Inorganic
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
164 Terms
Study of matter, composition, properties and transformations including energy changes accompanying them
Chemistry
Has mass and volume
Matter
Known as the fourth state of matter, occurs in the form of ions and electrons that exist at high temperature
Plasma
The particle motion of electrons and ions in plasma _______
Move freely
_______ consists of two or more elements or compounds
Mixtures
_________ is a process that changes the physical properties of a substance w/o changing its chemical composition
Physical change
______ is a process in which one or more substances are converted into one or more new substances; change in the chemical makeup
Chemical change
Physical or chemical property: Color, odor, taste
Physical
_________ property that can be observed or measured without changing its composition
Physical property
Physical or chemical property: Flammability and reactivity
Chemical property
Physical or chemical property: Mass, volume, density, and magnetism, conductivity and temperature
Physical prop.
___________ described the material world as made up of tiny indivisible particles they called atomos, meaning “indivisible or uncuttable.”
Dalton
The law of constant composition based on what postulate in dalton’s atomic theory
Postulate 4
law of conservation of mass, based on what postulate in dalton’s atomic theory
postulate 3
J.J. Thompson proposed the _________ model where atom is made up of negative electrons floating in a sphere similar to a plums in a fruit cake
Plum pudding model
This model was the result of Rutherford’s gold foil experiment where alpha particles pass through a foil
Rutherford’s Nuclear model
________ model depicts atoms as small, positively charges nuclei surrounded by electrons in circular orbit
Bohr’s planetary model
Which law states: In a given compound, the relative numbers and kinds of atoms are constant.
Law of constant composition
What law states: The total mass of materials present after a chemical reaction is the same as the total mass present before the reaction.
Law of conservation of mass
What law states: If two elements A and B combine to form more than one compound, the masses of B that can combine with a given mass of A are in the ratio of small whole numbers.
Law of multiple proportions
Compound A contains 1.333 g of oxygen per gram of carbon, whereas compound B contains 2.666 g of oxygen per gram of carbon.
What chemical law do these data illustrate?
If compound A has an equal number of oxygen and carbon atoms, what can we conclude about the composition of compound B?
True or false: Particles with the same charge repel one another, whereas particles with unlike charges attract one another.
True
_______ Nuclear model demonstrated that atom has a tiny, heavy nucleus
Ernest Rutherford
the number of protons or electrons in an atom of any particular element is called
atomic number
number of protons plus neutrons in an atom is called
mass number
Atoms with identical atomic numbers but different mass numbers (that is, same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons) are called
Isotope
How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in (a) 197 Au (b.) an atom of strontium-90?
79 protons, 79 electrons, and 118 neutrons
38 protons, 38 electrons, and 52 neutrons
How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in (a) a 138Ba atom, (b) an atom of phosphorus-31?
56 protons, 56 electrons, and 82 neutrons
15 protons, 15 electrons, and 16 neutrons
Magnesium has three isotopes with mass numbers 24, 25, and 26. (a) Write the complete chemical symbol (superscript and subscript) for each. (b) How many neutrons are in an atom of each isotope?

the average atomic mass of an element, usually called the element’s _________ is the weighted average mass of the atomic masses of the isotopes of a given element
atomic weight
Naturally occurring chlorine is 75.78% 35Cl (atomic mass 34.969 amu) and 24.22% 37Cl (atomic mass 36.966 amu). Calculate the atomic weight of chlorine.


28.09 amu
Known as coinage metals, these elements are less reactive than most metals, which is why they are used throughout the world to make coins.
Copper, Silver and Gold
Which two ofthese elements would you expect to show the greatest similarity in chemical and physical properties:B,Ca,F,He,Mg,P?
Elements in the same group ofthe periodic table are most likely to exhibit similar properties. We therefore expect Ca and Mg to be most alike because they are in the same group (2A,the alkaline earth metals).
A molecule made up of two atoms is called
Diatomic molecule
Compounds composed of molecules contain more than one type of atom are
Molecular compounds
Chemical formulas that indicate the actual numbers of atoms in a molecule are called
Molecular formulas
Chemical formulas that give only the relative number of atoms of each type in a molecule are called
Empirical formulas
Write the empirical formulas for
(a) glucose, a substance also known as either blood sugar or dextrose, molecular formula C6H12O6
(b) nitrous oxide, a substance used as an anesthetic and commonly called laughing gas, molecular formula N2O.
The subscripts of an empirical formula are the smallest whole-number ratios. The smallest ratios are obtained by dividing each subscript by the largest common factor, in this case 6. The resultant empirical formula for glucose is CH2O.
Because the subscripts in N2O are already the lowest integral numbers, the empirical formula for nitrous oxide is the same as its molecular formula, N2O.
Give the empirical formula for diborane, whose molecular formula is B2H6.
BH3
Give the chemical symbol, including superscript indicating mass number, for (a) the ion with 22 protons, 26 neutrons, and 19 electrons; (b) the ion of sulfur that has 16 neutrons and 18 electrons.
(a) The number of protons is the atomic number of the element. A periodic table or list of elements tells us that the element with atomic number 22 is titanium (Ti). The mass number (protons plus neutrons) of this isotope of titanium is more protons than electrons, it has a net charge of 16 + 16 = 32 is 2and the ion symbol is 32S222 + 26 = 48 3+ : 48Ti3+ . Because the ion has three .
(b) The periodic table tells us that sulfur (S) has an atomic number of 16. Thus, each atom or ion of sulfur contains 16 protons. We are told that the ion also has 16 neutrons, meaning the mass number is . Because the ion has 16 protons and 18 electrons, its net charge . In general, we will focus on the net charges of ions and ignore their mass numbers unless the circumstances dictate that we specify a certain isotope.
How many protons, neutrons, and electrons does the 79Se2-
34 protons, 45 neutrons, and 36 electrons
Predict the charge expected for the most stable ion of barium and the most stable ion of oxygen.
Ba 2+
O 2-
Predict the charge expected for the most stable ion of (a) aluminum and (b) fluorine.
Al 3+
F 1-
Which of these compounds would you expect to be ionic: N2O, Na2O, CaCl2,SF4?
Na2O and CaCl2
True or False: The effective nuclear charge increases from left to right across any period of the periodic table.
True
________ is affected by the principal quantum number and the Zeff of the outermost electron of the atom
Atomic radius
Down a group, electrons occupy increasing energy levels which causes the atomic radius to _______
increase
Due to lanthanide contraction, there is a _______ in size from left to right among lanthanide metals, where outer electrons fill 4f orbitals
Decrease
_______ is half the distance of between nuclein in metal
Metallic radius
__________ half the distance between nuclein in the molecule consisting of identical atoms
Covalent radius
_________ half the distance between ions in ionic compound
Ionic radius
Within each group,bonding atomic radius tends to increase from top to bottom. This trend results primarily from the increase in the __________
principal quantum number (n)
Within each period, bonding atomic radius tends to decrease from left to right. The major factor influencing this trend is the increase in ________
effective nuclear charge Zeff
Arrange 11Na, 4Be, and 12Mg in order of increasing atomic radius.
Be < Mg < Na
Arrange Mg 2+, Ca 2+ and Ca in order ofdecreasing radius.
Ca > Ca2+ Mg 2+
Which of the following atoms and ions is largest: S2-, S, O2-
S2-
group of ions all containing the same number ofelectrons.
isoelectronic ions
is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from the ground state of the isolated gaseous atom or ion.
ionization energy
True or False: The greater the ionization energy, the more difficult it is to remove an electron.
True
The _________ metals show the lowest ionization energy in each period, and the noble gases show the highest.
alkalip
When electrons are removed from an atom to form a cation, they are always removed first from the occupied orbitals having the _________ principal quantum number, n.
largest
The energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom is called the _________
Electron affinity
Chemical property that describe the tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards itself
Electronegativity
Most metal oxides are ________ (acidic or basic) and dissolve in water react to form metal hydroxides
basic
(a) Would you expect scandium oxide to be a solid, liquid, or gas at room temperature?
(b) Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of scandium oxide with nitric acid.

Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction between copper(II) oxide and sulfuric acid.
CuO(s) + H2SO4(aq) ——— > CuSO4(aq) + H2O(l)
Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of solid selenium dioxide, SeO2(s), with (a) water, (b) aqueous sodium hydroxide.
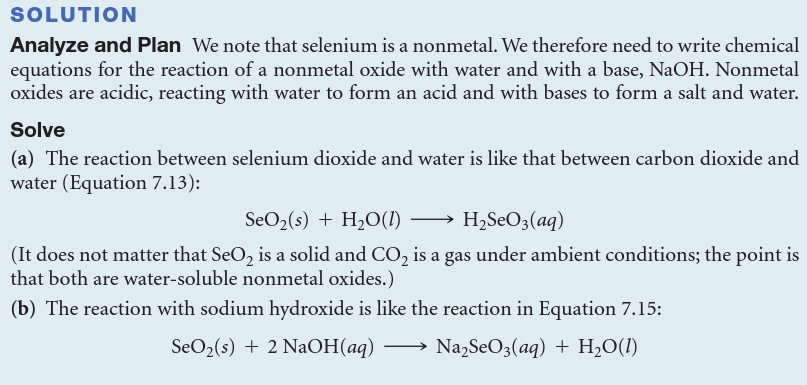
Most nonmetal oxides are ________, which means that those that dissolve in water form acids:
acidic
Like acids, most nonmetal oxides dissolve in basic solutions to form
salt + water
_________ have properties intermediate between those of metals and those of nonmetals.
metalloids
Law that states: Middle element in certain triads had an atomic weight that was the average of two members
Law of Triads
Law that states; elements are aligned according to their atomic weight, every eight element shares similar properties
Law of octaves
Dmitri Mendeleev formulated the __________ where the properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic masses
Periodic Law
The main group’s chemical properties are determined by the valence level of _________
s and p electrons
The chemical properties of transition metals result from the filling
d orbitals
the chemical properties of lanthanides and actinides result from the filling of ________
4f and 5f orbitals
This group is known for its silvery, metallic luster and high thermal and electrical conductivity; they have low densities and melting points
Group 1 Alkali metals
Group 1 metals are stored in ______ to prevent air oxidation
Oil
When alkali metals react vigorously with water it produces
Hydrogen gas and alkali metal hydroxide
When alkali metals react with oxygen it produces
Oxide
_________ metals are solids at room temperature and have typical metallic properties, they are lustrous silver-colored metals with 2+ cations
Group 2 Alkaline Earth metals
Alkaline earth metals react with water or steam, even when heated red-hot to form hydroxide except:
Beryllium
Elements with partially-filled d subshell, or which can give rise to cation with an incomplete d subshell
Group 3-12 transition metals
Together with actinides they are also known as the inner transition metal
Lanthanides
________ forms stable 3+ ions which many are colored
Lanthanides
_________ are dense, radioactive metals, many of which are unstable. They are synthetically produced and named after scientists
Actinides
_________ are synthetic, radioactive and very unstable elements that exists for only a fraction of a second
transactinides
Also known as Icosagens. They have low melting point and form hardness.
Group 13 Boron group
Also known as crystallogens, they are composed of metals, metalloids, and nonmetals
Group 14 Carbon group
In Group 13, all are metals except
Boron
In group 16 all are solids except
Nitrogen
Also known as Pnictogens, this group has five valence electrons, they composed of netals, metalloids, and nonmetals
Group 15 Nitrogen group
Composed electronegative nonmetals and metalloids with six valence electrons
Group 16 Oxygen group
Only groupnthat contains solid, liquid, and gas. They have seven VE and form diatomic molecules
Group 17 halogen
Composed of monoatomic nonmetals, they are colorless gas and low chemical reactivity
Group 18 Noble gases
The three magnetic metals
Iron, cobalt and nickel
Most abundant element in Earth’s atmosphere
Nitrogen
Most abundant element in Earth’s crust and the human body
Oxygen
Metal with the highest melting point (3422c)
Tungsten