Chapter 23: Respiratory ANATOMY (work in progress)
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
the respiratory pathway in order
1. external nares (nostrils)
2. nasal cavity (nose)
3. nasopharynx
4. oropharynx
5. laryngopharynx
6. larynx
a. epiglottis
>> enter glottis
b. corniculate cartilage
c. cuneiform cartilage
d. arytenoid cartilage
e. thyroid cartilage
f. cricoid cartilage
7. trachea
a. carina
8. primary bronchi
9. secondary bronchi
10. tertiary bronchi
11. bronchioles
12. alveoli
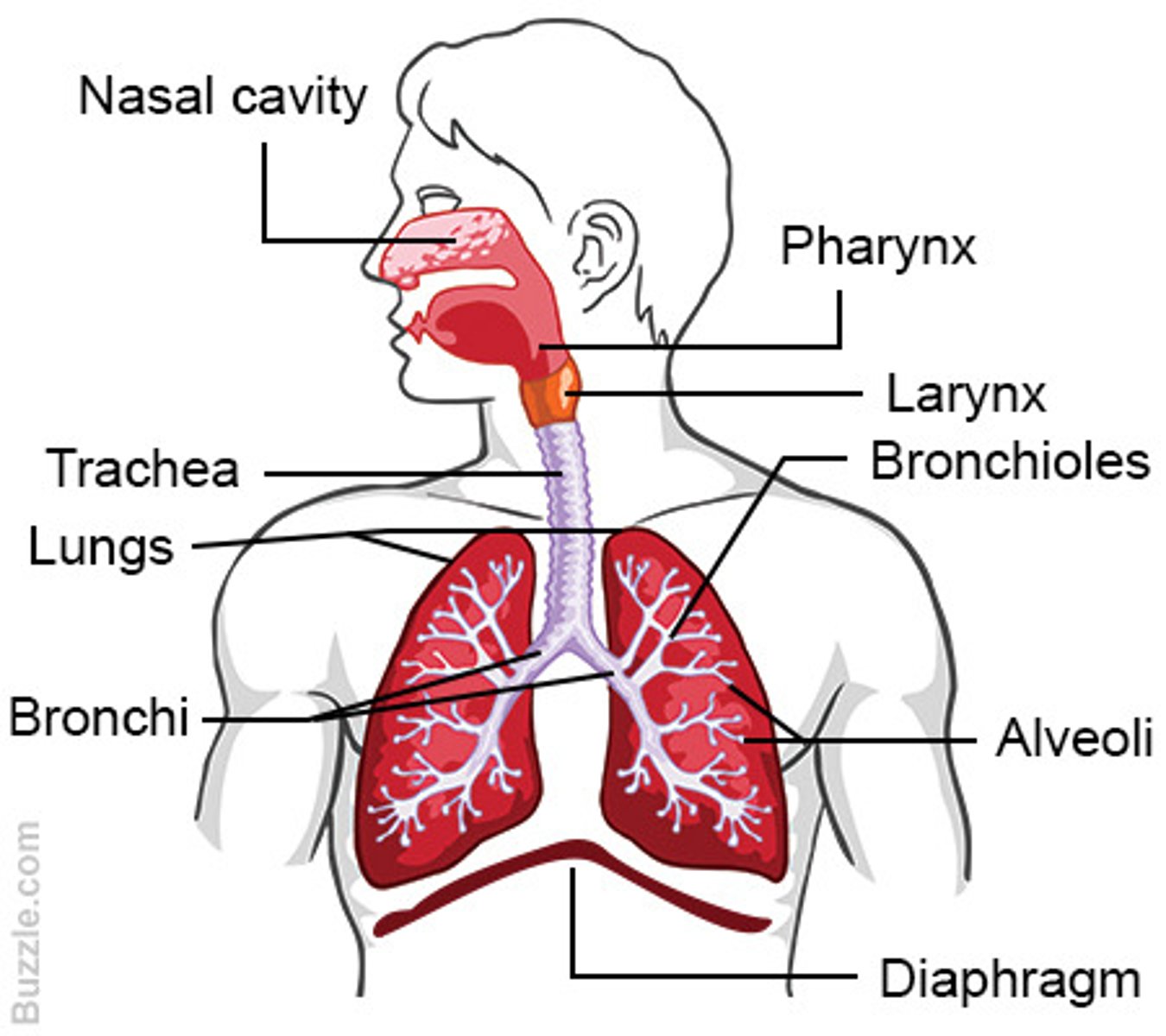
conducting zone
external nares to terminal bronchioles
- Includes respiratory passageways, cleanses, humidifies and warms incoming air
respiratory zone
alveoli
- site of gas exchange
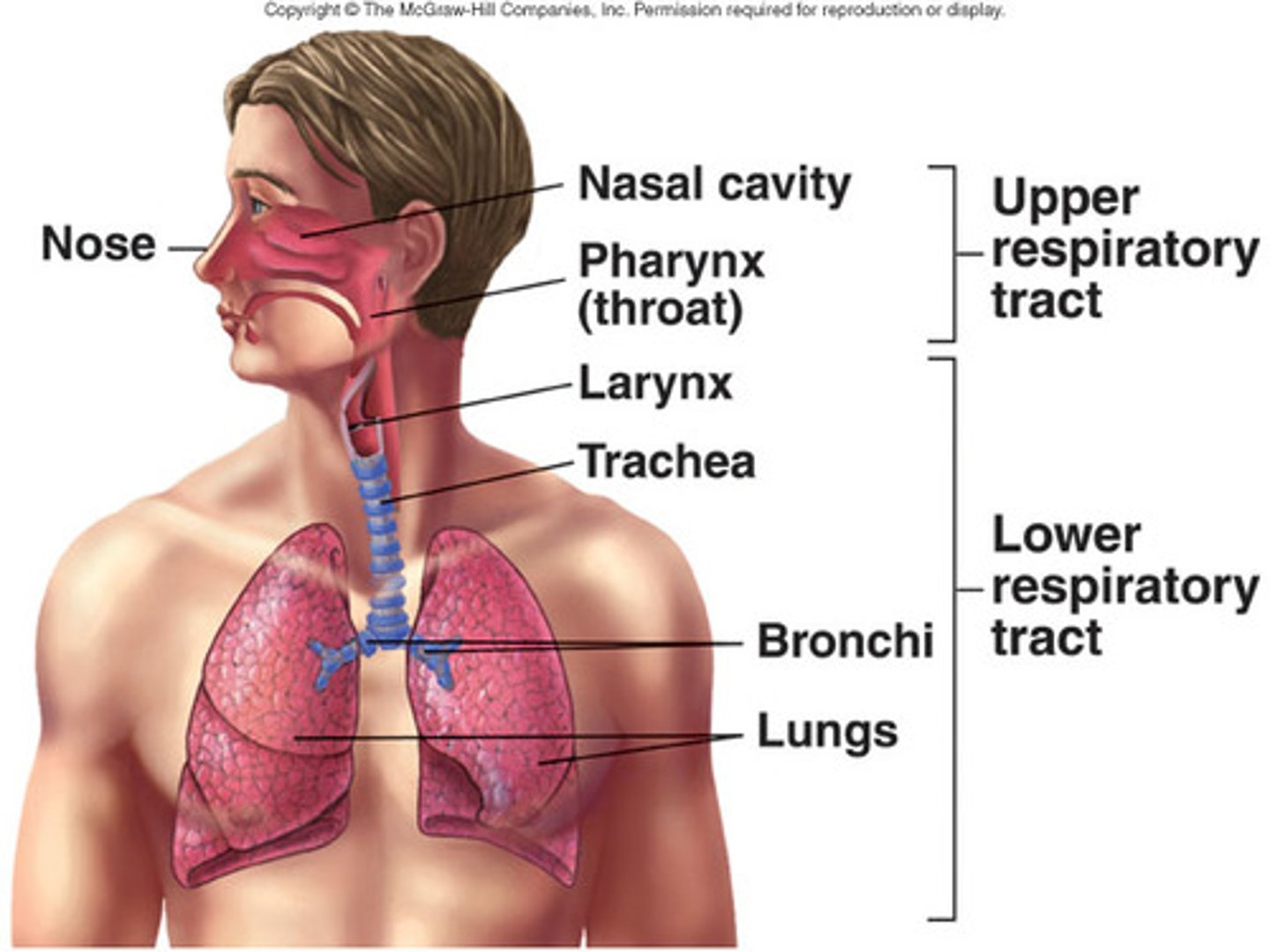
upper respiratory tract
external nares
nose
nasopharynx
oropharynx
laryngopharynx
-
larynx in some texts
lower respiratory tract
larynx in some texts
trachea
bronchi
respiratory epithelium
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelial cells containing mucous membranes (goblet cells)
1. filters the air (mucus & cilia)
2. warming
3. humidifying
general, anywhere that air passes pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium w/ goblet cells
"nasal epithelium" is just simply referring to where it is (nasal cavity)
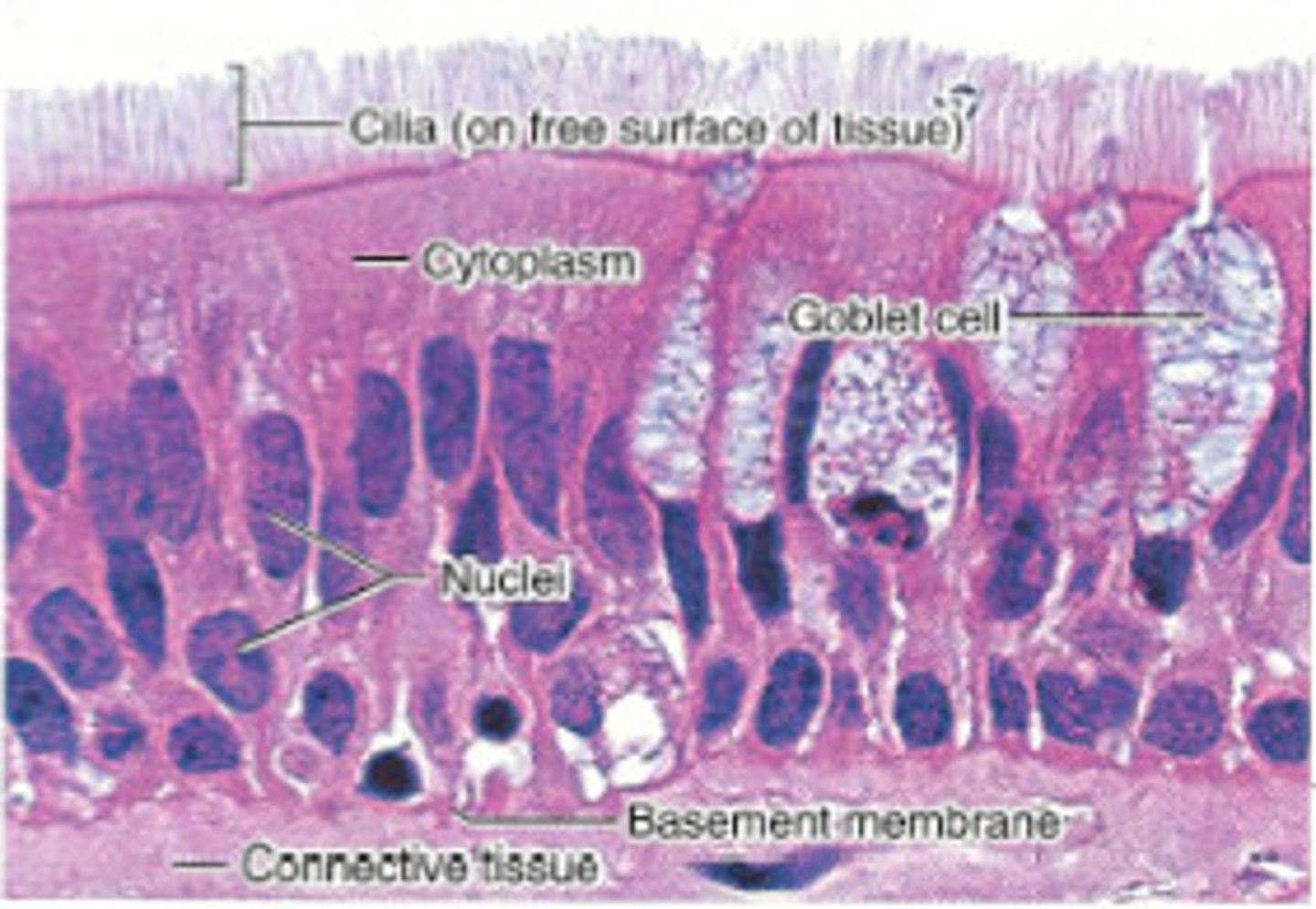
What type of epithelial cells are found in respiratory epithelium?
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelial cells containing goblet cells.
What is the function of mucus and cilia in the respiratory epithelium?
They filter the air.
What is one function of the respiratory epithelium besides filtering air?
Warming the air.
What is another function of the respiratory epithelium besides filtering and warming air?
Humidifying the air.
Where is pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with goblet cells found?
Anywhere that air passes in the respiratory system.
What does 'nasal epithelium' refer to?
The respiratory epithelium located in the nasal cavity.
external nares
two openings of the nose; aka nostrils
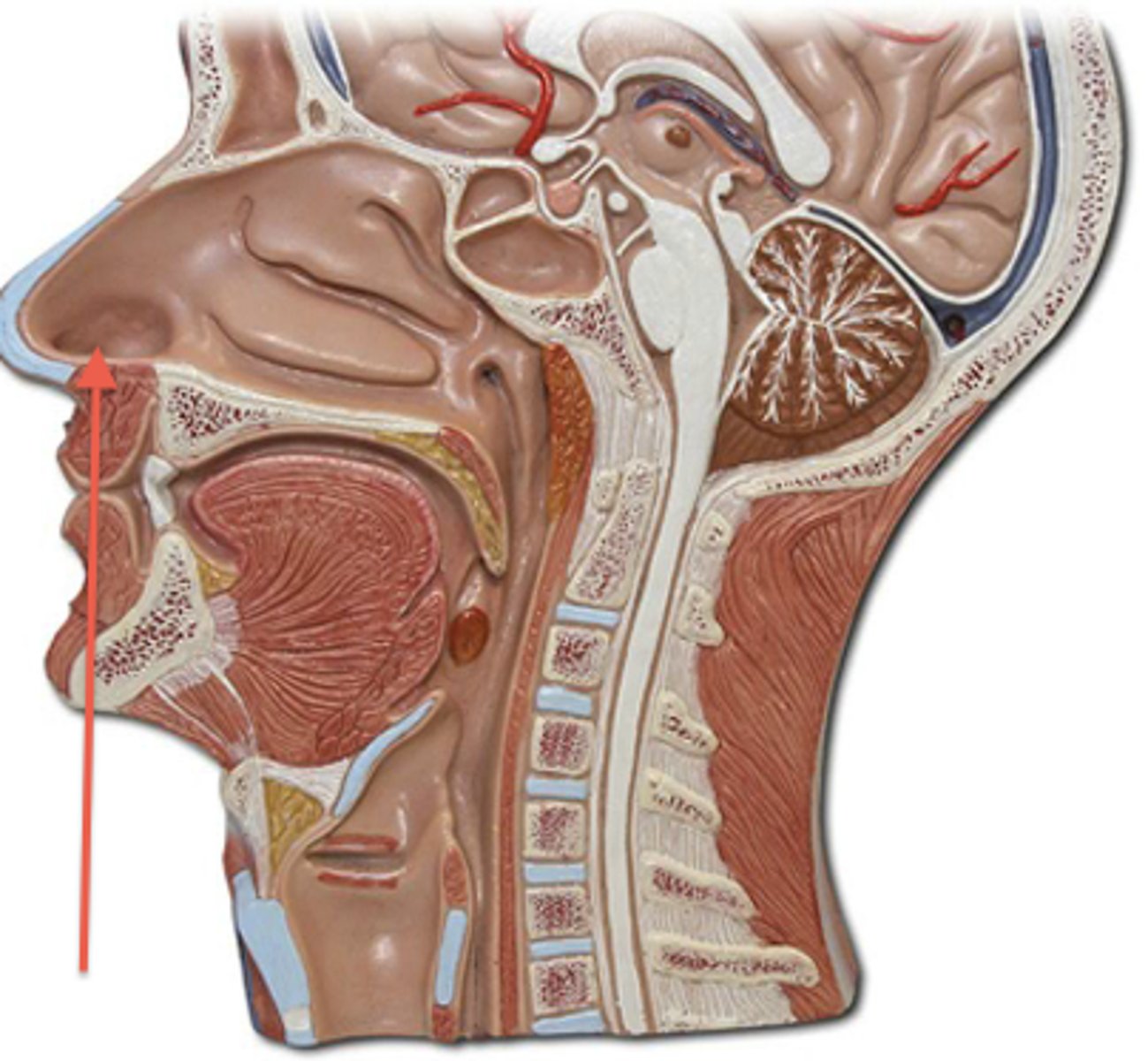
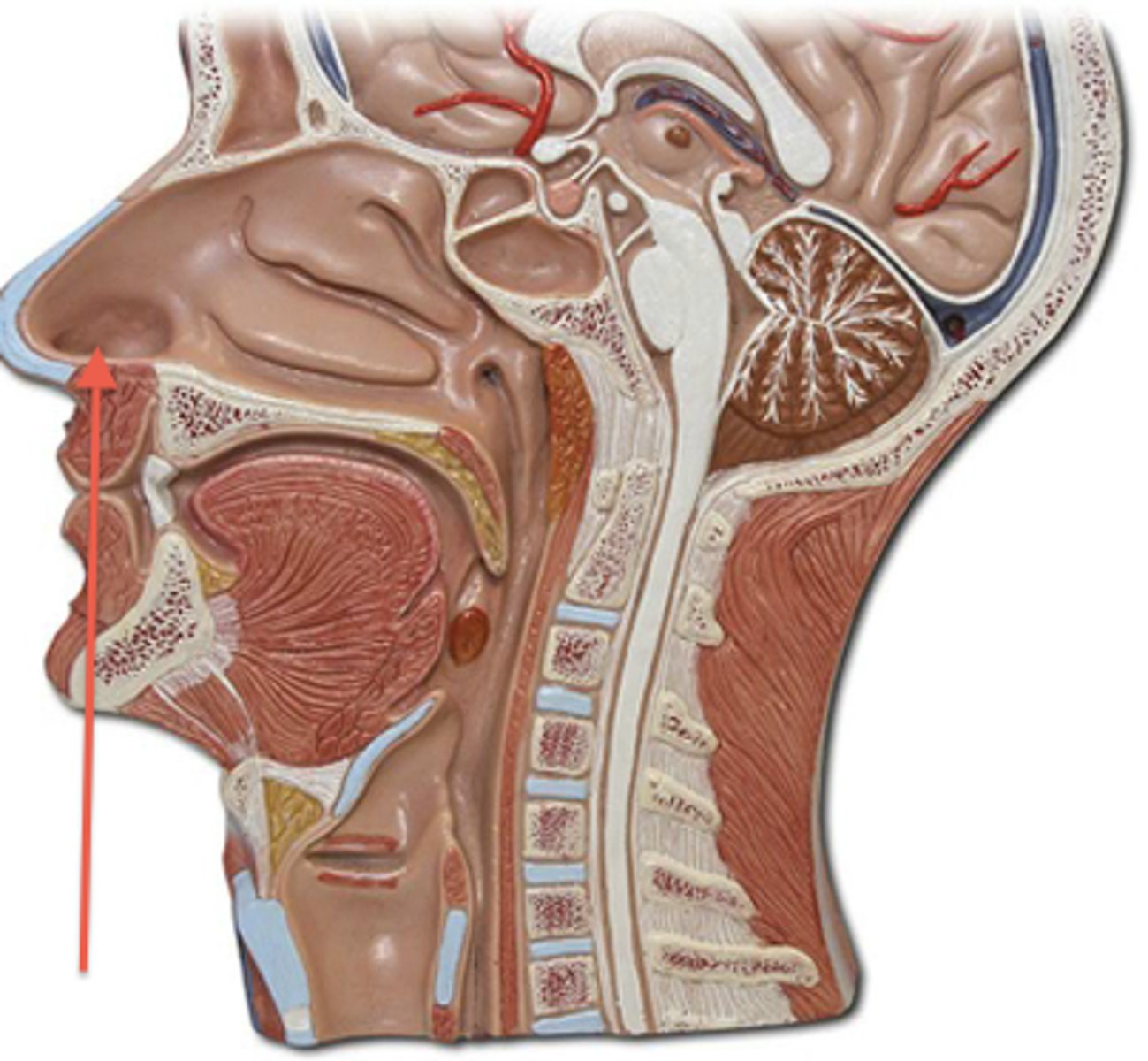
vestibule of nose
located just internal to the external nares and is lined with skin and hairs
right after the external nares nostril opening
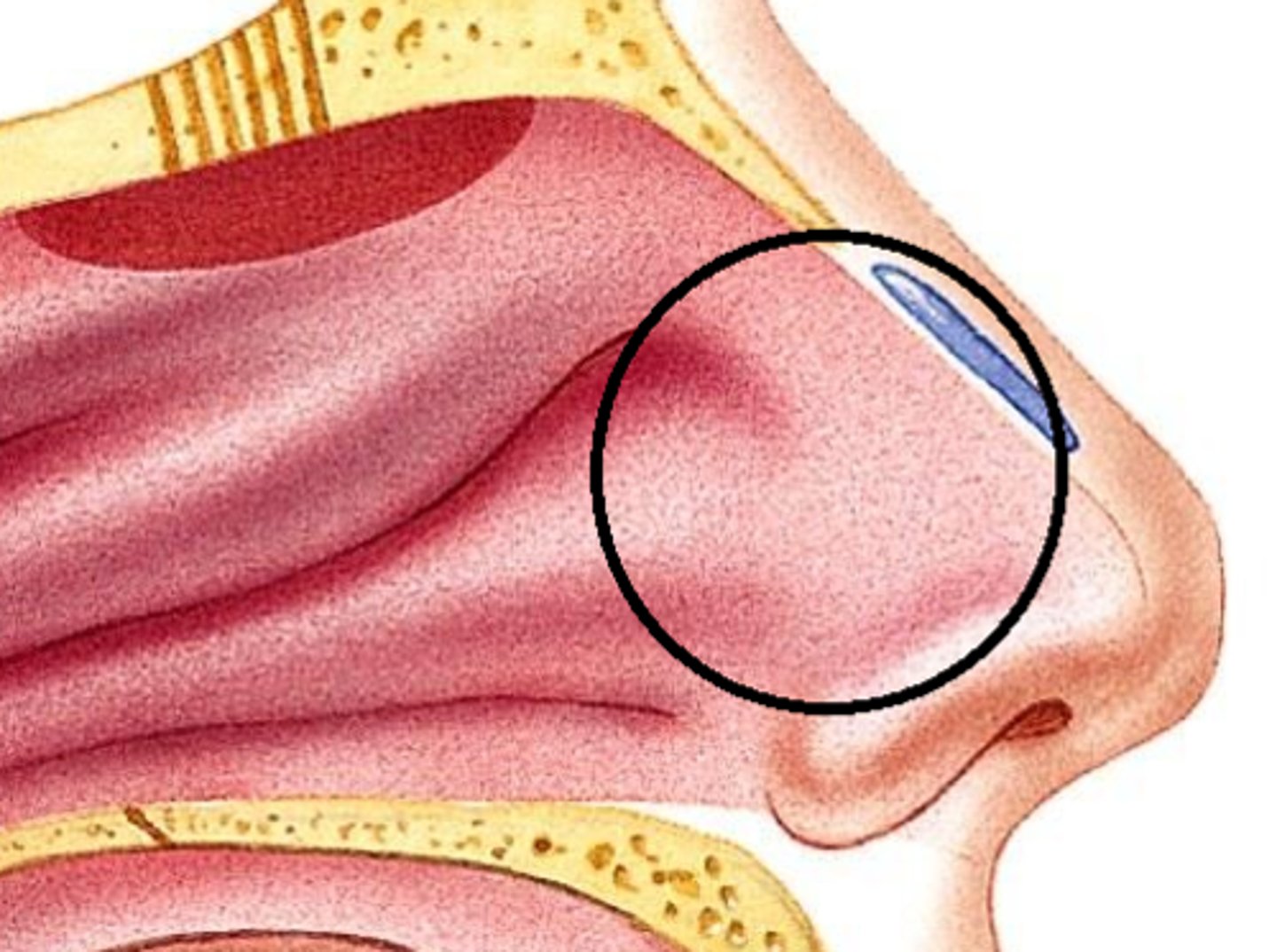
Where is the vestibule of the nose located?
Just internal to the external nares
What lines the vestibule of the nose?
Skin and hairs
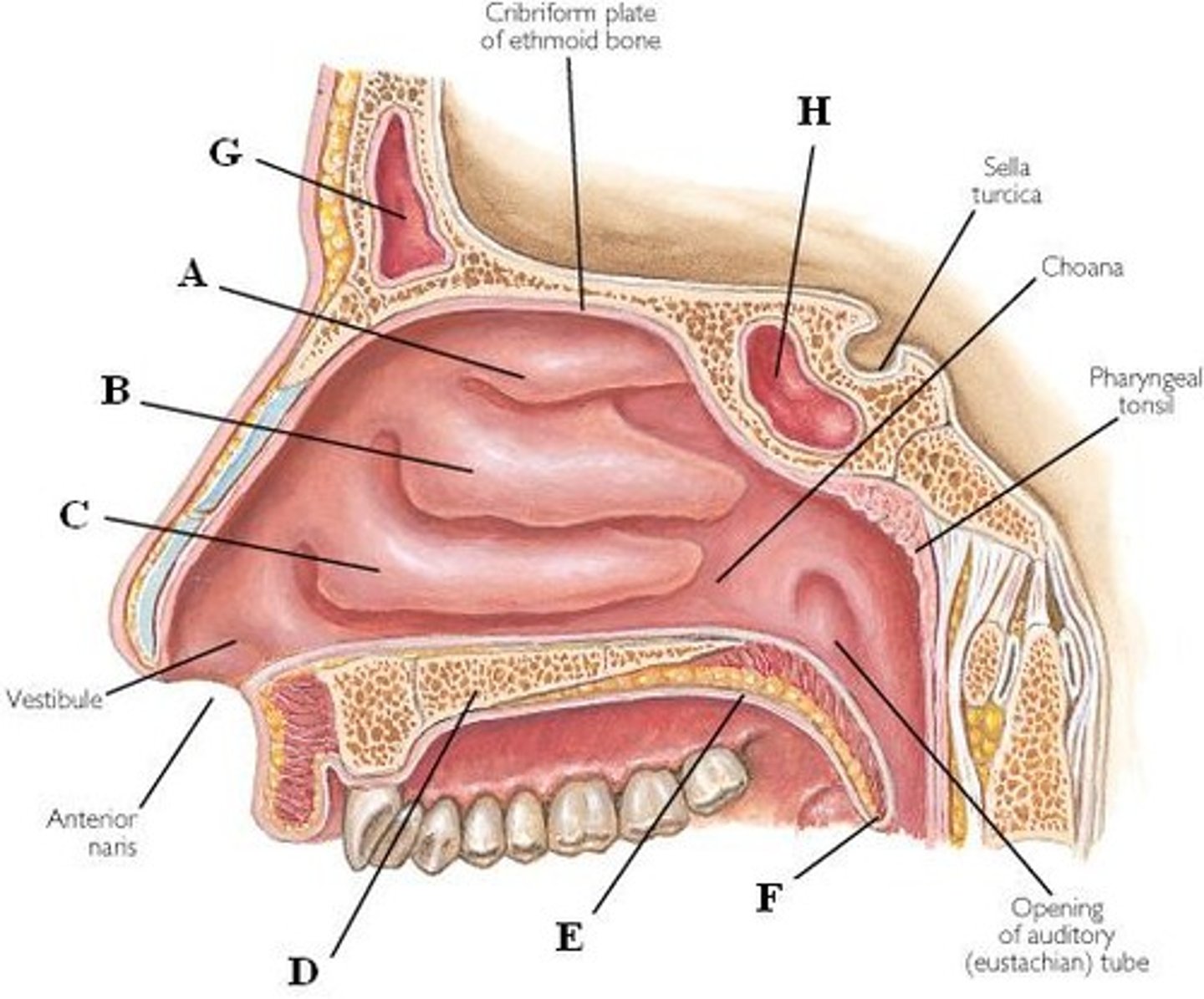
nasal cavity (nose)
contains a nasal septum that is made of bone & cartilage
- this is to provide support and structure to inner structures
surfaces lined by nasal epithelium in the which contain mucus membrane
- cilia of these cells move mucous towards the pharynx so that it can be swallowed or spit out
contains three (3) nasal conchae
1. superior conchae
2. middle conchae
3. inferior conchae
underneath nasal conchae there are openings
- opening to the nasolacrimal duct
- opening to the paranasal sinuses
there is a anatomical connection between nasal cavity and eye as well as the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses
What is the function of the nasal septum?
To provide support and structure to inner structures of the nasal cavity.
What type of epithelium lines the nasal cavity?
Nasal epithelium.
What is the role of cilia in the nasal epithelium?
They move mucus towards the pharynx to be swallowed or spit out.
How many nasal conchae are there?
Three.
What are the names of the three nasal conchae?
Superior conchae, middle conchae, inferior conchae.
What openings are located underneath the nasal conchae?
Opening to the nasolacrimal duct and opening to the paranasal sinuses.
What anatomical connections exist related to the nasal cavity?
Connection between the nasal cavity and the eye, and between the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses.
nasal conchae
bony projections into the nasal cavity that are covered with mucus membrane
- cause the air to “swirl” and force it against the mucus membrane so that the air is moistened, filtered, and warmed
underneath nasal conchae there are openings
- opening to the nasolacrimal duct
- opening to the paranasal sinuses
there is a anatomical connection between nasal cavity and eye as well as the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses
What are nasal conchae?
Bony projections into the nasal cavity that are covered with mucus membrane.
What is the function of the nasal conchae?
They cause the air to swirl and force it against the mucus membrane so that the air is moistened, filtered, and warmed.
What openings are located underneath the nasal conchae?
Opening to the nasolacrimal duct and opening to the paranasal sinuses.
What anatomical connections exist related to the nasal cavity?
There is an anatomical connection between the nasal cavity and the eye, as well as between the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses.
two ducts that drain into the nasal cavity
one from the eye nasolacrimal
one from the sinuses paranasal sinuses
there is a anatomical connection between nasal cavity and eye as well as the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses
nasolacrimal duct
passageway for tears from the eye's lacrimal sac into the nose
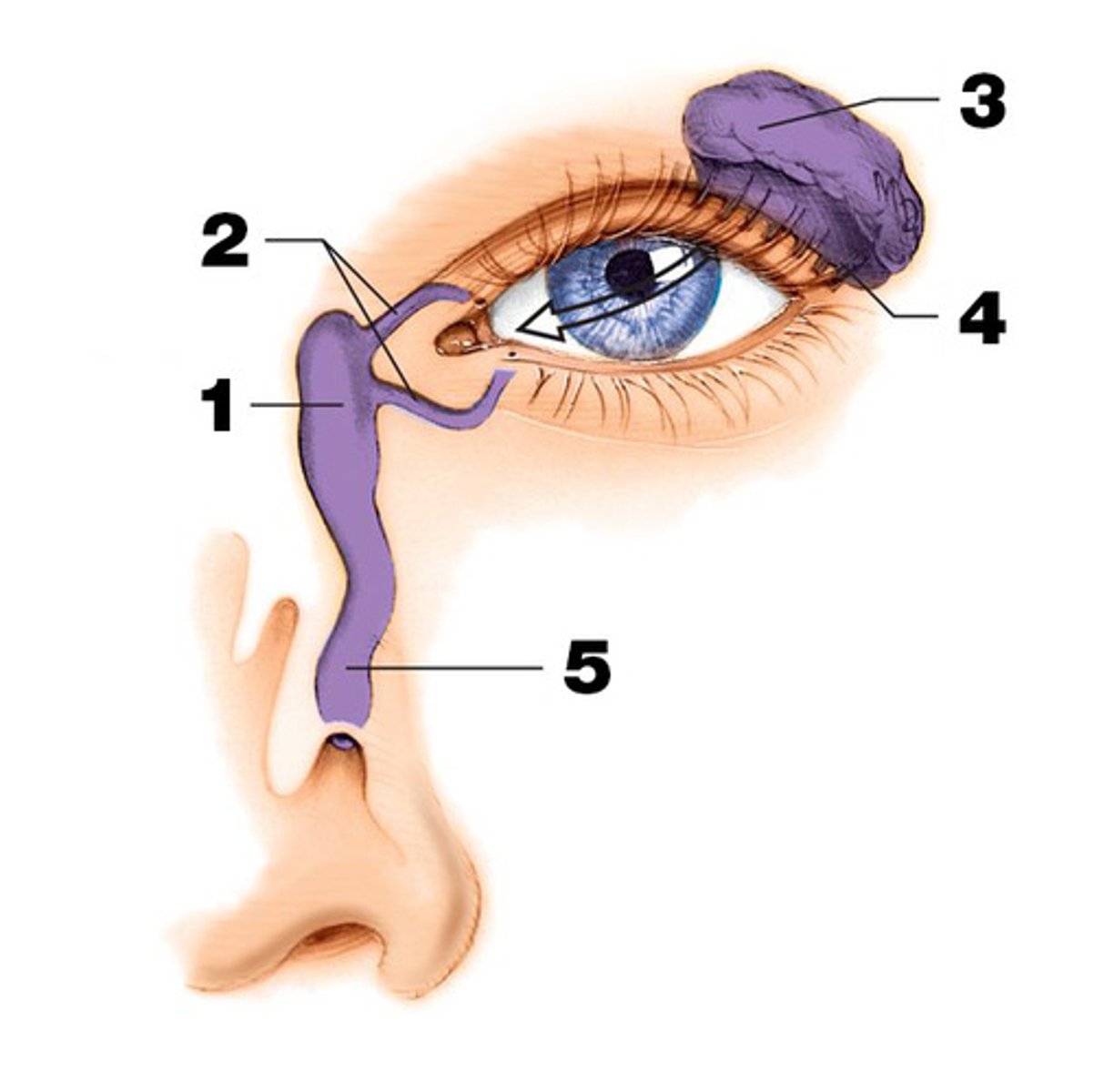
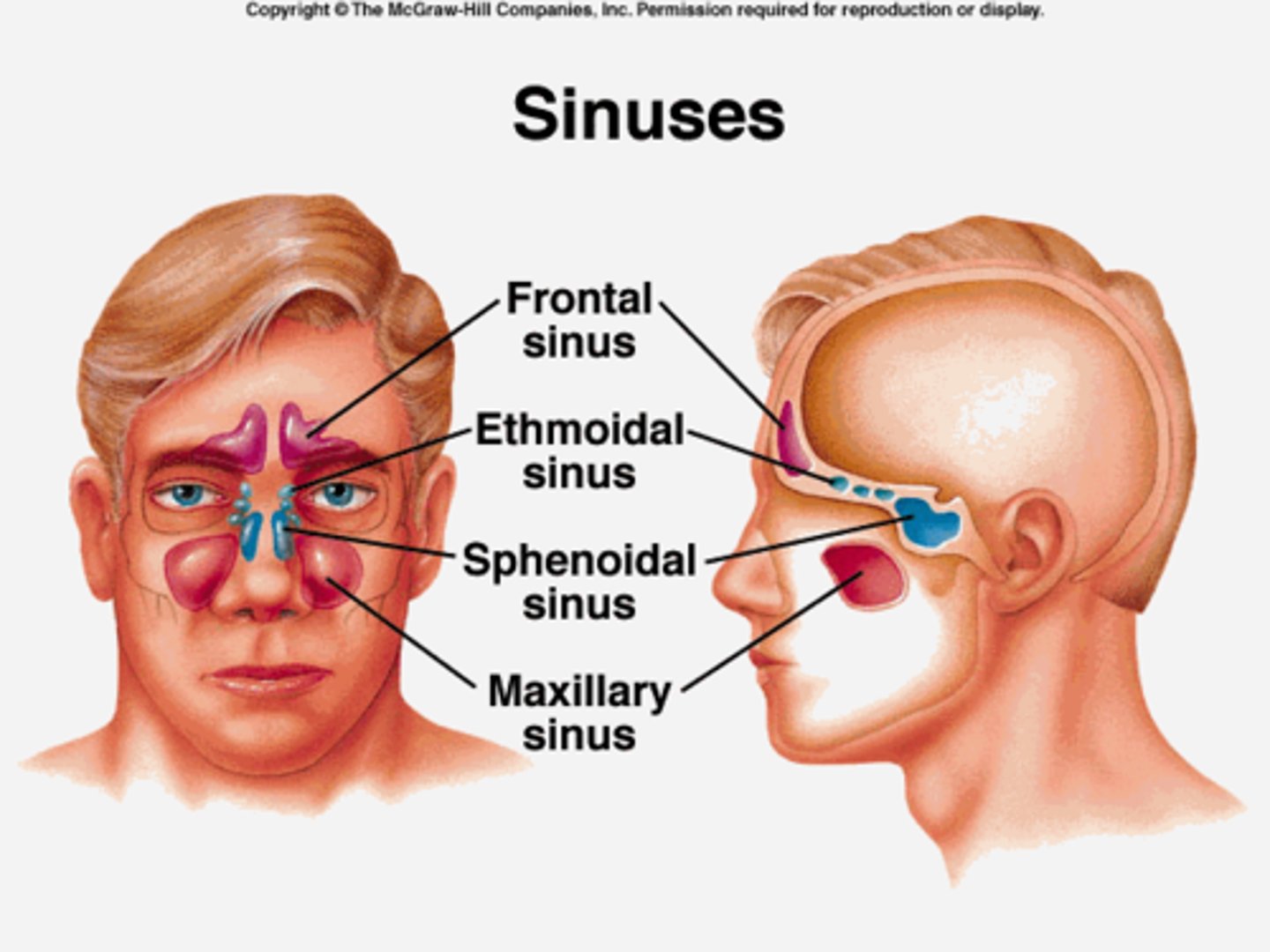
paranasal sinuses
frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, maxillary
air-filled cavities lined with mucous membrane, located in the bones of the skull
functions:
- weight reduction of skull
- humidify, filter/produces mucus (lined by mucous membrane)
- resonates voice
What are the paranasal sinuses?
Air-filled cavities lined with mucous membrane, located in the bones of the skull.
What are the four types of paranasal sinuses?
Frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, maxillary.
What are the function of the paranasal sinuses?
Weight reduction of the skull.
Humidify and filter air/produce mucus.
Resonates voice.
What is a function of the paranasal sinuses related to sound?
Resonates voice.
how does a sinus infection occur (example)
person gets a cold
-> mucous membranes swell
-> sinus drainage blocked = sinus infection
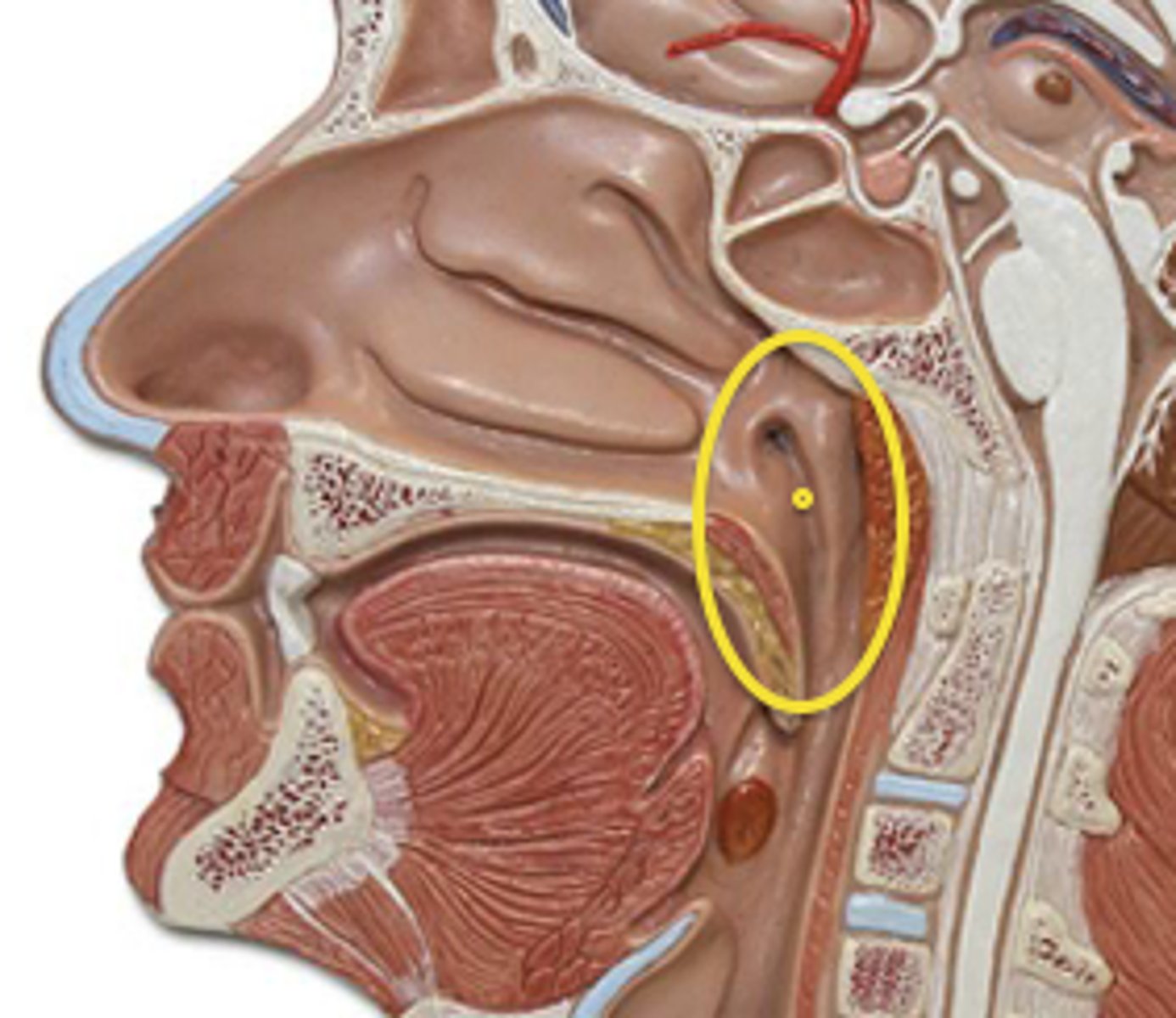
internal nares
connects the nasal cavity with the nasopharynx
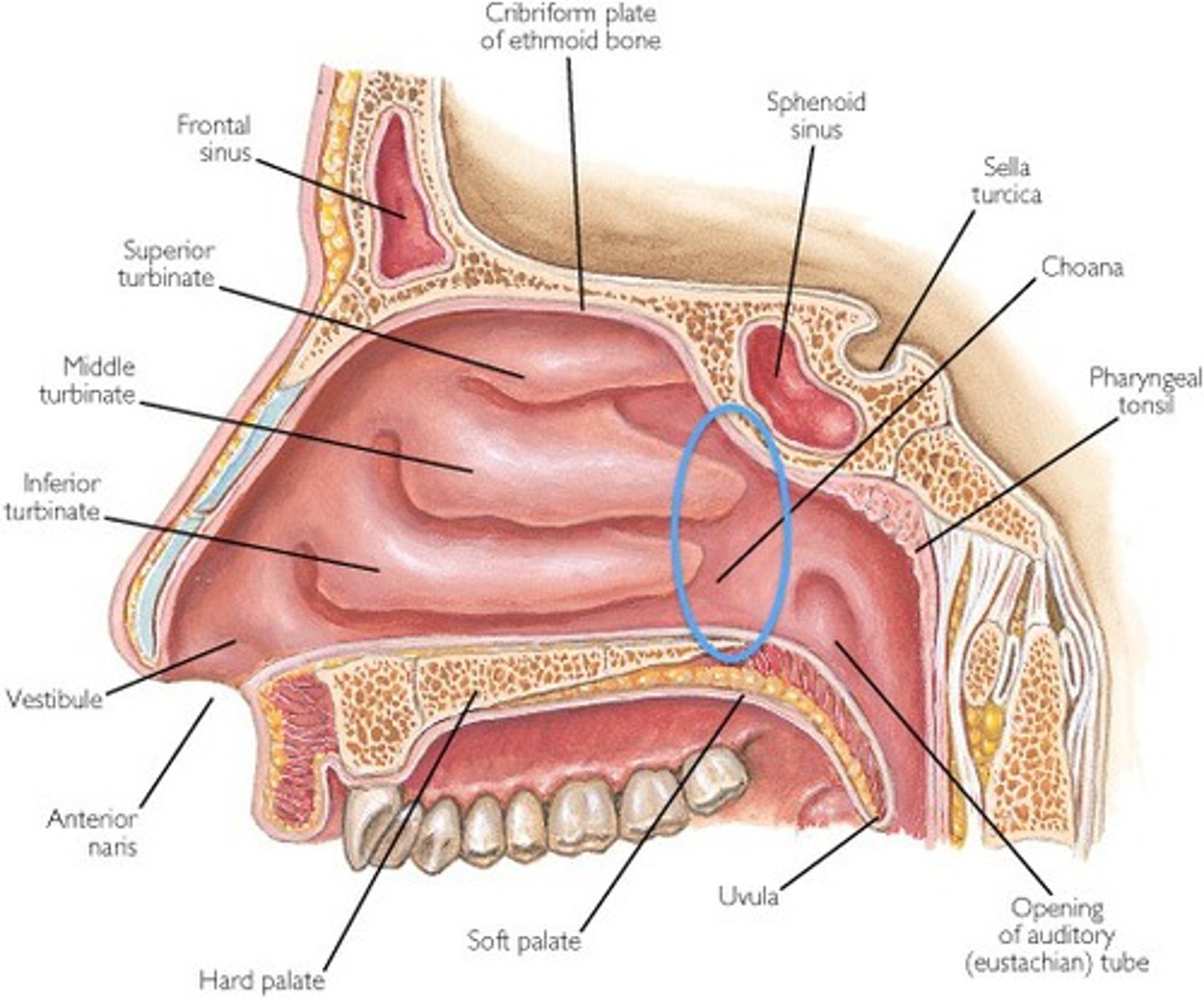
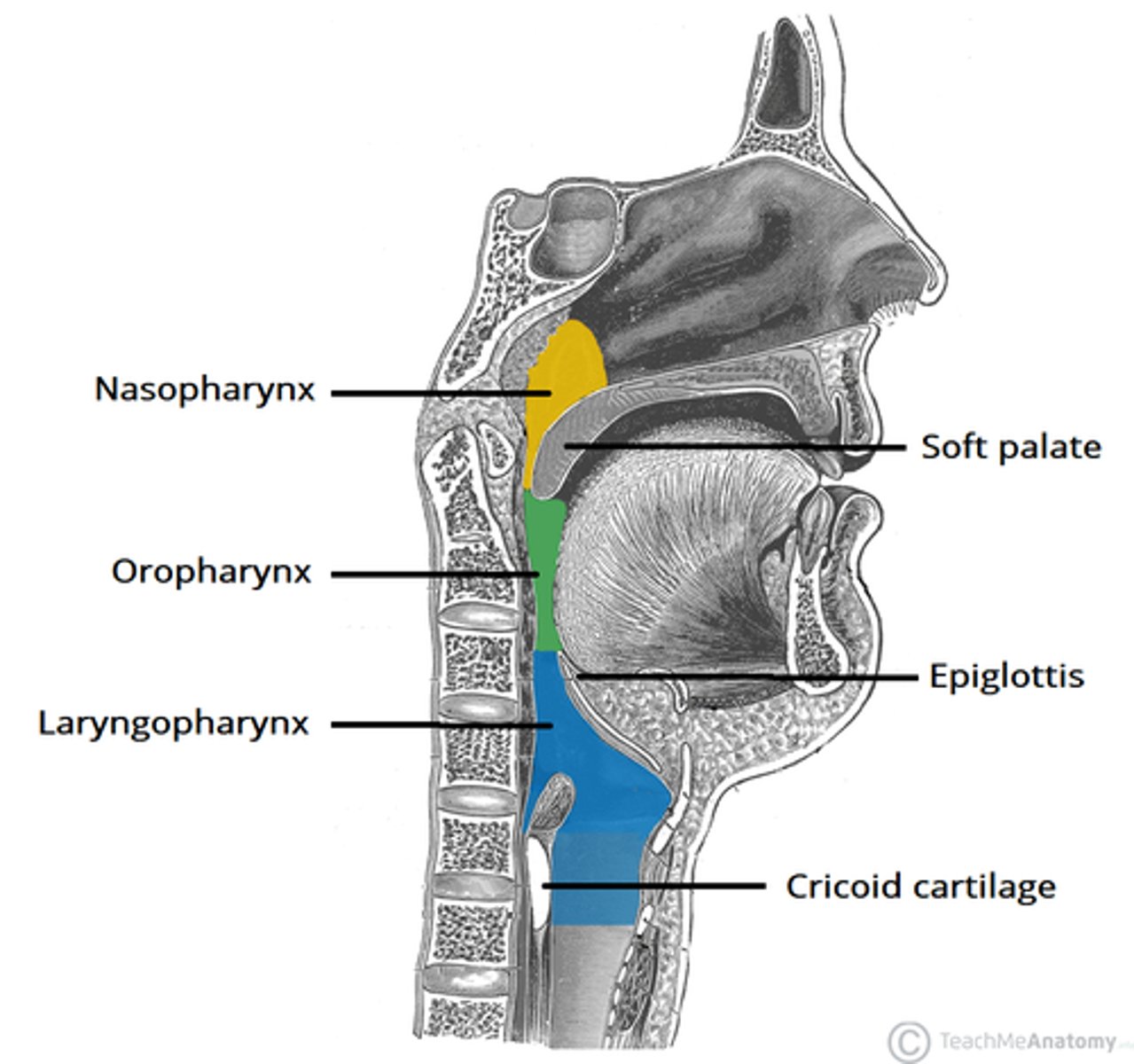
nasopharynx
begins at the internal nares
ends at the cricoid cartilage
contains
(1) eustachian tube
- purpose is to equalize air pressure
(2) pharyngeal tonsil
- lymphatic nodule w/ immune cells to fight foreign pathogen
consists of pseudostratified epithelium w/ goblet cells
Where does the nasopharynx begin?
At the internal nares
Where does the nasopharynx end?
At the cricoid cartilage
What is the purpose of the eustachian tube?
To equalize air pressure
What type of immune structure is the pharyngeal tonsil?
A lymphatic nodule with immune cells to fight foreign pathogens
What type of epithelium is found in the nasopharynx?
Pseudostratified epithelium with goblet cells
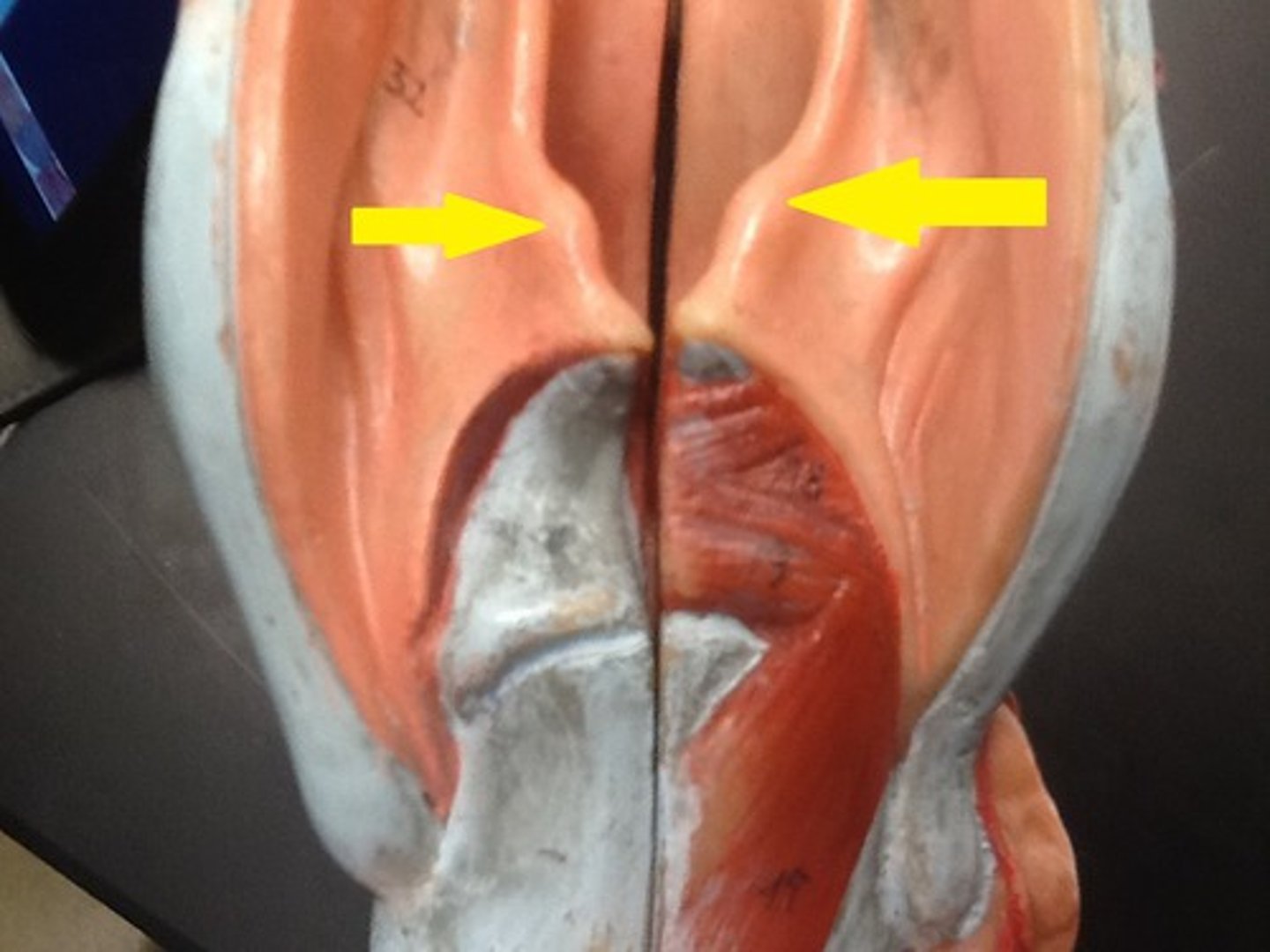
oropharynx & laryngopharynx
stratified squamous epithelium
- air food and drink passage
palatine tonsils and lingual tonsils
- located in the oropharynx
What type of epithelium is found in the oropharynx and laryngopharynx?
Stratified squamous epithelium
- why? Passage for air, food, and drink protection
Where are the palatine tonsils and lingual tonsils located?
In the oropharynx
palatine tonsils and lingual tonsils found where?
oropharynx
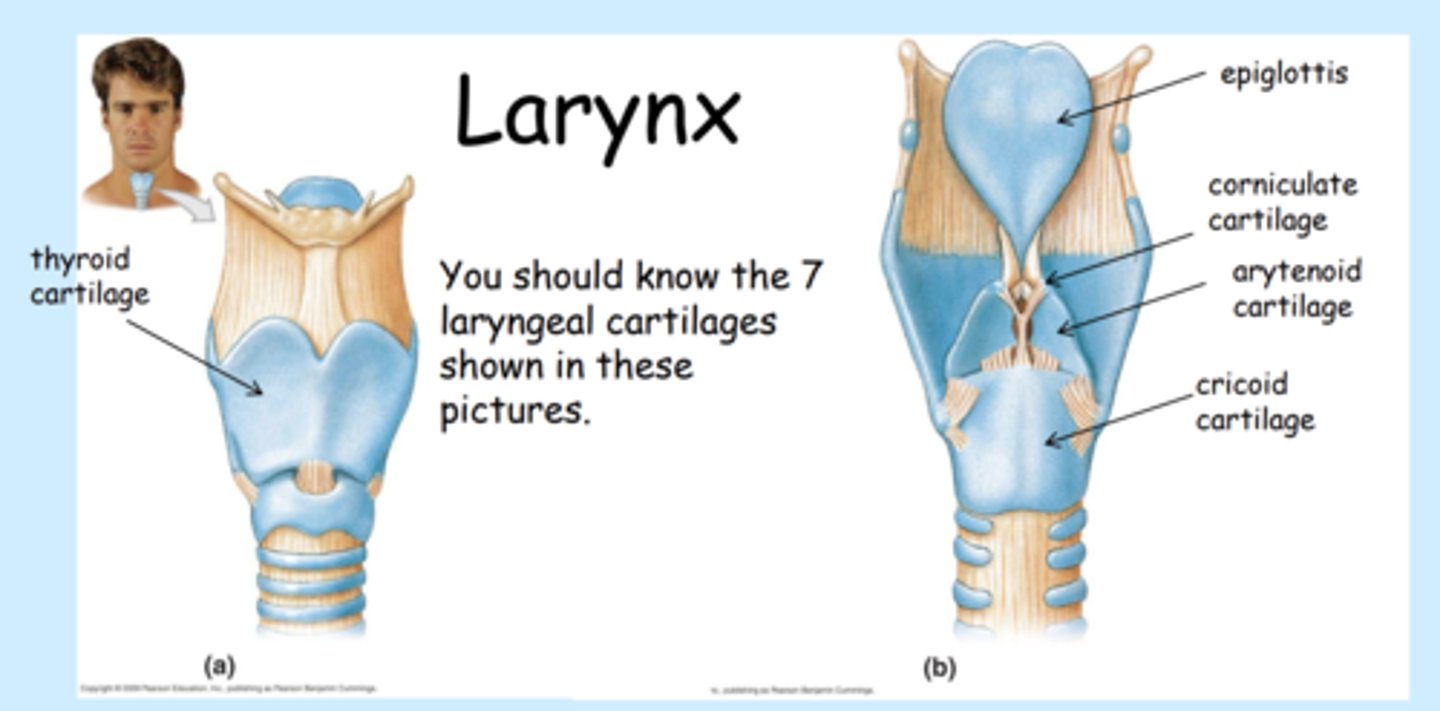
larynx
voice box; passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea;
contains:
- vocal cords
- nine (9) cartilages
single cartilages:
1x - epiglottis (made of elastic cartilage)
1x - thyroid cartilage (hyaline cartilage)
1x - cricoid cartilage (hyaline cartilage)
double cartilages:
2x - arytenoid cartilages
2x - corniculate cartilages
2x - cuneiform cartilages
from most superior to inferior (cephalocaudal)
a. epiglottis
>> enter glottis
b. corniculate cartilage
c. cuneiform cartilage
d. arytenoid cartilage
e. thyroid cartilage
f. cricoid cartilage
note: all but epiglottis is made of hyaline cart.
larynx
voice box; passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea;
contains:
- vocal cords
- nine (9) cartilages
single cartilages:
1x - epiglottis (made of elastic cartilage)
1x - thyroid cartilage (hyaline cartilage)
1x - cricoid cartilage (hyaline cartilage)
double cartilages:
1 pair of arytenoid cartilages
1 pair of corniculate cartilages
1 pair of cuneiform cartilages
from most superior to inferior (cephalocaudal)
a. epiglottis
>> enter glottis
b. corniculate cartilage
c. cuneiform cartilage
d. arytenoid cartilage
e. thyroid cartilage
f. cricoid cartilage
note: all but epiglottis & true vocal cords is made of hyaline cart.
What is the larynx commonly known as?
Voice box
What is the function of the larynx?
Passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea
What structures are contained within the larynx?
Vocal cords and nine cartilages
What type of cartilage is the epiglottis made of?
Elastic cartilage
What type of cartilage is the thyroid cartilage made of?
Hyaline cartilage
What type of cartilage is the cricoid cartilage made of?
Hyaline cartilage
How many pairs of arytenoid cartilages are there?
One pair
How many pairs of corniculate cartilages are there?
One pair
How many pairs of cuneiform cartilages are there?
One pair
What is the order of the laryngeal cartilages from most superior to inferior?
Epiglottis, corniculate cartilage, cuneiform cartilage, arytenoid cartilage, thyroid cartilage, cricoid cartilage
Which cartilages in the larynx are made of hyaline cartilage?
All except epiglottis and true vocal cords
Epiglottis
a flap of elastic cartilage that covers the windpipe while swallowing
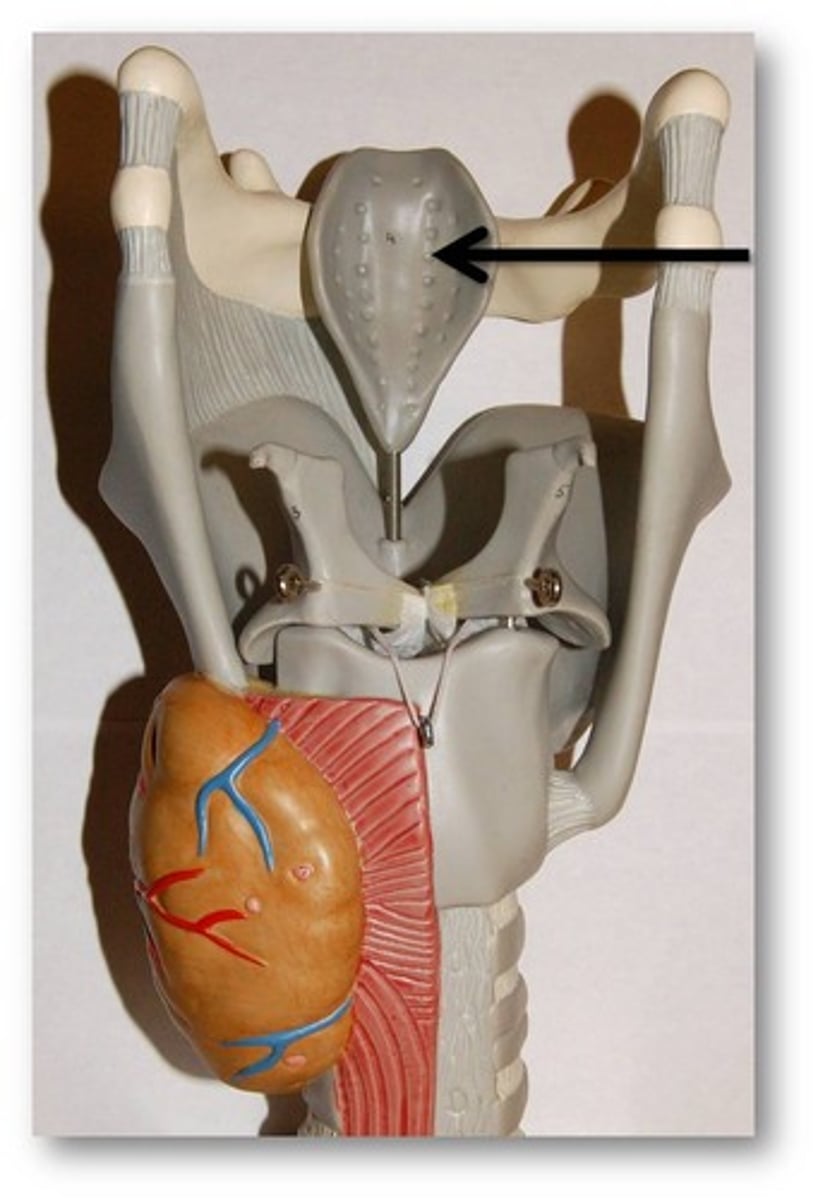
glottis
Opening between vocal cords
- space between vocal folds of larynx
the epiglottis covers this
corniculate cartilage
paired cartilages (2x)
a pair of horn-like pieces of elastic cartilage located at the apex of each arytenoid cartilage
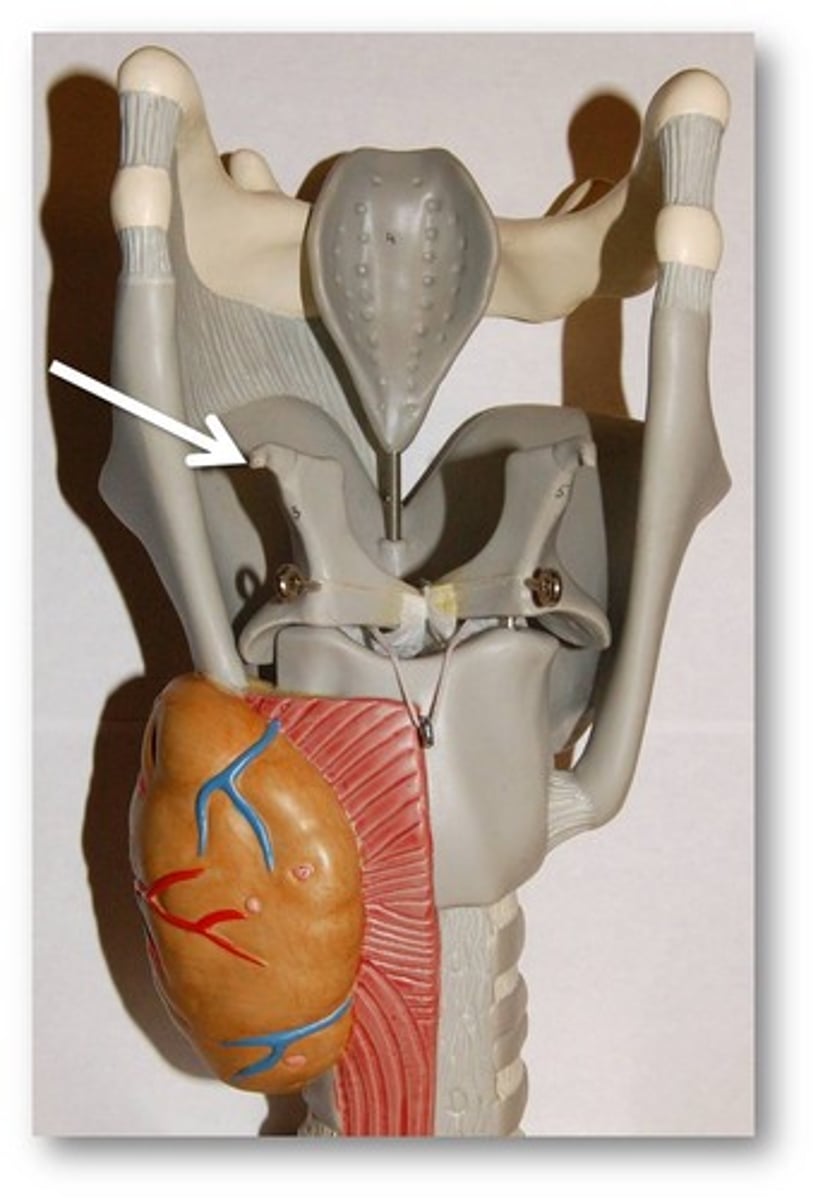
cuneiform cartilages
paired cartilages (2x)
support soft tissue between arytenoids and epiglottis
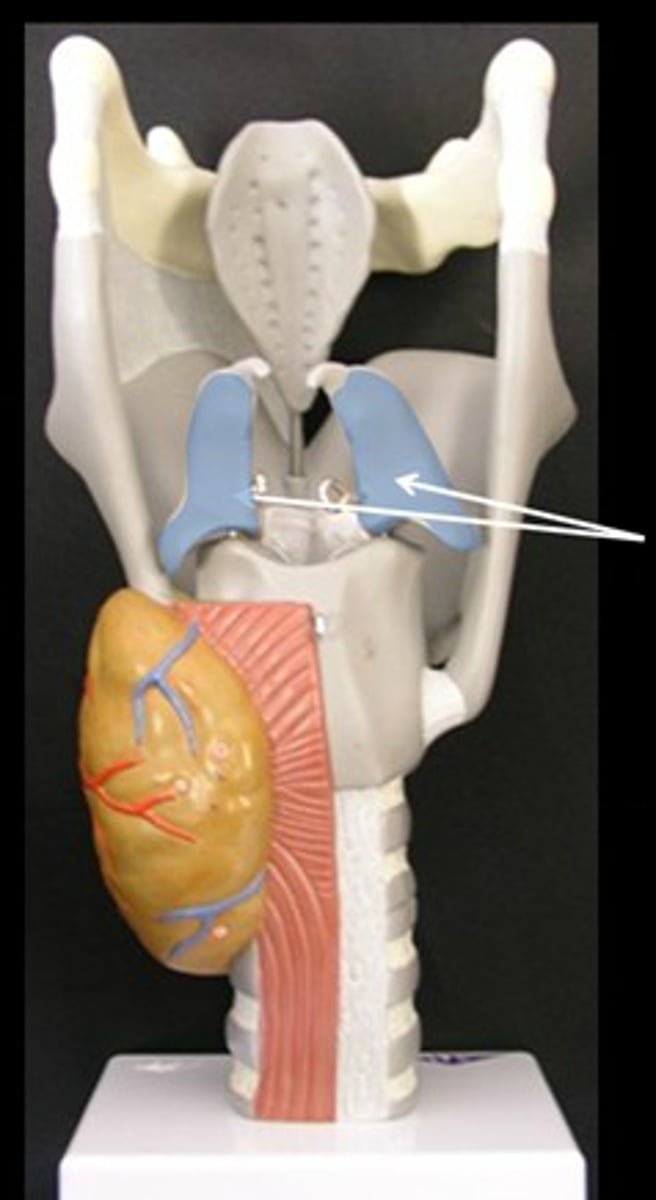
arytenoid cartilages
paired cartilages (2x)
attach to true vocal cords and thyroid cartilage
attaches to true vocal cords posteriorly
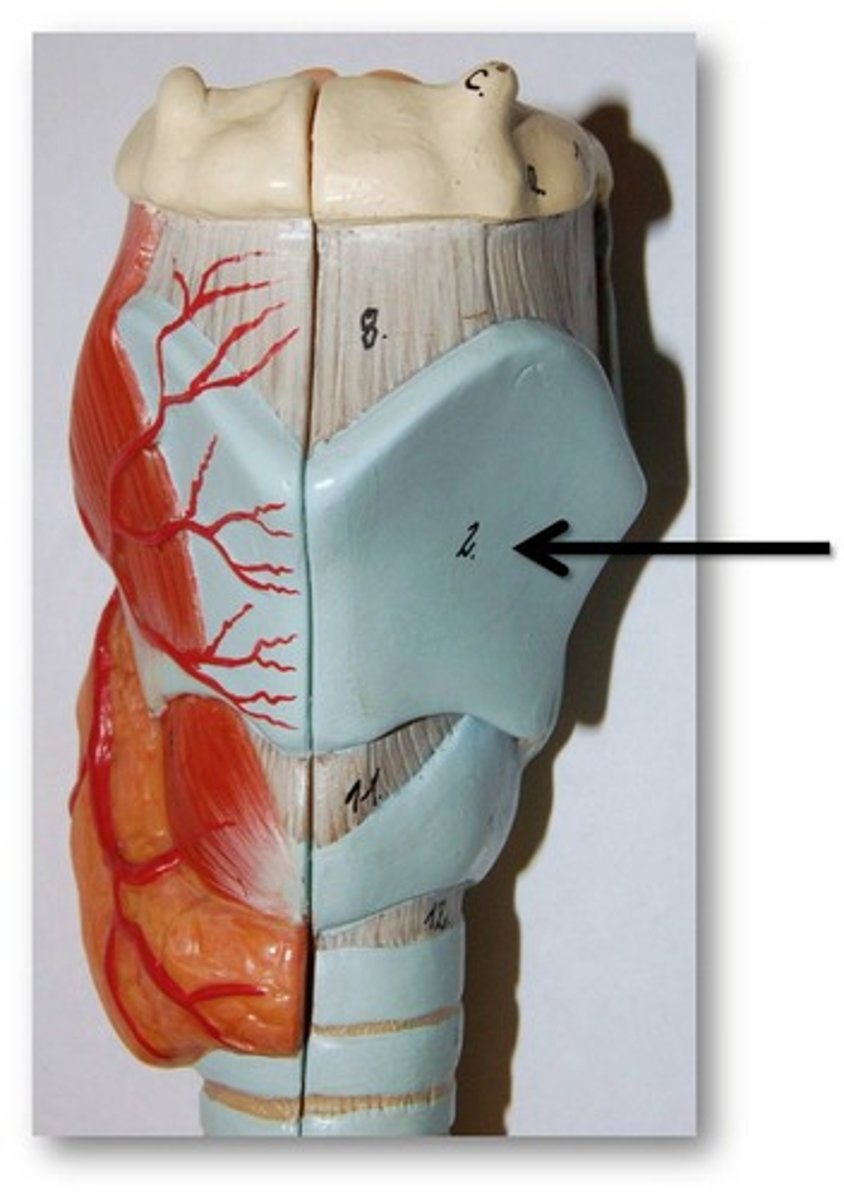
thyroid cartilages
true vocal cords attach to this anteriorly
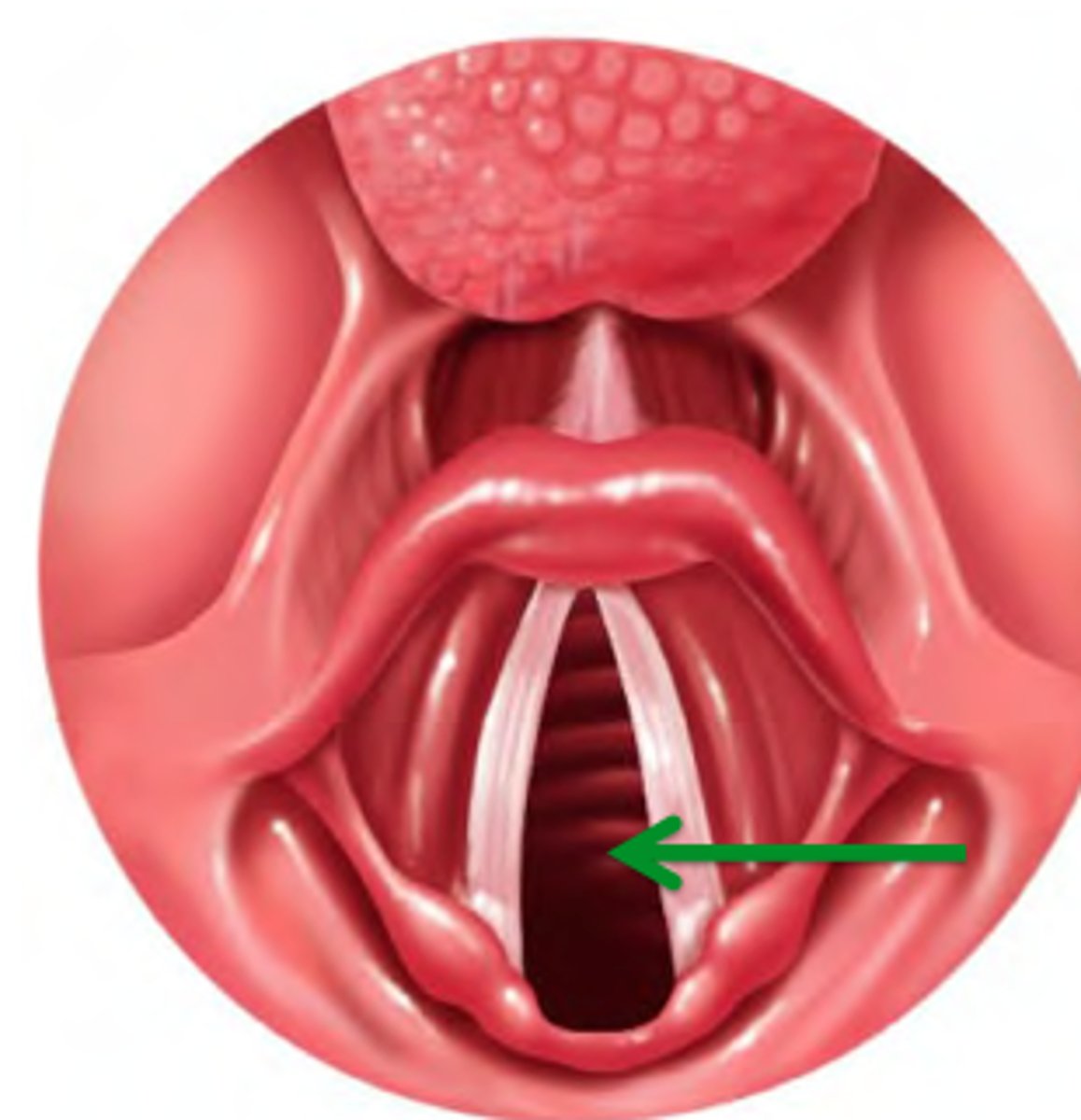
true vocal cords
true vocal cords made of elastic tissue and stratified squamous lining
- tension/tautness on vocal cords from the extrinsic & intrinsic muscles of the larynx controls pitch
- the amount of air passing through the vocal cords controls volume
vibration of the vocal cords create sound
men's vocal cords are thicker; during puberty testosterone enlarges
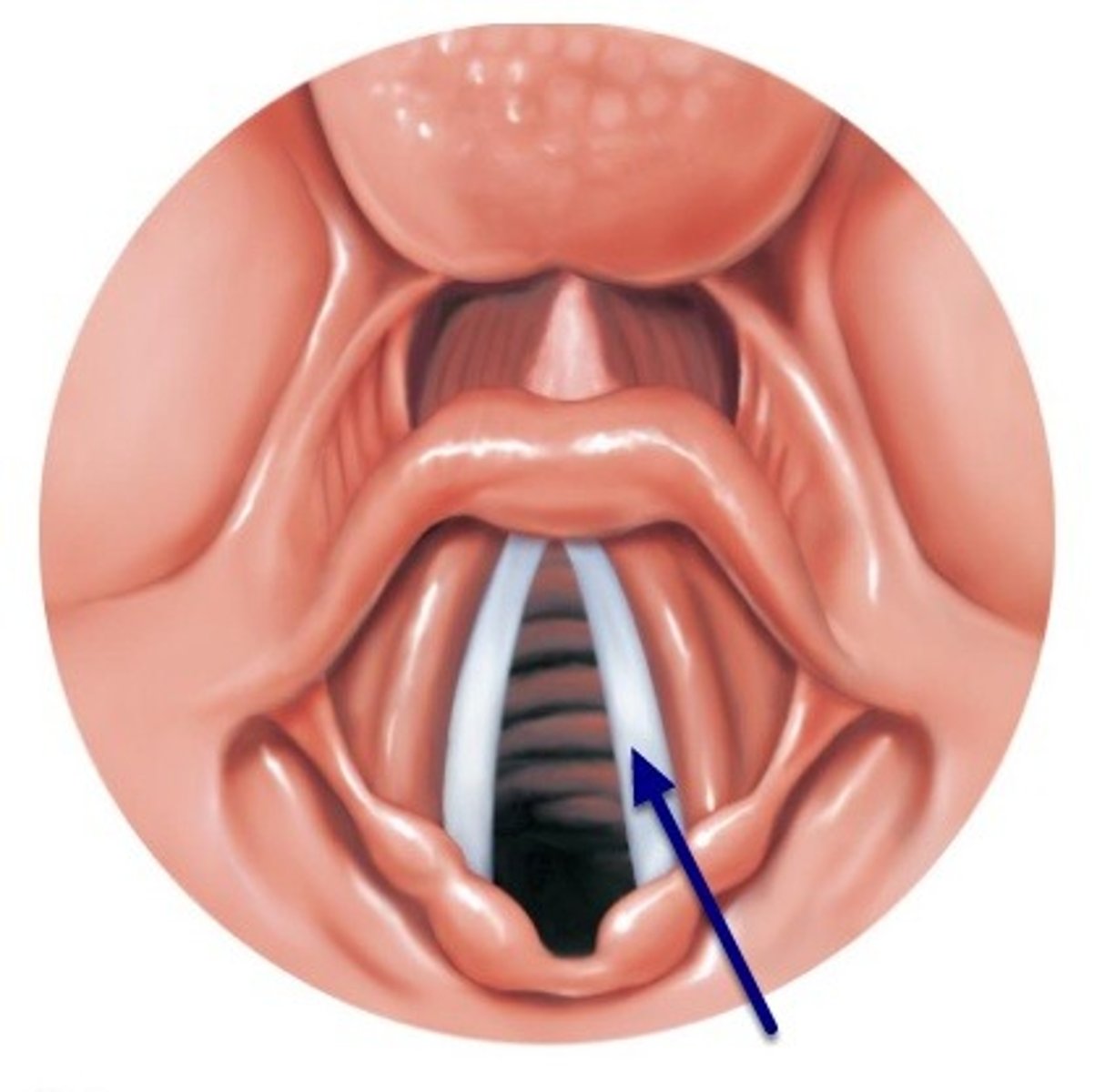
What are true vocal cords made of?
Elastic tissue and stratified squamous lining
false vocal cords
do not make sound, elastic ligament serves to close off the larynx
this increases abdominal pressure "baring down"
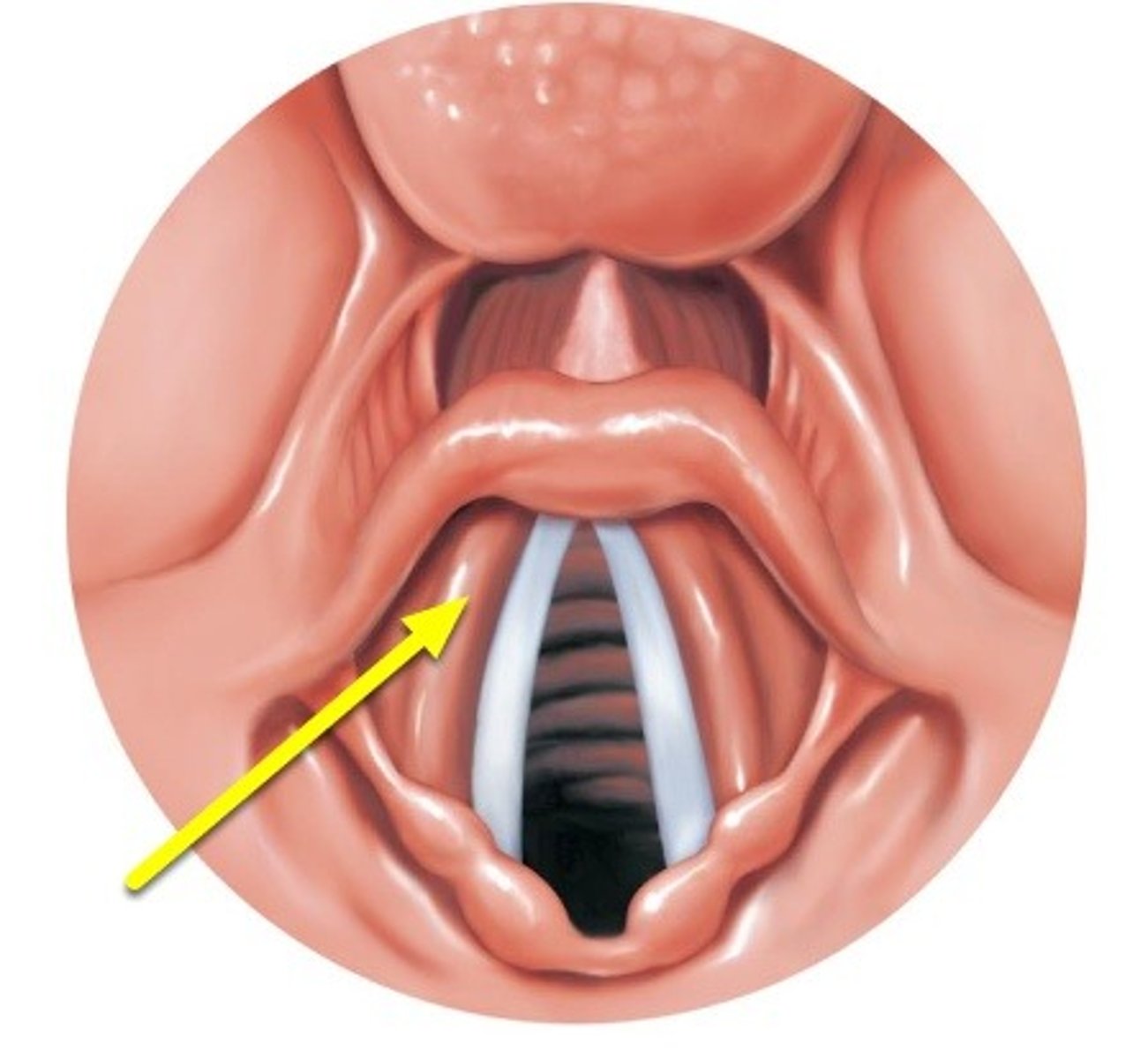
What controls the pitch of the voice?
Tension/tautness on vocal cords from the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the larynx
What controls the volume of the voice?
The amount of air passing through the vocal cords
What creates sound in the voice?
Vibration of the vocal cords
How do men's vocal cords differ from women's?
Men's vocal cords are thicker
what structures in the respiratory system is required for normal speech
- diaphragm
- larynx extrinsic & intrinsic muscles (pulls on vocal cords)
- true vocal cords
- sinuses (resonance of voice)
- nasal & oral cavities
laryngitis
inflammation of the larynx
causes:
- infection
- overuse (lost voice)
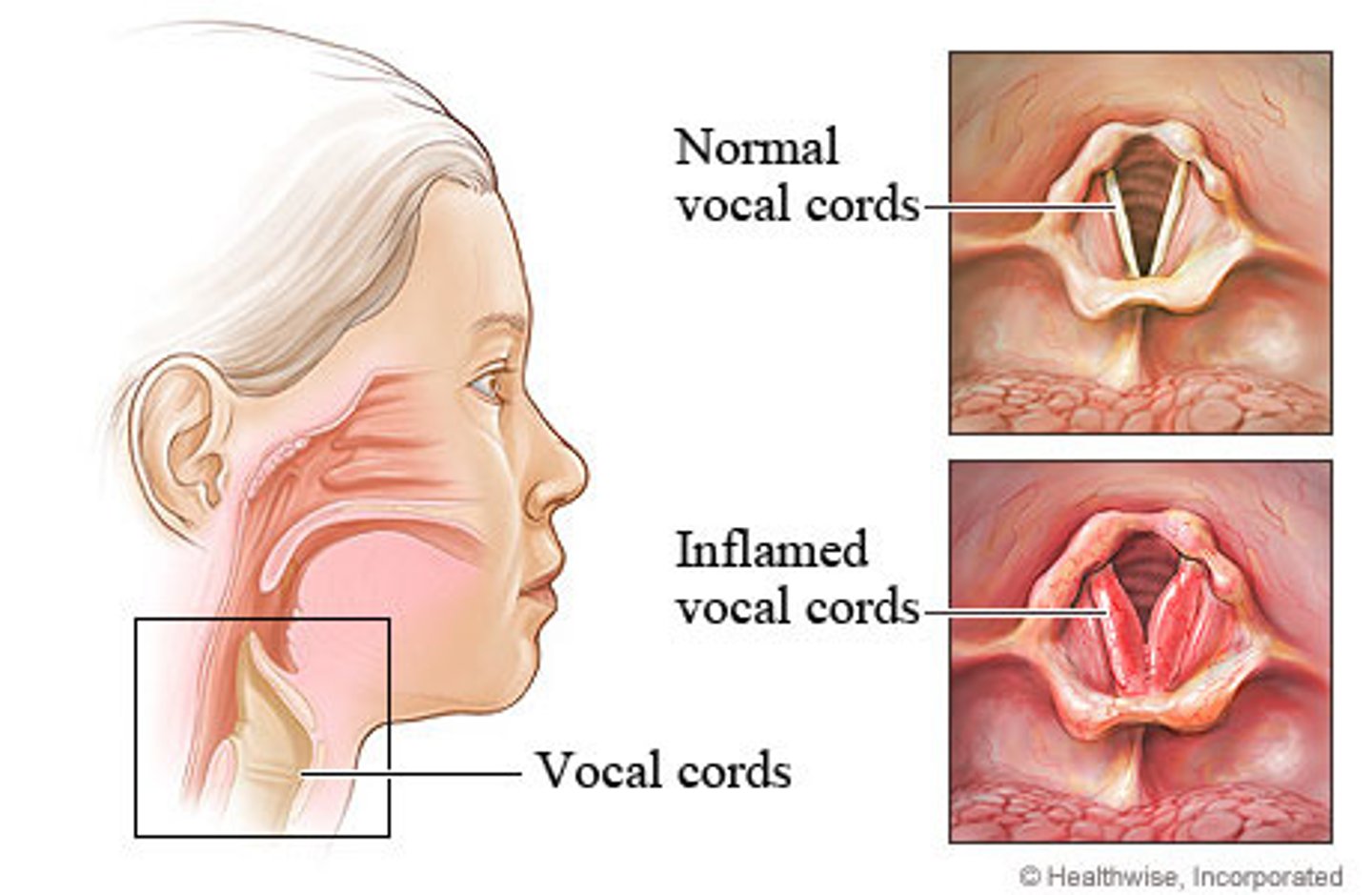
trachea
approx 5 inches long
contains: mucosa, submucosa, cartilage and adventitia
mucosa is pseudo strat epithelium with goblet cells
Mucous glands are present in the submucosa of the trachea to produce mucus which helps trap inhaled particles, dust, and pathogens, allowing for their removal from the airways through the mucociliary clearance mechanism
hyaline cartilage is the cartilage thats made up in the trachea
- c shaped and empty on the backside to allow for esophagus to expand during deglutition of a large bolus
- helps to keep the air way open
tracheotomy preformed below thyroid cartilage
What is the carina?
The point at which the trachea splits into the left and right mainstem bronchi.
What is the function of the cough receptors located at the carina?
To trigger a cough reflex to expel food or other foreign objects that enter the airway.
primary left and right bronchus
right bronchus is lower and runs more vertical
- more susceptible to food going this way (into the right)
each supply one lung
secondary bronchi
3 on right and 2 on left, each goes to one lobe of lung
3R2L
tertiary bronchi (segmental bronchi)
each supplies a segment of a lobe of each lung
as we go from primary to secondary to tertiary bronchi what happens to the walls
cartilage gets thinner
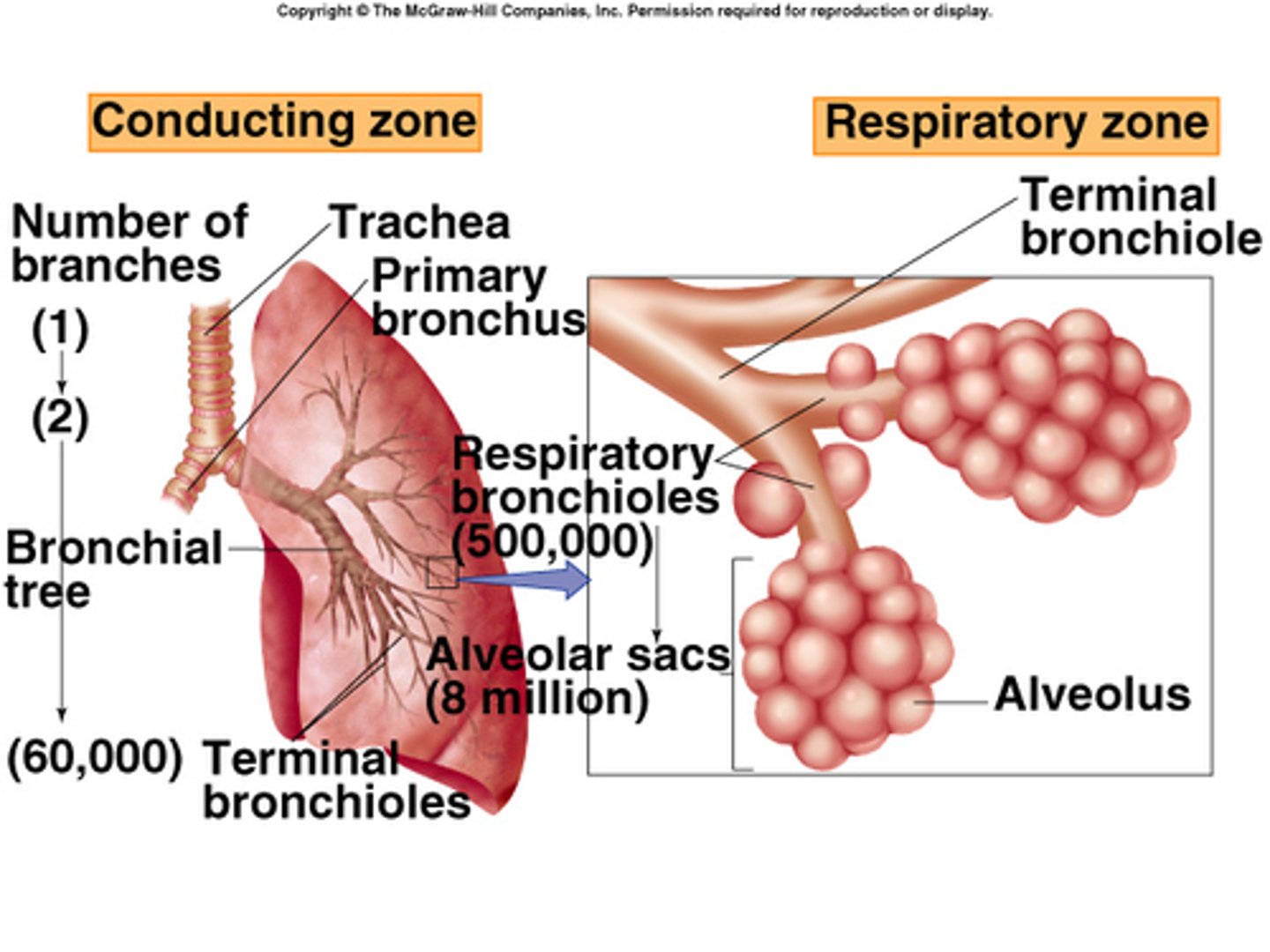
bronchioles
bronchiole -> terminal bronchiole -> respiratory bronchiole
simple columnar w/ cillia -> cuboidal w/ cillia-> squamous
bronchodilation and constriction
sympathetic nervous system, adrenaline, dilates the bronchioles
parasympathetic nervous system & beta blockers constrict the bronchioles
alveolus
made up of respiratory membrane
a. simple squamous epithelium (type 1 cells)
b. basement membrane of the alveolus
c. basement membrane of the capillary
d. simple squamous endothelium of the capillary
very thin and has up to 70m^2 of surface area
- this allows for good gas exchange as with more surface area
alveoli are surrounded by elastic fibers
- this allows for stretch
has alveolar macrophages
- fixed macrophages
has septal cells (type 2 cells)
- produces surfactant which reduces surface tension to help alveoli open
What is the structure that makes up the respiratory membrane of an alveolus?
Simple squamous epithelium (type 1 cells)
What is the function of the basement membrane of the alveolus?
Provides structural support
What type of cells line the capillary in the respiratory membrane?
Simple squamous endothelium of the capillary
What is the total surface area of alveoli?
Up to 70m²
Why is the large surface area of alveoli important?
It allows for good gas exchange
What surrounds the alveoli to allow for stretch?
Elastic fibers
What type of immune cells are found in the alveoli?
Alveolar macrophages (fixed macrophages)
What do septal cells (type 2 cells) produce?
Surfactant
What is the role of surfactant in the alveoli?
Reduces surface tension to help alveoli open
what are type 1 cells
Responsible for gas exchange in the lungs
- simple squamous cells
what are type 2 cells
surfactant producing cells
- septal cells
how many lobes does the lung have
5 (3 right, 2 left)
horizontal fissure of right lung
separates the superior and middle lobes
- only the right lobe has this because left has only two lobes no middle lobe
oblique fissure of the right lung
separates the middle lobe from the inferior lobe