bio421 (examII)
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lec 17
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What are the functions of microtubules
Provide structure for the cell
Provide structure to Enable movement
Vital for chromosome segregation
Used for intracellular transport
What are the general use for motor proteins
move across microtubules for intracellular transport
What are the families for microtubules motor proteins
Kinesin
Dynein
What are the major need to have two different microtubule directions
to have the motor proteins have different directionality
What stabilizes microtubules
MAP
How do motor proteins provide movement
Both use ATP to walk along microtubules in there specific direction
dynein walk
towards the microtubule minus end
kinesins walk
in both the positive and minus direction
just not and the same time
and direction is specific to the molecule
Which axon has the greater speed
a. axon with shorter synapses and wider distance
b. axon with wider synapses and shorter distance
c. axon with skinny synapses and longer distance
d. axon with wider synapses and longer distances
axon with wider synapses and shorter distance
speed of action potential conduction is primarily determined by the axon's diameter and myelination. A wider axon has less internal resistance, allowing for faster ion flow and thus, faster conduction velocity.
What direction is towards the synapses for the axon?
anterograde
What direction is towards the cell body for the axon?
retrograde
Which motor type is responsible for retrograde in neurons?
a. dynein
b. kinesin
-dynein bc dynein can move in the minus direction (only)
-kinesin bc kinesin can move in both the minus and positive end (although minus is preferred)
Spindle fibers are ___ and spindle poles are ____
a. microtubules; centrosomes
b. centrosomes; microtubules
microtubules centrosomes
List 3 different role for MT during chromosome division (no definition)
Astral
Polar Microtubules
Kinetochore Microtubules
Astral Microtubules
radiate outward from the centrosome and connect with the cell cortex
Polar Microtubules
Antiparallel Microtubules connecting opposite centrosomes
Kinetochore Microtubules
Connect to each side of chromosome
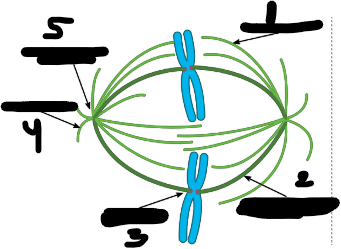
label this diagram
1. Polar microtubule
Kinetochore microtubule
kinetochore
Astral microtubule
Microtubule organizing center

Considering the walking direction what mt motor protein is located at #3?
kinesin

Considering the walking direction what mt motor protein is located at #2?
kinesin
Considering the walking direction what mt motor protein is located at #5?
dynein
Considering the walking direction what mt motor protein is located at #4?
kinesin
How do cells function as communities?
They interact with other cells via cell junctions and through the extracellular matrix
The space between cells is filled with the _____
extracellular matrix
Extracellular matrix composition
Proteins
collagen
intergrins )
Gel fomring polyssachrides
(proteins, polysaccharides (secreted locally and assembled into a meshwork with the surface of the cell that produced them))
What is collagen’s responsibility in the extracellular matrix (ECM)?
provides tensile strength
What is collagen’s gel forming polysaccharides in the extracellular matrix (ECM)?
delete (make up soft tissue ig eye also called GAGs—> glycosaminoacids)
Integrins
adaptors connect outside the ECM to the actin inside the cytoskeleton
What are the five factors that contribute to the ECM?
Functions as adhesive substrate
Provides structure
Presents growth factors as their receptors
Sequesters and stores growth factors
senses and transduces mechanical signals (transport force throughout the cell)
Collagen fiber are assembled outside the cell
(((FIX CARD))
steps for collagen production
Procollagen —>
What is Procollagen?
Precursor collagen molecules that have unstructured terminal ends.
Triple-helix form
slide 31