breakdown of classical mechanics
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
what is black body radiation
the light radiated by an object when is it hot
why was the quantisation of light idea developed
classical physics was failing to explain several phenomena (eg black body radiation, photoelectric effect), but these could be explained by the quantisation of light into discrete particles (photons).
energy of a photon equation
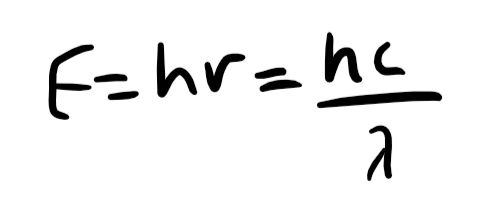
explain the photoelectric effect
equation?
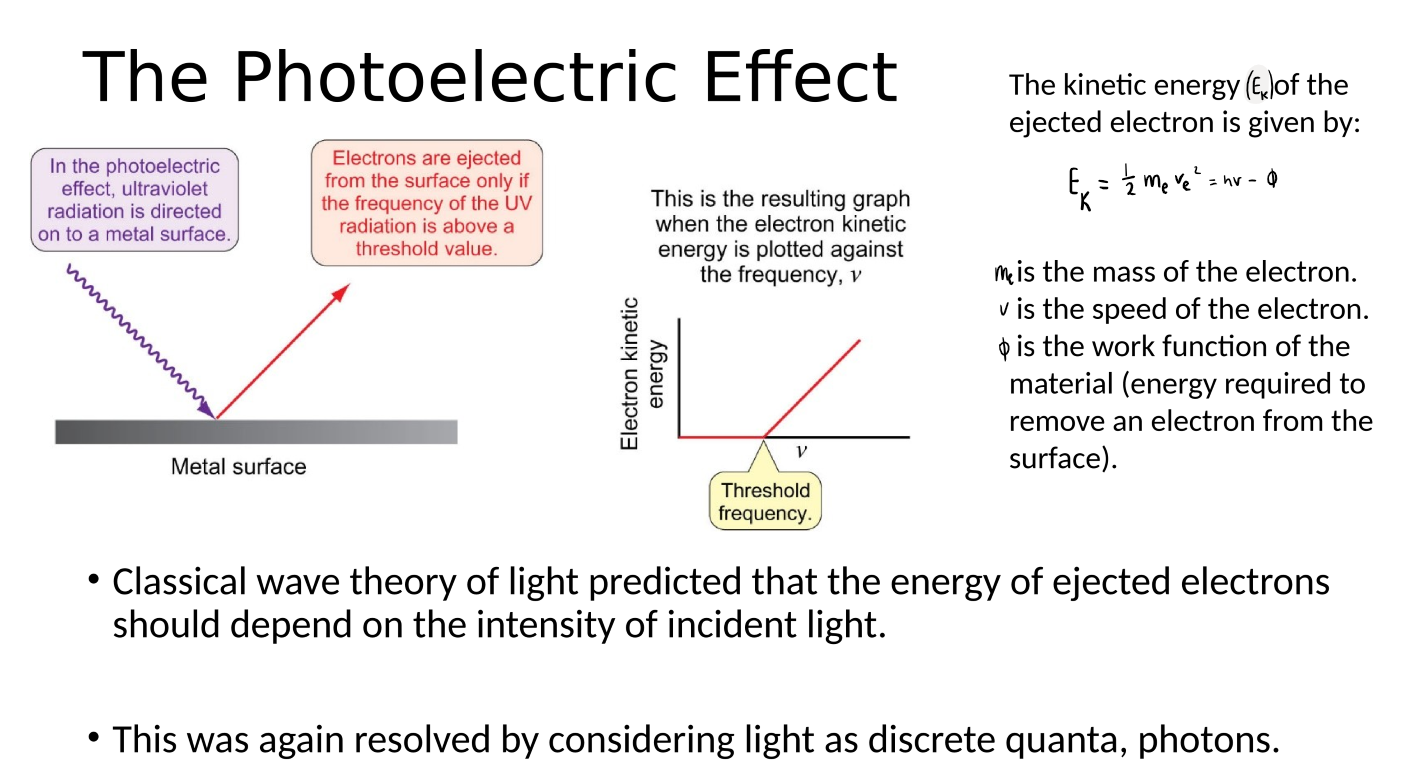
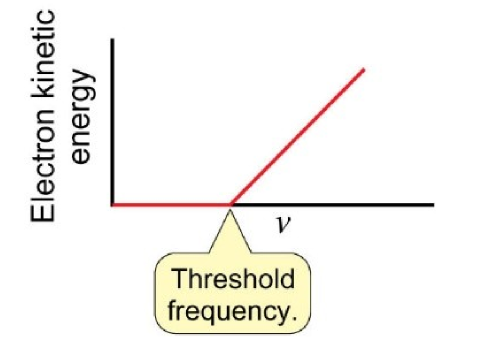
graph resulting from the photoelectric effect
equation for the kinetic energy of the ejected electron in the photoelectric effect
where me is the mass of the electron, v is the speed of the electron and Φ is the work function of the material (energy required to remove an electron from the surface)
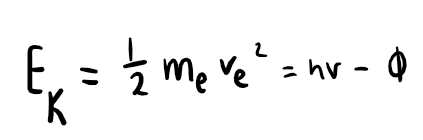
what are the emission spectrum transition series
series of lines in the atomic emission spectrum corresponding to transitions between energy levels in the atom. each transition corresponds to a line in the spectrum.
hydrogen atomic emission spectrum transition series:
n = ?
name?
region?
transitions to n=1 → Lyman series (UV)
transitions to n=2 → Balmer series (visible)
transitions to n=3 → Paschen series (IR)
transitions to n=4 → Brackett (IR)
transitions to n=5 → Pfund (IR)
equation for the quantization of the electronic energy levels in a hydrogen atom
(transition between lower/higher)
hv = E1 - E2
what is the Rydberg equation
where v is the frequency of light in Hz, RH is the Rydberg constant and n1 and n2 are integers representing the energy levels, where n2 > n1.
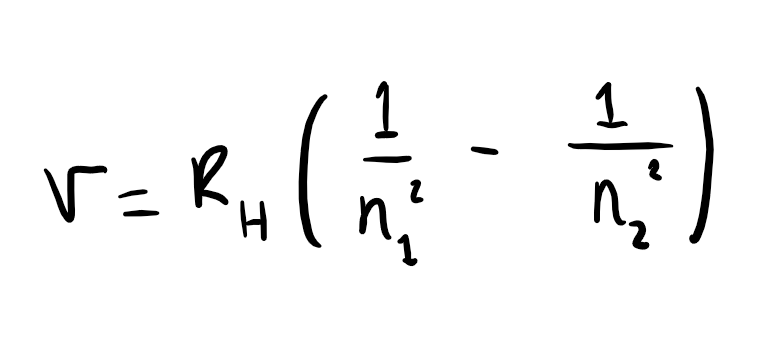
what came before the Rydberg equation
Balmer identified patterns in hydrogen’s emission spectrum and showed that all the frequencies fit the equation.
how was the Rydberg equation developed
after Balmer, further series of lines were discovered in other regions. Rydberg demonstrated that the frequencies of all the lines in the atomic spectrum of hydrogen are given by the Rydberg equation
how can ionization energy (kJ mol-1) be found using the Rydberg equation
-in the emission spectrum, the lines get closer together until they reach a continuum. at this continuum, n2 = ∞ and the electron is no longer part of the atom.
-this means the frequency of radiation needed to remove an electron completely can be found, and hence ionization energy can be calculated.
-the electron is going from n1 = 1 to n2 = ∞.
-use the Rydberg equation to find the corresponding frequency of the transition.
-use E=hv to convert the frequency into the energy of the transition for a single atom (kJ)
-convert the energy of the transition for one atom into that for a mole of atoms (MULTIPLY)
how does the hydrogen spectrum show the universe is expanding
-position of hydrogen spectrum from distant stars is shifted to longer wavelengths
-this red shift is due to the doppler effect
-led to conclusion that universe is expanding
what is wave-particle duality of light
photons behave as particles in some instances (photoelectric effect) an as waves in others (Young’s double slit)
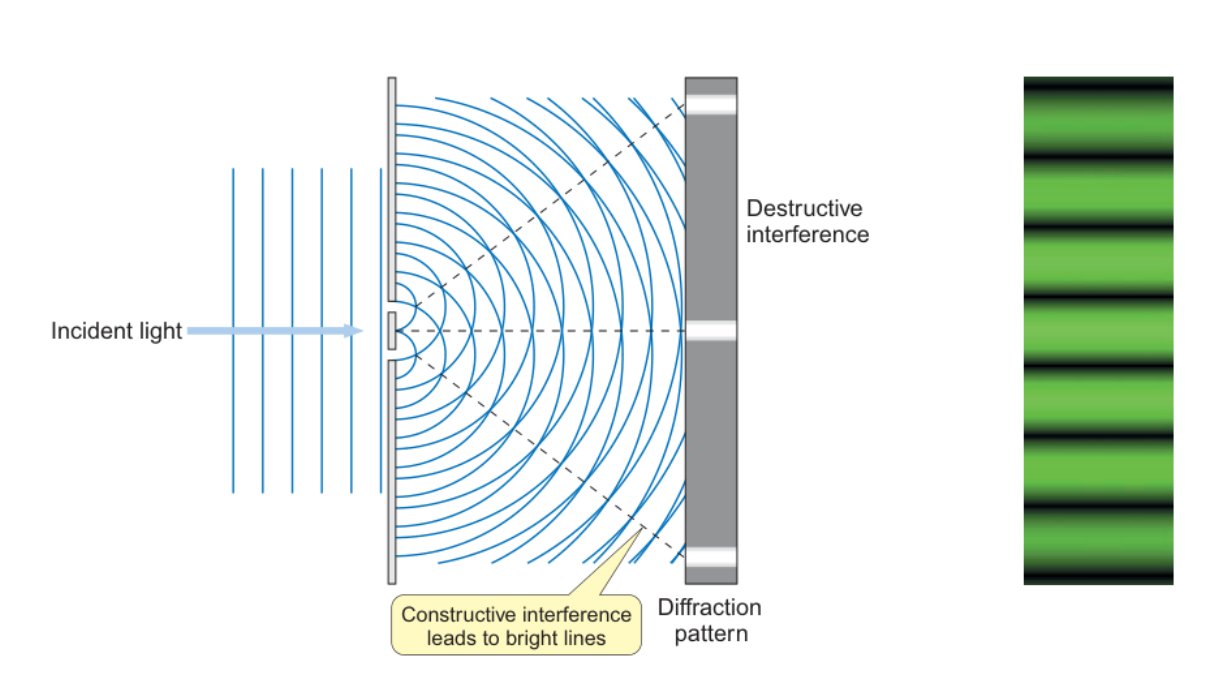
how did Young demonstrate wave behaviour of photons
double slit experiment
when light pass through two closely spaced slits, each slit gives rise to a circular wave and these waves interfere with each other to give a diffraction pattern consisting of a series of bright and dark lines
when the peak of the first wave coincides with the peak of the second, constructive interference occurs and the amplitudes of the two waves add together. when the peak of the first wave coincides with the trough of the second, destructive interference occurs and the two waves cancel each other out.