PHRM 808 Dr. Cushman Antibiotic Structures + Information
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
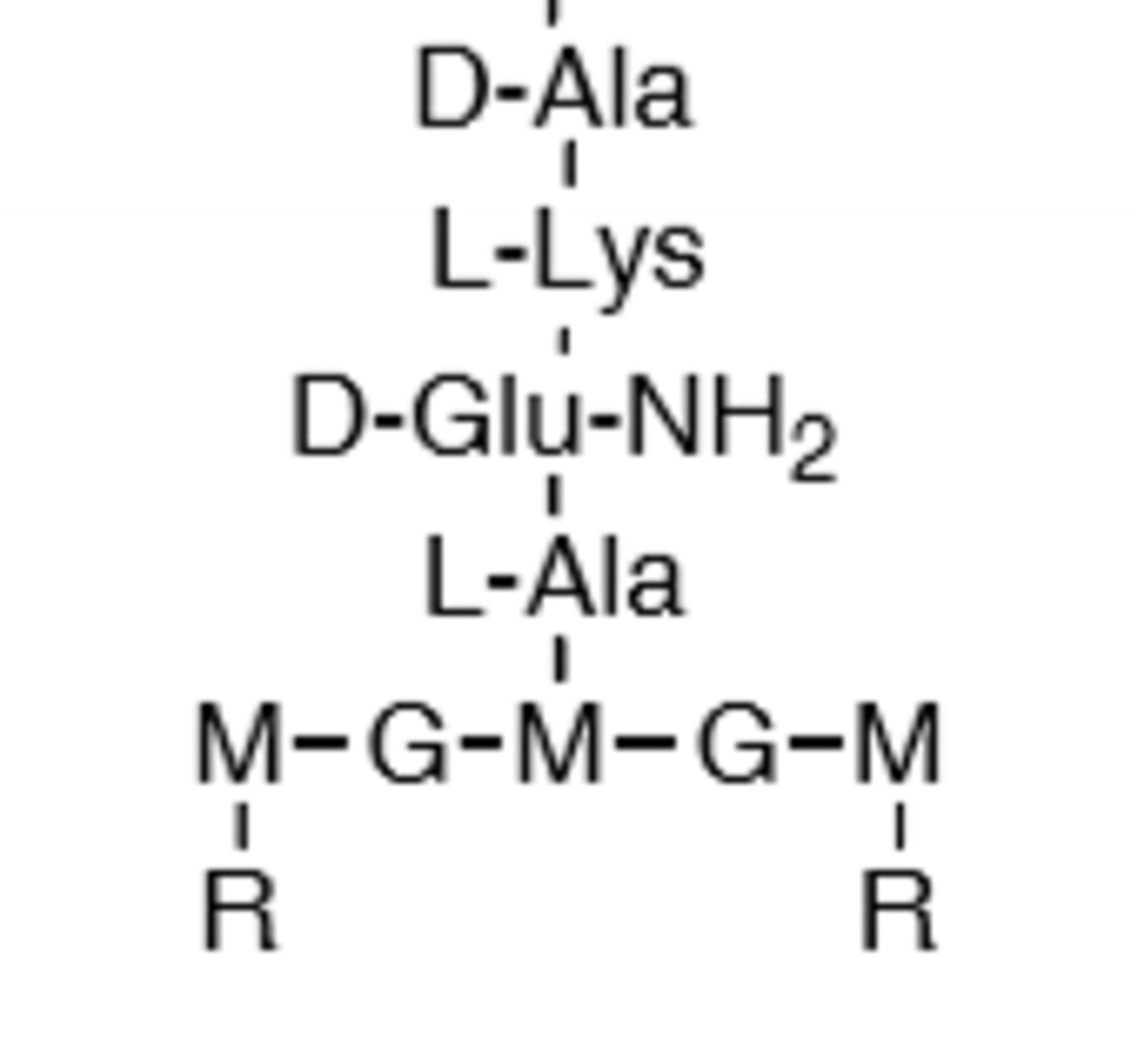
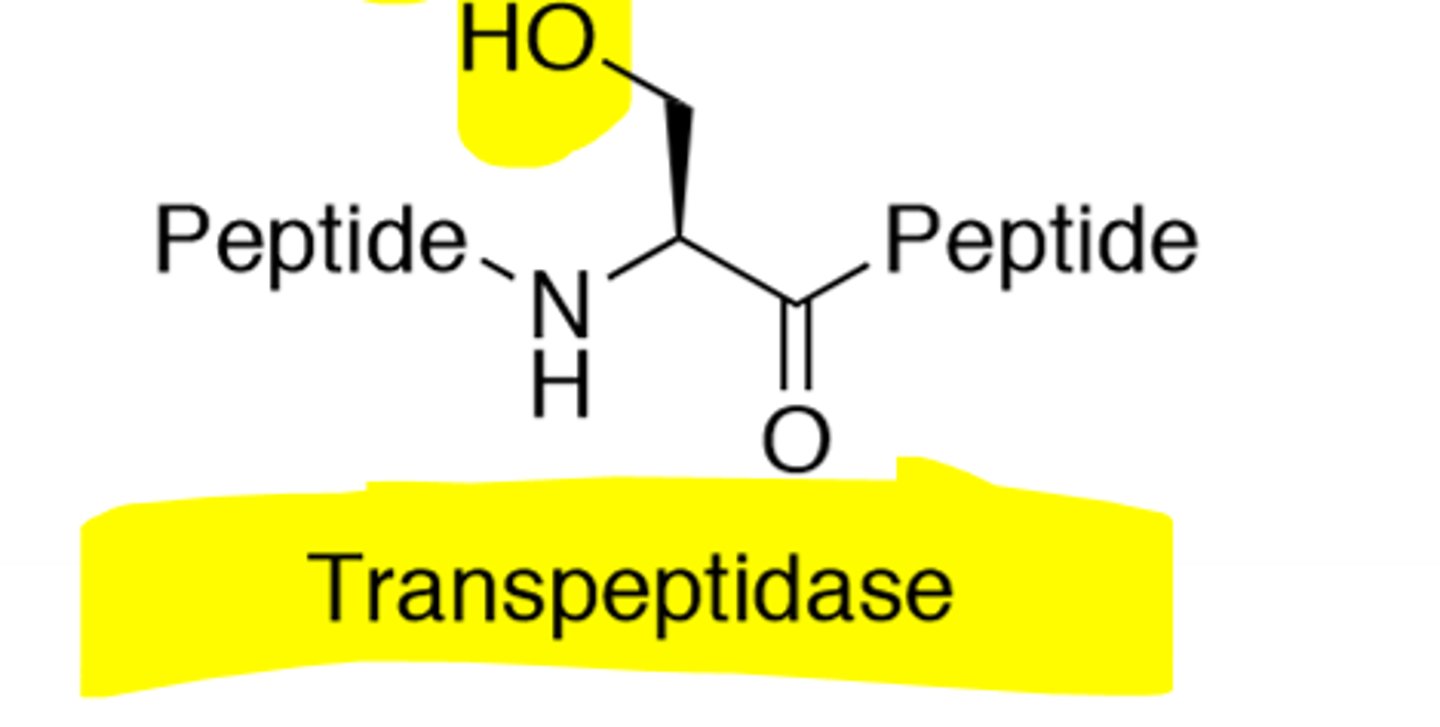
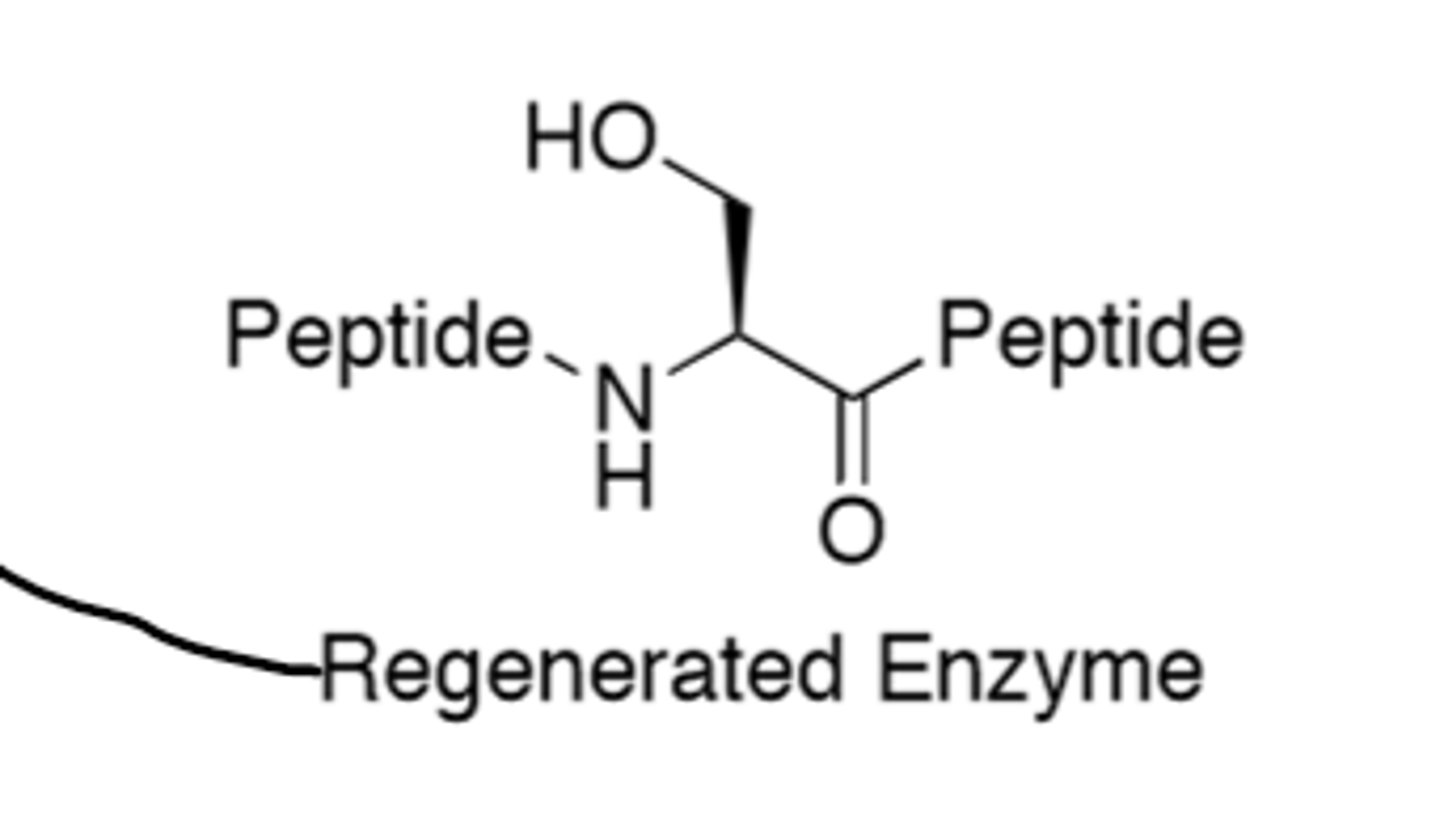
Strand That Connects to D-Ala
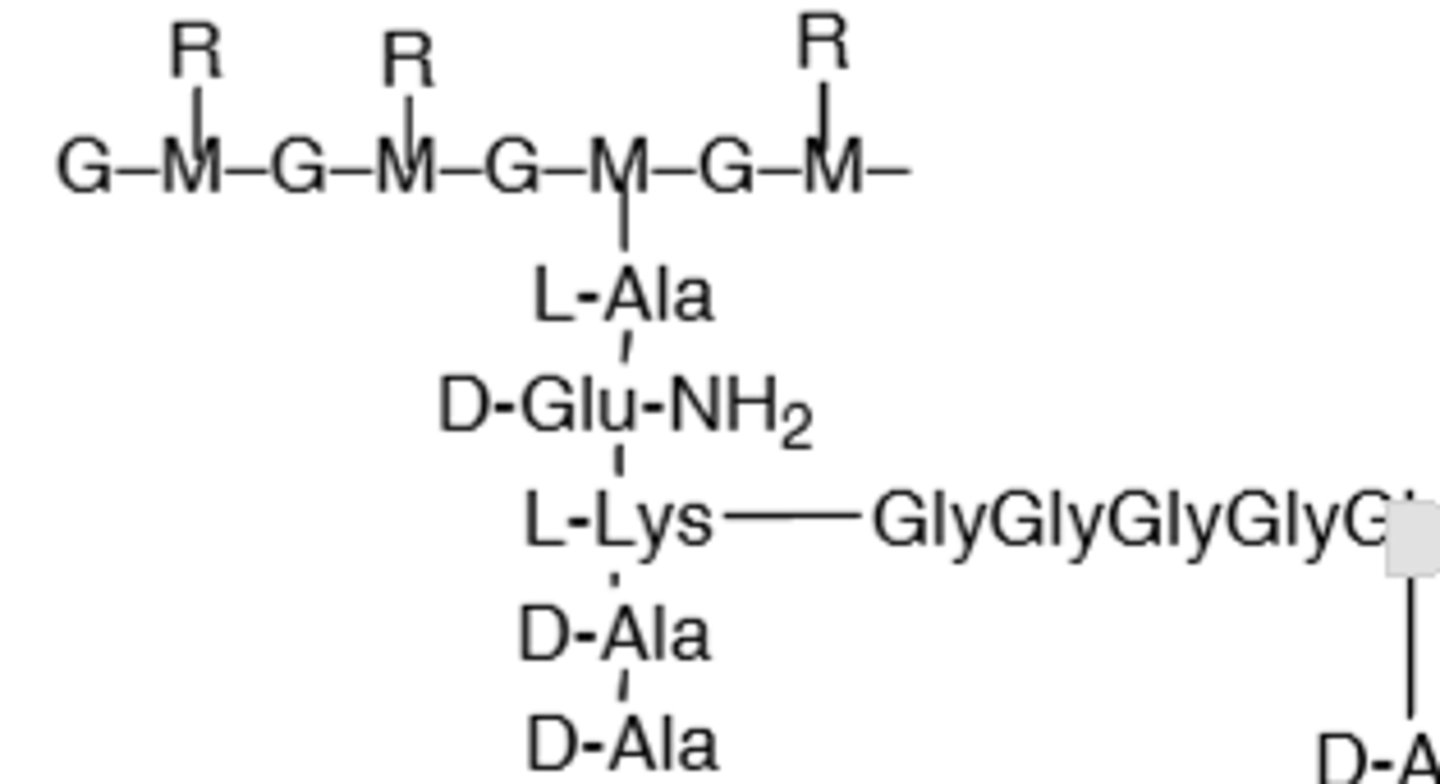
What is this
D-Ala-D-Ala terminal chain
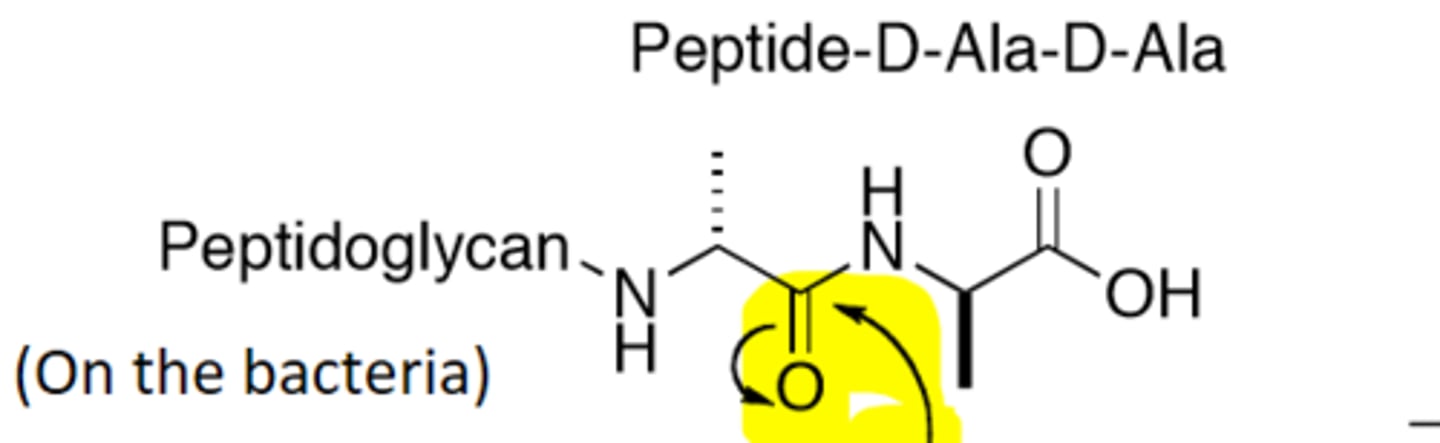
Peptide D-Ala-D-Ala
Transpeptidase
Can also be called Penicillin-Binding-Protein (PBP)
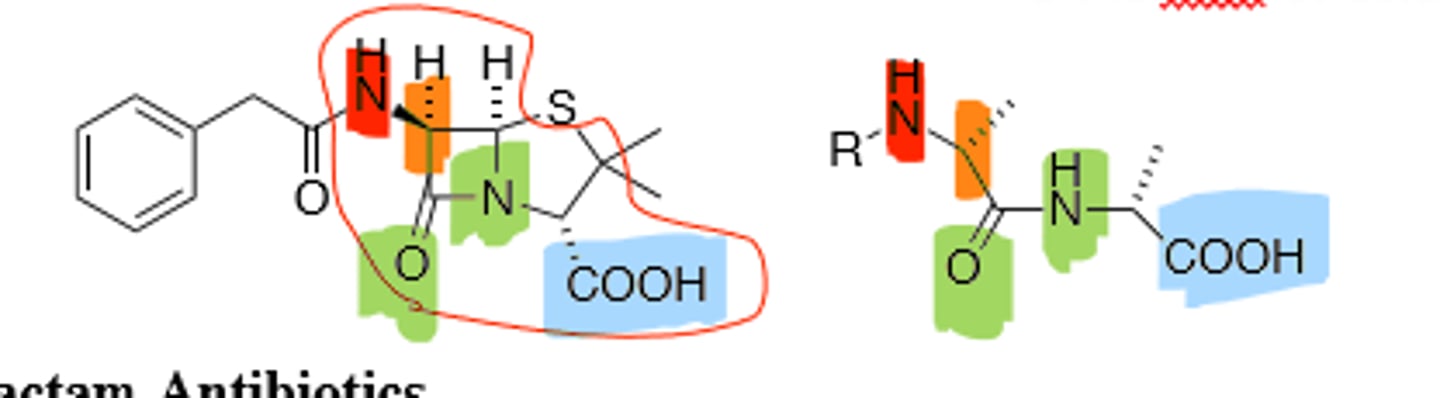
B-Lactam (Left) vs D-Ala-D-Ala Structure (Right)
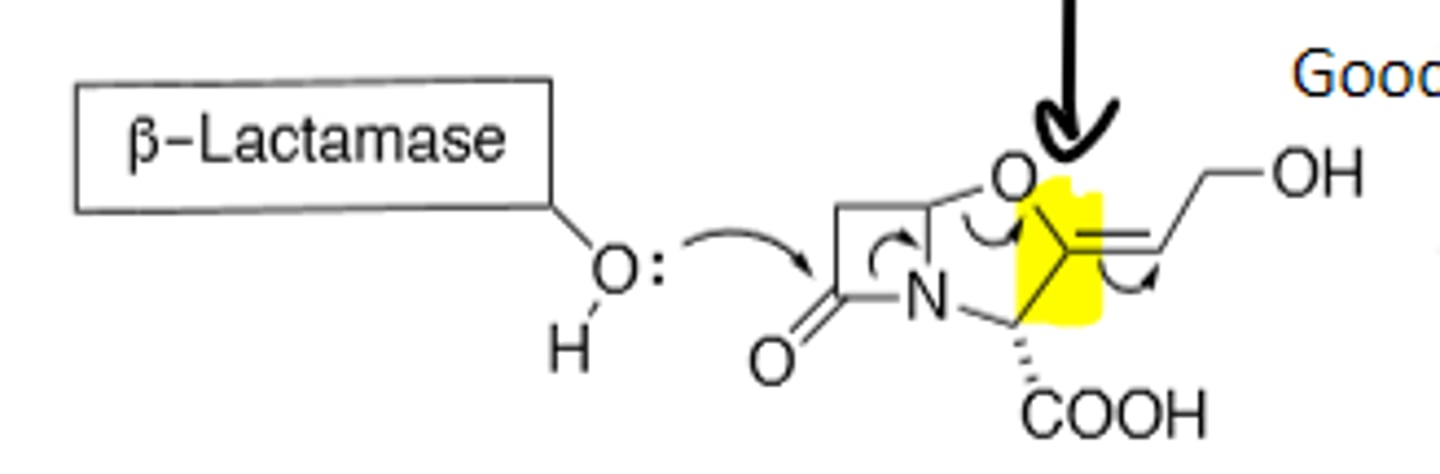
B-Lactamase Enzyme
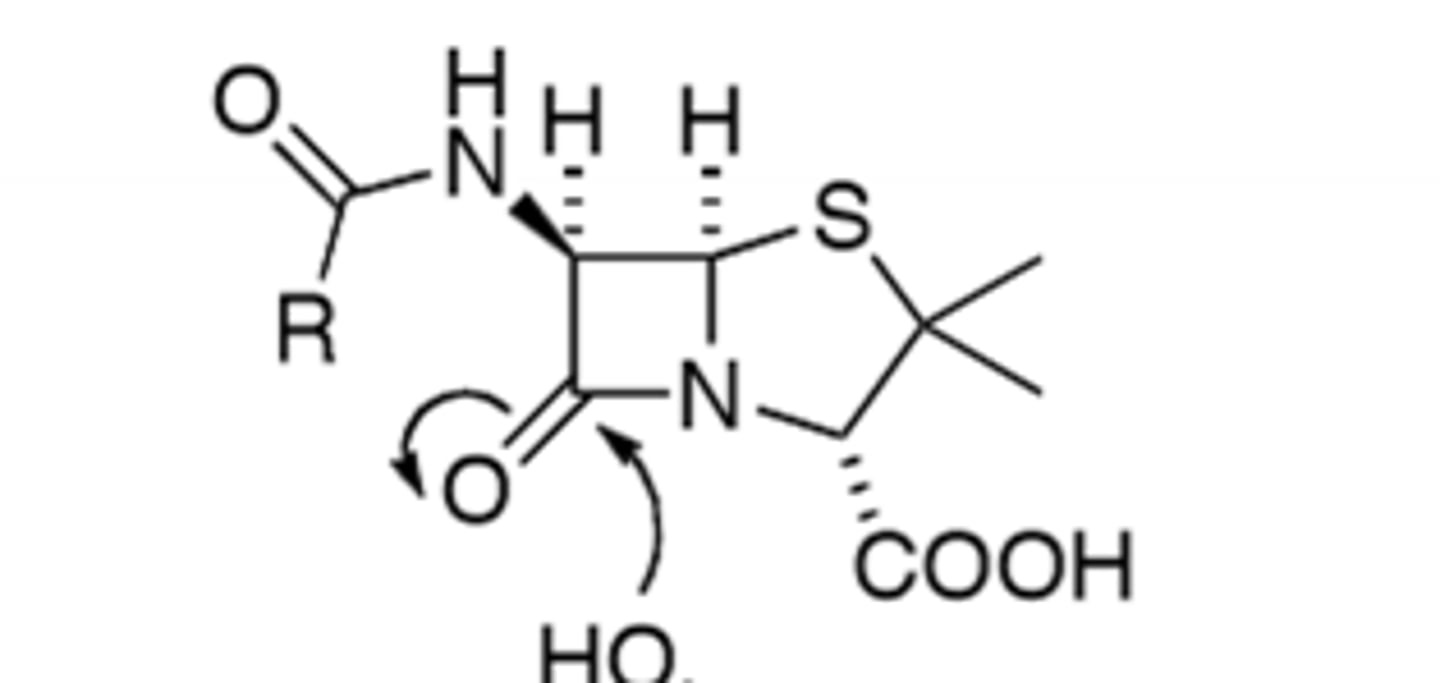
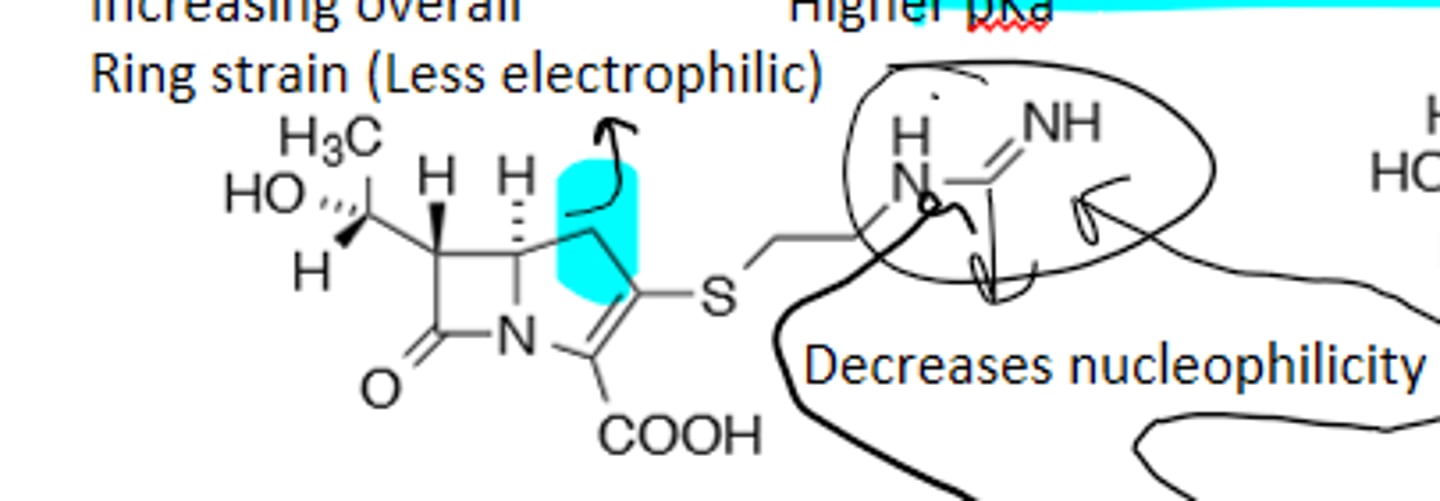
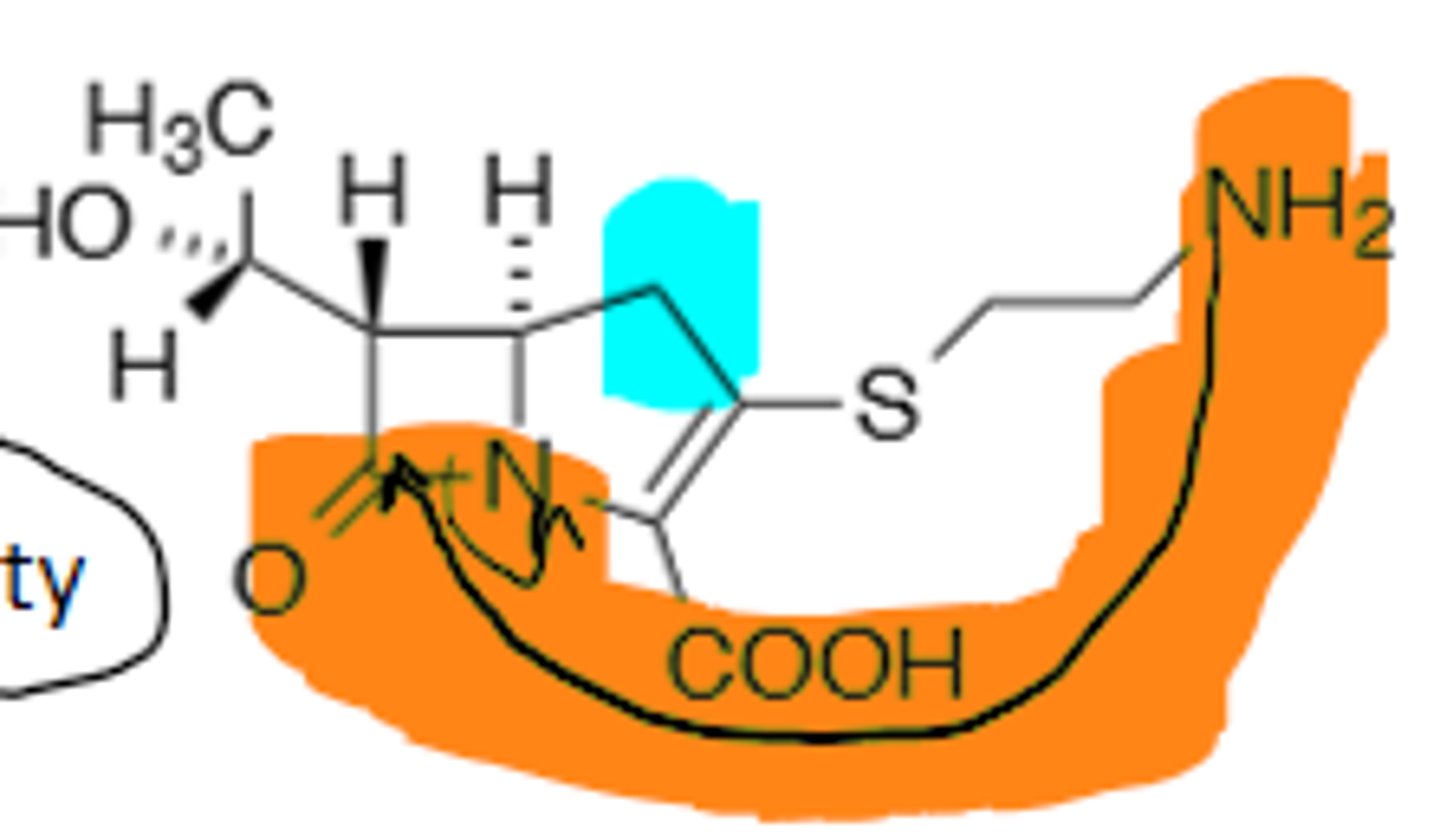
B-Lactam
Penicillin G
Benzylpenicillin, B-Lactam, More Nucleophilic, B-Lactamase Sensitive, not orally available
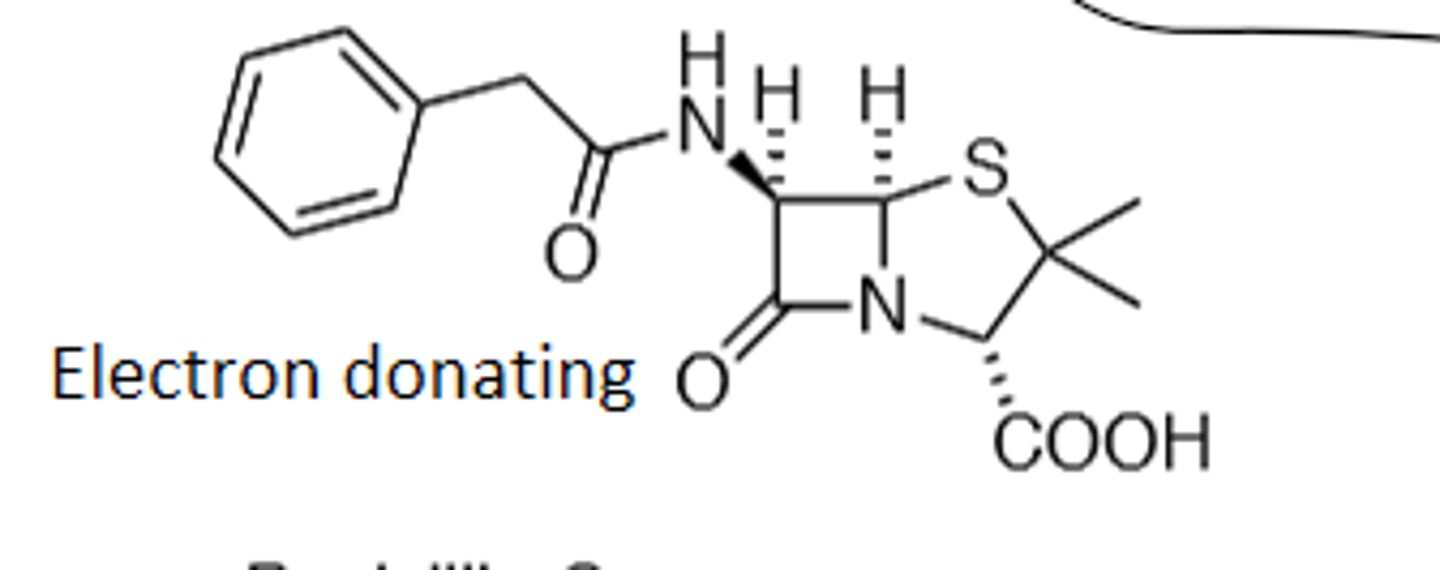
Penicillin V
Phenoxymethylpenicillin, B-Lactam, Much More orally available (Ether Oxygen), B-Lactamase Sensitive
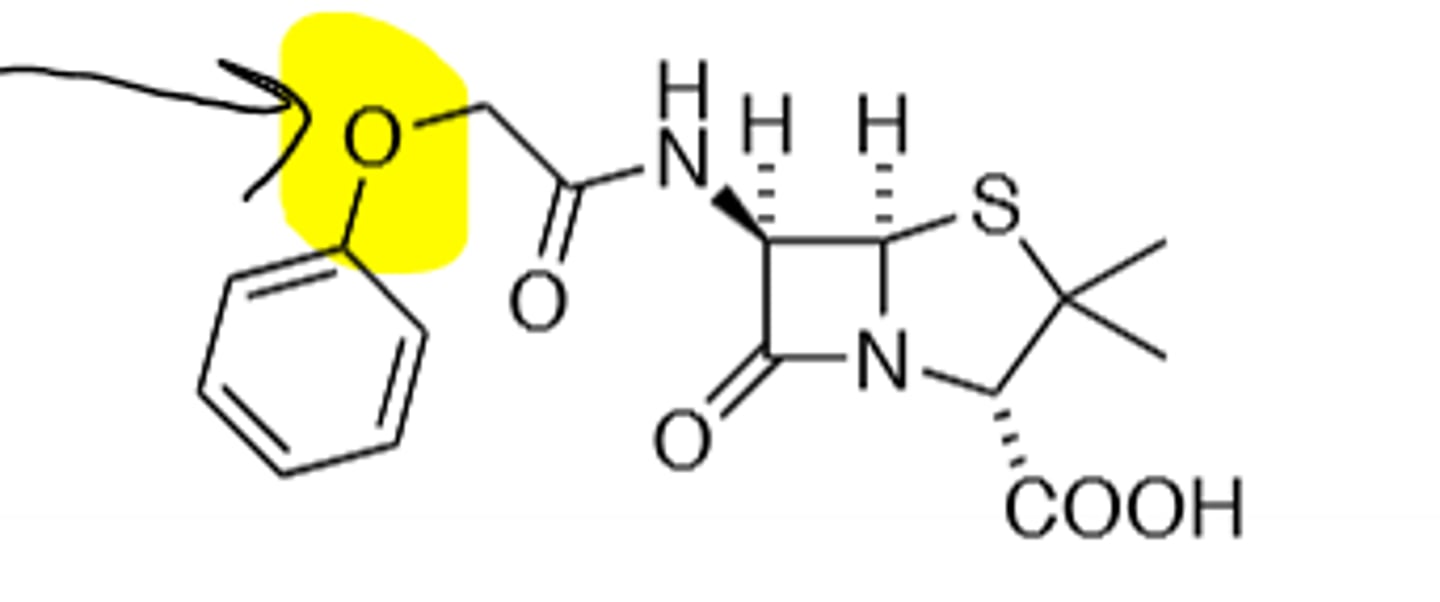
Ampicillin
B-Lactam, Broad Spectrum, NH2 protonated at physiological pH, B-Lactamsse Sensitive
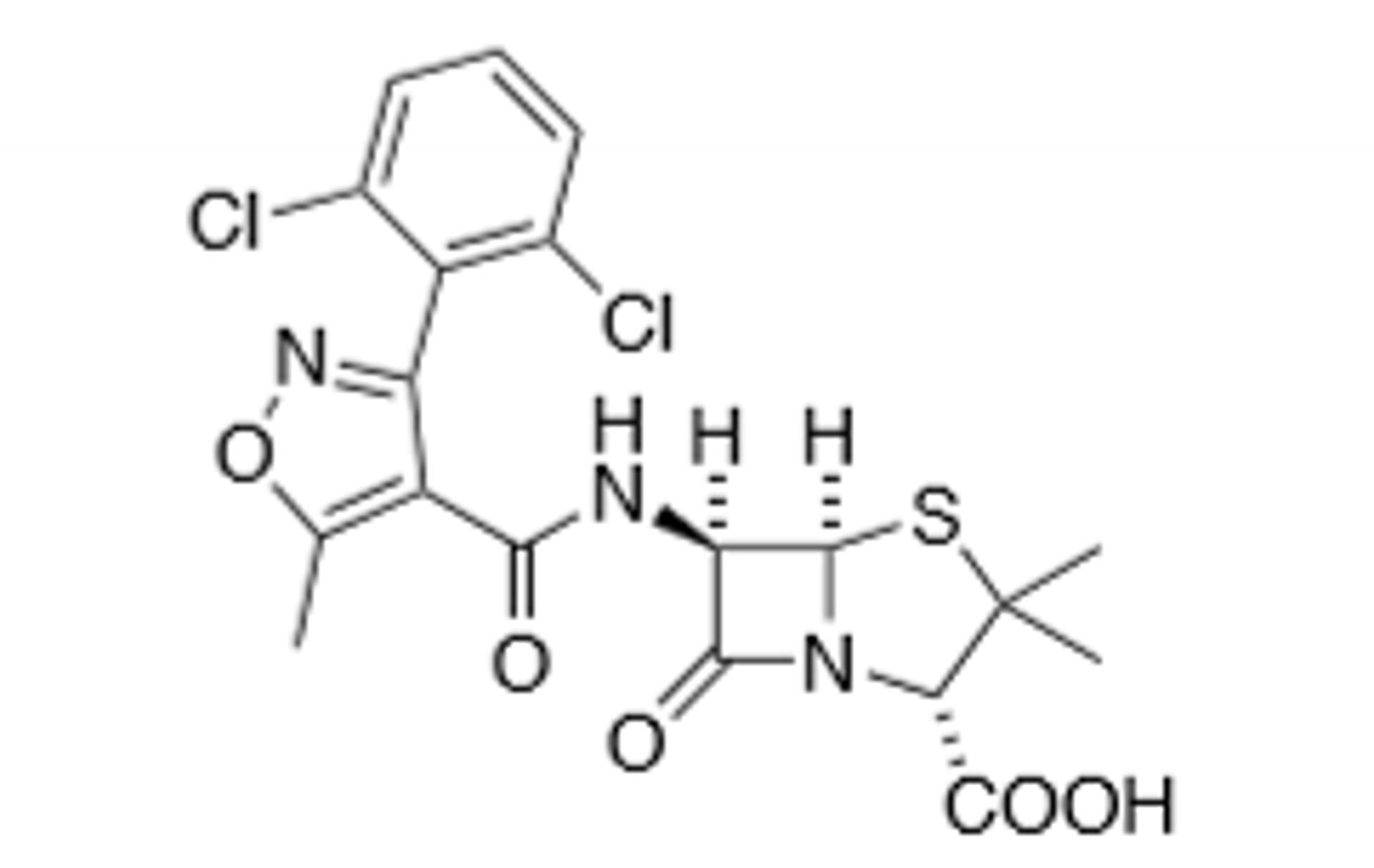
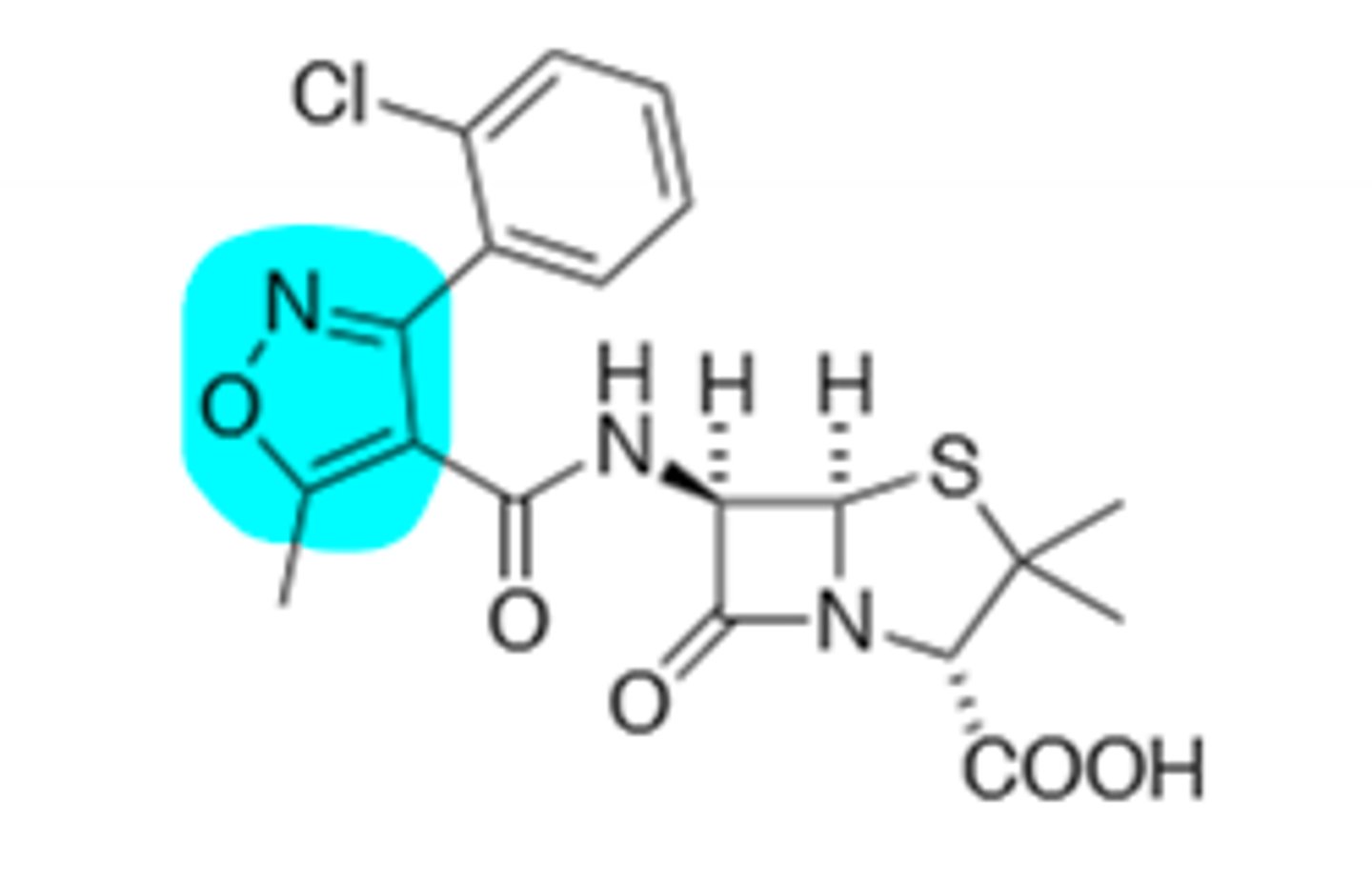
Dicloxacillin
B-Lactam Resistant, Lipophilic, Oral Only
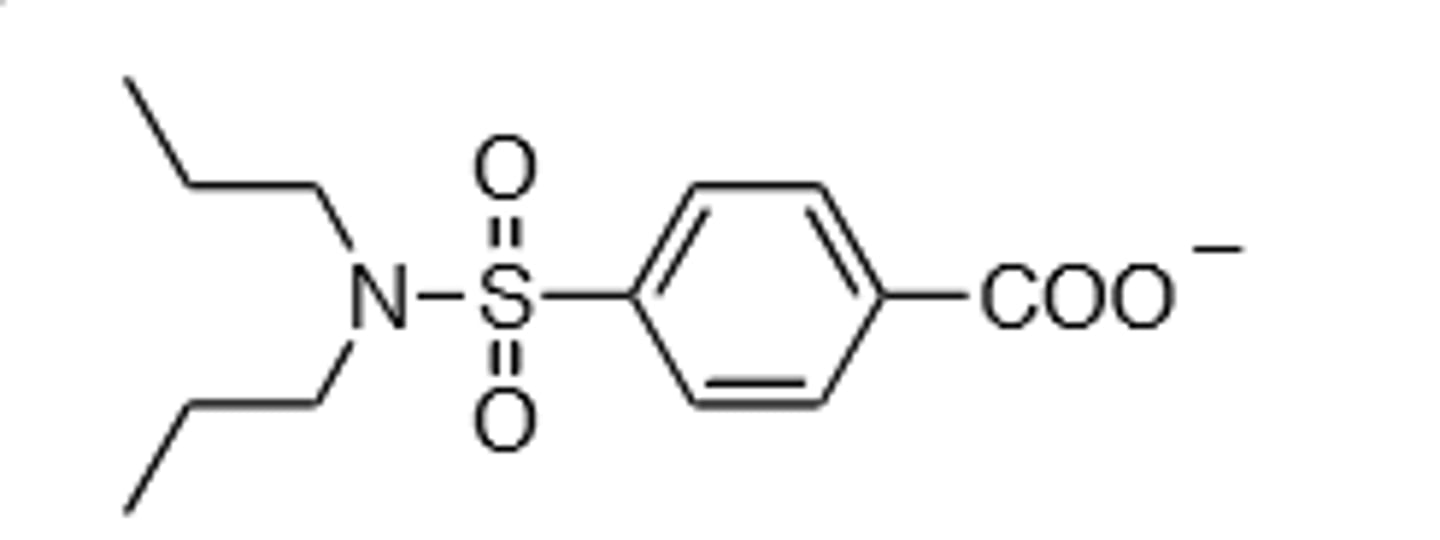
Probenecid
Increases half-life of Penicillin when co-administered
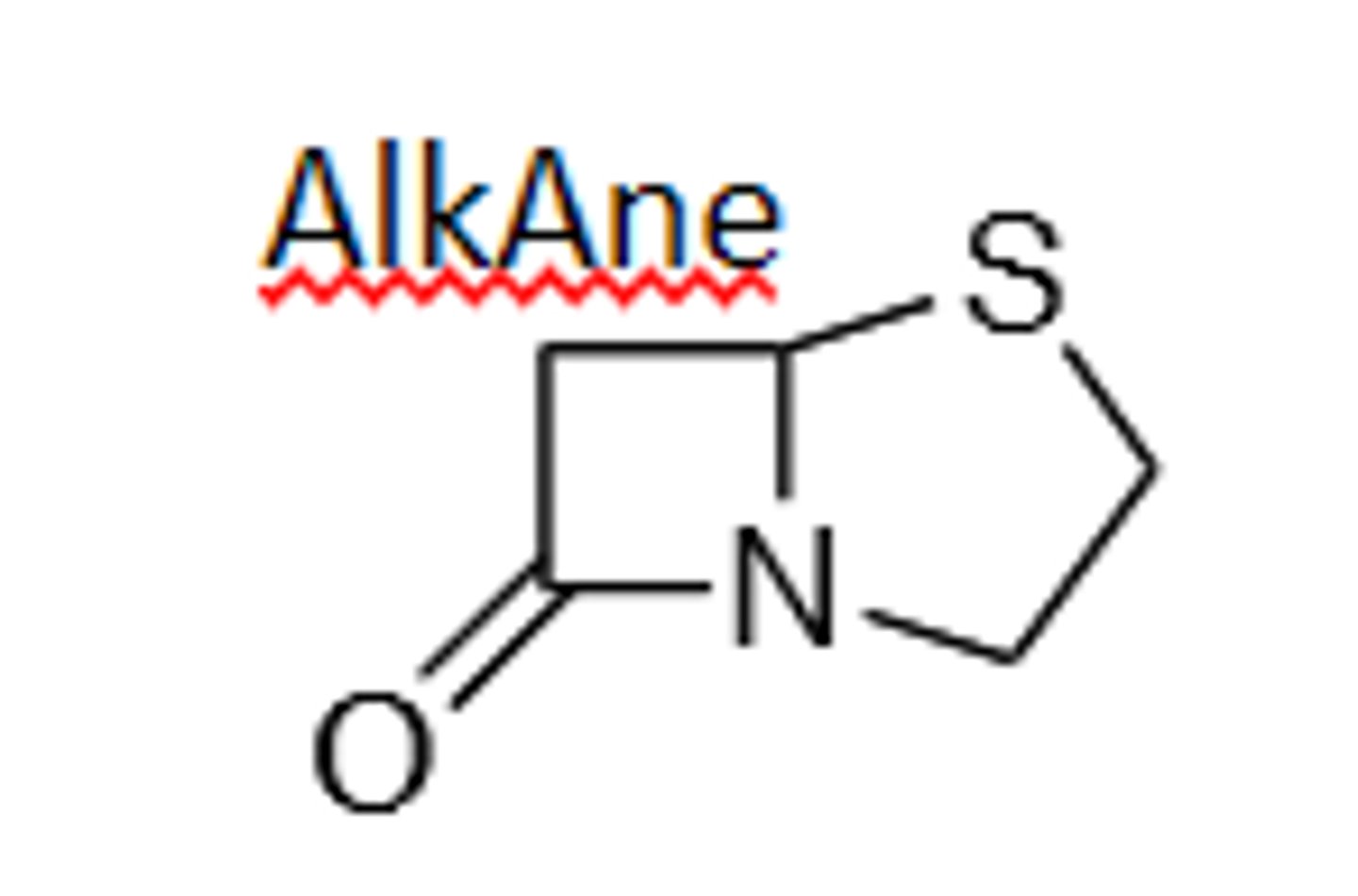
Penam
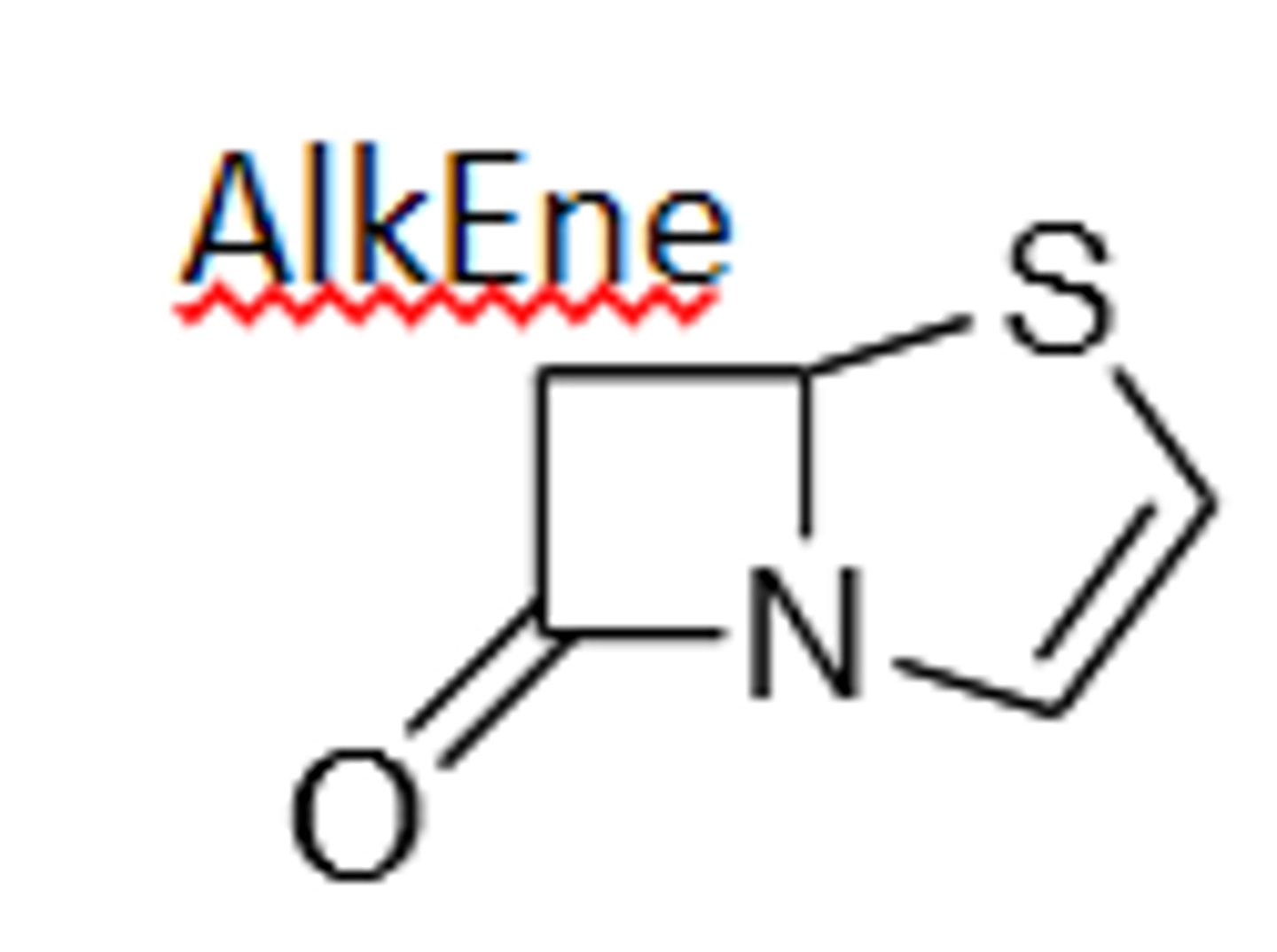
Penem
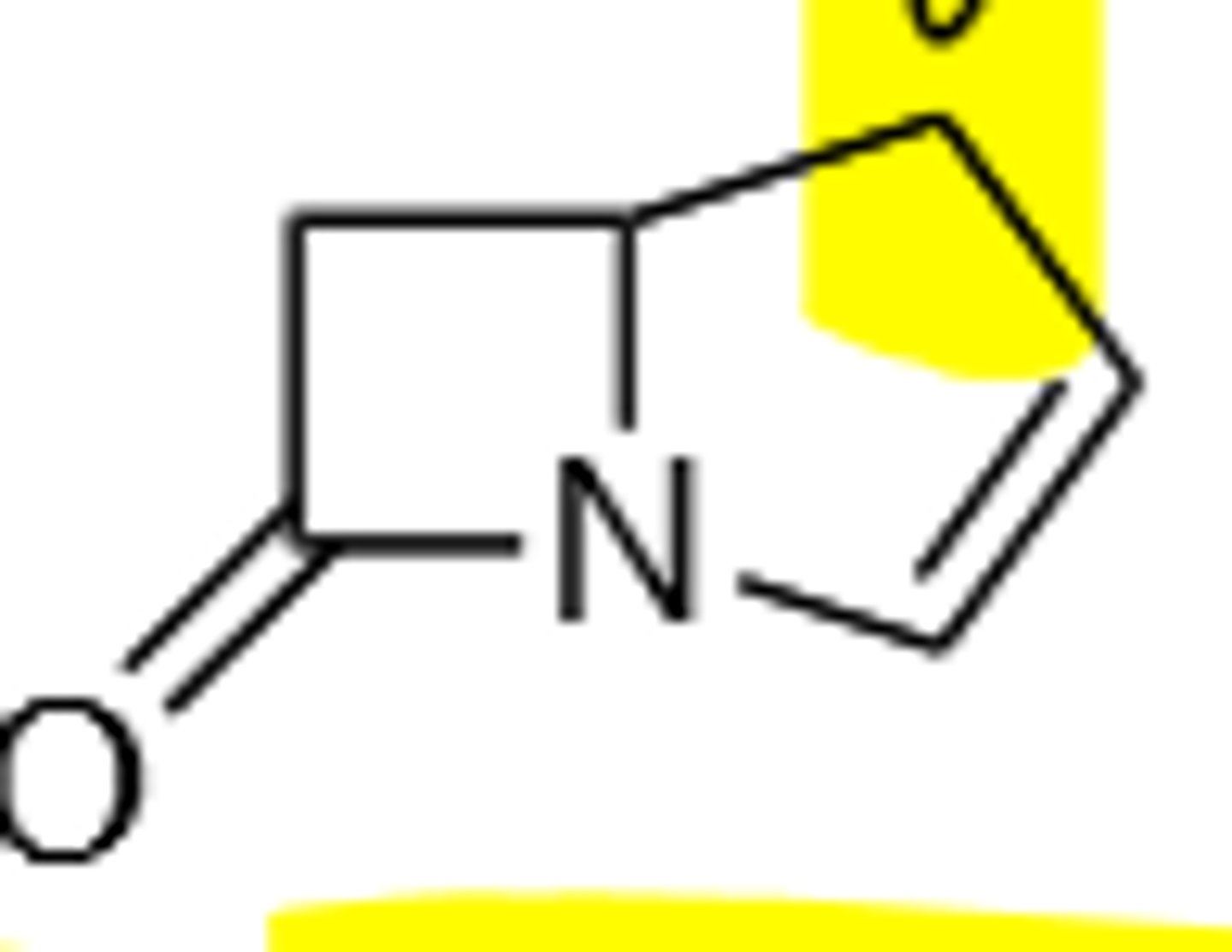
Carbapenem
Cephem
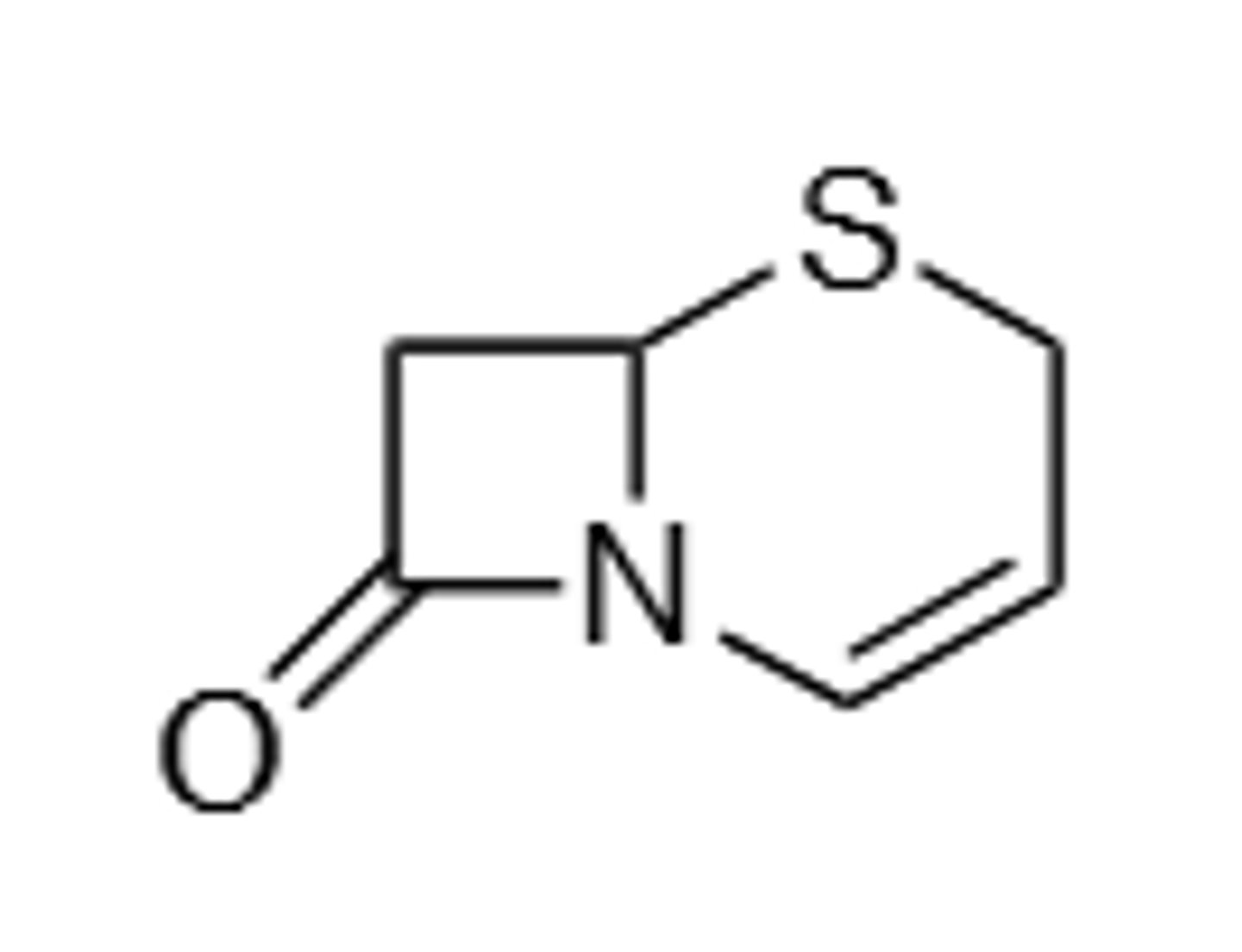
Monobactam
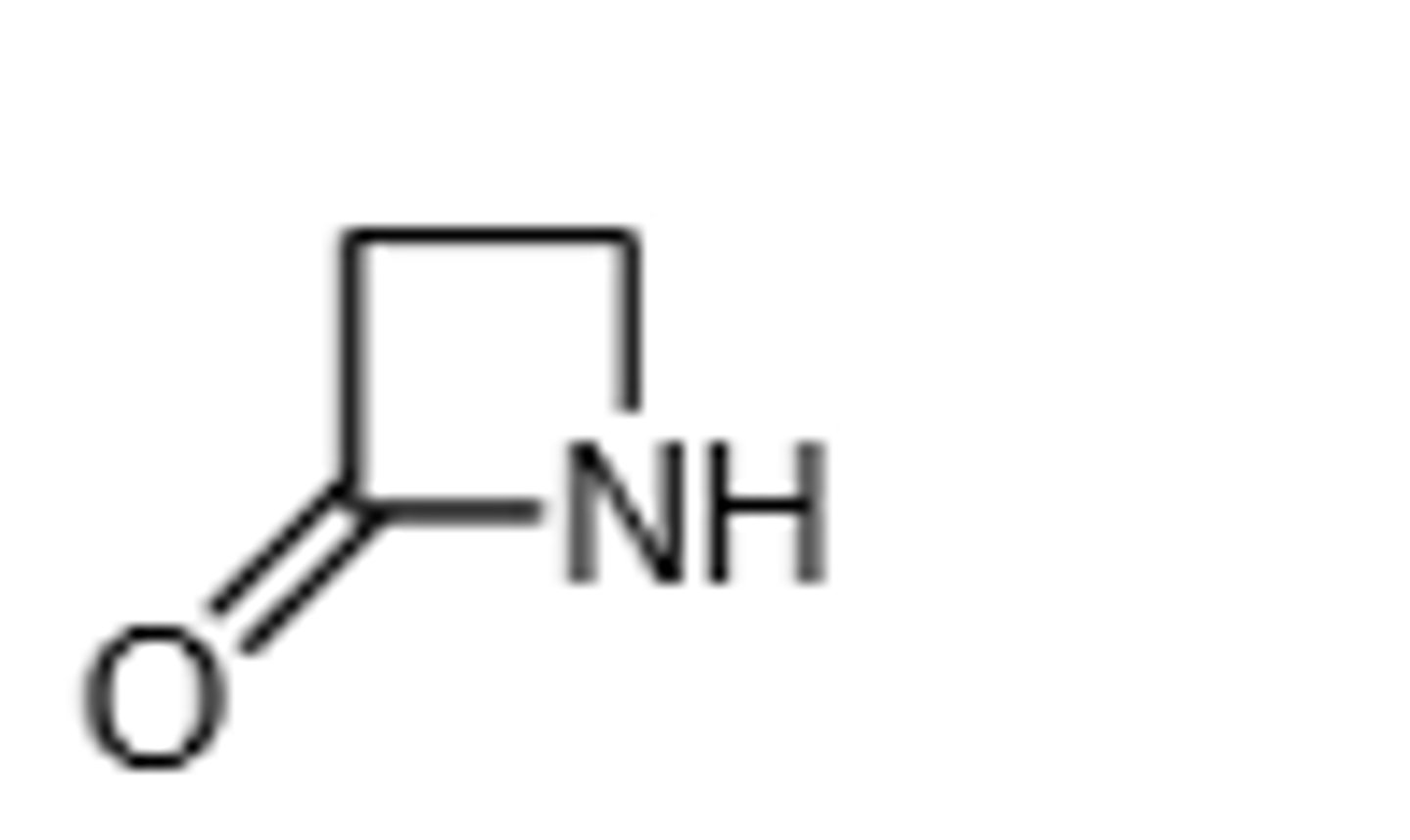
Methicillin
B-Lactamase Resistant, Injected
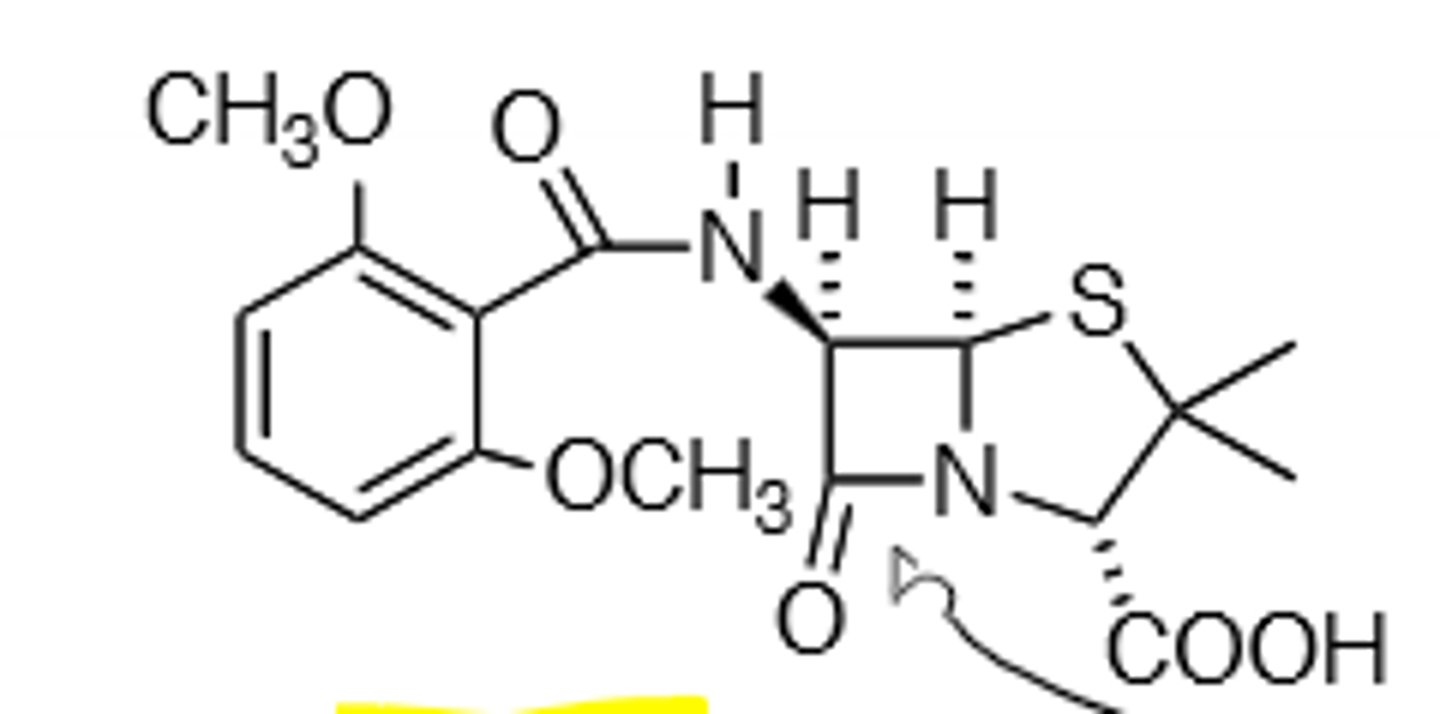
Nafcillin
B-Lactamase Resistant, Clinically identical to methicillin
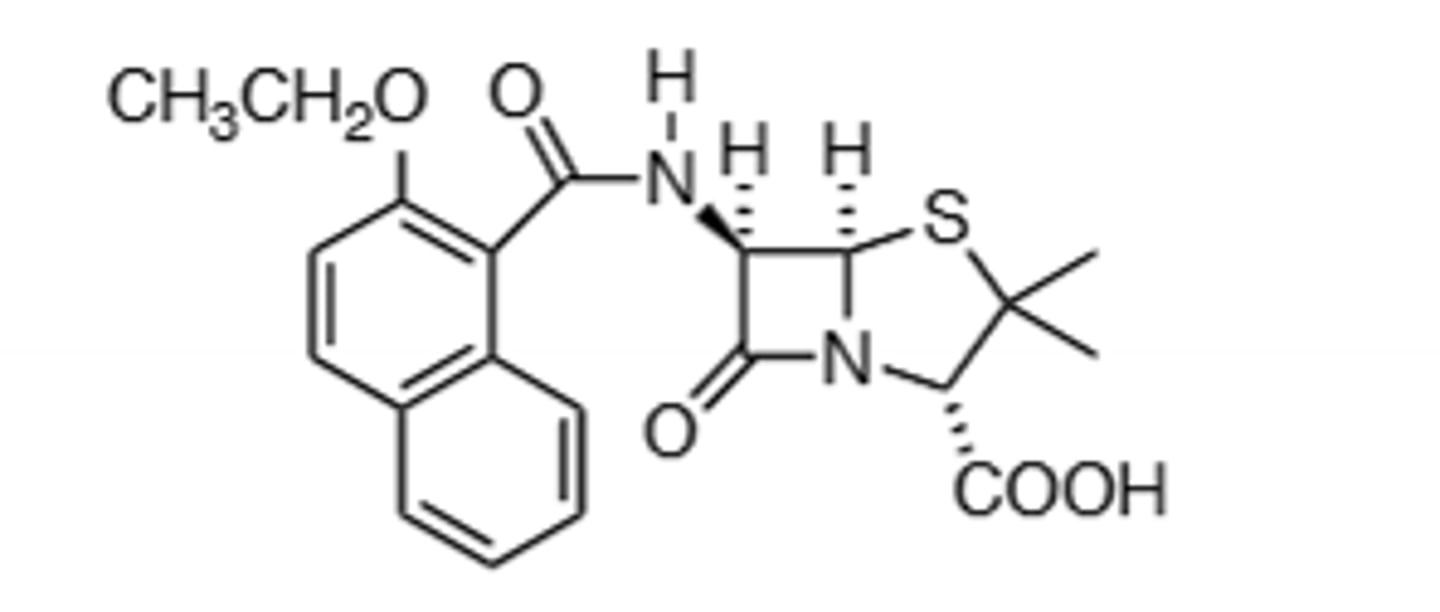
Oxacillin
B-Lactamase Resistant, injected
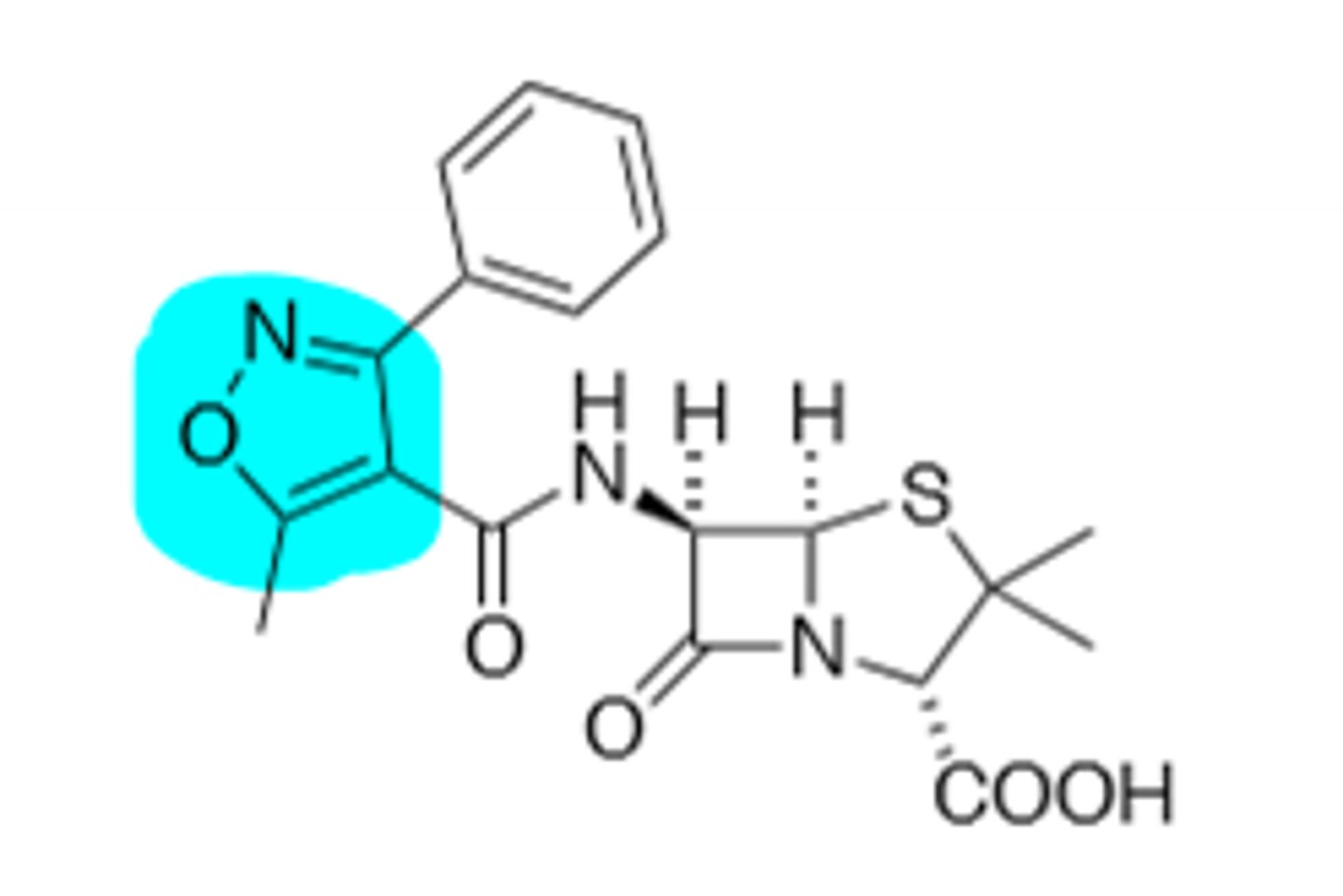
Cloxacillin
B-Lactamase Resistant
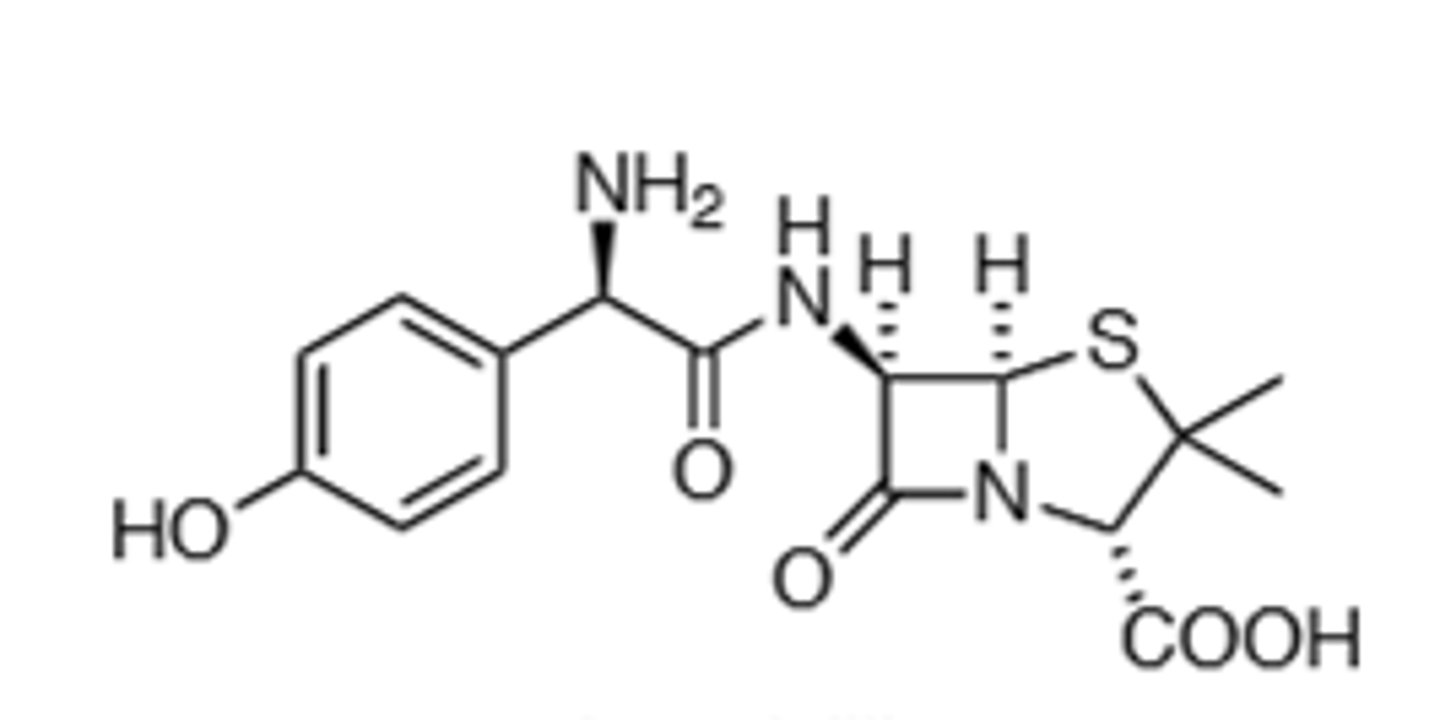
Amoxicillin
Beta-Lactamase, better oral absorption than ampicillin, protonated at physiological pH (More broad spectrum)
What is important for B-Lactamase inhibitors?
Must be able to open the ring, carbon is not going to get pulled off.
Clavulanic Acid
B-lactamase inhibitor
Sulbactam
B-lactamase inhibitor
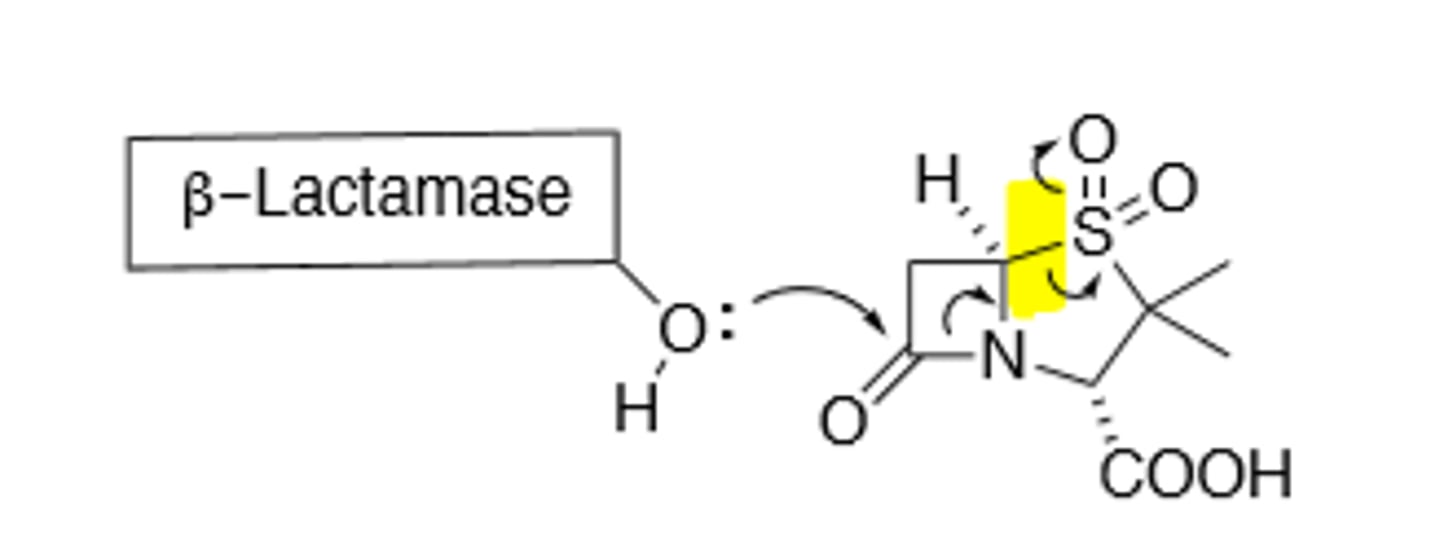
Tazobactam
B-lactamase inhibitor
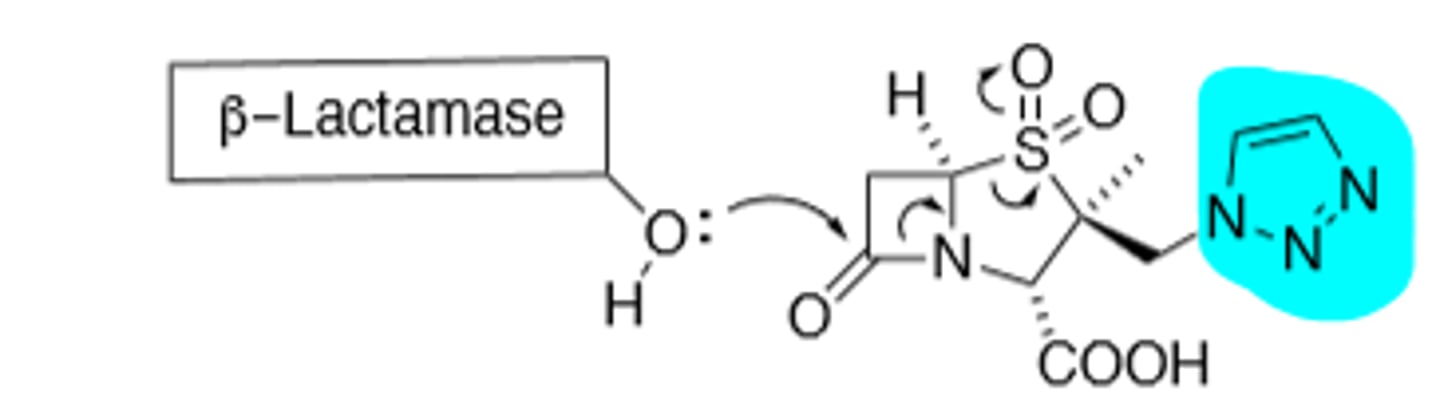
Avibactam
B-lactamase inhibitor
Amoxicillin + Potassium Clavulanate
Augmentin
3 multiple choice options
Ampicillin + Sulbactam
Unasyn
3 multiple choice options
Piperacillin + Tazobactam
Zosyn
3 multiple choice options
Ceftazidime + Avibactam
Avycaz
3 multiple choice options
Pipericillin
Penicillin, B-Lactamase Sensitive, Broad Spectrum (Side Chain expands spectrum), IV only
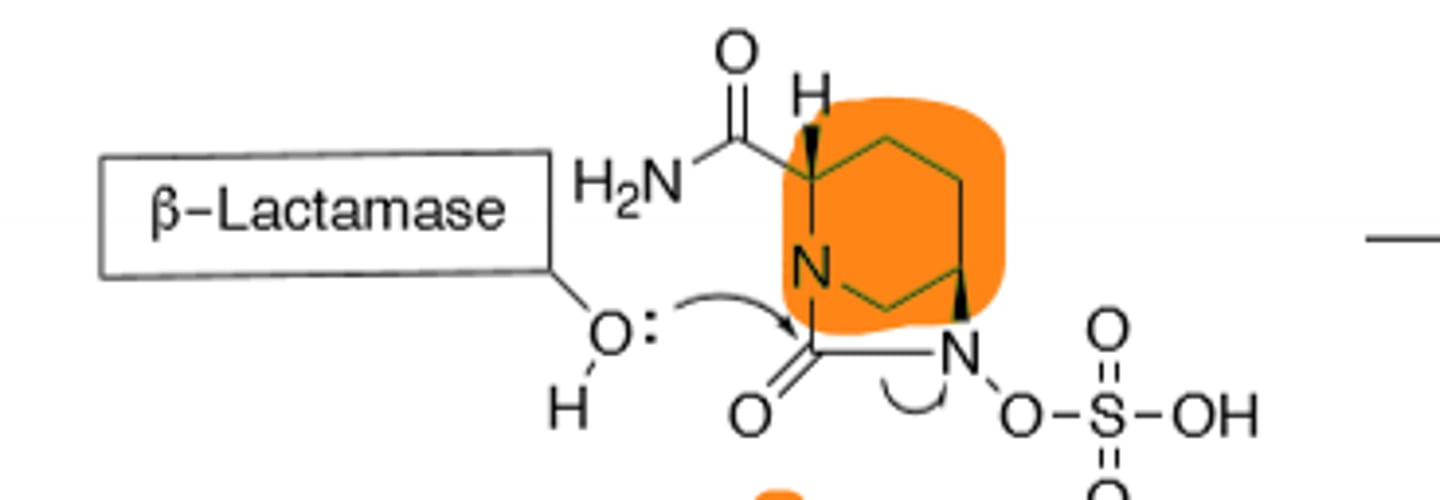
Cefazolin
1st Gen Cephalosporin, Good Leaving Group (Parenteral Administration)
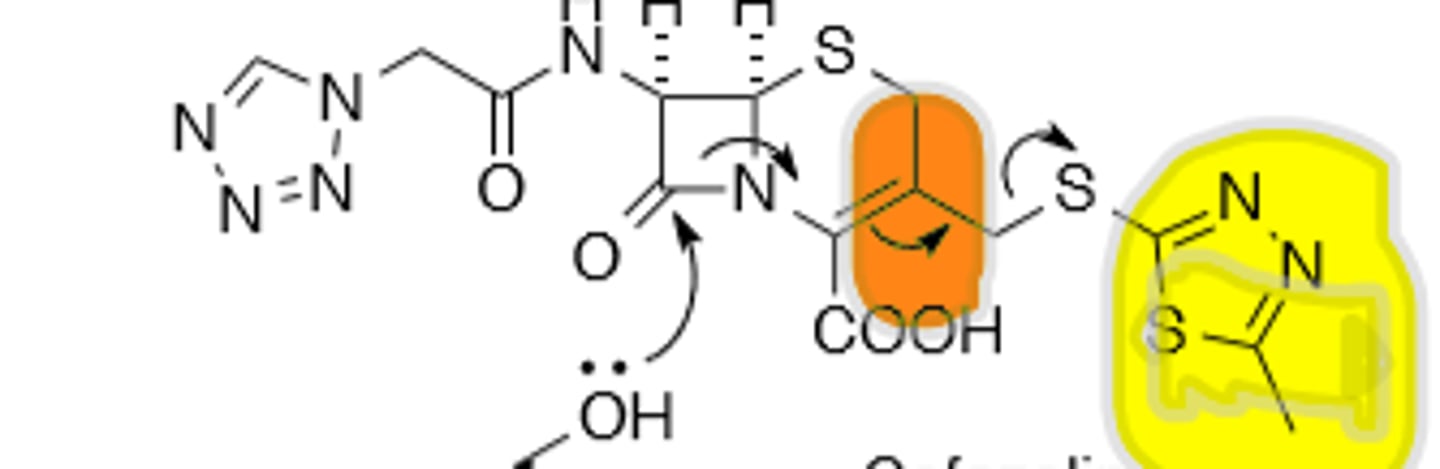
Orally active cephalosporins have what at C-3
Substituents that are not chemically active
Cephalexin
1st Generation Cephalosporin, Orally Active (Bad Leaving Group at C-3)
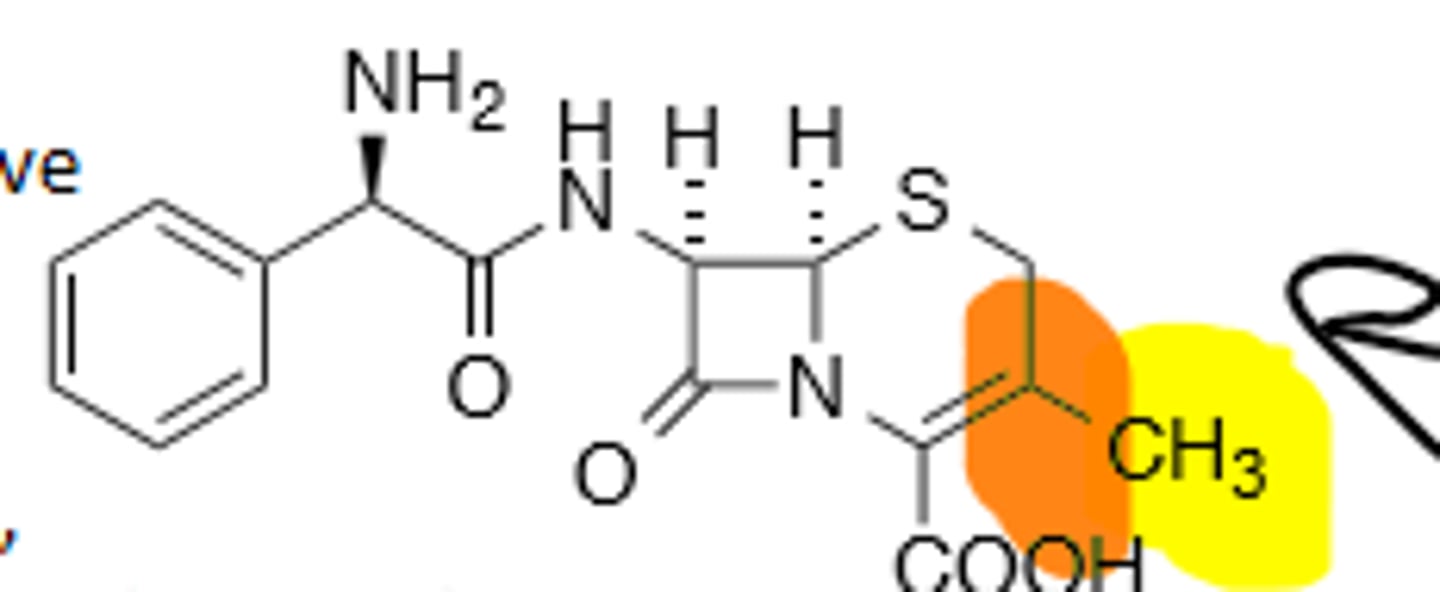
Cefuroxime
2nd Generation Cephalosporin, Bad Leaving Group due to carbamate resonance (Both oral and parenteral). More gram (-) coverage than first gen.
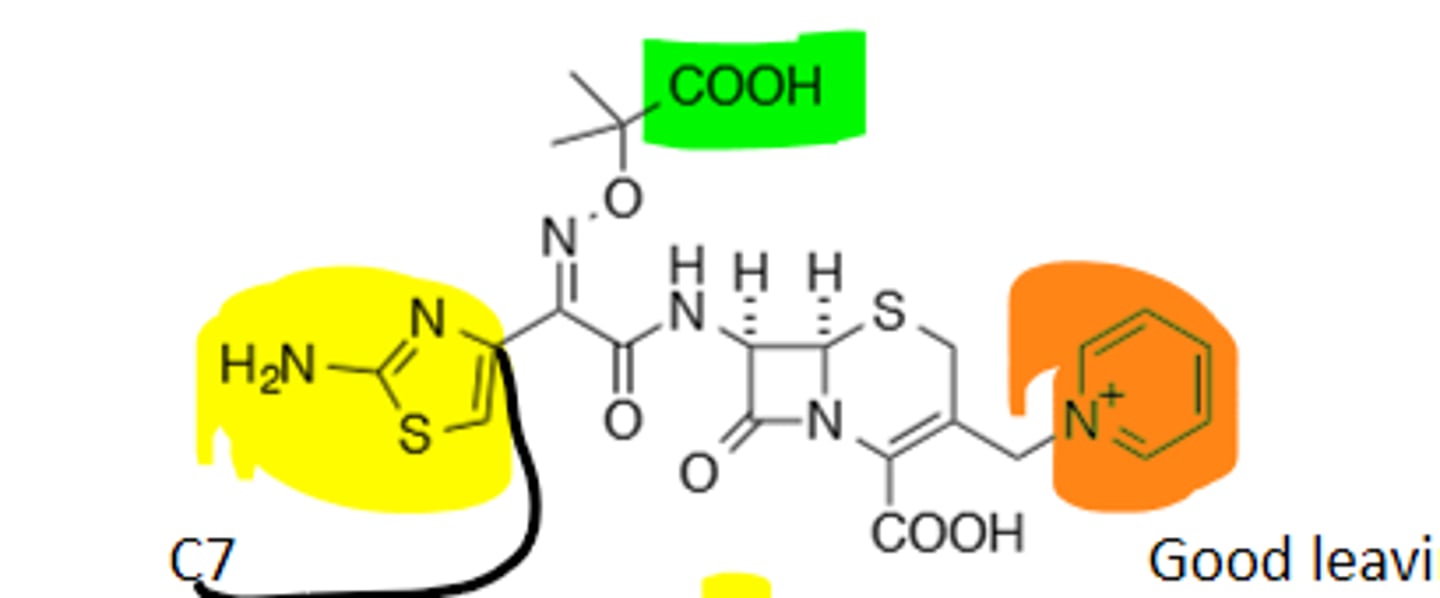
Ceftazidime
3rd Generation Cephalosporin, more gram (-) coverage, enhanced stability vs B-Lactamases, good leaving group (Parenteral only). Cross allergenicity with penicillins.
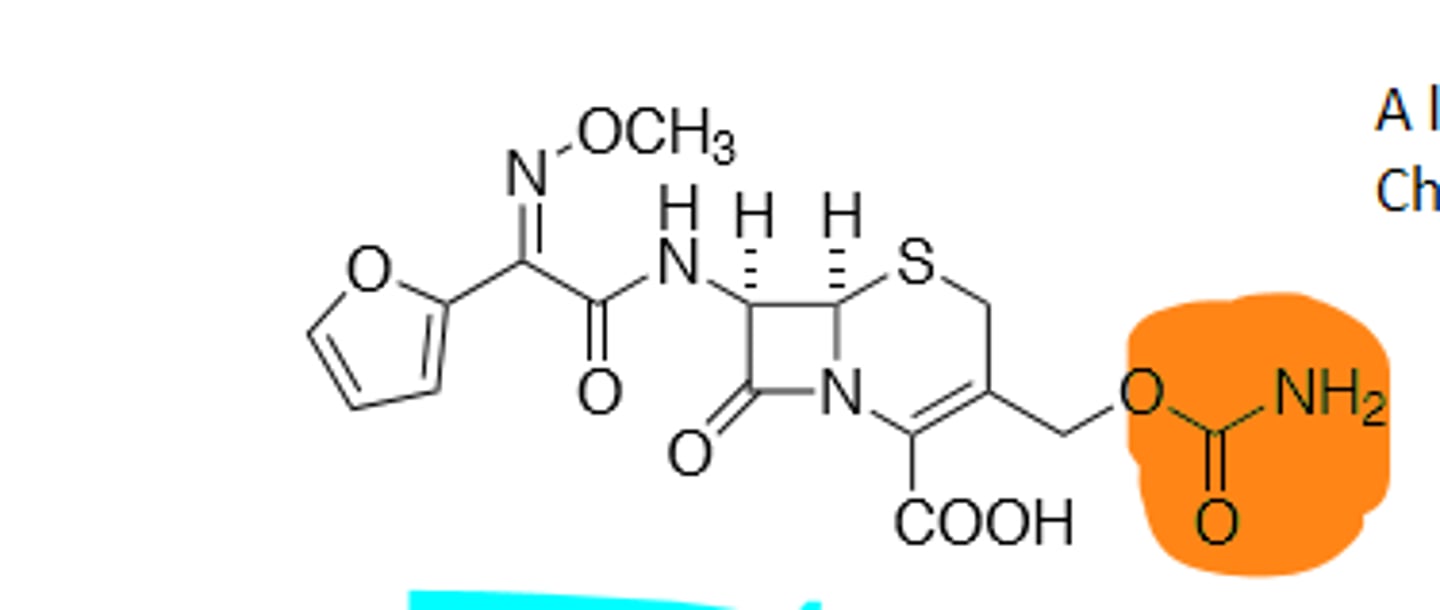
Cefexime
Third Generation Cephalosporin, Bad leaving group (Orally active), more gram (-) coverage, enhanced stability vs B-Lactamases
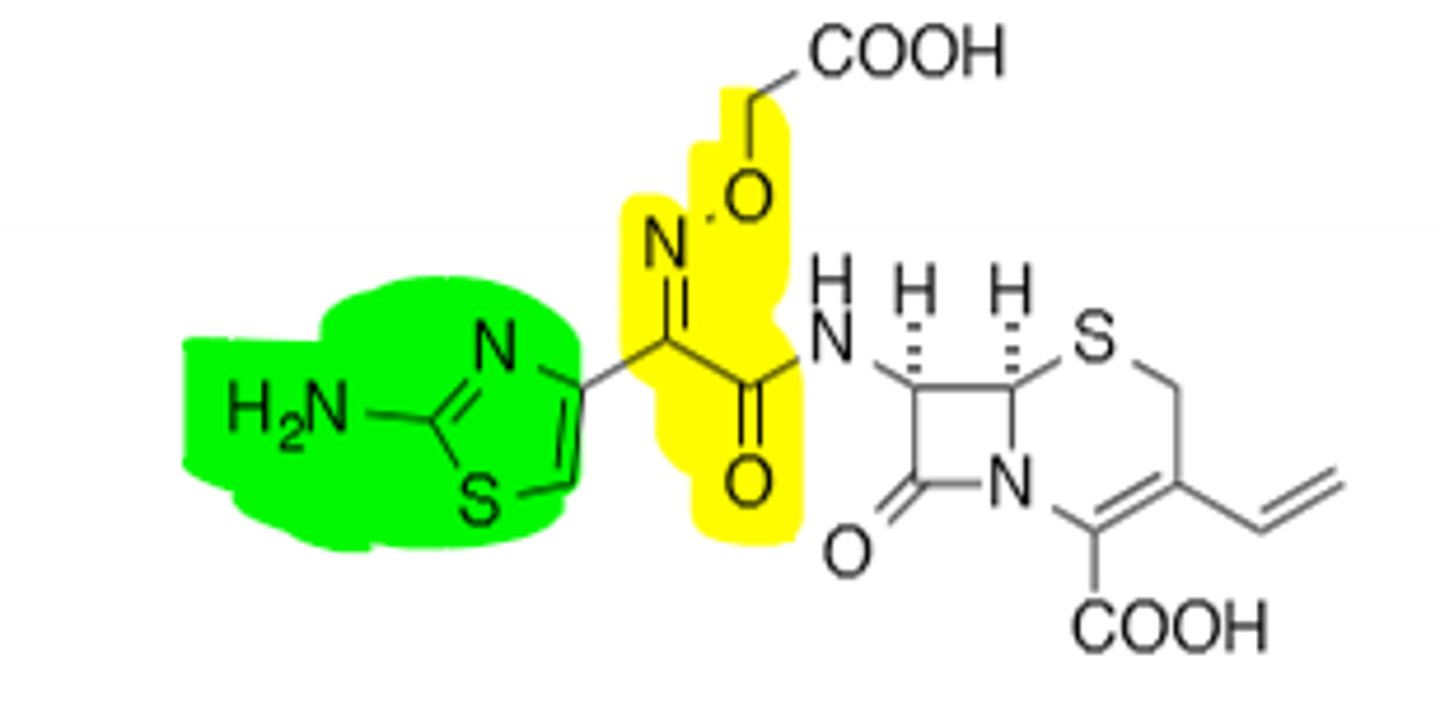
Cefepime
4th Generation Cephalosporins, Good leaving group (Parenterally Active), even more gram (-) coverage, first line in treating AmpC
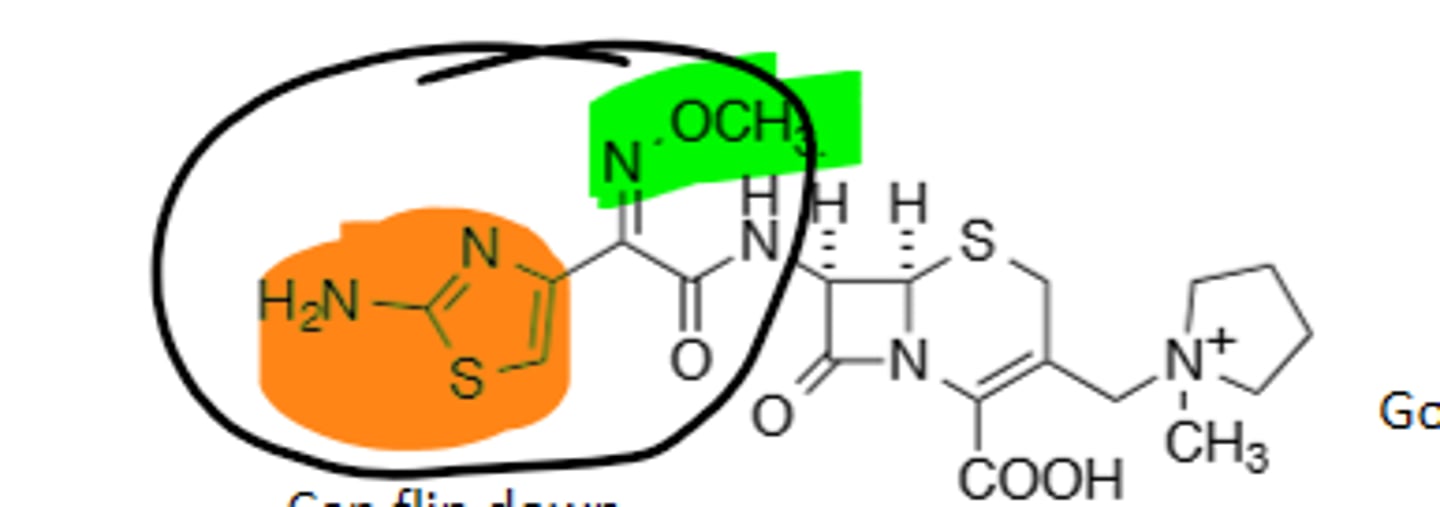
Ceftaroline
5th Generation Cephalosporin, very broad spectrum coverage, agent can be used against MRSA, resistant to B-lactamases, good leaving group (Parenteral only), ceftaroline fosamil is the prodrug
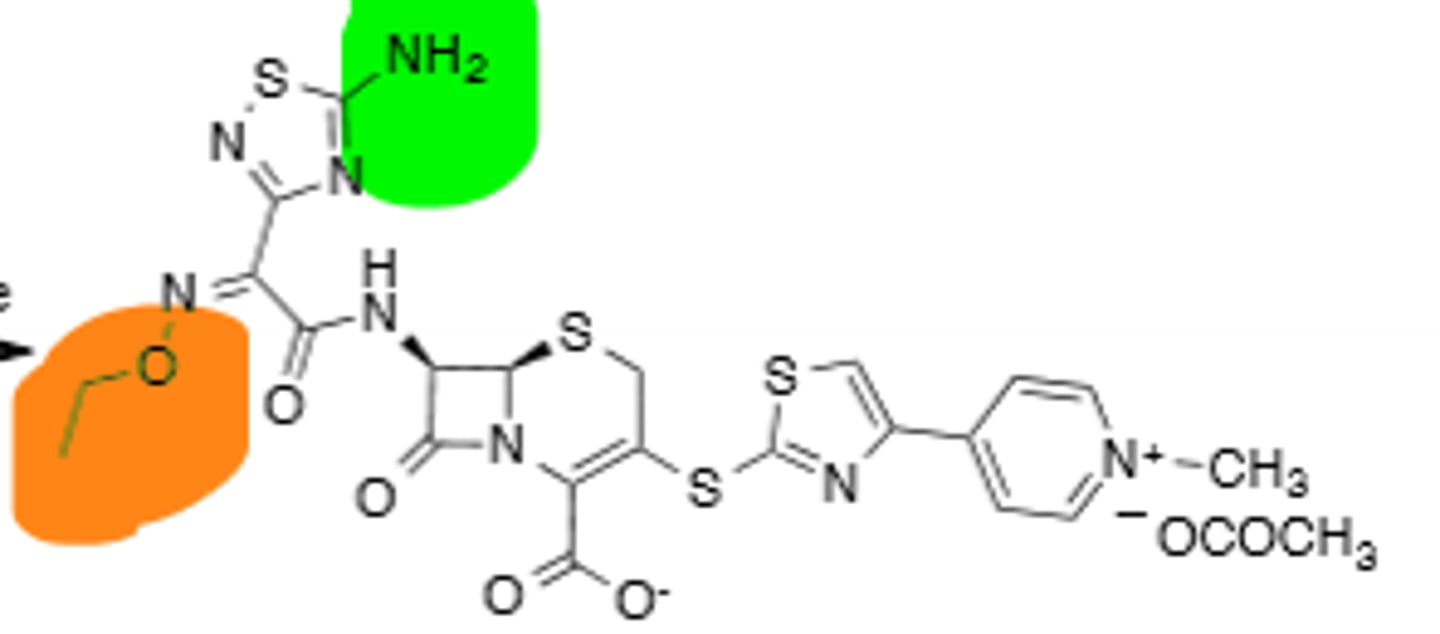
Cefotetan
Cephamycin, 2nd Generation Cephalosporin, Methoxyl Group (Pink) increases stability vs B-Lactamases, good leaving group (Parenteral), can cause hypothrombinemia (More prone to bruising), can cause disulfram reaction
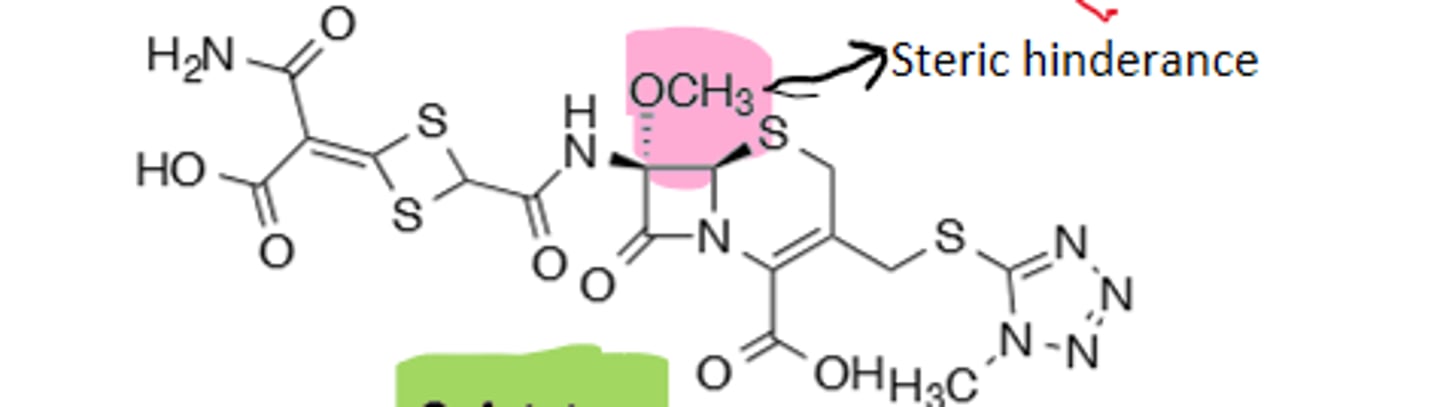
Imipenem
Carbapenem (Greater ring strain than penicillins), derivative of thienamycin (Too reactive to be used as a drug), hydrolyzed by renal dehydropeptidase-1 (Can overcome with cilastatin co-aministration), broad-spectrum and restricted use ("Magic Bullet")
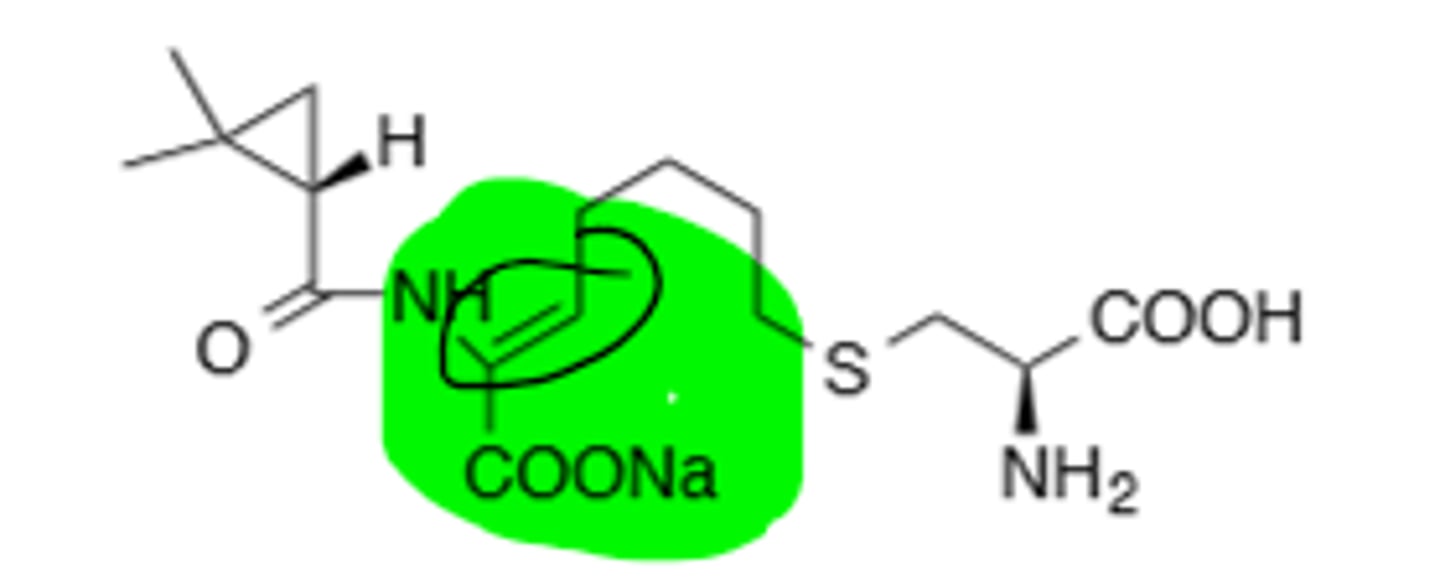
Thienamycin
Origin of Imipenem, too reactive, as the primary amino group attacks the B-Lactam Ring intermolecularly, inactivates itself from therapeutic use.
Cilastatin
Use with imipenem to overcome renal dehydropeptidase-1 hydrolyzation, helps treat infections in the gut with imipenem. Administered parenterally with imipenem
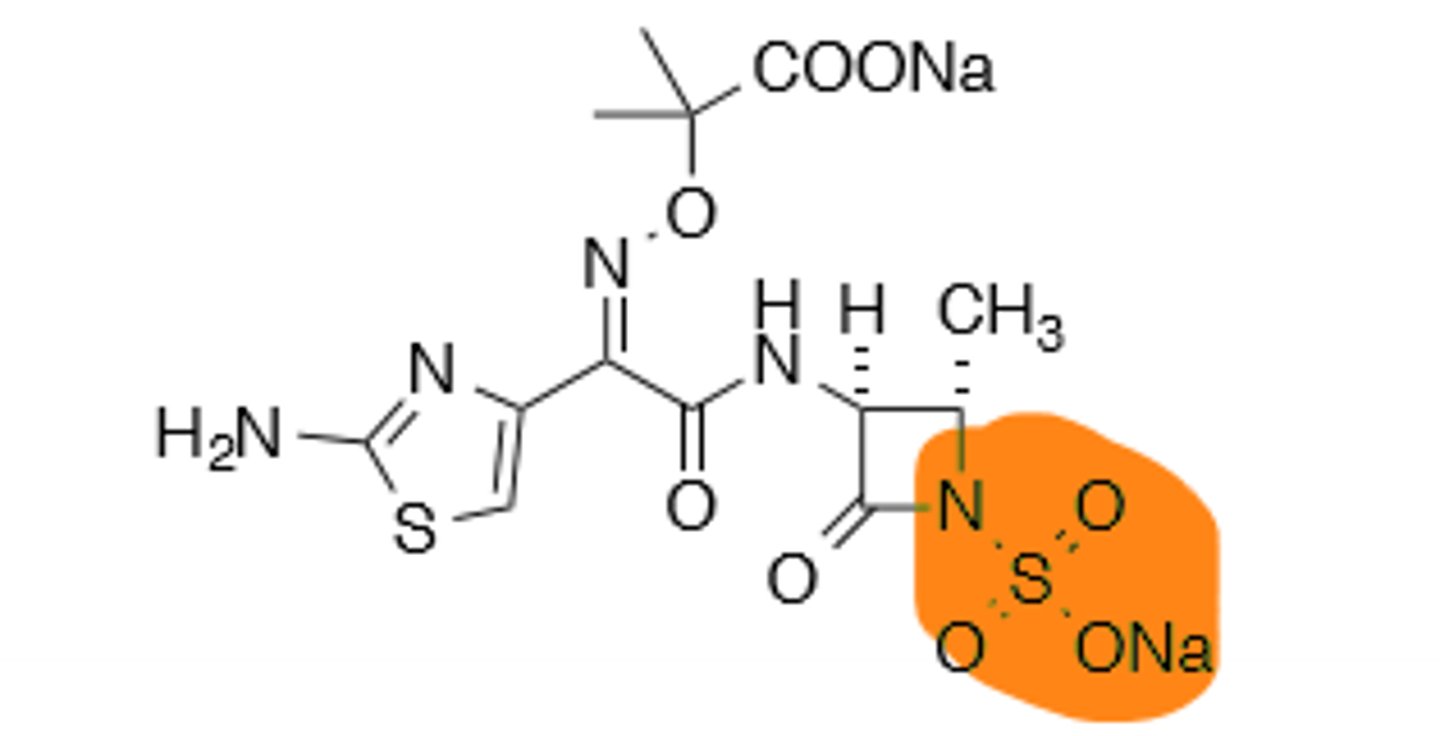
Aztreonam
Monobactam, synthetic drug, sulfamic acid at the C-2 position to increase electronegativity for better reaction with transpeptidase. B-Lactamase resistant. No cross allergenicity with penicillins and cephalosporins (Except ceftazidime). Treats gram (-) bacteria.
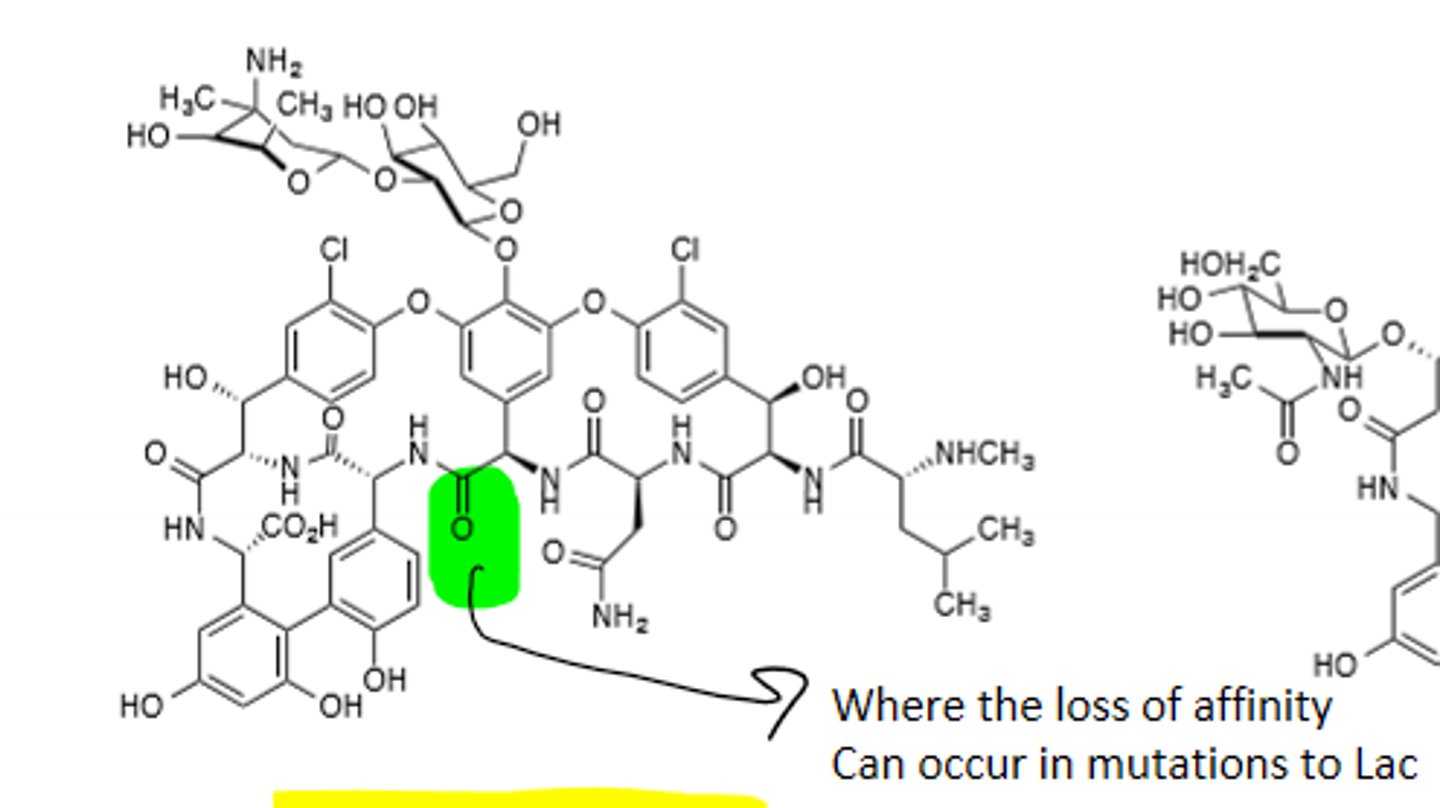
Vancomycin
Glycopeptide, gram (+), binds to peptidyl side chain D-Ala-D-Ala terminus (Before cross-linking), also inhibits transglycosylation step, red skin rash occurs with high concentrations of drug, nephrotoxic, parenteral administration only
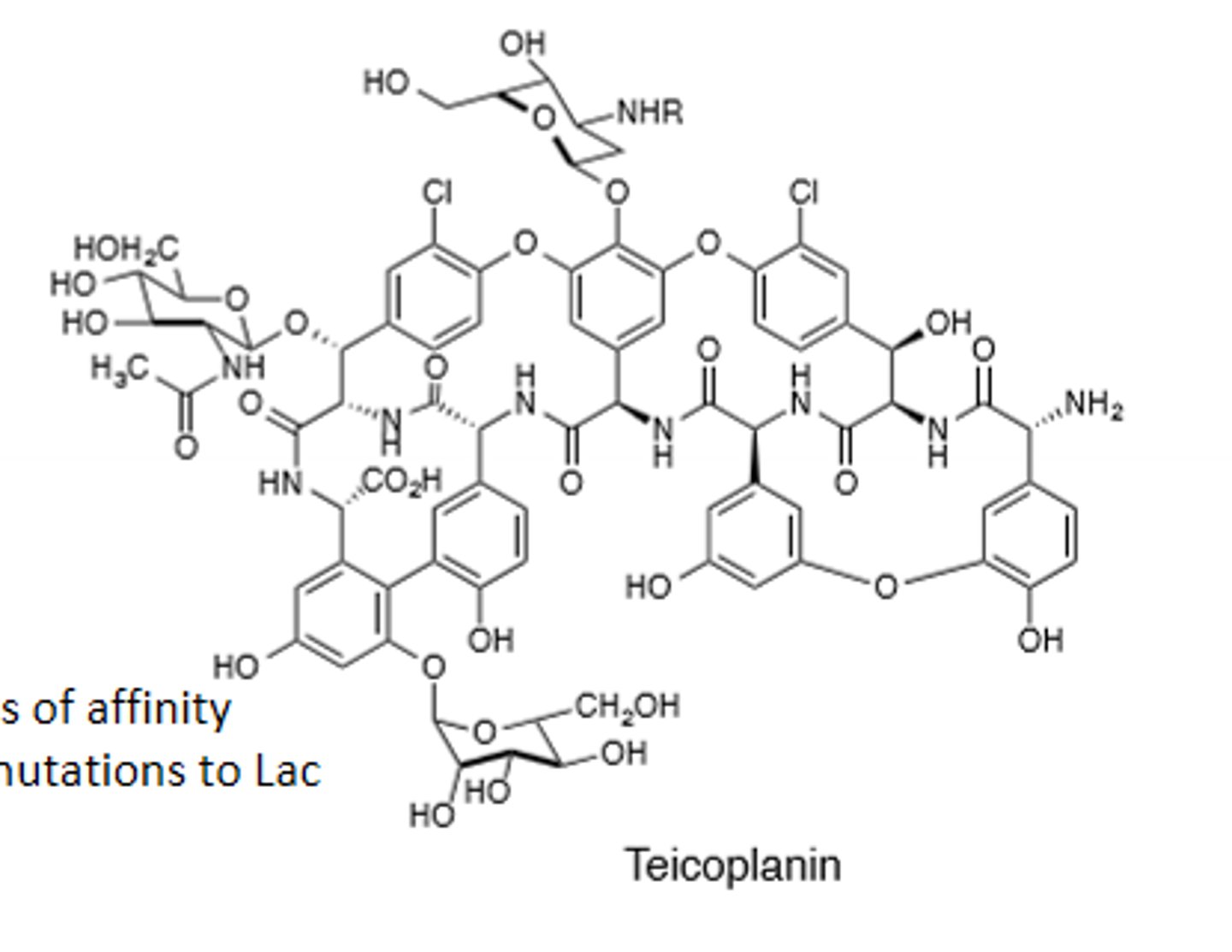
Teicoplanin
Glycopeptide, not approved for use in the United States
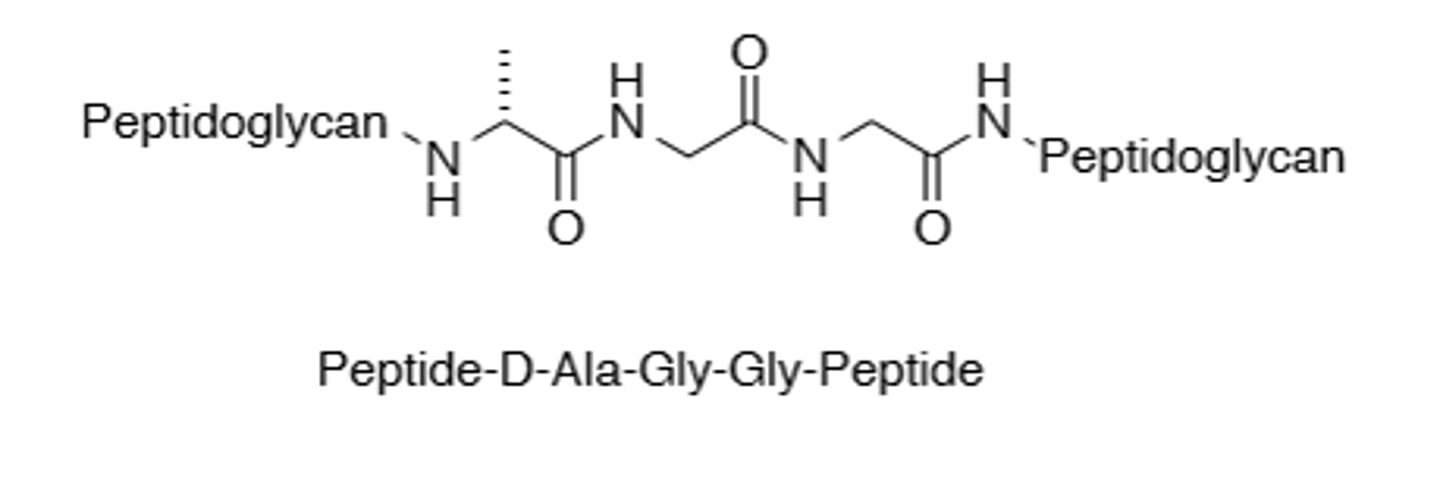
Peptide D-Ala-Gly-Gly-Peptide structure
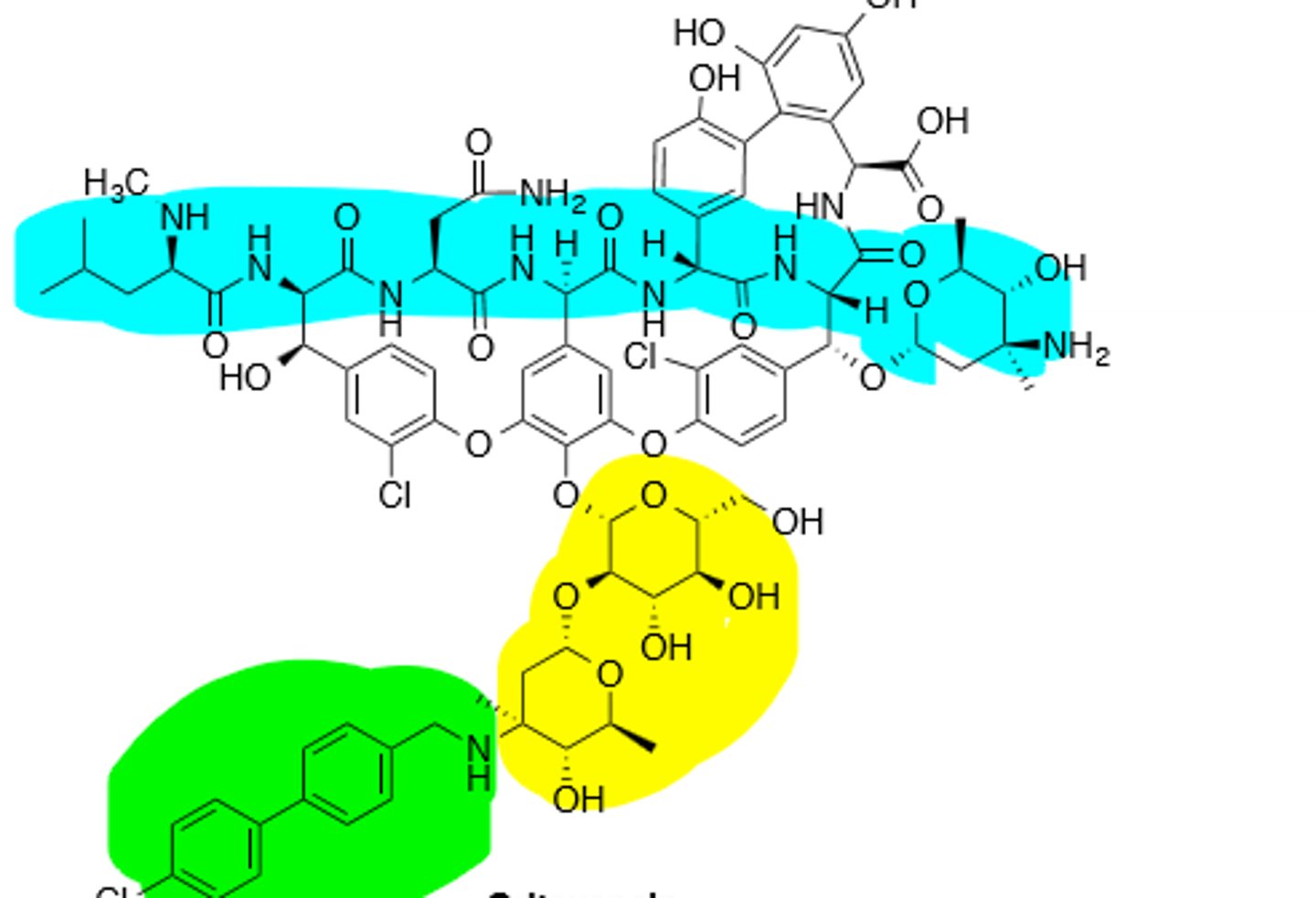
Oritavancin
Lipoglycopeptide, inhibits transpeptidation and transglycosylation, inhibits gram (+) bacteria, including MRSA. Extremely long half life (245 hrs)
Telavancin
Lipoglycopeptide, binds to D-Ala-D-Ala terminus of the peptidoglycan in the cell wall (Gram (+)), also can treat MRSA, half life 7-9 hrs.
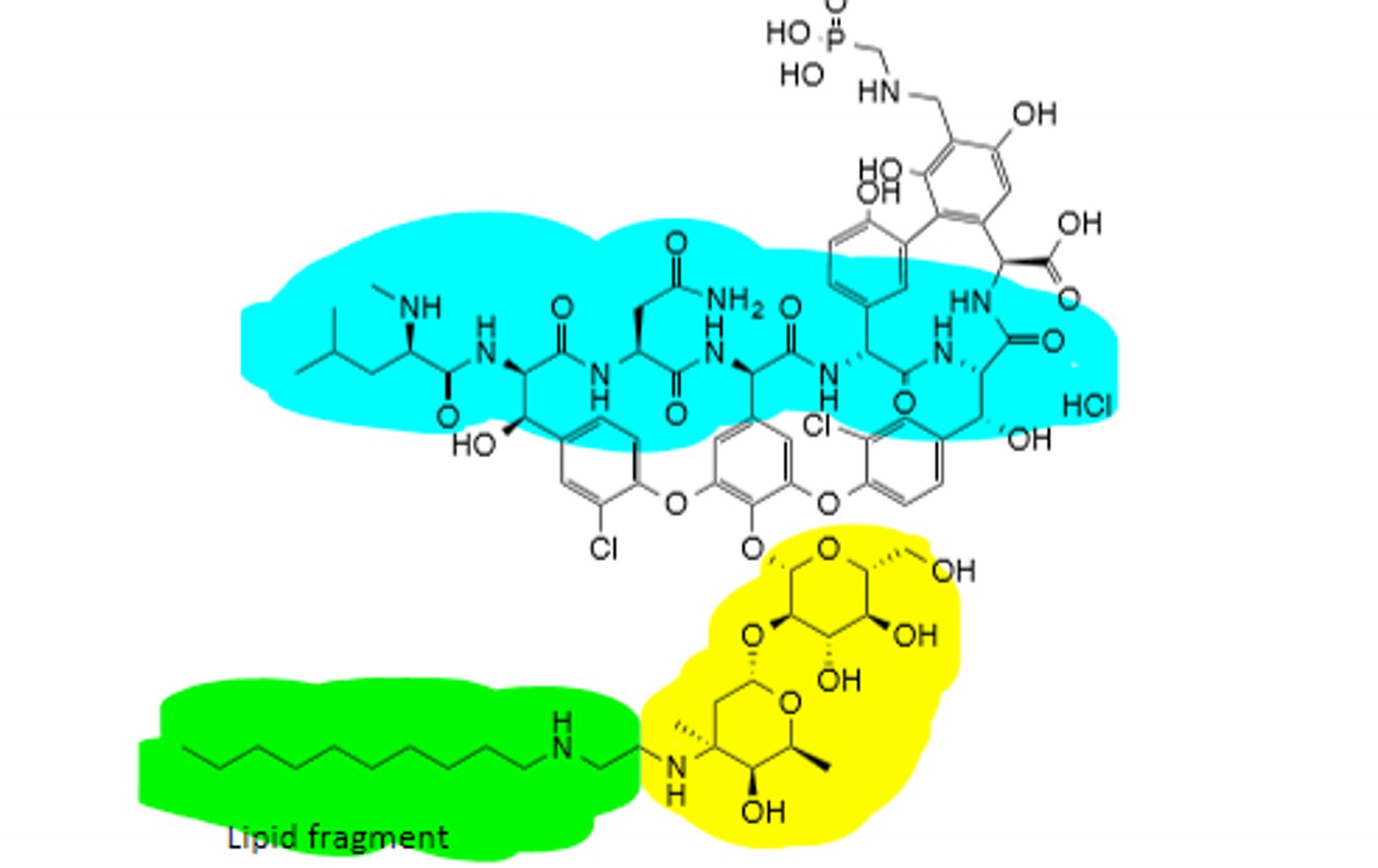
Dalbavancin
2nd Generation Lipoglycopeptide, identical MOA to vancomycin, gram (+) species only, can treat MRSA and MRSE, extremely long half life (204 hrs)
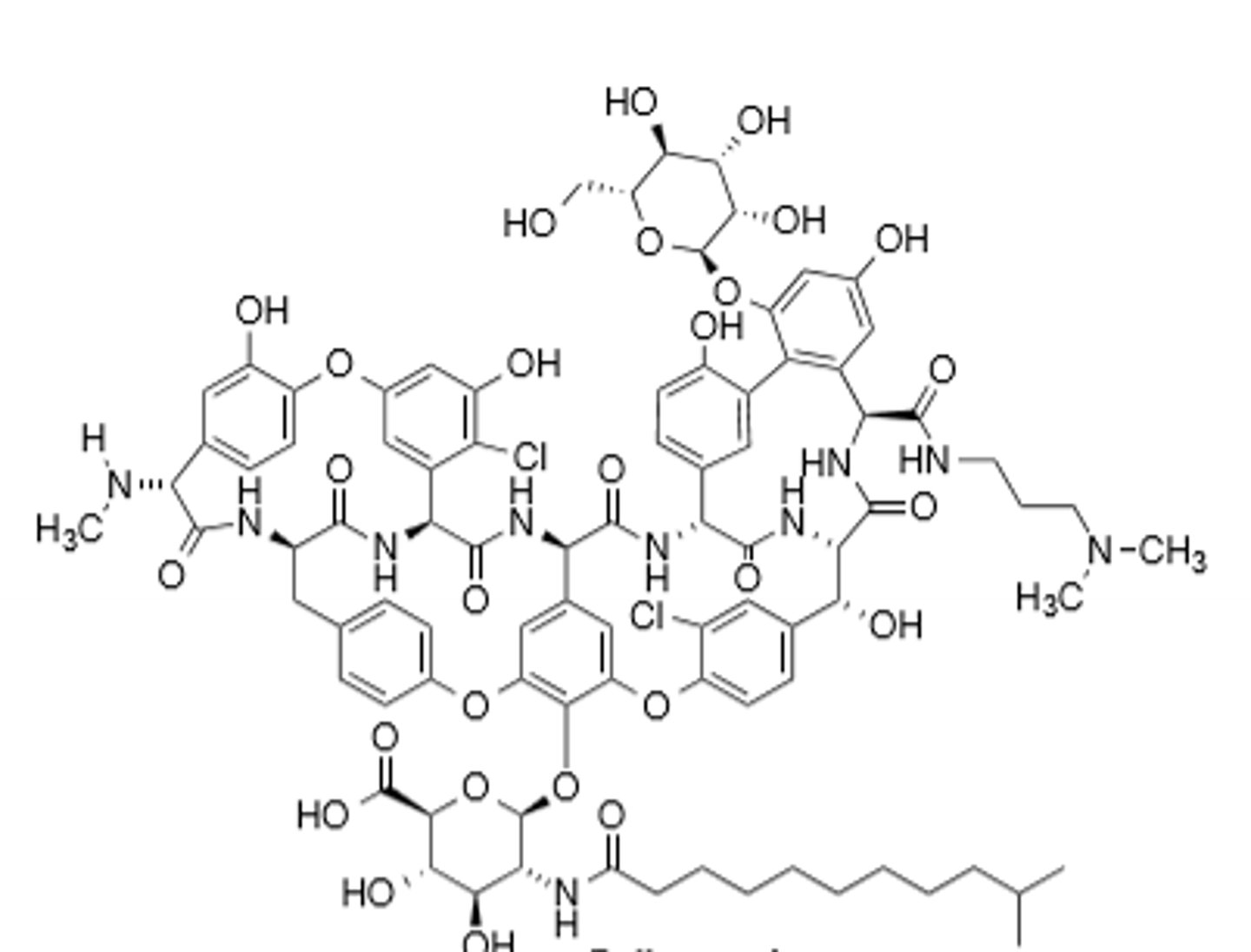
Quinupristin
Streptogramin, derivative of pristinamycin I and pristinamycin II, binds in ribosomal tunnel and causes blockage of tunnel, A2062 mutation creates resistance to this drug. Main resistance is a methylation in A2058 in the 23S rRNA causing decrease binding the the ribosome. Reserved for life-threatening gram (+) organisms. CYP3A4, concentrated in macrophages.
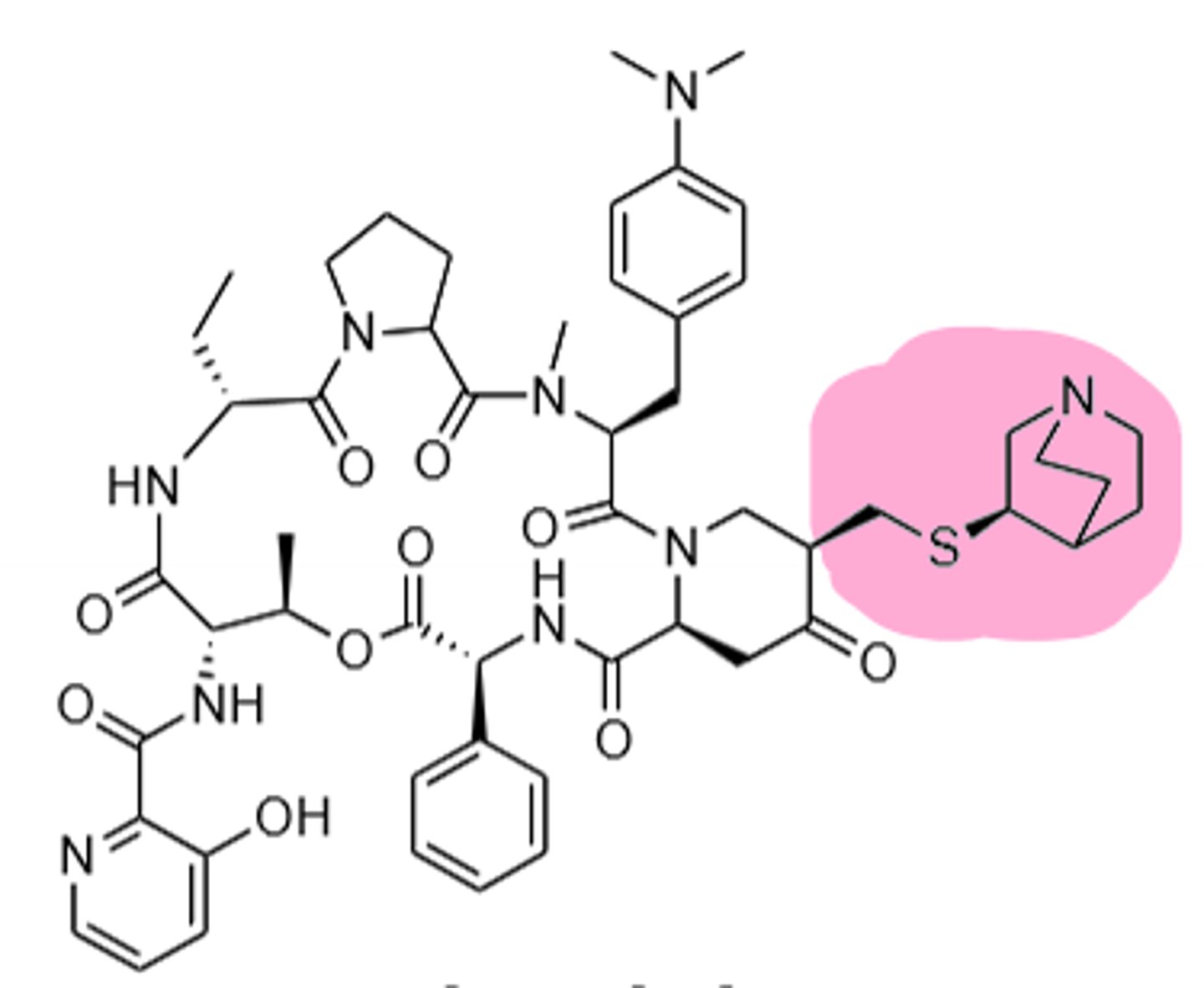
Dalfopristin
Streptogramin, derivative of pristinamycin I and pristinamycin II, blocks the peptidyl transferase step in rRNA which blocks formation of peptide bonds between amino acids, A2062 mutation creates resistance to this drug. Main resistance is a methylation in A2058 in the 23S rRNA causing decrease binding the the ribosome. Reserved for life-threatening gram (+) organisms. CYP3A4, concentrated in macrophages.
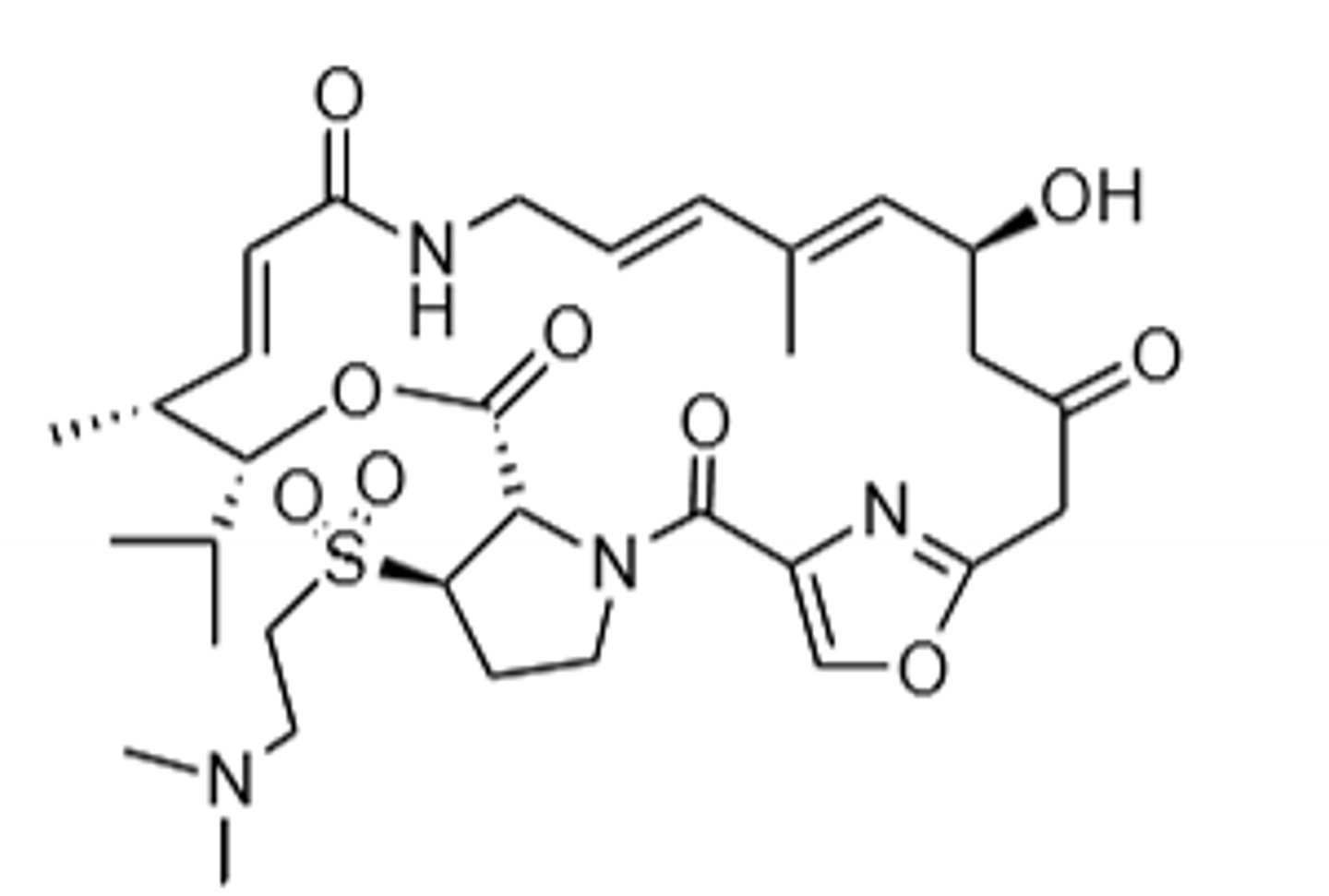
Linezolid
Oxazolidinone, binds to the 50S ribosomal subunit, inhibits protein synthesis at peptide elongation stage, specifically interacts with 23S rRNA inside the 50S subunit, good for drug resistant gram (+) bacteria, excellent oral bioavailability, but can be used IV as well, target site modification is the main form of resistance to reduce binding affinity to 23S rRNA, can cause tongue discoloration and oral thrush, must get CBC because thrombocytopenia risk, neuropathy after 6 months, *MAO-Inhibitor --> Watch with adrenergic and serotonergic agents, and food rich is tyramine.
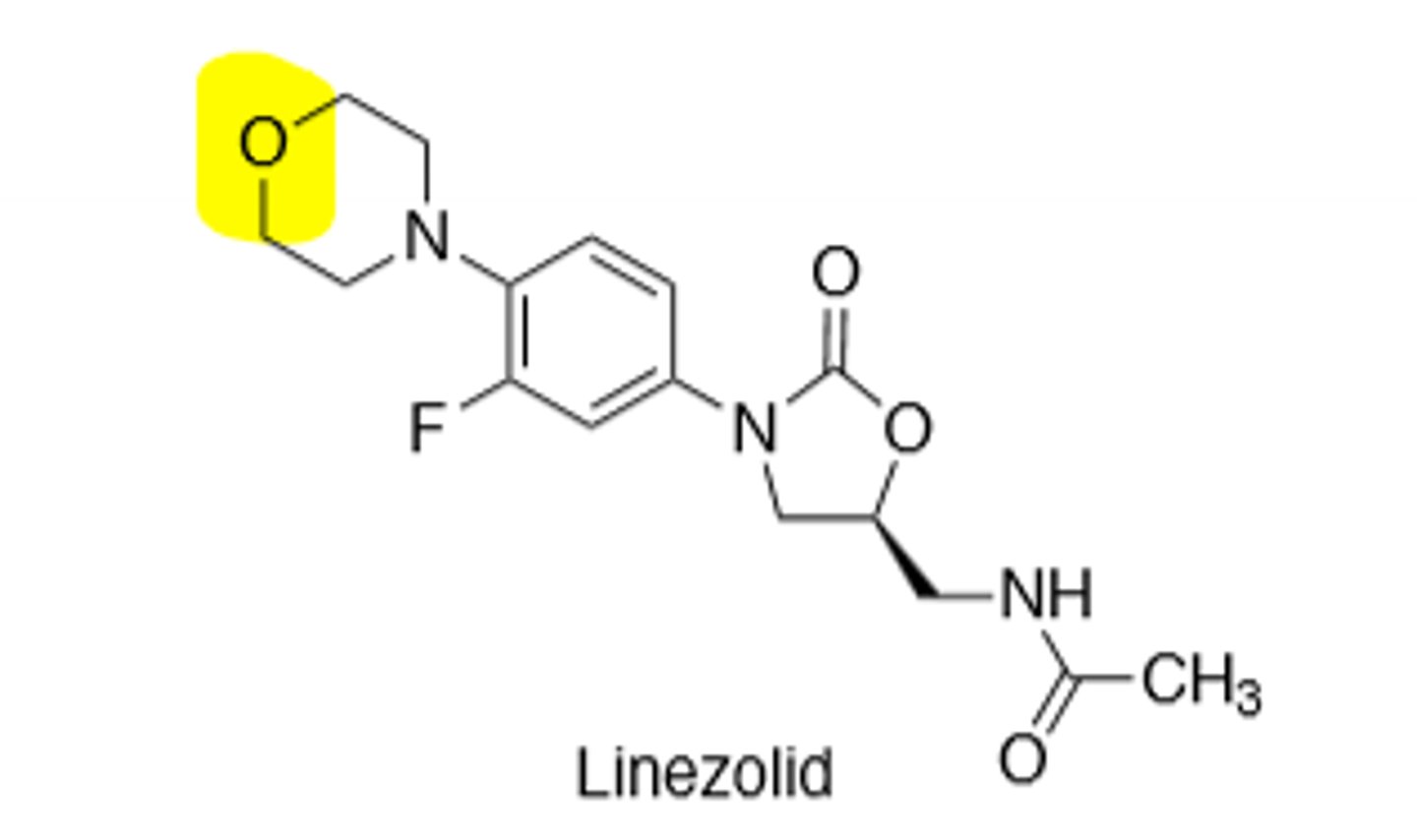
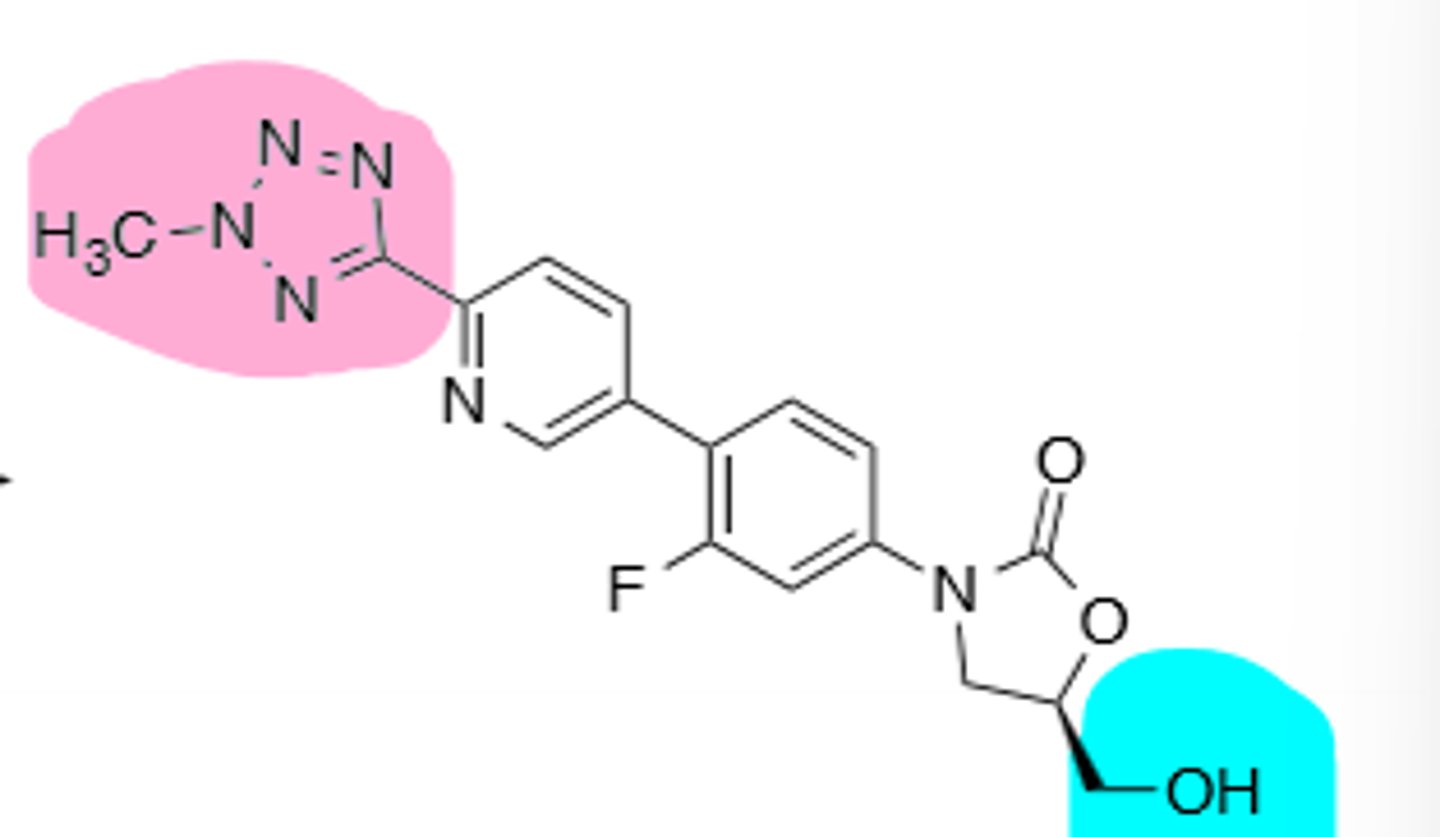
Tedizolid
Active metabolite of Tedizolid Phosphate, 2nd generation oxazolidinone, more potent than Linezolid vs MRSA, oral or IV administration, *MAO-Inhibitor --> Watch with adrenergic and serotonergic agents, and food rich is tyramine.
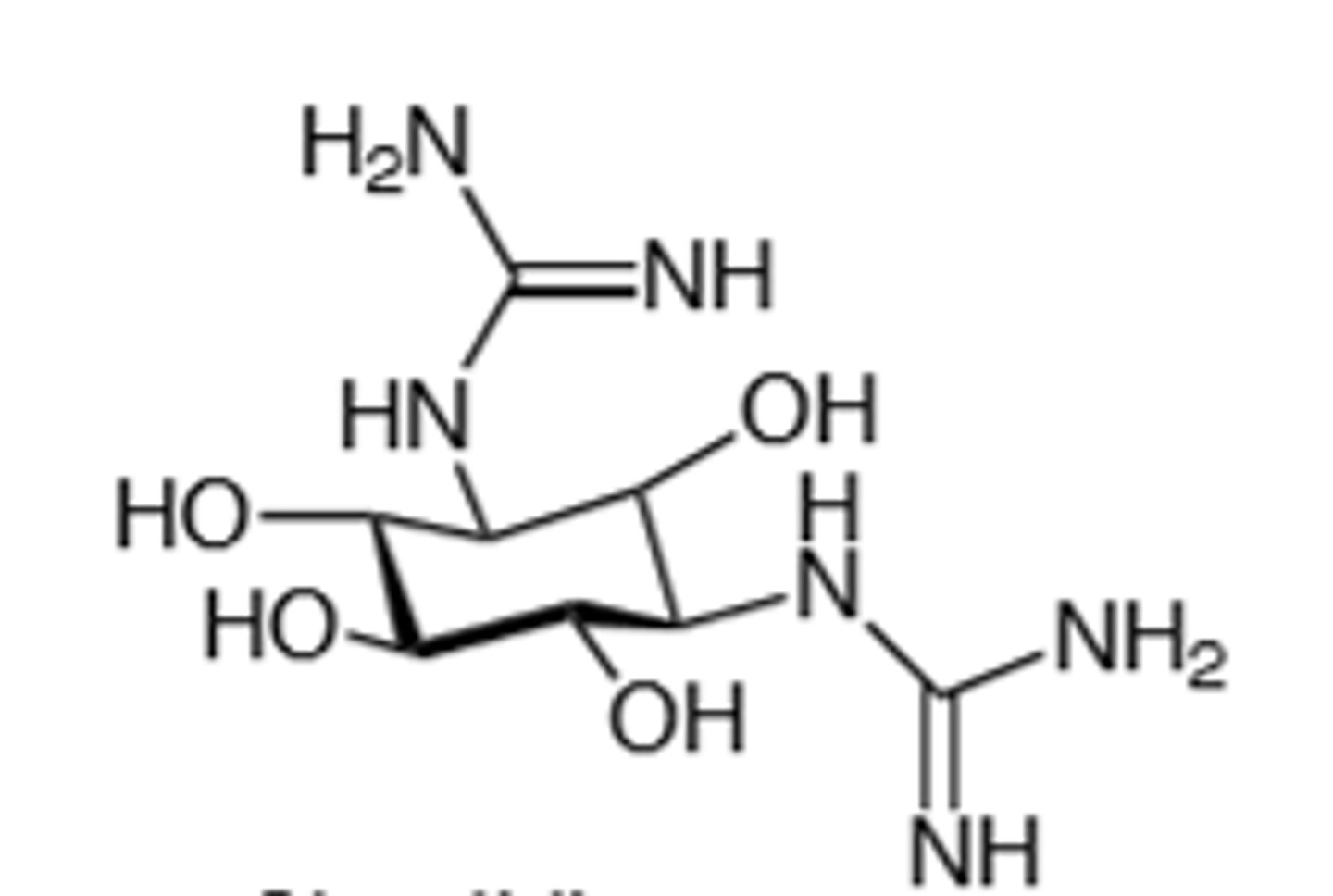
Streptidine
Core structure of the aminoglycosides, contain a 1,3-diaminocyclitol.
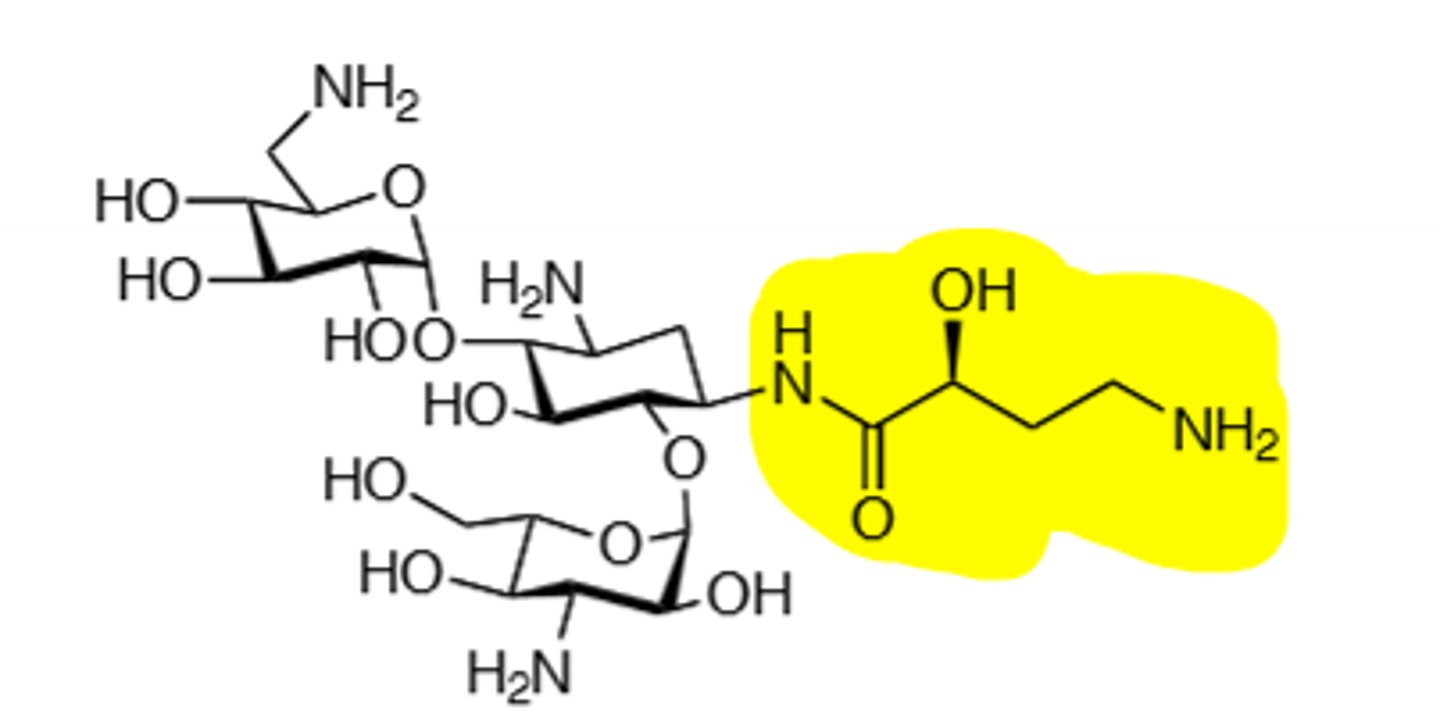
Amikacin
Synthesized from kanamycin A, aminoglycoside, inhibits bacteria metabolism by R-factors with presence of L-hydroxyaminobuteryl amide moiety. Ototoxic, nephrotoxic, can induce neuromuscular blockade, binds to 30S subunit and cause a frame shift mutation, inactivated by acetylation, adenylation, and phosphorylation, displace Mg and Ca ions to make membrane more permeable in gram (-), do not mix with penicillin, toxicity more likely if treatment exceeds 5 days, teratogen.
Tobramycin
Aminoglycoside, lacks a 3' hydroxyl group, so it cannot be phosphorylated at that position, treats gentamicin-resistant infections, broad spectrum. Ototoxic, nephrotoxic, can induce neuromuscular blockade, binds to 30S subunit and cause a frame shift mutation, inactivated by acetylation, adenylation, and phosphorylation, displace Mg and Ca ions to make membrane more permeable in gram (-), do not mix with penicillin, toxicity more likely if treatment exceeds 5 days, teratogen. Does not undergo phosphorylation
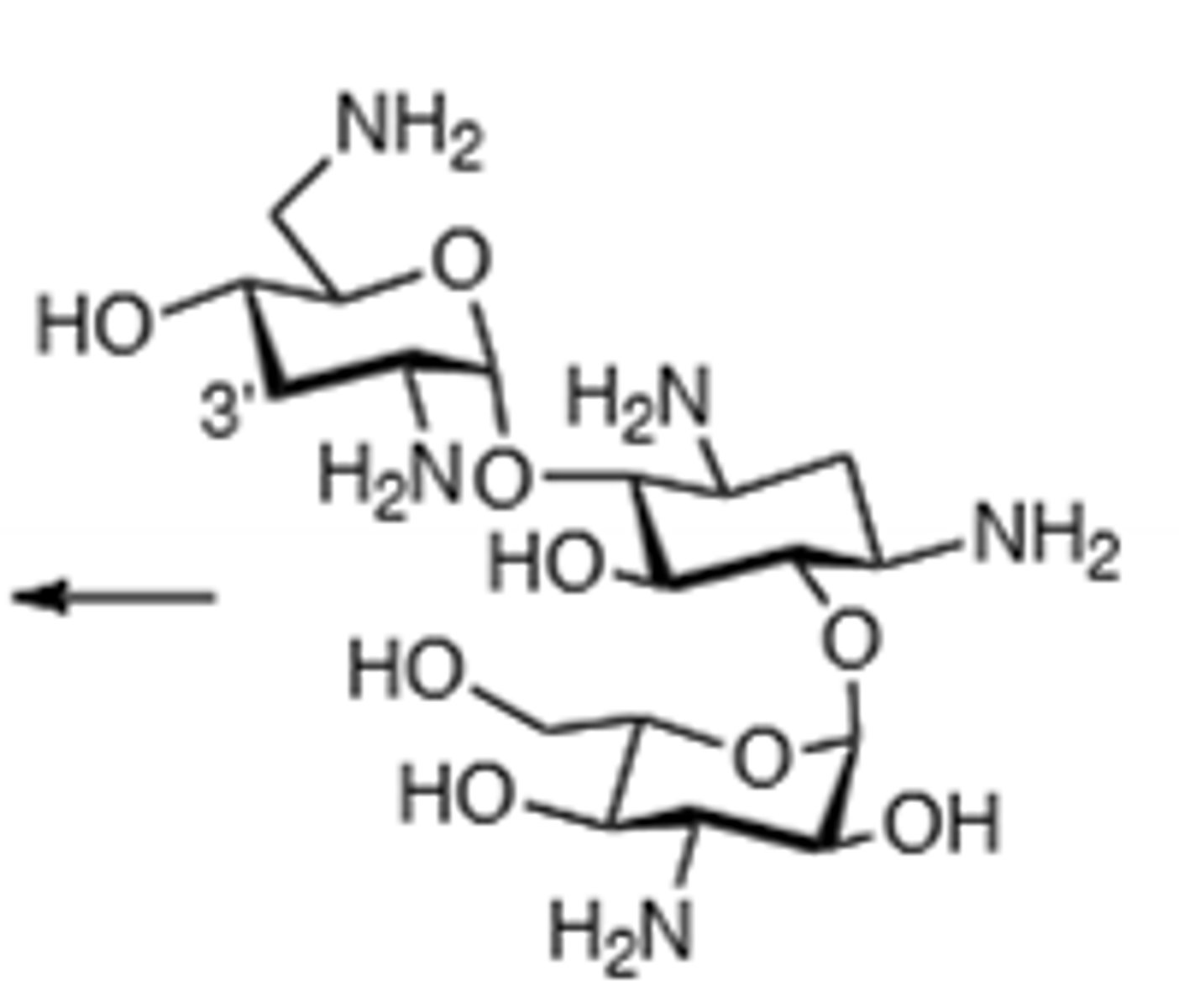
Gentamicin
Aminoglycoside, broad spectrum (excluding gentamicin resistant infections). Ototoxic, nephrotoxic, can induce neuromuscular blockade, binds to 30S subunit and cause a frame shift mutation, inactivated by acetylation, adenylation, and phosphorylation, displace Mg and Ca ions to make membrane more permeable in gram (-), do not mix with penicillin, toxicity more likely if treatment exceeds 5 days., teratogen.
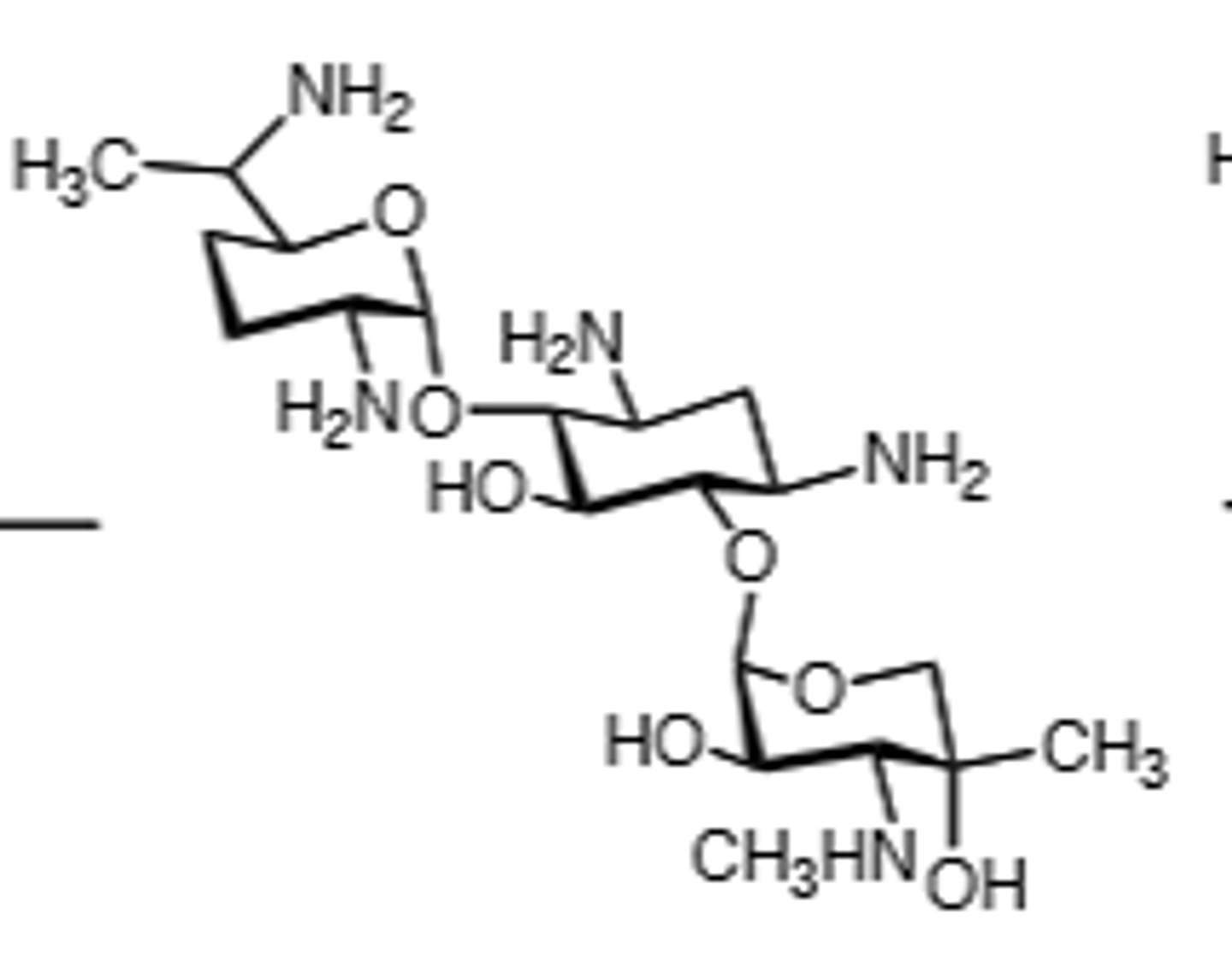
Neomycin B
Orally used aminoglycoside, suppress flora in travelers diarrhea, prophylactic GI surgery use. Ototoxic, nephrotoxic, can induce neuromuscular blockade, binds to 30S subunit and cause a frame shift mutation, inactivated by acetylation, adenylation, and phosphorylation, displace Mg and Ca ions to make membrane more permeable in gram (-), do not mix with penicillin, toxicity more likely if treatment exceeds 5 days, teratogen.
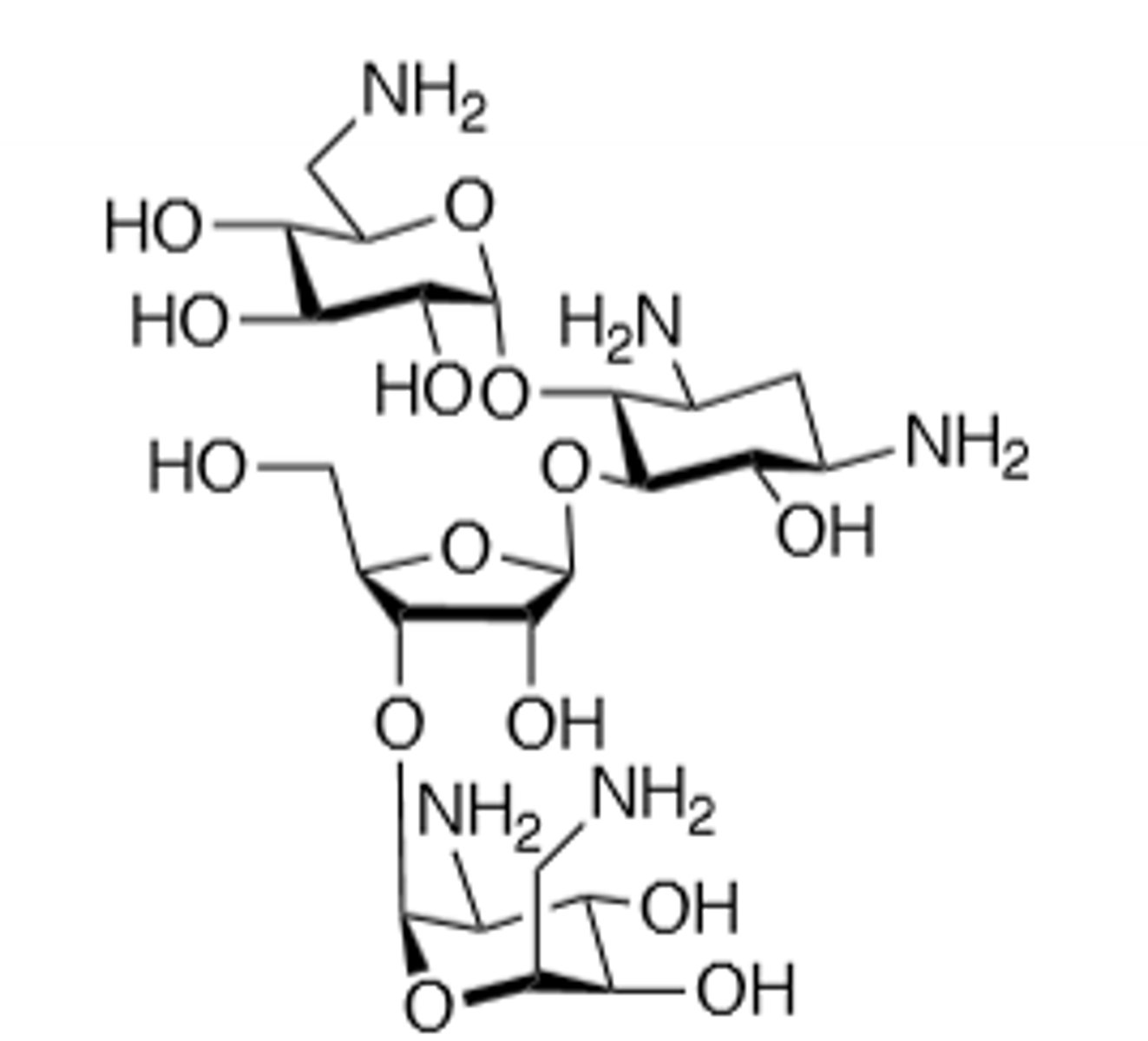
Paromomycin
Orally used aminoglycoside, suppress flora in travelers diarrhea, prophylactic GI surgery use. Treat amoebic dysentery as well as dwarf tapeworm and beef tapeworm. Ototoxic, nephrotoxic, can induce neuromuscular blockade, binds to 30S subunit and cause a frame shift mutation, inactivated by acetylation, adenylation, and phosphorylation, displace Mg and Ca ions to make membrane more permeable in gram (-), do not mix with penicillin, toxicity more likely if treatment exceeds 5 days, teratogen.
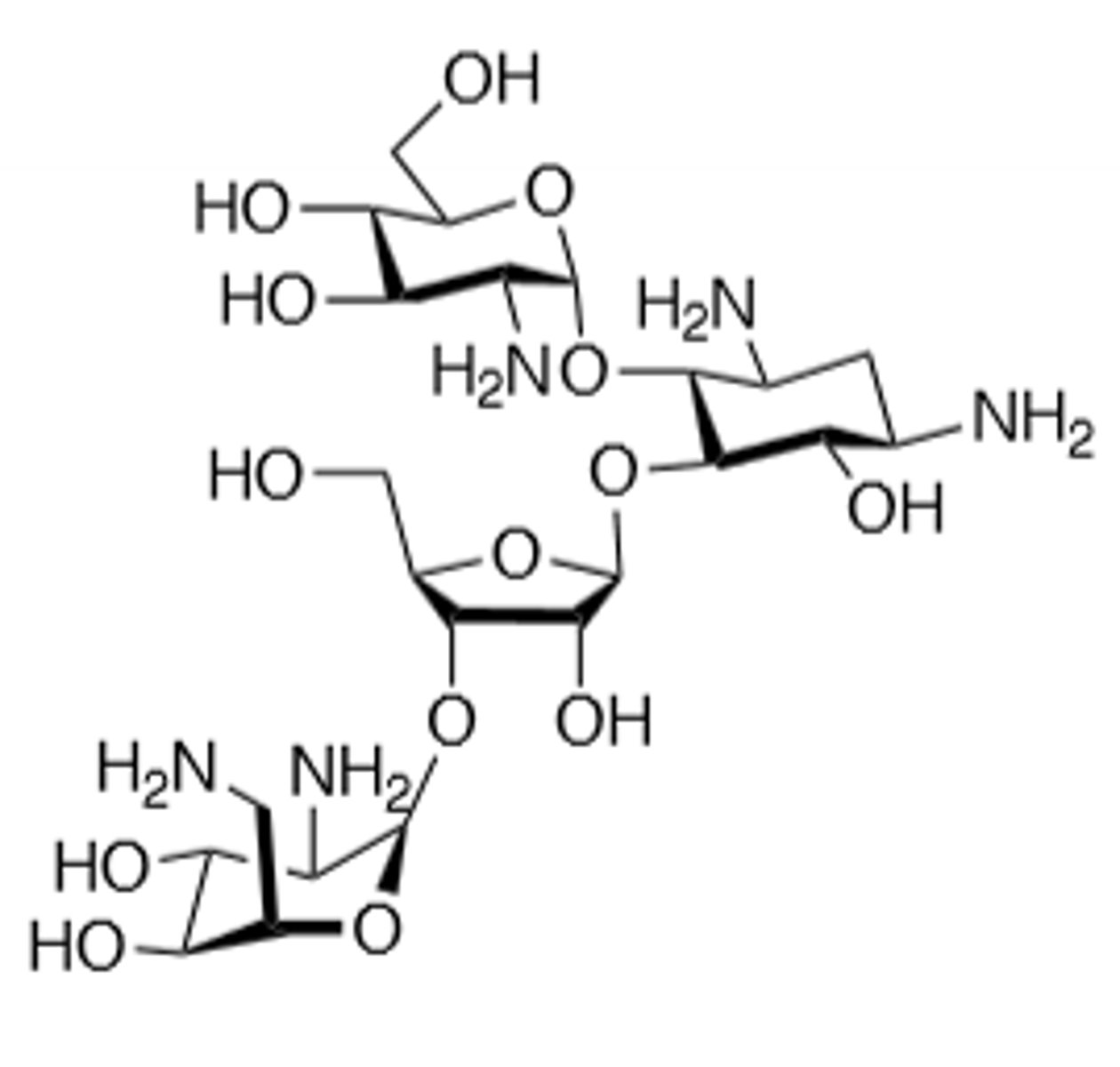
Streptomycin
First aminoglycoside isolated, administered by deep IM injections, ototoxic, nephrotoxic, can induce neuromuscular blockade, binds to 30S subunit and cause a frame shift mutation, inactivated by acetylation, adenylation, and phosphorylation, displace Mg and Ca ions to make membrane more permeable in gram (-), do not mix with penicillin, toxicity more likely if treatment exceeds 5 days, teratogen.
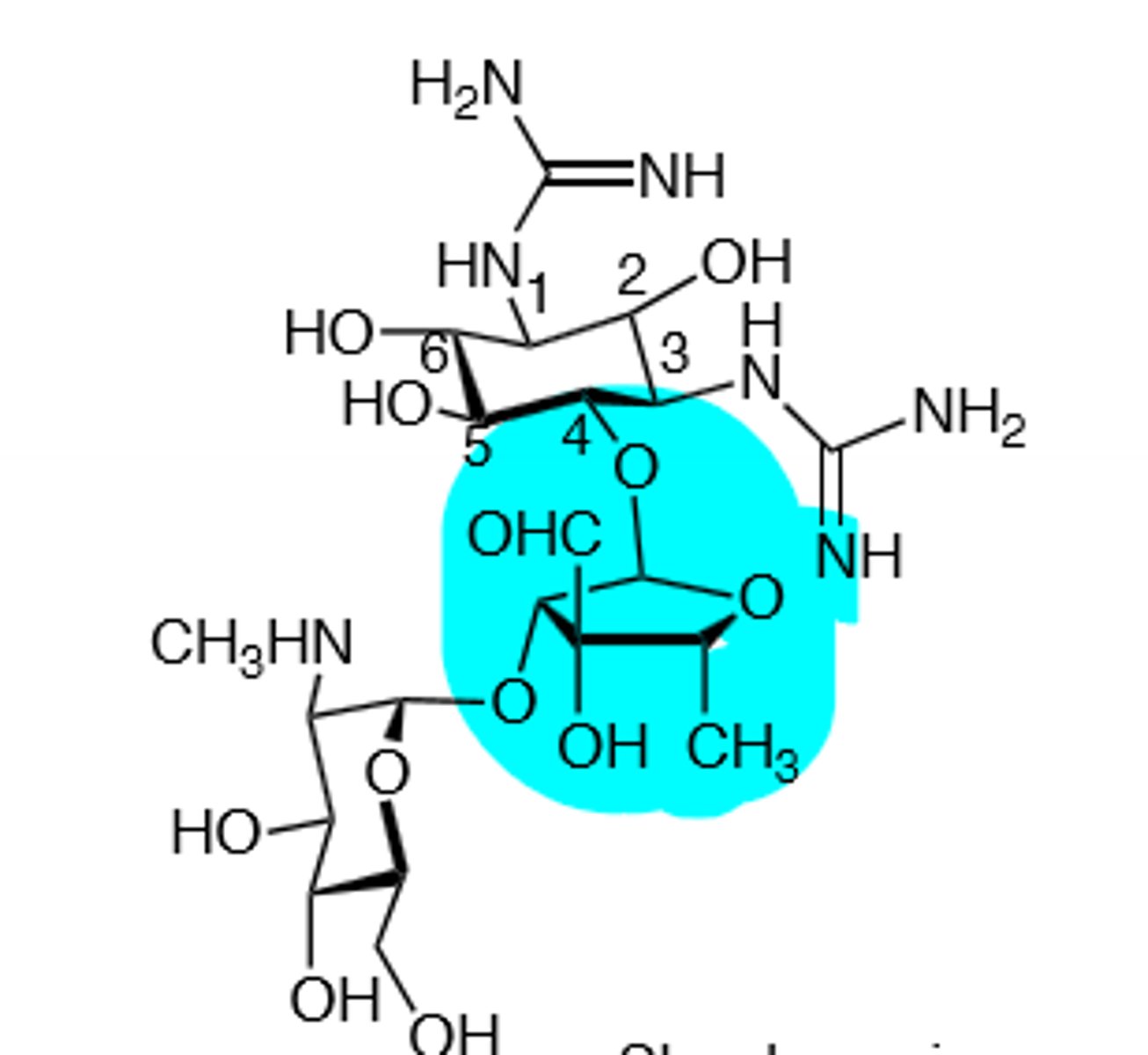
Plazomicin
Semisynthetic aminoglycoside, weight based dosing, ototoxic, nephrotoxic, can induce neuromuscular blockade, binds to 30S subunit and cause a frame shift mutation, inactivated by acetylation, adenylation, and phosphorylation, displace Mg and Ca ions to make membrane more permeable in gram (-), do not mix with penicillin, toxicity more likely if treatment exceeds 5 days, teratogen.
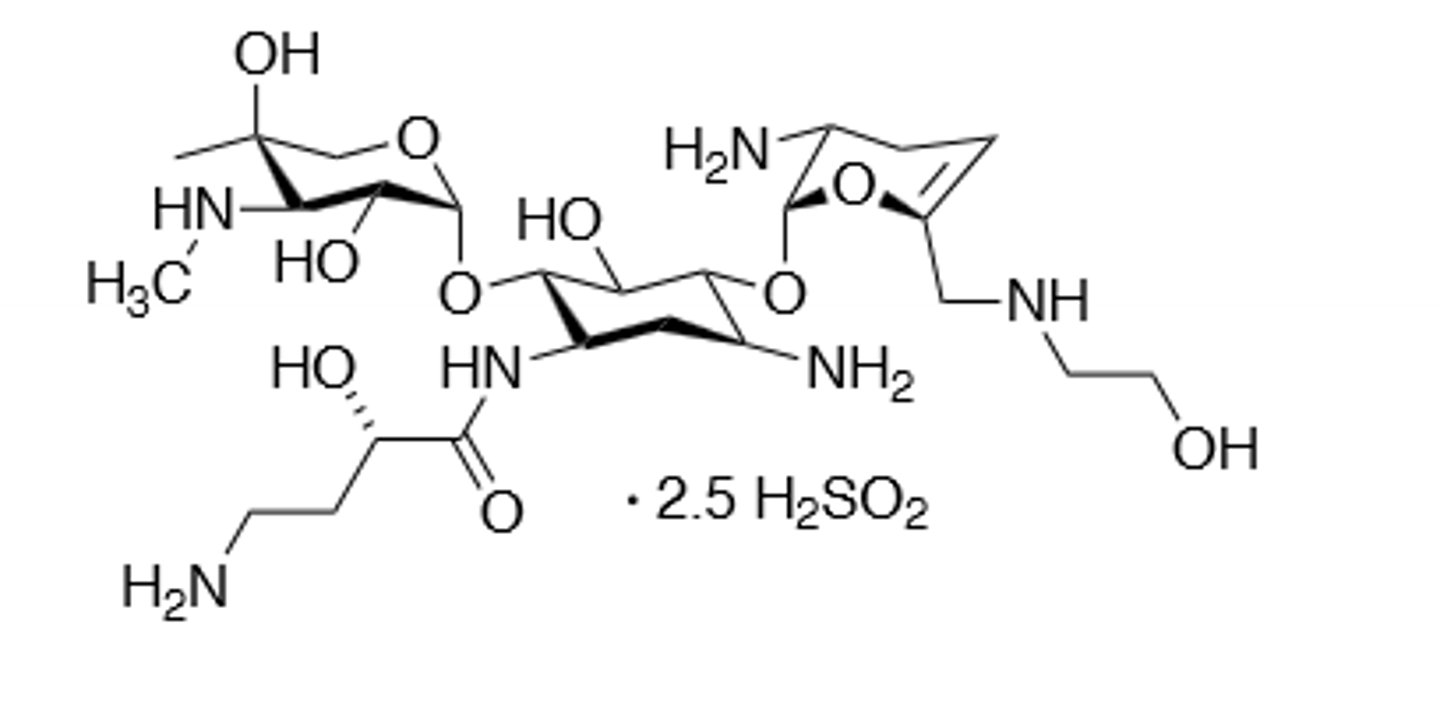
Erythromycin
Macrolide antibiotic, desosamine sugar is relevant for activity, polyketides that are produced by sequential addition of propionate groups to a growing chain, mainly for gram (+) but can be used broad spectrum. Binds to the 50S subunit of the ribosome and binds specifically to the 23S RNA subunit and inhibits translocation of peptidyl tRNA from the A site to the P site to inhibit peptide bond formation. Resistance comes via lactone ester hydrolase, methylation of an adenine base in the 23S rRNA (inhibits binding), reduction of 23S rRNA binding affinity via A2058 mutation, and via efflux pump. Resistance decreases with decreased use. Undergoes an acid-catalyzed ketal formation in acidic condition, so must be given with enteric coating when oral therapy. Metabolized via demethylation in the liver. CYP450 inhibitor. Highly concentrated in phagocytes, can cause pyloric stenosis in children where their moms took the drug during the late stages of pregnancy or while breast feeding.
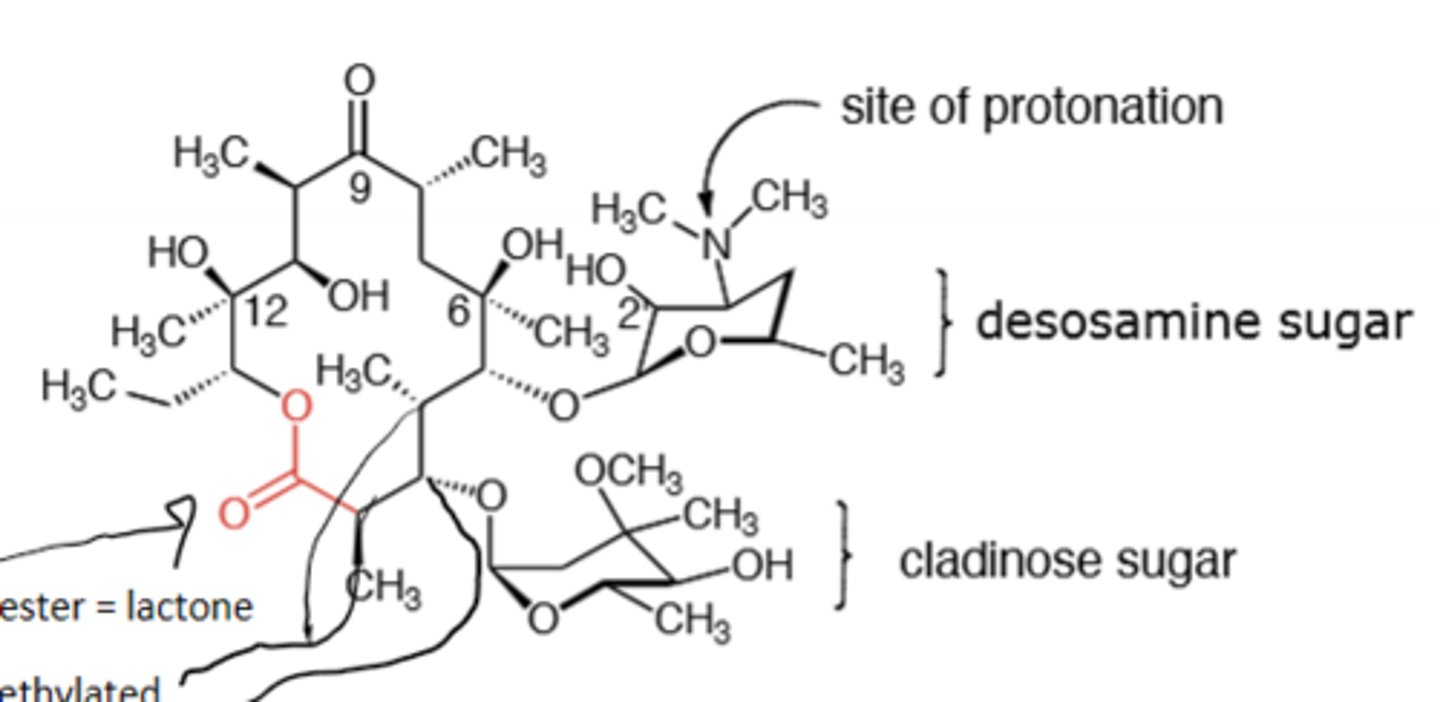
Clarithromycin
Macrolide antibiotic, desosamine sugar is relevant for activity, polyketides that are produced by sequential addition of propionate groups to a growing chain, mainly for gram (+) but can be used broad spectrum. Binds to the 50S subunit of the ribosome and binds specifically to the 23S RNA subunit and inhibits translocation of peptidyl tRNA from the A site to the P site to inhibit peptide bond formation. Resistance comes via lactone ester hydrolase, methylation of an adenine base in the 23S rRNA (inhibits binding), reduction of 23S rRNA binding affinity via A2058 mutation, and via efflux pump. Resistance decreases with decreased use. Replaces 6-OH with OCH3 to block ketal formation at low pH. CYP450 inhibitor.
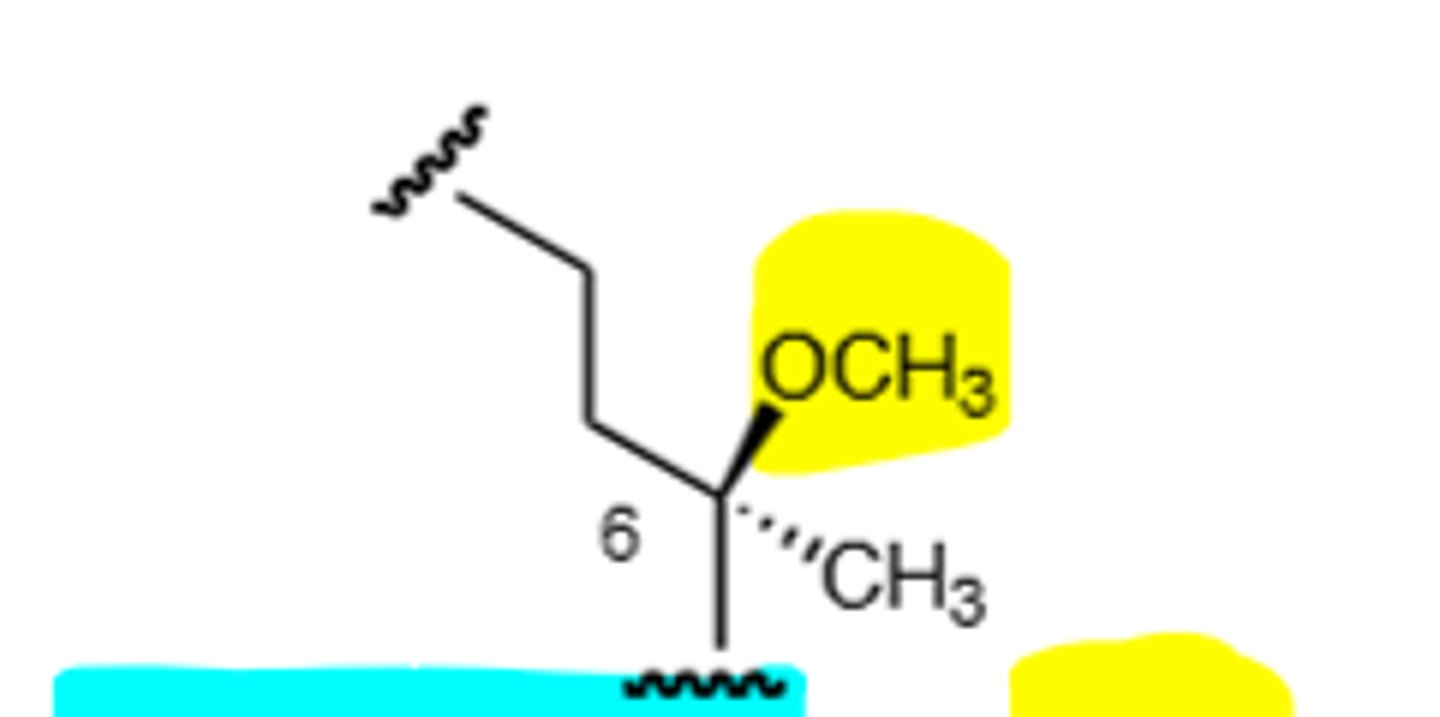
Azithromycin
Macrolide antibiotic, desosamine sugar is relevant for activity, polyketides that are produced by sequential addition of propionate groups to a growing chain, mainly for gram (+) but can be used broad spectrum. Binds to the 50S subunit of the ribosome and binds specifically to the 23S RNA subunit and inhibits translocation of peptidyl tRNA from the A site to the P site to inhibit peptide bond formation. Resistance comes via lactone ester hydrolase, methylation of an adenine base in the 23S rRNA (inhibits binding), reduction of 23S rRNA binding affinity via A2058 mutation, and via efflux pump. Resistance decreases with decreased use. N-methylated methylene amino moiety replaces the C-9 ketone to permanently block ketal formation
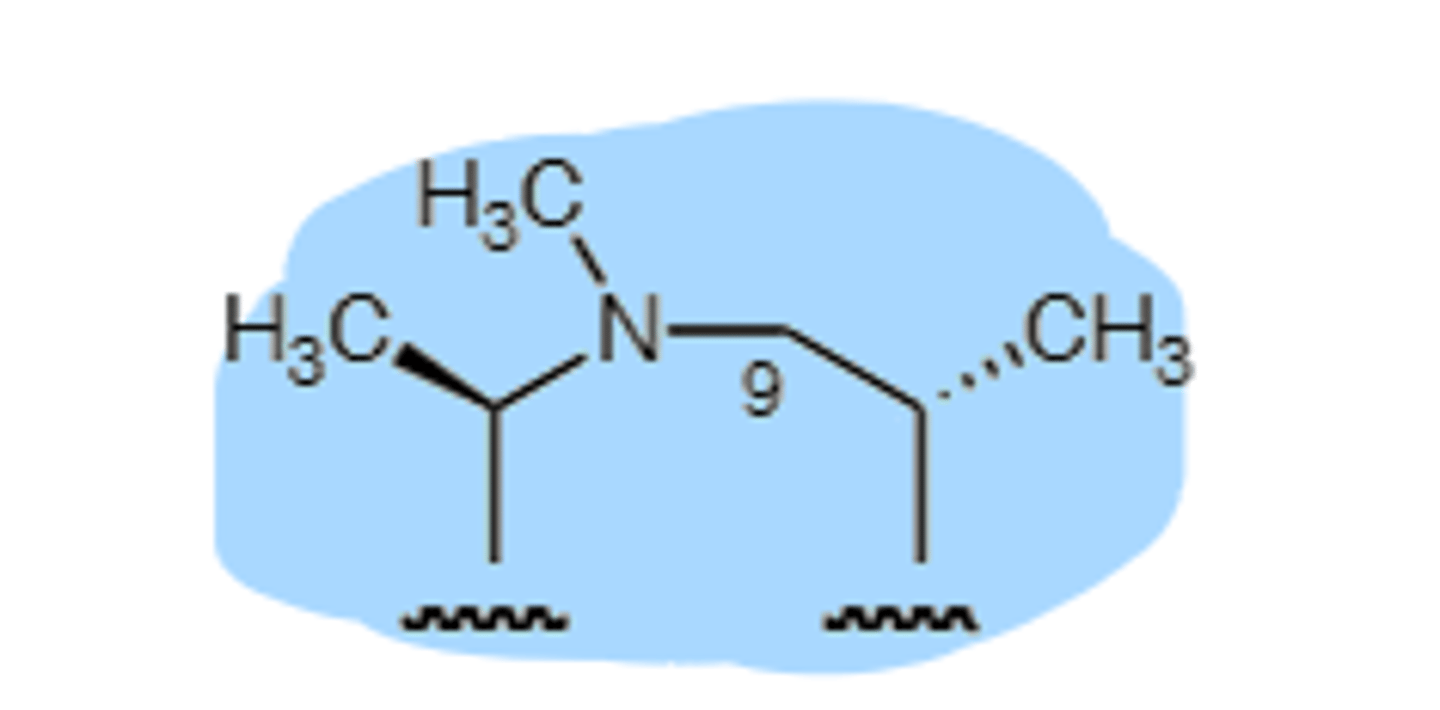
Clindamycin
Synthesized from lincomycin (Too toxic), binds to 50S ribosomal subunit, similar to erythromycin MOA. Broad spectrum. Co-administered with pyrimethamine and leucovorin to treat AIDS patients. Pseudomembranous colitis and diarrhea limit the use of clindamycin, metabolized via P450 enzymes, topical application may cause contact dermatitis.
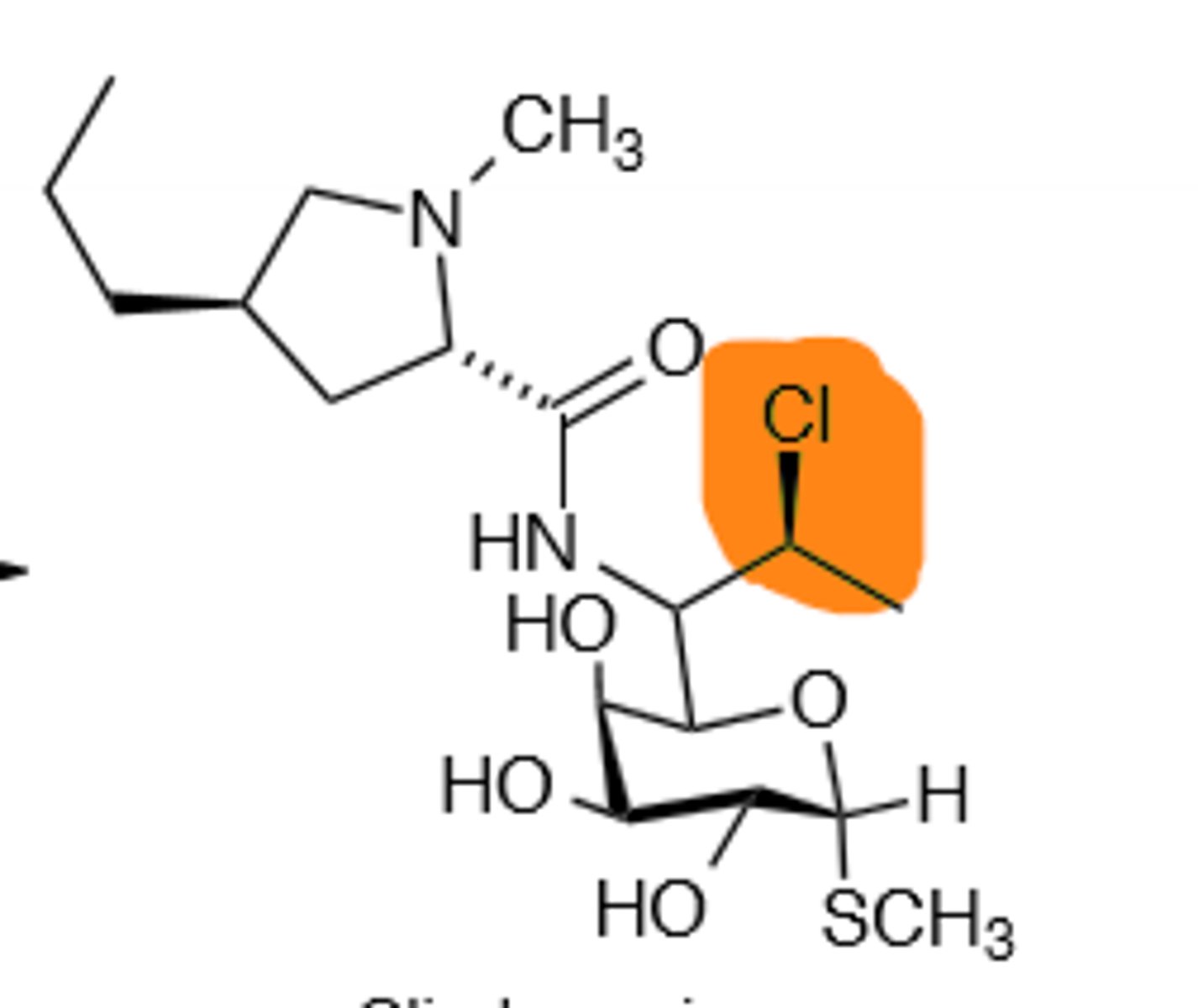
Tetracycline
Bind to the 30S ribosomal subunit and inhibit bacterial protein synthesis, mainly at the Tet1 site. Chelating agent, will bind to metal ions, which causes the drug to not get absorbed in the GI tract as well, avoid drinking milk to prevent 50% absorption decrease. broad-spectrum. Do not give to children while forming their permanent teeth (Discoloration occurs, becomes worse with photooxidation). Do not give after 4th month of pregnancy (Fetal bone deformation). Undergoes empirization in acidic conditions, and undergoes dehydration at the tertiary hydroxyl group, forming an inactive and severely nephrotoxic metabolite.
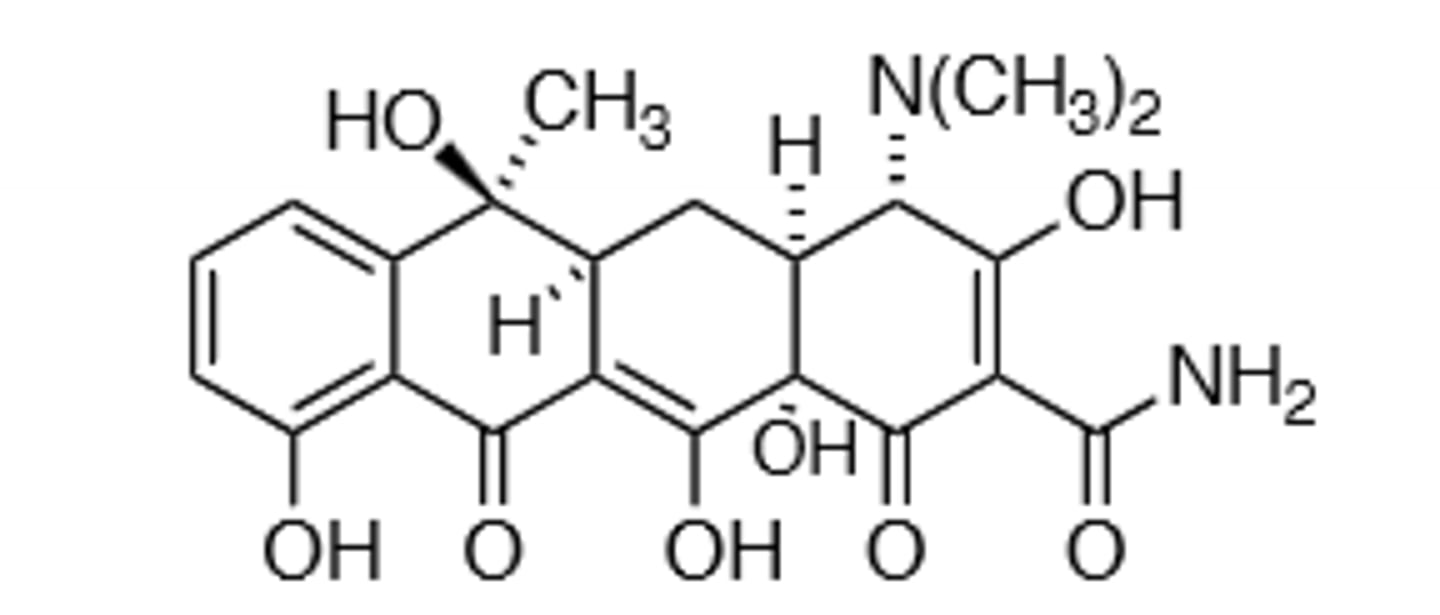
Demeclocycline
Contains a secondary hydroxyl group instead of a tertiary hydroxyl group, which makes demeclocycline dehydrate slower than tetracycline, preventing the toxic intermediate from forming. Chelating agent, will bind to metal ions, which causes the drug to not get absorbed in the GI tract as well, avoid drinking milk to prevent 50% absorption decrease. broad-spectrum.
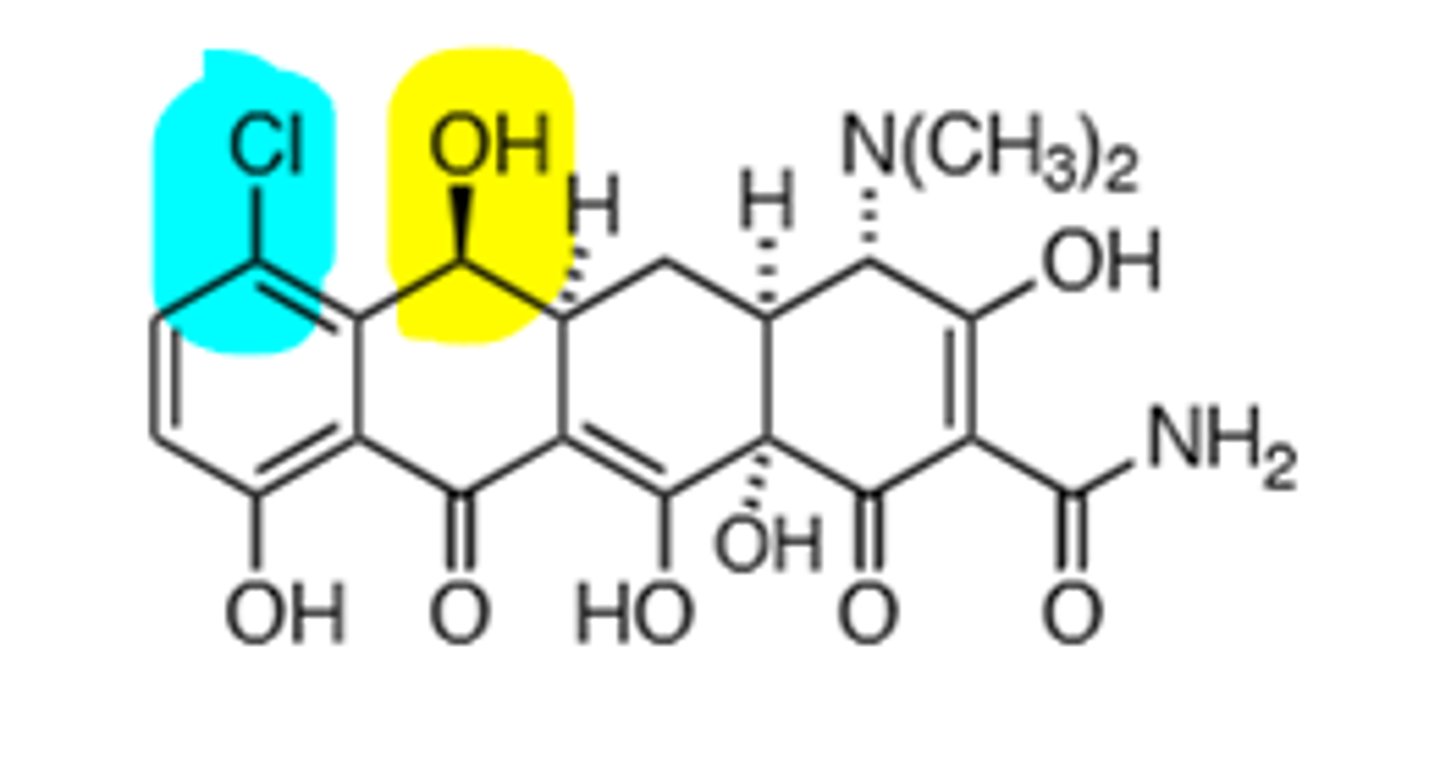
Minocycline
Lacks a C-6 hydroxyl group, which means it does not undergo dehydration, synthesized from demeclocycline, 90-100% oral bioavailability, chelating agent, will bind to metal ions, which causes the drug to not get absorbed in the GI tract as well, avoid drinking milk to prevent 20% absorption decrease. broad-spectrum. Vestibular toxicities unique to this drug.
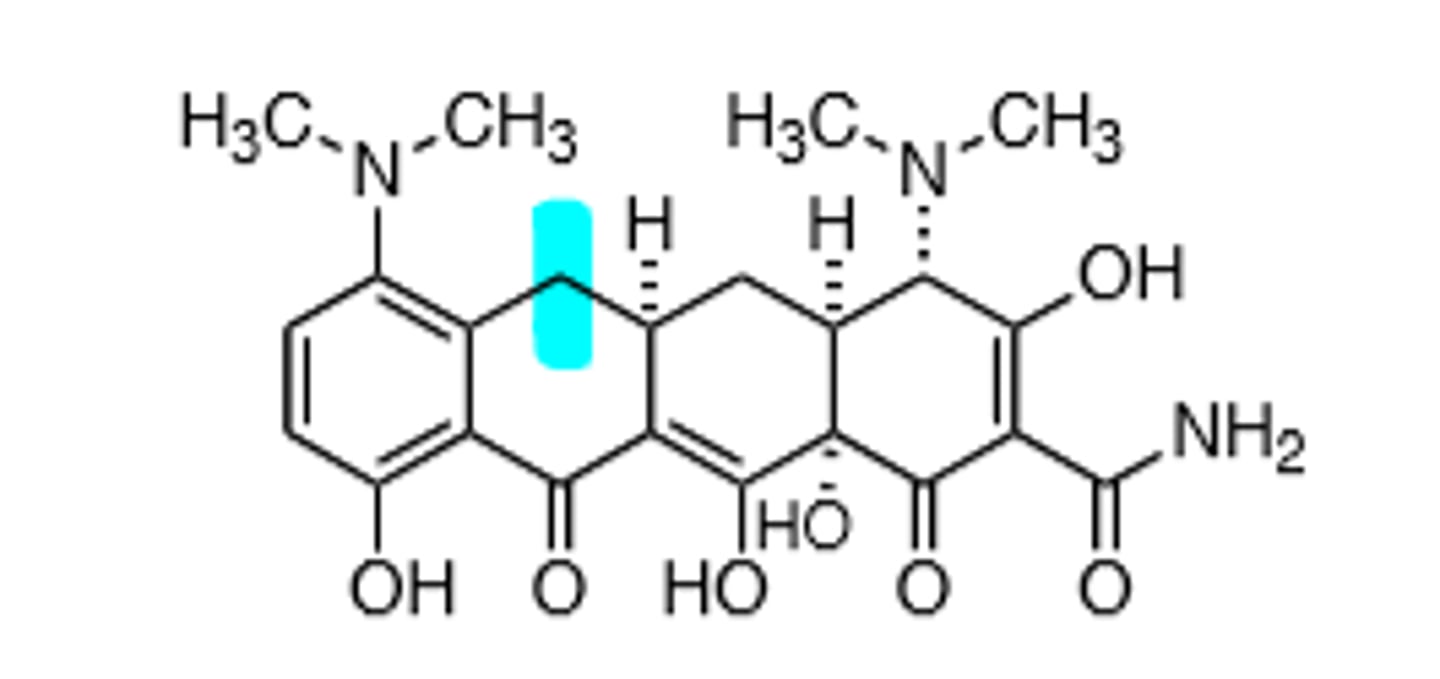
Doxycycline
Synthesized from oxytetracycline, lacks a C-6 hydroxyl group, and does not undergo dehydration, fewer GI symptoms, 18-22 hour half life, 90-100% oral bioavailability. Chelating agent, will bind to metal ions, which causes the drug to not get absorbed in the GI tract as well, avoid drinking milk to prevent 20% absorption decrease. broad-spectrum.
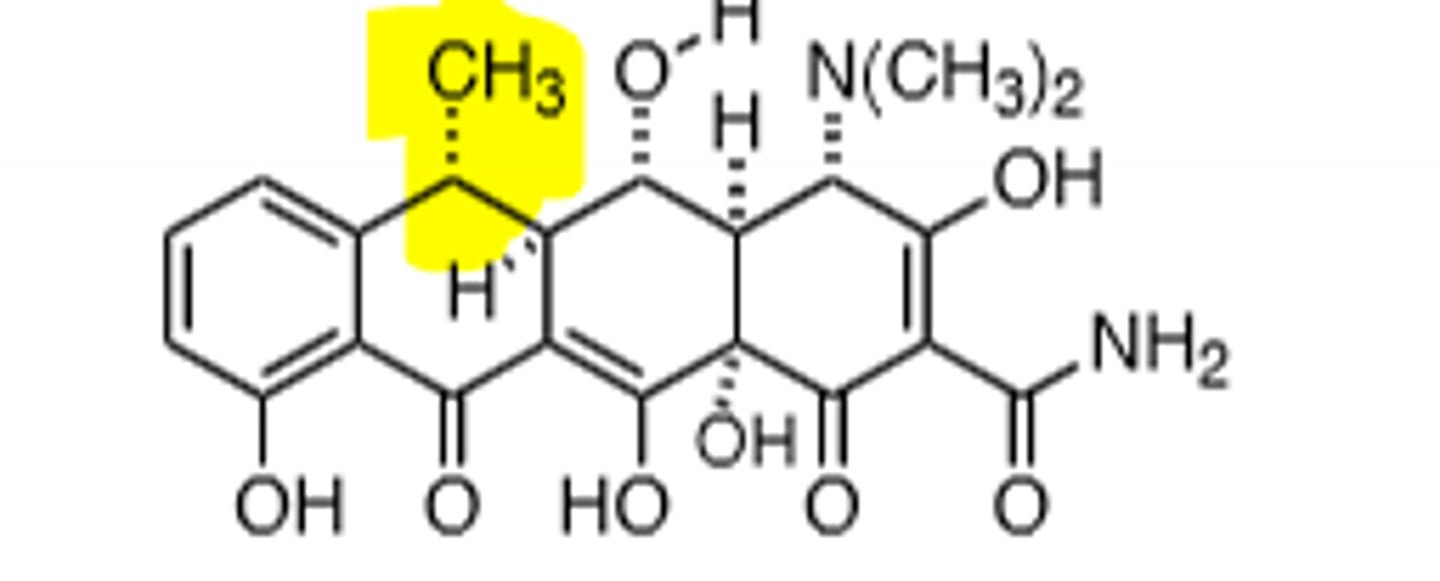
Tigecycline
Derivative of minocycline, parenteral only, lacks a C-6 hydroxyl group, and does not undergo dehydration, overcomes modifications in ribosomal protection proteins from bacteria, Chelating agent, will bind to metal ions, which causes the drug to not get absorbed in the GI tract as well, broad spectrum
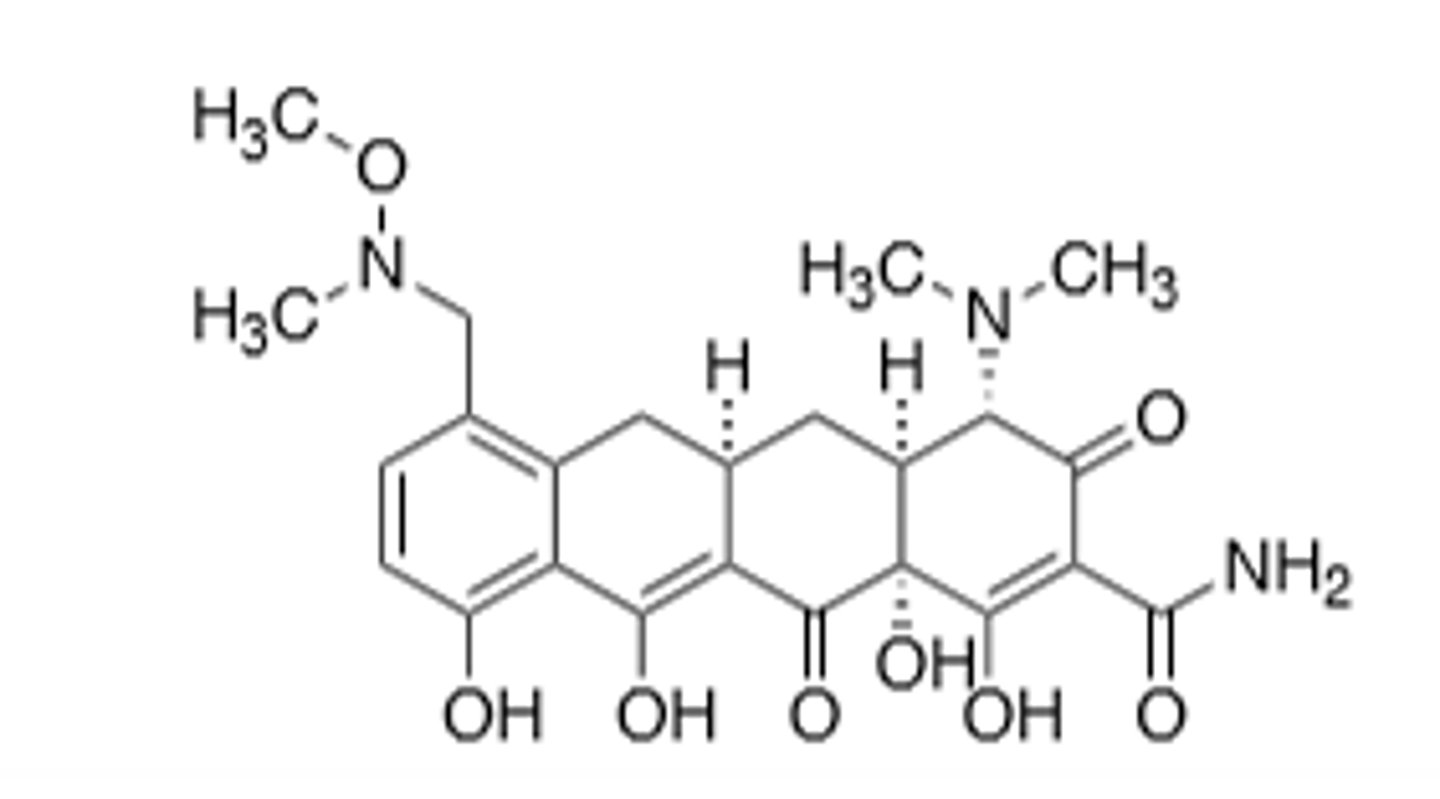
Sarecycline
Weight based dosing, newer tetracycline that overcomes ribosomal protection proteins, can cause fetal harm when administering to pregnant women, may interfere with action of penicillins due to mechanism of inhibiting 30S subunit in tetracyclines, can increase intracranial pressure --> (all tetracyclines). Chelating agent, will bind to metal ions, which causes the drug to not get absorbed in the GI tract as well, broad spectrum
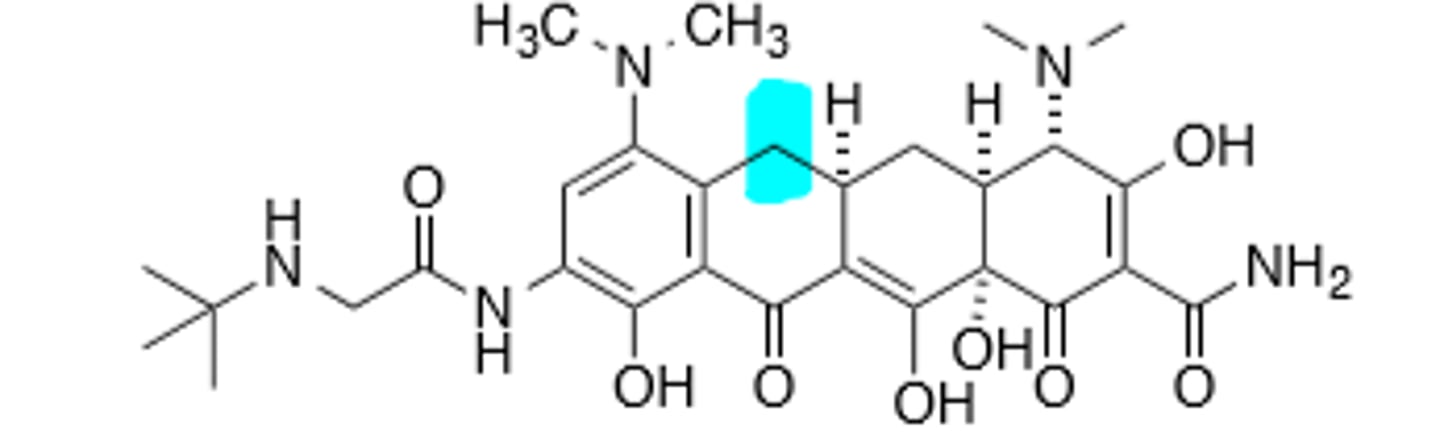
Omadacycline
IV infusion only, broad spectrum, teratogenic, breast feeding not recommended, may depress prothrombin activity (Change anticoagulant dose). Chelating agent, will bind to metal ions, which causes the drug to not get absorbed in the GI tract as well.
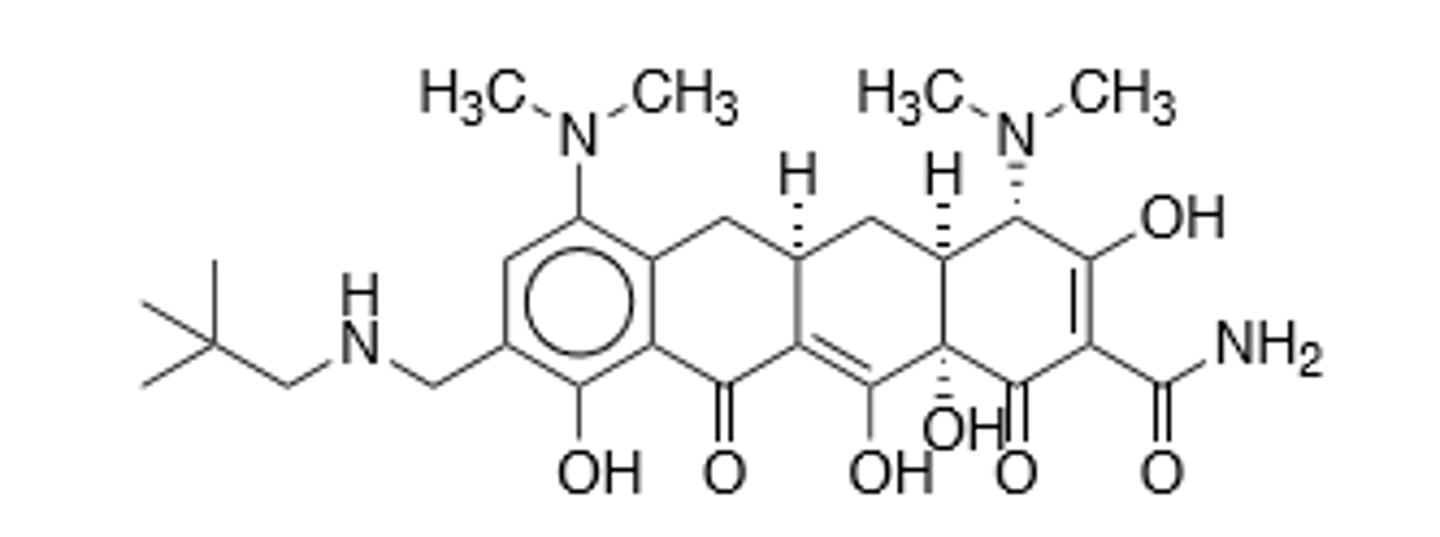
Chloramphenicol
Binds reversibly to 50S ribosomal subunit (Near the site of erythromycin and clindamycin) and inhibits peptidyl transferase activity of the ribosome, lipid soluble but remains unbound to plasma proteins, penetrates all tissues including the brain. Resistance via reduced membrane permeability, mutation of 50S ribosomal subunit, elaboration of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (bacteria cells), or metabolized the nitro group to an amino via NADPH (mammalian cells). Aplastic anemia risk (Highest with oral), will occur potentially months after treatment, bone marrow suppression, P450 inhibitor, concentration of drug increases with inflamed meninges.
Oxolinic Acid
First generation quinolone, activity more against gram (-) bacteria, only useful for treatment of lower urinary tract infections. Rare hallucinations, delirium, and sezirues in patients also taking NSAIDs and theophylline, don't give under the age of 18 due to growing tendons, risk of tendon rupture main resistance is point mutations in A and B subunit of DNA gyrase, leading to decreased binding affinity of quinolones to DNA gyrase.
Nalidixic Acid
First generation quinolone, activity more against gram (-) bacteria, only useful for treatment of lower urinary tract infections. Rare hallucinations, delirium, and sezirues in patients also taking NSAIDs and theophylline, don't give under the age of 18 due to growing tendons, risk of tendon rupture main resistance is point mutations in A and B subunit of DNA gyrase, leading to decreased binding affinity of quinolones to DNA gyrase.
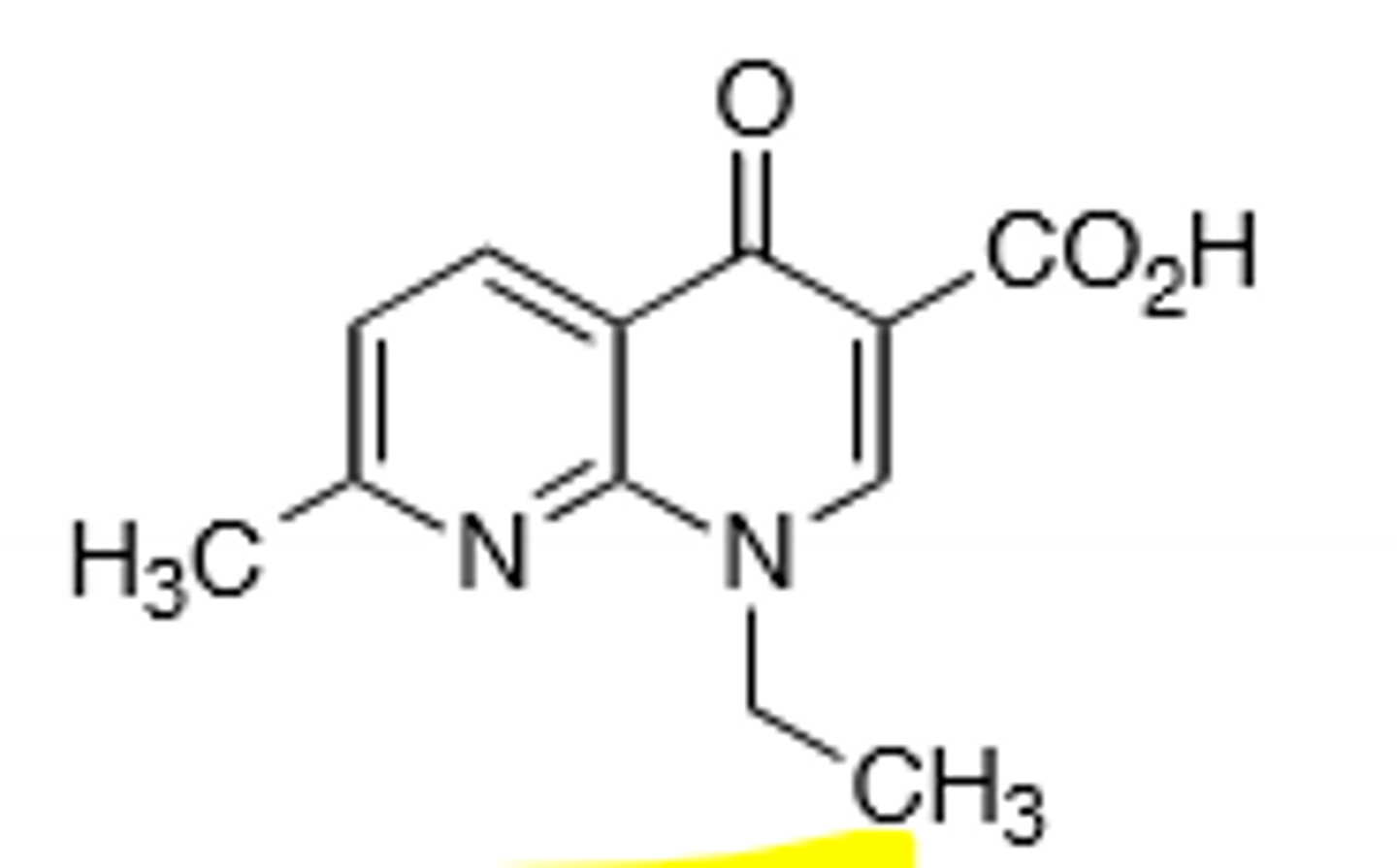
Ciprofloxacin
Second generation quinolone, has a fluorine substituent at C-6 and a heterocyclic ring (usually piperazine) at C-7. More gram (+) activity than first generation, but is the most potent gram (-) quinolone. Inhibits DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV in bacterial DNA production. Rare hallucinations, delirium, and sezirues in patients also taking NSAIDs and theophylline, don't give under the age of 18 due to growing tendons, risk of tendon rupture main resistance is point mutations in A and B subunit of DNA gyrase, leading to decreased binding affinity of quinolones to DNA gyrase.
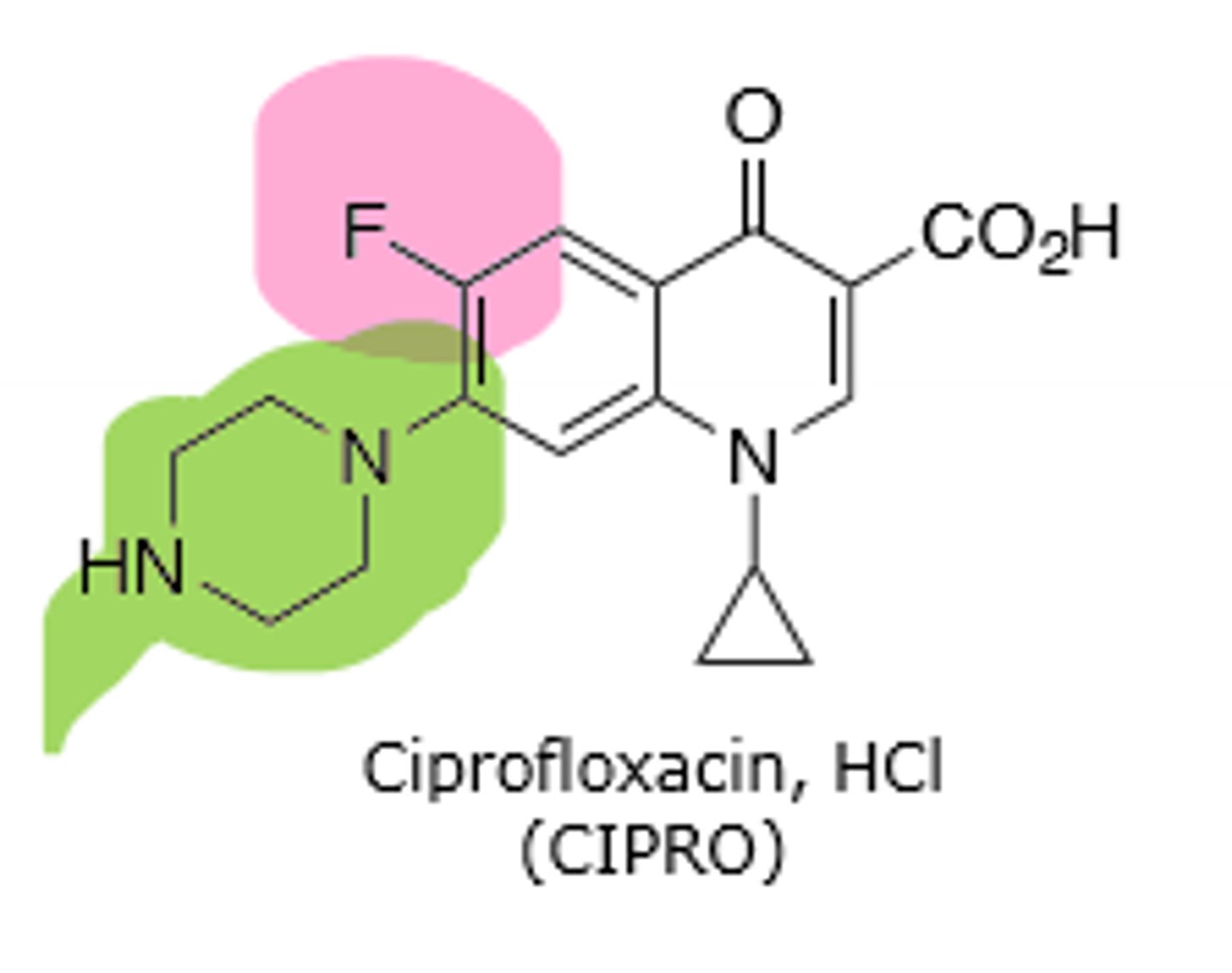
Levofloxacin
Third generation quinolone, improved activity against gram (+), but still hits gram (-). Inhibits DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV in bacterial DNA production. Rare hallucinations, delirium, and sezirues in patients also taking NSAIDs and theophylline, don't give under the age of 18 due to growing tendons, risk of tendon rupture main resistance is point mutations in A and B subunit of DNA gyrase, leading to decreased binding affinity of quinolones to DNA gyrase.
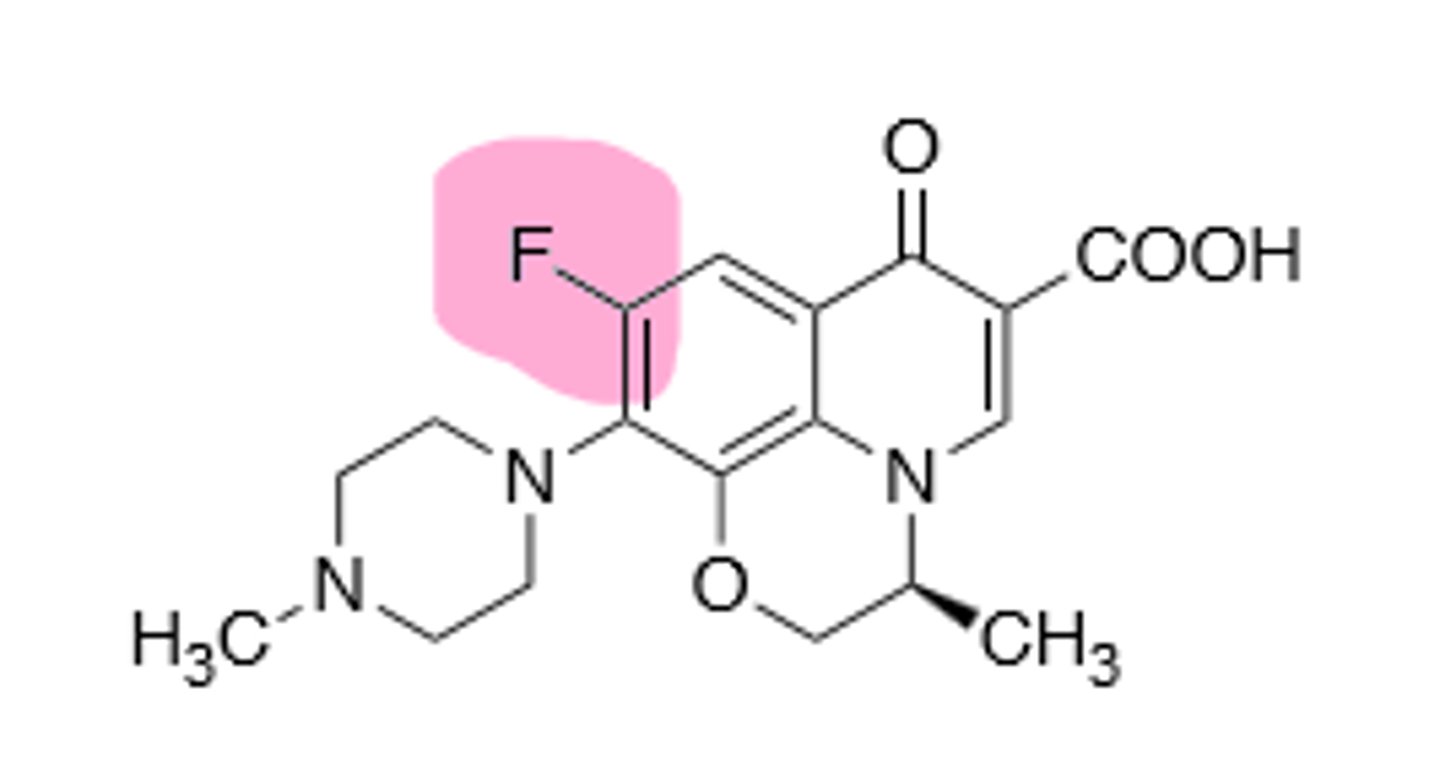
Moxifloxacin
Fourth generation quinolone, considered a drug of last resort due to toxic side effects, improved activity against gram (+), but still hits gram (-). Inhibits DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV in bacterial DNA production. Rare hallucinations, delirium, and sezirues in patients also taking NSAIDs and theophylline, don't give under the age of 18 due to growing tendons, risk of tendon rupture main resistance is point mutations in A and B subunit of DNA gyrase, leading to decreased binding affinity of quinolones to DNA gyrase.
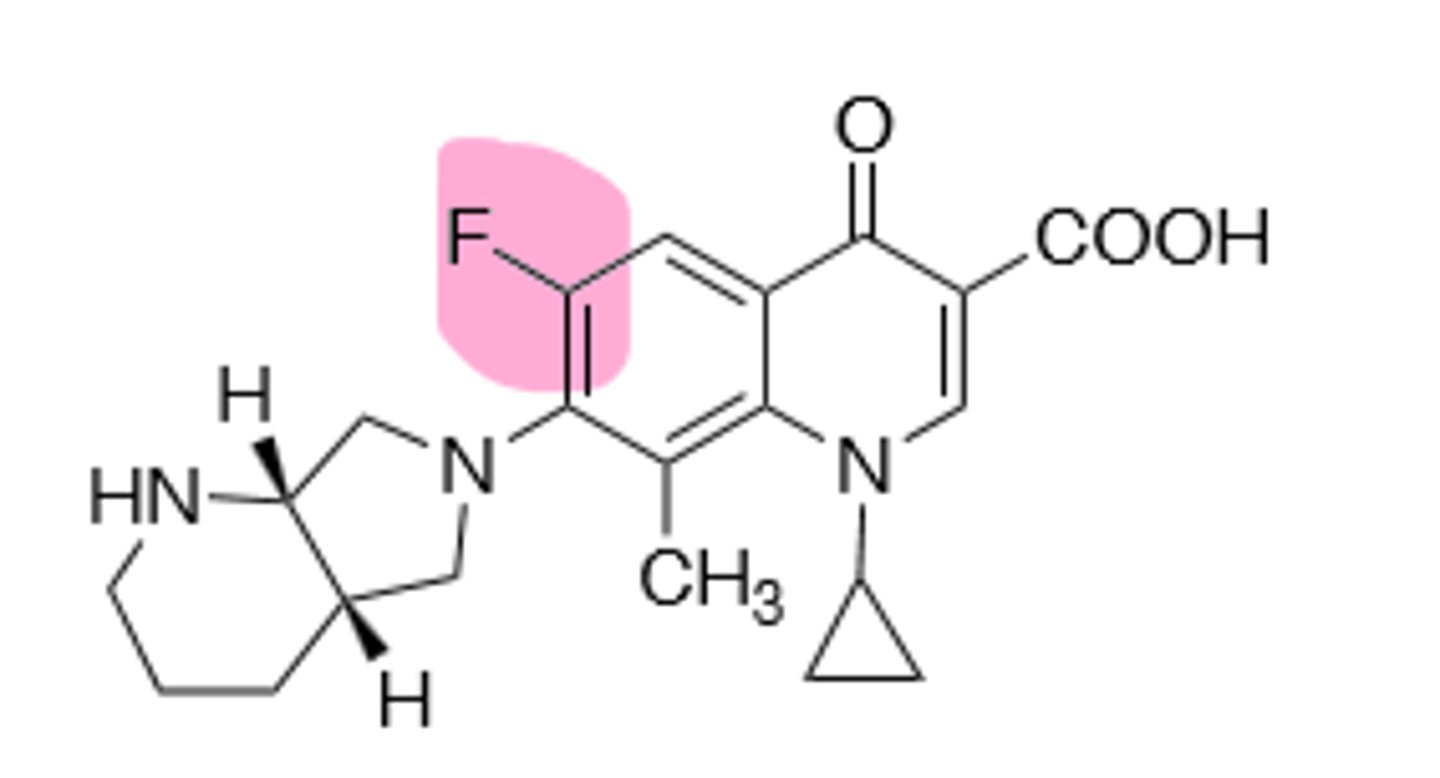
Ozenoxacin
New quinolone, no fluorine group, used to treat impetigo, overgrowth with nonsusceptible bacteria and fungi possible, improved activity against gram (+), but still hits gram (-). Inhibits DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV in bacterial DNA production. Rare hallucinations, delirium, and sezirues in patients also taking NSAIDs and theophylline, don't give under the age of 18 due to growing tendons, risk of tendon rupture main resistance is point mutations in A and B subunit of DNA gyrase, leading to decreased binding affinity of quinolones to DNA gyrase.
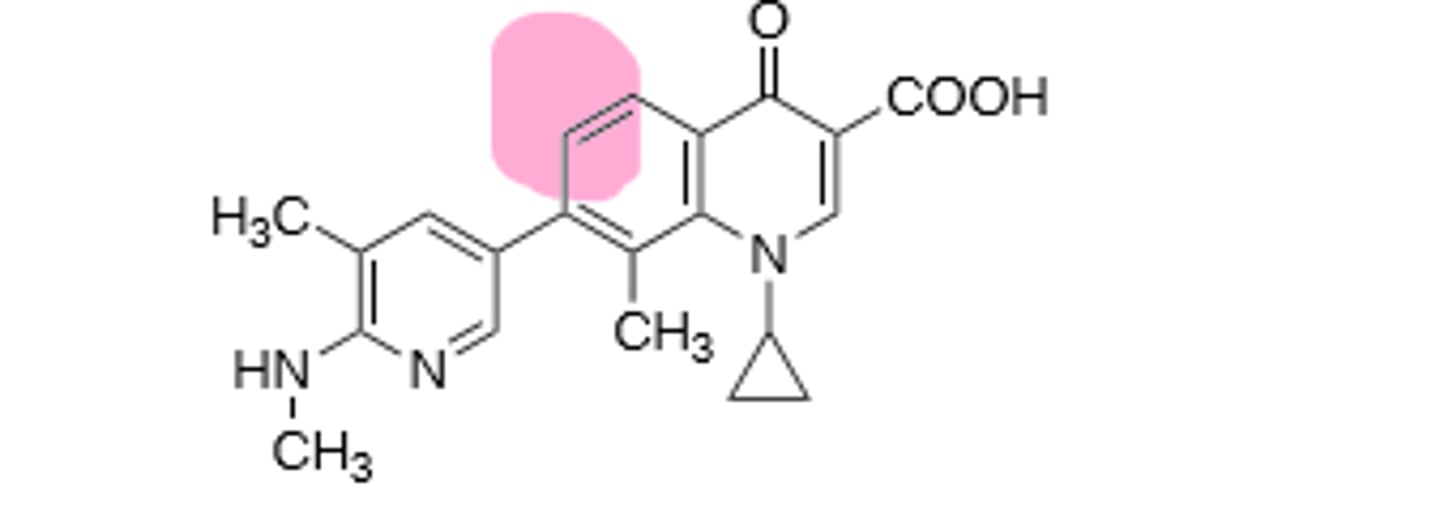
Delafloxacin
New quinolone, approved for oral or IV use, improved activity against gram (+), but still hits gram (-). Inhibits DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV in bacterial DNA production. Rare hallucinations, delirium, and sezirues in patients also taking NSAIDs and theophylline, don't give under the age of 18 due to growing tendons, risk of tendon rupture main resistance is point mutations in A and B subunit of DNA gyrase, leading to decreased binding affinity of quinolones to DNA gyrase.
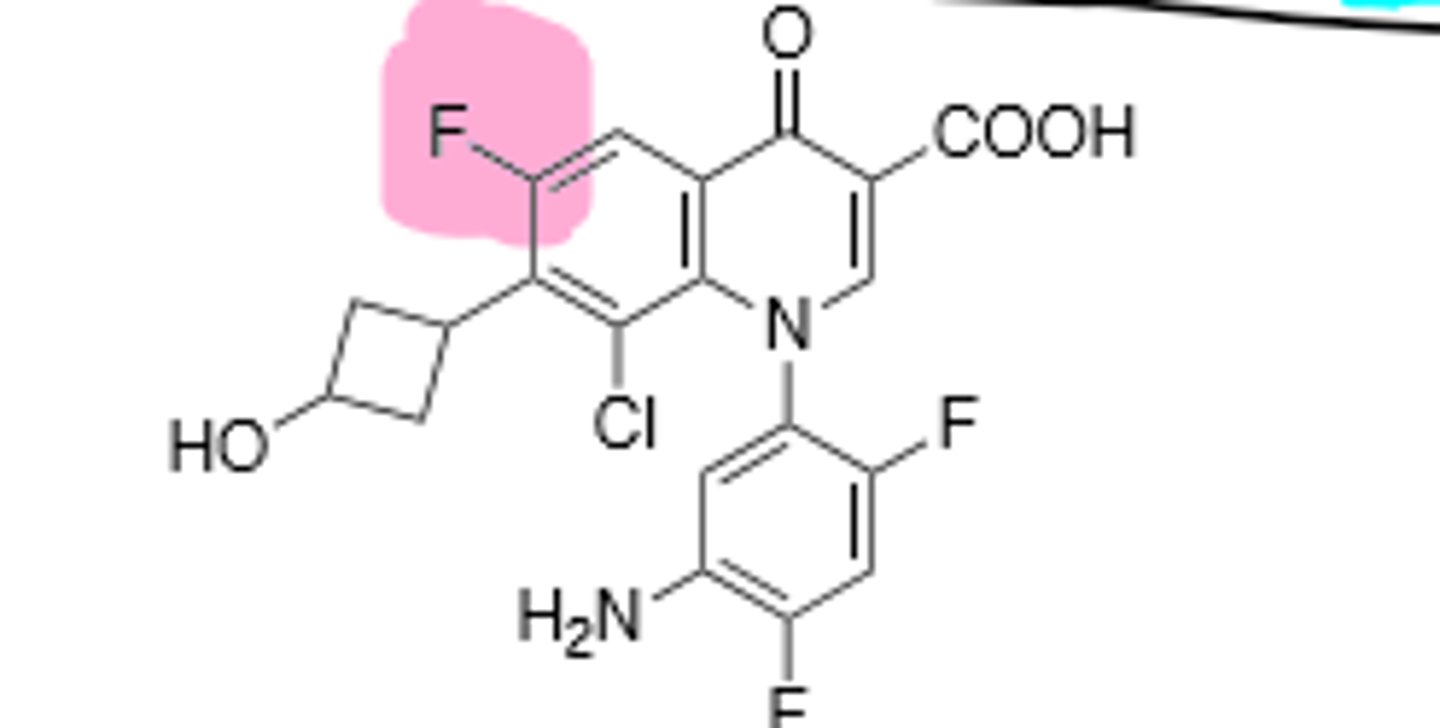
Gatifloxacin
New quinolone, approved for oral or IV use, improved activity against gram (+), but still hits gram (-). Inhibits DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV in bacterial DNA production. Rare hallucinations, delirium, and sezirues in patients also taking NSAIDs and theophylline, don't give under the age of 18 due to growing tendons, risk of tendon rupture main resistance is point mutations in A and B subunit of DNA gyrase, leading to decreased binding affinity of quinolones to DNA gyrase. Associated with hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia in diabetic patients.
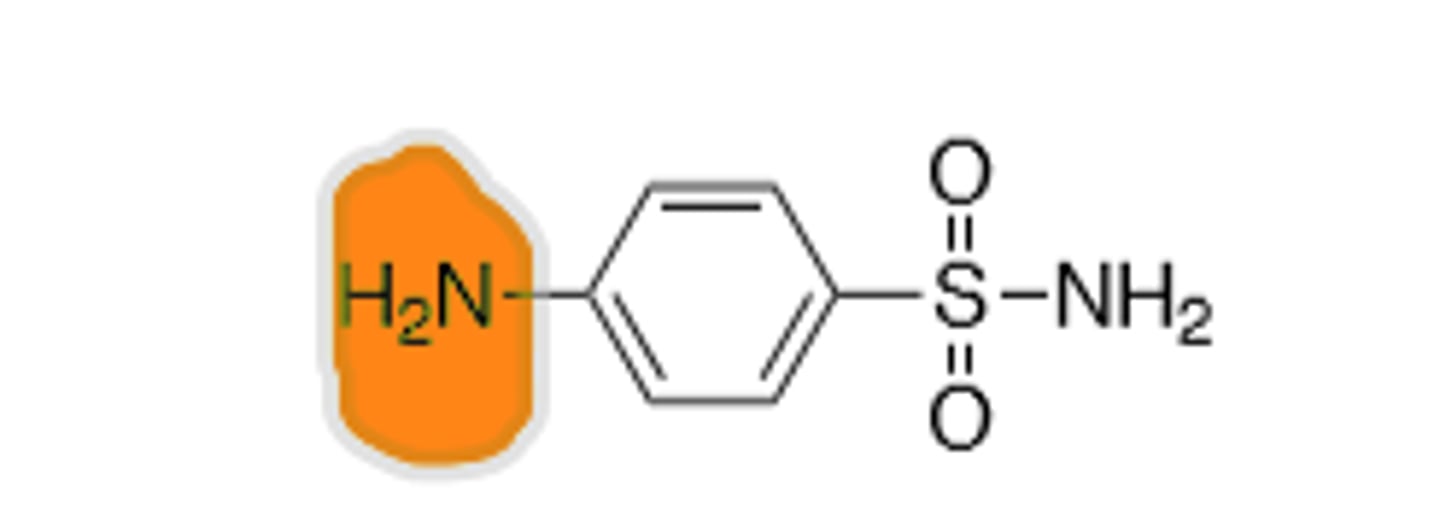
Sulfanilamide
Sulfonamide, comes from prodrug prontosil, inhibition of p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) into the folic acid nucleus, blocking Thymine synthesis in bacterial cells, preventing the creation of new DNA, leading to cell death. pKa of 10.4 allows drug to out compete PABA in physiologic pH, allowing for therapeutic effect. Broad spectrum. Commonly used in combination due to increased resistance mechanisms over the years. All drug class derivatives (Sulfas) are cross-allergenic. Crystalluria and hematopoietic disturbances, main resistance is from bacteria that cause overproduction of PABA, mutations in the target enzyme (dihydropteroate synthase), and mutations that decrease cell permeability. Metabolized by N-4-N-acetylation and sometimes N-1 glucuronidation
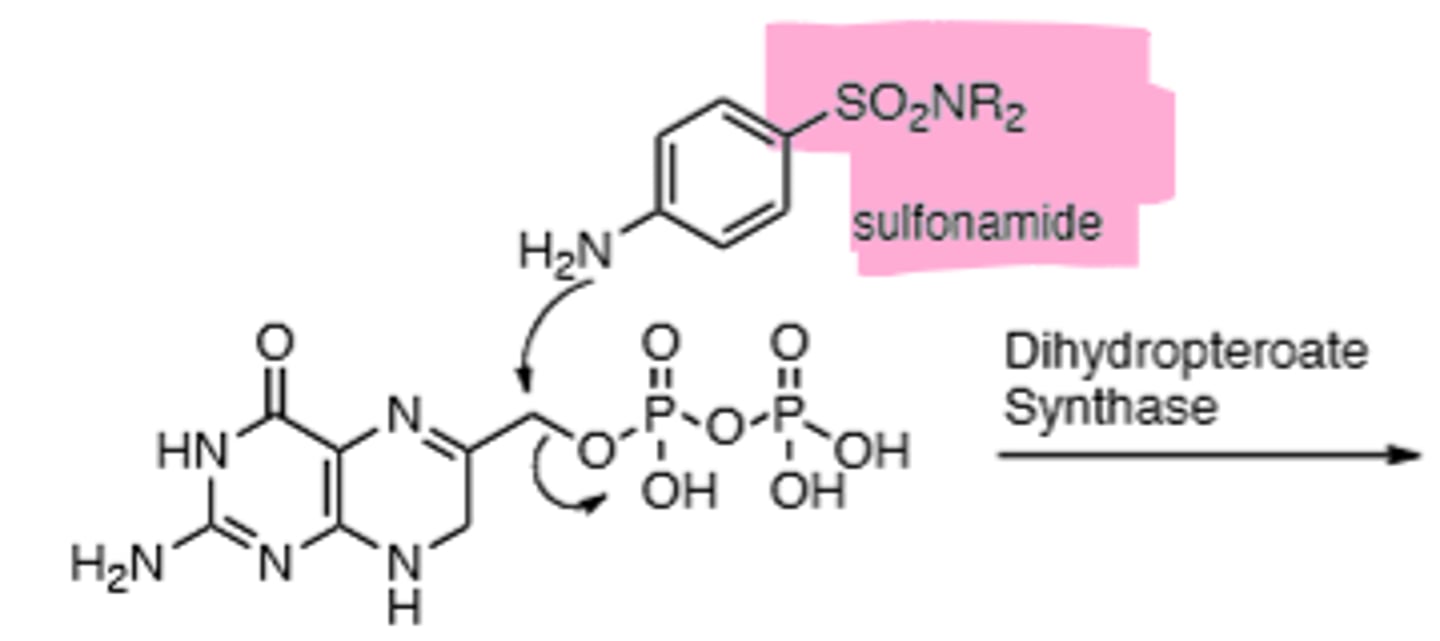
Sulfonamide Mechanism of binding to folic acid nucleus
The product is not capable of undergoing the next reaction --> No thymine
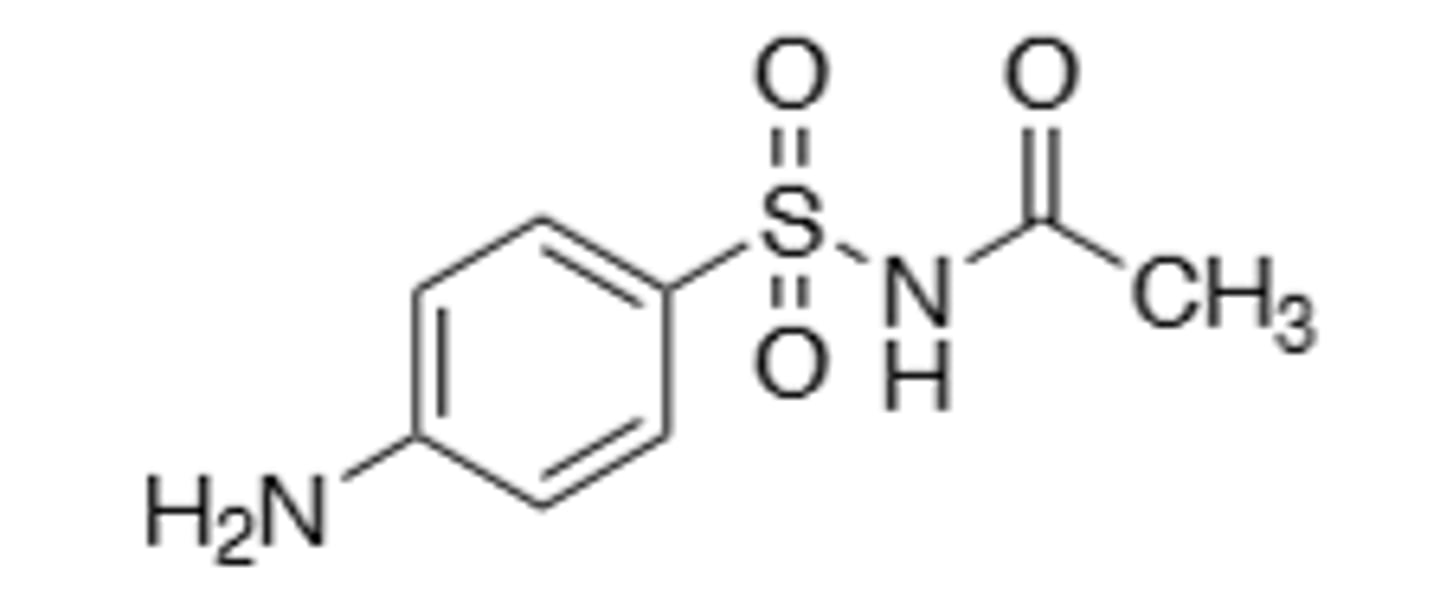
Sulfacetamide
Sulfonamide, comes from prodrug prontosil, inhibition of p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) into the folic acid nucleus, blocking Thymine synthesis in bacterial cells, preventing the creation of new DNA, leading to cell death. Broad spectrum. Commonly used in combination due to increased resistance mechanisms over the years. All drug class derivatives (Sulfas) are cross-allergenic. Crystalluria and hematopoietic disturbances, main resistance is from bacteria that cause overproduction of PABA, mutations in the target enzyme (dihydropteroate synthase), and mutations that decrease cell permeability. Metabolized by N-4-N-acetylation and sometimes N-1 glucuronidation
Sulfadiazine
Sulfonamide, comes from prodrug prontosil, inhibition of p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) into the folic acid nucleus, blocking Thymine synthesis in bacterial cells, preventing the creation of new DNA, leading to cell death. pKa of 6.6 allows drug to out compete PABA even more in physiologic pH, allowing for therapeutic effect. Broad spectrum. Commonly used in combination, especially with pyrimethamine due to increased resistance mechanisms over the years. All drug class derivatives (Sulfas) are cross-allergenic. Crystalluria and hematopoietic disturbances, main resistance is from bacteria that cause overproduction of PABA, mutations in the target enzyme (dihydropteroate synthase), and mutations that decrease cell permeability. Metabolized by N-4-N-acetylation and sometimes N-1 glucuronidation
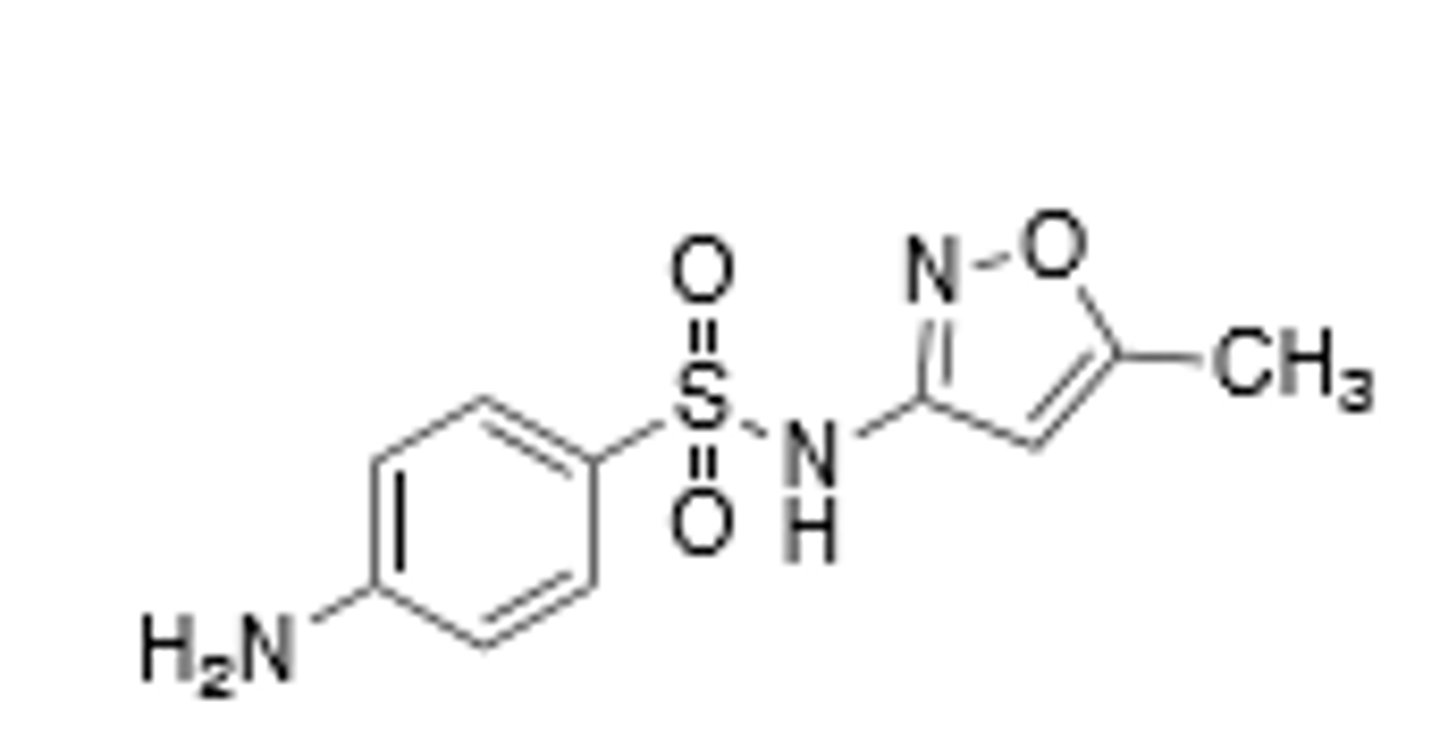
Sulfamethoxazole
Sulfonamide, comes from prodrug prontosil, inhibition of p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) into the folic acid nucleus, blocking Thymine synthesis in bacterial cells, preventing the creation of new DNA, leading to cell death. Broad spectrum. Commonly used in combination, especially with trimethoprim due to increased resistance mechanisms over the years. All drug class derivatives (Sulfas) are cross-allergenic. Crystalluria and hematopoietic disturbances, main resistance is from bacteria that cause overproduction of PABA, mutations in the target enzyme (dihydropteroate synthase), and mutations that decrease cell permeability. Metabolized by N-4-N-acetylation and sometimes N-1 glucuronidation
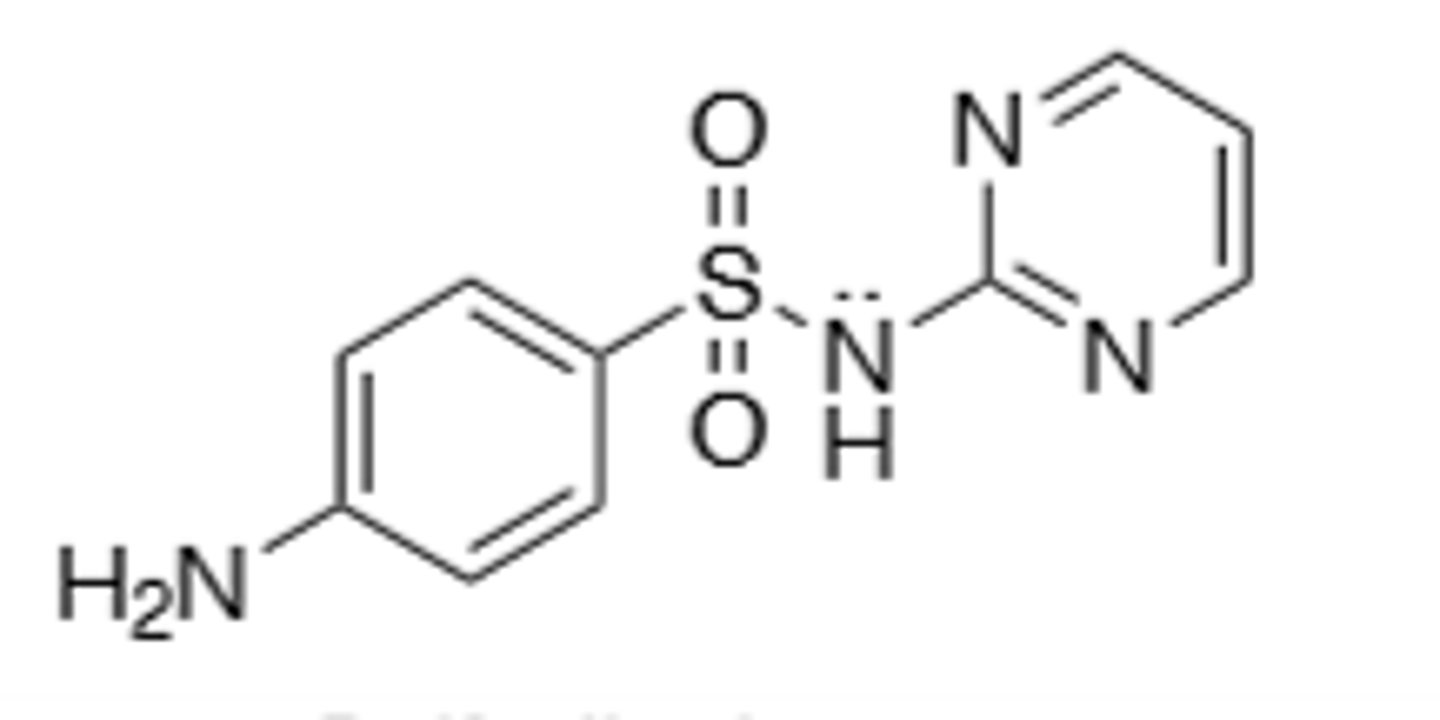
Pyrimethamine
DHFR inhibitor, given with sulfadiazine
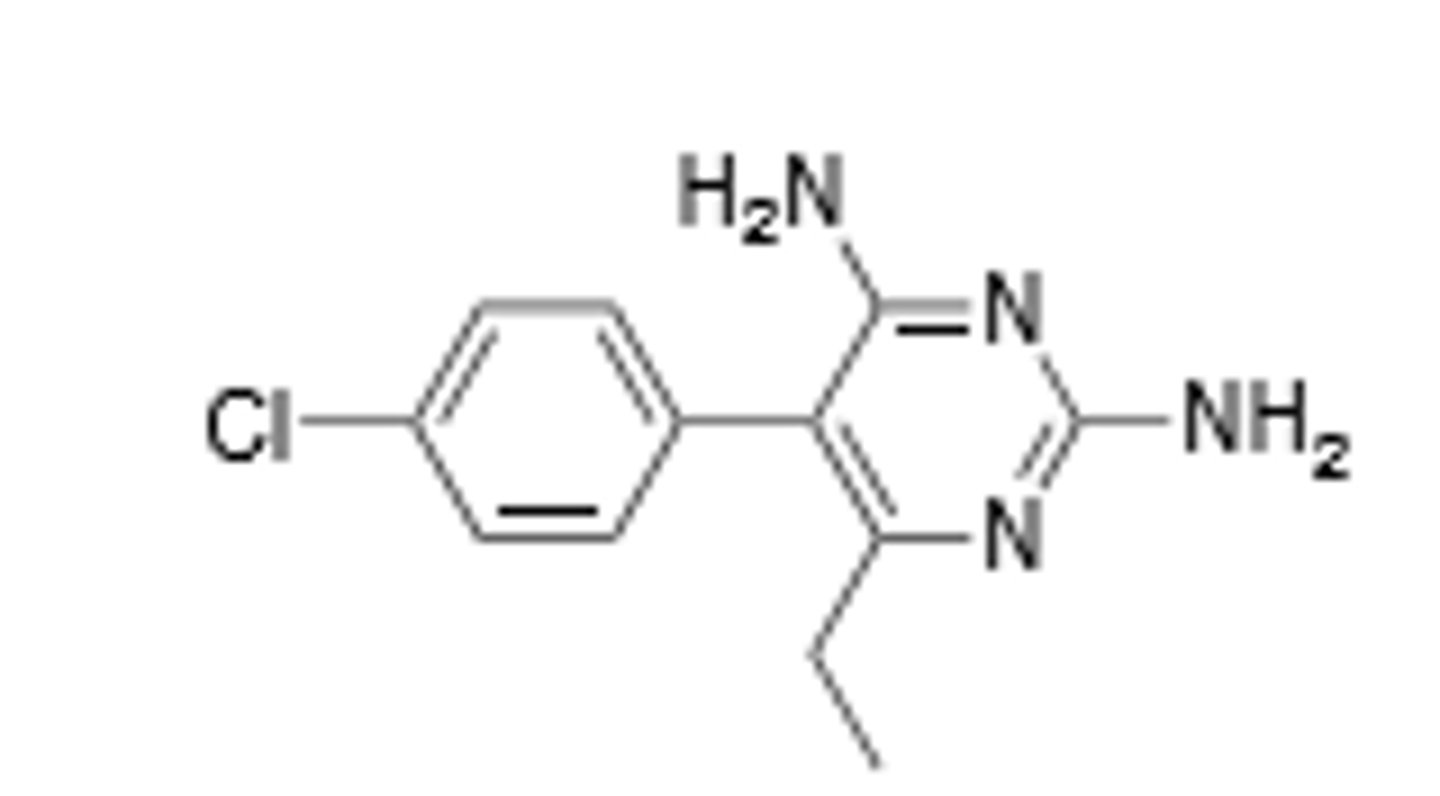
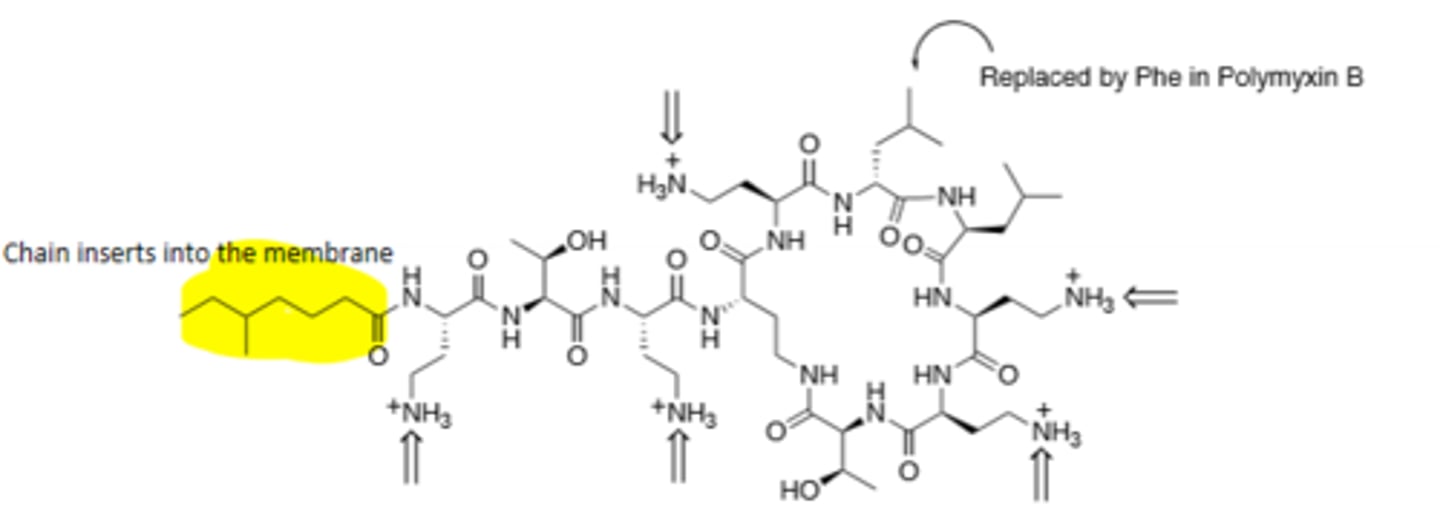
Colistin
Misc drug, last resort drug, displaces cations in the bacterial membrane, broad spectrum, given IM or intrathecally.
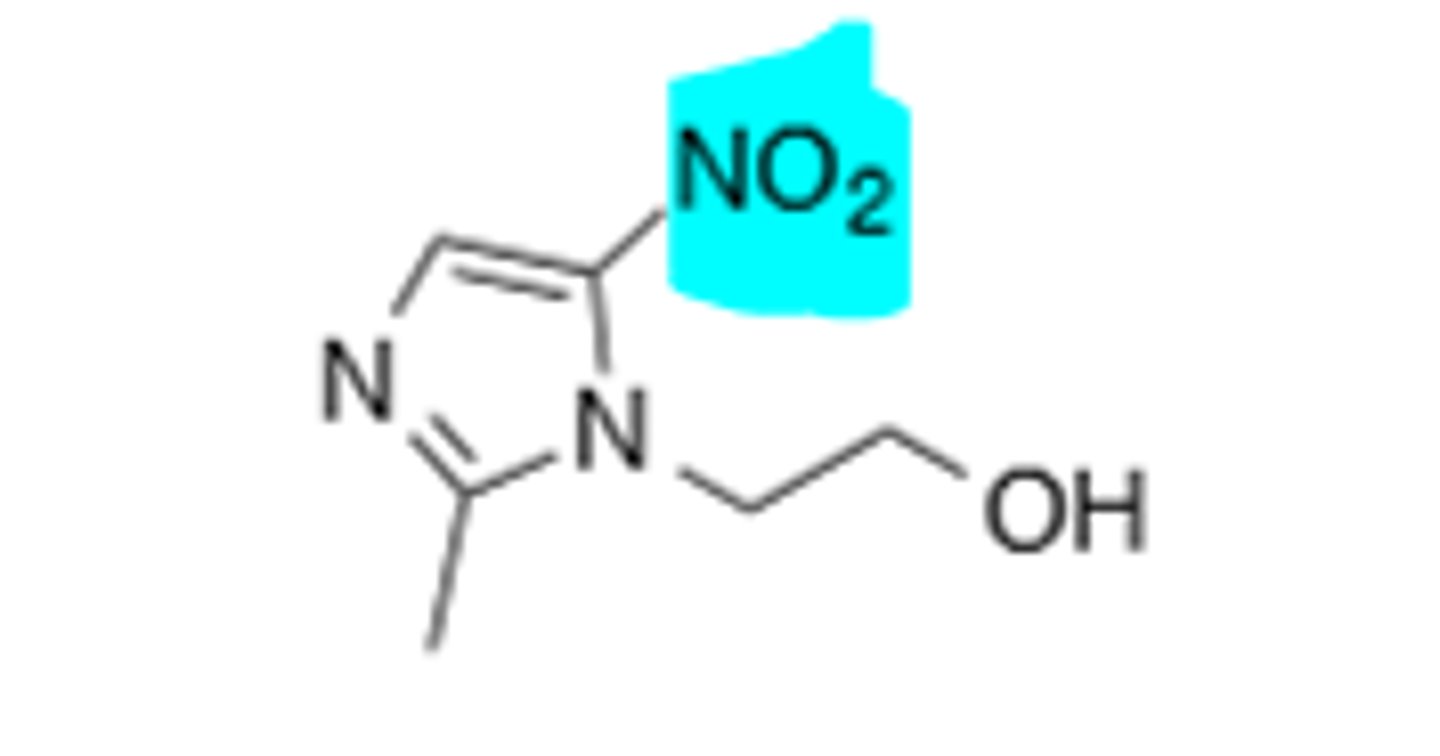
Metronidazole
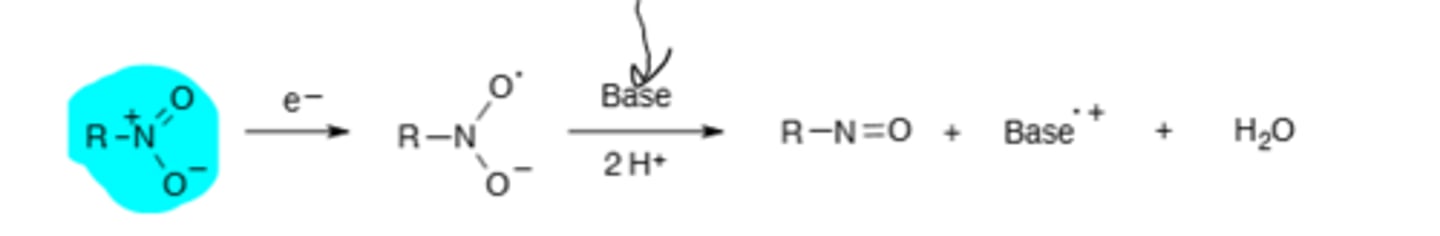
Misc drug, reduction of the (blue) nitro group leads to a radical ion that degrades bacterial DNA, selective cytotoxicity for anaerobic bacteria.
Metronidazole Nitro Group Radicalization
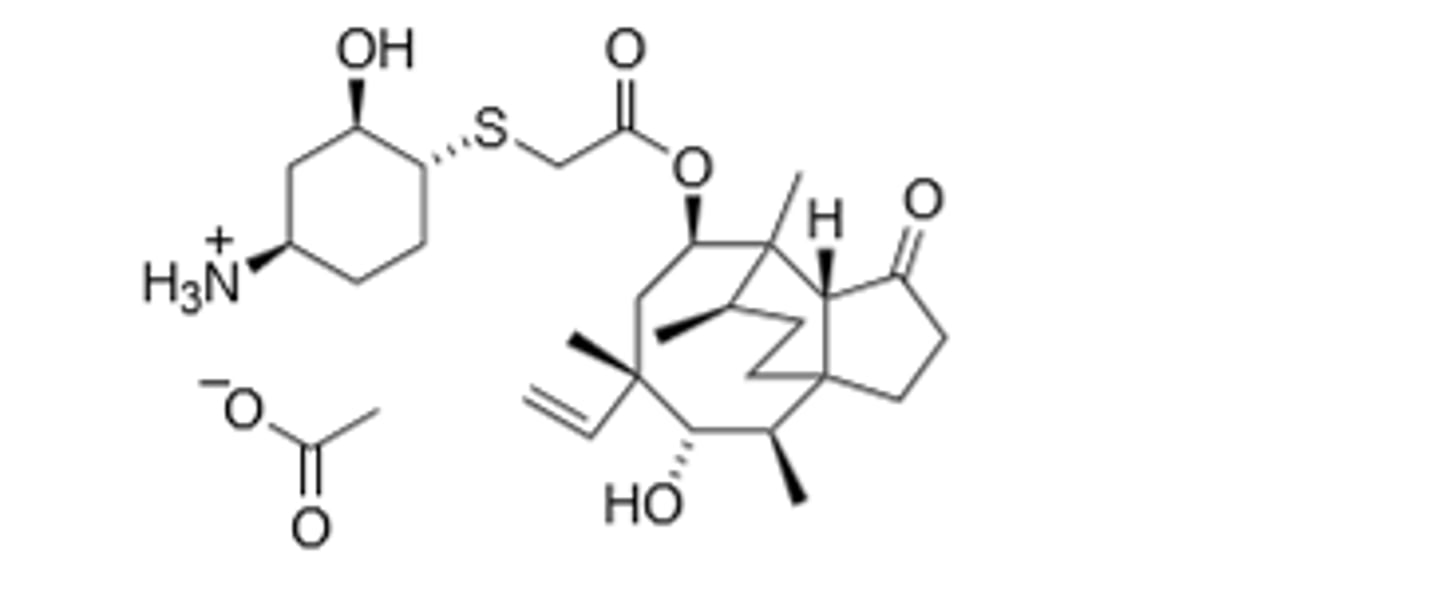
Lefamulin Acetate
Selectively binds to peptidyl transferase center of the 50S ribosomal subunit to prevent protein synthesis.
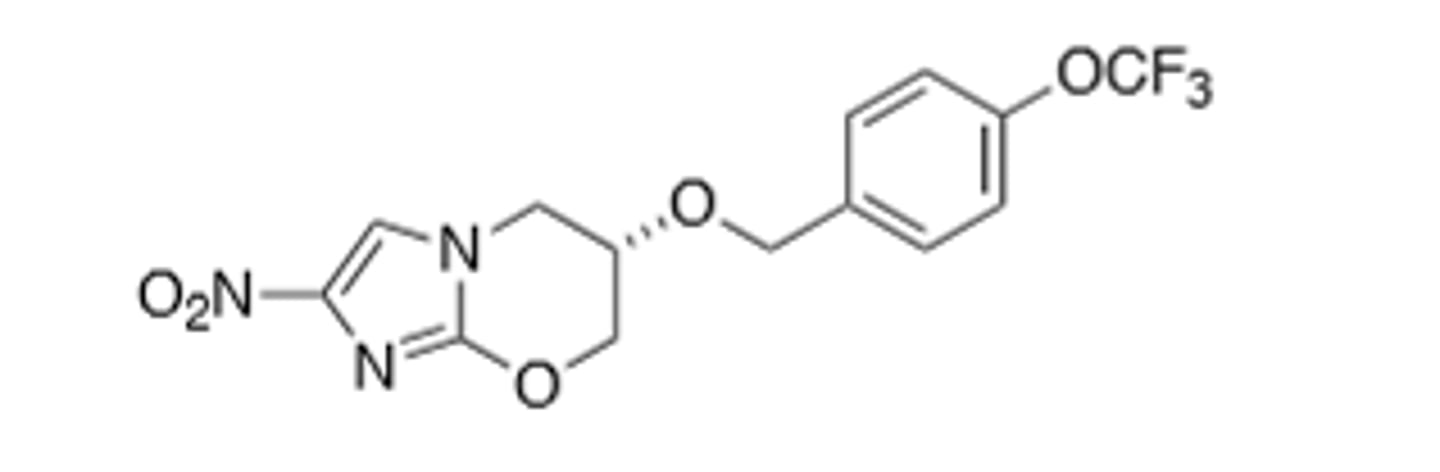
Pretomanid
Inhibits mycolic acid biosynthesis through an unknown mechanism, and poisons mitochondria through nitric oxide generation