Time Complexity and Algorithm Classifications
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:47 AM on 4/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
1
New cards
what is a selection sort?
Selection Sort algorithm repeatedly finds the smallest element in the unsorted tail region of a list and moves it to the front
2
New cards
what is the time complexity for a selection sort?
With an array of size n, count how many primitive operations are needed:
1st run = n + 2
2nd run = (n -1) elements + 2 operations
3rd run = (n-2) elements + 2 operations
2 is the swapping operations
minus 1 from n each time because biggest value at the end so doesn't need to be swapped
simplified to O(n²)
1st run = n + 2
2nd run = (n -1) elements + 2 operations
3rd run = (n-2) elements + 2 operations
2 is the swapping operations
minus 1 from n each time because biggest value at the end so doesn't need to be swapped
simplified to O(n²)
3
New cards
what is a search algorithm?
check for an element from any data structure where it is stored
4
New cards
what are the 2 main search algorithms?
sequential search
interval search
interval search
5
New cards
what is a sequential search + example?
eg. linear search
list traversed sequentially and every element checked
list does not need to be sorted
brute force algorithm
list traversed sequentially and every element checked
list does not need to be sorted
brute force algorithm
6
New cards
what is an interval search + example?
eg. binary search
divide and conquer algorithm
list must be sorted
divide and conquer algorithm
list must be sorted
7
New cards
what is the time complexity for binary search?
O(log₂n)
8
New cards
what is the time complexity for linear search?
O(n)
9
New cards
is binary search or linear search faster?
binary search
10
New cards
for an unsorted list of millions of elements, is binary or linear search better + why?
* binary search needs an already sorted array so combined with selection sort, time complicity = n² causing overall algorithm slower
* if performing search multiple times, use binary as we only have to sort once
* if performing search once, better to use linear
* if performing search multiple times, use binary as we only have to sort once
* if performing search once, better to use linear
11
New cards
what is polynomial time?
an algorithm is solvable in polynomial time if the number of steps required to complete the algorithm for a given input is O(nᵏ) for some non-negative integer k, n being the complexity of the input
12
New cards
for algorithms with high computational complexity, how do we know there isn't a better algorithm with a lower time complexity?
we are dividing algorithms into classifications which limits the lowest time complexity it can have
13
New cards
what are the ways a problem can be classified
computable
non-computable
P problems
NP problems
NP-complete problems
NP-Hard problems
non-computable
P problems
NP problems
NP-complete problems
NP-Hard problems
14
New cards
what is a computable problem?
problem can be solved using computer
15
New cards
what is a non computable problem?
can't be solved using computer
eg. halting problem
eg. halting problem
16
New cards
what are P problems?
* solved in polynomial time aka. a reasonable amount of time
17
New cards
what are examples of P problems?
eg. search and sort algorithms
18
New cards
what are NP-Complete problems?
The hardest problems in NP set
* No polynomial-time algorithm is discovered for any NP-complete problem
* Verifiable in polynomial time but time complexity is greater than polynomial time
* No polynomial-time algorithm is discovered for any NP-complete problem
* Verifiable in polynomial time but time complexity is greater than polynomial time
19
New cards
what are examples of NP-complete problems?
travelling salesperson?
knapsack problem
finding shortest common superstring
Given three positive integers a, b, and c, do there exist positive integers (x and y) such that ax2 + by2 = c
knapsack problem
finding shortest common superstring
Given three positive integers a, b, and c, do there exist positive integers (x and y) such that ax2 + by2 = c
20
New cards
what are NP problems?
* difficult to solve in polynomial time
* easy to verify the solution in polynomial time
\
* easy to verify the solution in polynomial time
\
21
New cards
what are examples of NP problems?
eg. network routing, database problems, scheduling
non-deterministic algorithms
decision-making problems
non-deterministic algorithms
decision-making problems
22
New cards
why are NP-Complete problems the intersection of P and NP problems?
Nobody was able to prove that no polynomial-time algorithm exist for any of the problems even though there currently aren't any
23
New cards
what are NP-Hard problems?
* Difficult to solve problems which cannot be solved in polynomial time
* difficult to verify in polynomial time
* difficult to verify in polynomial time
24
New cards
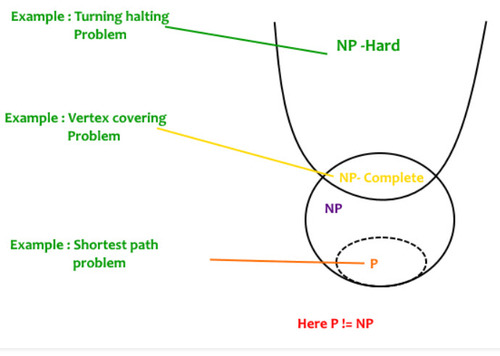
what is the main structure of algorithm classification?
P problems are a subset of NP problems
Non-computable problems are a subset of NP-Hard problems
NP-Complete problems are the intersection of NP and NP-Hard problems
Non-computable problems are a subset of NP-Hard problems
NP-Complete problems are the intersection of NP and NP-Hard problems
25
New cards
what are the consequences if a polynomial time algorithm is found for any problem in the NP-Complete set?
every problem in NP can be solved in polynomial time
NP-Complete would no longer be in intersection and would be a proper subset of NP
NP-Complete would no longer be in intersection and would be a proper subset of NP
26
New cards
what are the consequences if P problems are equal to NP problems?
all problems we have would be solvable in polynomial time
no security possible as any encryption could be decrypted in polynomial time
no security possible as any encryption could be decrypted in polynomial time