Anatomy practical #4
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Spinal nerves
nerves that bring information to and from the spinal cord
Cranial nerves
nerves bringing information to and from the brainstem
Reflex
-involuntary
-not subject to conscious thought/control
-greater speed of response
-goes straight to spinal cord, skips brain
-ex: knee jerk, removing hand from hot stove
Reaction
-voluntary
-conscious thought
-slower speed of response
-involves the brain
-ex: hearing a stimulus and pushing a button
What are the two different types of neurons?
Sensory (afferent) and motor (efferent) (SAME)
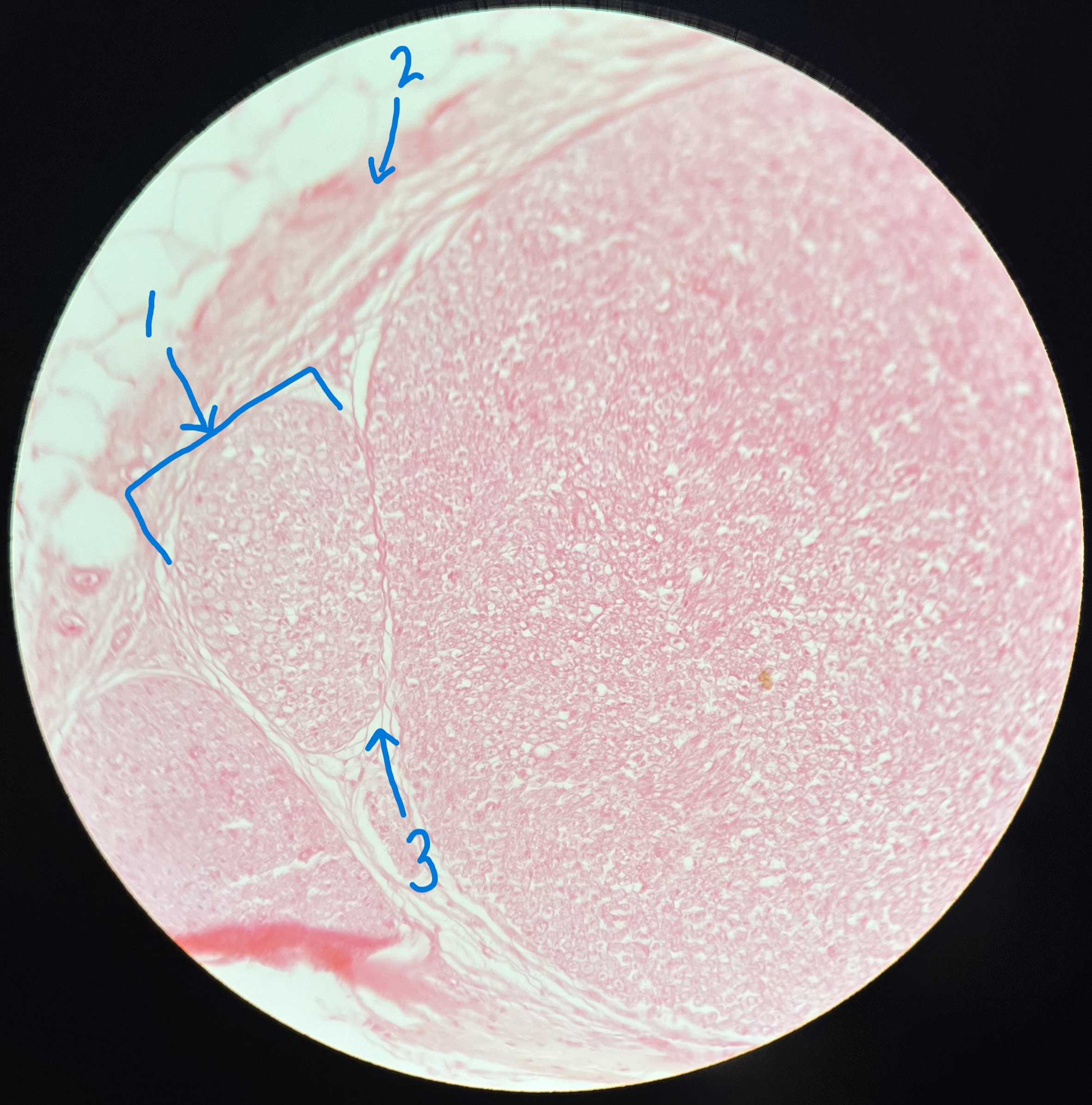
What is #1 pointing to?
fasicle
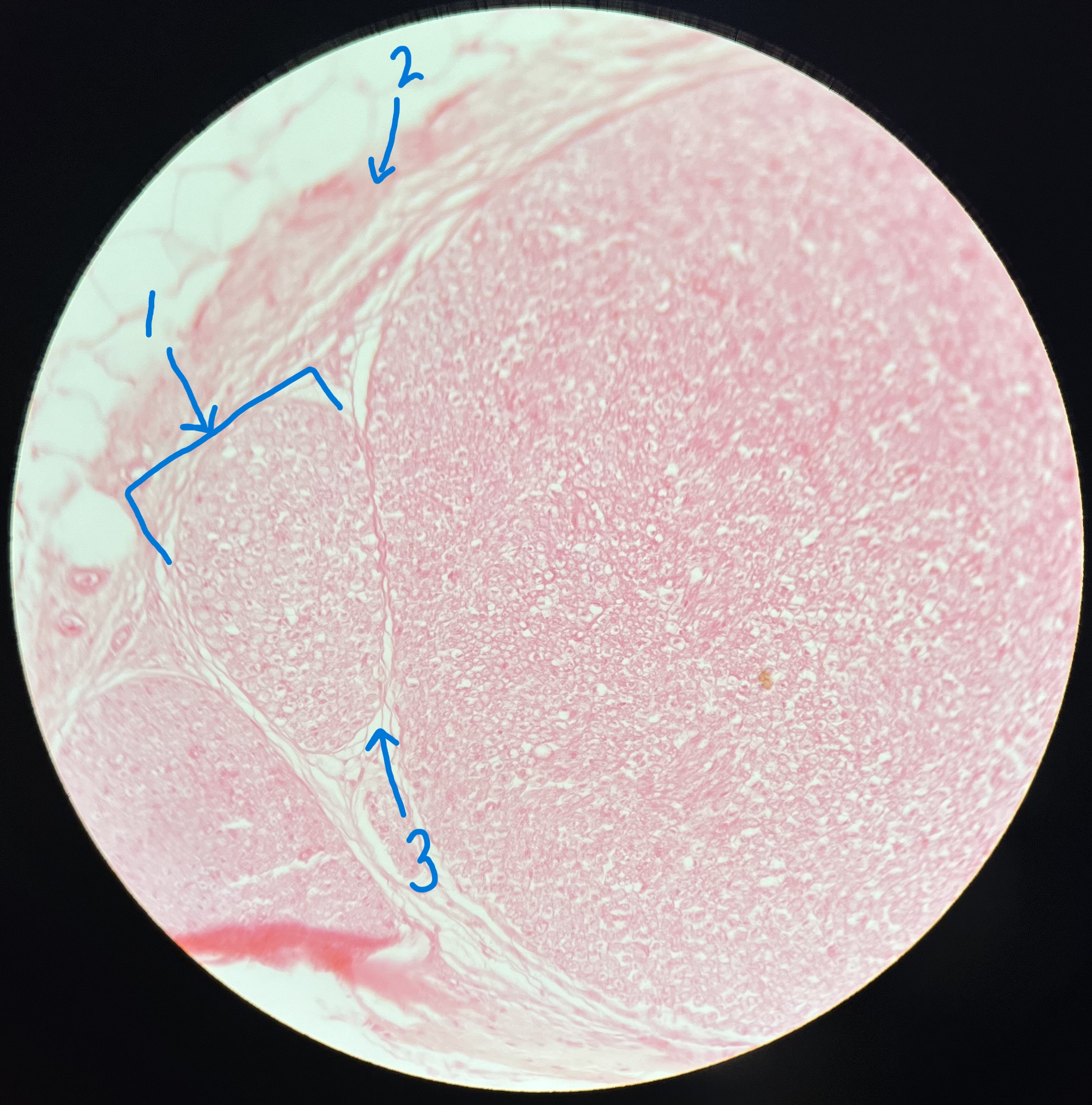
What is #2 pointing to?
epineurium
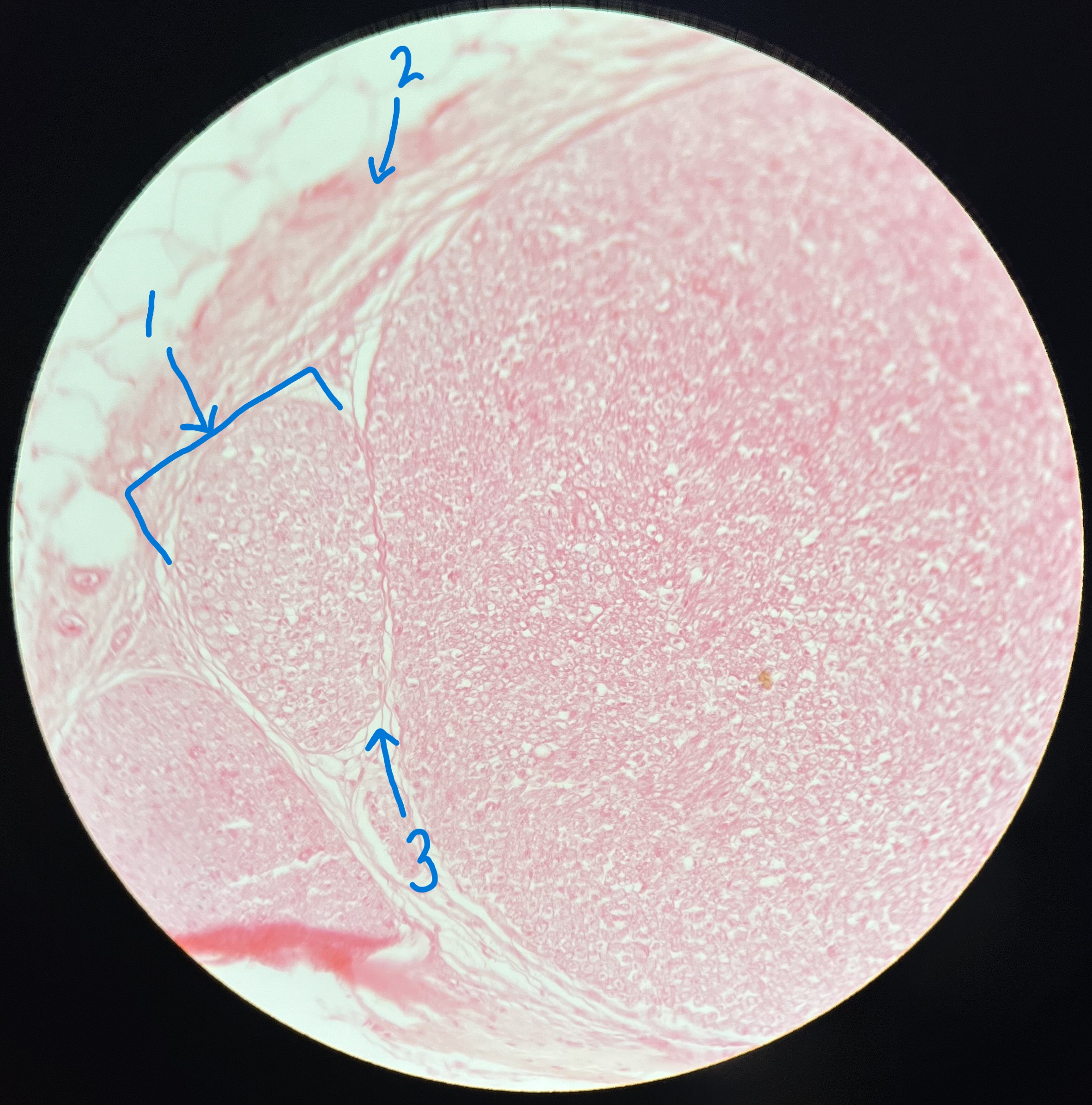
What is #3 pointing to?
perineurium
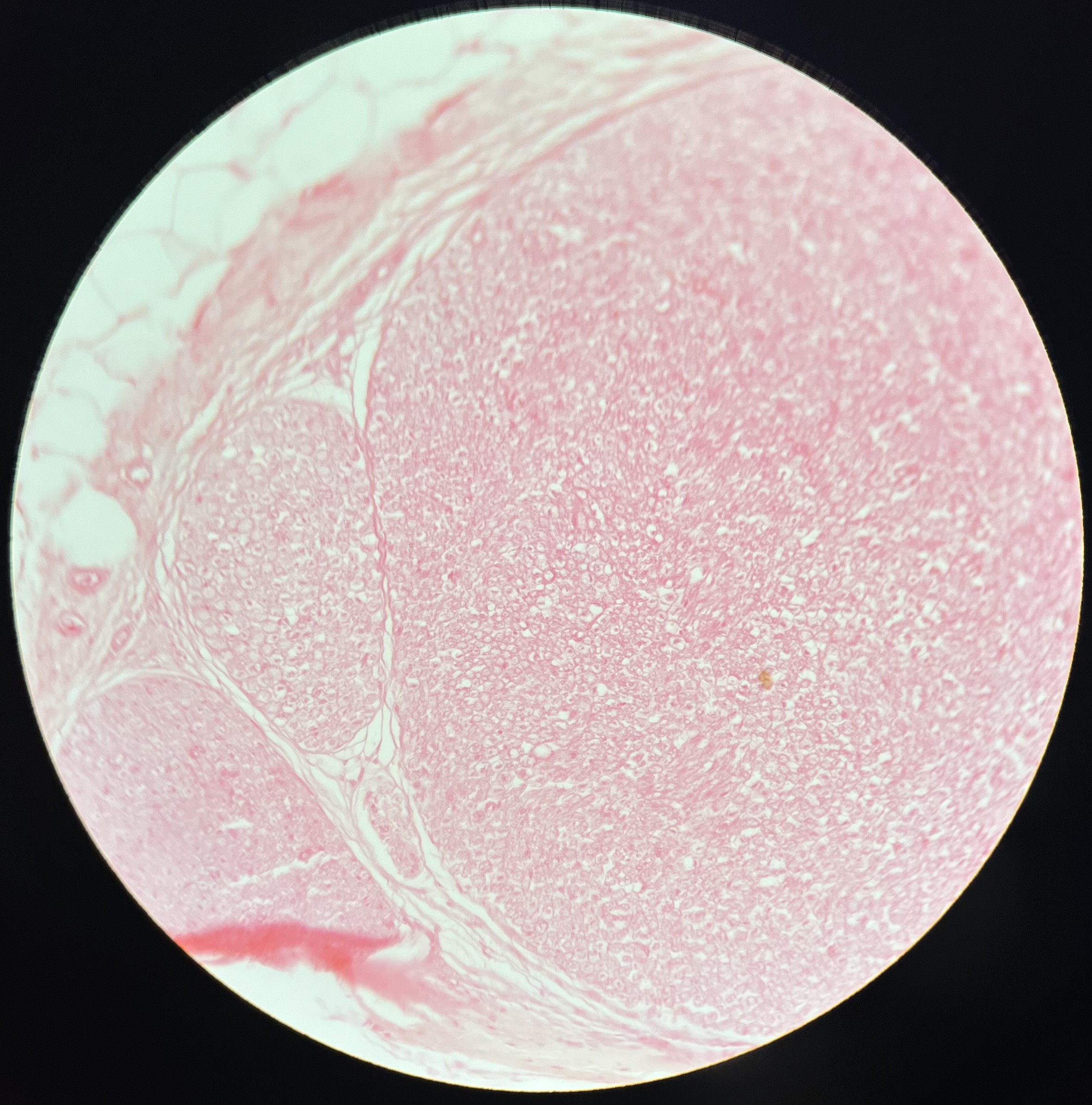
What kind of tissue is this?
peripheral nerve
What is cranial nerve I?
Olfactory nerve
What is cranial nerve II?
Optic nerve
What is cranial nerve VII?
Facial nerve
What is cranial nerve VIII?
Vestibulocochlear/auditory nerve
What is cranial nerve IX?
Glossopharyngeal
What is cranial nerve X?
Vagus nerve
What is the function of the olfactory nerve?
smell, sensory nerves send odor impulse
What is the function of the optic nerve?
transmits visual information from retina
What is the function of the facial nerve?
taste sensation, muscles in facial expression
What is the function of the vestibulocochlear/auditory nerve?
transmits sound and equilibrium information
What is the function of the glossopharyngeal nerve?
enervates muscles for swallowing and taste/speaking, coughing, swallowing ability
What is the function of the vagus nerve?
speech, swallowing, salivary glands
What are the components of a reflex arch?
receptor, spine, effector
What is the visual pathway?
1. Photoreceptors in Retina
(Rods/Cones) →
2. Optic Nerve (CN II) →
3. Optic Chiasm →
4. Optic Tract →
5. LGN of Thalamus →
6. Occipital Lobe (Primary Visual Cortex)
What is the auditory pathway?
1. Mechanoreceptors in Cochlea →
2. Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII) →
3. Medulla oblongata →
4. Inferior colliculus →
5. Thalamus →
6. Temporal Lobe (Primary Auditory Cortex)
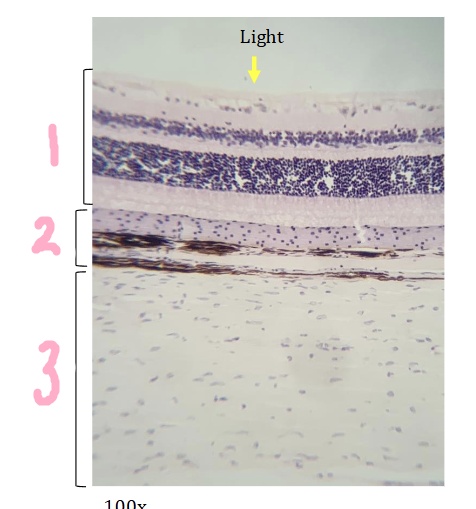
What is #1 pointing to?
retina
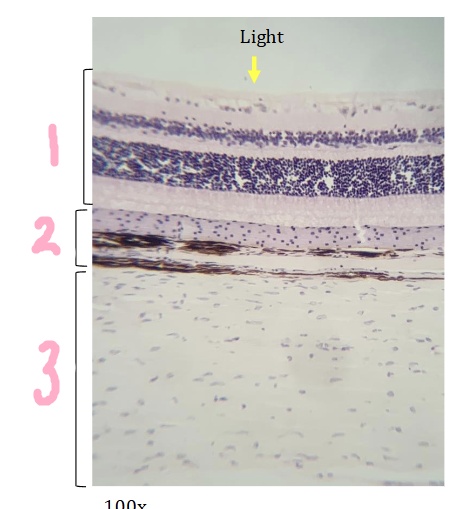
What is #2 pointing to?
Choroid
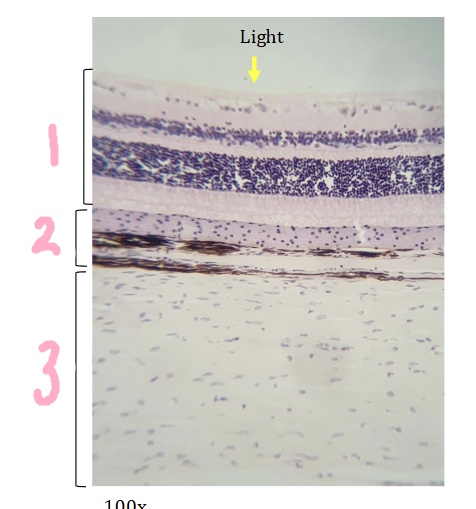
What is #3 pointing to?
sclera
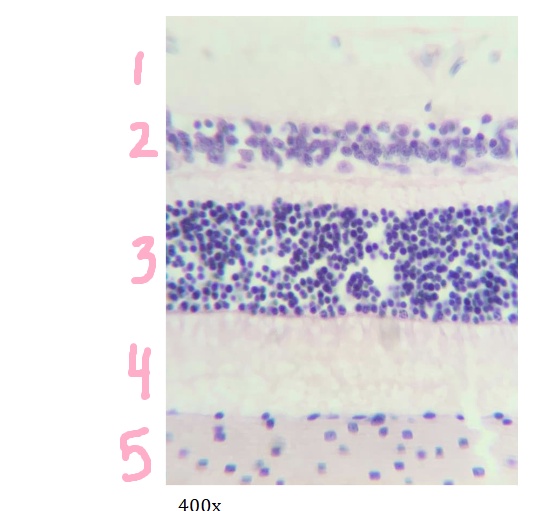
What is #1 pointing to?
nerve fiber layer
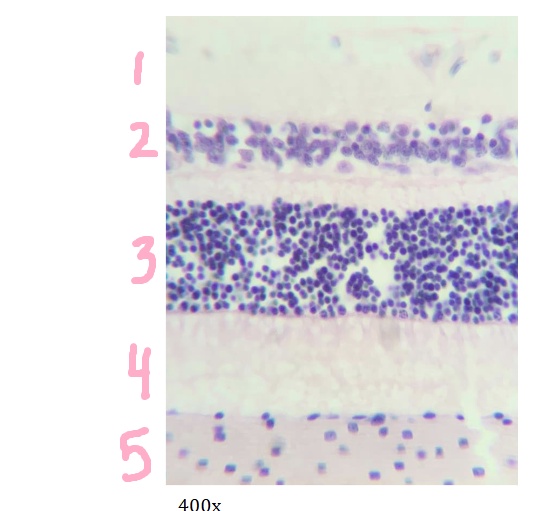
What is #2 pointing to?
inner nuclear layer
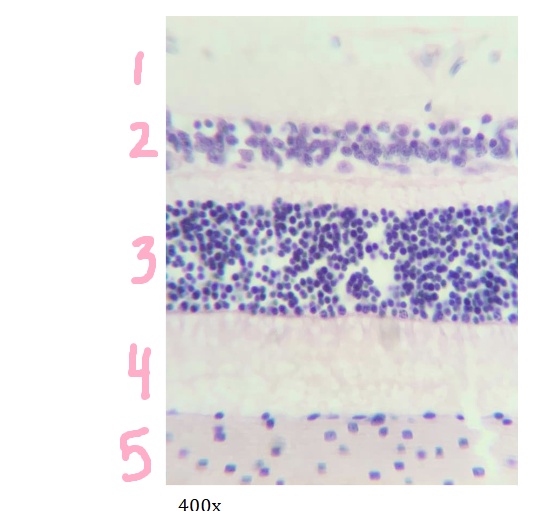
What is #3 pointing to?
outer nuclear layer
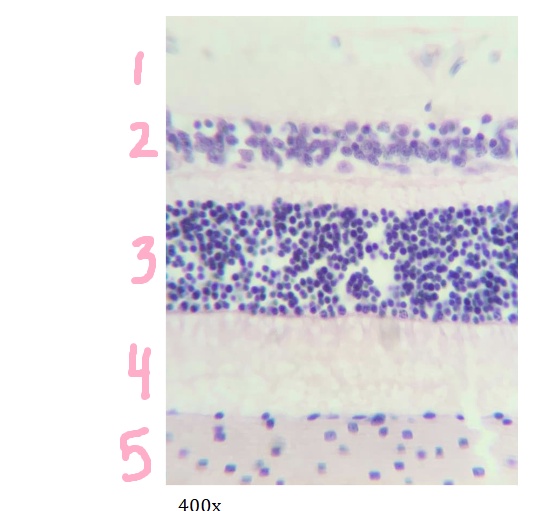
What is #4 pointing to?
layer of rods and cones
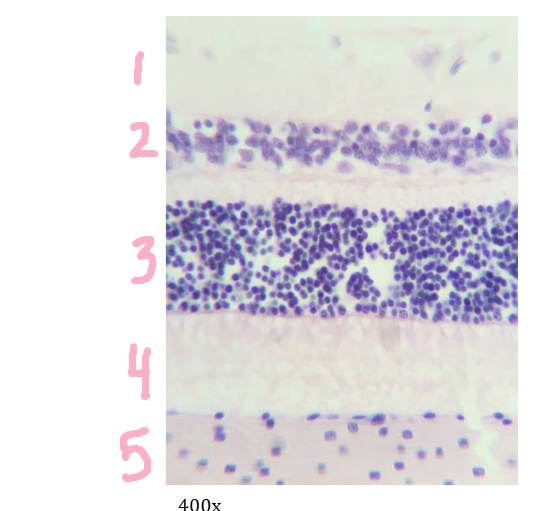
What is #5 pointing to?
choroid
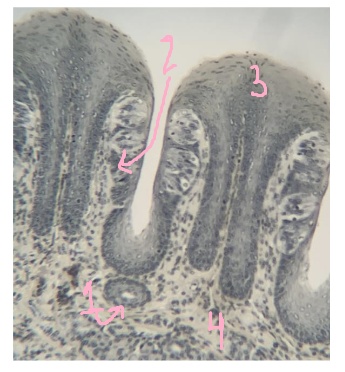
What is #1 pointing to?
duct
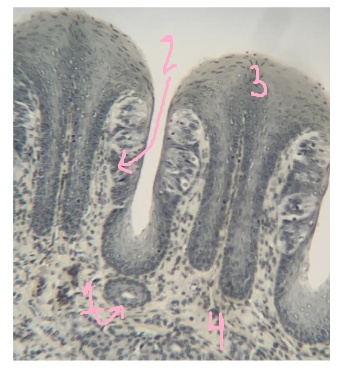
What is #2 pointing to?
taste buds
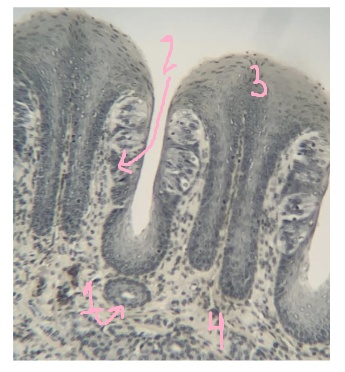
What is #3 pointing to?
epithelium
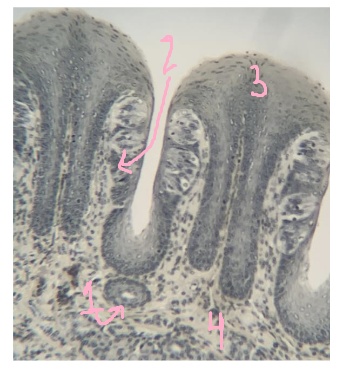
What is #4 pointing to?
lamina propria
What is the tongue made up of?
papillae
What sensations do Meissner’s (tactile) corpuscles feel?
light touch
What sensations do Pacinian corpuscles feel?
deep/hard touch
What eye receptor senses black, white, and grey?
rods
What eye receptor senses colors?
cones
What are the two types of mechanoreceptors for touch?
Meissner’s and Pacinian corpuscles
What senses have mechanoreceptors?
hearing and touch
What sense has photoreceptors?
vision
What senses have chemoreceptors?
smell and taste
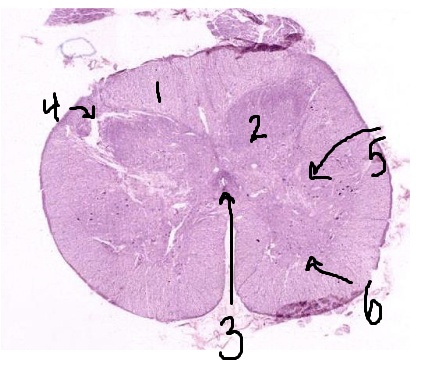
What is #1 pointing to?
white matter
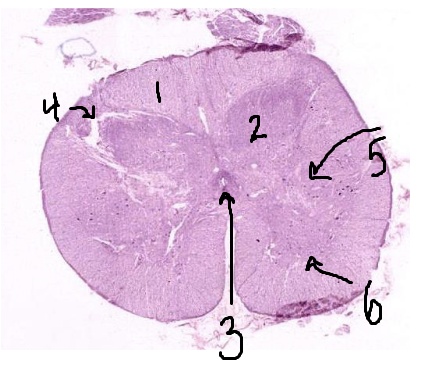
What is #2 pointing to?
grey matter
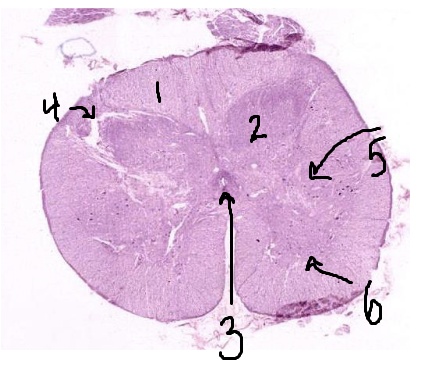
What is #3 pointing to?
central canal
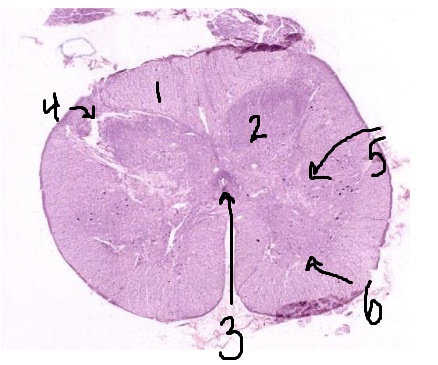
What is #4 pointing to?
posterior horn
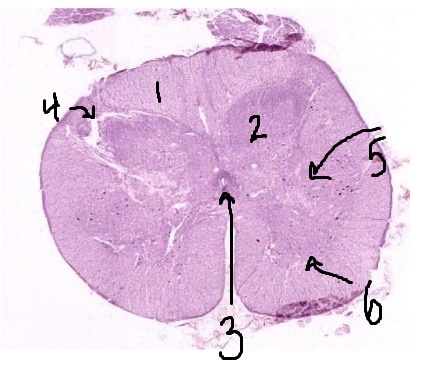
What is #5 pointing to?
lateral horn
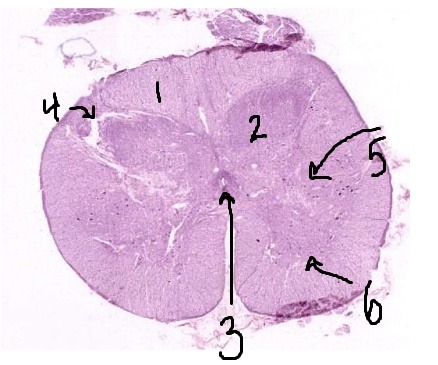
What is #6 pointing to?
anterior horn
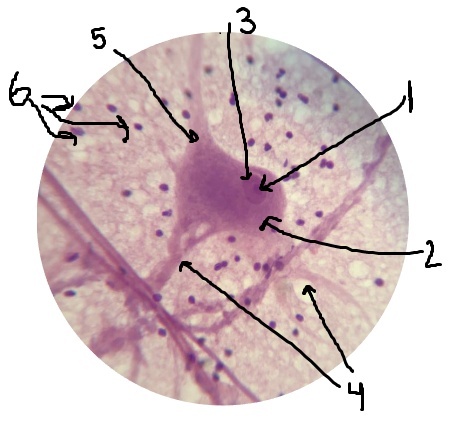
What is #1 pointing to? Inside of the nucleus.
nucleolus
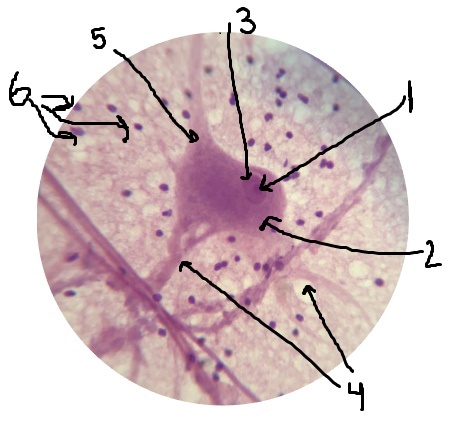
What is #2 pointing to?
cell body
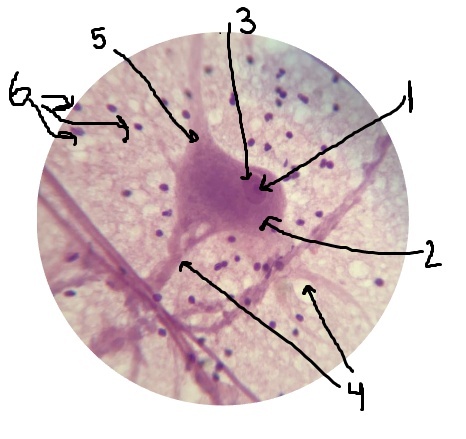
What is #3 pointing to?
nucleus
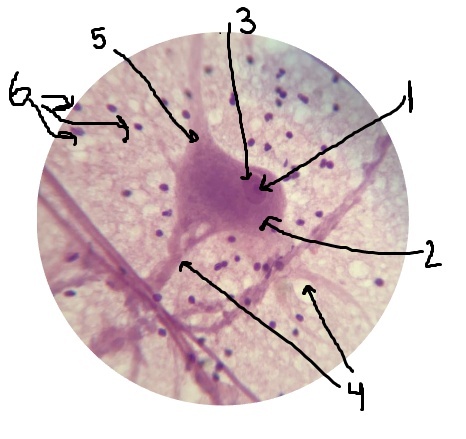
What is #4 pointing to?
dendrites
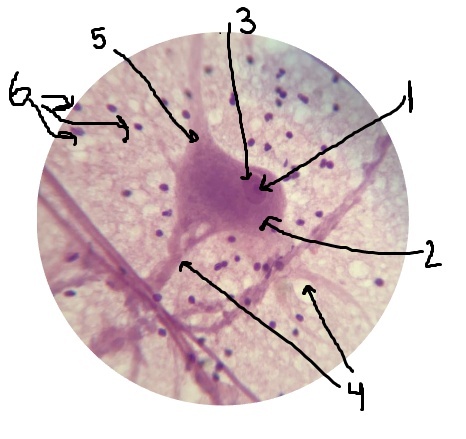
What is #5 pointing to?
axon
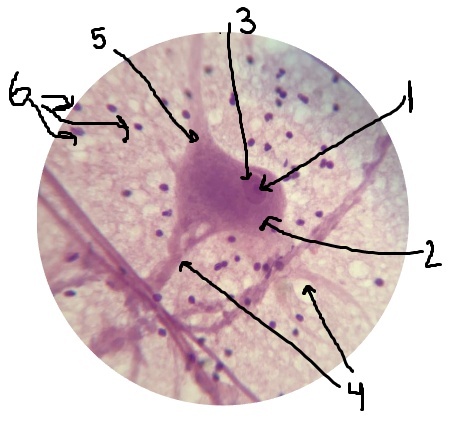
What is #6 pointing to?
neuroglial cells
What bony structure is associated with the olfactory nerve?
cribriform plate of ethmoid bone
What bony structure is associated with the optic nerve?
optic canal
What cavity does the brain sit in?
cranial cavity
What cavity does the spine sit in?
vertebral cavity