LOM Ch. 15 Musculoskeletal System Chabner 11 ed.
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
musculoskeletal system
the system of bones and skeletal muscles that support and protect the body and permit movement
consists of bones, muscles, and joints
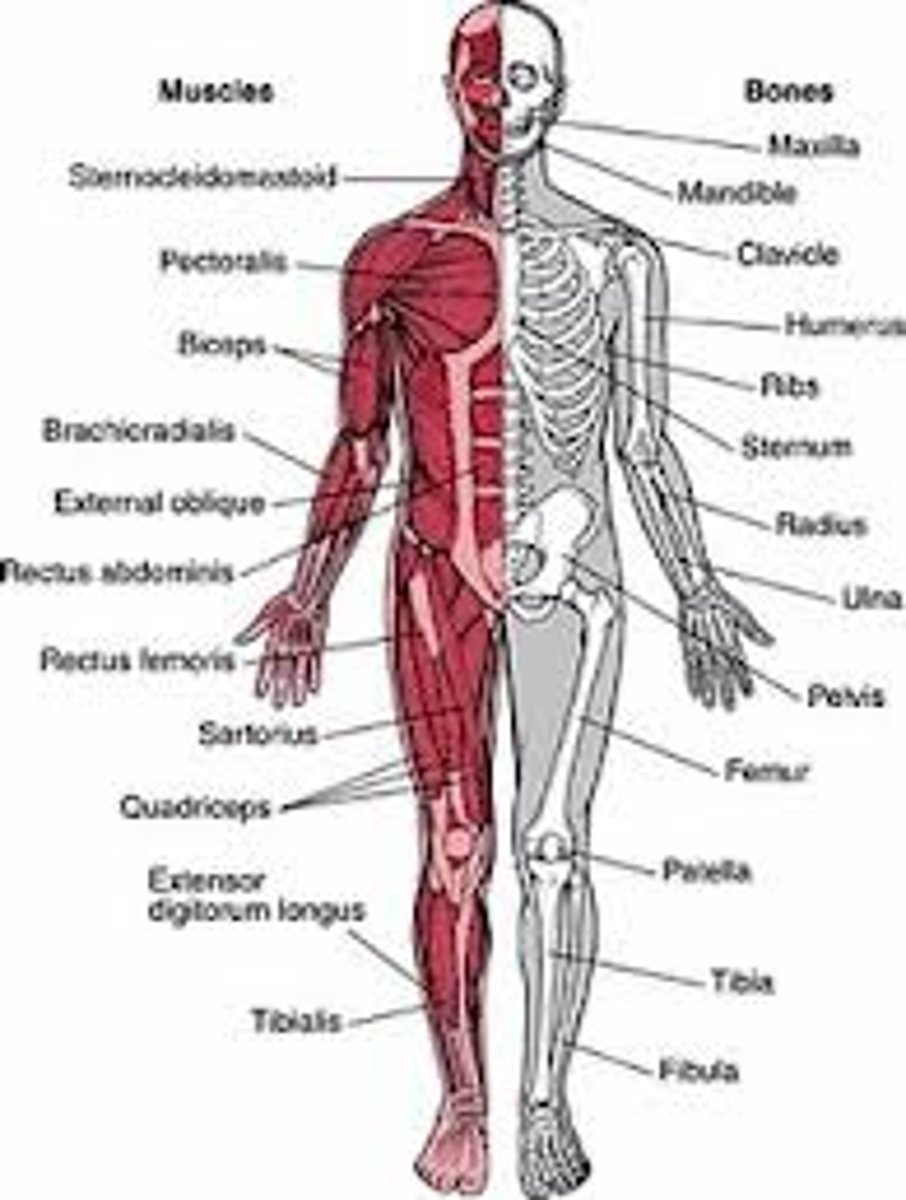
Bones
provide the framework on which the body is constructed and protects and supports vital organs
assist in movement because they serve as anchors for muscle attachments
Joints
Areas where two or more bones join together
aka articulations
muscles
tissues or fibers that cause movement of body parts and organs
Tendons
connective tissue that connects muscle to bone
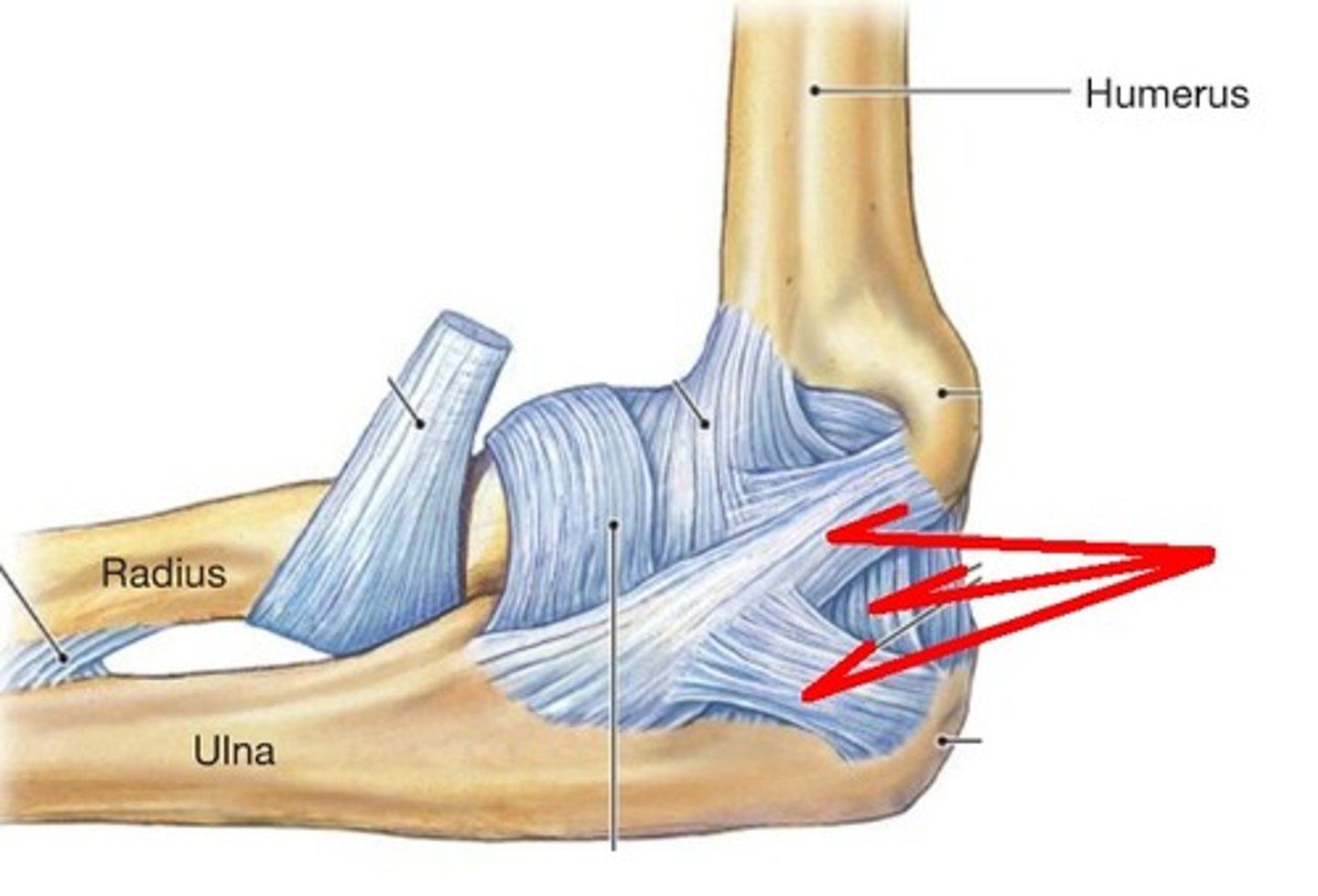
Ligaments
Connect bone to bone
Cartilage
strong connective tissue that supports the body and is softer and more flexible than bone
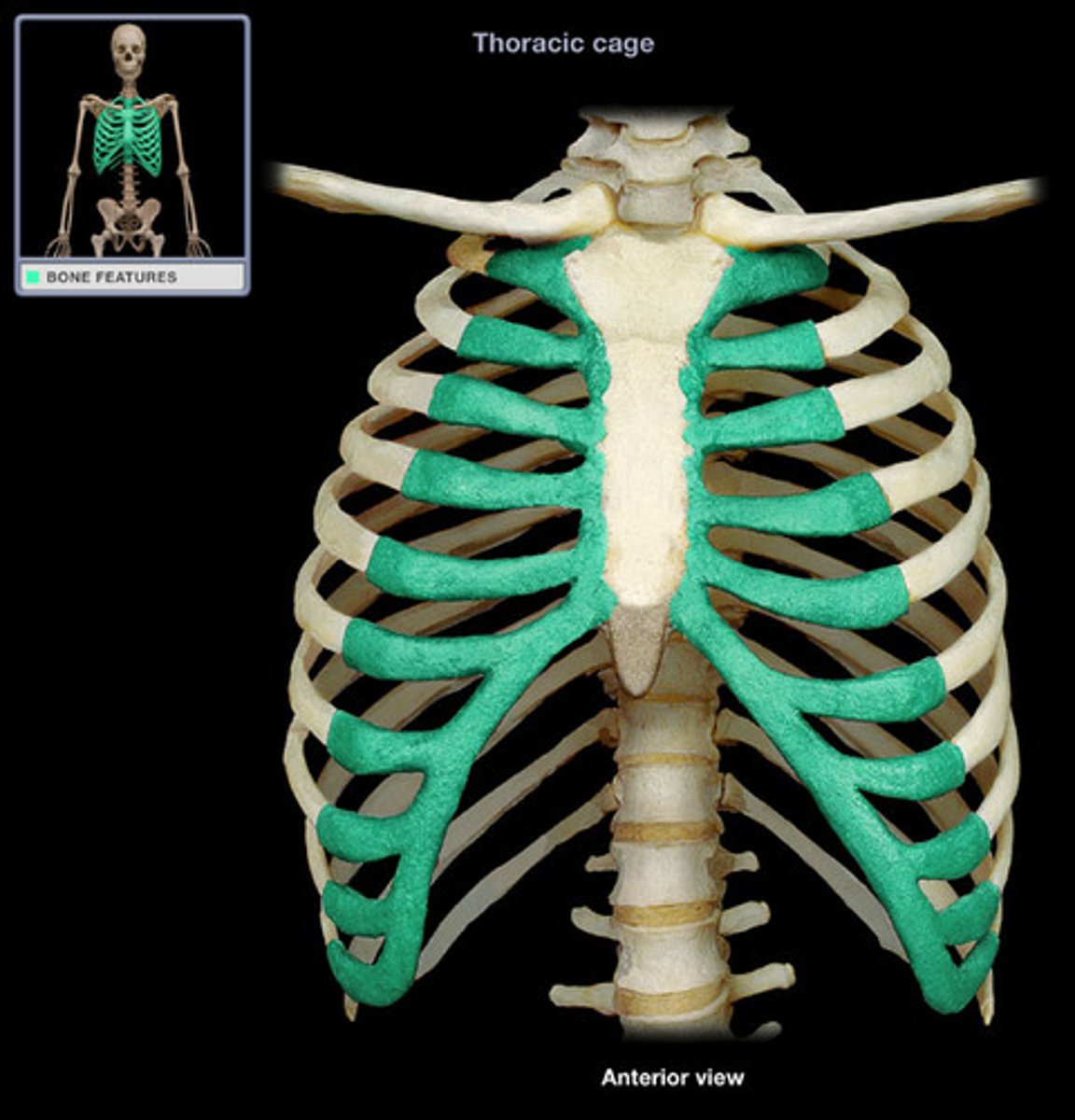
osseus tissue
bony tissue which is the connective tissue present in bones. It consists of a combination of osteocytes, collagen,and intercellular calcium salts
Osteoblasts
immature bone cells that actively produce bony tissue by replacing cartilage during ossification
Osteoclasts are
bone cells that reabsorb, or digest bone tissue
-aka bone phagocytes
bone formation
depends largely on the presence of calcium and phosphorous that must be taken into the body --transport into the body depends on Vitamin D
Calcium
without proper amount in the blood nerve fibers are unable to transmit impulses effectively to muscles, the heart muscle becomes weak and muscles attached to bones will spasm

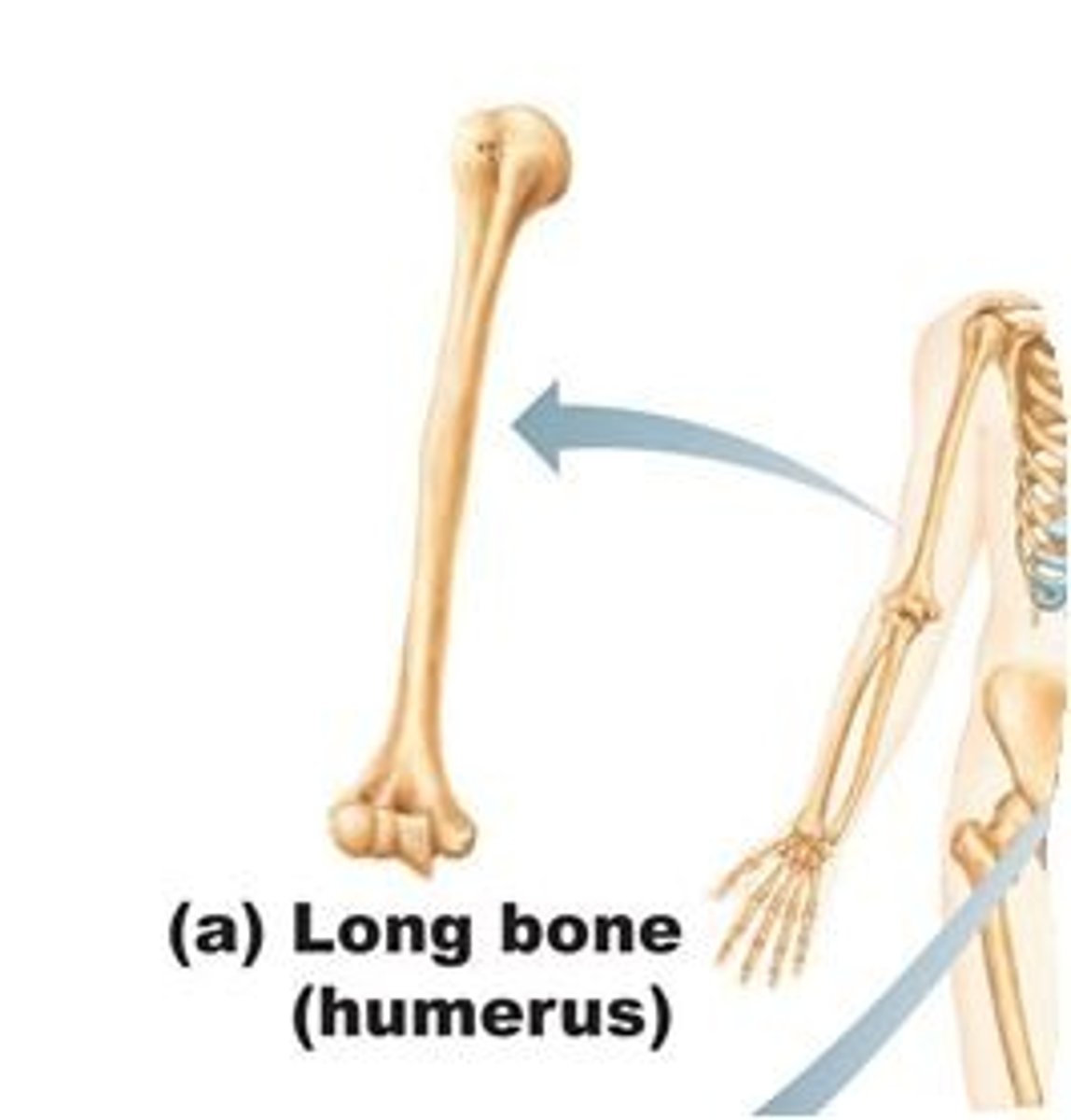
long bones
found in the thigh, lower leg, and upper and lower arm
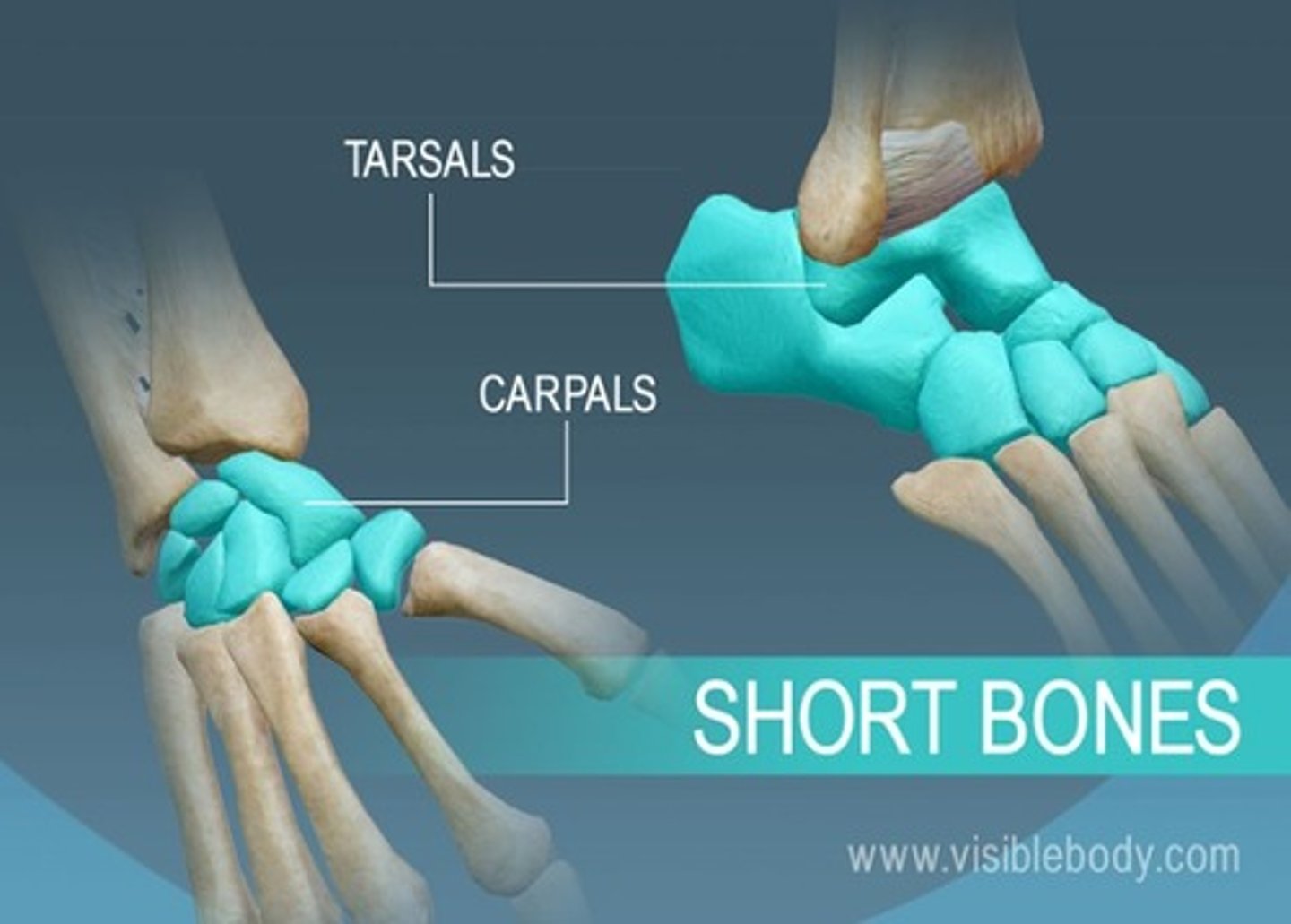
short bone examples
wrist and ankle bones and are small with irregular shapes
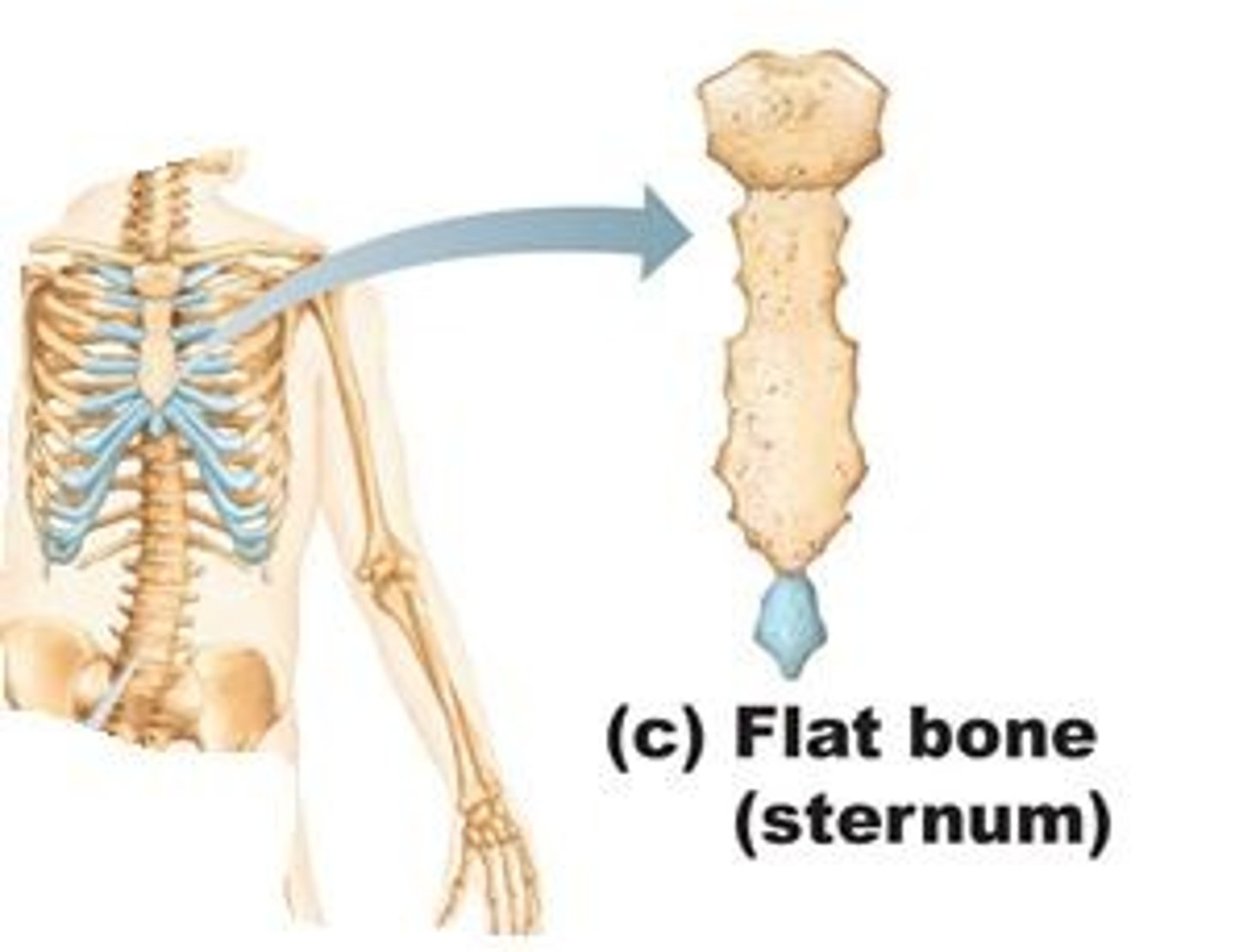
flat bones
bones of the ribs, shoulder blades, pelvis, and skull
-they are found covering soft body parts
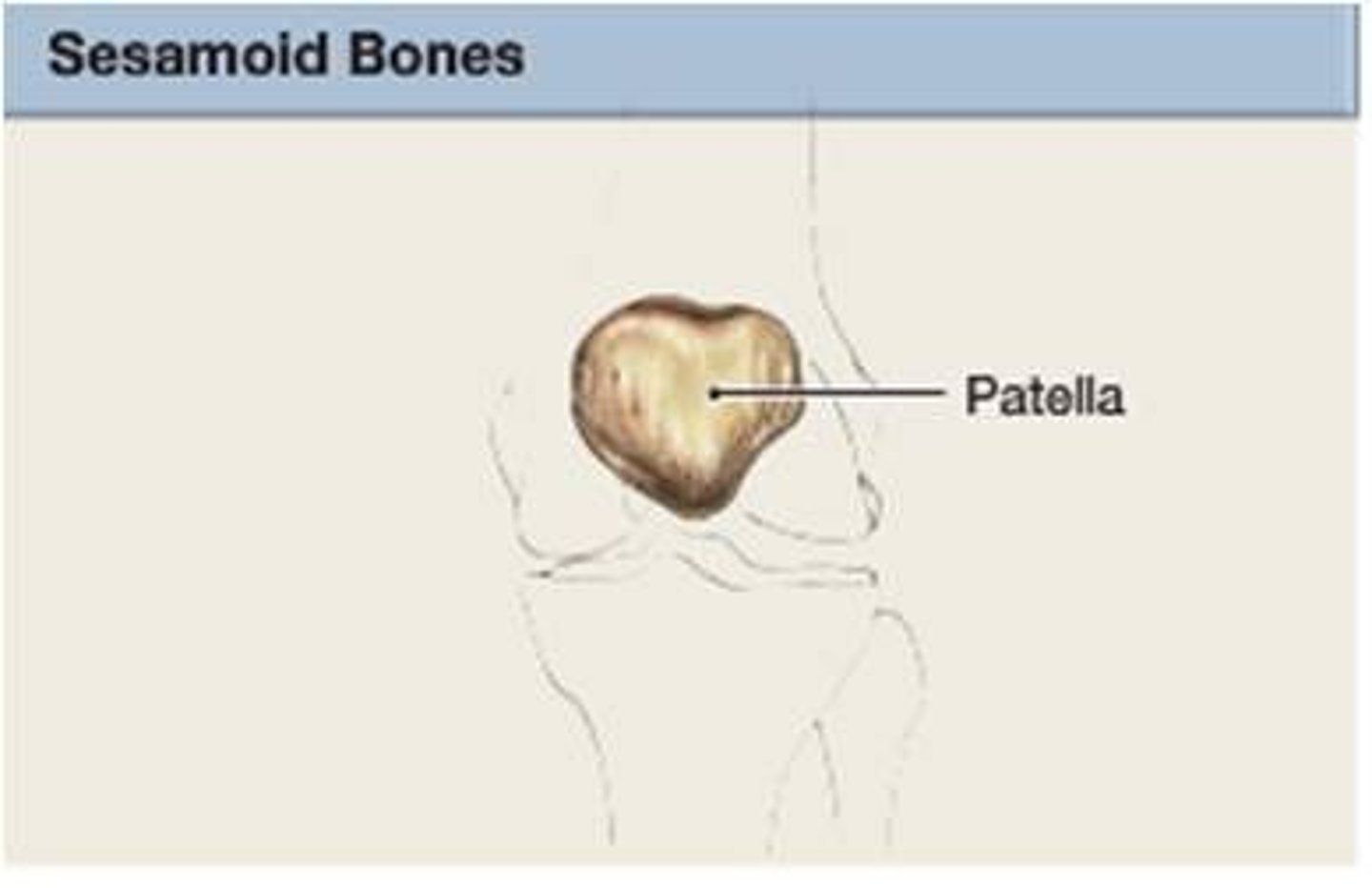
sesamoid bones
small, round bones found near joints (e.g., the patella)
-the knee cap is the largest sesamoid bone
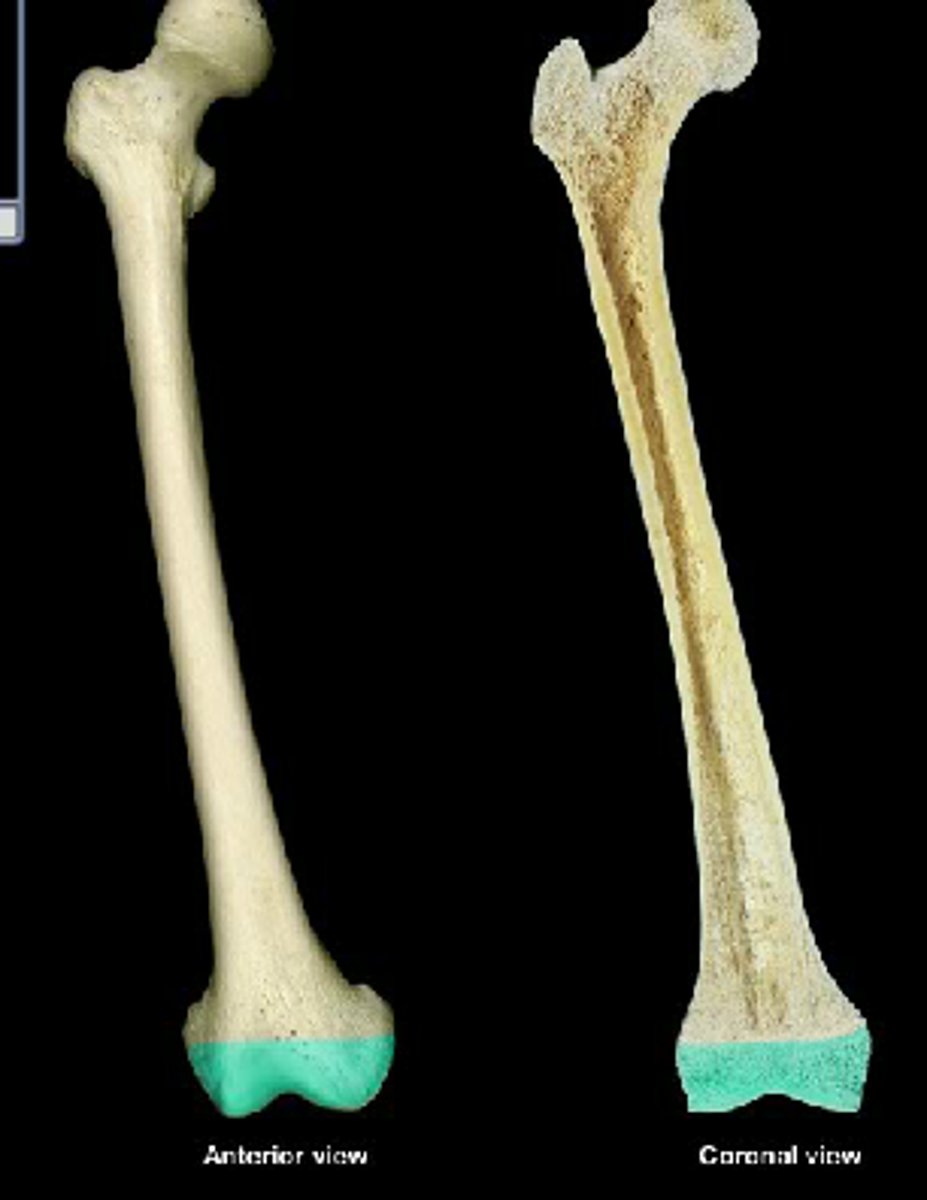
Diaphysis
shaft or middle region of a long bone, composed mostly of compact bone
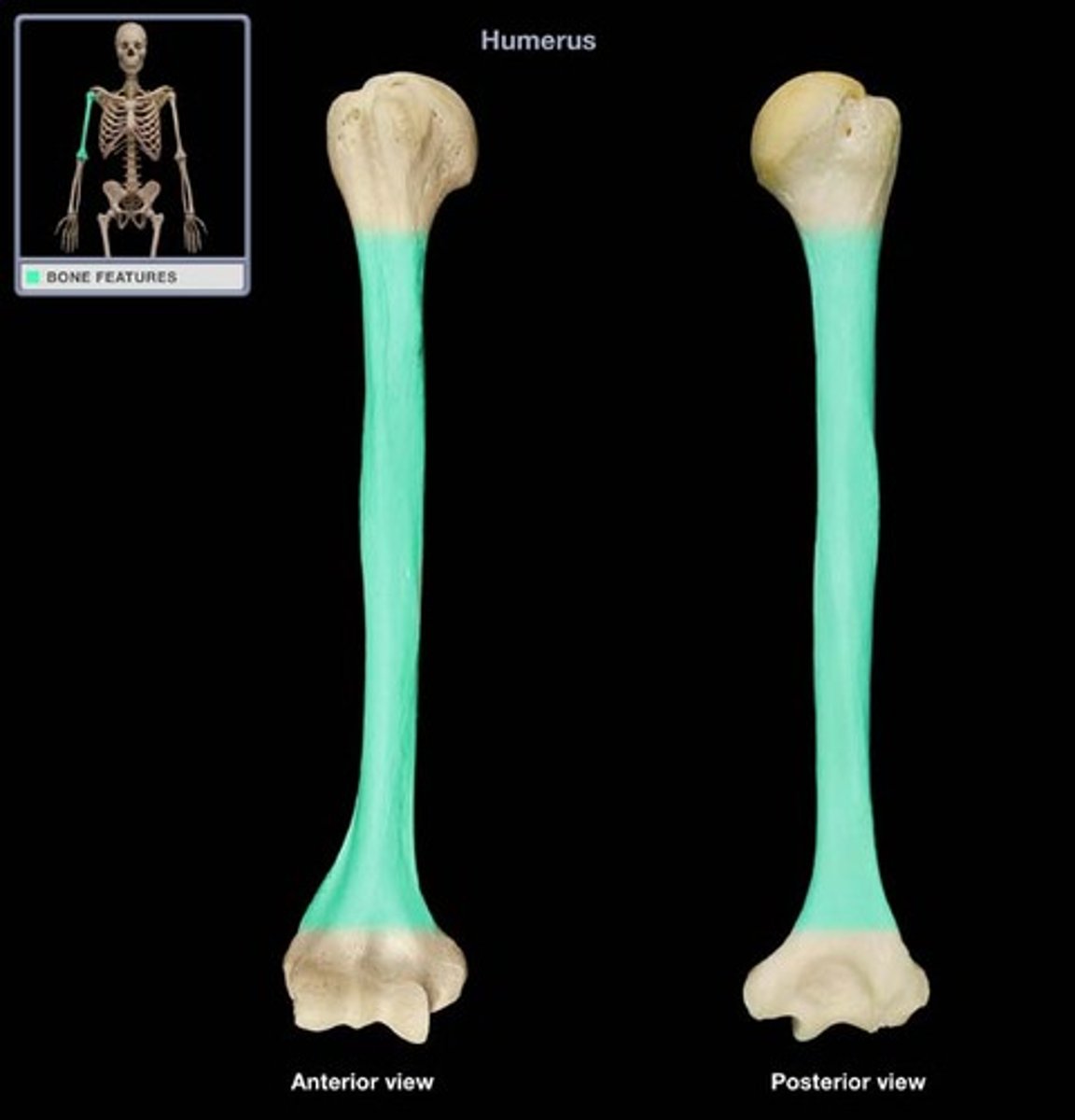
Epiphysis
End of a long bone, composed mostly of spongy bone
epiphyseal plate
-cartilaginous area at the ends of long bones where lengthwise growth takes place in the immature skeleton
-aka epiphyseal line
-it disappears when the bone has achieved its full growth
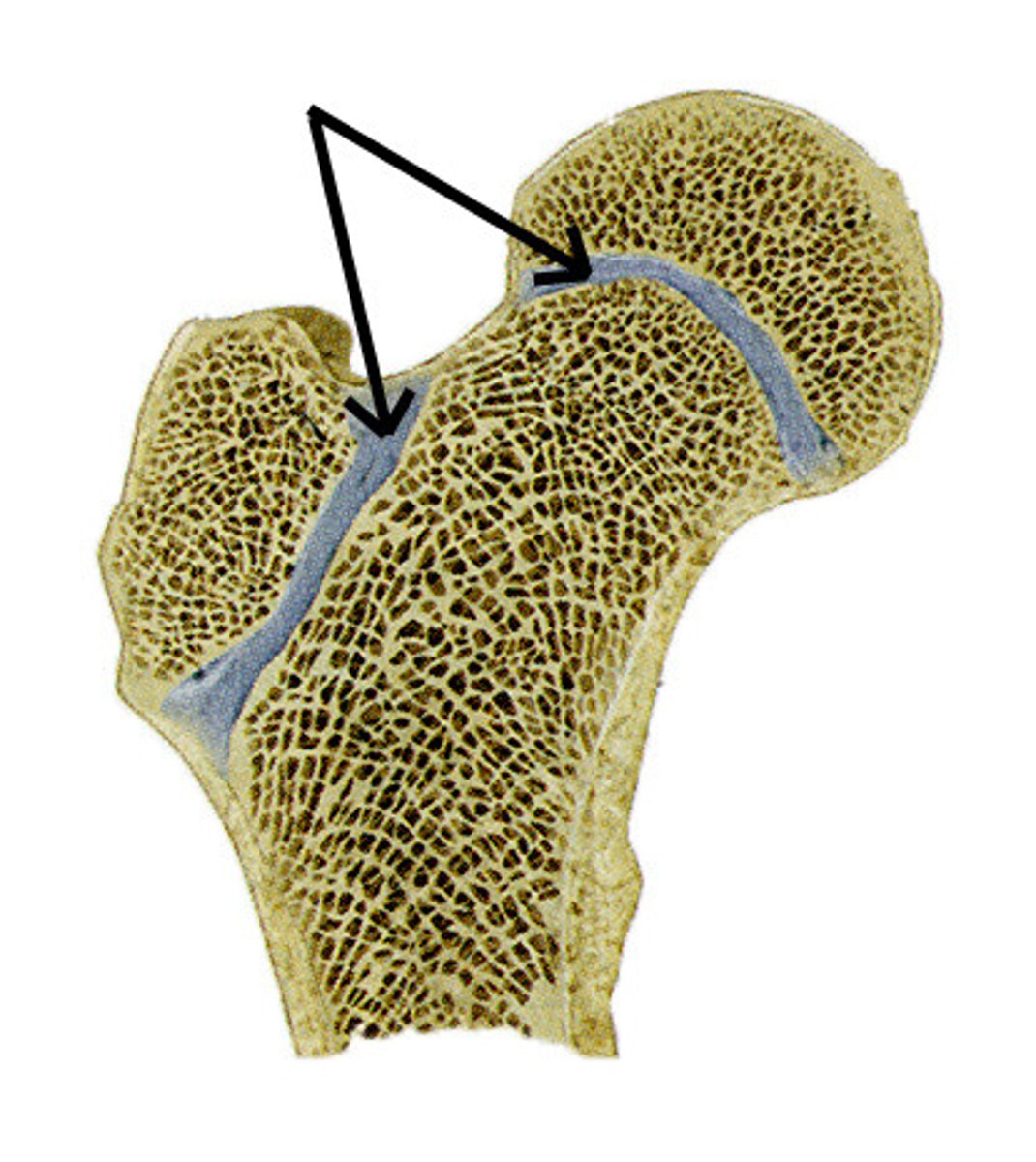
Metaphysis
Area where the epiphysis and diaphysis meet
Periosteum
a dense layer of vascular connective tissue enveloping the bones except at the surfaces of the joints (or the ends of the bones)
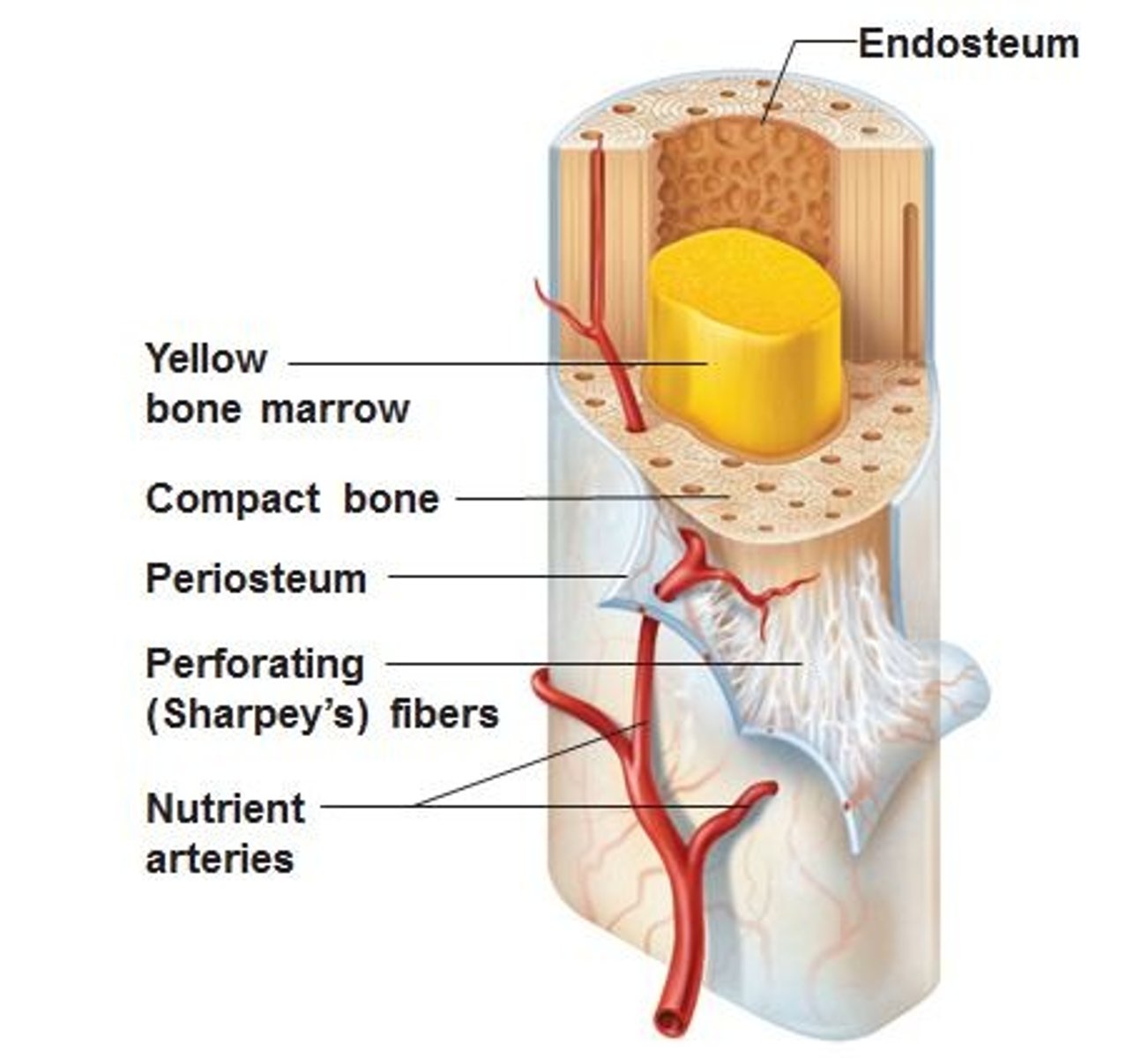
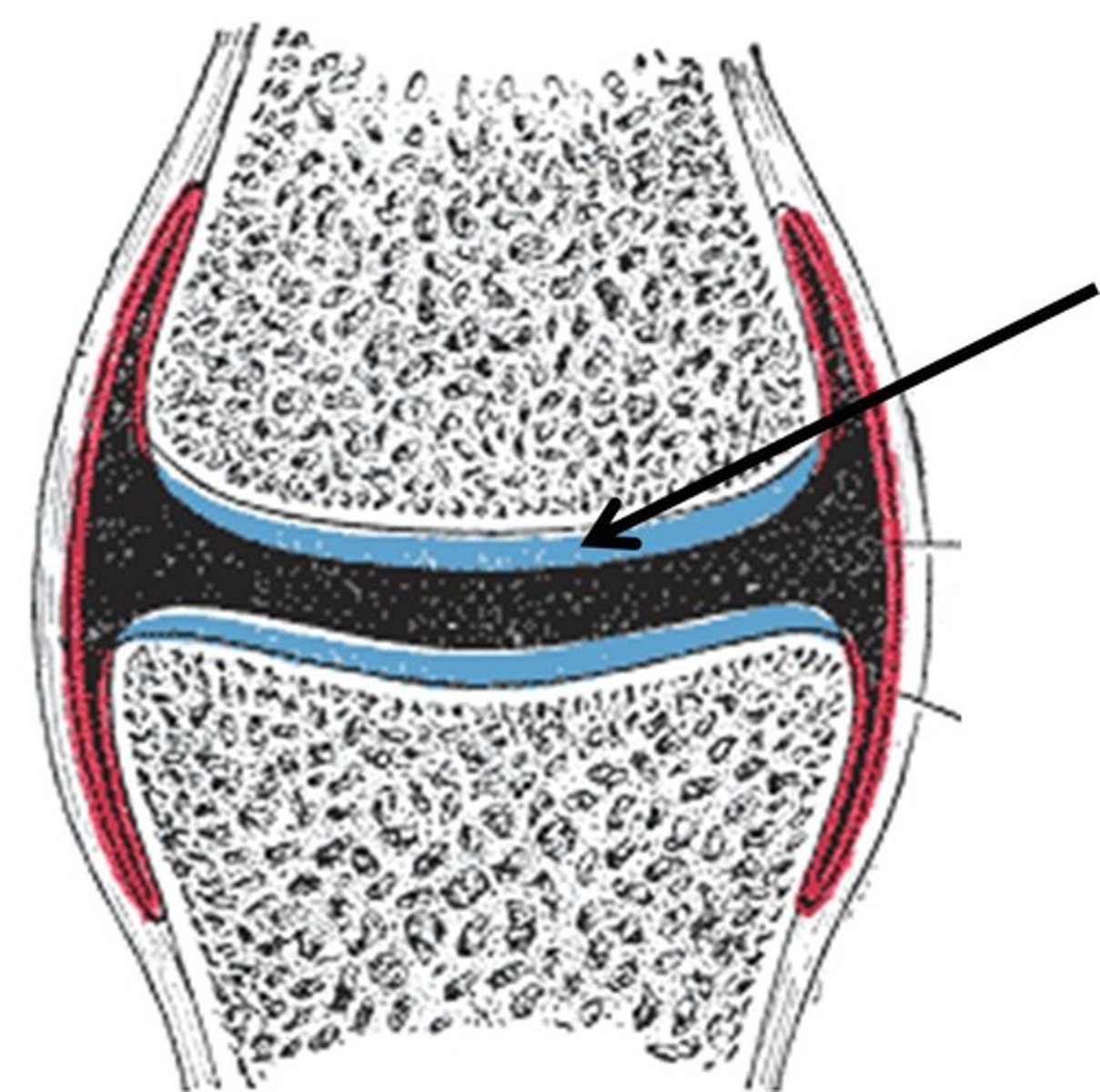
articular cartilage
covers the surfaces of bones where they come together to form joints
compact bone
dense, hard layers of bone tissue that lie underneath the periosteum
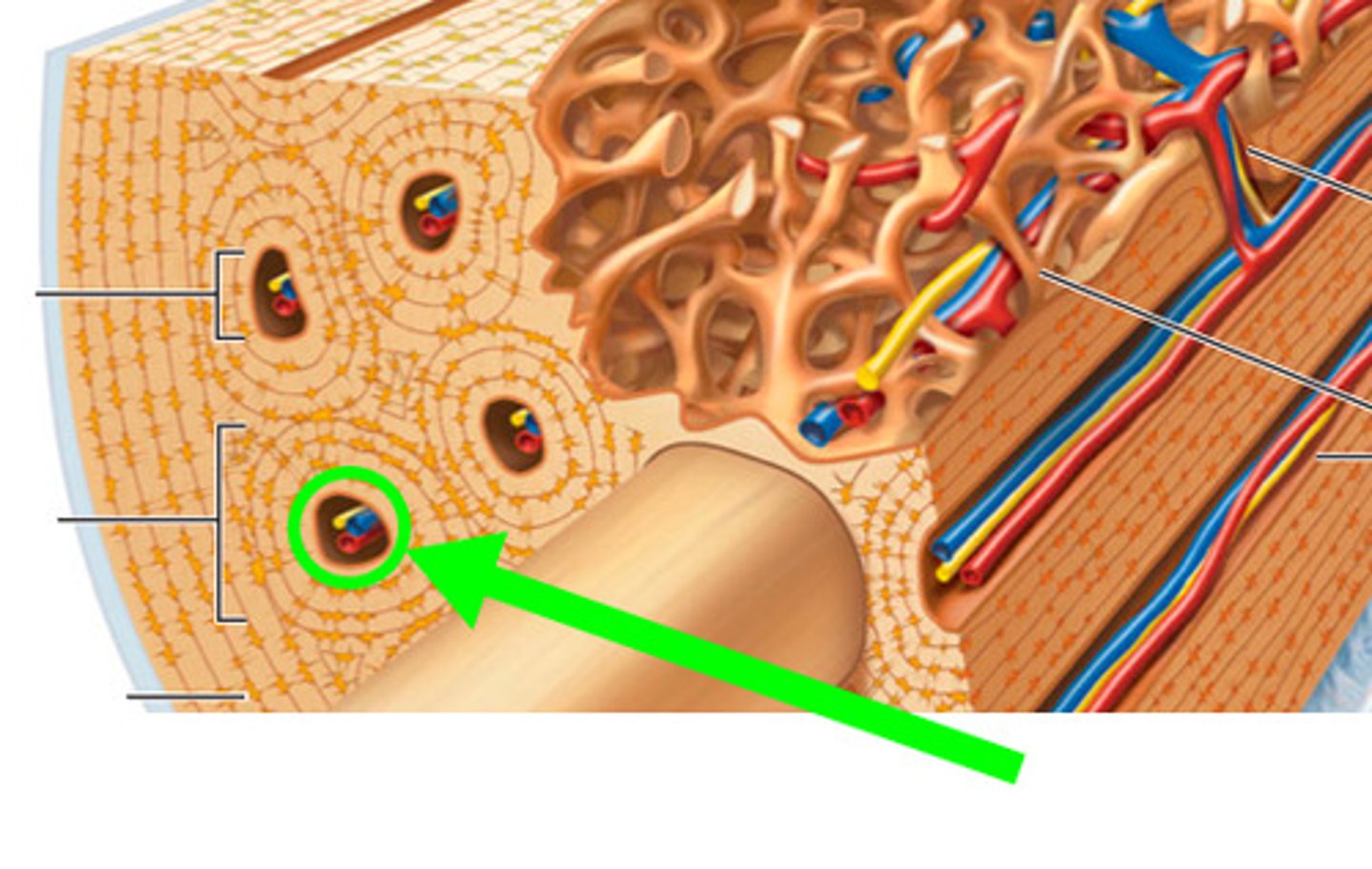
-contain Haversian canals
Haversian canal
a system of small canals containing blood vessels that bring oxygen and nutrients to the bone and remove waste products such as carbon dioxide
cancellous bone
spongy, porous, bone tissue in the inner part of a bone
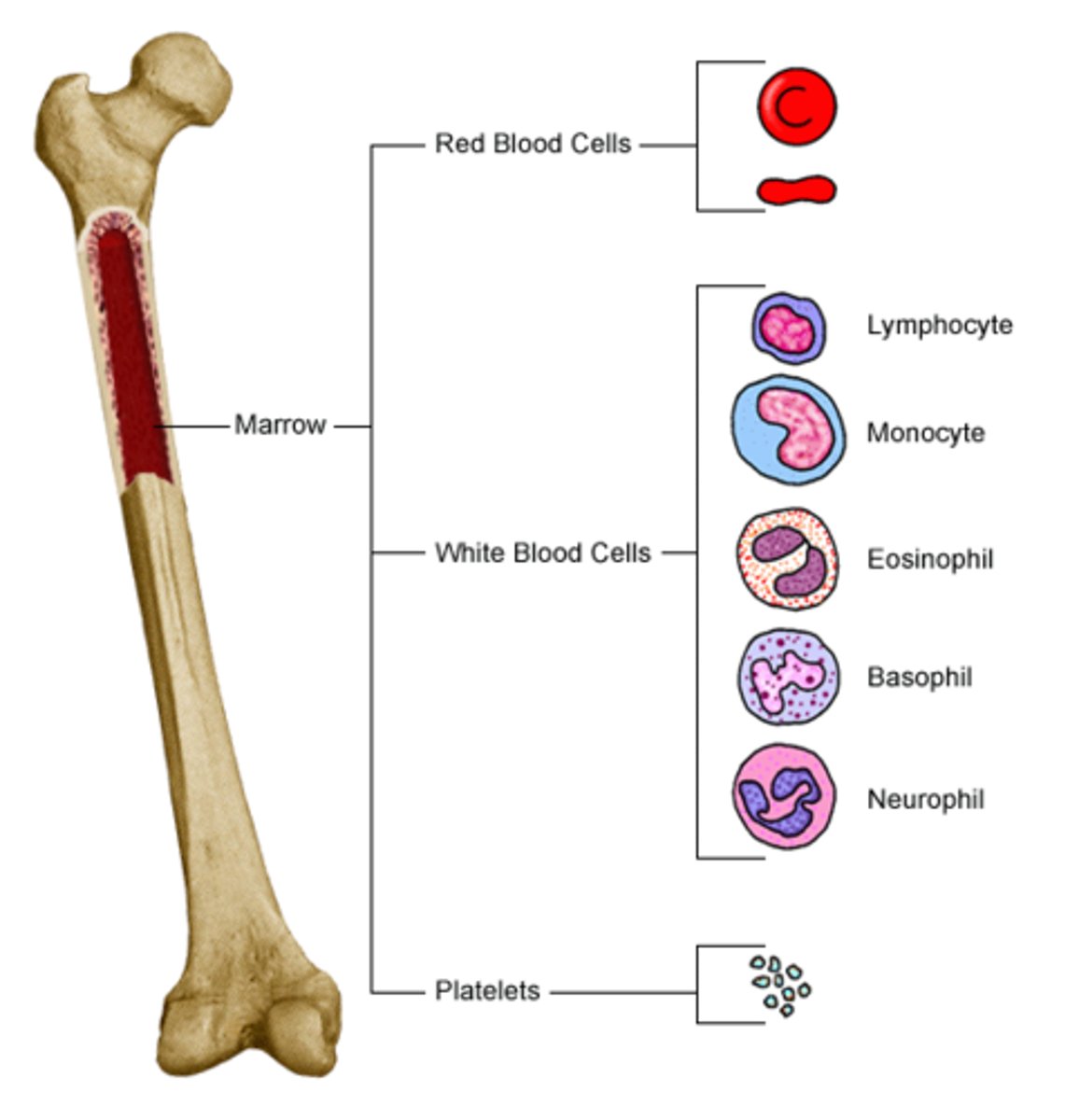
Hematopoiesis
is the production of all types of blood cells in the bone marrow
yellow bone
fatty tissue found in the medullary cavity of most adult long bones
-it is composed of mainly fat cells
red bone marrow
found in cancellous bone; site of hematopoiesis
-it is abundant in young children but decreases with age and is replaced by yellow marrow
bone process
enlarged area that extends from bones as an attachment for muscles, tendons, and ligaments
examples: bone head, condyle, epicondyle, trochanters, tuberosity
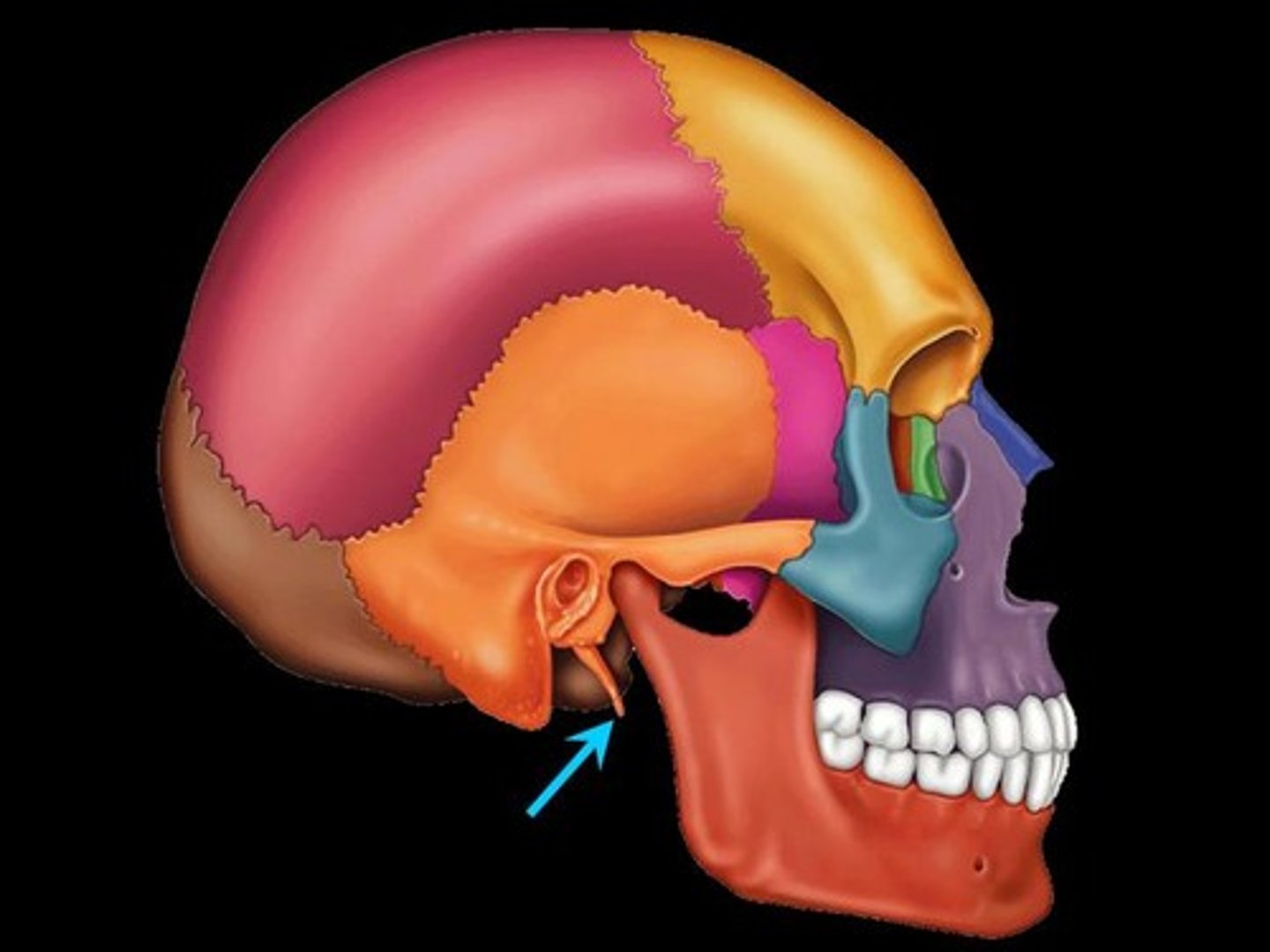
bone depression
opening or hollow region serving as a connection for bones, or passageways for blood vessels and nerves
Examples: fissure, foramen, fossa, sinus
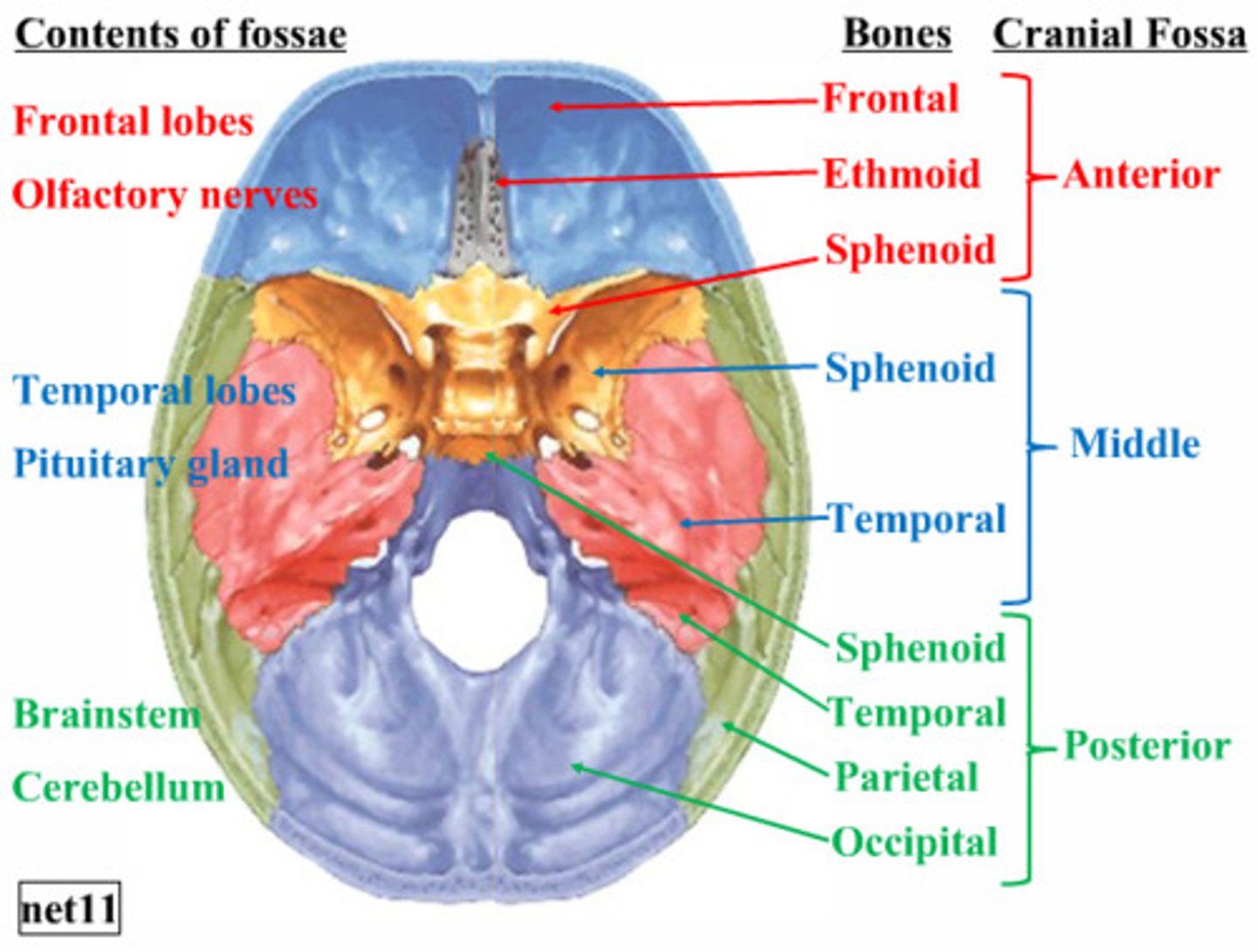
cranial bones
protect the brain and structures related to it, like sense organs
cranial bones are joined by sutures
skull bones: ethmoid, frontal, occipital, parietal, sphenoid, and temporal
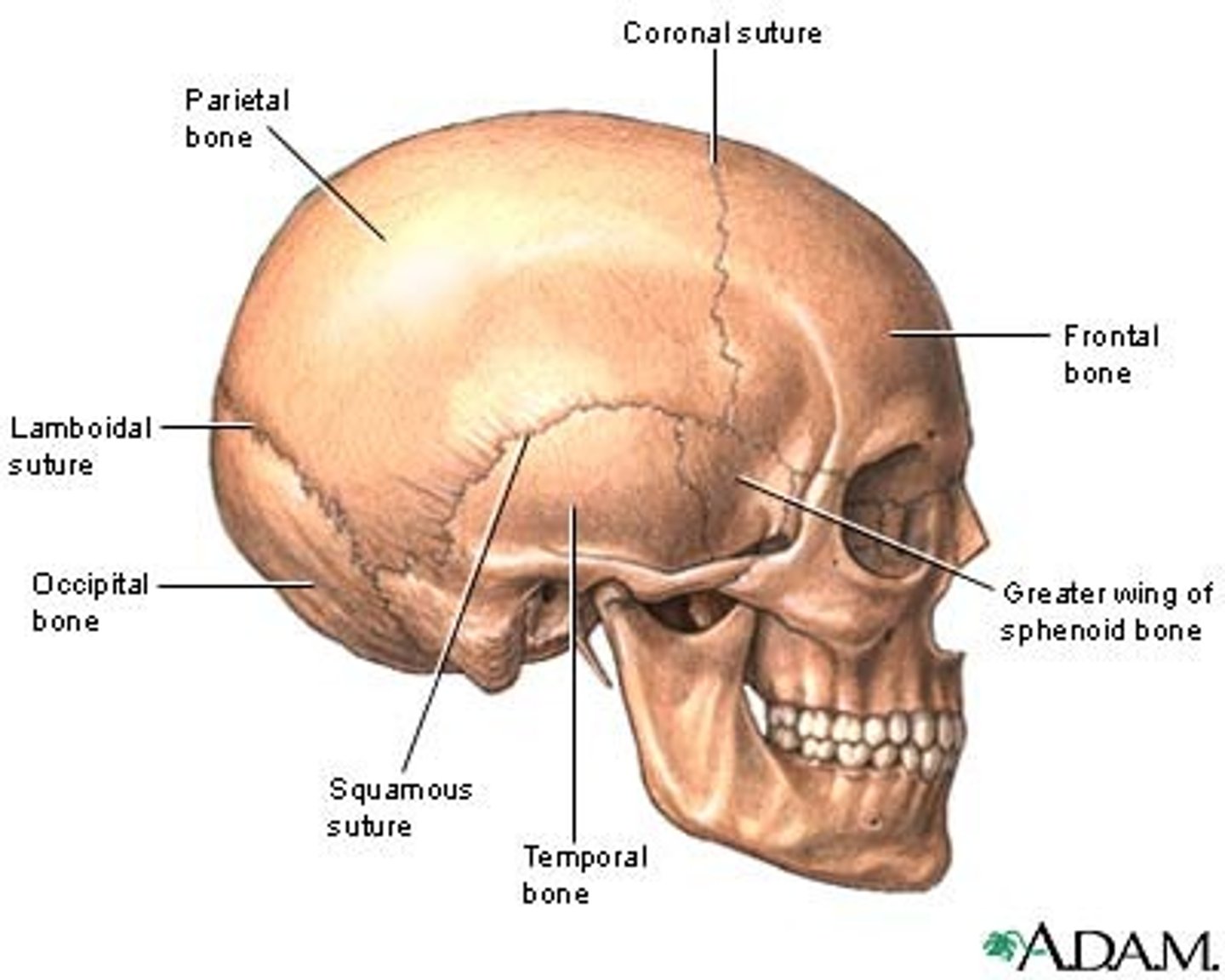
Sutures of the skull
immovable joint between bones, such as the skull(cranium)
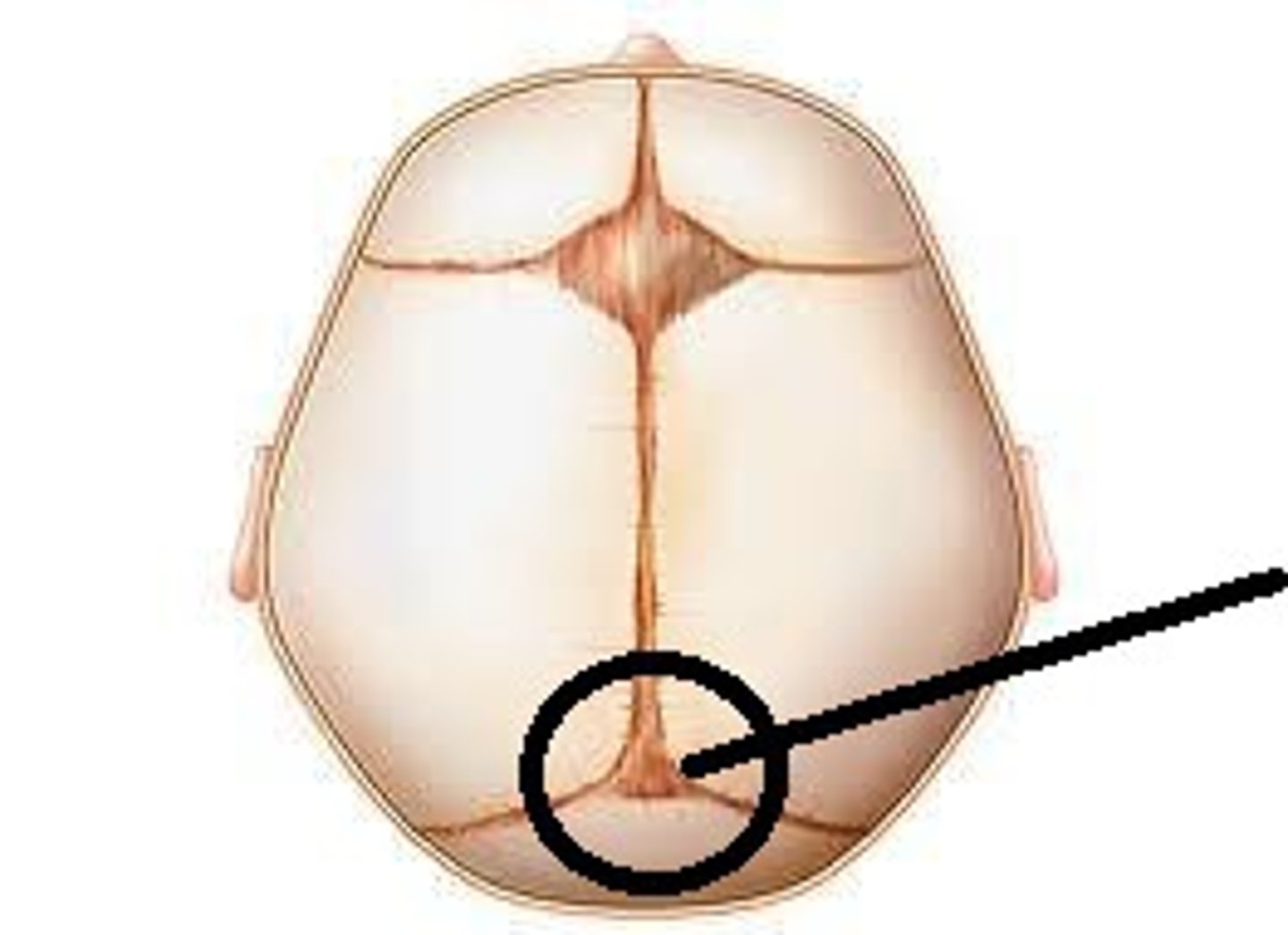
fontanelle/fontanel
A space covered by tough membrane between the bones of an infant's cranium, called a "soft spot"
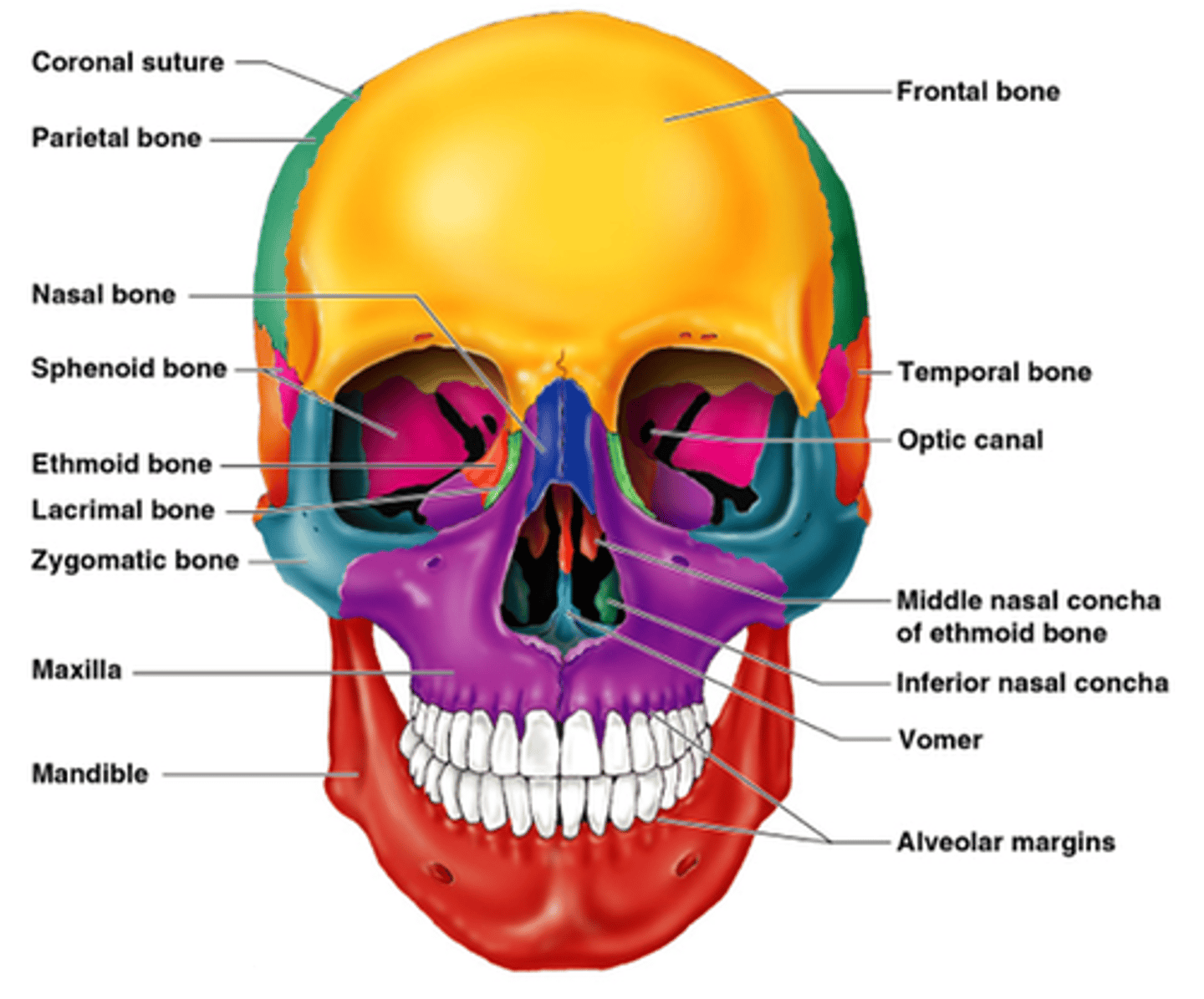
facial bones
bones of the face: lacrimal, mandibular, maxillary, nasal, vomer, and zygomatic
-all of the facial bones are joined together by sutures, except the mandible which makes it capable of movement
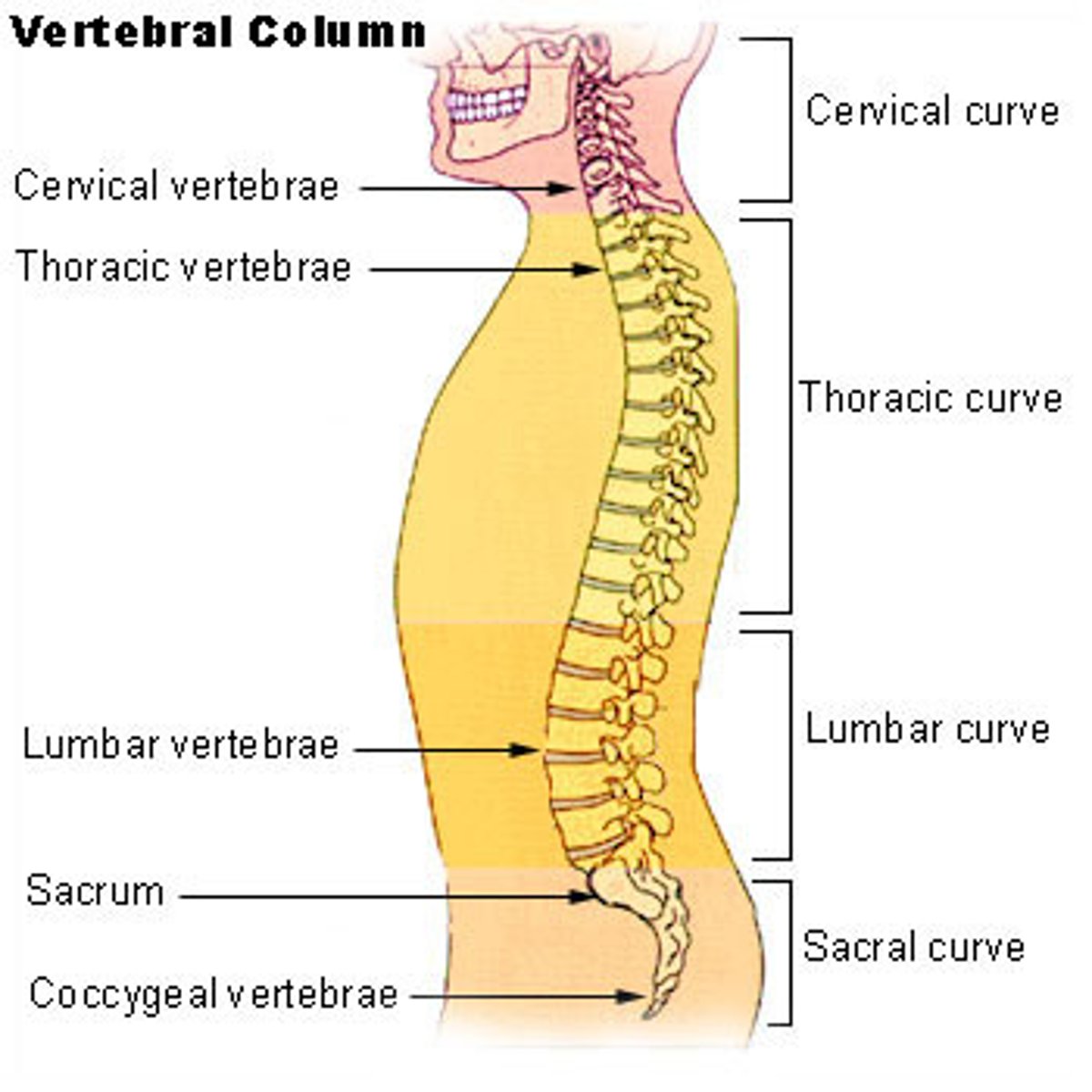
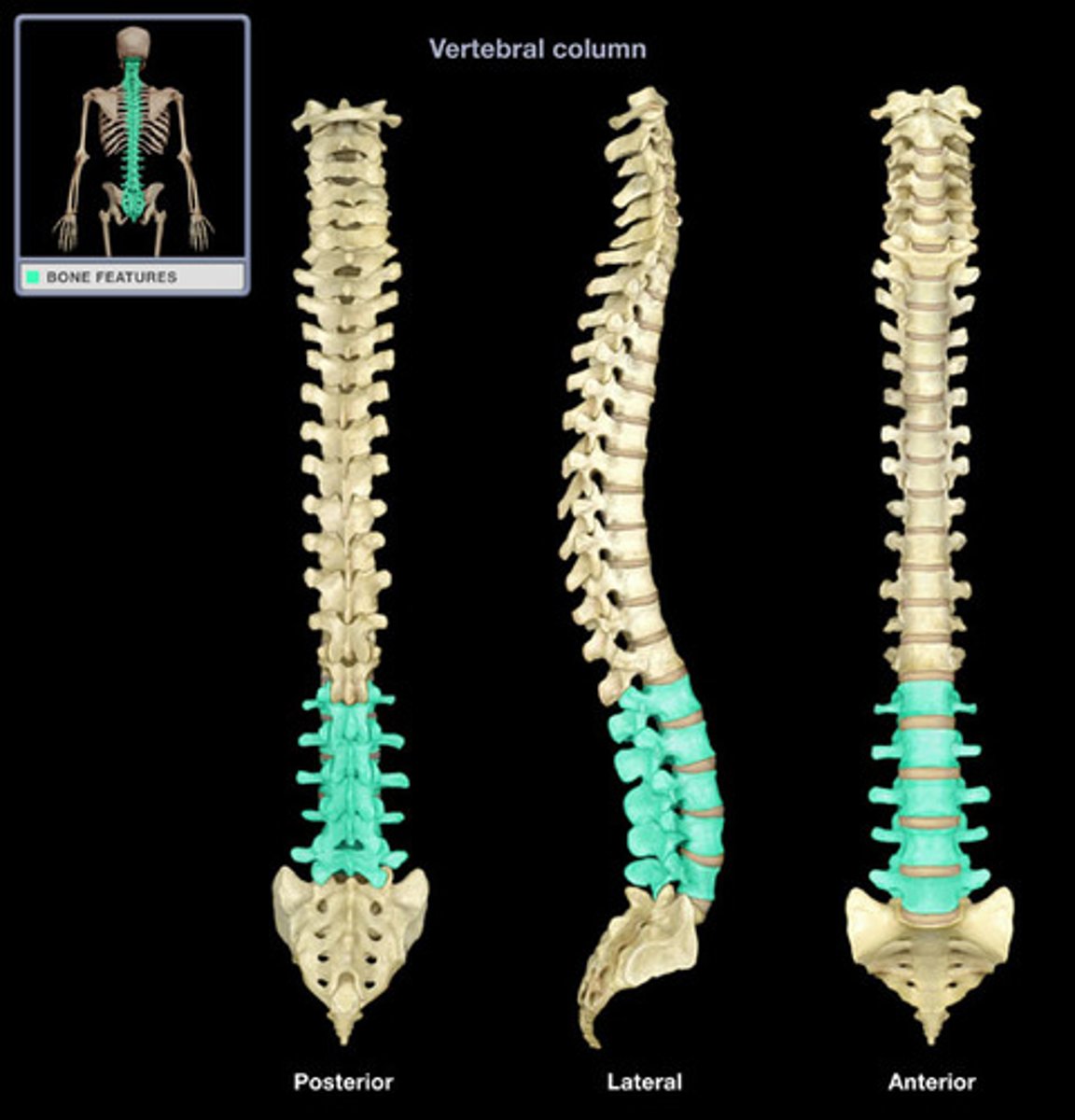
vertebral column
A series of irregularly shaped bones called vertebrae that houses the spinal cord.
-26 bones segments called vertebrae
-5 parts from the base of the skull to the tailbone
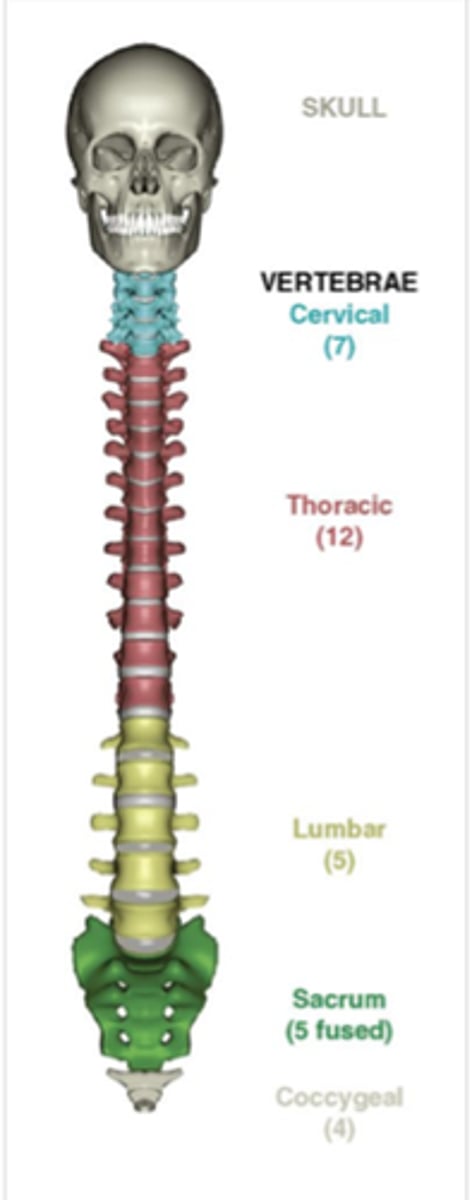
vertebral column
Cervical (7), Thoracic (12), Lumbar (5), Sacrum , Coccyx
sacral vertebrae
5 vertebrae which are fused to form the sacrum in the pelvis
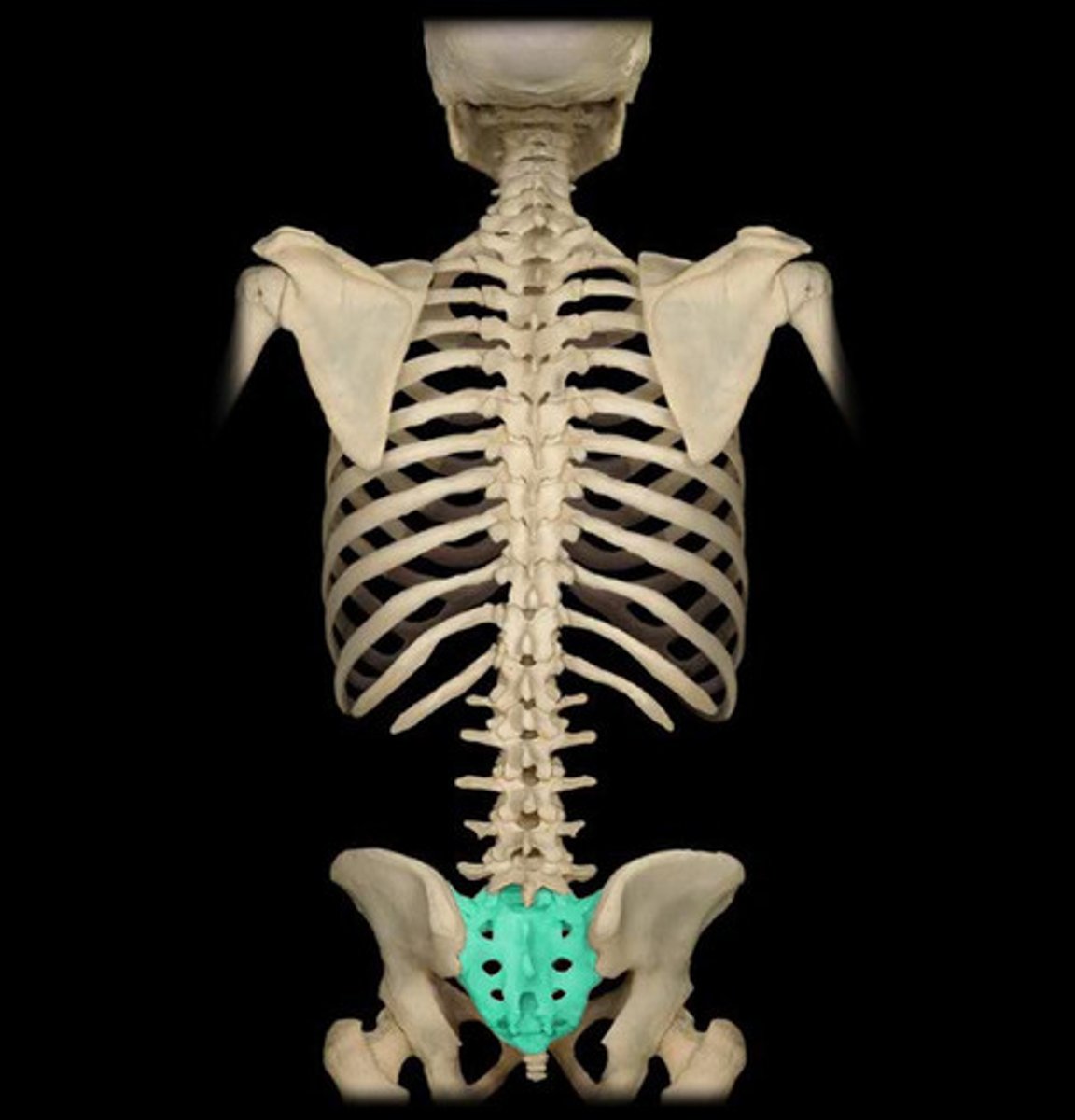
Coccyx
four vertebrae fused together to form the tailbone
thorax
chest cavity
bones of the thorax: clavicle, scapula, sternum, ribs
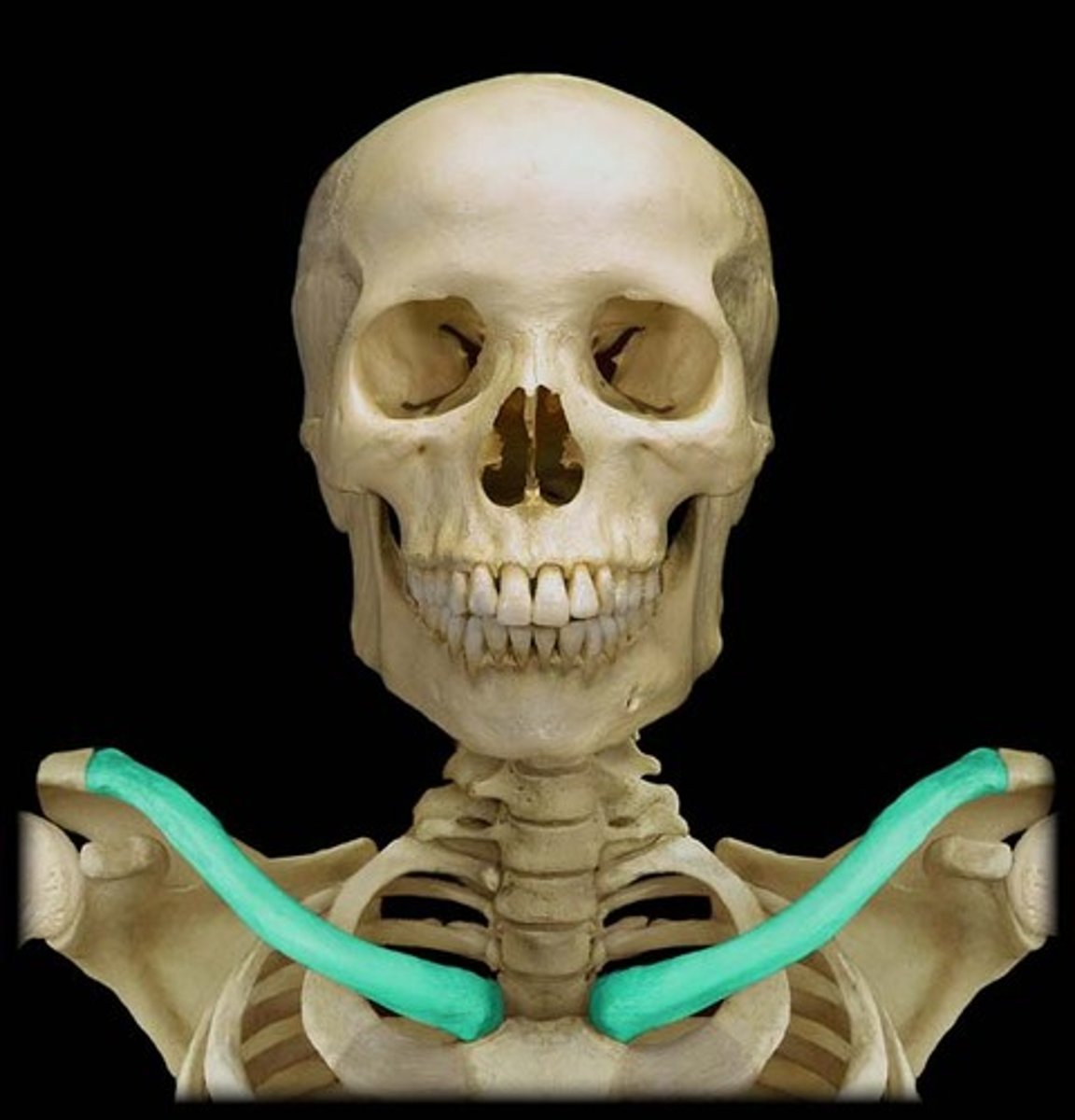
Clavicle
collar bone
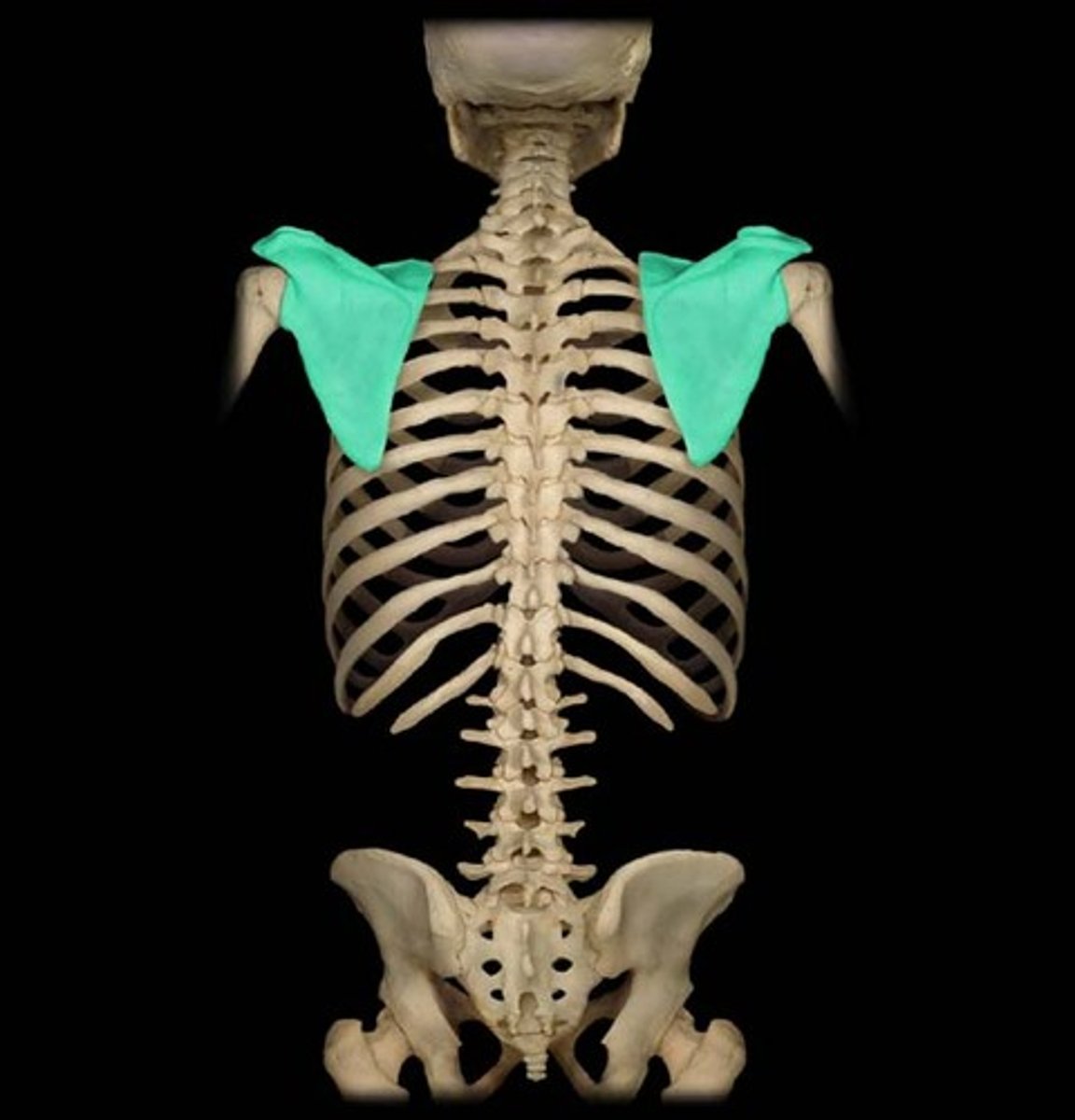
Scapula
shoulder blade
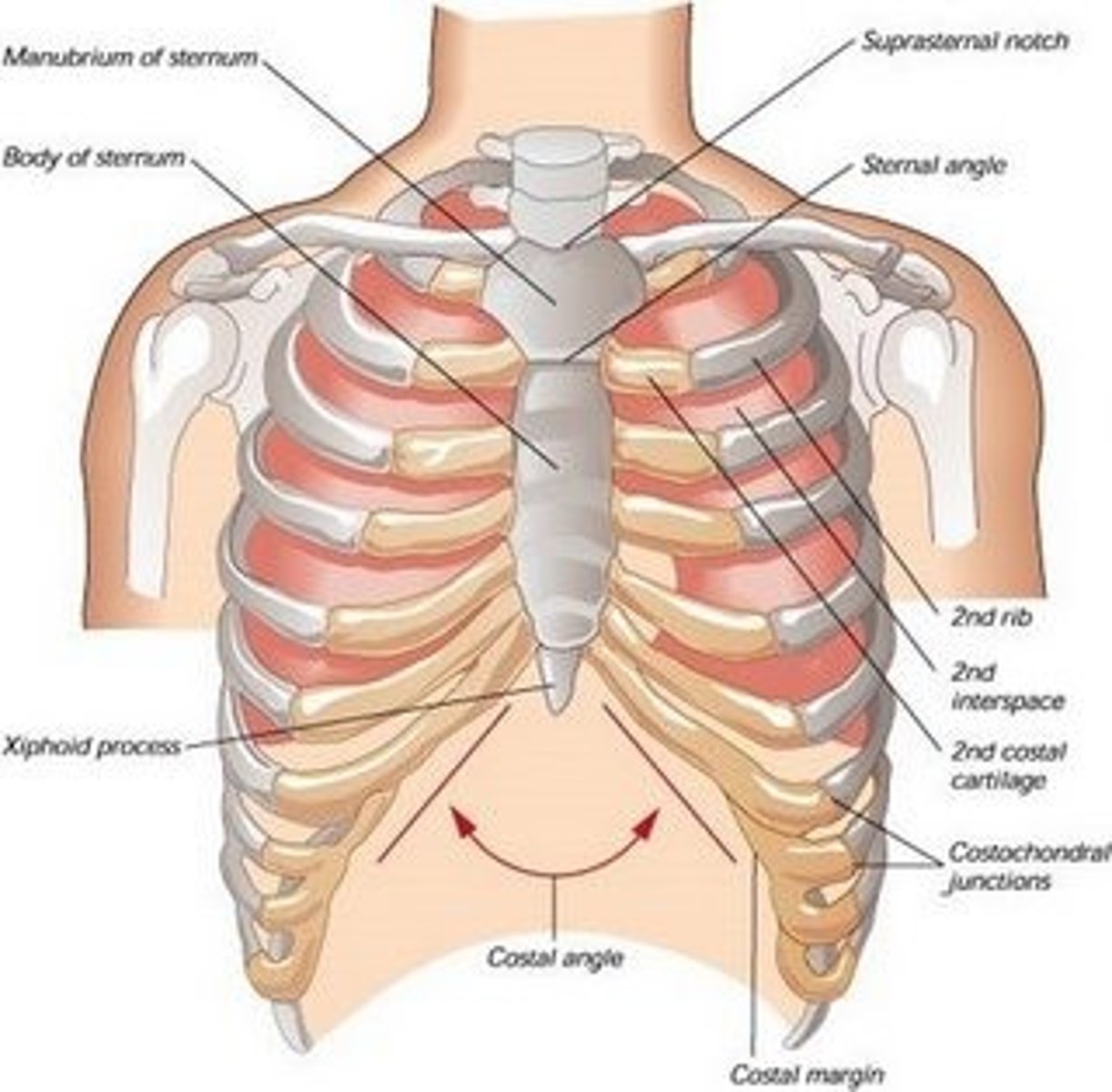
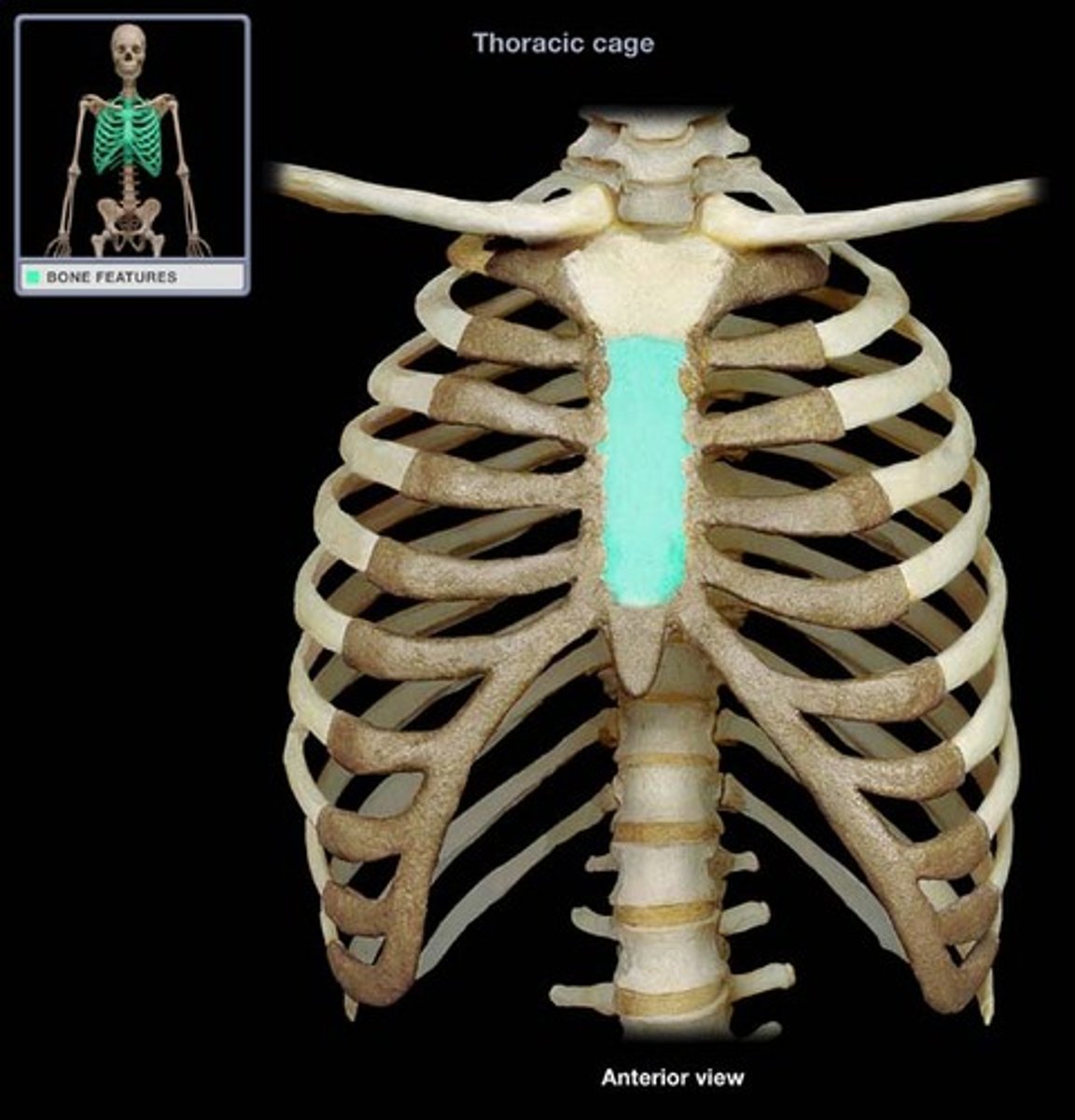
Sternum
the breastbone, forms the middle of the front of the rib cage and is divided into three parts
-the 3 parts are the manubrium, body, xiphoid process
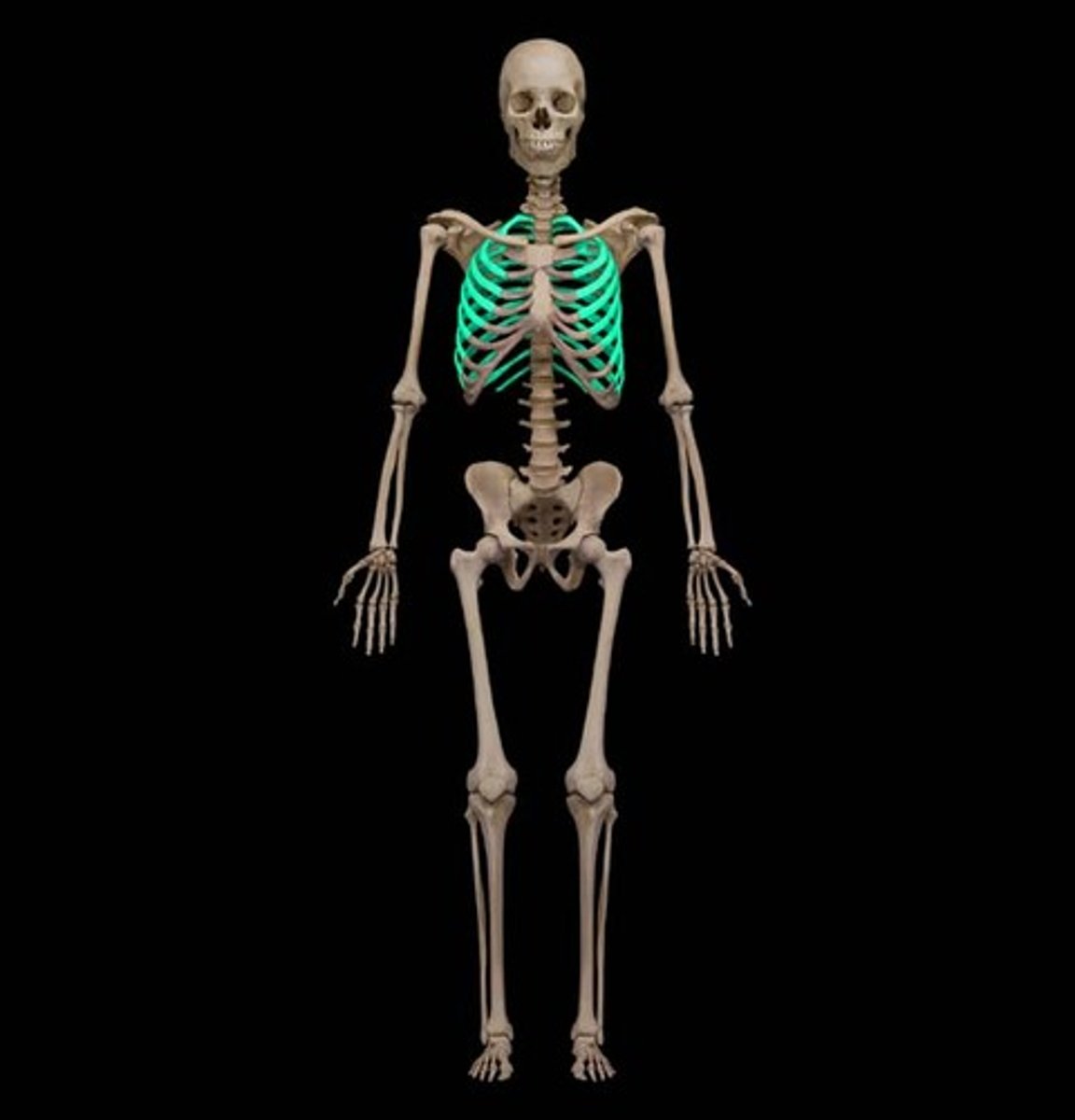
Ribs
The bones in the chest that protect the heart and lungs. There are 12 pairs
-Pairs 1-7 are true ribs they are joined anteriorly and posteriorly by costal catilage
8-10 are false ribs they do not join the sternum anteriorly but rather they attach to the 7th rib but do join the vertebral column posteriorly
11-12 are floating ribs because they are completely free at the anterior ends
Bones of the arm and hand
humerus, ulna, radius, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges
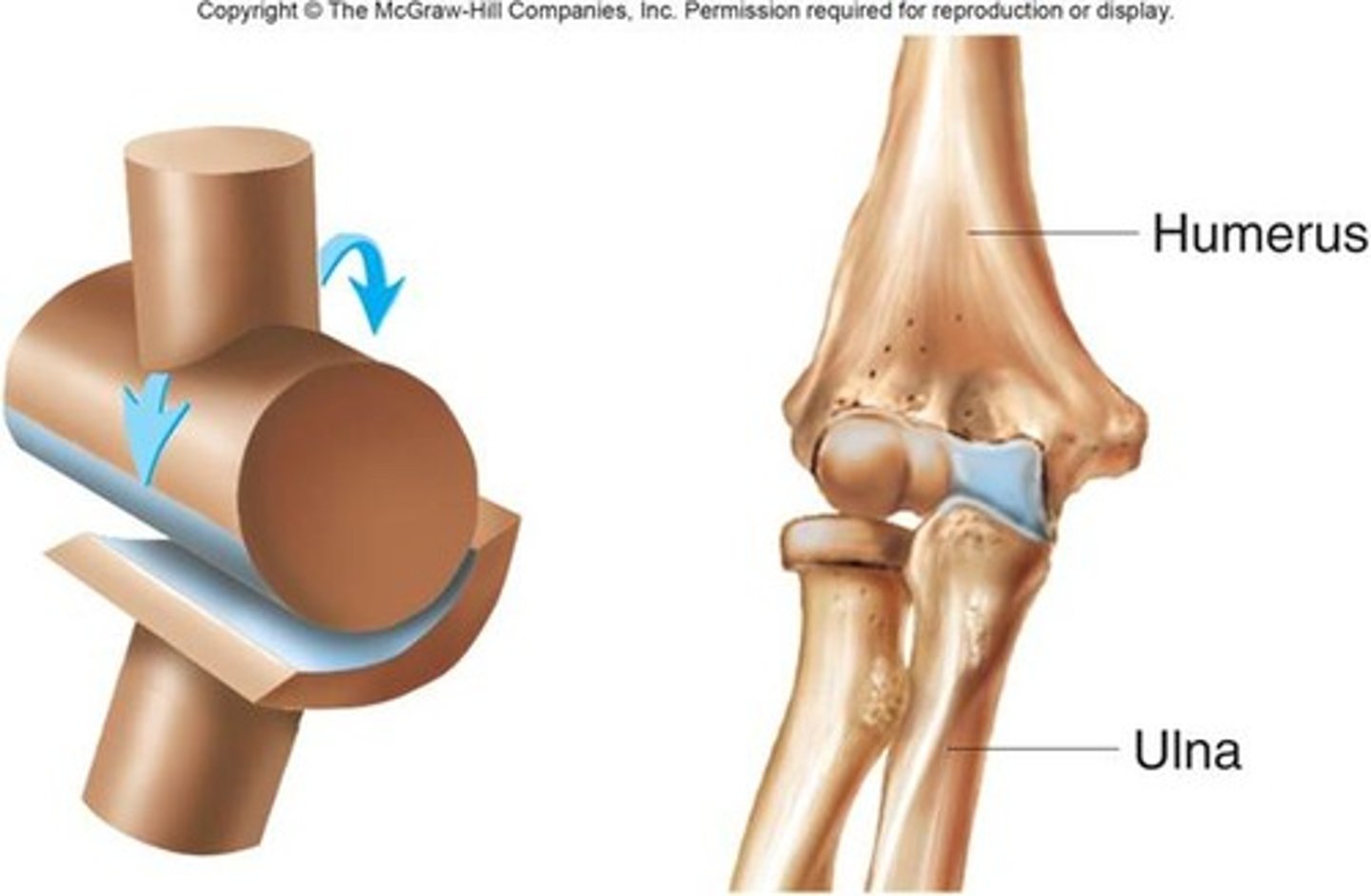
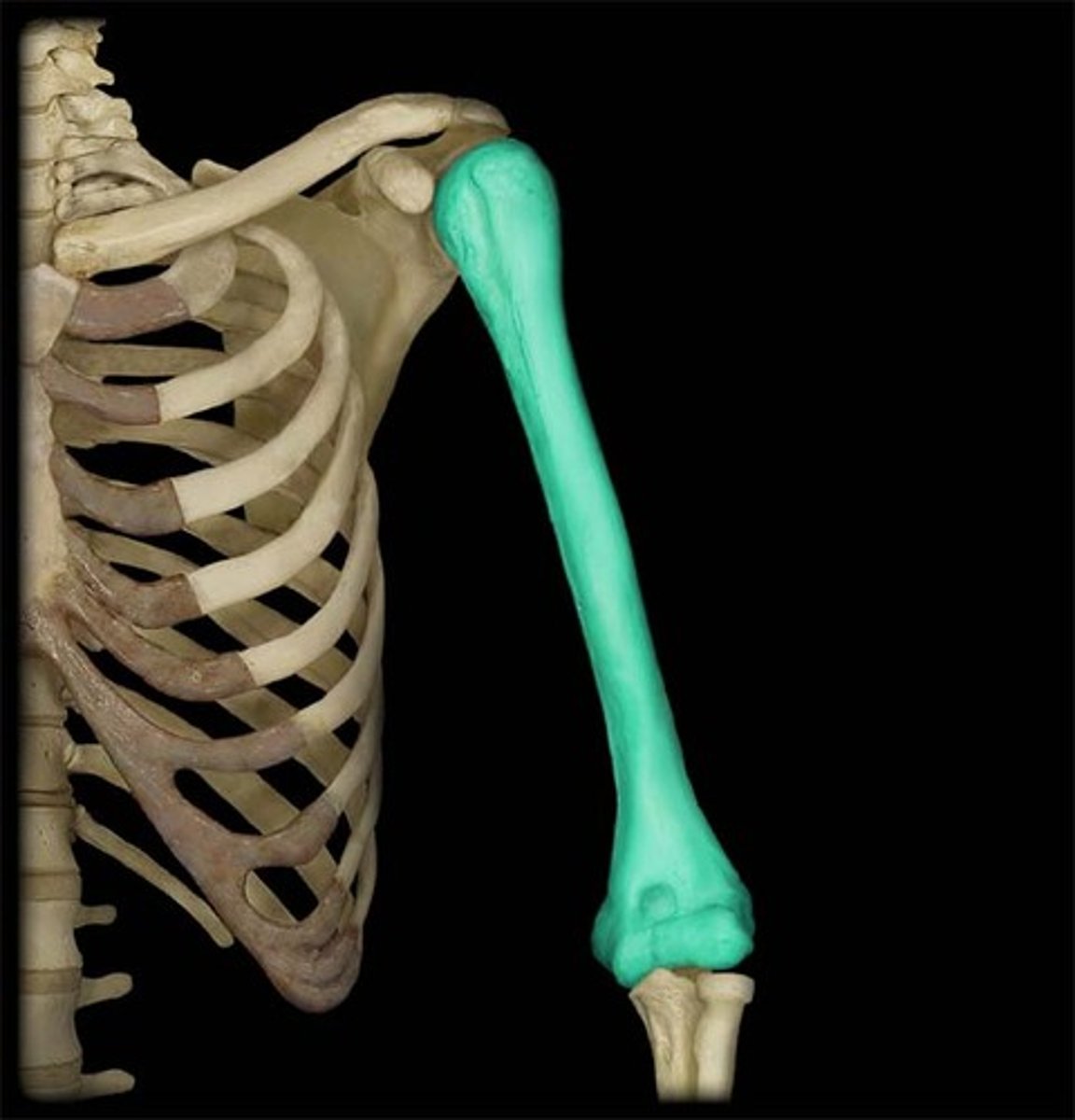
Humerus
upper arm bone
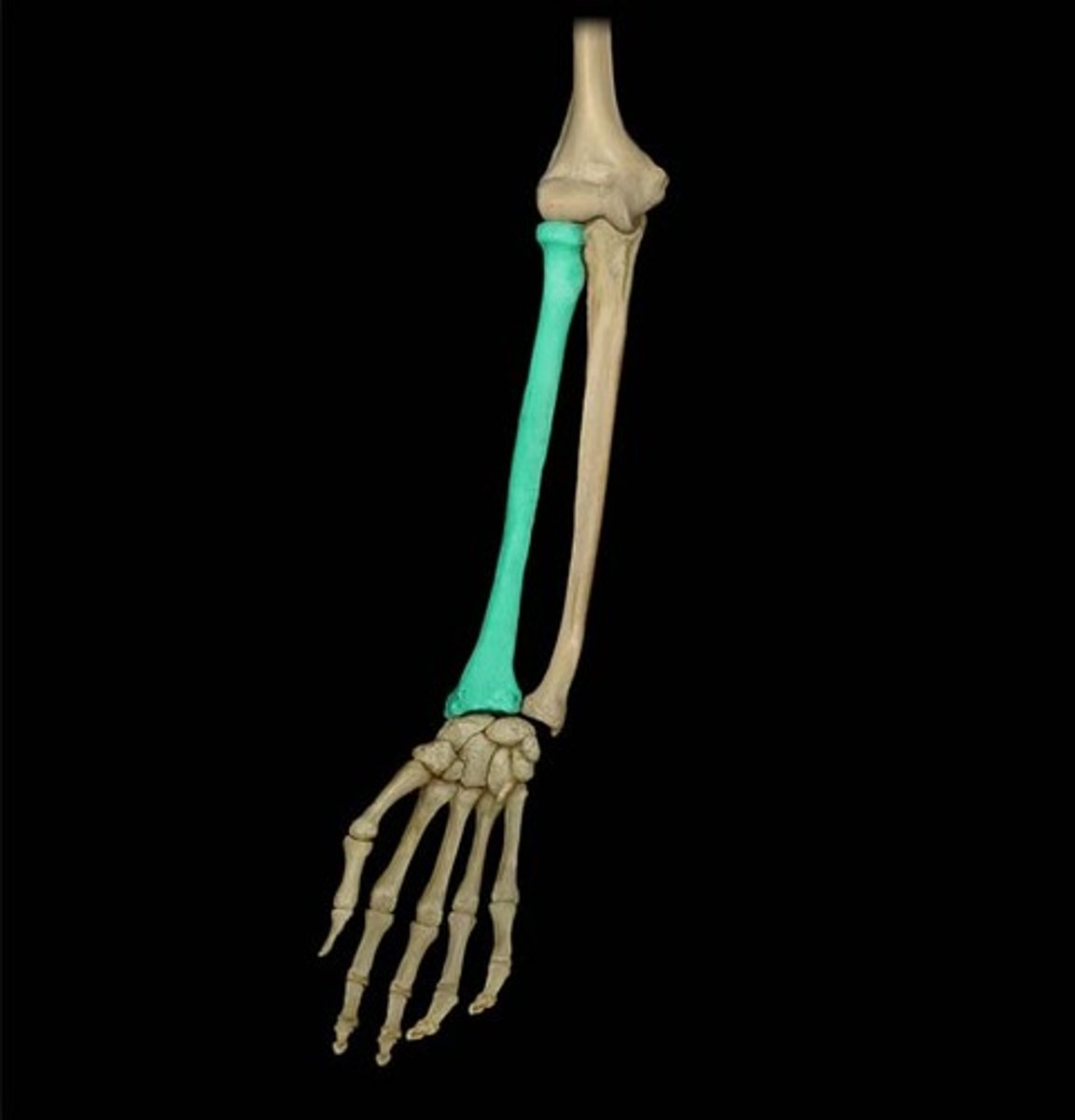
Ulna
Inner and larger bone of the forearm, attached to the wrist and located on the side of the little finger.
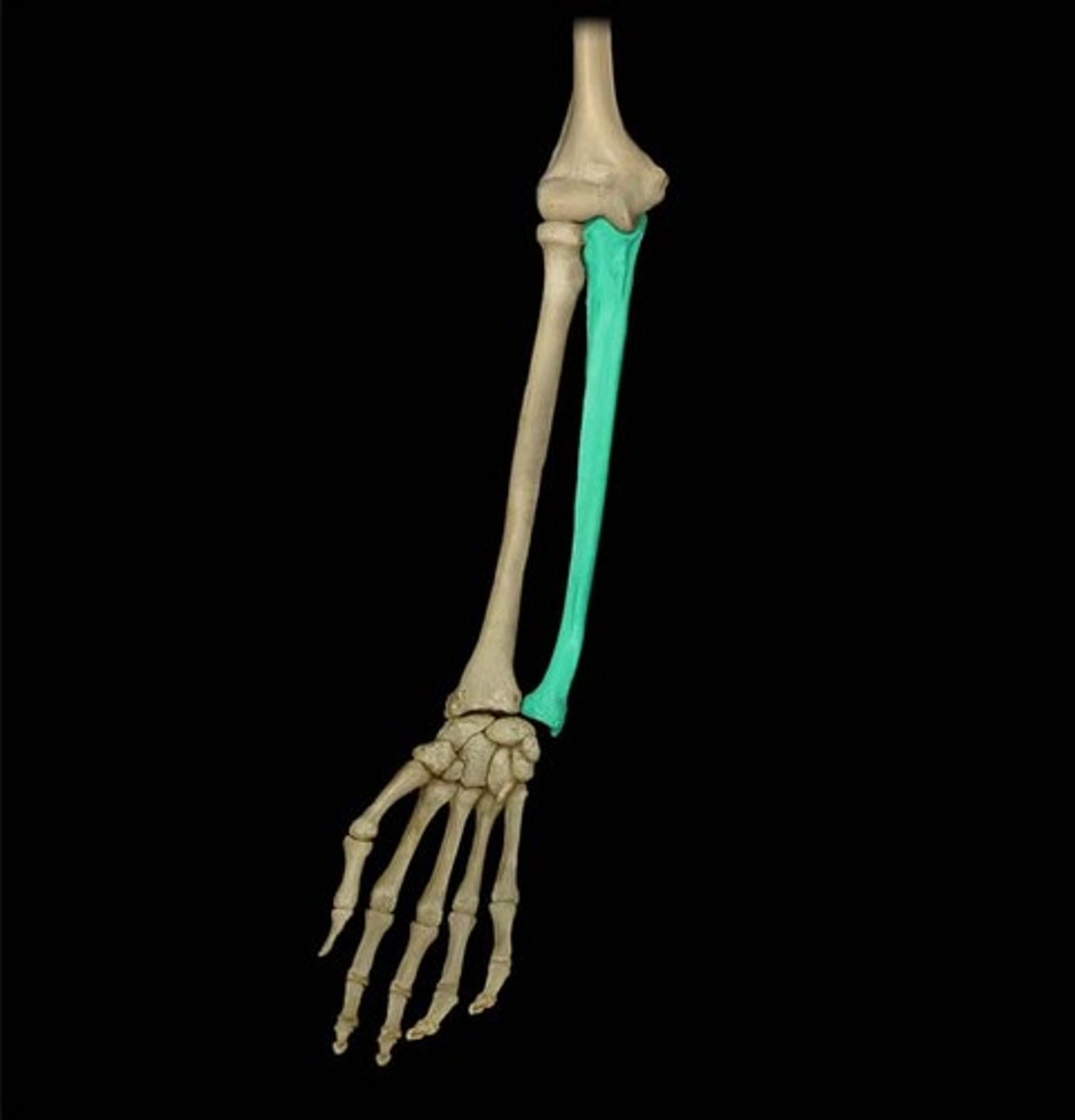
radius
lateral bone of the forearm
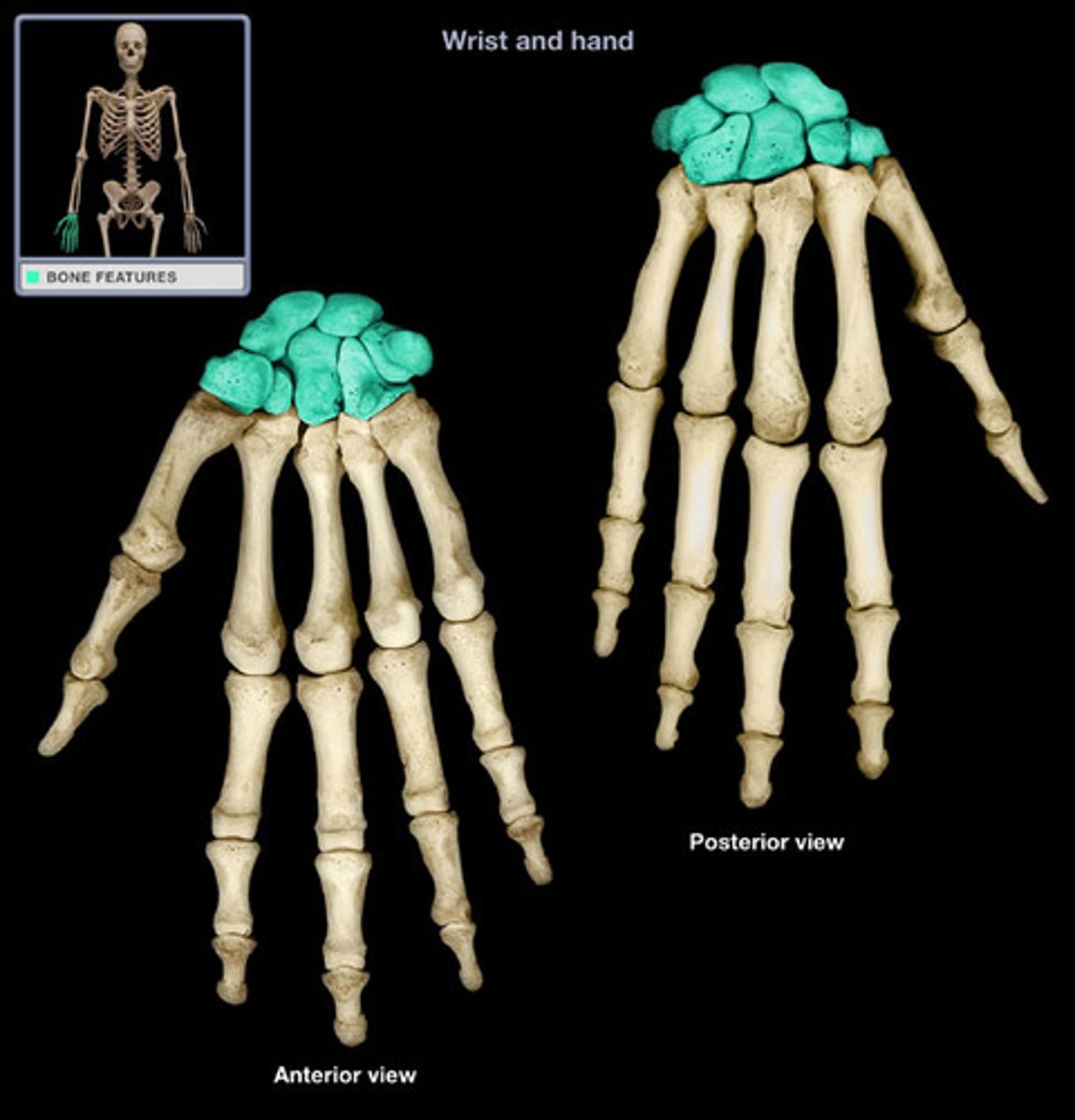
Carpals
wrist bones
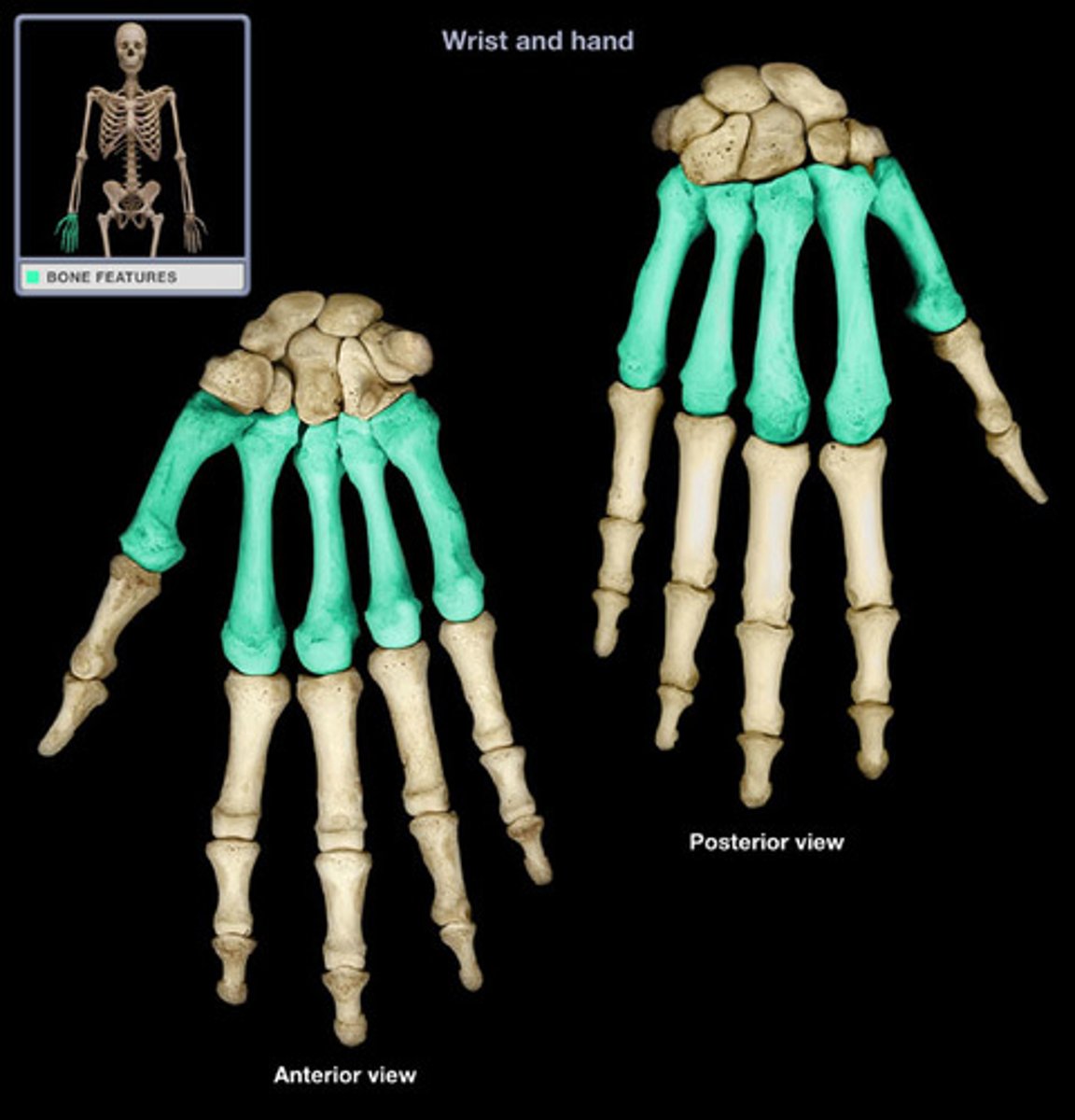
Metacarpals
5 bones of the palm of the hand
Phalanges
bones of the fingers
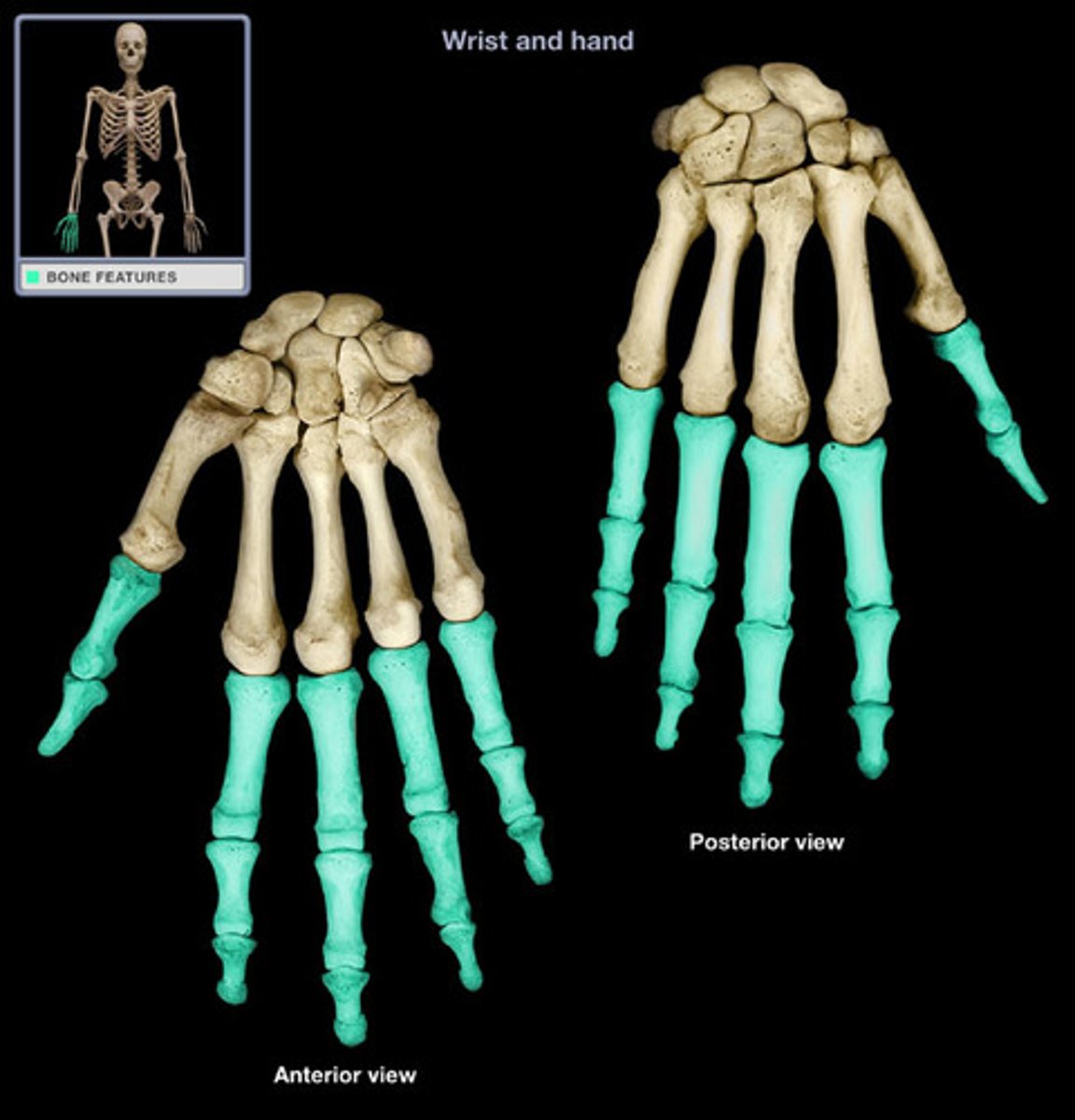
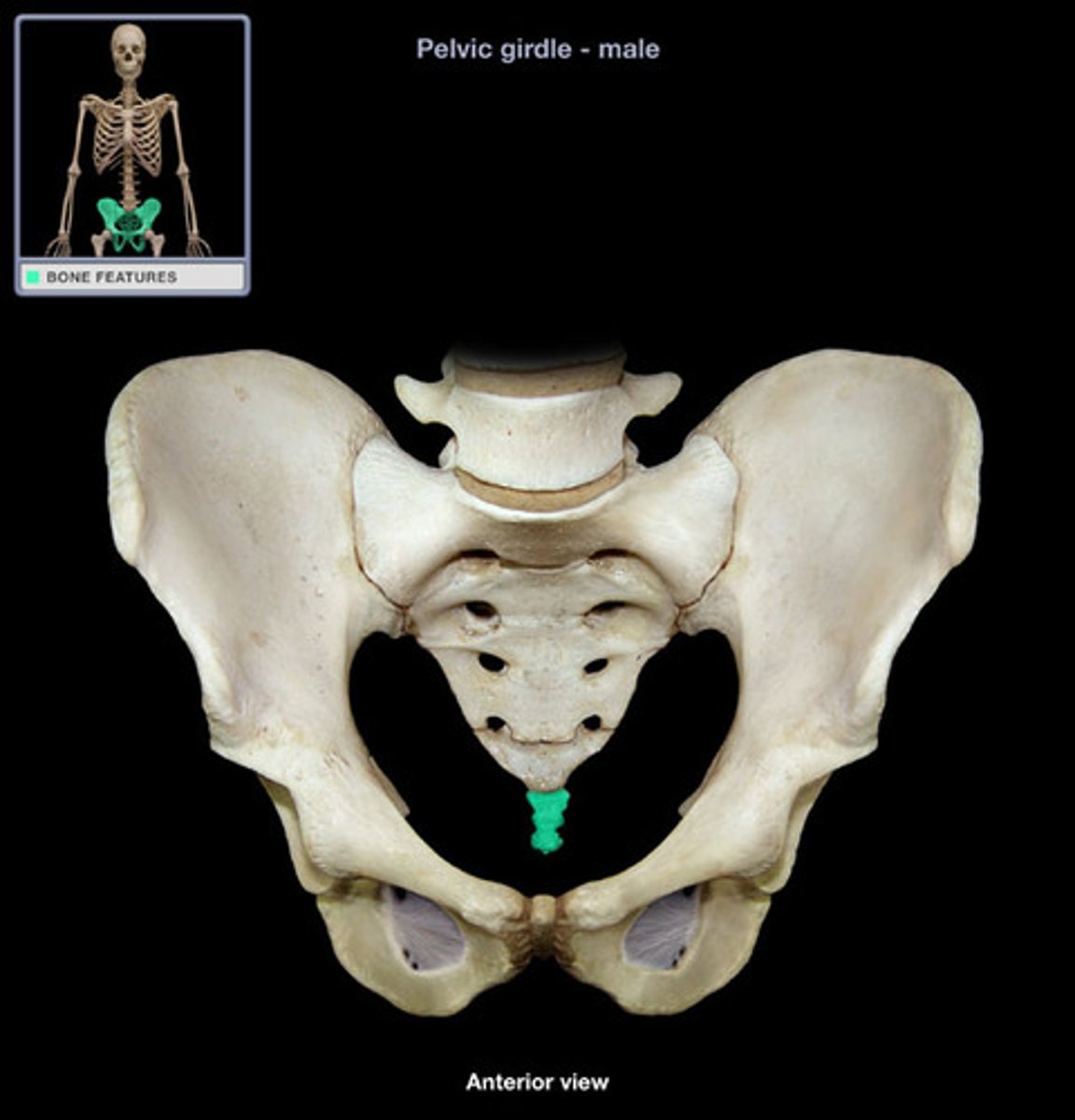
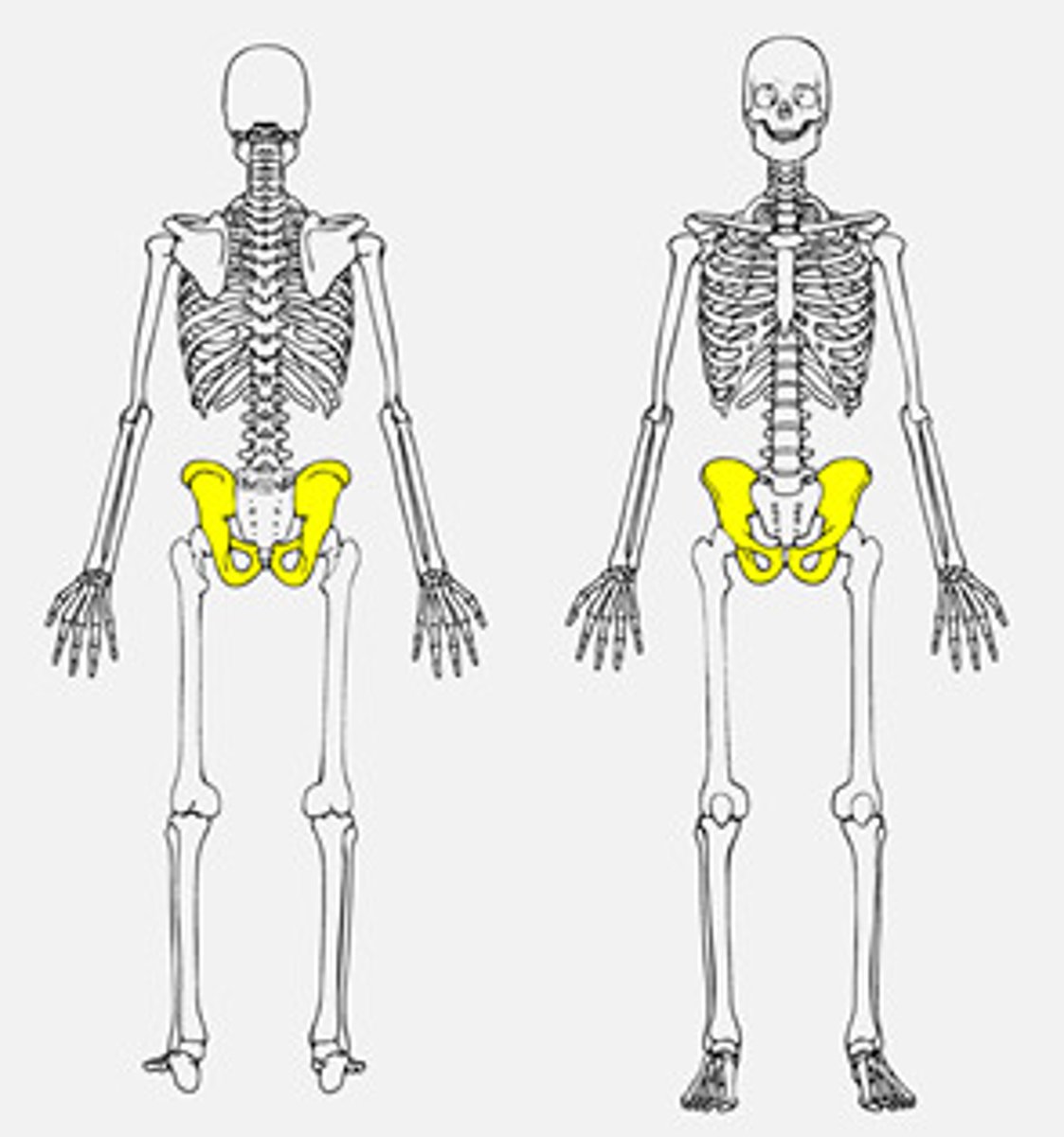
Bones of the pelvis
ilium, ischium, pubis
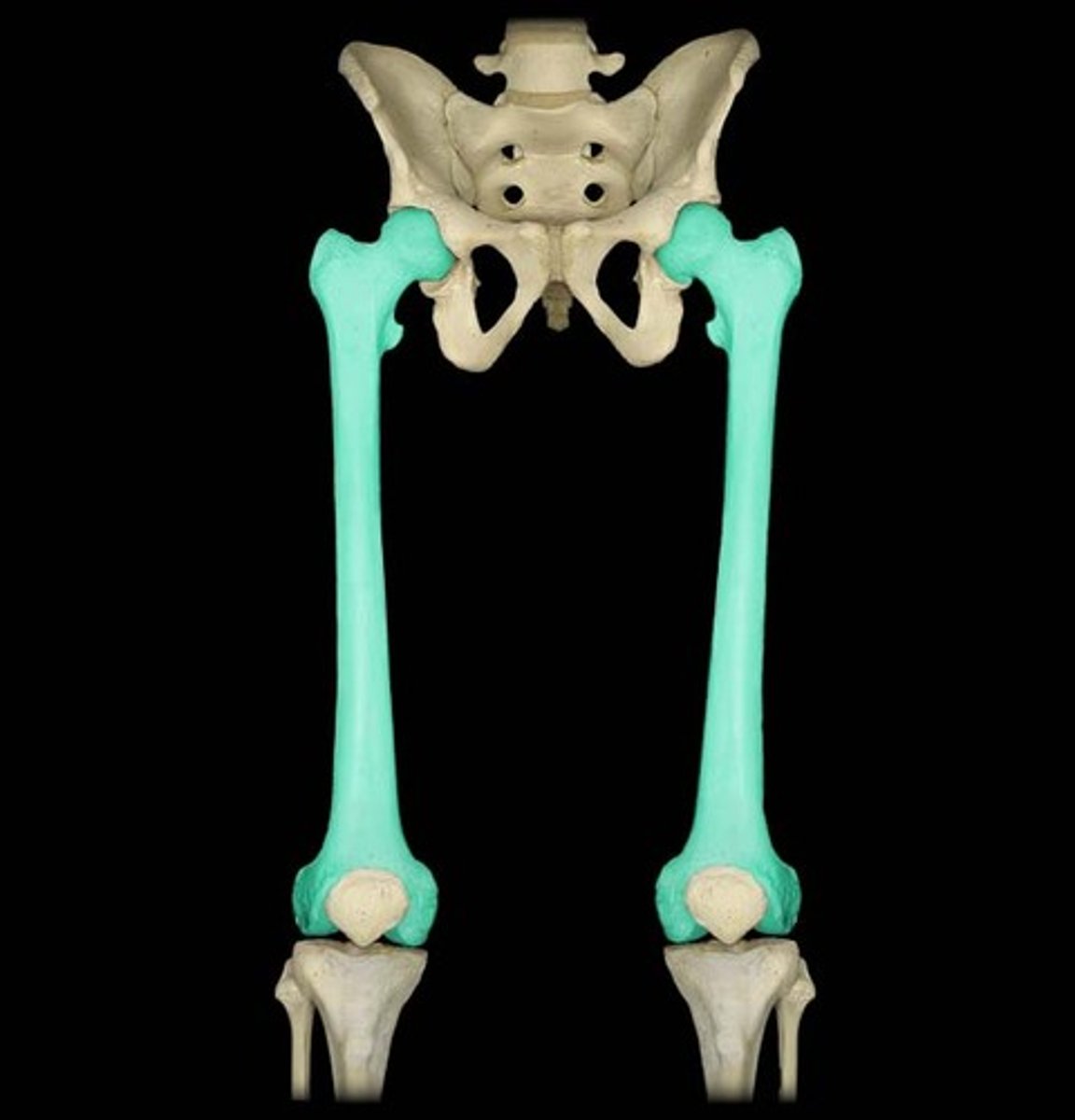
Bones of the leg and foot
femur, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges
Femur
thigh bone, it is the longest bone in the body
calc/o, calci/o
Calcium
kyph/o
humpback, hunchback
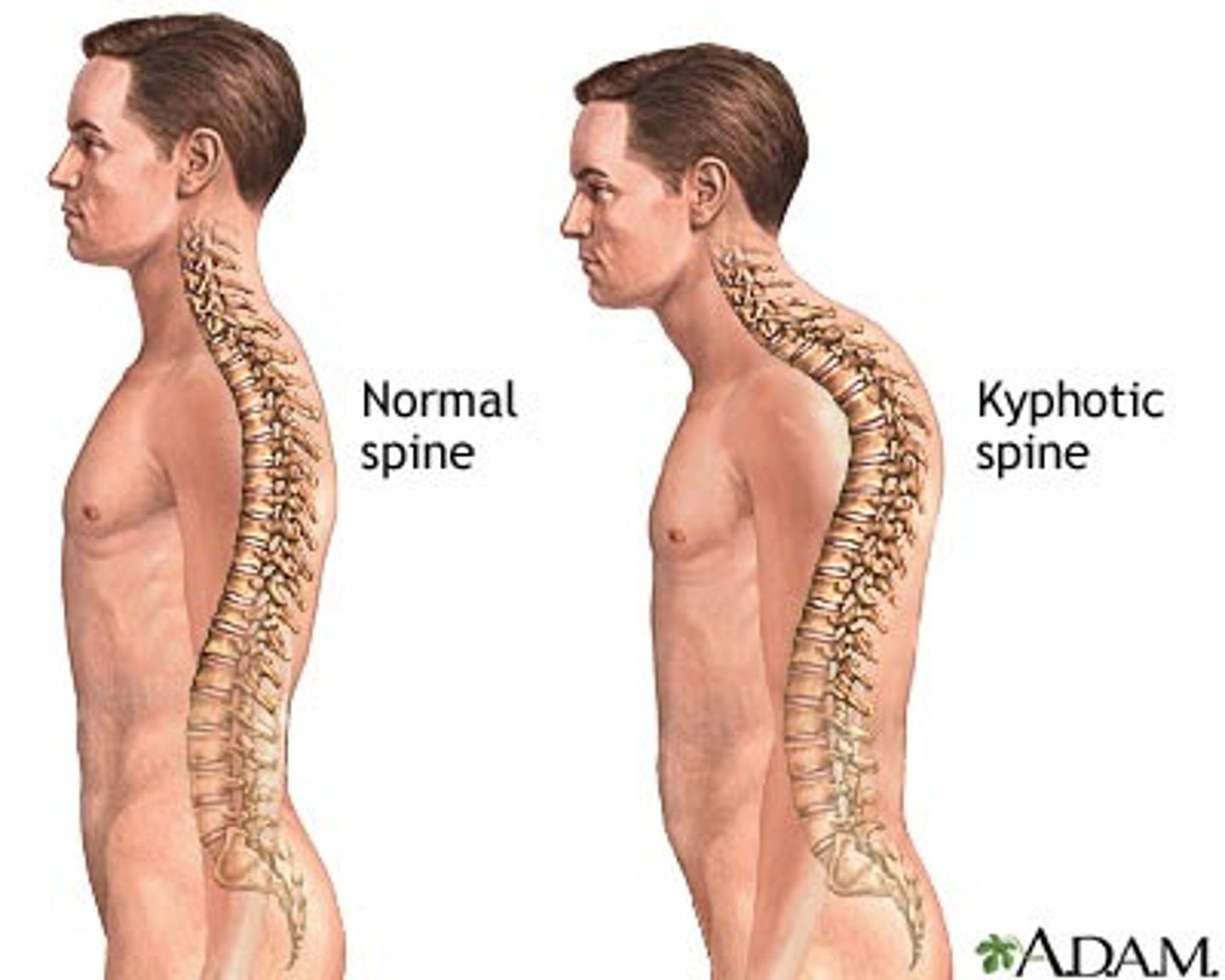
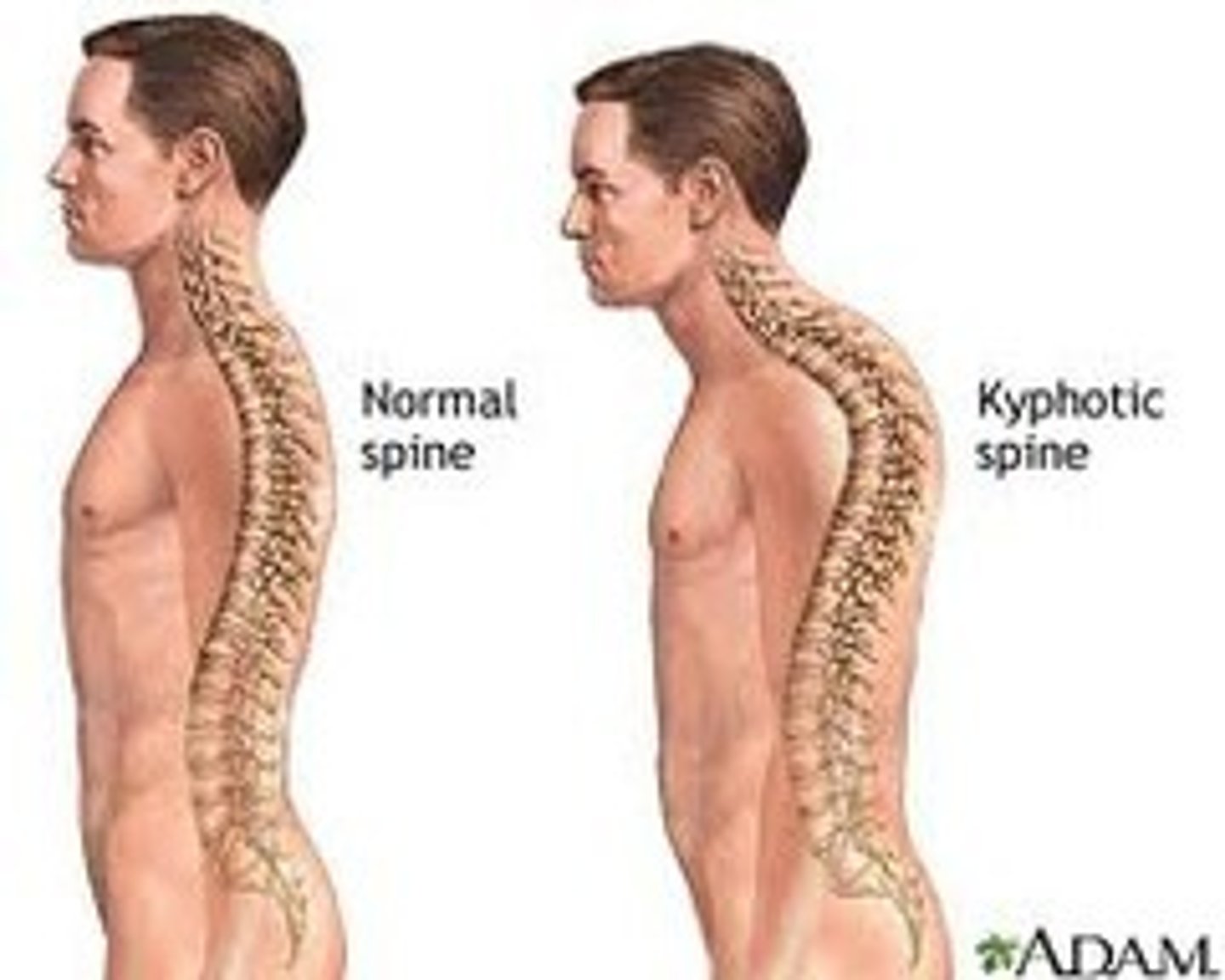
Kyphosis (hunchback)
An excessive curvature in the thoracic portion of the vertebral column.
-causes reduced height, may lead to pressure on the spinal cord or peripheral nerves
lamin/o
lamina (part of vertebral arch)
lord/o
curve, swayback (anterior curvature in the lumbar region) lordosis
lumb/o
loins (lower back)
myel/o
bone marrow
oste/o
bone
orth/o
straight
(think orthodontist straightens teeth)
osteogenesis imperfecta
inherited condition when bone formation is incomplete, leading to fragile, easily broken bones
scoli/o
crooked, bent
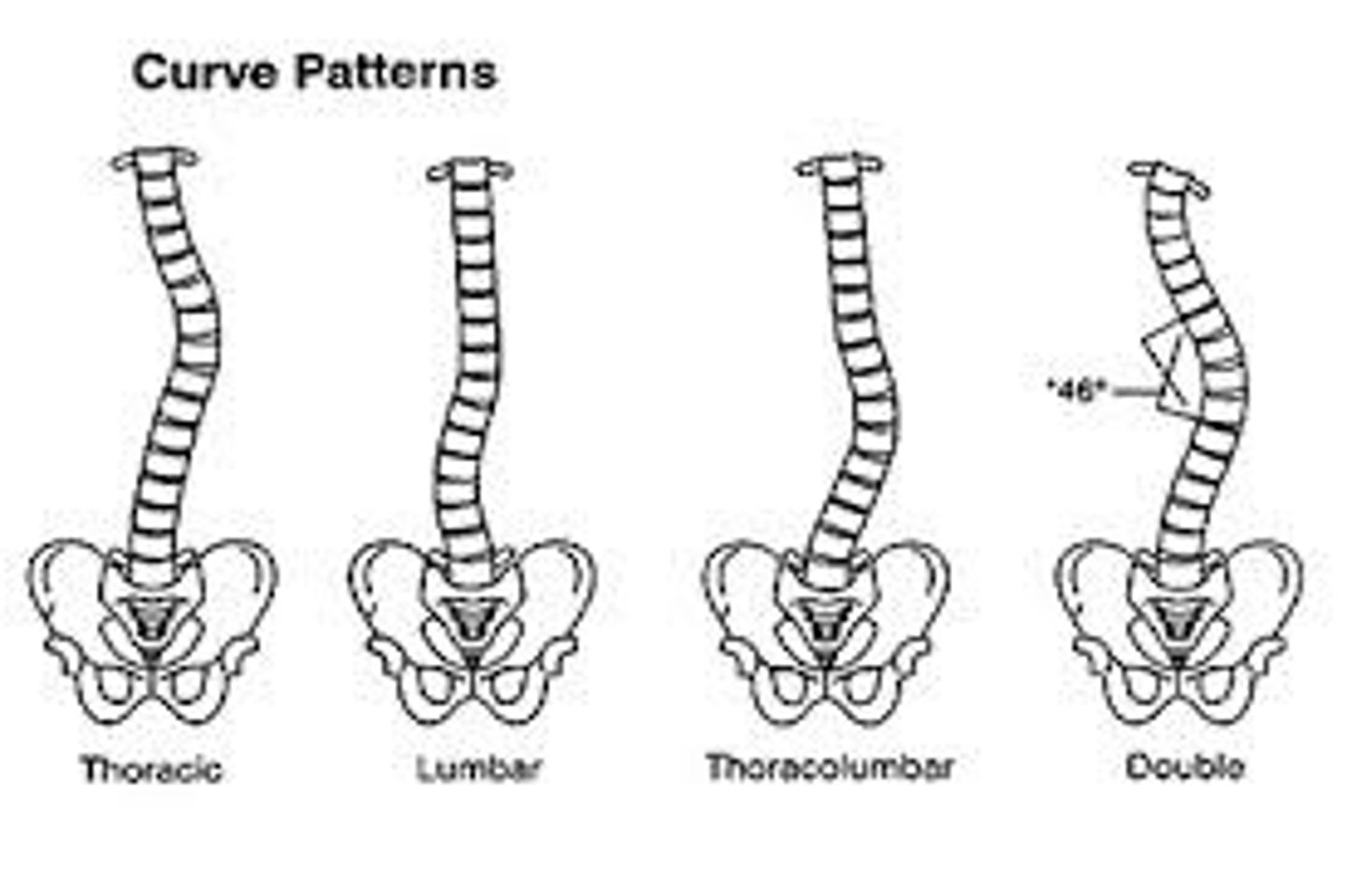
Scoliosis
an abnormal lateral curvature of the spine
-it is the most common spinal deformity in adolescent girls
spondyl/o (used to make words about conditions of the structure)
vertebra
vertebr/o (used to describe the structure itself)
vertebra
-blast
embryonic, immature cell
-clast
to break
Osteoblasts
cell synthesizes collagen and protein to form bone tissue
the immature osteocytes that produce the bony tissue that replaces cartilage during ossification
-listhesis
slipping
-malacia
softening
-physis
to grow
-porosis
pore, passage
-tome
instrument to cut
cost/o
ribs (true ribs, false ribs, and floating ribs)
crani/o
cranium (skull)
femor/o
femur (thigh bone)
fibul/o
fibula (smaller lower leg bone)
humer/o
humerus (upper arm bone)
ili/o
ilium (upper part of pelvic bone)
ischi/o
ischium (posterior part of pelvic bone)
malleol/o
malleolus (process on each side of the ankle)
mandibul/o
mandible (lower jaw)
Maxill/o (Maxilla)
upper jaw bone
metacarp/o
metacarpals (hand bones)
metetars/o
metatarsals(foot bones)
olecran, olecran/o
olecranon, elbow
Patell/o is the combining form for:
patella, kneecap
pelv/o
pelvis (hip bone)
perone/o
fibula
phalang/o
finger or toe bones
pub/o
pubis (anterior part of the pelvic bone)
radi/o
radius (forearm bone-thumb side)
Scapul/o is the combining form for:
scapula, shoulder blade
stern/o
sternum (breastbone)
tars/o
tarsals (bones of the hindfoot)
tibi/o
tibia (shin bone)
uln/o
ulna (forearm bone - little finger side)
Ewing sarcoma
rare malignant tumor arising in bone; most often occurring in children