Chapter 21 - The Great War: The World in Upheaval
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
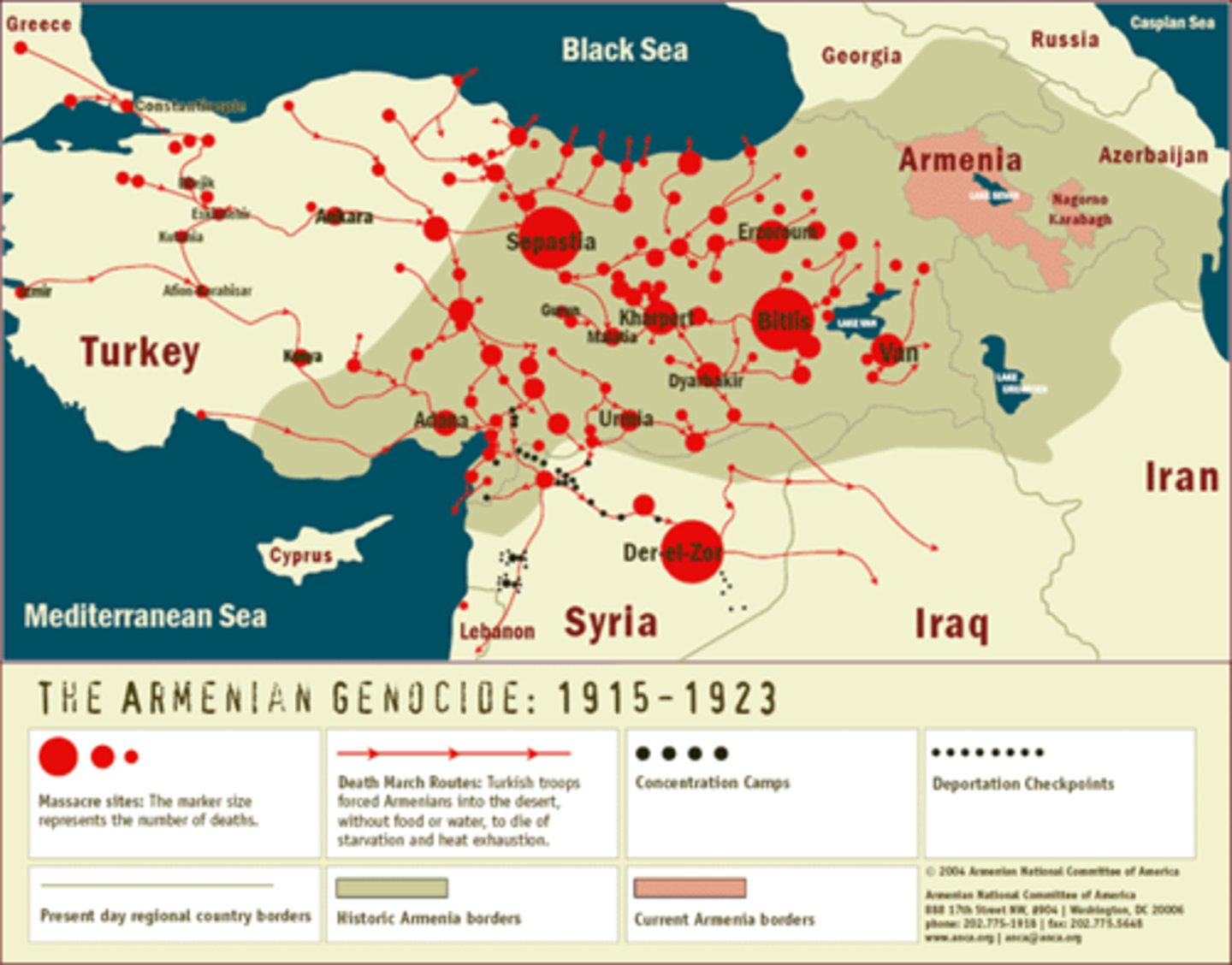
Armenian Genocide
Campaign of extermination undertaken by the Ottomans against two million Armenians living in Ottoman territory during World War I.
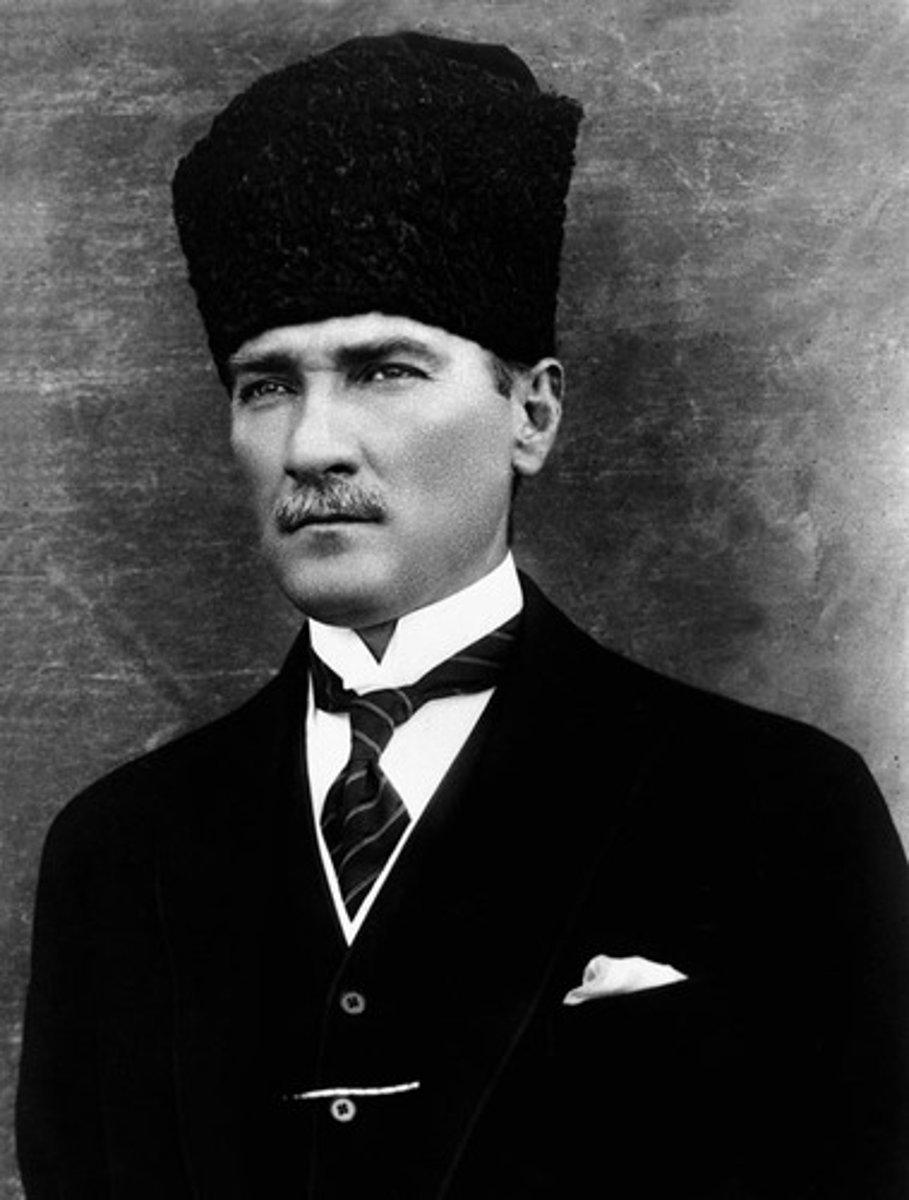
Atatürk
1881-1938 C.E. Meaning "Father of the Turks," his real name was Mustafa Kemal. He was a Turkish army officer, reformer, and the first president of the modern Republic of Turkey after the Ottoman defeat in World War I.

Balfour Declaration
British declaration from 1917 that supported the creation of a Jewish homeland in Palestine.
Black Hand
Pre-World War I secret Serbian society; one of its members, Gavrilo Princip, assassinated Austrian archduke Francis Ferdinand and provided the spark for the outbreak of the Great War.

Bolshevik
a member of the faction of the Russian Social Democratic Workers' Party, founded by Vladimir Lenin, which was renamed the Communist Party after the 1917 revolution

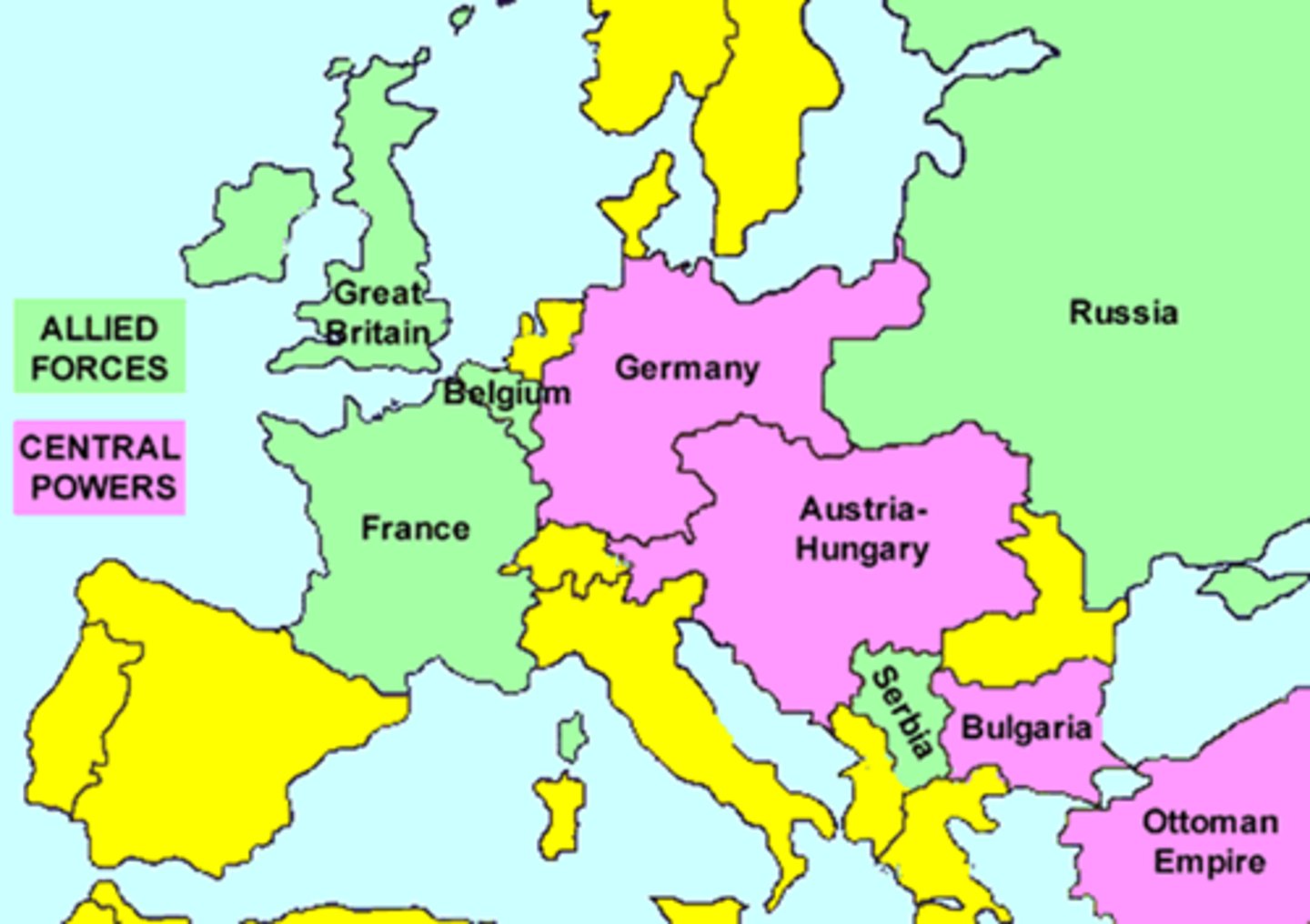
Central Powers
World War I term for the alliance of Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman empire.
dreadnoughts
A class of British battleships whose heavy armaments made all other battleships obsolete overnight.

February Revolution
the revolution against the Czarist government of Russia which led to the abdication of Nicholas II and the creation of a provisional government in March 1917

Fourteen Points
A series of proposals in which U.S. president Woodrow Wilson outlined a plan for achieving a lasting peace after World War I.

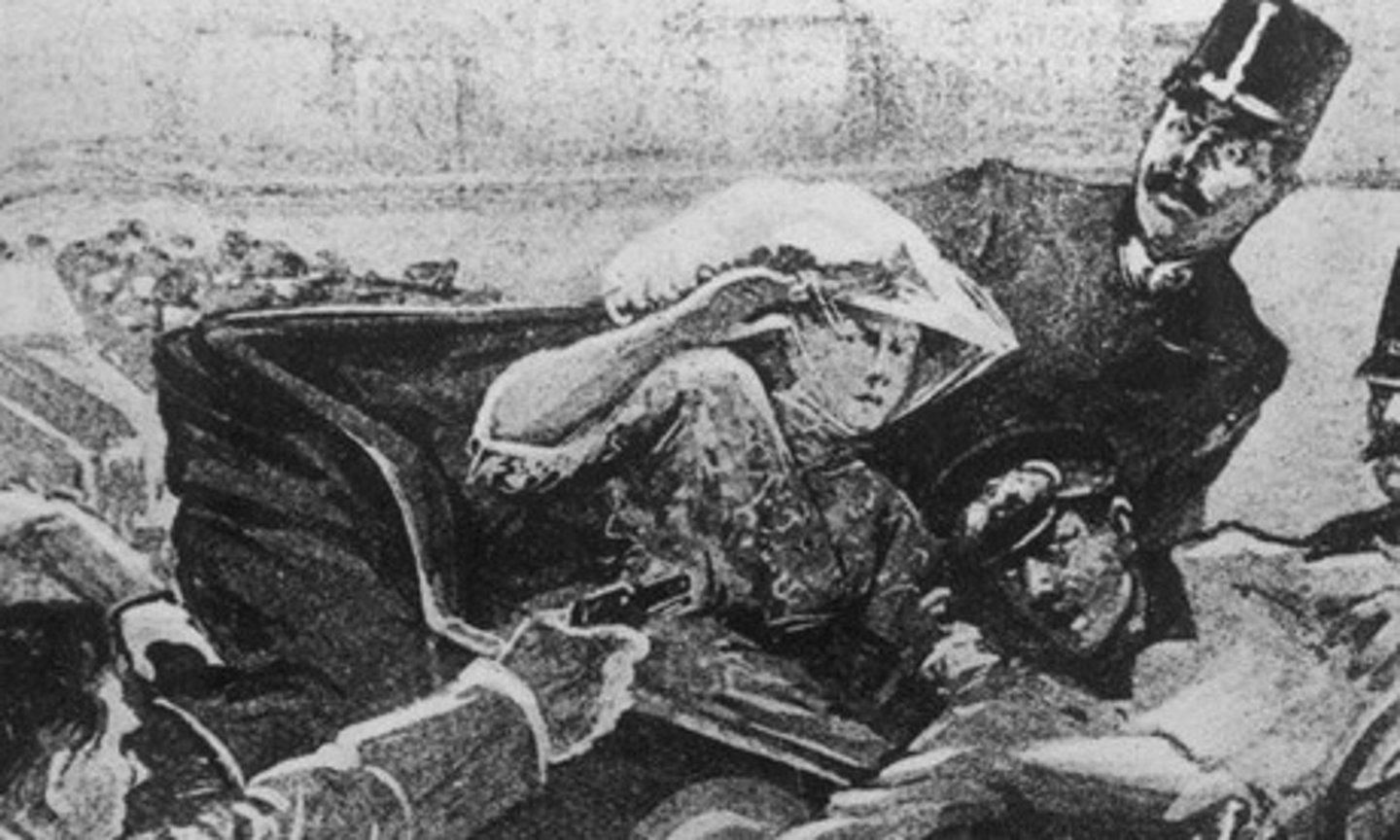
Franz Ferdinand
Archduke of Austria-Hungary assassinated by a Serbian nationalist. A major catalyst for WWI.
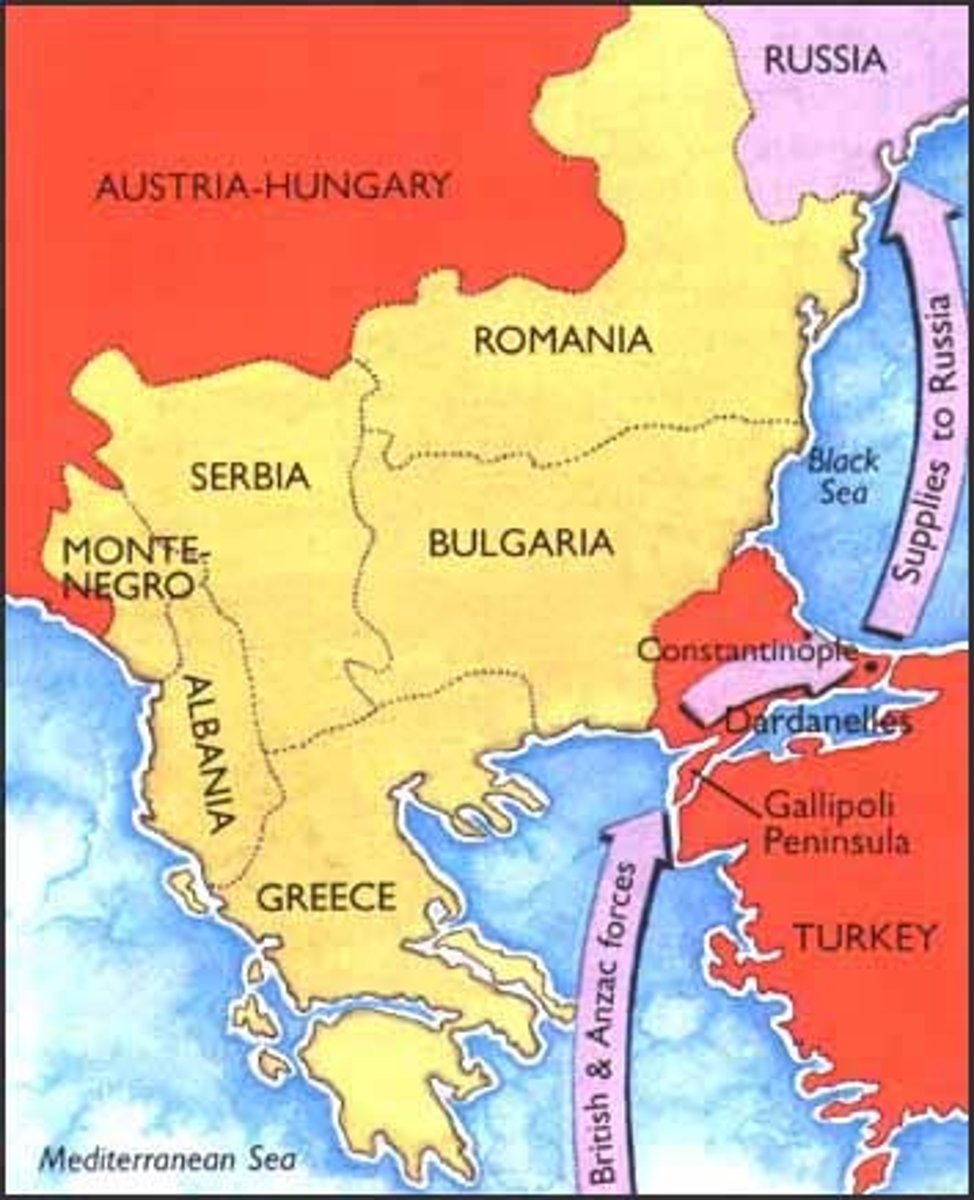
Gallipoli
A poorly planned and badly executed Allied campaign to capture the Turkish peninsula of Gallipoli during 1915 in World War I. Intended to open up a sea lane to the Russians through the Black Sea, the attempt failed with more than 50 percent casualties on both sides.
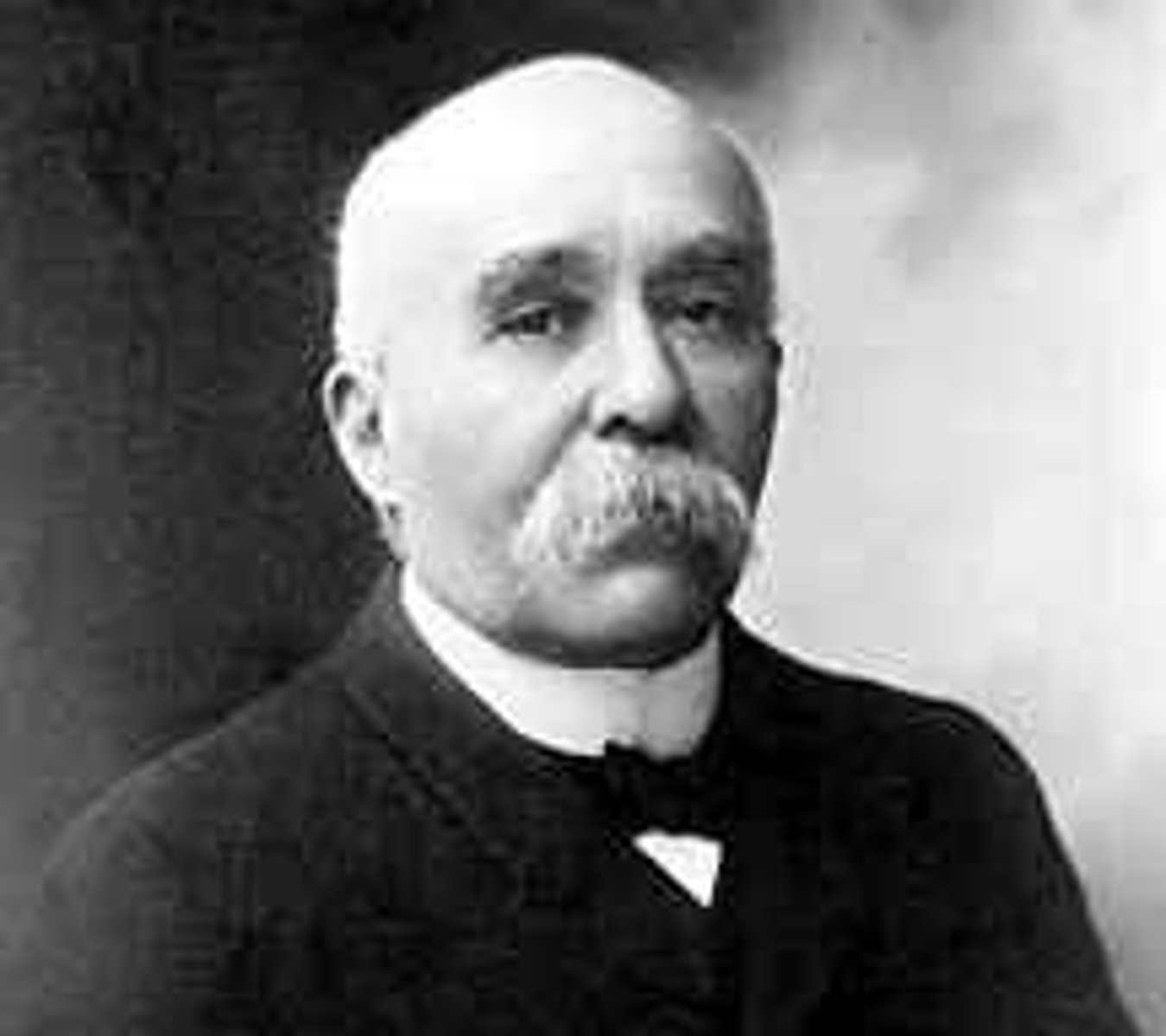
George Clemenceau
French prime minister in last years of WWI and during Versailles Conference of 1919. Pushed for heavy reparations from Germans. Wanted to make Germans suffer and help break Germany up.

home front
Term made popular in World War I and World War II for the civilian "front" that was symbolic of the greater demands of total war.

influenza pandemic
1918 global outbreak of influenza, a highly contagious viral infection, killing as many as 30 million people worldwide.

League of Nations
Forerunner of the United Nations, the dream of American president Woodrow Wilson, although its potential was severely limited by the refusal of the United States to join.

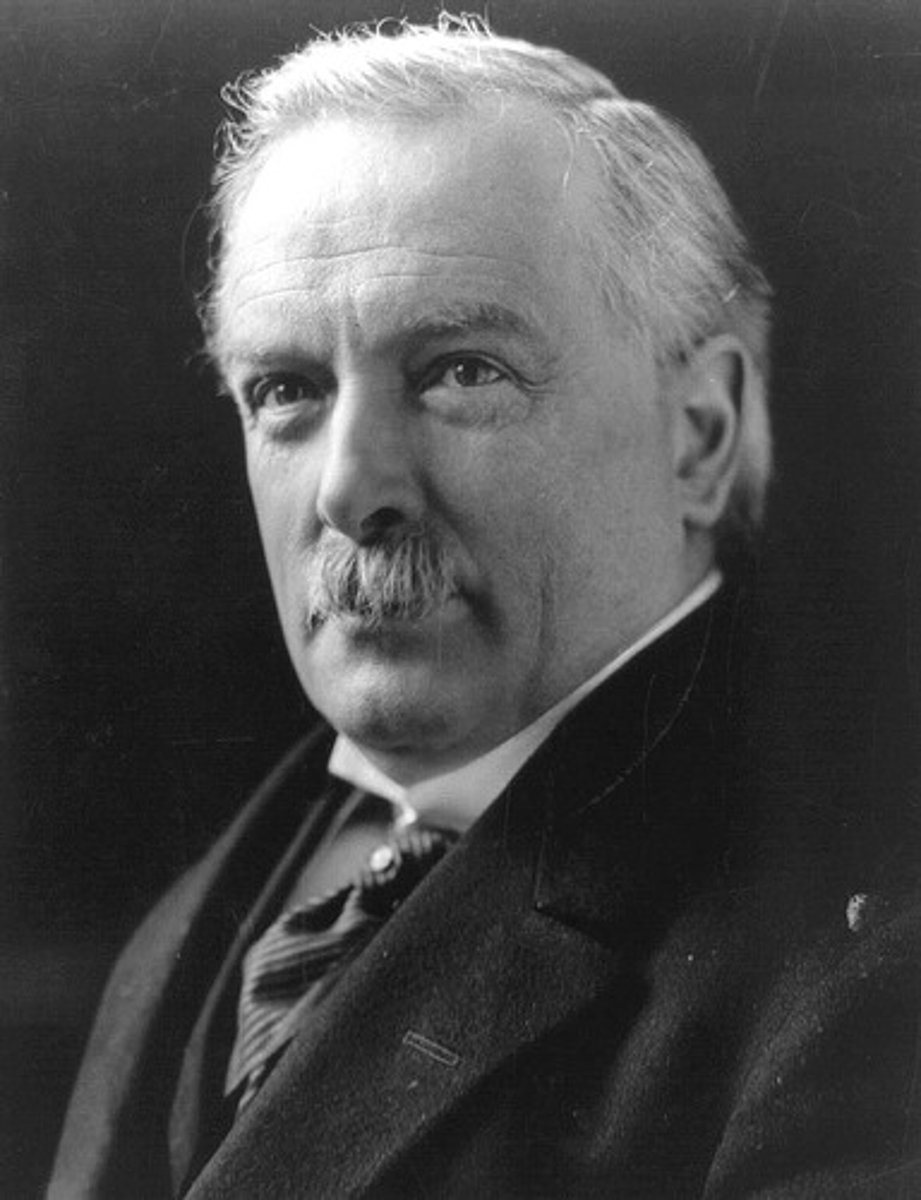
Lloyd George
British prime minister, although he was re-elected for his popular campaign of making Germany pay for the war, he ended up fighting the most for German interests in the Versailles Treaty because he feared communism

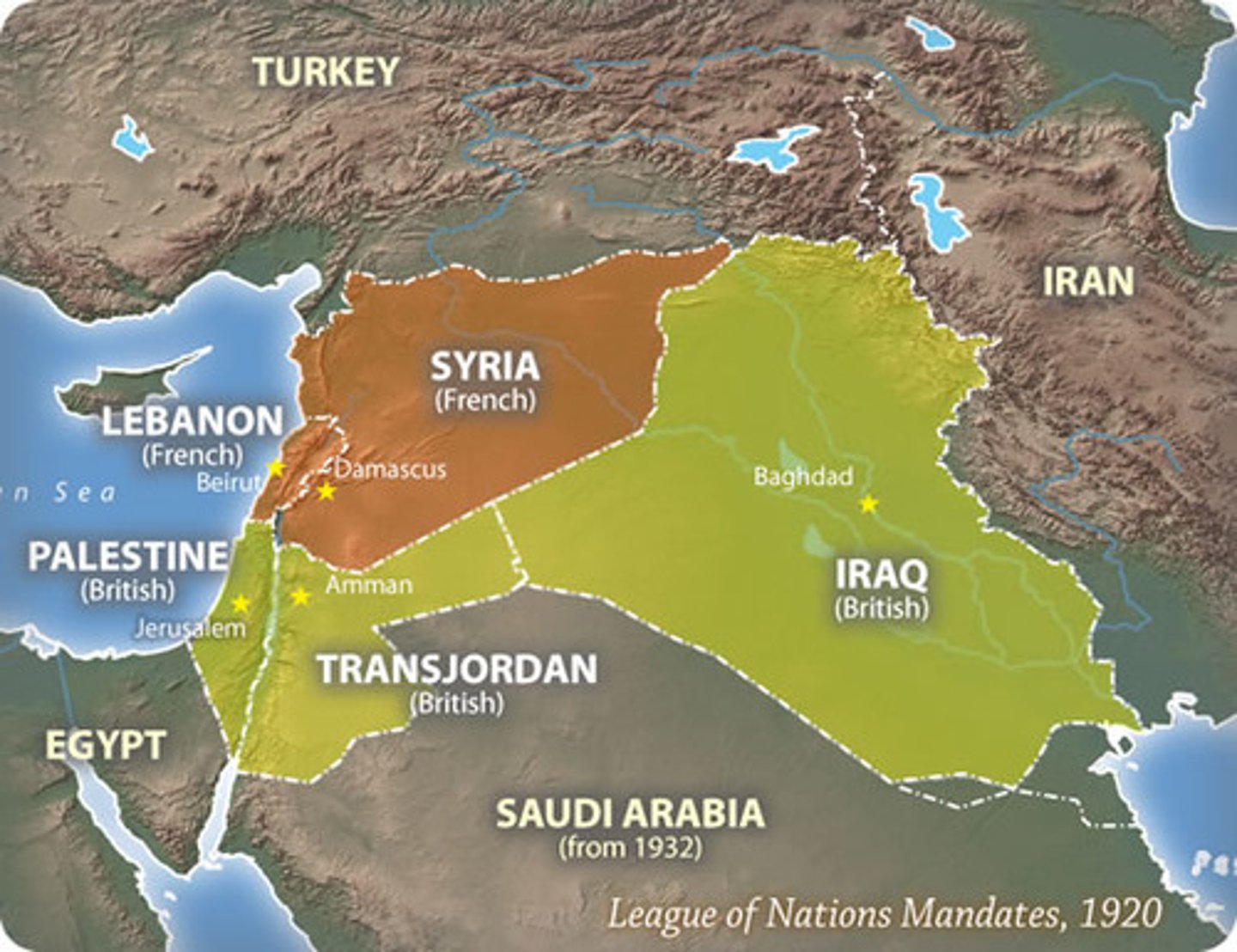
mandate system
System that developed in the wake of World War I when the former colonies ended up mandates under European control, a thinly veiled attempt at continuing imperialism.
mustard gas
a liquid agent that, when exposed to air, turned into a noxious yellow gas
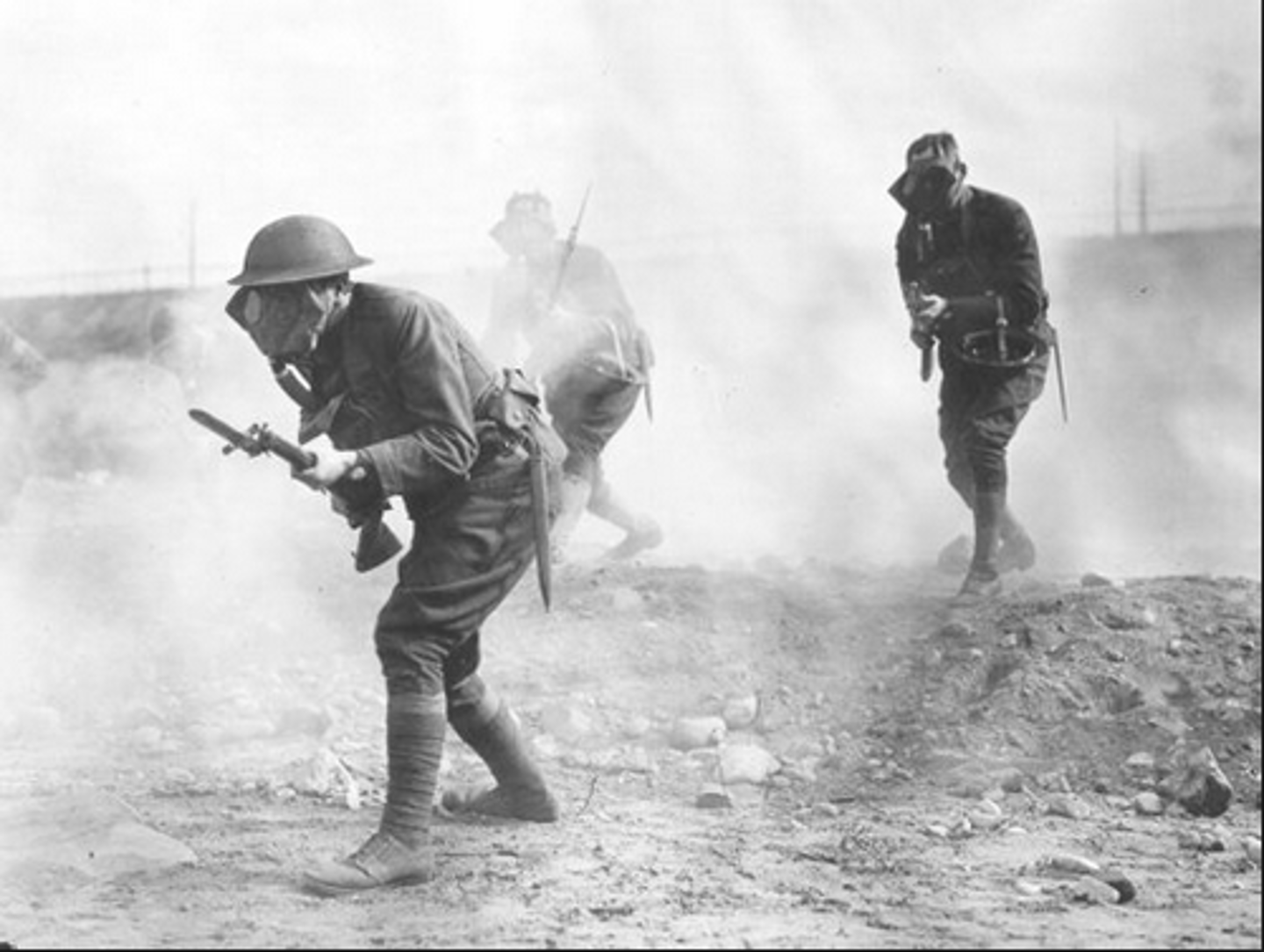

no-man's-land
A strip of land between the trenches of opposing armies along the Western Front during WW1

October Revolution
the coup d'etat by the Bolsheviks under Lenin in November 1917 that led to a period of civil war which ended in victory for the Bolsheviks in 1922

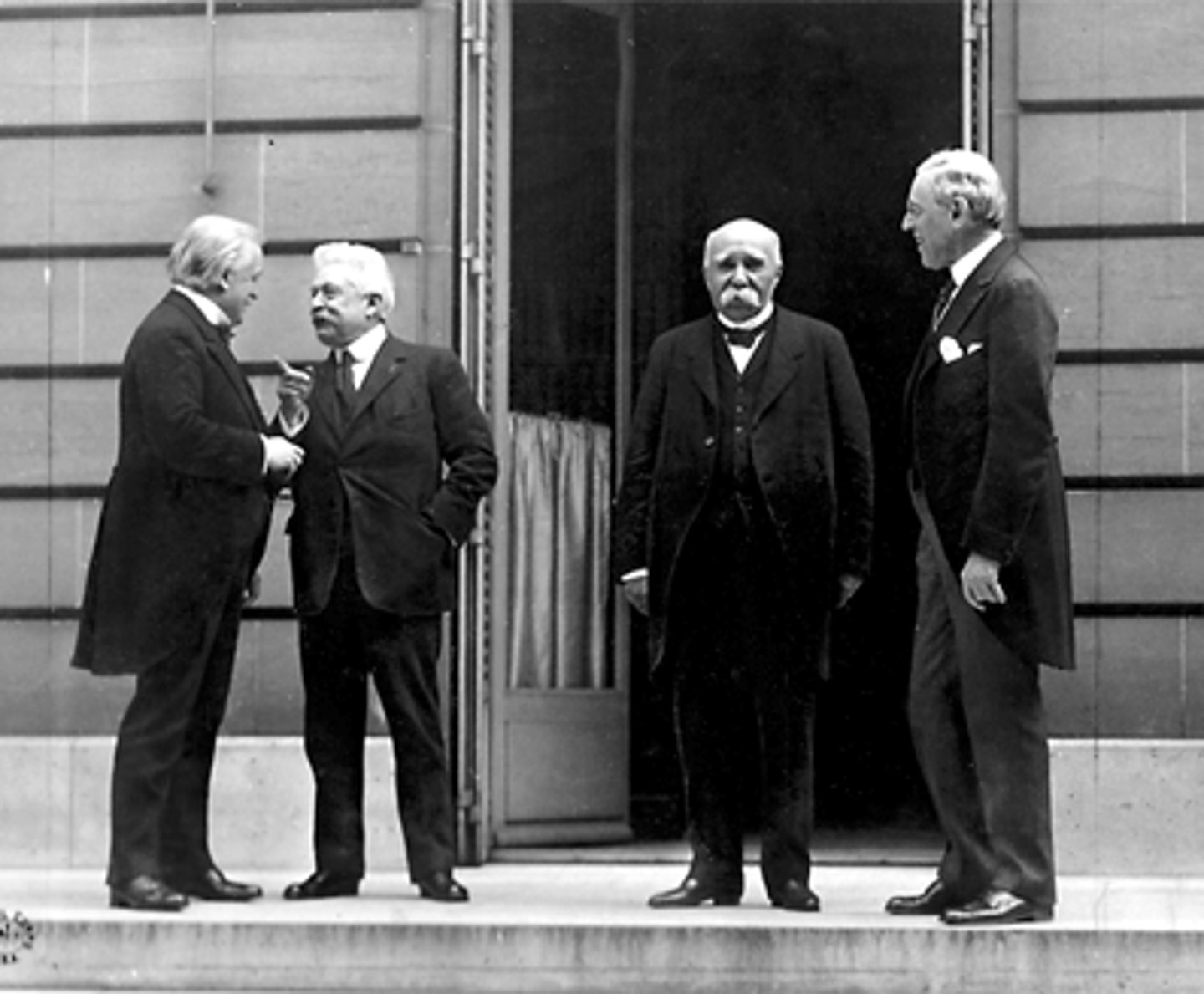
Paris Peace Conference
The great rulers and countries excluding Germany and Russia met in Versailles to negotiate the repercussions of the war, such leaders included Lloyd George (Britain), Woodrow Wilson (America), Clemenceau (France) and Italy. The treaty of Versailles was made but not agreed to be signed and the conference proved unsuccessful.

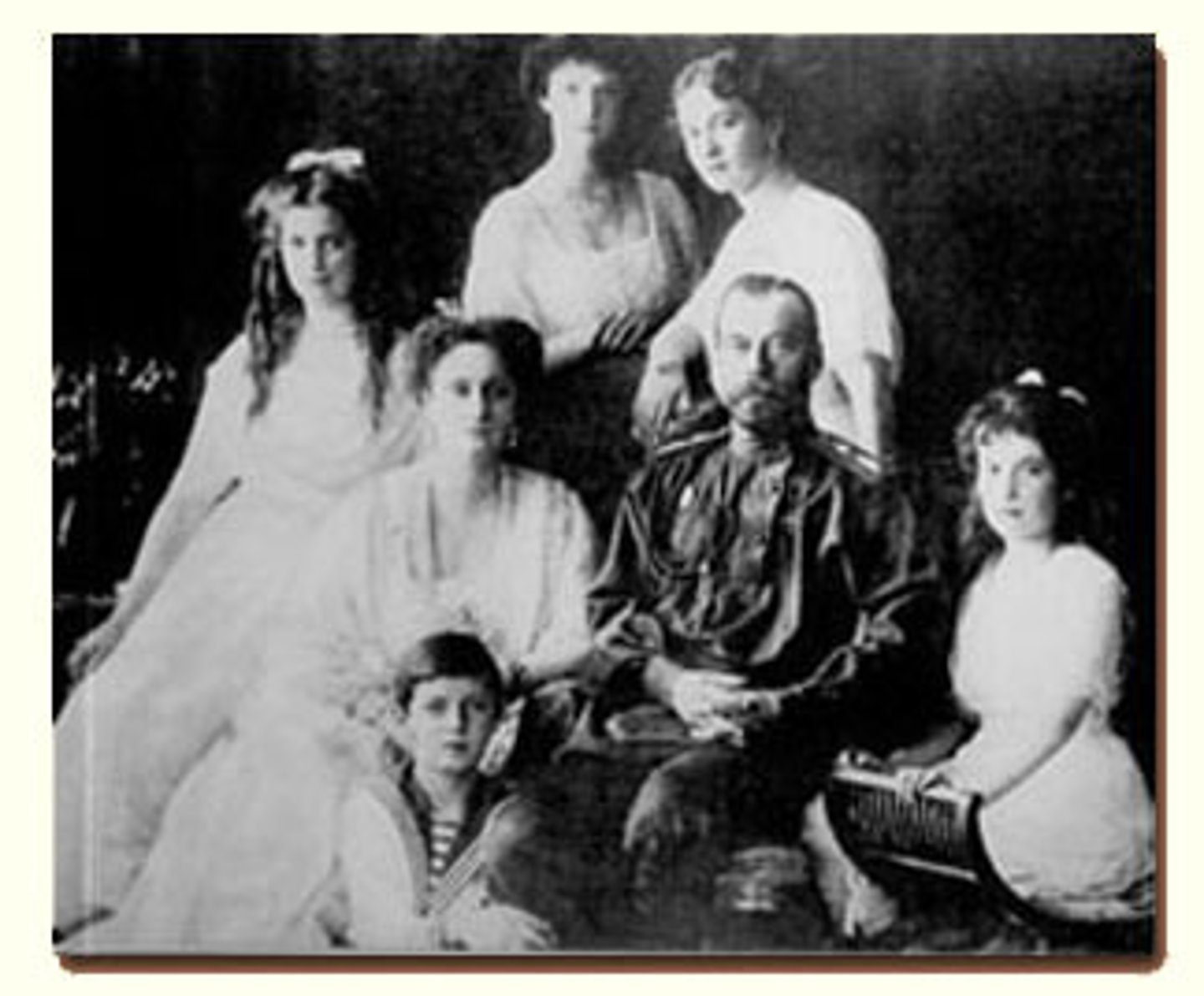
Romanov Dynasty
Russian dynasty (1610-1917) founded by Mikhail Romanov and ending with Nicholas II.

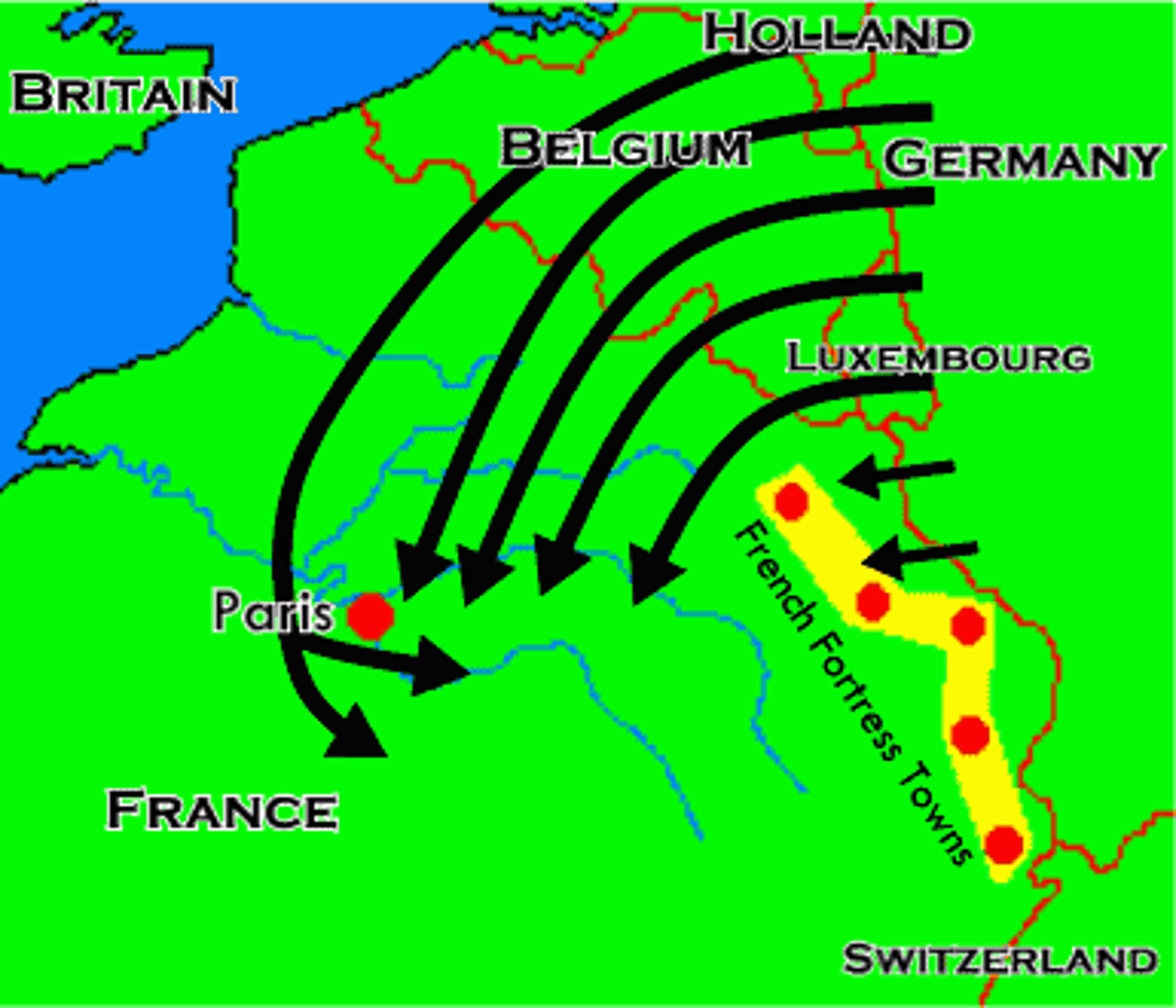
Schlieffen Plan
The name of German war plans to deal with a war in which battles would have to be fought on two fronts. The plan was implemented at the start of World War I, when it was clear that Germany would go to war with Russia and France.
self-determination
Belief popular in World War I and after that every people should have the right to determine their own political destiny; the belief was often cited but ignored by the Great Powers.

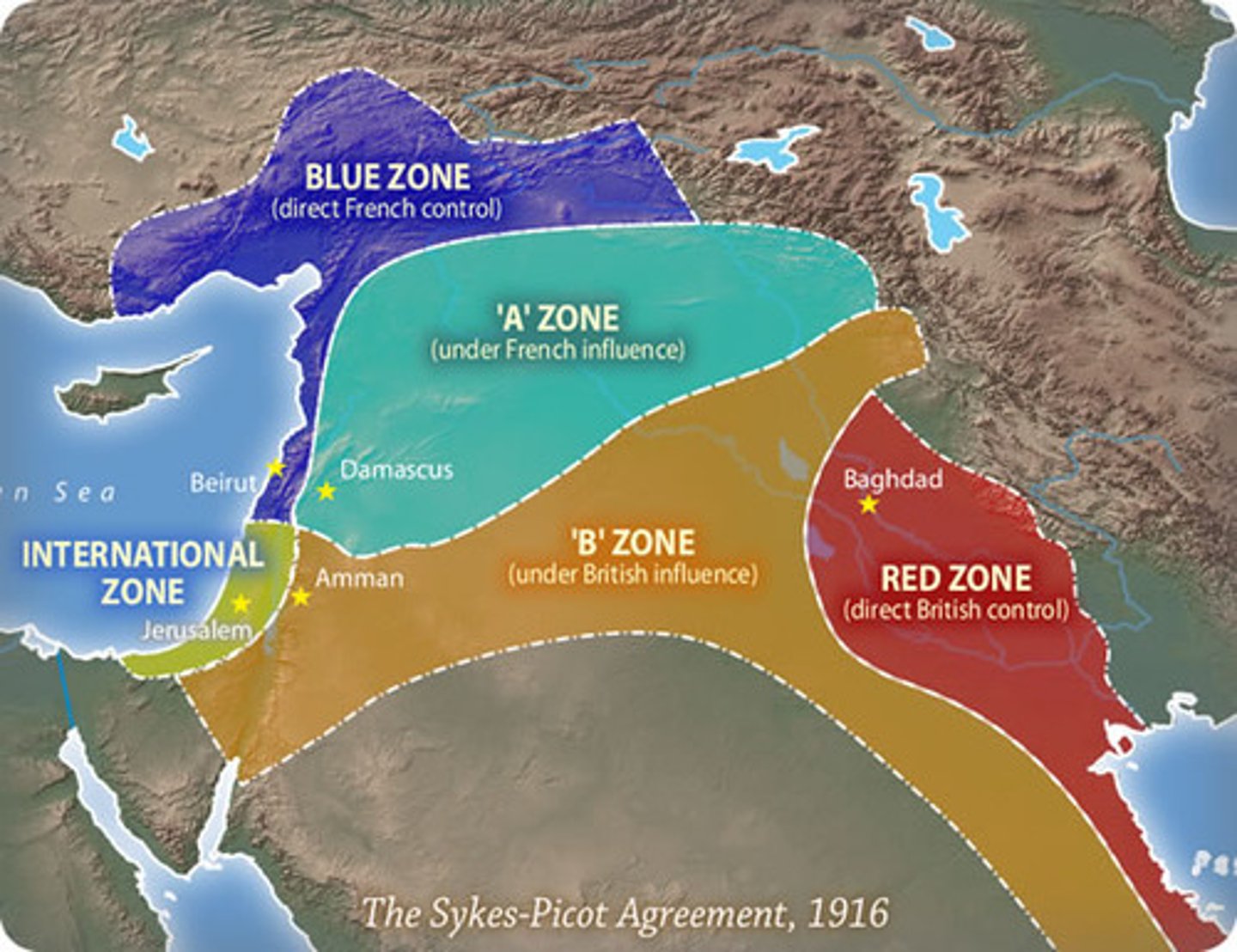
Sykes-Picot Agreement
Secret 1917 treaty between the British and French, with the agreement of Russia, to divide the modern Middle East between them after the end of World War I.
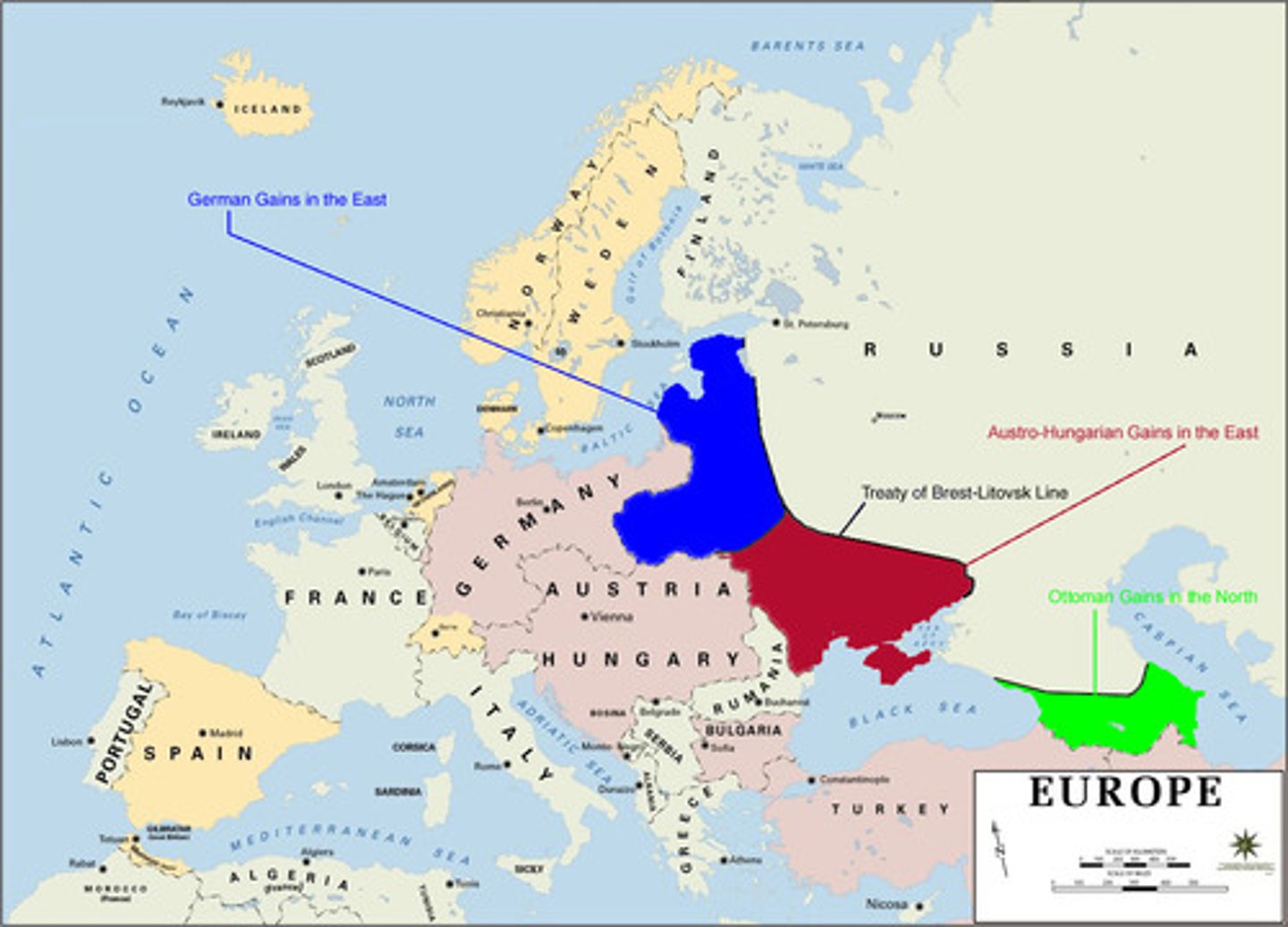
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
Treaty in which Russia lost substantial territory to the Germans. This ended Russian participation in the first world war (1918).
Treaty of Versailles
1919 treaty between the victorious Entente powers and defeated Germany at the end of World War I, which laid the blame for the war on Germany and exacted harsh reparations.

Triple Entente
Pre-World War I alliance of England, France, and Russia.

Twenty-One Demands
list of demands given to China by Japan in 1915 that would have made China a protectorate of Japan
Unrestricted Submarine Warfare
Germany's Policy of sinking ships with their U-boats, enemy or neutral, that carry war material

Verdun
A battle in WWI. Is considered some of the bloodiest fighting in WWI and the German offense was stopped; offensive battle on the western front initiated by Germany in which they hoped to crush France and taken them out of the war, however France was in a very good defensive position and French held it for 10 months. Nearly a million killed. French drew reserve troops from the Somme to help defend. No territory was gained; Battle in WWI that ended in massive casualties and had little direct result

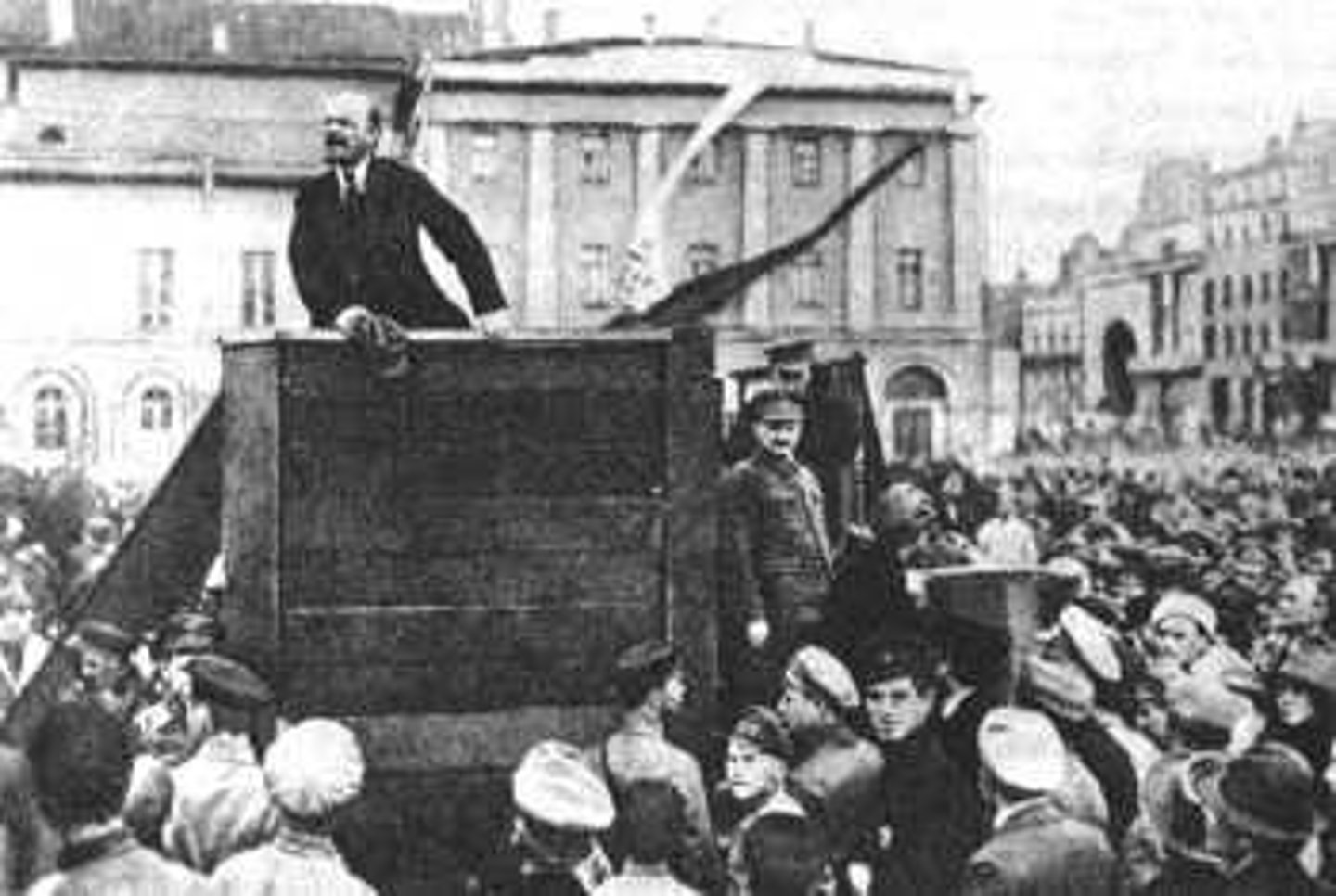
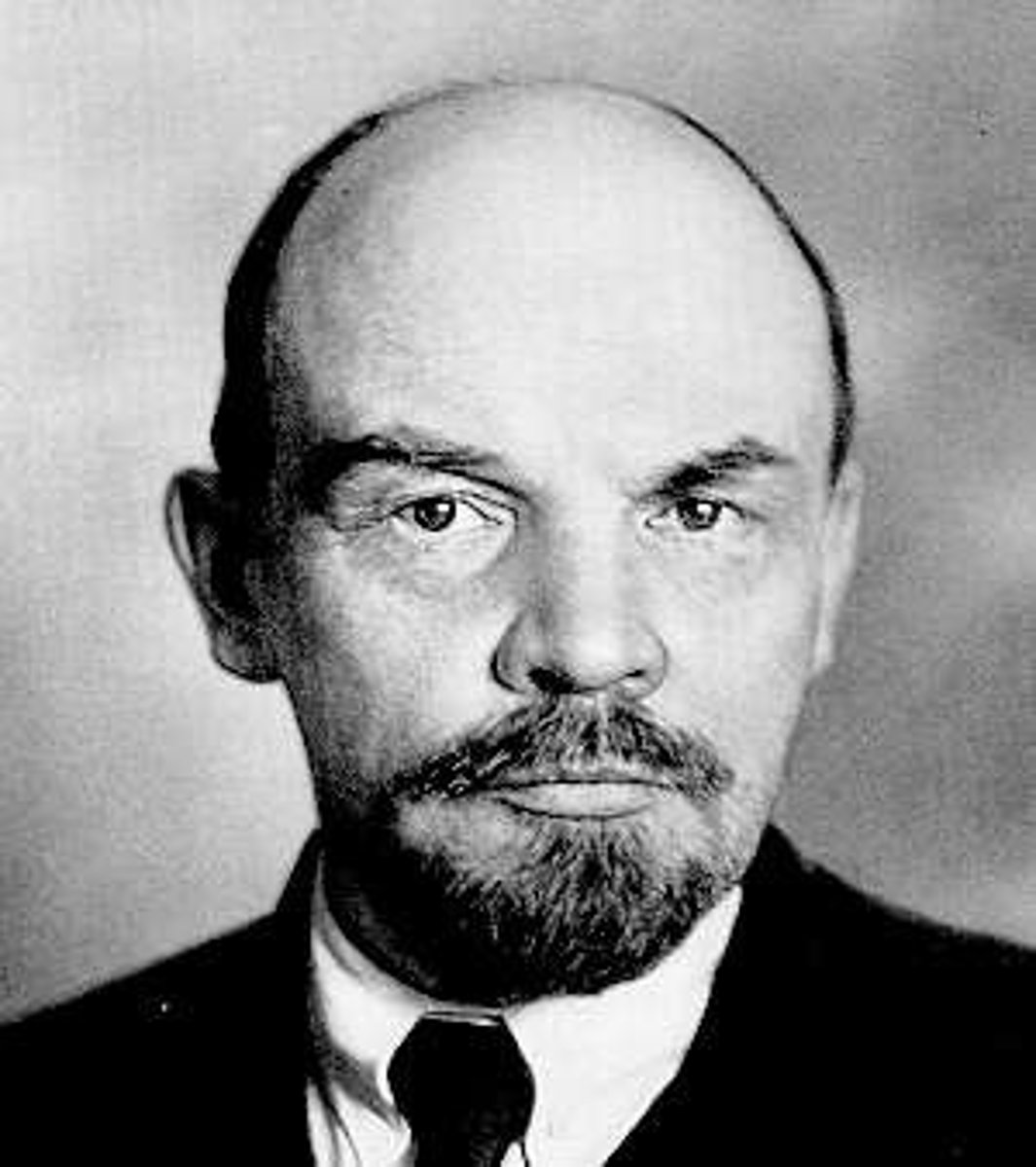
Vladimir Ilyich Lenin
1870-1954 C.E. Russian revolutionary and politician who led the Bolshevik Revolution in November 1917 and became the first head of state of the Soviet Union until his death.

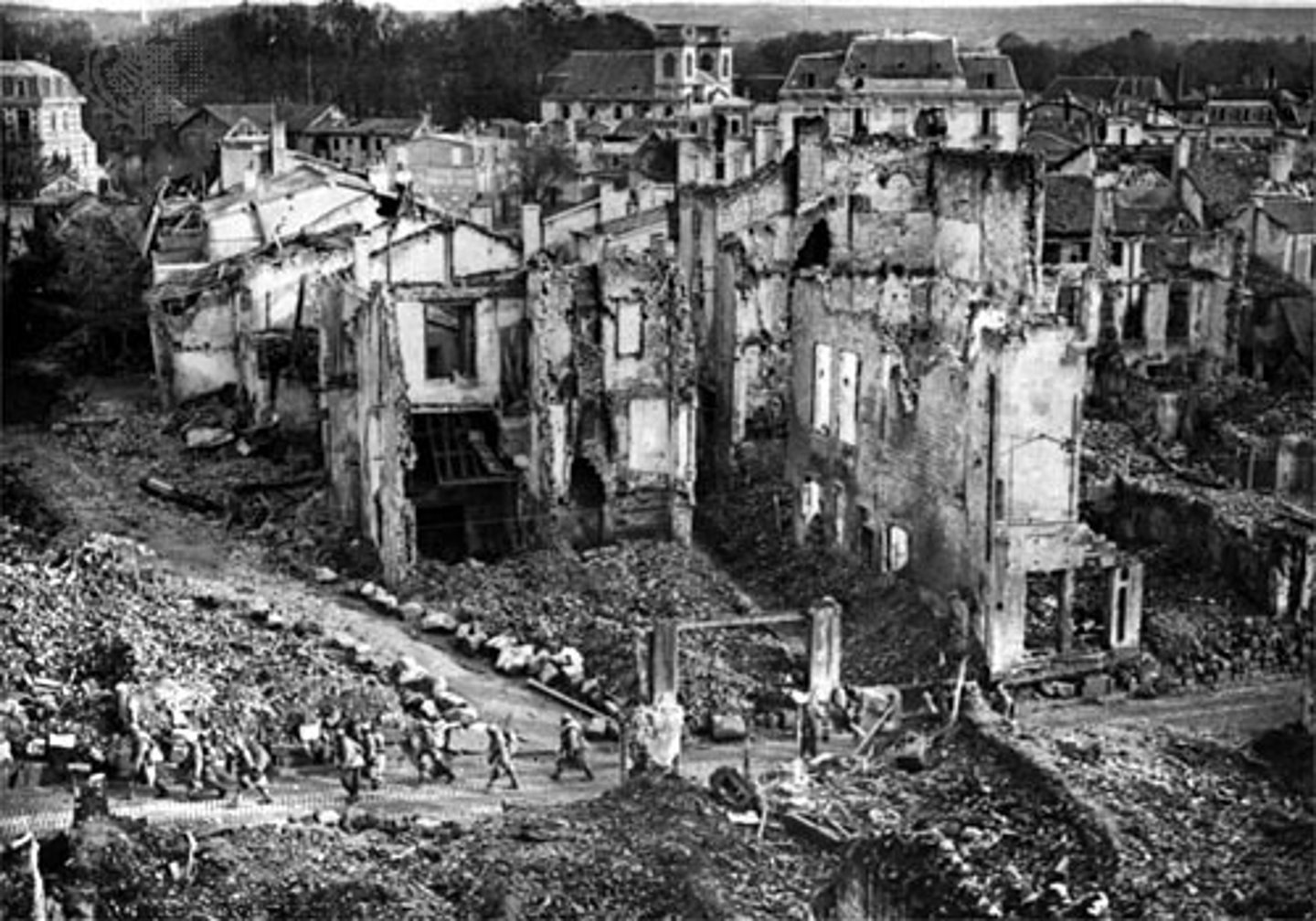
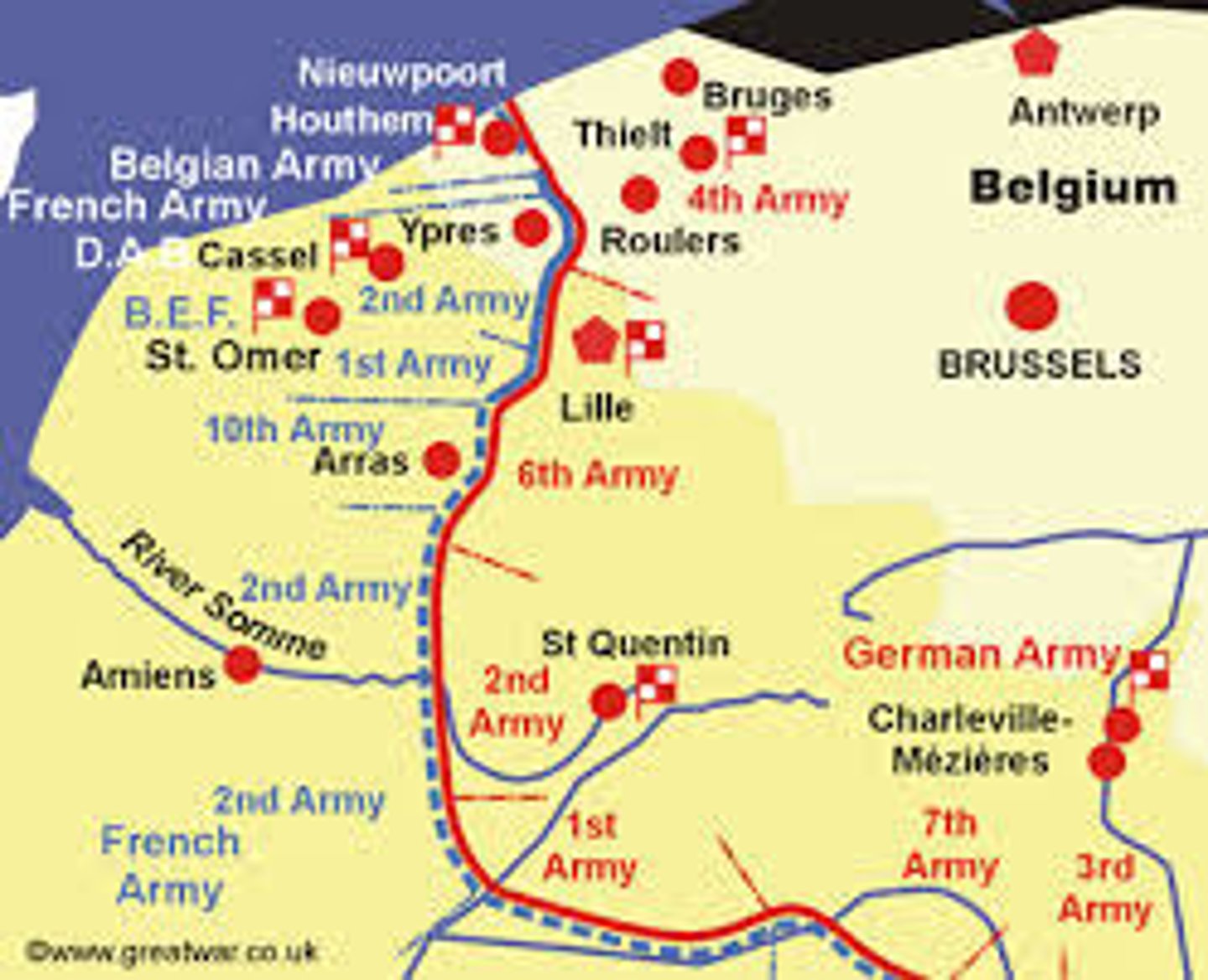
western front
A line of trenches and fortifications in World War I that stretched without a break from Switzerland to the North Sea. Scene of most of the fighting between Germany, on the one hand, and France and Britain, on the other.
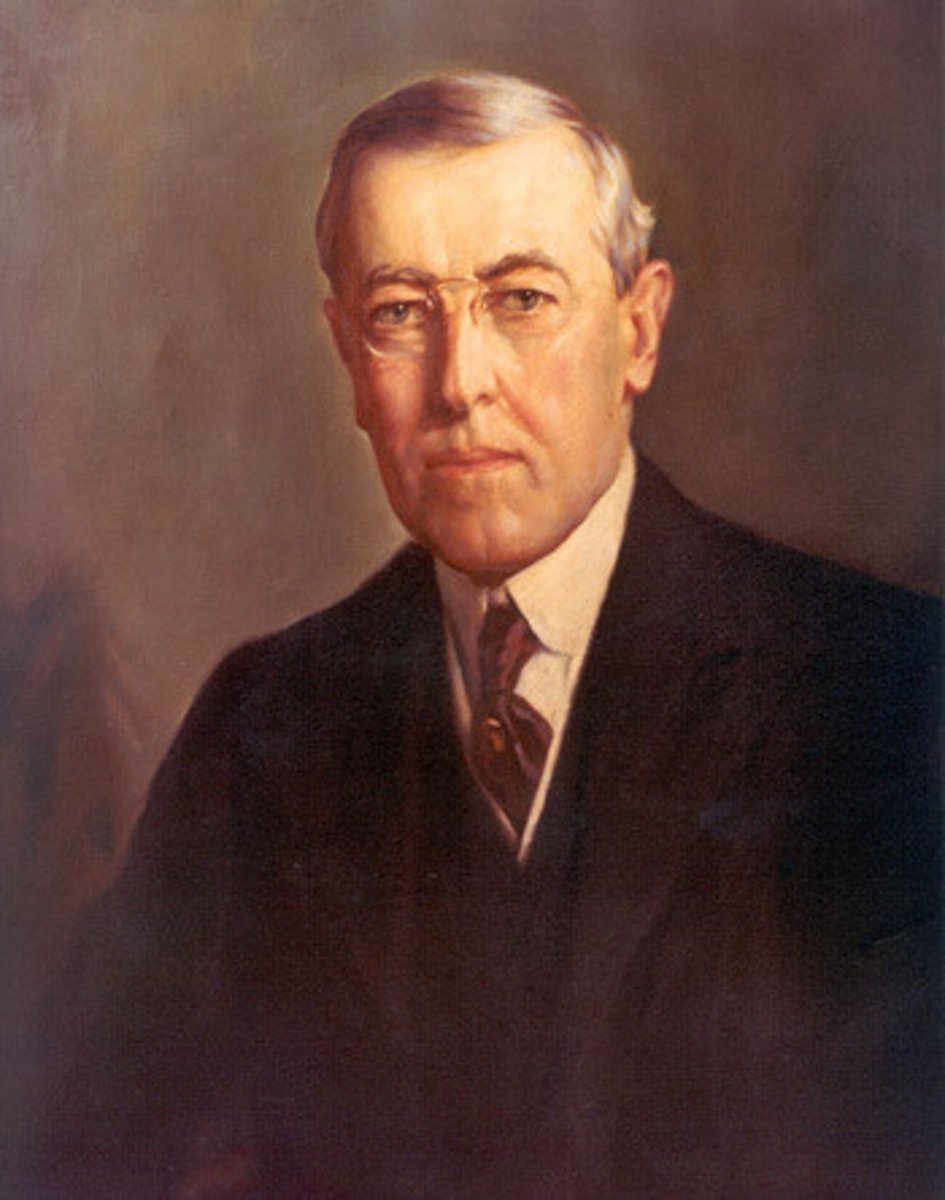
Woodrow Wilson
1856-1924. President of the United States during World War I and author of the "Fourteen Points," one of which envisioned the establishment of the League of Nations.

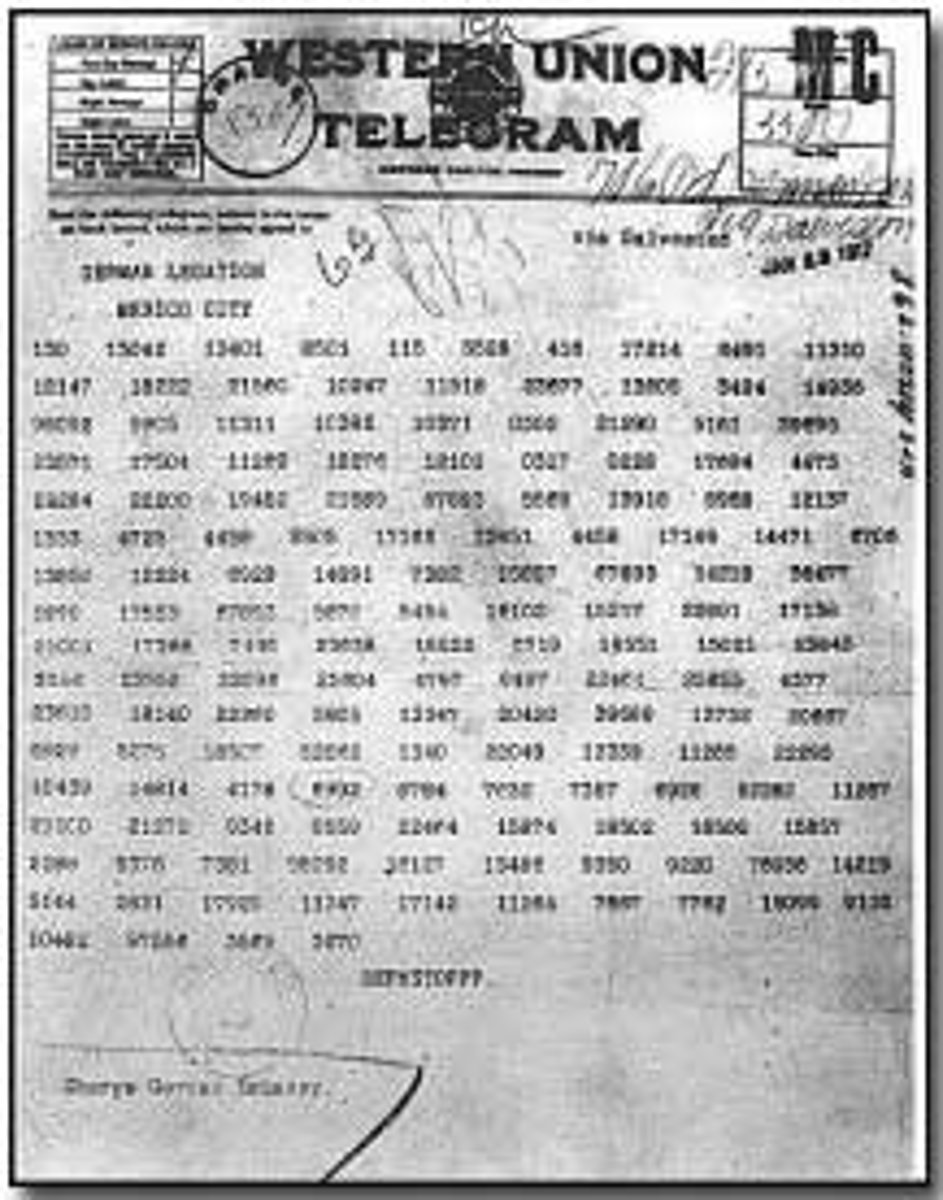
Zimmermann Telegram
January 1917 the British intercepted a telegram from the German government to the Mexican government offering German support if Mexico declared war against the US; offered to return land Mexico lost the US
Blitzkrieg
German style of rapid attack through the use of armor and air power that was used in Poland, Norway, Denmark, Belgium, the Netherlands, and France in 1939-1940.
