Physical GEOL Final
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
___ is not an example of brittle deformation.
Folded Quartzite
Collision of oceanic and contiental plates result in formation of extensive fold-thrust belts with ___.
Magmatic Arcs or Volcanoes
Collision of two continental plates result in formation of extensive fold-thrust belts with ___.
Plateaus
Appalachian orogen is an example of ___.
Contient to continent collision in geologic past
Andes orogen is an example of ___.
Ocean to contient collision
Himalayan oregon is an example of ___.
Contient to contient collision
The ___ fold-thrust belt is characterized with a neighboring chain of volcanoes.
Andean
Orogenic Collapse
The act of hot rocks at the base of mountains moving outwards over time.
Mountains reflect a balance between ___ and ___.
Rock uplift and rock erosion
Fold-Thrust Belt
Deformation recorded over a geographic region in an orogen.
Given the West has an elevation of 6000, the Central 7000m, and the East 4000m, which has the thickest crustal root?
Central
Andes is produced by the subduction of the ___ plate under the ___ plate.
Oceanic Nazca, Continental South American
Himalaya is produced by the collision of the ___ plate and the ___ plate.
Continental Indian, Continental Asian
The axial plane ___.
Divides the fold symmetrically
Anticline
The part of the fold that closes up.
Syncline
The part of the fold that closes down.
Fold Axis
The line of intersection of axial plane and the folded surface.
The fold axis is also known as the ___.
Hinge Line
Section View
The side-side view of a geologic structure.
Map View
The top-down view of a geologic structure.
In an ___, the youngest rock lies in the center.
Syncline
In an ___, the oldest rock lies in the center.
Anticline
In a ___, the oldest rock lies in the center.
Dome
In a ___, the youngest rock lines in the center.
Basin
The depth at which transition from bittle to ductile deformation occurs inside the Earth is ___ to ___km.
10 to 15km
Given that ~500Ma fossil rocks are overlying ~200Ma fossil rocks, you’d suspect there is a ___ in the region.
Thrust-Fault
Law of Superposition
If naturally occuring, younger rocks will always overlay older rocks.
Slickenlines
Striations left behind on exposed fault surfaces due to movement.
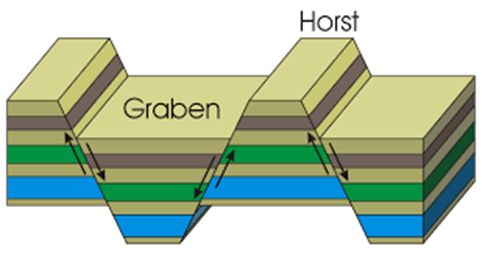
Basin and Range Province is dominantly made up of ___ faults.
Normal
The type of force or stress involved in the development of the Basin and Range Province is ___.
Extensional
Basins and Ranges are also known as ___ and ___.
Grabens and Horsts
The Appalachian mountain belt is dominantly made up of ___ faults.
Thrust
___ faults transport older rocks on top of younger rocks.
Thrust
The San-Andreas fault is a ___ fault.
Right-Lateral Strike-Slip
Left-Lateral Strike-Slip Fault
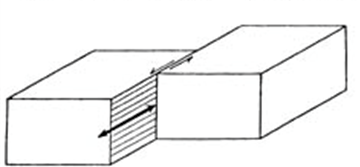
Right-Lateral Strike-Slip Fault
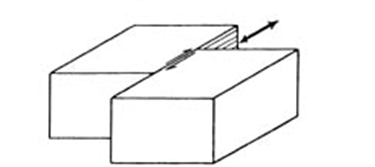
Normal Fault
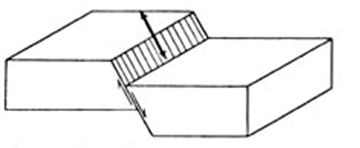
Reverse Fault
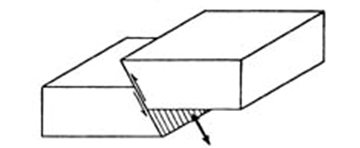
Anticline
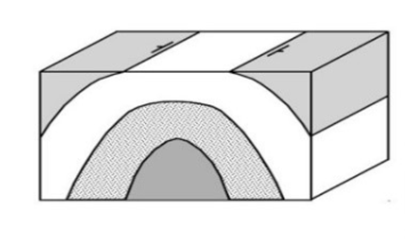
Syncline
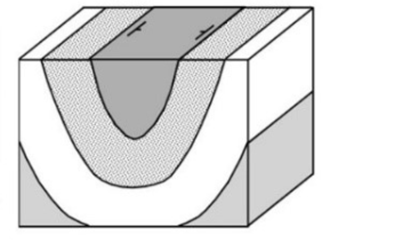
The faults in this image are all ___ faults.
Normal
The Japanese word for harbor waves is ___.
Tsunami
Deep-focus EQs along convergent plate boundaries result from ___.
Mineral Phase Transformations
Most modern-day skyscrapers use ___ to neutralize seismic waves.
Tuned Mass Dampeners
Focus
The point inside the Earth where an EQ originates.
The 1811 New Madrid EQ was an ___ EQ.
Intraplate
The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was caused by a ___.
Tsunami
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is offset by ___.
Strike-Slip Faults
The faults that offset mid-ocean ridges coincide with ___.
Transform Plate Boundaries
Divergent Plate Boundaries are characterized by ___ focus EQs.
Shallow
P-Waves vibrate:
Back and forth.
S-Waves vibrate:
Up and down.
R-Waves vibrate like:
Vertical Circles.
L-Waves vibrate like:
Snakes.
P and S waves only travel on the ___.
Surface
R and L Waves travel ___.
Through everything
The absolute value of an EQ is measured via the ___.
Amplitude
___ have the highest amplitude.
Surface Waves
___ cause the most damage.
Surface Waves
Richter Scale
Measures the magnitude.
Mercalli Scale
Measures the intensity.
The Incas used ___ geometry to EQ-proof their buildings.
Trapezoidal
___ have the highest velocity.
P-Waves
The difference in P and S-Wave arrival times corresponds to ___.
Distance from the epicenter