Ch. 9: Perceiving Color
1/32
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
3 Functions of Color
Color helps us c_____ and i_____ colors.
Color facilitates perceptual o_________.
Color allows us to s_____.
Provide 3 examples for the three functions.
classify, identify.
organization.
survive.
3 examples:
red = stop or anger.
seeing one object from another.
recognizing colors of food.
Monochromat =
(only one of the wavelengths intact).
color blindness, only 1 of the wavelengths intact.
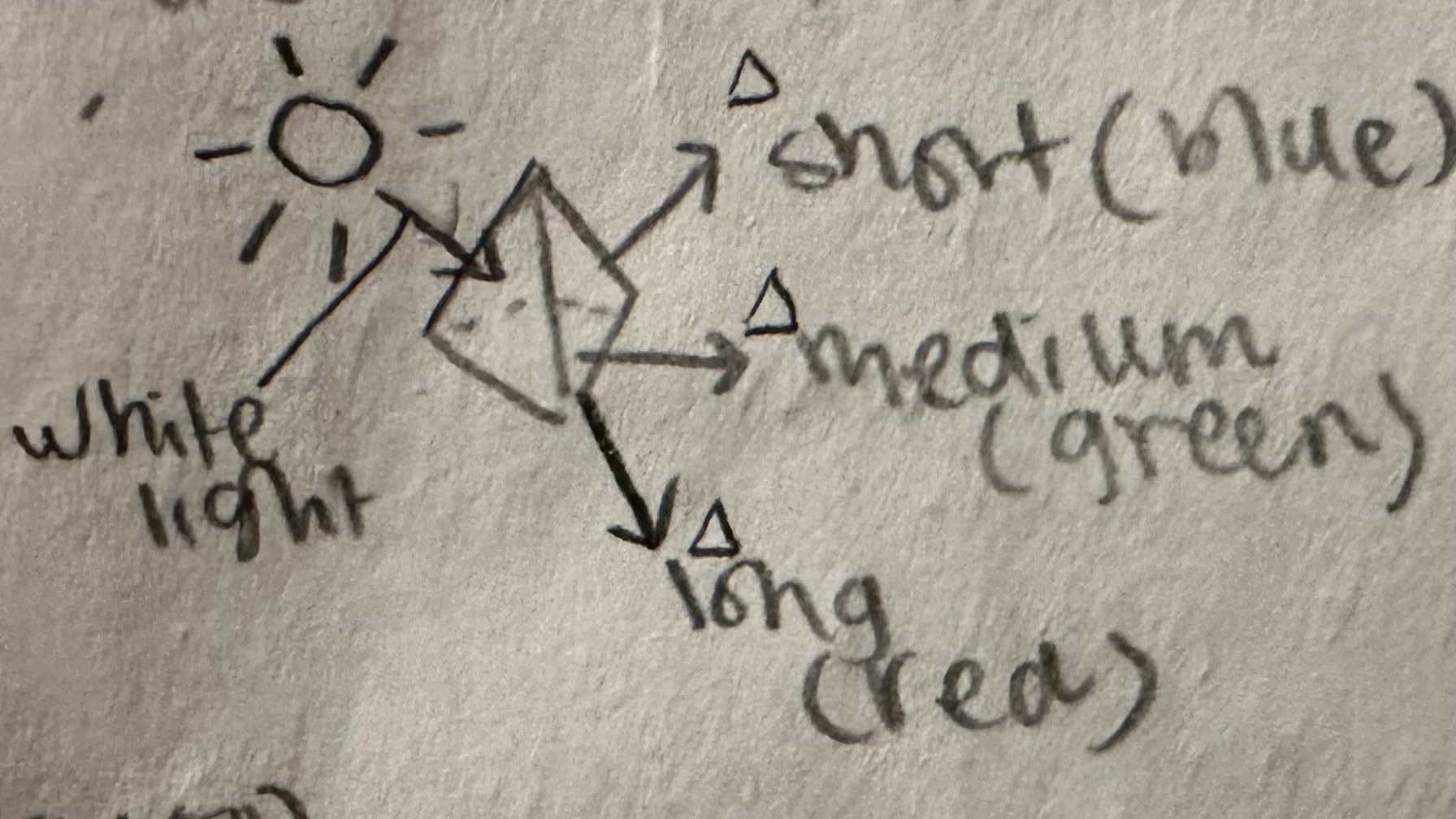
Color and Light
(Sick man) ______ ________ proposed that _____ light was a mixture of many ______.
A ____ was an object that could s_______ the different colors from the _____ light.
Isaac Newton, white, colors.
prism, separate, white.
What Colors do we Perceive
Visual spectrum - colors that humans can p______; 400 to ___ nanometers.
Blue - ____ wavelength
Green - ______ (middle) wavelength
Yellow - ______/____ wavelength
Red - ____ wavelength
perceive, 400 to 700 nm.
short.
medium.
medium/long.
long.
Reflect =
Bend.
Colors and Wavelength
Colors of objects are determined by w__________ that are reflected by light into the e__.
Reflected light is influenced by…
Chromatic colors - light is able to reflect (or ____) different w__________. (e.g. red, green, blue).
Selective reflection - some colors r_____ more than others.
Achromatic colors - light reflects equal w__________ (e.g. white, black, gray).
Transparent objects such as, liquids, plastics, and glass, allow w__________ to p___ through.
wavelengths, eye.
bend, wavelengths.
reflect.
wavelengths.
wavelengths, pass.
Chromatic - “Relating to color perceived (hue) or to have a saturation greater than zero”
Curve =
Graph.
Reflectance and Transmission
Curves are used to plot the percentage (%) of light reflected or transmitted to perceive specific w__________.
wavelengths.
Subtractive =
loses.
Additive =
combining, adding.
Mixing Colors
There are two ways to describe w__________ based on m_____ colors.
Mixing paints.
Mixing lights.
Mixing Paints
Paint a______ or t____ away colors - short, medium, and long w___________ mixed together creates black.
Paint is a sub______ (-) color mixture. When 2 mixed wavelengths l___ their colors. (e.g. blue (short) + yellow (long) = green (medium) → blue and yellow are NO longer present).
Mixing Lights
When light of short, medium, and long wavelengths are superi_____ (placed over each other), they reflect w____ light.
(e.g. = blue (short) + green (medium) + red (long) = white (wavelengths).
Light produces an a_______ (+) color mixture when two different w___________ come together to create a n__ color.
(e.g. = green (medium) + red (long) = yellow (medium/long).
wavelengths, mixed.
absorb, takes, wavelength.
subtractive.
superimposed, white.
additive, wavelengths, new.
MIXING COLORS
MIXING PAINTS = S________, loses/deletes wavelengths.
MIXING LIGHTS = A_______, just adding.
SUBTRACTIVE.
ADDITIVE.
We perceive color based on three dimensions
1) Hue - the color being _______.
2) Saturation - Perceived in_____ and p___ness of the color.
Desaturation - the f_____ of a color due to more white in it.
3) Value/lightness - Perceived bright____ of the color.
assessed.
intensity, pureness.
fading.
brightness.
Dimension = means of describing a _____.
color.
-“Colors are generally ordered in three dimensions, with hue and saturation as polar coordinates of a color circle, and brightness as the third dimension. Intuitively, lines of constant hue (but variable saturation) in such a color space should converge on an achromatic point devoid of hue.” New dimensions in color perception, Donald I.A. MacLeod
-HSV; hue, saturation, and value.
Trichromatic Theory of Color Vision
3 different re_____ mec_______ are responsible for color vision.
Behavioral Evidence:
Color-matching experiment:
Adjust 3 wavelengths in a c________n field to match a t__t field of 1 w_________.
(Test field = the color light the experimenter wants the observer to match.
Comparison field = the observer must manipulate the lighting to match the test field color.)
Key findings:
- Adjusting 3 wavelengths = p______le to match any colors in the test field.
- Adjusting 2 wavelengths only = c____t match all colors.
- NORMAL VISION = REQUIRES _ RECEPTORS.
Physiological Evidence:
C___s consist of _ pigments (colors): (1) short wavelength, (2) medium wavelength, and (3) long-wavelength.
Visual p______ m_______ - retinal bends from o____ to produce light.
Opsin - p______ structure differs representing the 3 different pigments.
receptor mechanisms.
comparison, test, wavelength.
possible.
cannot.
3.
Cones, 3.
Visual pigment molecules - opsin.
protein.
Meta/ = ac___s, b____nd. Procedure of putting things together.
/mer= _____. The actual product.
Pigment= c_______ for c____.
across, beyond.
parts.
chemicals for color.
Cone Response and Color Perception
We perceive colors based on _ different wavelengths firing in the c___s.
Color perception varies depending on available w_________.
Metamerism = a situation in which colors of d______nt wavelengths create an i____cal color.
Metamers = different w_________s that come together to make a similar color.
3, cones.
different, identical.
wavelengths.
Are 3 Visual Pigments Necessary?
_ receptor = 1 pigment.
Wavelengths cannot be identified - color from light looks the s__me (shades of gray).
Principle of univariance - receptors cannot d____ct differences in wavelengths, only in the i______ of light.
_ receptors = 2 pigments.
Ability to identify 2 wavelengths and not just intensity of light.
_ receptors = 3 pigments.
Ability to identify 3 wavelengths, creating perception of m___ colors.
1 receptor = 1 pigment.
same.
detect, intensity.
2 receptors = 2 pigments.
3 receptors = 3 pigments.
Theories of Color Vision
Trichromatic theory of color vision - proposed by Helmholtz, Young, Maxwell.
Another theory of color vision is called Opponent Process Theory - proposed by Hering.
Write down the two theories of color vision, and the individual(s) who proposed the theory.
HSV VS RGB:
→ Helmolts, Young, Maxwell.
→ Hering.
3 people for trichromatic theory of color vision, 1 person for opponent process theory.
Hering’s Phenomenological Evidence for Opponent Process Theory (1800’s)
Phenomenological method - describing an ob_________.
People observed a c____ circle and identified changes of h__.
H______ showed that differences in colors were observed as primary c______ that are added in small amounts.
Red, yellow, green, blue = primary colors or unique h___ (pure c_____ that cannot be m____ with other c_____).
He noticed that certain colors do not mix. e.g., you can have blueish red, and blueish green, but not blueish yellow. This led to the idea that…
certain pairs of c_____ are op_______ and do not m__.
observation.
color, hue.
Hering, colors.
hues. colors, mixed, colors.
colors, opposite, mix.
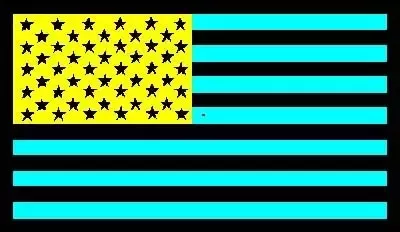
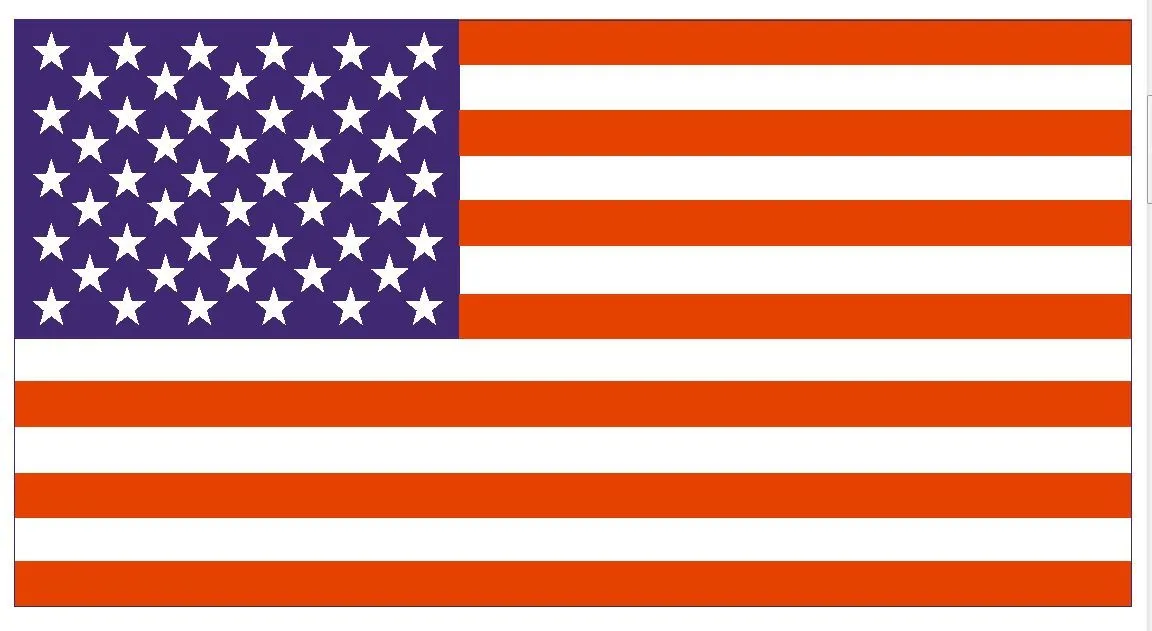
Opponent Process Theory of Color Vision
Colors that do not m__ and represent opp____t n_____s.
Blue/yellow
Green/red
Black/white
^rewrite these for the flashcard.
A good demonstration of the theory is the (inverted colors U.S. flag).
mix, opponent neurons.
Physiological Evidence for Opponent Process Theory
Researchers found opp_____ neurons located in the r_____ and l______ g________ n_____ (LGN).
Opponent neurons - respond in an e_________ manner to one end of the visible spectrum and an i_________ manner to the other for color pai___ngs..
Excitatory (positive) = neurons f___.
Inhibitory (negative) = neurons don’t ___.
opponent, retina, lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN).
excitatory, inhibitory, pairings.
fire.
don’t.
Trichromatic and Opponent Process Theory Working Together
Each theory describes phy__________ me_______sms in the v____l sy___m.
Trichromatic Theory - explains c___s in the r____a.
Opponent Process Theory - explains neural response from c___s to the b___n.
physiological mechanisms, visual system.,
cones, retina.
cones, brain.
Color Deficiency
Partial l__s of color per______.
Color blindness - they cannot see colors at all, just white, gray, and, black; a monochromat.
Color deficient - some colors can still be observed; dichromat.
3 types:
1) Monochromat - has _ wavelength to see color, sees shades of gray.
2) Dichromat - has _ wavelengths to see color.
3) Anomalous Trichromat - has _ wavelengths but mixes colors at different proportions in nanometers, causing to perceive color abnormally than what a normal trichromat sees.
loss, perception.
1.
2.
Monochromat
Rare h________y condition of color b_______.
Only r___ and no functioning c___s.
Perceives white, gray, and black tones.
Poor visual ac__ty (unable to see details).
Sensitive to bright l____.
hereditary, blindness.
rods, cones.
acuity.
light.
Dichromat
Perceives s___ color, but not a__; lacks _ type of wavelength.
M____ tend to have it more than f______. Why? Lack of an extra X chromosome.
If your only X chromosome has a genetic defect, color becomes deficient.
Females have 2 X’s preventing them from being color deficient if 1 X is deficient - you only need _ X for normal vision.
Remember: XY = male, XX = female.
There are 3 different types of dichromats.
Protanopia (primary - red/long)
Deuteranopia (secondary - green/medium)
Tritanopia (third - blue/short).
How are these 3 types identified?
Based on observations of unilateral dichromats - ppl with dichromatic vision in one eye and ? normal vision in the other.
→ Name the 3 different types of dichromats, and how the 3 types are identified.
some, all. 1.
Males, females.
Protanopia (primary - red/long).
Deuteranopia (secondary - green/medium).
Tritanopia (third - blue/short).
Identified by observing unilateral dichromats.
Ishihara Plates = A color v____ test to diagnose ppl with color d_________.
vision, deficiencies.
Neutral Point = fades to g__y.
Fades to gray.
Protanopia - Lacking Red Cones
Person sees: s____ wavelengths = b___.
Fades to gray (neutral point) at 4__ nanometers.
Difficulty seeing g____ color.
Long wavelengths = yellow above neutral point.
Difficulty seeing r__ (lacks long wavelength pigment)
short, blue.
492 nanometers.
green.
red.
“,neutral point' refers to the wavelength that the animal cannot distinguish from achromatic light such as white or grey because it stimulates both cone types equally.” Colour perception in a dichromat, Roth et al.
Deuteranopia - Lacking Green Cones
Person sees:
s____ wavelengths = blue
Fades to gray (neutral point) at 4_8 nm.
Difficulty seeing g____ (lacks medium wavelength pigment).
Long-wavelengths = yellow above neutral point (cannot see red as m__ch).
short.
498 nm.
green.
as much.
Tritanopia - very rare dichromat
Person sees:
Difficulty seeing b___ (lacks short-wavelength pigment).
Fades to gray (neutral point) at 5_0 nm.
Long wavelength = red above neutral point (cannot see y_____w).
blue.
570 nm.
yellow.

Color Constancy
We perceive the colors of objects as not ch____ing even when under different l___ting.
Prolonged exposure to a chro___tic color leads to recep__rs in the c___s to adapt to that color, making us less sen___ive to that color and more sen___ive to other colors not exposed as much.
e.g.) #thedress - the blue/black and yellow/white dress. How you see color can be inf____ced by the illum____tion of the light (the type of light reflecting on the object). Researchers still dkwtf going on, why ppl interpret dress differently.
changing, lighting, .
chromatic, receptors, cones, sensitive, sensitive.
influenced, illumination.
Lightness Constancy
We perceive achrom__c colors (white, gray, black) as remaining relatively con___nt.
Although we might see different shades of gr_y (lightn__s) due to the am___nt of light reflected from the object to our own eyes, the colors itself does_’t actually change.