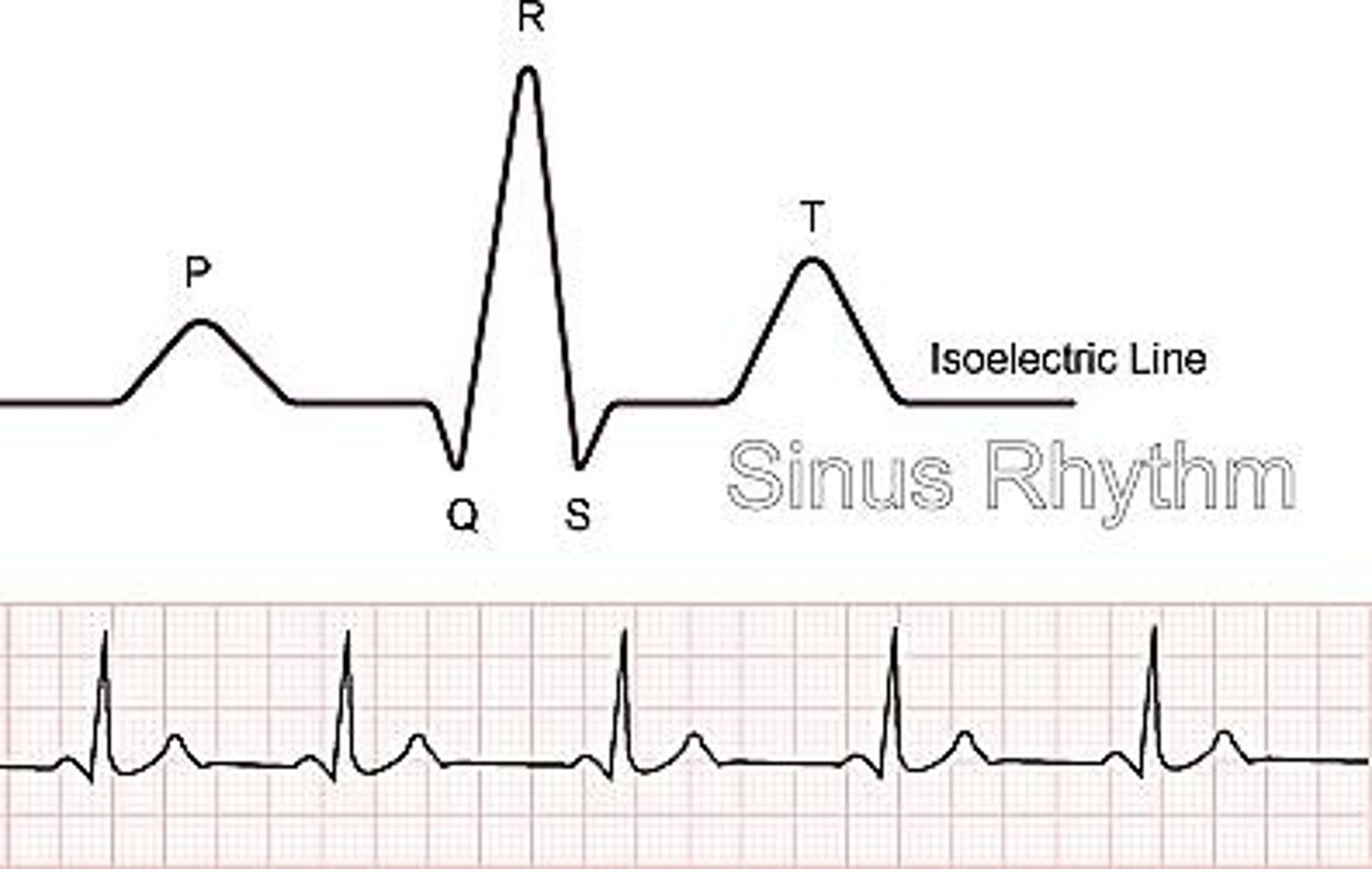
What does the QRS complex on an ECG indicate?
Ventricular depolarization.
What is represented by the T wave on an ECG?
Ventricular repolarization.
What is the significance of the atrio-ventricular node (AVN) in the cardiac impulse conduction?
It delays the impulse before it invades the ventricles.
How is heart rate measured using the ECG?
By measuring the R-R interval between consecutive QRS complexes.
What is the normal range for heart rate in beats per minute?
55-75 beats/minute.
What are sinus arrhythmias?
Variations in heart rhythm, including sinus rhythm, sinus bradycardia, and sinus tachycardia.
What can ST segment changes on an ECG indicate?
Myocardial infarction, either ST depression or ST elevation.
What are the standard limb leads in an ECG?
Leads I, II, and III.
What is the significance of the isoelectric line on an ECG?
It represents the baseline electrical activity of the heart.
What does the term 'ventricles uniformly depolarised' refer to in an ECG?
It refers to the ST segment.
What is the role of the sino-atrial node in the heart?
It initiates the cardiac impulse.
What does the term 'cardiac output' refer to?
The volume of blood the heart pumps per minute.
What are the two circulatory systems mentioned in the notes?
Systemic and pulmonary circulations.
What is the next session topic following ECG interpretation?
Cardiac output (Volume).
What anatomical structures are involved in the electrical conduction system of the heart?
Sino-atrial node, atrio-ventricular node, and ventricles.
What is the significance of measuring intervals and segments on an ECG?
They help in assessing the heart's electrical activity and rhythm.
What is coronary circulation?
The flow of blood to and from the tissues of the heart.