1-2 Introduction: Soil functions and definition
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Soil functions
Raw material → ressource (gravel f.e.)
Support → constructions over the soil (buildings, roads, sewer system…)
Production → food but also wood…
Living space → microorganism and soil biota → lot’s of ecosystems in the soil
Regulation → between different sphere → atmosphere, biosphere, hydrosphere and lithosphere → the pedosphere is in the middle, really important → stores, buffers, filters and transports nutrients, pollutant and water
Archive → cultural archive but also for natural history (Löss Soil sequences in China)
Threats to soil functions
Land consumption → urbanisation, in CH 1m2 per second
Sealing → because of urbanisation the precipitation are drainde by channels, there’s less infiltration in the soil → water not available for plants of groundwater reserve, higher flood risks
Soil compaction → heavy machinery and soil drought → less oxygen for organism, less infiltration and increasing risk of floods
Soil erosion → washing away of fertile arable soil → causes: inappropriate soil management, soil compaction → consequences: economic damage, water eutrophication, damage to infrastructure
Soil pollution
Four sources:
atmospheric pollution
ground/surface water pollution
direct effects of land management (agriculture, industry, waste, mining)
geogenic pollution (bedrock)
Three types of pollutant:
Inorganic pollutant
organic pollutant
radioactive pollutant
Soil acidification → decrease of pH in soil due to sulfuric and nitric acid emissions/formation → strong laws to stop it
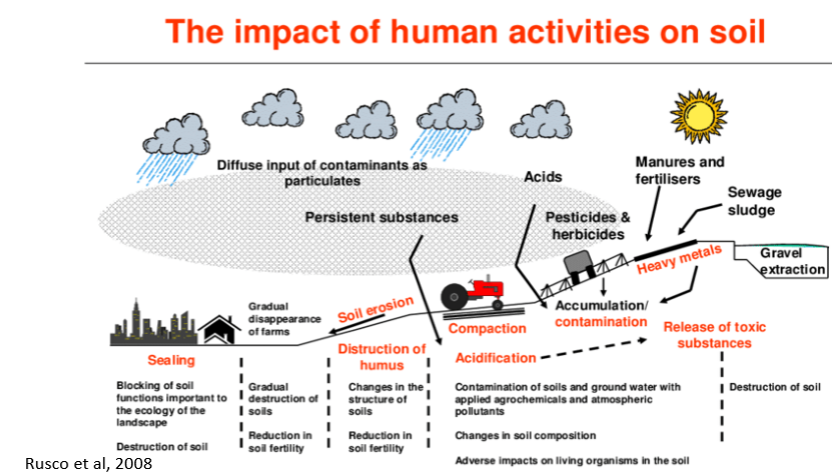
Impact of human activity on soil (image)
10 key points for soil protection
1. Knowledge (soil is not dirt)
2. Precautionary soil protection
3. Coordinated soil monitoring and surveillance (NaBo)
4. Sustainable, careful use
5. Remediate polluted soils to such an extent that there is no danger
6. Soil = common property. Whoever uses soil is responsible for its protection
7. Integrity of the soil is ensured by legal standards
8. Soil protection = corporate mandate > improve institutional conditions for soil protection + financial resources
9. Implement soil protection by all actors
10. Important partners in soil protection: spatial planning, agriculture and forestry
Legislation EU
New soil strategy and monitoring for 2030
60% of EU soils are unhealthy, big economic cost
Legislation CH
Strategy soil 2020
Six general objectives are to be achieved in order to preserve soil functions in the long term:
reduction of soil consumption
consideration of soil functions in spatial planning
protection of the soil against persistent damage
restoration of degraded soils
awareness of the value and vulnerability of the soil
strengthening international engagement
Important institution CH:
Agroscope: Federal Competence Centre for Agricultural Research
Swiss Federal Institute for Forest, Snow and Landscape Research (WSL): Forest soils
Federal Office for Agriculture (BLW)
Federal Office for the Environment (BAFU) → Department Soil & Biotechnology
KoBo
National centre of competence for soil science: KoBo. Started in 2020. Objectives: “improve the basis for the implementation of measures promoting the sustainable use and effective protection of soil resources.”
Tasks:
Standardize and improve methods of surveying and analysing soil
Define technical standards for soil mapping
National information platform for the Confederation, the cantons and private organisations
Provides methods for evaluating soil functions and threats
Promotes interdisciplinary exchange between the different actors
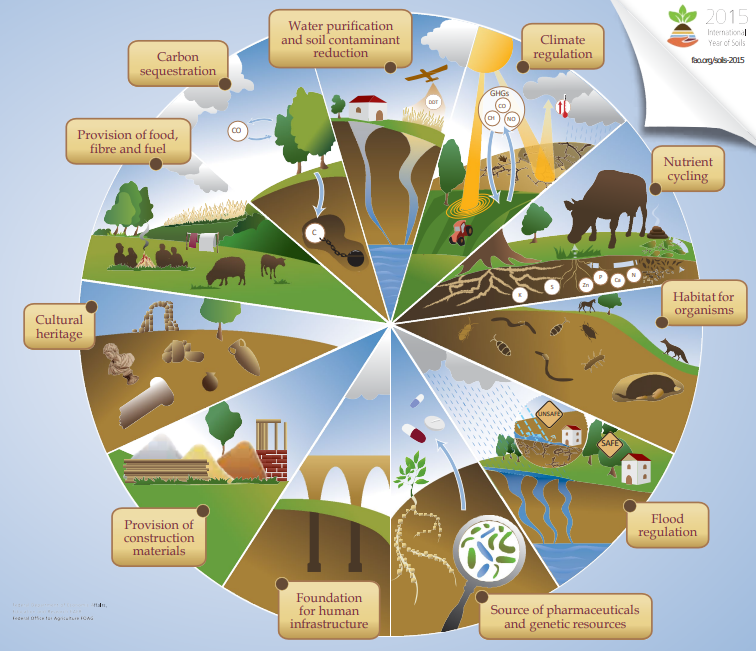
Soil functions circle
Different soil definition
Soil is the living, breathing skin of our planet
Soil is any loose material on the surface of the Earth that is capable of supporting life
Definition: surface component of the Earth that developed from geological materials (lithosphere, bottom) and dead biomass (biosphere, top) by physical, chemical and biological processes
Other definition (sediment, regolith, coal and peat, pedosphere)
Sediment = Displaced soil without in situ soil formation → not a soil
Regolith = weathered rock without biological influence → not a soil
Coal and peat = biogenic sediments → not a soil
Pedosphere = uppermost part of the lithosphere
Pedosphere
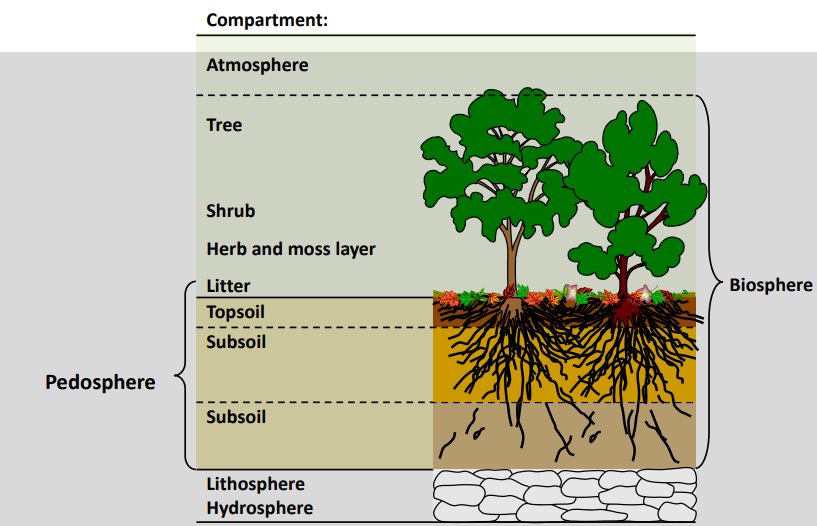
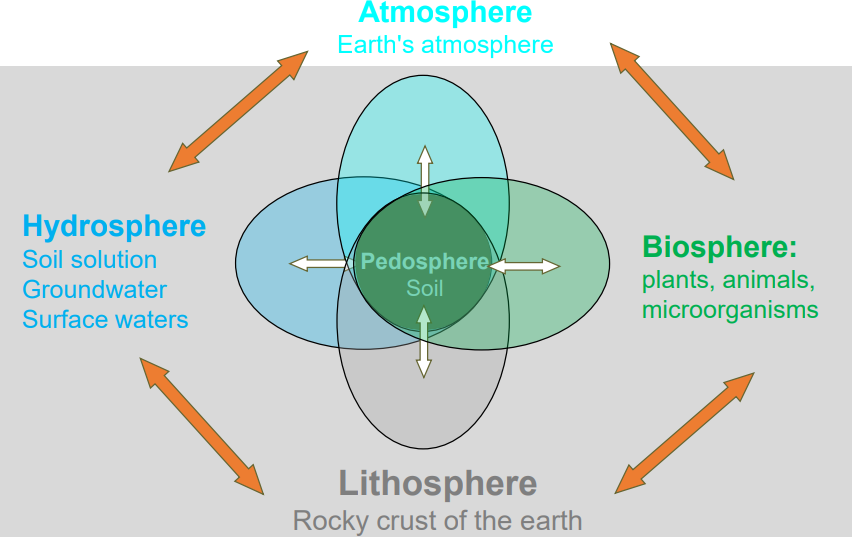
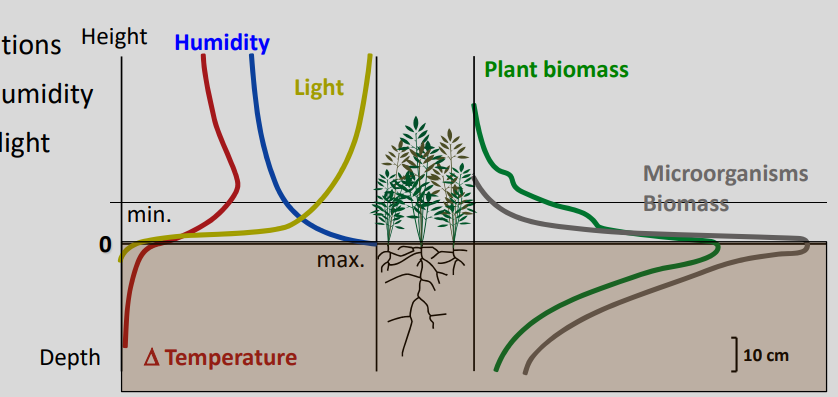
Environmental condition around pedosphere
Extremes: Sharp temperature fluctuations, low to very high relative humidity, complete darkness to full light
Soils definition (horizon and group/type/unit)
Soils are made of horizons (total of horizons = solum, no OM layer or bedrock)
Soil group, soil type, soil unit (Bodenart): same horizon sequence, same characteristics of the horizons, not necessarily the same bedrock
Soil type can also refer to grain size (Bodentyp)
Horizons arise from the (geologic) substrate through soil-forming processes: Weathering, Mineral formation, Decomposition of litter and humus formation, Microstructure formation, Material transfer
Horizon is different from a layer which include OM and bedrock
Soil unit definitions
Elementary Soil unit: Pedon (1-10 m2 and 0.5 – 2 m deep)
Vertical pit: soil profile
Polypedon = company of pedons (few m²-1000 km²)
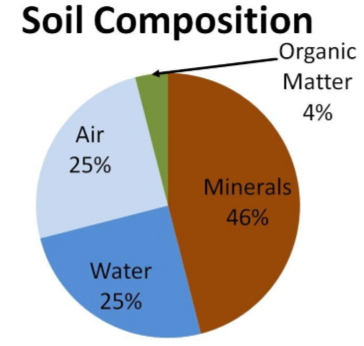
Soil composition

Fine pores < 0.2 µm uninhabited
Medium pores 0.2 - 10 µm bacteria, fungi, algae, root hairs, unicellular organisms
Coarse pores & secondary pores > 10 µm roots, nematodes, mites, collembola and other fauna
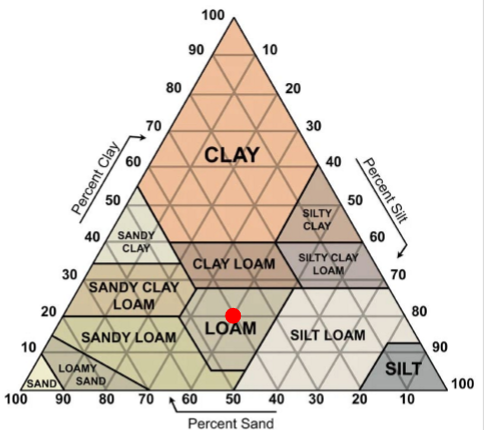
Grain size
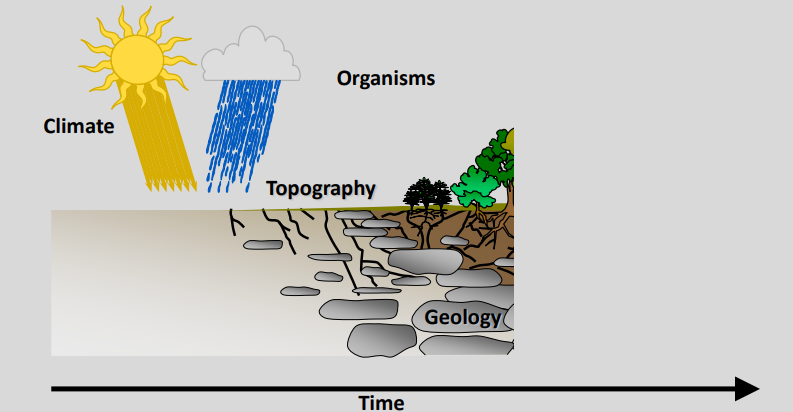
Soil formation
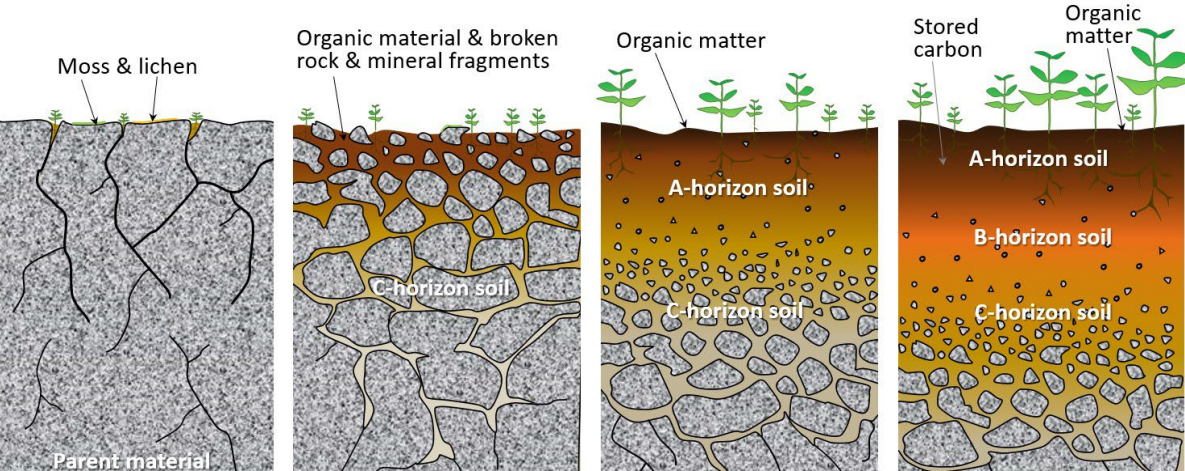
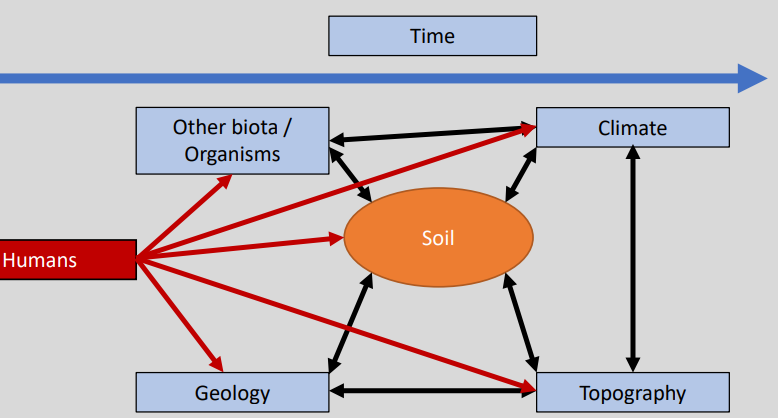
Soil definitions → zonal, intrazonal and azonal
Zonal soils = climate & vegetation determine development
Intrazonal soils = differentiation within climate zones due to specific influences of relief, water balance, bedrock and age
Azonal soils = young soils without characteristic profile
Other definitions
Catena = Relief-controlled soil sequence (typically a slope)
Chronosequence = chronological sequence of soil development