B3.1 Gas exchange
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
In which organisms is gas exchange an important function in?
All
What happens to the SA:V as the size of an organism increases?
SA:V decreases
Problem when organisms increase in size
SA:V decreases → distance from the centre of an organism to its exterior increases
So longer diffusion distance
Properties of gas-exchange surfaces (eg alveoli)
Thin tissue layer → reduces DD
Permeable to gases
Large SA:V
Moist → gases diffuse better (small, non-polar)
Diffusion
Passive net movement of particles from an area of high to low conc down a CG until dynamic equilibrium is reached
How to increase diffusion rate using CGs?
Steeper concentration gradient
Larger difference
CG in unicellular organisms
Consumes O2 during cell respiration
So O2 conc in cell is always low
How do exchange surfaces maintain a CG?
Dense networks of blood vessels
Continuous blood flow
Ventilation:
With air for lungs
With water for gills
How does a dense network of blood vessels maintain a CG?
Remove O₂ + deliver CO₂ efficiently
How does a continuous blood flow maintain a CG?
Maintains low O₂ + high CO₂ in tissues
Opposite in lungs/gills
How does ventilation maintain a CG?
Lungs: fresh air brings in O₂ + removes CO₂.
Gills: water brings in O₂ + carries away CO₂
Fish move O2 rich water thru gills
How do unicellular organisms gain substances eg oxygen?
Simple diffusion thru the plasma membrane
How do multicellular organisms gain substances eg oxygen?
Transport system delivers the substances to the cells via diffusion
Why can unicellular organisms only be a maximum size?
Takes too long for the substances to diffuse into the centre of the cells bc the distance from the exterior of the cell to the centre of the cell increases
What do larger organisms need for gas exchange- bc they can’t rely on simple diffusion?
Specialized gas exchange systems
Adaptations of mammal lungs for gas exchange (alveolar lungs)
Presence of surfactant
A branched network of bronchioles
Extensive capillary beds (rich blood supply to maintain CG)
High SA (alveoli)
Surfactant
Substance that reduces surface tension → prevents alveoli from collapsing
+ Provides moisture
What cells in the alveoli produce surfactant?
Type II pneumocytes
How do alveoli help with gas exchange?
Increase SA
How is a CG maintained for efficient gas exchange?
Capillaries (lots)→ moves blood w high O2 conc away, continuous blood flow
Ventillation
Inhale → increases CG of O2 betw alveoli + blood → diffuses into blood
Exhale → increases CG of CO2 betw alveoli + blood → CO2 diffuses out of blood + into alveolus
Movement of water thru gills → high O2 conc + low CO2 outside gills
Ventilation in mammals vs fish
Lungs → air movement maintains CG of O₂ + CO₂.
Gills → water flow maintains CG for dissolved gases
Respiration
Release of ATP energy from organic compounds (food)
What do capillaries provide?
A continuous supply of blood w low O2 conc + high CO2 conc to the alveoli
Gas exchange
Exchange of gases at cells + tissues thru diffusion
Moves O₂ into cells for respiration + CO₂ out as waste.
Occurs at the alveoli in the lungs + at respiring tissues
Ventilation
Movement of air in + out of the alveoli in the lungs
Facilitates gas exchange
Breathing
What does ventilation maintain CG of?
CG of O2 + CO2 betw air in alveoli + blood flowing in adjacent capillaries
2 stages of ventilation
Inspiration- breathing in
Expiration- breathing out
role of the diaphragm, intercostal muscles, abdominal muscles and ribs
What happens in inspiration?
Diaphragm, intercostal muscles, abdominal muscles, ribs
Diaphragm contracts (flattens) + moves downwards
External intercostal muscles contract → ribcage move up + out.
Thorax volume increases → decreases the pressure in the lungs
Air passively moves from the surrounding air (high pressure) into the lungs (low pressure)
Ab muscles relax
What happens in expiration?
Diaphragm, intercostal muscles, abdominal muscles, ribs
Ab muscles contract → push diaphragm upwards
External intercostal muscles relax, internal contract → ribcage move down + in.
Thorax volume decreases → increases the pressure in the lungs
High pressure in lungs moves air out of the lungs to surrounding air (lower pressure)
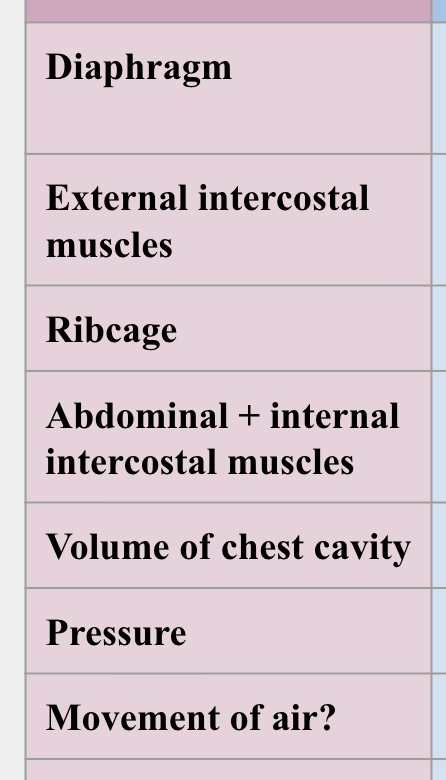
Inspiration vs expiration summary
What muscle pushes the diaphragm up?
Abdominal muscle- contract
What does the ribcage do?
Protect lungs
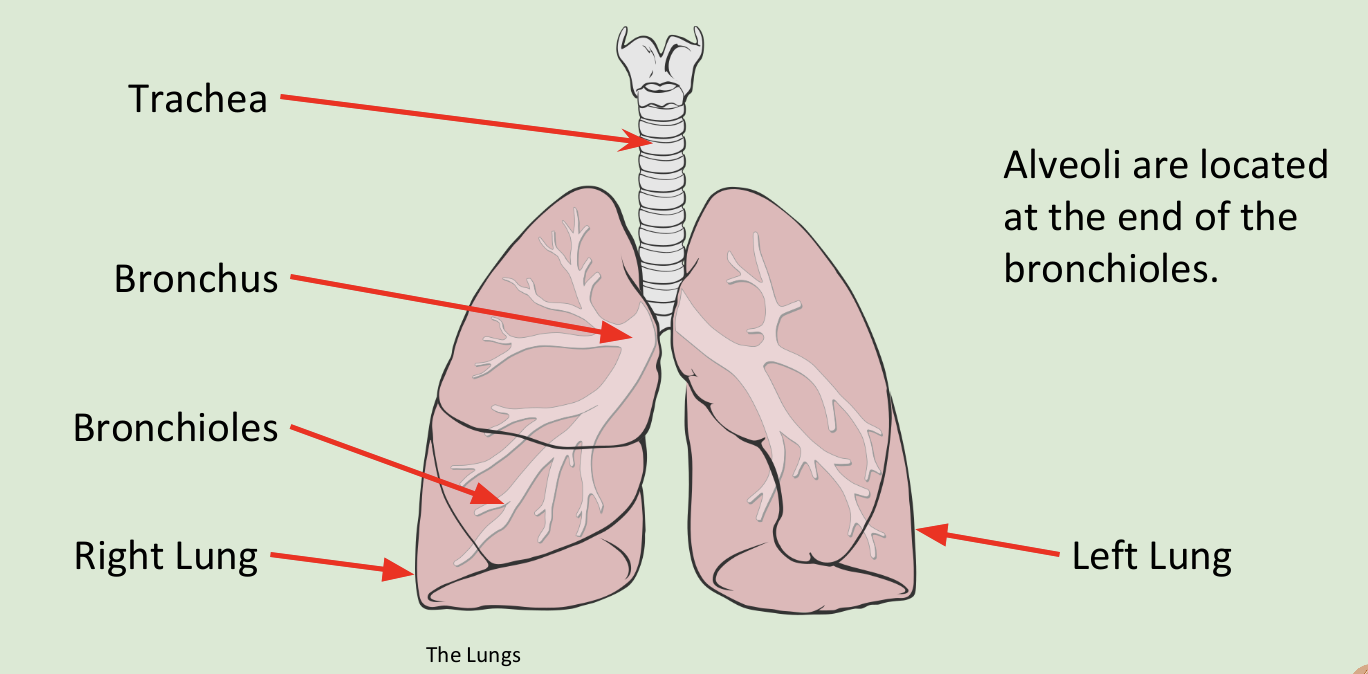
Ventilation rate
No of inhalations / exhalations per min
Tidal volume
Vol of air inhaled / exhaled in a normal breath
Inspiratory reserve volume
The additional vol of air that can be inhaled w maximum effort (after a normal breath)
Expiratory reserve volume
The additional vol of air that can be exhaled w maximum effort (after a normal breath)
Vital capacity
Max amt of air the lungs can hold
Max vol exhaled after max inhalation
Vital capacity equation
TV + IVR + EVR
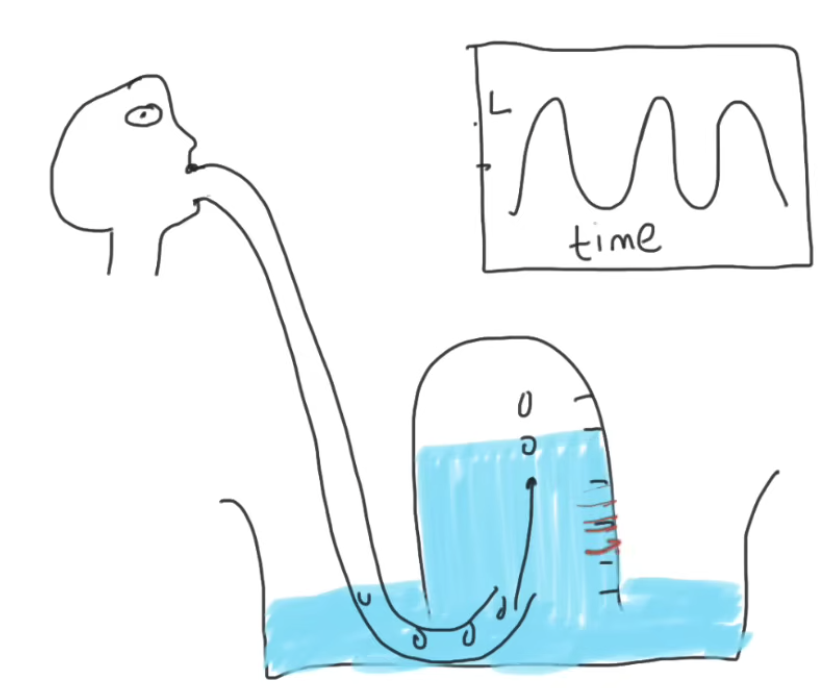
In a lab, what can be used to find vital capacity?
Balloons
Water displacement
Spirometer
Instruments used to measure air capacity of the lung
By inhaling + exhaling
Digital
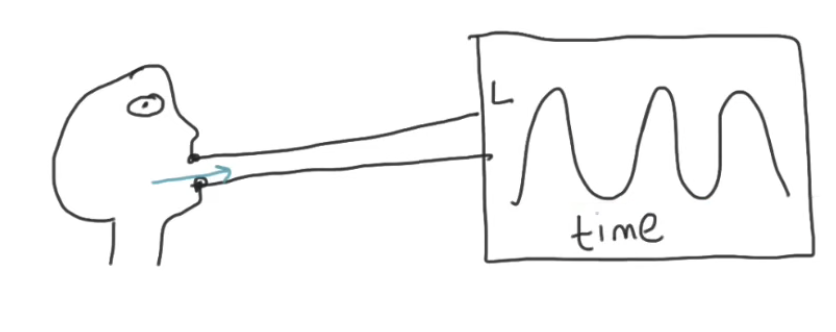
Pros of spirometers vs bell jars
Spirometer:
Works for inhalation + exhalation
Bell jar only works for exhalation
Digital
Bell jar prone to human error
Why is gas exchange important for respiration?
Aerobic respiration relies on O2
O2 taken into organisms by GE
Adaptations for gas exchange in leaves
Waxy cuticle
Epidermis
Air spaces
Spongy mesophyll
Stomatal guard cells
Veins
Explain the adaptations for gas exchange in leaves
Waxy cuticle
Epidermis
Air spaces
Spongy mesophyll
Stomatal guard cells
Veins
Waxy cuticle: reduces water loss
Epidermis: protective, transparent for light entry.
Air spaces (spongy mesophyll): allow diffusion of gases
Spongy mesophyll cells: moist → gas dissolves for diffusion.
Guard cells & stomata: regulate opening for gas exchange.
Veins (xylem + phloem): transport water for photosynthesis and sugars.
Stomata
Pores / openings for gas exchange + water loss
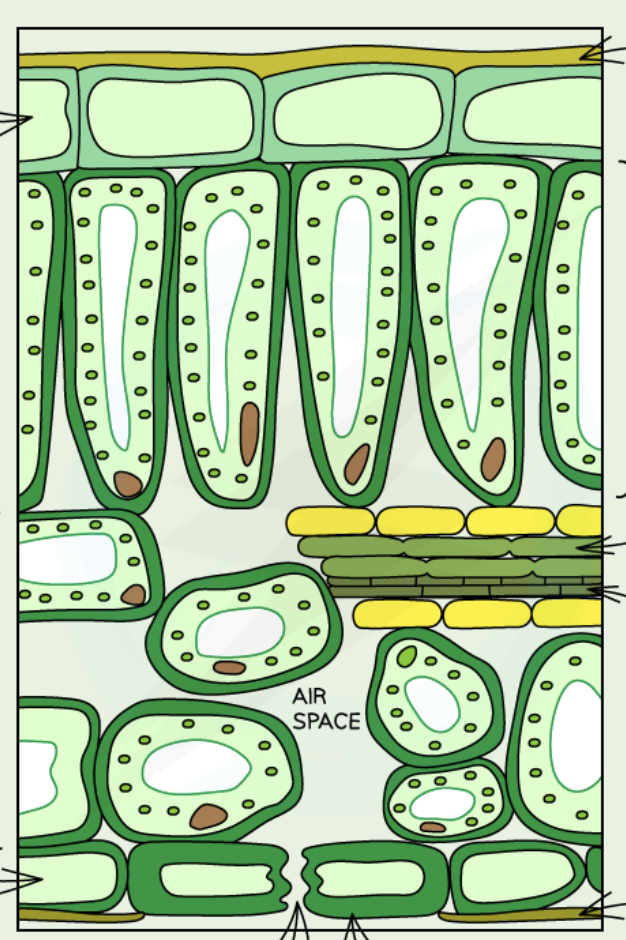
Label the tissues in a (dicotyledonous) leaf
Upper epidermis: protective, transparent.
Palisade mesophyll: many chloroplasts, photosynthesis.
Spongy mesophyll: gas exchange, some photosynthesis.
Lower epidermis: contains stomata + guard cells.
Veins (vascular bundles): xylem (water), phloem (sugars)
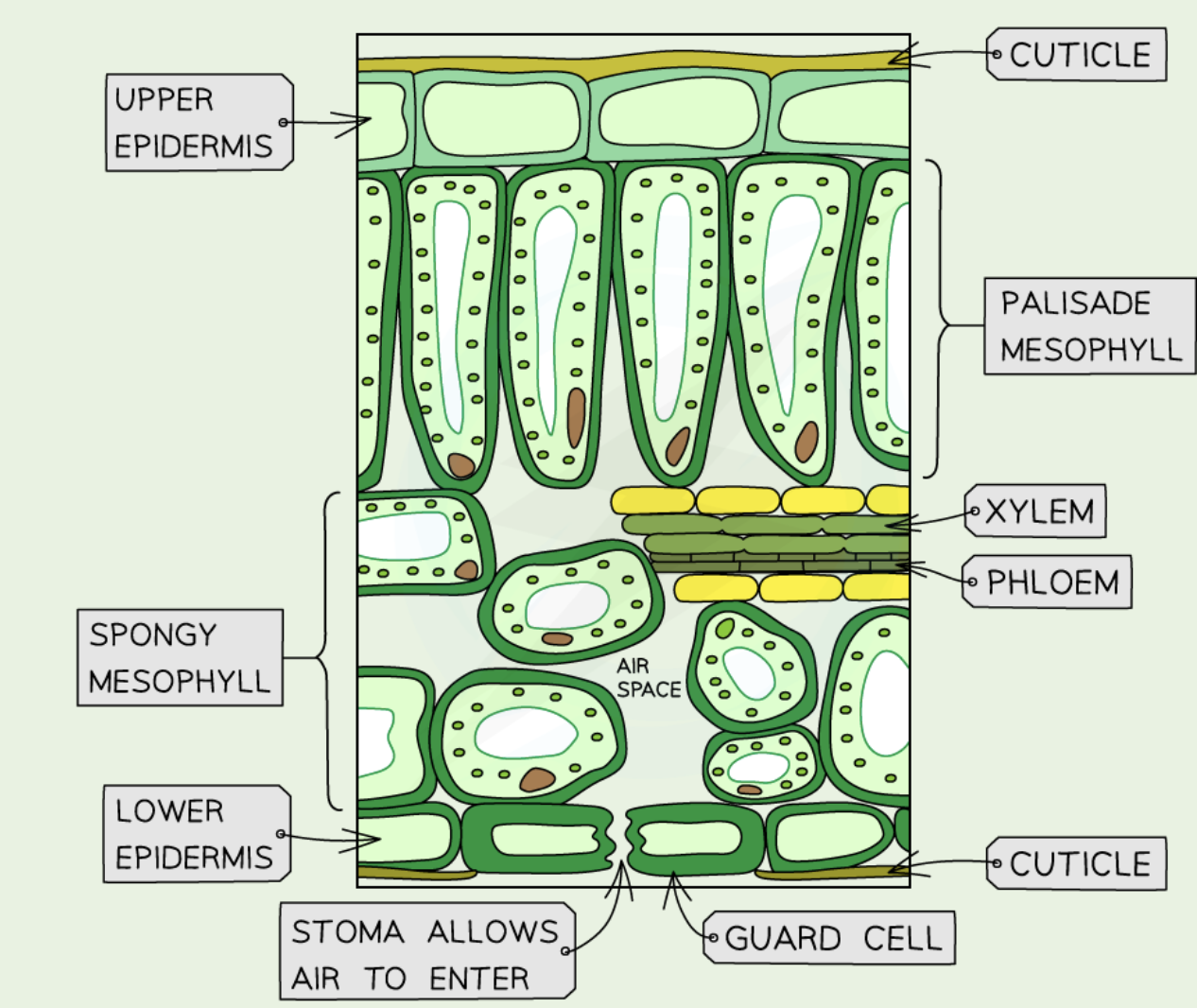
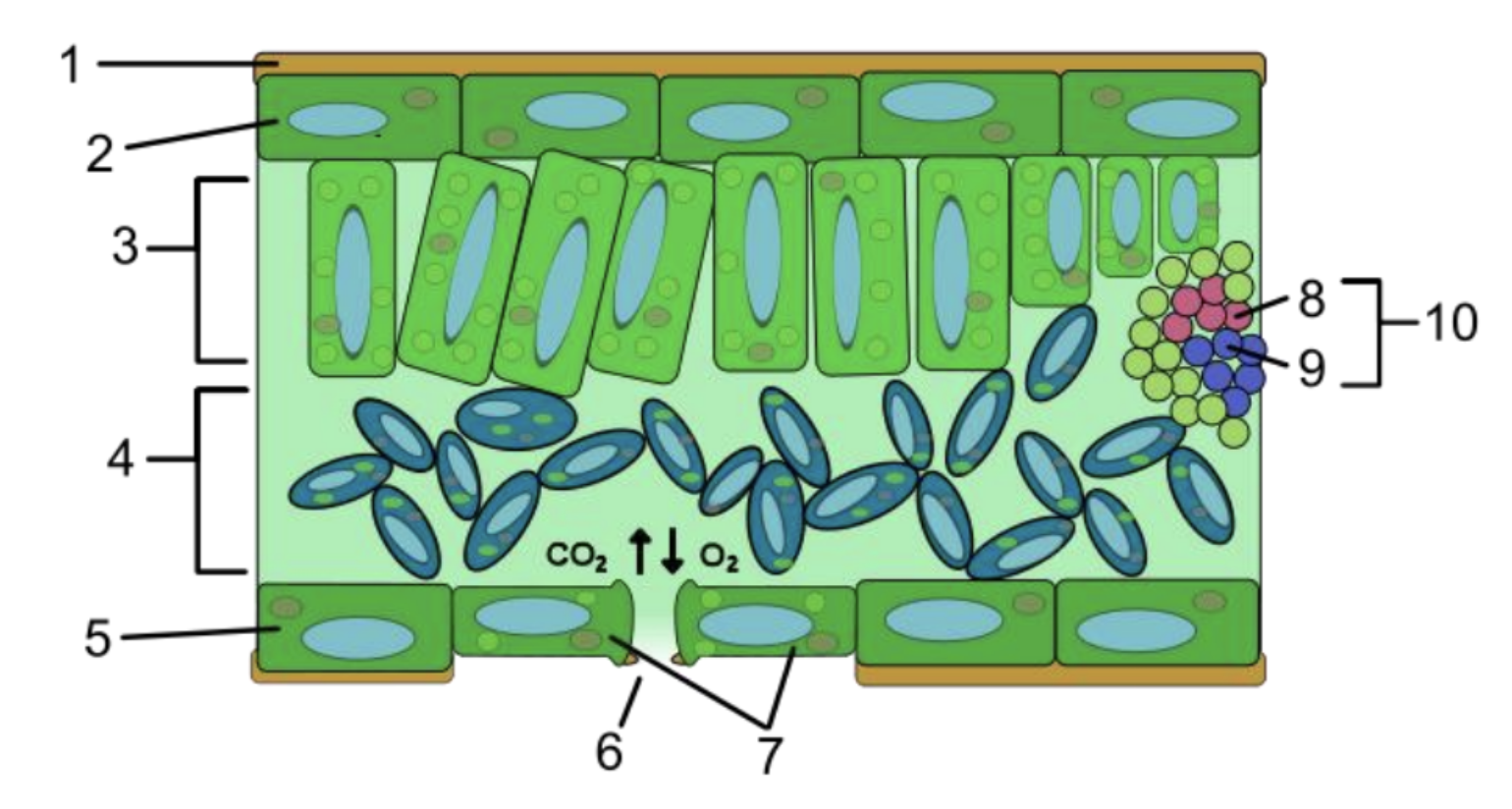
Name the parts of the leaf
find answer
What is transpiration a consequence of?
Gas exchange in a leaf
Bc stomata are open
Transpiration
Loss of water vapour from the leaves via the stomata
Transpiration stream
The continuous flow of water thru the xylem from the roots to the leaf, against gravity
Driven by the tension created by transpiration, cohesion of water molecules, and capillary action.
Water rises through xylem vessels bc of what 2 properties of water?
Cohesion
Adhesion
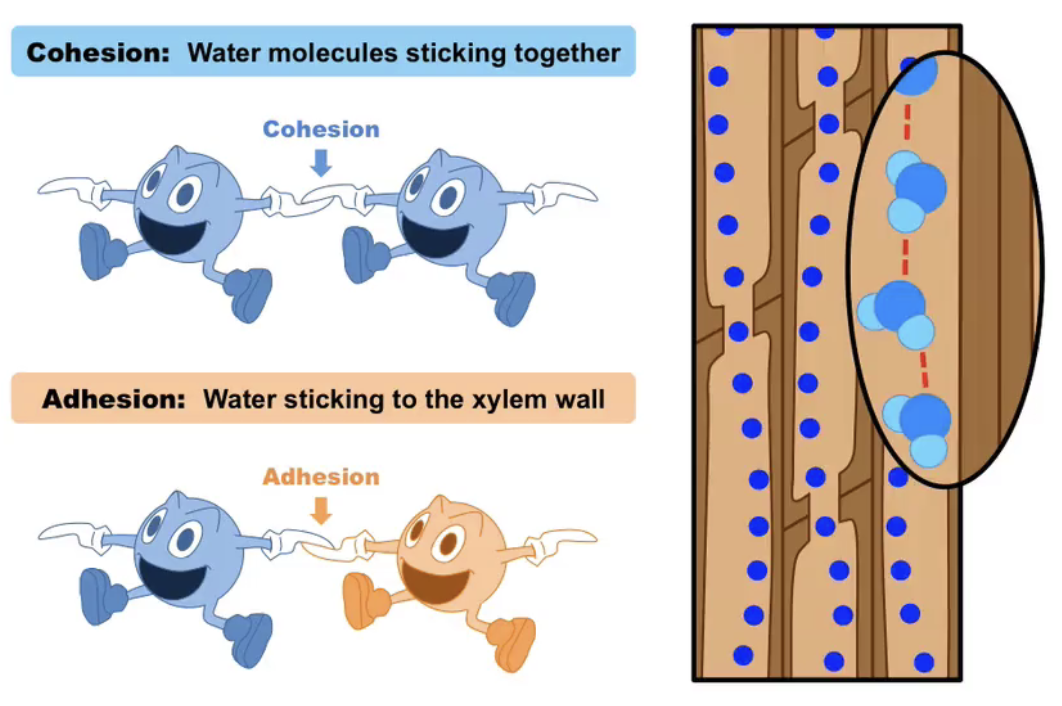
How does cohesion allow water to move up the xylem?
Cohesion provides an unbroken column of water in the xylem
Water molecules evaprate + diffuse → other water molecules move to replace them
Ceates tension in the xylem.
Due to the cohesive nature water is pulled upwards.
Role of adhesion in the transpiration stream
Adhesion betw water molecules creates tension in cell walls after water has evaporated from the leaf
Role of cohesion in the transpiration stream
Cohesion betw water molecules maintains the continuity of the water column in xylem.
Structure of xylem that makes it suitable for transport
Lignin
Provide strength → xylem doesn’t collapse
Perforated
Water can move in/out of xylem
Dead, hollow cells with no end walls
No organelles → water flow is unobstructed
Factors affecting rate of transpiration
Temperature
Humidity
Air movement
Light intensity
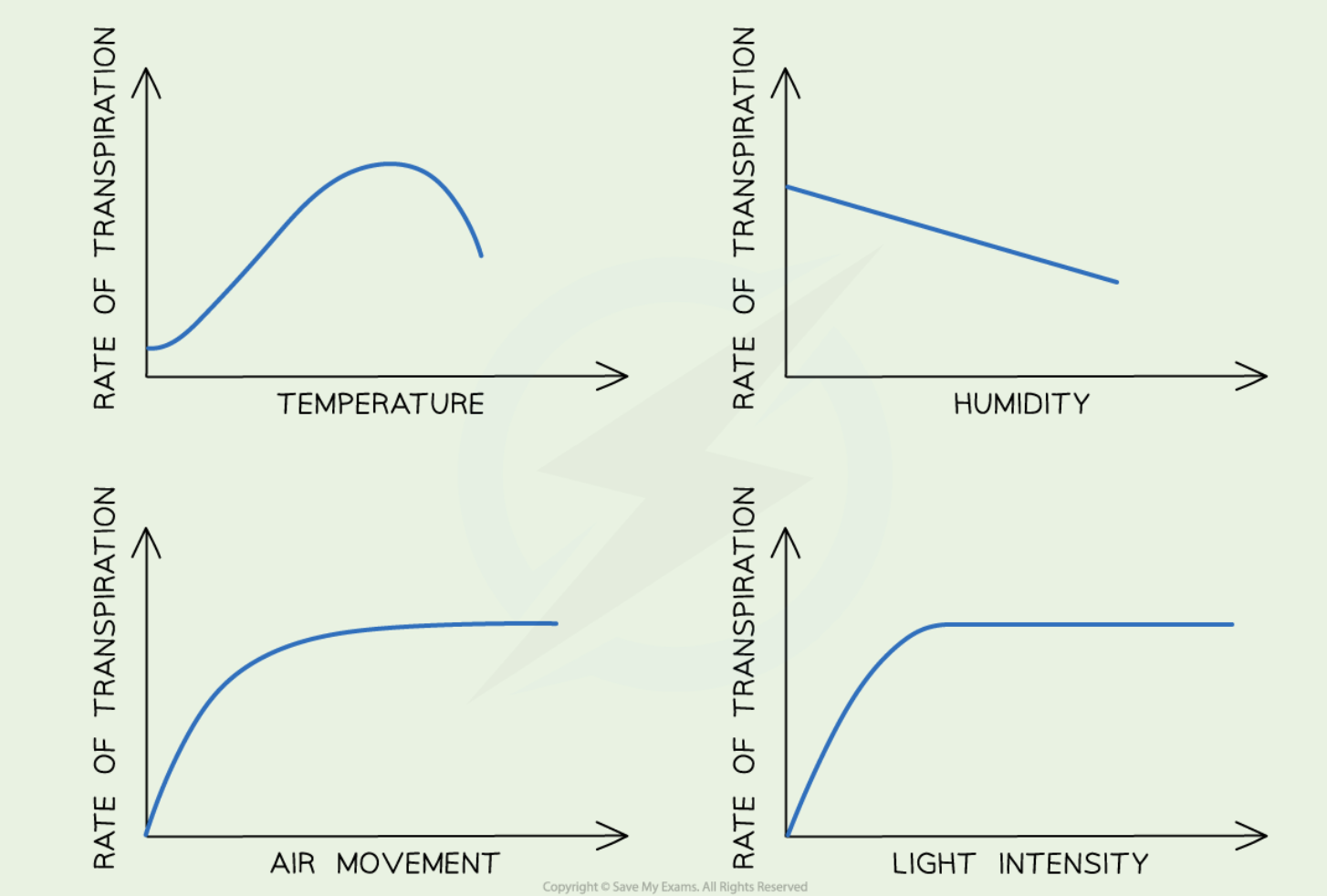
How do the following factors affect transpiration
Temperature
Humidity
Air movement
Light intensity
Higher temp = more
More evaporation
Higher humidity = less
Water conc outside is high → less CG
Higher air movement = more
Removes air → increases CG
Higher light intensity = more
More stomata open for PS (allow more CO2 in)
Why do stomata need to be open in the day?
For GE for PS
What controls the opening + closing of stomata?
Guard cells
Control water loss
What does a potometer measure?
Rate of transpiration
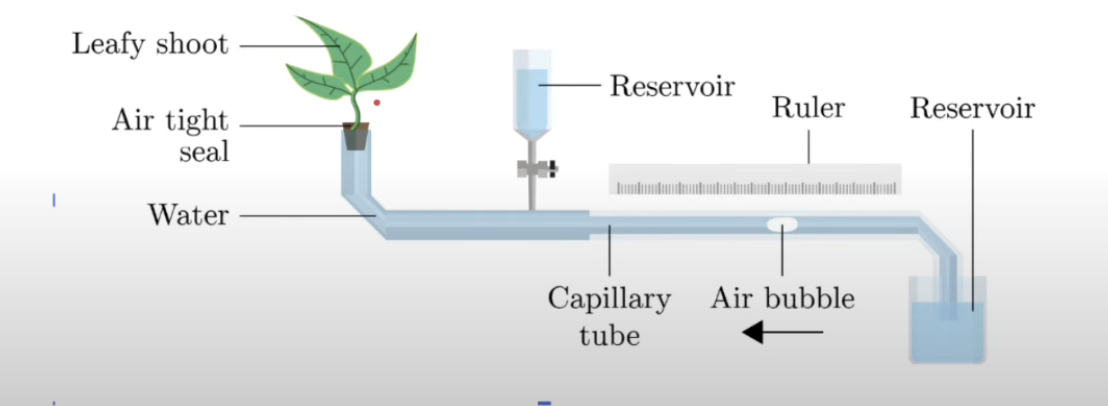
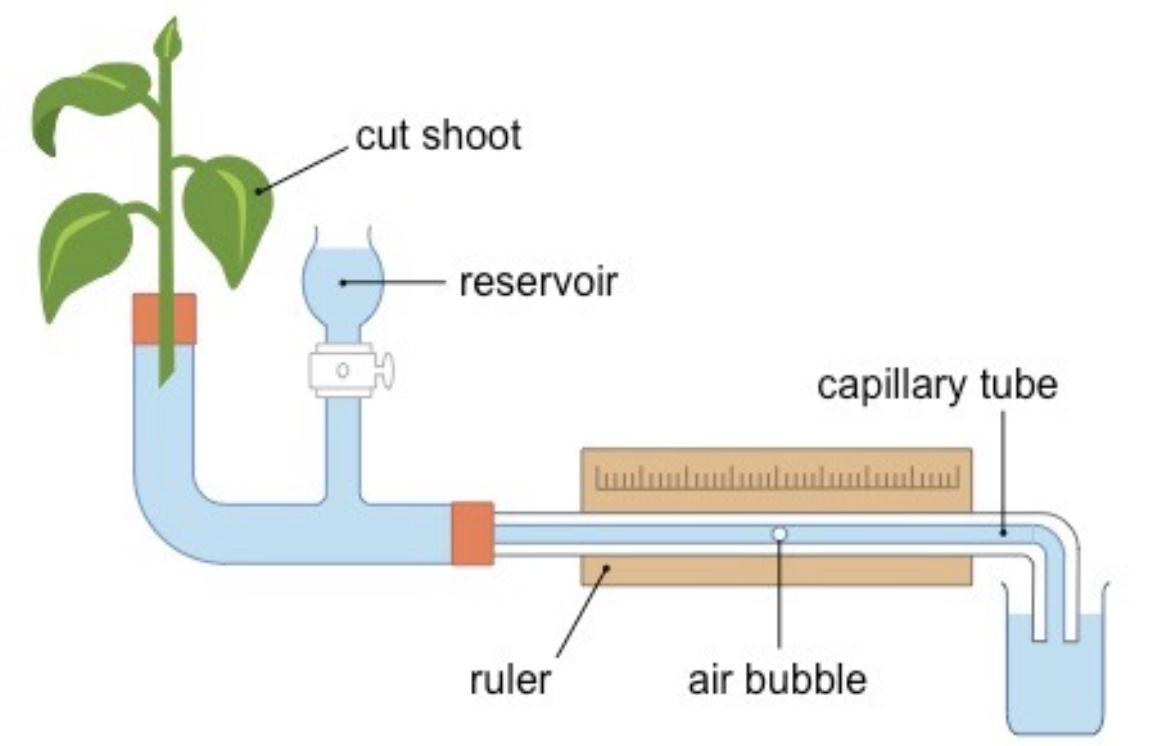
How to find transpiration rate using a potometer?
Measure distance moved by an air bubble every min (w ruler)
Indicates the rate of water uptake by the plant
Explain how a potometer works
Tube filled w water, connected to leaf (represents xylem)
Transpiration → water leaves plant thru leaf → pulls water up thru the tube
Air bubble is pulled along as well. Measure distance air bubble travelled
Multiply by SA of tube → to calc vol of water transpired
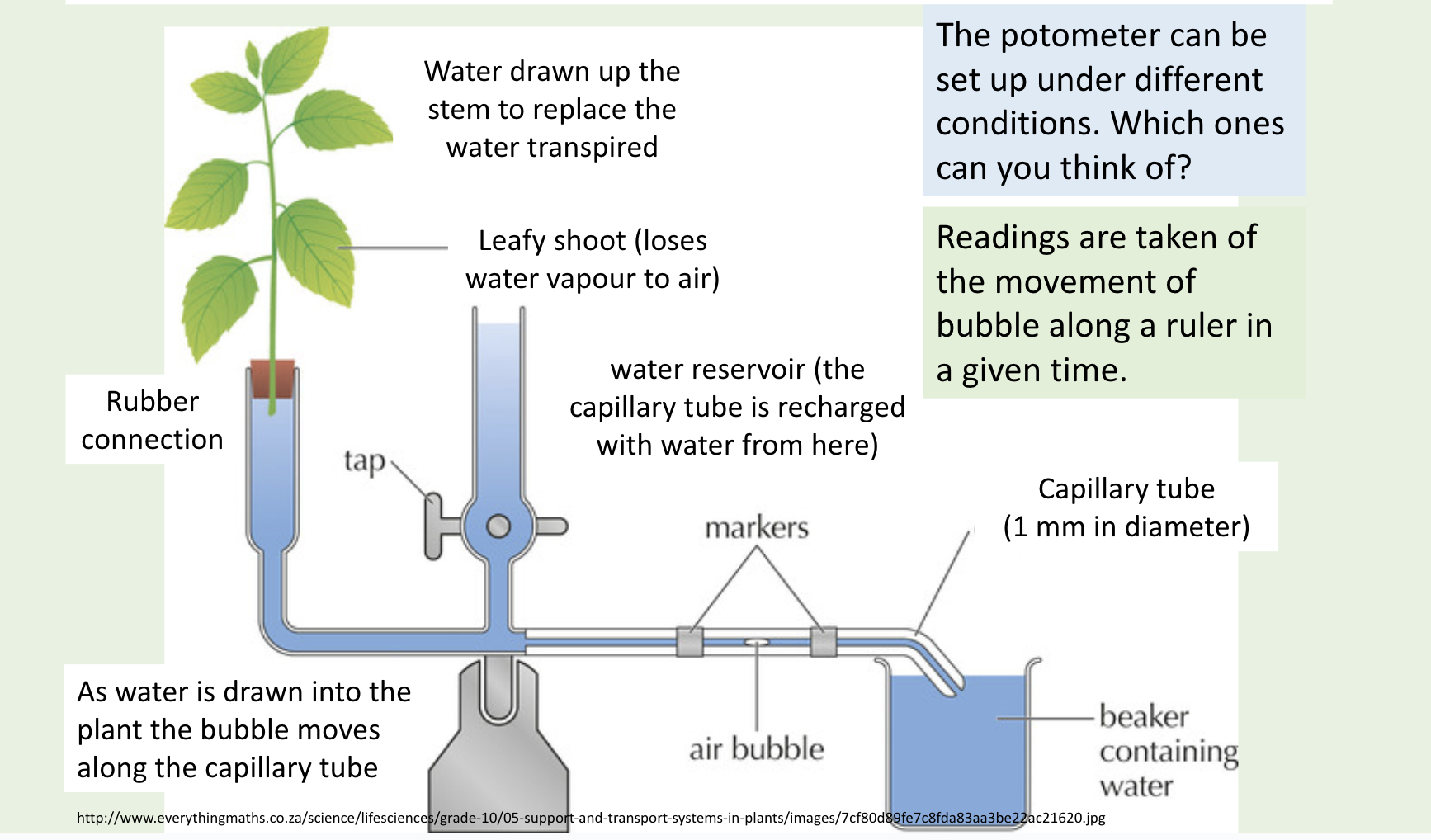
What do you need to do if you are doing another trial with a potometer?
Open reservoir of water
Pushes air bubble back
Precaution (not safety) when using a potometer
Don’t allow air to enter, cut shoot underwater
Ensures continuous column of water
Keep abiotic factor constant (eg LI)
Affects rate of transpiration
Keep screw clip closed
Prevents entry of water when measuring
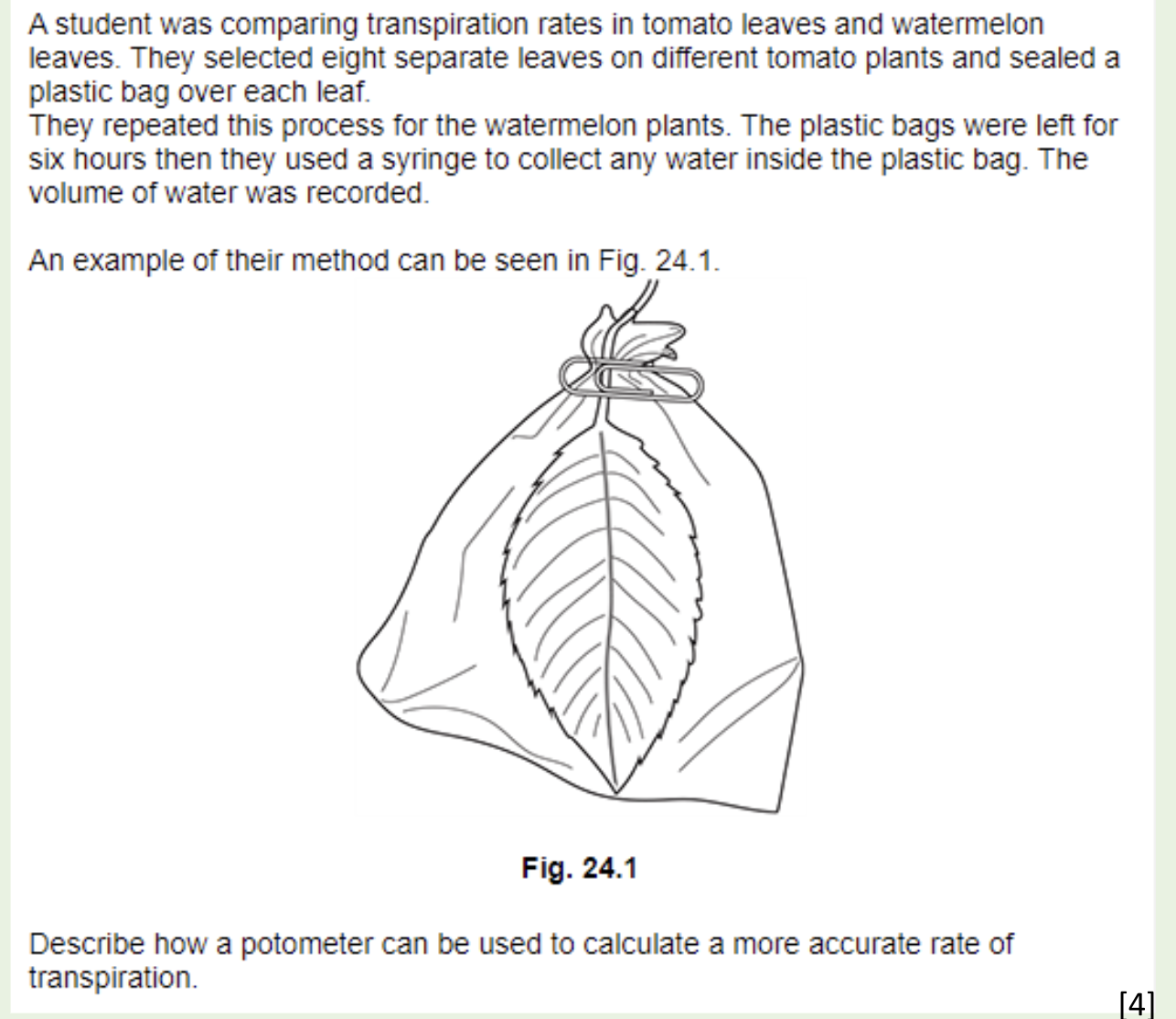
Potometer airtight
Dry leaves
Cut shoot under water / slanted
Measure distance air bubble travels per (named) time interval
OR
Measure time for air bubble to travel known distanceCalc volume of water uptake
Maintain (named) constant conditions
Stomatal density
No. of stomata per unit area of leaf surface
Eg per mm²
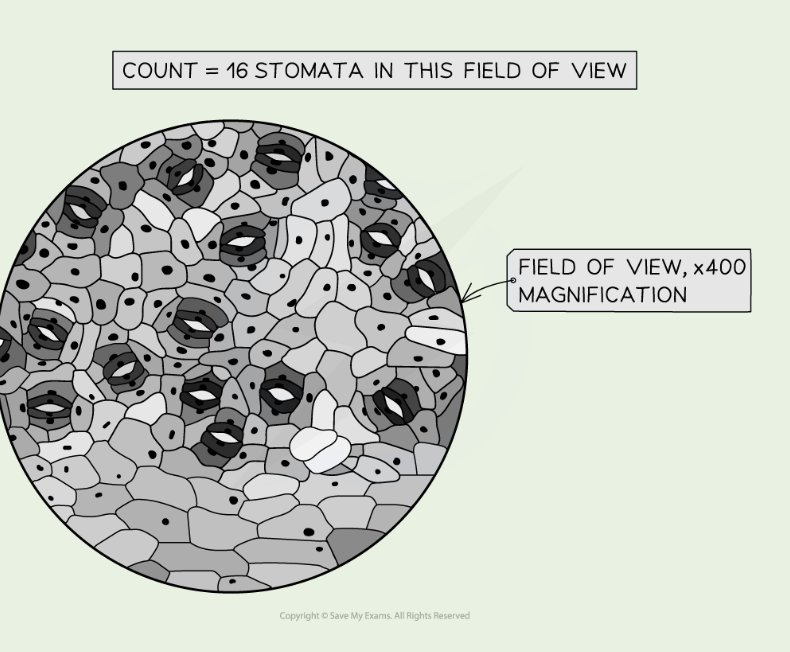
How to calc stomatal density
Use microscope to count no. of stomata in FoV
Calc radius of field of view
Calc area of field of view
Stomatal density = mean no. of stomata ÷ area of the FoV
How to increase reliability of quantitative data?
Repeat measurements
Reduces random errors
In relation to stomatal density, what shows that it is neccesary to replicate trials?
Repeated counts of the no. of stomata visible in diff FoV (at high power) show the variability of biological material
2 diff methods to calc stomatal density
Peel epidermis, mount on slide
Paint LE w clear nail polish → dry → peel to make a cast. Study under microscope
Cons of measuring stomatal density with the nail polish method
Some plant species don’t have easily accessible stomata. Won’t create strong imprint
Solvent-based nail polish can destroy some of the cell structure
Water-based nail polish safer but dries slower
Compare stomatal density betw?
Diff species of plants
Same species grown in diff conditions