All practice exam
1.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/295
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:16 AM on 6/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
296 Terms
1
New cards
True-false.
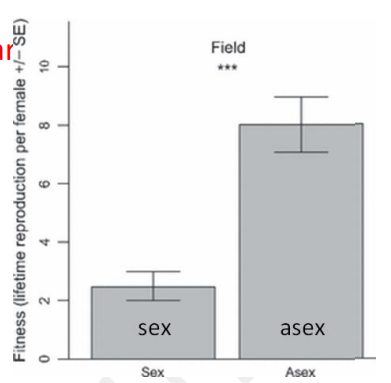
According to the bar graph on the right, facultatively sexual rotifers have fewer offspring when they have sex than when they don’t.
According to the bar graph on the right, facultatively sexual rotifers have fewer offspring when they have sex than when they don’t.
True
2
New cards
True-false.
According to the definition discussed in class, when a bacterium transfers a single gene to another bacterium, that is sex.
According to the definition discussed in class, when a bacterium transfers a single gene to another bacterium, that is sex.
False
3
New cards
True-false.
Habitat fragmentation makes it easier for populations to move to new suitable habitats as the climate changes.
Habitat fragmentation makes it easier for populations to move to new suitable habitats as the climate changes.
False
4
New cards
True-false.
\[See the diagram on the right\] Your coefficient of relatedness (r) to your half-uncle (i.e. whose father is not your grandfather) would be 0.5 x 0.5 x 0.5 = 0.125
\[See the diagram on the right\] Your coefficient of relatedness (r) to your half-uncle (i.e. whose father is not your grandfather) would be 0.5 x 0.5 x 0.5 = 0.125
True
5
New cards
True-false.
With inclusive fitness, individuals can gain fitness by behaving altruistically towards non-relatives.
With inclusive fitness, individuals can gain fitness by behaving altruistically towards non-relatives.
False
6
New cards
True-false.
In eusocial species, most of the individuals reproduce
In eusocial species, most of the individuals reproduce
False
7
New cards
True-false.
When a population far overshoots its carrying capacity, the carrying capacity increases.
When a population far overshoots its carrying capacity, the carrying capacity increases.
False
8
New cards
True-false.
Human subpopulations show evidence of geographic structure.
Human subpopulations show evidence of geographic structure.
True
9
New cards
True-false.
A species range (such as is shown for Ficus sycomorus on the right) is made up entirely of suitable habitat for the species.
A species range (such as is shown for Ficus sycomorus on the right) is made up entirely of suitable habitat for the species.
False
10
New cards
True-false.
In discrete population growth, breeding takes place at a certain season of the year, not all the time.
In discrete population growth, breeding takes place at a certain season of the year, not all the time.
True
11
New cards
True-false.
Compared to stable populations, unstable populations tend to have lower growth rates.
Compared to stable populations, unstable populations tend to have lower growth rates.
False
12
New cards
True-false.
According to the Red Queen hypothesis, sex might have evolved because of parasites and disease.
According to the Red Queen hypothesis, sex might have evolved because of parasites and disease.
True
13
New cards
True-false.
According to the studies discussed in class, a zebra’s bold stripes are adaptive because they disrupt a lion’s search image for prey.
According to the studies discussed in class, a zebra’s bold stripes are adaptive because they disrupt a lion’s search image for prey.
False
14
New cards
True-false.
An r-selected life history maximizes the population growth rate, r.
An r-selected life history maximizes the population growth rate, r.
True
15
New cards
True-false.
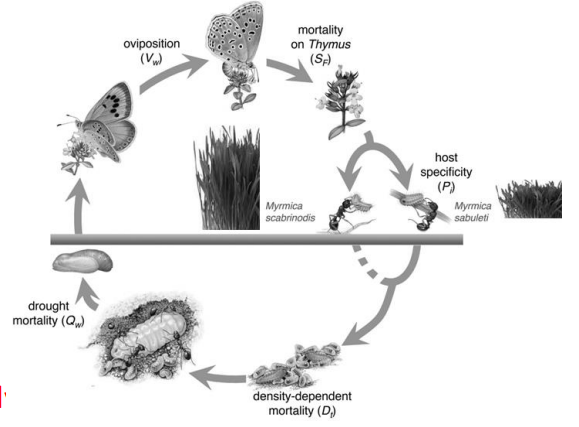
When livestock are excluded from habitat patches and the grass grows tall, European Large Blue butterflies usually cannot complete their life cycle (on the right).
When livestock are excluded from habitat patches and the grass grows tall, European Large Blue butterflies usually cannot complete their life cycle (on the right).
True
16
New cards
True-false.
According to the articles on the “hive mind” that you were invited to read, the way a honeybee colony makes decisions is similar to the way neurons in our brain interact to make decisions.
According to the articles on the “hive mind” that you were invited to read, the way a honeybee colony makes decisions is similar to the way neurons in our brain interact to make decisions.
True
17
New cards
True-false.
According to ecologists, the human population does not have a carrying capacity.
According to ecologists, the human population does not have a carrying capacity.
False
18
New cards
True-false.
According to the articles you were invited to read, evidence for the advantage of life history evolution in humans to extend the post-reproductive lifespan includes that hunter-gatherer grandmothers helped provide more meat to their grandchildren, and that grandfathers contributed substantially to the care of their grandchildren.
According to the articles you were invited to read, evidence for the advantage of life history evolution in humans to extend the post-reproductive lifespan includes that hunter-gatherer grandmothers helped provide more meat to their grandchildren, and that grandfathers contributed substantially to the care of their grandchildren.
False
19
New cards
True-false.
Competition between two species of microbe growing together (compared to each growing separately) results in reduction of the population of only the poorer competitor.
Competition between two species of microbe growing together (compared to each growing separately) results in reduction of the population of only the poorer competitor.
False
20
New cards
Questions (20-23). Choose the letter (A-E) of the interaction below that best matches each description. Each letter may be used only once.
A. Mutualism B. Predation/herbivory C. Parasitism D. Competition E. Commensalism
A paloverde tree shades a young saguaro cactus, thus allowing it to establish. There is enough water for both tree and cactus at this point, so the cactus does not affect the tree.
A. Mutualism B. Predation/herbivory C. Parasitism D. Competition E. Commensalism
A paloverde tree shades a young saguaro cactus, thus allowing it to establish. There is enough water for both tree and cactus at this point, so the cactus does not affect the tree.
E
21
New cards
Questions (20-23). Choose the letter (A-E) of the interaction below that best matches each description. Each letter may be used only once. A. Mutualism B. Predation/herbivory C. Parasitism D. Competition E. Commensalism
Deer eat the acorns of oaks, but the deer don’t disperse or bury any of the acorns.
Deer eat the acorns of oaks, but the deer don’t disperse or bury any of the acorns.
B
22
New cards
Questions (20-23). Choose the letter (A-E) of the interaction below that best matches each description. Each letter may be used only once. A. Mutualism B. Predation/herbivory C. Parasitism D. Competition E. Commensalism
A female fly pollinates a Stapelia flower, which smells like a dead animal, and lays its eggs on the flower. There is nothing for the young maggots to eat, however.
A female fly pollinates a Stapelia flower, which smells like a dead animal, and lays its eggs on the flower. There is nothing for the young maggots to eat, however.
C
23
New cards
Questions (20-23). Choose the letter (A-E) of the interaction below that best matches each description. Each letter may be used only once. A. Mutualism B. Predation/herbivory C. Parasitism D. Competition E. Commensalism
Bromeliads (tank plants) growing on branches of a rainforest tree collect falling dead leaves and dead insects in a central “cup.” The leaves and bugs decompose, releasing nitrogen. When it rains, some of the N splashes down to the roots of the tree and is used by the tree.
Bromeliads (tank plants) growing on branches of a rainforest tree collect falling dead leaves and dead insects in a central “cup.” The leaves and bugs decompose, releasing nitrogen. When it rains, some of the N splashes down to the roots of the tree and is used by the tree.
A
24
New cards
Questions (24-27). Choose the letter (A-E) of the term below that best matches each description. Each letter may be used only once. A. Allelopathy B. Niche partitioning C. Competitive exclusion D. Sexual selection E. Zonation
A male bowerbird creates a more elaborate display then his male neighbor, and a female arrives and mates with him but not the neighbor.
A male bowerbird creates a more elaborate display then his male neighbor, and a female arrives and mates with him but not the neighbor.
D
25
New cards
Questions (24-27). Choose the letter (A-E) of the term below that best matches each description. Each letter may be used only once. A. Allelopathy B. Niche partitioning C. Competitive exclusion D. Sexual selection E. Zonation
Sparrows do better than cardinals in suburbs, but cardinals do better than sparrows in the forest
Sparrows do better than cardinals in suburbs, but cardinals do better than sparrows in the forest
B
26
New cards
Questions (24-27). Choose the letter (A-E) of the term below that best matches each description. Each letter may be used only once. A. Allelopathy B. Niche partitioning C. Competitive exclusion D. Sexual selection E. Zonation
Decomposing Eucalyptus leaves prevent seeds of other tree species from growing.
Decomposing Eucalyptus leaves prevent seeds of other tree species from growing.
A
27
New cards
Questions (24-27). Choose the letter (A-E) of the term below that best matches each description. Each letter may be used only once. A. Allelopathy B. Niche partitioning C. Competitive exclusion D. Sexual selection E. Zonation
On the South FL coast, red mangroves grow closest to the ocean (in salt water), with black mangroves farther inland, and buttonwoods the farthest inland (in mostly fresh water).
On the South FL coast, red mangroves grow closest to the ocean (in salt water), with black mangroves farther inland, and buttonwoods the farthest inland (in mostly fresh water).
E
28
New cards
A male spider offering food to a potential mate supports which hypothesis for sexual selection?
A. Material benefits B. Good genes C. Good health D. Runaway A. Averageness
A. Material benefits B. Good genes C. Good health D. Runaway A. Averageness
A
29
New cards
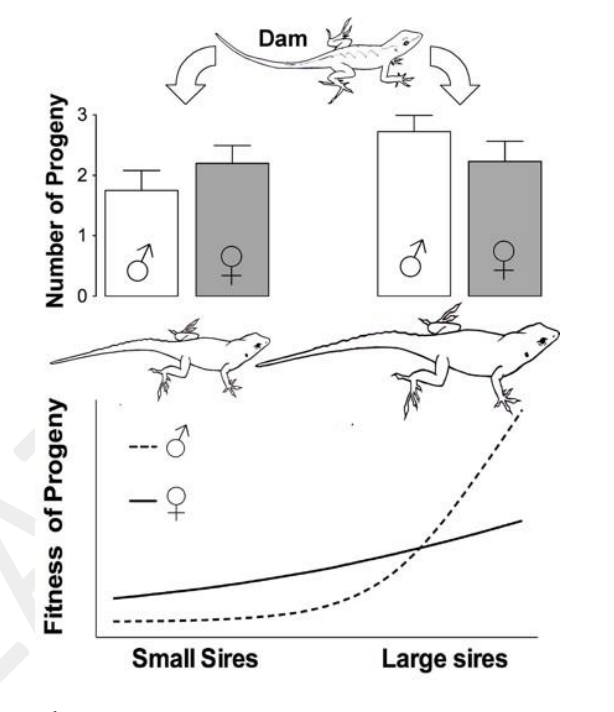
Similar to red deer, female anole lizards can adjust the sex ratio of their developing offspring. According to the figure on the right, when a female brown anole (dam) chooses a small mate (sire), the overall fitness of her offspring (progeny) is _____, and she adjusts the sex ratio of her brood to be ______ biased.
A. lowest; male B. lowest; female C. highest; male D. highest; female E. highest; un-
A. lowest; male B. lowest; female C. highest; male D. highest; female E. highest; un-
B
30
New cards
A plant that has separate male and female flowers on the same plant is
A. Asexual B. Dioecious C. Hermaphroditic D. Monoecious
A. Asexual B. Dioecious C. Hermaphroditic D. Monoecious
D
31
New cards
In tortoises, each female mates with several males, and so a clutch of eggs laid by a female has several fathers. This mating system is
A. Promiscuity B. Polygyny C. Polyandry D. Monogamy E. Sexual conflict
A. Promiscuity B. Polygyny C. Polyandry D. Monogamy E. Sexual conflict
C
32
New cards
In the “Body invaders” video we watched in class, a caterpillar with wasp parasitoids
A. Is able to complete its life cycle and become a moth
B. Dies immediately when the parasitoids emerge
C. Lives after the parasitoids emerge and then protects them
D. Is lured and eaten by the “femme fatale” firefly
E. Has mutualistic bacteria that can kill the parasitoids
A. Is able to complete its life cycle and become a moth
B. Dies immediately when the parasitoids emerge
C. Lives after the parasitoids emerge and then protects them
D. Is lured and eaten by the “femme fatale” firefly
E. Has mutualistic bacteria that can kill the parasitoids
C
33
New cards
Sexual dimorphism with the male much bigger than the female is most likely associated with
A. Male competition for mates
B. Flight, as in birds
C. Sexual parasitism by males
D. Higher female investment in reproduction
E. Higher male investment in reproduction
A. Male competition for mates
B. Flight, as in birds
C. Sexual parasitism by males
D. Higher female investment in reproduction
E. Higher male investment in reproduction
A
34
New cards
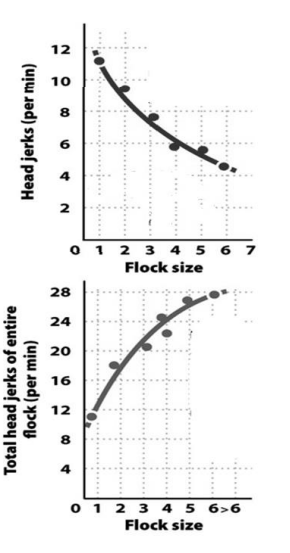
In the European goldfinch results on the right, decreasing flock size means ______ time spent on defense by each bird, and _____ effective defense for the group as a whole.
A. Less; less
B. Less; more
C. More; less
D. More; more
A. Less; less
B. Less; more
C. More; less
D. More; more
C
35
New cards
A tree population shows a clustered (clumped) dispersion pattern. This would most likely result from
A. Adaptation to a wide variety of soil types
B. Strong preference for riparian habitat
C. Intense competition by seedlings for water in a desert
D. Seed dispersal by far-ranging birds
E. Infection by a highly contagious pathogen
A. Adaptation to a wide variety of soil types
B. Strong preference for riparian habitat
C. Intense competition by seedlings for water in a desert
D. Seed dispersal by far-ranging birds
E. Infection by a highly contagious pathogen
B
36
New cards
Studies of mutualism we discussed in class showed all of the following except
A. Resident ants form an obligate defensive mutualism with trees that house and feed the ants.
B. Plant roots reward mycorrhizal fungi that provide nutrients to the root.
C. Endophytic fungi help leafcutter ants by killing pathogens in the ants’ fungus garden.
D. Loss of forest elephants reduces dispersal of rainforest canopy trees.
E. A plant that depends on a moth for pollination can select against moths that cheat on the mutualism.
A. Resident ants form an obligate defensive mutualism with trees that house and feed the ants.
B. Plant roots reward mycorrhizal fungi that provide nutrients to the root.
C. Endophytic fungi help leafcutter ants by killing pathogens in the ants’ fungus garden.
D. Loss of forest elephants reduces dispersal of rainforest canopy trees.
E. A plant that depends on a moth for pollination can select against moths that cheat on the mutualism.
C
37
New cards
The most spatially complex models of population structure include A. How easy it is to move through the matrix between patches B. Patches of different quality C. Shifting patterns of patch occupancy D. Source and sink patches E. All of the above
E
38
New cards
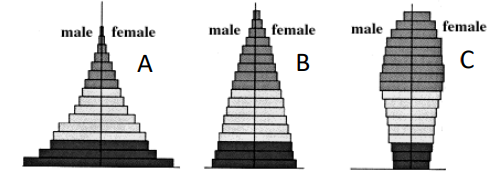
The population (as shown by the age distributions A-C on the right) that is not growing is
C
39
New cards
N(t) = N(0)λ t . An initial population of 10 Florida panthers breeds once a year, and has a discrete growth rate of 1.0. How many panthers will there be in this population in 3 years?
A. 10 B. 30 C. 60 D. 90 E. 120
A. 10 B. 30 C. 60 D. 90 E. 120
A
40
New cards
Fig trees (Ficus spp.) are pollinated only by specialized fig wasps, which mate and reproduce only inside figs. This mutualism is _____ for the fig tree and _____ for the fig wasp.
A. Facultative, facultative B. Facultative; obligate C. Obligate; facultative D. Obligate; obligate
A. Facultative, facultative B. Facultative; obligate C. Obligate; facultative D. Obligate; obligate
D
41
New cards
r = r0 (1 – N/K). A population of mosquitoes has a maximum (intrinsic) continuous growth rate of 1.0, a carrying capacity of 400 and initial population of 40. What will the logistic growth rate be when the population is 300?
A. 0.1 B. 0.25 C. 0.5 D. 0.75 E. 0.9
A. 0.1 B. 0.25 C. 0.5 D. 0.75 E. 0.9
B
42
New cards
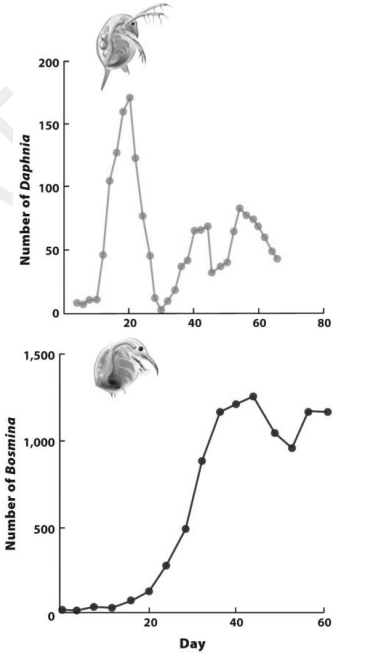
The graphs on the right show population growth curves of two water fleas, Daphnia (top) and Bosmina (bottom). These results show that
A. Bosmina outcompeted Daphnia
B. Daphnia overshot its carrying capacity more
C. Bosmina overshot its carrying capacity more
D. The carrying capacity of Daphnia was about 175
E. Bosmina had more time delay in its population growth
A. Bosmina outcompeted Daphnia
B. Daphnia overshot its carrying capacity more
C. Bosmina overshot its carrying capacity more
D. The carrying capacity of Daphnia was about 175
E. Bosmina had more time delay in its population growth
B
43
New cards
In the ideal free distribution, a habitat patch with 3 times the resources of another patch would have
A. 3 times the population
B. 2 times the population
C. 4 times the population
D. the same population
E. its population distributed randomly
A. 3 times the population
B. 2 times the population
C. 4 times the population
D. the same population
E. its population distributed randomly
A
44
New cards
Use the survivorship curves below. For elephants, the death rate of young adults (25-50% of lifespan) is ____ and the death rate of old adults (90-100% of lifespan) is ____.
A. High; high C. Low; high B. High; low D. Low; low
A. High; high C. Low; high B. High; low D. Low; low
C
45
New cards
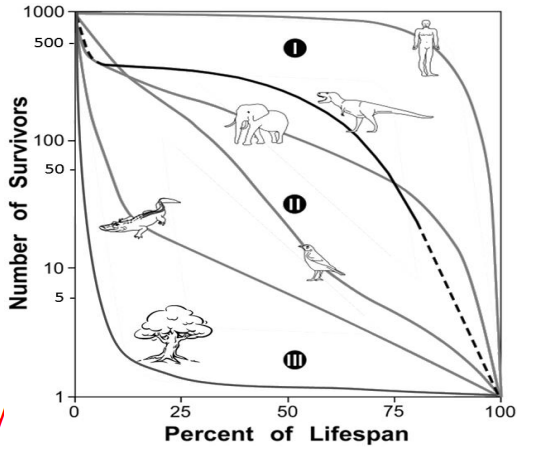
Use the survivorship curves on the right. Albertosaurus (the dinosaur) reached adulthood at about 15 years old, and lived to be about 30. Thus, about ___ of dinosaur hatchlings reach sexual maturity.
A. 90% B. 40% C. 10% D. 4% E. 1%
A. 90% B. 40% C. 10% D. 4% E. 1%
B
46
New cards
In milkweed-corn-human agroecology, which is not true?
A. Aphids on milkweed feed insects beneficial to corn.
B. Gene flow from unsprayed milkweed slows development of resistance to herbicides.
C. Patches of milkweed on the farm earn extra money by conserving monarch butterflies.
D. Genetically modified (GM) corn has much higher yield than non-GM corn on temperate zone farms.
E. Milkweed competes with corn, potentially lowering yields.
A. Aphids on milkweed feed insects beneficial to corn.
B. Gene flow from unsprayed milkweed slows development of resistance to herbicides.
C. Patches of milkweed on the farm earn extra money by conserving monarch butterflies.
D. Genetically modified (GM) corn has much higher yield than non-GM corn on temperate zone farms.
E. Milkweed competes with corn, potentially lowering yields.
D
47
New cards
In predator prey dynamics (from actual results)
A. Predator and prey populations do not interact
B. Predator and prey populations always oscillate
C. Prey populations cannot oscillate if predators are removed
D. Prey populations lag in response behind predator populations
E. Predator populations lag in response behind prey populations
A. Predator and prey populations do not interact
B. Predator and prey populations always oscillate
C. Prey populations cannot oscillate if predators are removed
D. Prey populations lag in response behind predator populations
E. Predator populations lag in response behind prey populations
E
48
New cards
The Lotka-Volterra model would be the most realistic if what else were considered?
A. Nothing—it is most realistic with no modification
B. Other predator species only
C. Multiple predator species and food availability for prey
D. Multiple predator species, prey food availability, and multiple prey species
A. Nothing—it is most realistic with no modification
B. Other predator species only
C. Multiple predator species and food availability for prey
D. Multiple predator species, prey food availability, and multiple prey species
D
49
New cards
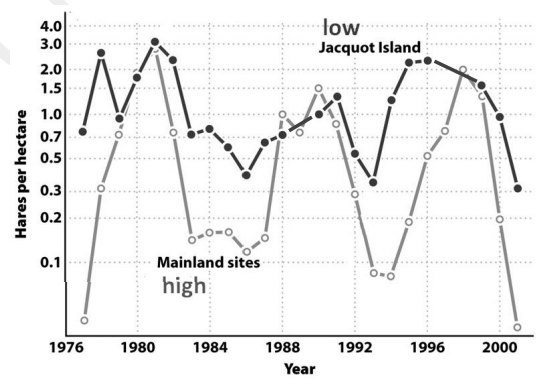
In the data for prey populations (on the right) at mainland (high predator density, open circles) and island (low predator density, closed circles) sites, the prey populations have a _____ cycle frequency, and _____ prey density is lower on the mainland.
A. Similar; minimum
B. Similar; maximum
C. Different; minimum
D. Different; maximum
A. Similar; minimum
B. Similar; maximum
C. Different; minimum
D. Different; maximum
A
50
New cards
Competition between populations of different species is
A. Independent
B. Intrinsic
C. Interspecific
D. Intraspecific
E. Apparent
A. Independent
B. Intrinsic
C. Interspecific
D. Intraspecific
E. Apparent
C
51
New cards
An example of positive density dependence in a (sub)population would be
A. Earthworms can’t find mates if they are too far apart
B. Widely spaced rainforest trees attract pollinating hummingbirds from long distances
C. Fishermen catch fewer fish when other fishermen are in the area
D. A human village can’t grow enough food on their land
E. A human disease is more prevalent in rural areas than in the city
A. Earthworms can’t find mates if they are too far apart
B. Widely spaced rainforest trees attract pollinating hummingbirds from long distances
C. Fishermen catch fewer fish when other fishermen are in the area
D. A human village can’t grow enough food on their land
E. A human disease is more prevalent in rural areas than in the city
A
52
New cards
The days to maturity for a crop of spinach grown hydroponically under various treatments are as follows (note: fewer days to maturity = faster growth).
Low light, low N: 30 days
Low light, high N: 20 days
High light, low N: 30 days
High light, high N: 20 days
Under these conditions, the limiting resource(s) for spinach growth was/were
A. Light only
B. N only
C. Both light and N
D. Some other resource such as P
Low light, low N: 30 days
Low light, high N: 20 days
High light, low N: 30 days
High light, high N: 20 days
Under these conditions, the limiting resource(s) for spinach growth was/were
A. Light only
B. N only
C. Both light and N
D. Some other resource such as P
B
53
New cards
Plasmodium cells live inside human red blood cells (RBCs) and eat hemoglobin. When the RBCs burst, releasing the Plasmodium, a malarial fever results, but killing the human host is not a necessary part of the Plasmodium life cycle. Plasmodium is
A. an endoparasite B. an ectoparasite C. a hyperparasite D. non-virulent E. a parasitoid
A. an endoparasite B. an ectoparasite C. a hyperparasite D. non-virulent E. a parasitoid
A
54
New cards
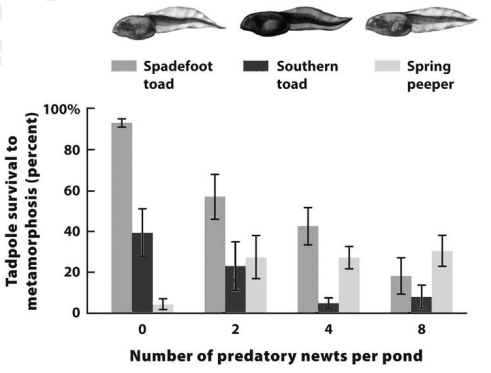
Please use the results of the experiment (below) where 3 species of tadpoles (larval frogs and toads) were kept together in artificial pond mesocosms, with the number of predatory newts present shown on the x-axis. The error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM).
These results show that competition can be affected by
A. each species’ competitive ability only
B. multiple limiting resources
C. the abiotic environment
D. trade-offs, for example of foraging vs. defense ability
E. defense against predators that never has a fitness cost
These results show that competition can be affected by
A. each species’ competitive ability only
B. multiple limiting resources
C. the abiotic environment
D. trade-offs, for example of foraging vs. defense ability
E. defense against predators that never has a fitness cost
D
55
New cards
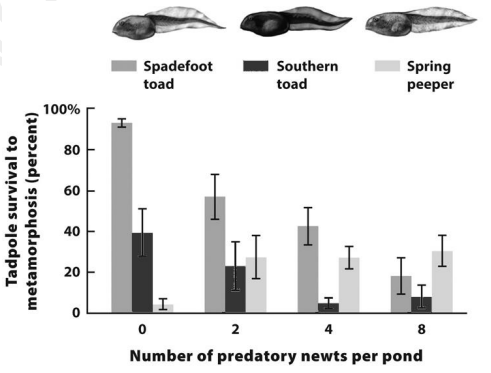
Please use the results of the experiment (below) where 3 species of tadpoles (larval frogs and toads) were kept together in artificial pond mesocosms, with the number of predatory newts present shown on the x-axis. The error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM).
Comparing the error bars, it is probable that with 8 newts present, survival of spadefoot toads was _____ survival of spring peepers.
A. Greater than
B. Not different from
C. Less than
D. Can’t infer without a P value
Comparing the error bars, it is probable that with 8 newts present, survival of spadefoot toads was _____ survival of spring peepers.
A. Greater than
B. Not different from
C. Less than
D. Can’t infer without a P value
B
56
New cards
In the four videos on the giant Asian hornets that you were invited to watch, and the video on naked mole rats, which event occurred?
A. Hornets raided a European honeybee colony for food, but didn’t eat the worker bees.
B. Native Japanese honeybees killed a hornet scout by mobbing it and smothering it (depriving it of oxygen).
C. Native Vietnamese honeybees captured attacking hornets by smearing their hive box with sticky tree sap.
D. A Japanese beekeeper made the entrance to his hive boxes wider, so more of his bees could attack a hornet at once.
E. A female naked mole rat worker “cheated” on the queen by having sex with a male, and was exiled from the colony.
A. Hornets raided a European honeybee colony for food, but didn’t eat the worker bees.
B. Native Japanese honeybees killed a hornet scout by mobbing it and smothering it (depriving it of oxygen).
C. Native Vietnamese honeybees captured attacking hornets by smearing their hive box with sticky tree sap.
D. A Japanese beekeeper made the entrance to his hive boxes wider, so more of his bees could attack a hornet at once.
E. A female naked mole rat worker “cheated” on the queen by having sex with a male, and was exiled from the colony.
A
57
New cards
Honeypot ants have helpless larvae and live in a desert environment where food is often hard to find—thus there are many foragers, and those that find food hoard it in their “replete” sisters, safe in their underground nest. Only the queen ant reproduces. This description best supports which hypothesis?
A. Cost of males in the evolution of sex
B. Dominance hierarchy promoting cooperation (+/+) in a social group
C. Inclusive fitness hypothesis for eusociality
D. Ecology hypothesis for eusociality
E. Food storage as a cause of population oscillations
A. Cost of males in the evolution of sex
B. Dominance hierarchy promoting cooperation (+/+) in a social group
C. Inclusive fitness hypothesis for eusociality
D. Ecology hypothesis for eusociality
E. Food storage as a cause of population oscillations
D
58
New cards
The set of conditions under which invasive Chinese bushclover grows in Asia can be used to predict the extent of its spread in various habitats after being introduced to North America. This is an example of a(n)
A. Ecological niche model
B. Seasonal metapopulation model
C. Habitat corridor
D. Enemy release hypothesis
E. Stage-based population model
A. Ecological niche model
B. Seasonal metapopulation model
C. Habitat corridor
D. Enemy release hypothesis
E. Stage-based population model
A
59
New cards
In the article about the carbon footprints of the rich that you were invited to read, which of the following is advised?
A. In the interest of bipartisanship, we should not discuss the cover-up of climate science by fossil fuel corporations.
B. We should not shame people who have to drive a lot because of suburban sprawl and poor public transportation.
C. We should excuse billionaire’s huge carbon footprints because there are not that many of them.
D. We should encourage developing countries to continue using fossil fuels to speed their economic development.
E. We should concentrate on lowering our individual carbon footprints as the best solution to climate change.
A. In the interest of bipartisanship, we should not discuss the cover-up of climate science by fossil fuel corporations.
B. We should not shame people who have to drive a lot because of suburban sprawl and poor public transportation.
C. We should excuse billionaire’s huge carbon footprints because there are not that many of them.
D. We should encourage developing countries to continue using fossil fuels to speed their economic development.
E. We should concentrate on lowering our individual carbon footprints as the best solution to climate change.
B
60
New cards
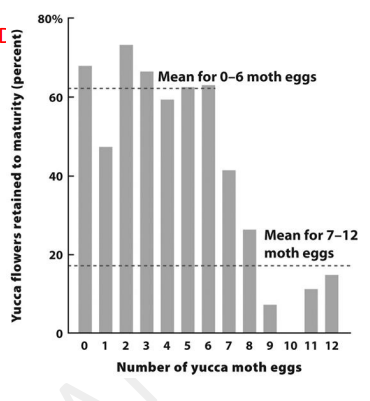
Please use the figure on the right. A yucca moth that lays 4 eggs in a yucca flower would, on average, produce how many offspring compared to a moth that lays 12 eggs in the flower? Use the means given, rounding to the nearest 10%. Show your work!
A. 2 fewer
B. 1 fewer
C. The same number
D. 1 more
A. 2 more
A. 2 fewer
B. 1 fewer
C. The same number
D. 1 more
A. 2 more
C
61
New cards
The term “ecology” comes from a word meaning “house.” (True or False)
True
62
New cards
The action of an “ecological filter” is also known as “natural selection.” (True or False)
True
63
New cards
Mineral nutrients can be released from soil particles with the help of secretions by plant roots (True or False)
True
64
New cards
The side of a mountain facing into the prevailing winds from the ocean has less rainfall than the side facing away from the winds (True or False)
False
65
New cards
According to the hypothesis developed in class, marine ray-finned fish are hyposmotic because the MRCA of all extant (alive today) ray finned fishes lived in salt water. (True or False)
False
66
New cards
In C4 photosynthesis, stomates are open at night and CO2 is fixed at night, allowing stomates to be closed during the day. (True or False)
False
67
New cards
Hair on the head helps keep the human brain cool in sunny, hot climates (True or False)
True
68
New cards
If a tadpole metamorphoses into a frog faster in the presence of a predator fish, compared to when it is kept alone, this is an example of phenotypic plasticity (True or False)
True
69
New cards
We do not have any way to estimate what global temperatures were millions of years ago. (True or False)
False
70
New cards
An organism’s life history is the description of its life cycle. (True or False)
False
71
New cards
The shallow edge of a body of water. In the case of the ocean, it is the intertidal zone.
Littoral
72
New cards
Ocean tides enter the mouth of a river, producing a mixture of fresh and salt water and depositing an abundance of nutrient-rich sediments.
Estuary
73
New cards
Vegetation growing on the edge of a stream or river; often including trees that are adapted to more moisture than the trees in the surrounding forest.
Riparian
74
New cards
The bottom floor or sediments of a lake or the ocean
Benthic
75
New cards
In the ocean, the relationships of who eats whom, from plankton to invertebrate larvae to fish, is studied from the perspective of the A. Organism D. Ecosystem B. Population E. Biosphere C. Community
C
76
New cards
In the African savanna, antelopes browse the lower leaves of trees while zebras graze on grasses. This partitioning of resources means that antelopes and zebras have A. Different habitats B. Completely different niches C. Partly different niches D. The same niche
C
77
New cards
Animals and fungi are both heterotrophs, but animals mostly consume living plants and other animals, while fungi mostly consume dead plants. This means animals and fungi have \______ trophic modes and \______ functional roles. A. similar; similar B. similar; different C. different; similar D. different; different
B
78
New cards
According to the figure (on the right) showing the spatial vs. temporal scale of N deposition into the sea off the coast of Sweden, which water column process affects an area of 100 m and can last several hours? A. NOx oxidation B. Turbulent mixing in the water C. Atmospheric mesoscale processes D. Algal blooms E. Water exchange
B
79
New cards
“Alligators adjust the sex of their offspring to favor the rare sex in the population, increasing mating opportunities for the offspring” is an example of a(n) \______ hypothesis, and “The sex of alligators is determined by the temperature of the nest, which affects gene expression in the developing embryo” is an example of a(n) \______ hypothesis. A. Proximate; proximate B. Proximate; ultimate C. Ultimate; proximate D. Ultimate; ultimate
C
80
New cards
In a study to test the effects of biological control by weevil or psyllid insects on the invasive tree Melaleuca quinquenervia in South Florida, seedlings of the tree were placed in small cages. Each cage contained one tree seedling with either no insect (1 cage), 10 weevils (1 cage), 10 psyllids (1 cage), or 5 of each type of insect (1 cage); 4 cages in total. This study was a(n): A. On site field experiment (not a transplant) B. Microcosm experiment C. Transplant field experiment D. Natural experiment E. Correlational study
B
81
New cards
In a study to test the effects of biological control by weevil or psyllid insects on the invasive tree Melaleuca quinquenervia in South Florida, seedlings of the tree were placed in small cages. Each cage contained one tree seedling with either no insect (1 cage), 10 weevils (1 cage), 10 psyllids (1 cage), or 5 of each type of insect (1 cage); 4 cages in total. In this study, what is missing from the design, as described? A. Question B. Treatments C. Control(s) D. Replicates E. Nothing—it is a fully valid design
D
82
New cards
A property of water important to life is that it A. Does not dissolve minerals in the soil B. Is denser in the liquid state than in the solid state C. Is not able to support buoyant organisms D. Is liquid at only a narrow range of temperatures E. Is non-polar on the molecular level
B
83
New cards
A pH of 8.0 is \_______ more \_______ than a pH of 6.0. A. 2 times; acidic B. 2 times; basic C. 10 times; neutral D. 100 times; acidic E. 100 times; basic
E
84
New cards
Soil structure comprises A. Mineral particles B. Air C. Water D. Organic matter such as glomalin E. All of the above
E
85
New cards
You use the jar method to test the soil at a field site and obtain the result shown on the right. This soil is approximately A. 60% sand, 20% silt, 20% clay B. 50% sand, 10% silt, 40% clay C. 33% sand, 33% silt, 33% clay D. 30% sand, 10% silt, 60% clay E. Can’t determine from this result
B
86
New cards
A water molecule has just left a soil particle and entered a root cell to begin the process of transpiration. The water entered the root cell because A. The cell pumped it inside by active transport B. Its surface tension caused it to adhere to the cell C. Its cohesion with other water molecules pulled it inside D. The [solutes] outside the cell is greater than the [solutes] inside E. The [solutes] inside the cell is greater than the [solutes] outside
E
87
New cards
A mangrove acts partly as an osmoconformer when it A. Grows roots that emerge from the water to obtain oxygen B. Maintains function despite an increased [salt] in its roots C. Excludes salt from entering the roots D. Actively transports salt out of the roots E. Excretes salt from the leaves
B
88
New cards
Overall, plants expend energy to \______ N, and animals expend energy to \______ N. A. Obtain; obtain B. Obtain; remove excess C. Remove excess; obtain D. Remove excess; remove excess
B
89
New cards
On the right are the absorption spectra of the membranes of purple and green photosynthetic bacteria. According to DasSarma (2006), purple and green bacteria evolved together. This hypothesis is supported by the peak absorption of \______ light by the green bacteria and of \______ light by the purple bacteria. A. Blue and red; green B. Blue and red; blue and red C. Green; blue and red D. Green; green E. Green; purple
A
90
New cards
In which lowland environment(s) are C4 grasses expected to be more common than C3 grasses? A. Cool and dry B. Cool and wet C. Hot and dry D. Hot and wet E. All of the above
C
91
New cards
A plant could be kept cool by all of the following mechanisms except A. Closing its stomata to prevent water loss B. Folding leaves to shade from the sun C. Having most of its biomass underground D. Having silvery hairs on the leaves E. Having small leaves
A
92
New cards
On the diagram on the right, at which point in the Earth’s orbit (A-D) is it winter in the Northern Hemisphere?
C
93
New cards
On the diagram of the Earth’s Northern Hemisphere on the right, where (A-E) is dry air sinking and warming, causing low rainfall?
D
94
New cards
In the Northern Hemisphere, the south-facing slope of a hill will be \______ compared to the north-facing slope. Consider only sun exposure. A. Shadier and moister B. Shadier and drier C. Sunnier and moister D. Sunnier and dryer
C
95
New cards
South Florida pine rocklands are generally ______ than hardwood hammocks, and are maintained by ______.
A. Drier; salinity B. Drier; fire C. Drier; deep soil D. Wetter; salinity E. Wetter; fire
A. Drier; salinity B. Drier; fire C. Drier; deep soil D. Wetter; salinity E. Wetter; fire
B
96
New cards
As shown on the right,
A. Bogotá, Mérida, and Rio are at the same latitude
B. Rio has the most pronounced dry season
C. The sun is in the southern sky in June in Rio
D. The sun is in the northern sky in June in Rio E. It rains the least in Mérida in the months when the sun is overhead at noon
A. Bogotá, Mérida, and Rio are at the same latitude
B. Rio has the most pronounced dry season
C. The sun is in the southern sky in June in Rio
D. The sun is in the northern sky in June in Rio E. It rains the least in Mérida in the months when the sun is overhead at noon
D
97
New cards
Shrubs and grasses gradually replace trees in the transition from
A. Grassland to savanna to forest
B. Forest to savanna to grassland
C. Evergreen to deciduous forests
D. Tropical to subtropical to temperate
E. Temperate to subtropical to tropical
A. Grassland to savanna to forest
B. Forest to savanna to grassland
C. Evergreen to deciduous forests
D. Tropical to subtropical to temperate
E. Temperate to subtropical to tropical
B
98
New cards
In the tropical rainforest, which layer is formed by plants specialized to climb the tall trees? A. Emergent D. Liana B. Canopy E. Epiphyte C. Understory
D
99
New cards
About how many months out of the year is there sufficient precipitation for plant growth in Hong Kong? Do not consider the length of the growing season.
A. 0
B. 3
C. 9
D. 12
E. Need more data to estimate
A. 0
B. 3
C. 9
D. 12
E. Need more data to estimate
C
100
New cards
Please use the Walter diagram for Hong Kong and the Whitaker biome diagram above to answer these questions. On the Walter diagram, temperature is shown by the gray curve and precipitation by the black curve. Frost-free months are shown by the shaded box on the x-axis. The x-axis represents a year and is divided into 12 months, starting with January. Hong Kong has 23.1°C average annual temperature and 2211 mm average annual precipitation. The warmest month in Hong Kong has an average temperature of about _____.
A. 17°C B. 23°C C. 28°C D. 57°C E. 65°C
A. 17°C B. 23°C C. 28°C D. 57°C E. 65°C
C