ANAPHY BLOOD NEUROVASC
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
BLOOD
sticky and opaque
heavier, 5x thicker than water
alkaline, pH- 7.35 and 7.45
temp- 38
5-6 liters in adults
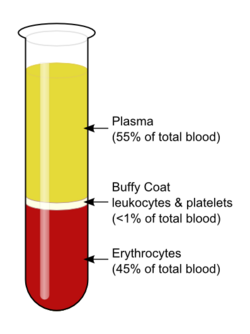
Plasma
90% water
Plasma proteins
from liver
Acidosis- blood too acidic
Alkalosis- blood too basic
Formed Elements
Erythrocytes (rbc)
Anucleate- no nucleus
Hemoglobin- iron bearing protein
slightly higher in men 13-18g
4 molecules/hb
Oxyhemoglobin- with 02
Deoxyhemoglobin- w/o 02
Biconcave discs- like donuts
the more rbc the thicker
Leukocytes (wbc)
contain nucleus and organelles
Diapedesis- can slip in n out blood vessels
Positive chemotaxis- locating damage
Leukocytosis- speed in production
Leukopenia- low wbc count
2 MAJOR GRPS
1. Granulocytes- granules in cytoplasm, lobed nuclei
Neutrophils- most numerous wbc
multilobes nucleus, cytoplasm pink
Specific and Azurophilic Granules
phagocytes in acute infection (bacteria and fungi)
respiratory burst
6-7 hrs blood, 1-4 days tissue
Eosinophils- blue-red bilobed nucleus
infection of worms
release enzymes
10 hrs blood, 10 days tissue
Basophils- rarest wbc
dark blue-purple, S-shaped nuclei
Histamine and Heparin- inflammatory
2. Agranulocytes- no granules in cytop, normal nuclei
Lymphocytes- sec most numerous
dark dark purple nuclei
in lymphatic tissues
B lymphocyte
T lymphocyte
Natural Killer Cell
Monocytes- largest wbc
u-shaped nuclei
Macrophage- eats infection, type of phagocyte
60-100 days in tissue
Most abundant to least- Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas
Platelets
fragments of Megakaryocytes
10 days
Hematopoiesis
blood cell formation
red bone marrow (myeloid tissue)
Hemocytoblast- common stem cell
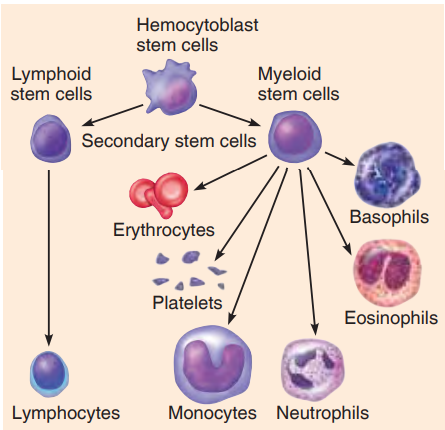
Formation of RBC
unable to synthesize, grow, or divide bcs no nucleus
100-120 days
eliminated by phagocytes
iron recycles by transferrin protein
Porphyrin to Bilirubin
Stercobilinogen- in large int
Stercobilin- color of feces
Stercobilinogen- absorbed in blood
Urobilinogen- urine
Urobilin- when exposed to air
Reticulocyte- baby rbc, still w some er. mature after 2 days
Erythropoietin- controls rbc production. kidney
Formation of WBC and Platelets
Colony Stimulating Factors (CSF)
Interleukins
both stimulates for WBC
Thrombopoietin- stimulates for platelets, liver
Megakaryocytes- produce platelets, in bone marrow
Hemostasis
stopping the bleeding
Phases
Vascular Spasm
immediate response
spasms narrow blood vessel
Platelet Plug Formation
exposed collagen fibers
platelets pile up
Primary Aggregation- formation
Secondary Aggregation- increase size of clot
Coagulation
blood clotting
Prothrombin
Thrombin- enzyme. converts Fibrinogen to Fibrin
Fibrin- forms clot
Serum- pulls ruptured edges together
3-6 minutes
Fibrinolysis- breakdown of clot
Blood Groups
loss of blood 15-30% weakens
above 30% can be fatal
Agglutination- binding of antibodies
if clumps in anti, thats the name
negative can only receive negative
Developmental Aspects
liver and spleen before 7ms
rbc count higher in children
Fetal Hemoglobin
Homeostatic Imbalances
Anemia- decrease in rbc or hemoglobin
Sickle Cell Anemia- crescent shaped rbc
Pernicious Anemia- high risk in elderlies vitamin b12
Polycythemia- abnormal increase of rbc
Polycythemia Vera- increase of rbc bcs of bone marrow cancer
Secondary Polycythemia- response to living in high altitudes
Leukemia- cancerous bone marrow, immature wbc
Thrombus- clot in unbroken blood vessel
Embolus- if it flows freely in bloodstream
Thrombocytopenia- platelet deficiency
Petechiae- small purplish blotches from bleeding blood vessels
Hemophilia- lack of any factors in clotting
Hemolytic- in newborns rh+ with rh- mothers
NERVOUS SYSTEM
Structural
Central Nervous System
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
nerves
Sensory Division (Afferent)
TO nervous system from sensory
Somatic Sensory Fibers- from skin, skeletal muscles, joints
Visceral Sensory Fibers- from visceral organs
Motor Division (Efferent)
FROM CNS to effector organs
Somatic Nervous System- voluntary
Autonomic Nervous System- involuntary
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Supporting Cells
CNS
Neuroglia- support neurons, always can divide
Astrocytes- star shaped, capillaries and neurons
Microglia- spiderlike phagocytes
Ependymal- lines central cavities and spinal cord, cerebrospinal fluid
Oligodendrocytes- flat extensions, produces myelin sheath
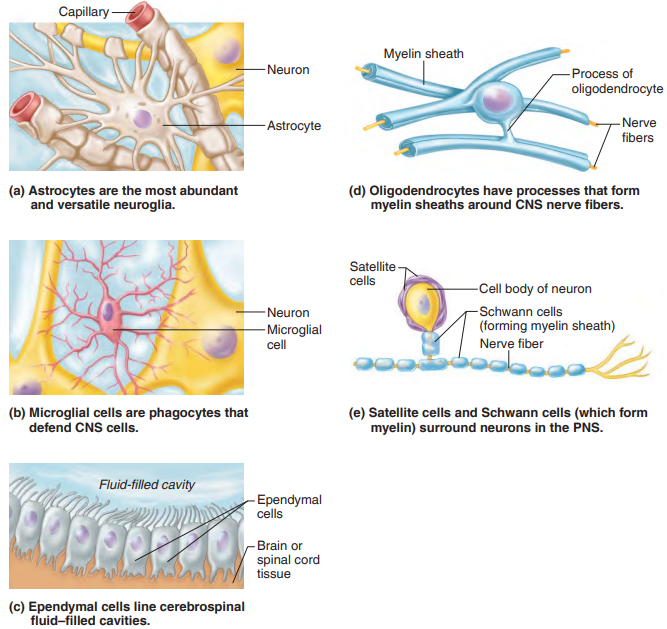
PNS
Schwann Cells- form myelin sheaths
Satellite Cells- protect cells
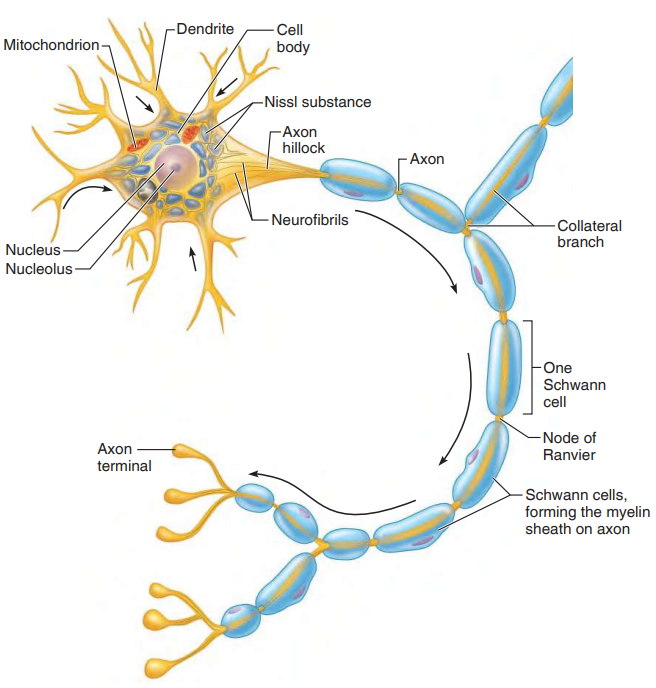
Neurons
Structure
nerve cells
all have cell body
Cell Body
metabolic center of neuron
all organelles except centrioles
Nissl bodies- rough ER
Neurofibrils- maintain cell shape
Processes
fibers
Dendrites- convey messages toward cell body, may be many
Axons- generate impulses away from cell body, only one
Axon Hillock- where axon arises
Axon Terminals- contain neurotransmitters
Synaptic Cleft- what separates axon terminal from next neuron
Synapse- junction to transmit impulse
Myelin Sheaths
waxy appearance
protects fibers
increase speed of impulse
Neurilemma- external to myelin sheath
Nodes of Ranvier- gaps
Clusters of neuron cell bodies
Nuclei- in CNS
Ganglia- PNS
Bundles of nerve fibers
Tracts- CNS
Nerves- PNS
White matter- myelinated
Gray matter- unmyelinated
Functional
Sensory Neurons (Afferent)
neurons carrying impulse from sensory to CNS
Based on dendrite endings
Cutaneous Sense Organs- sensory in skin
Proprioceptors- sensory in muscles and tendons
Motor Neurons (Efferent)
from CNS to muscles
Interneurons (Association)
connect motor and sensory in neural pathways
Structural
Multipolar Neuron- most common, several dendrites and axons
Bipolar Neurons- 2 processes, one axon one dendrite
Unipolar Neurons- single process, PNS
Nerve Impulses
Irritability- respond to stimulus
Conductivity- transmit impulse to other
Unmyelinated
Resting Neuron- neuron polarized, fewer +ions in than out
Action Potential Initiation- depolarization, sodium outside floods in
Action Potential Generation- if stimulus strong enough
Action Potential Propagation- propagates the entire length
Repolarization- restoring rest same direction
Myelinated
Saltatory Conduction- faster
Reflex
Two neuron- kneejerk
Three neuron- withdrawal reflex
Central Nervous System
Cerebral Hemispheres
Cerebrum
most superior part
Gyri- elevated ridges
Sulci- shallow grooves
Fissures- deeper grooves
3 Basic Regions
1. Gray Matter (cortex)
2. White Matter (internal)
3. Basal Nuclei
Cerebral Cortex
Primary Somatic Sensory Area- parietal lobe, recognize
Sensory Homunculus- spatial map
Primary Motor Area- conscious move, Corticospinal tract
Motor Homunculus- body map on motor conrtex
Broca’s Area- speaking
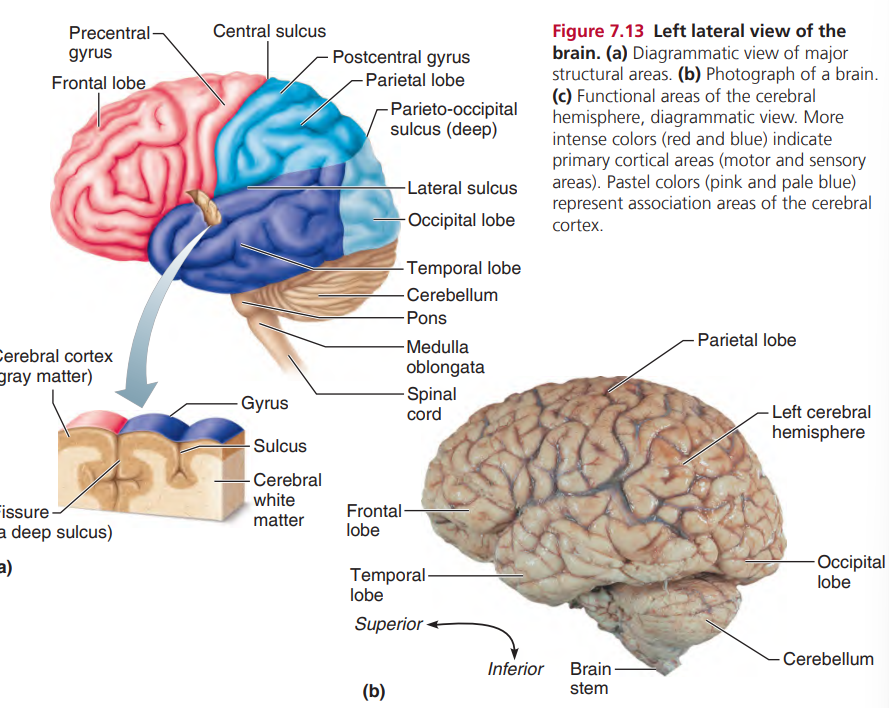
Cerebral White Matter
carries impulse
Corpus Callosum- connects cerebral hemispheres
Basal Nuclei
most gray matter islands
regulate voluntary acts
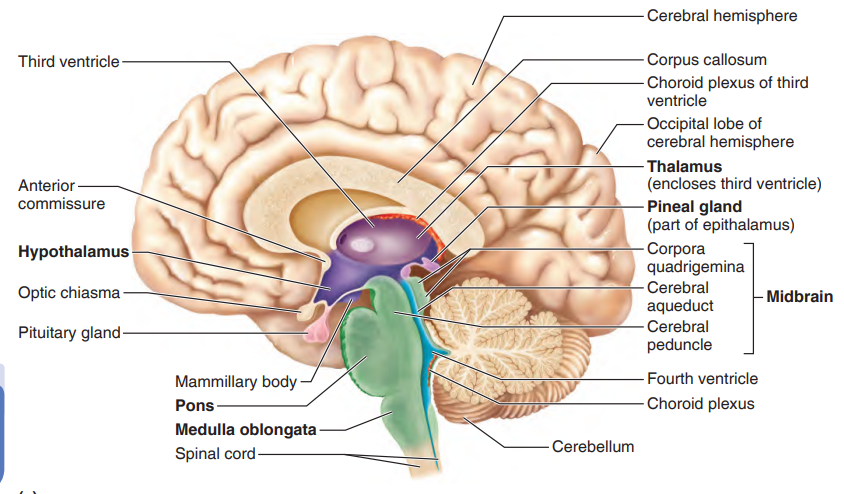
Diencephalon
interbrain
Major Structures
Thalamus- relay station for sensory impulses
Hypothalamus
floor of diencephalon
part of Limbic System
regulates Pituitary Gland
Mamillary Bodies- sense of smell
Epithalamus
Pineal Gland
Choroid Plexus- form cerebrospinal fluid
Brain Stem
pathway, many small gray matters
Major Structures
Midbrain
small part from mammillary bodies to pons inferiorly
Cerebral Aqueduct- tiny canal travels through midbrain
Cerebral Peduncles- convey ascending and descending impulses
Corpora Quadrigemina- reflex centers vision and hearing
Pons- rounded structure below midbrain, fiber tracts
Medulla Oblongata- pyramidal tracts and regulation
Reticular Formation- motor control of visceral organs
Reticular Activating System- consciousness
Cerebellum
cauliflower like
2 hemispheres
skeletal muscle activity and balance
Protection of Central Nervous System
Meninges
connective tissue membranes
1. Dura Mater- outermost, double layered membrane
Falx Cerebri- separate 2 cerebral hemispheres
Tentorium Cerebelli- separate cerebellum and cerebrum
2. Arachnoid Mater- cobweb
Subarachnoid space- threadlike extension
Pia Mater- clings to surface of brain
Cerebrospinal Fluid
helps brain float
flows inside brain
150ml
The Blood-Brain Barrier- capillaries
Spinal Cord
31 pairs of spinal nerves
Cauda Equina- collection of spinal nerves at vertebral canal
Gray Matter
looks like butterfly
Dorsal horns- contain interneurons, Dorsal Root Ganglion, Ventral Root
Ventral horns- contain motor neurons of somatic
surrounds central canal of the cord that contains CSF
White Matter
3 regions
Dorsal column- ascending sensory tracts
Lateral column- both asc and desc motor tracts
Ventral column- both asc and desc motor tracts
Peripheral Nervous System
Nerve
Endoneurium- delicate connective tissue
Perineurium- coarser connective tissue, form Fascicles
Epineurium- tough fibrous sheath, bound Fascicles
Sensory Nerves
Motor Nerves
Mixed Nerves- all spinal nerves
Cranial Nerves
12 pairs all serve head and neck except Vagus
Oh Oh Oh To Touch And Feel Very Good Velvet At Home
Olfactory- s. smell
Optic- s. vision
Oculomotor- m. eye movement and pupil
Trochlear- m. external eye movement down up
Trigeminal- mix. sensory face motor chewing
Abducens- m. eye move lateral
Facial- mix. facial expression. taste
Vestibulocochlear- mix. hearing and balance
Glossopharyngeal- mix. sensory taste motor gag reflex, swallowing
Vagus- mix. rest and digest
Accessory- m. shoulder shrug and head turn
Hypoglossal- m. tongue movements
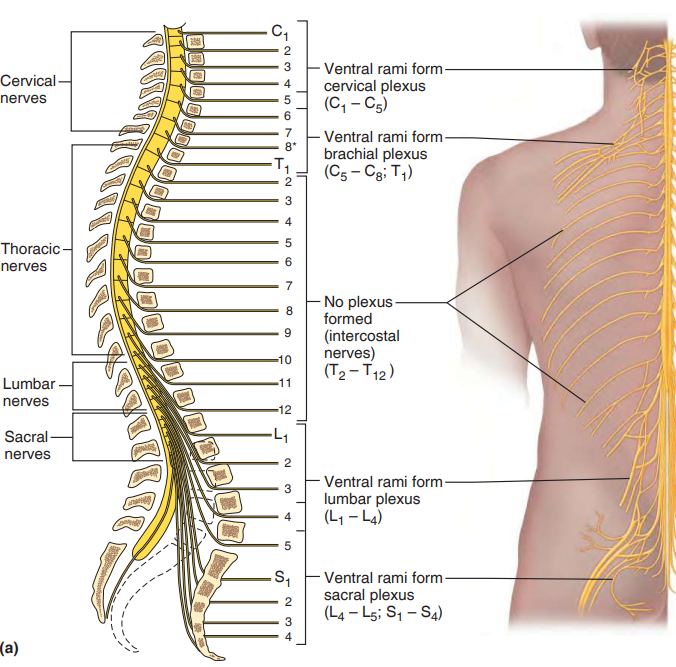
Spinal Nerves
31 pairs
joining of ventral and dorsal roots
Dorsal Ramus- posterior body trunk
Ventral Ramus- Intercostal Nerves
Plexuses- serve limbs C1-8 T1-12 L1-5 S1-4
Cervical C1-5: Phrenic, diaphragm
Brachial C5-8 T1: Arm
Lumbar L1-4: femoral to knees
Sacral L4-5 S1-3: gluteal, thigh divides to legs and feet
Autonomic Nervous System
2 motor neurons
1. Preganglionic Neuron- in brain or spinal cord
Preganglionic Axon- leaves CNS to form synapse
2. Postganglionic Axon- extend to organs
Sympathetic- extreme situations'
thoracolumbar division
preganglionic neurons in gray matter of spinal cord T1-L2
Ramus Communicans- small communicating branch
Sympathetic Trunk Ganglion- vertebral column on each side
Splanchnic Nerves- synapse with ganglionic neuron
Parasympathetic- conserve energy, rest and digest
craniosacral division
preganglionic neurons in brain and S2-4
synapse with Terminal Ganglion
Somatic Nervous System
motor neurons cell bodies INSIDE CNS extend to organs
Developmental Aspects
forms during first month
Hypothalamus- last areas to mature
coordination superior-inferior proximal-distal
Homeostatic Imbalances
Multiple Sclerosis- destroyed myelin sheaths
Huntington’s Disease- nerve cells decay
Parkinson’s Disease- affects movement, lack dopamine
Ataxia- cerebellum damaged, may appear drunk
Meningitis- inflammation of meninges
Encephalitis- inflammation of brain
Hydrocephalus- water in brain
Concussion- light brain injury
Contusion- marked tissue destruction, cerebral cortex injury
Intracranial Hemorrhage- bleeding of ruptured vessels
Cerebral Edema- swelling of brain
Cerebrovascular Accidents- strokes, blood circulation blocked
Hemiplegia- one sided paralysis
Aphasias- damage to left hemisphere language area
Motor Aphasia- damage to Broca, affect speech
Sensory Aphasia- affect ability to understand language
Transient Ischemic Attack- temporary brain ischemia (restricted blood flow)
Flaccid Paralysis- damage to ventral root
Spastic Paralysis- damage to spinal cord, uncontrollabe movements
Cerebral Palsy- temp lack of oxyg in baby delivery
Anencephaly- cerebrum fails to develop
Spina Bifida- vertebrae incomplete
Orthostatic Hypotension- blood pooling to feet
Arteriosclerosis- decreased elasticity of arteries, no oxyg to neurons
Senility- decline of oxygen due to aging