Cell membrane and transport
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Homeostasis of a cell is maintained by
the plasma membrane (cell membrane), controls what goes in and out
The cell membrane acts as
a barrier between the cell and the outside environment
The cell membrane controls the
movement of material in and out of the cell
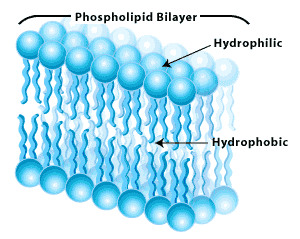
Describe the Bilayer of phospholipid are arranged
lipid tails are between phosphate heads creating a barrier
Transport proteins
aid in moving larger molecules in and out of the cell examples: ions, sugar , water
Cholesterol
add strength to the cell membrane, lipid molecules located in the bilayer that makes cell membranes more rigid
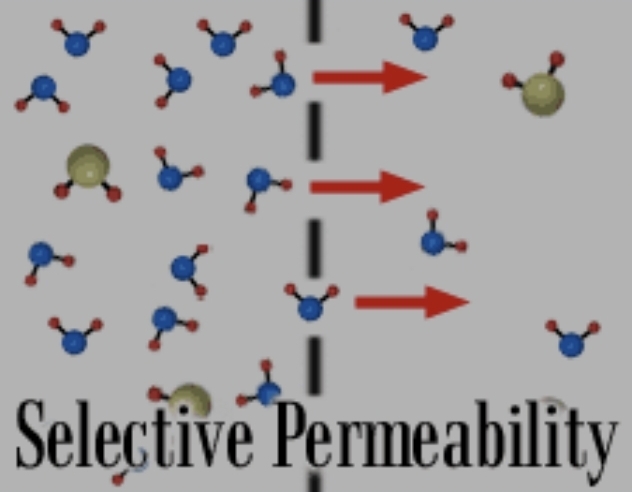
Selectively permeable
the property of the cell membrane that allows it to regulate what goes in and what goes out of the cell, usually based on size and charge of the substance
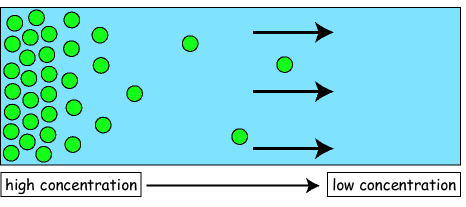
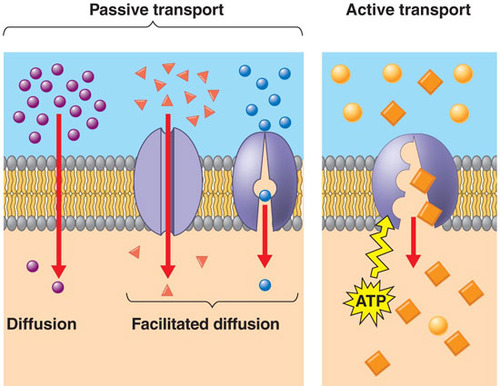
Diffusion (no energy required)
when substances move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
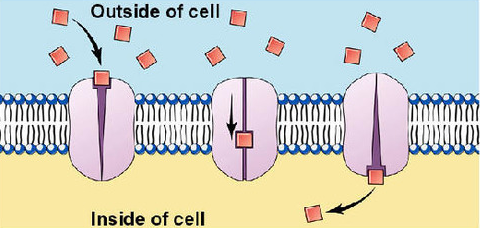
Facilitated diffusion (no energy required)
when larger substances are moved across the cell membrane from high to low concentrations with the help of carrier proteins (glucose sugars)
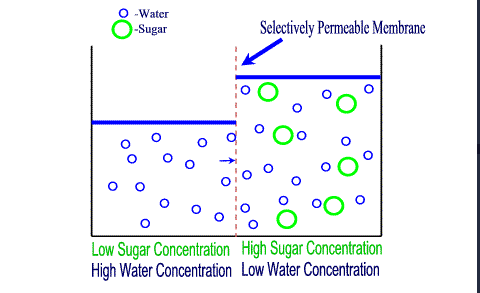
Osmosis (no energy required)
movement of water molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from an area of greater water concentration to an area of lower water concentration
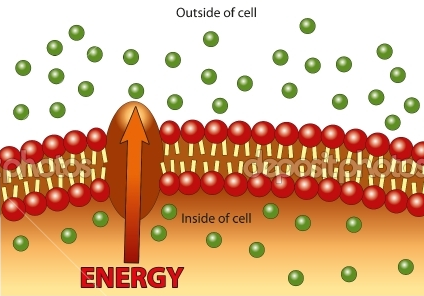
Active transport (energy required)
movement of solid or liquid particles into and out of the cell with an input of energy; moving particles from low to high concentration across a cell membrane (going against the concentration gradient), uses the help of a transport protein such as a protein pump.
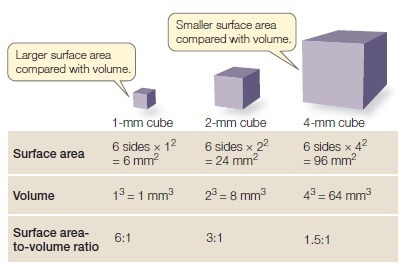
The surface to volume ratio of a cell limits
As cells increase in size, the surface area to volume ratios decrease, making cells less efficient in obtaining nutrients or remove wastes.
Small cells have a very large surface area to volume ratio
Cells divide to stay small and efficient
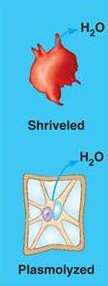
Hypertonic solution
a solution with more solutes than inside the cell, causing water to leave the cell
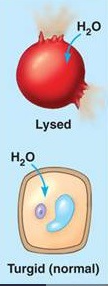
Hypotonic solution
a solution with fewer solutes than inside the cell, causing water to enter the cell
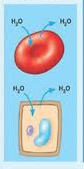
Isotonic solution
concentration of solutes is equal inside and outside cell; water moves in and out at Equilibrium
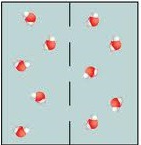
Equilibrium
A state of balance, molecules still move around but no net flow
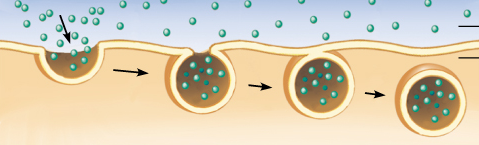
Endocytosis (active transport)
process where a cell takes in material by engulfing it with the membrane
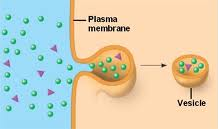
Pinocytosis (active transport)
type of endocytosis where the cell takes in liquid
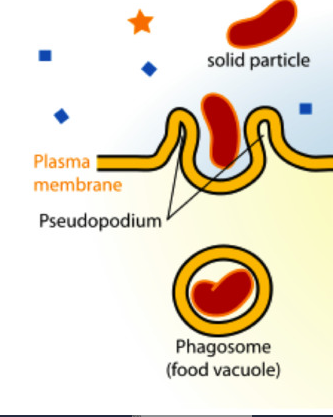
Phagocytosis
type of endocytosis where the cell takes in large particles or cells
(active transport)
when solids are moved into a cell creating a vacuole, cell eating (food/large particles)
Exocytosis (active transport)
the bulk removal of waste from a cell. removing large particles, large proteins, cell products, hormones, starch from the cell
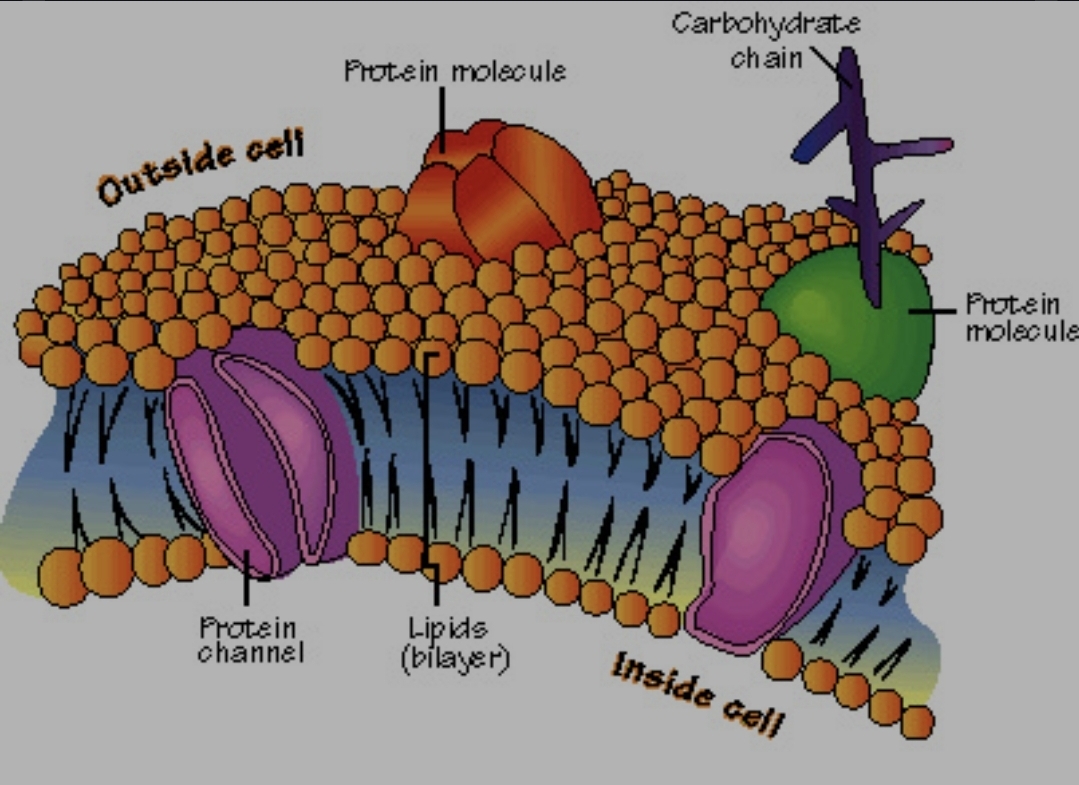
the plasma membrane diagram
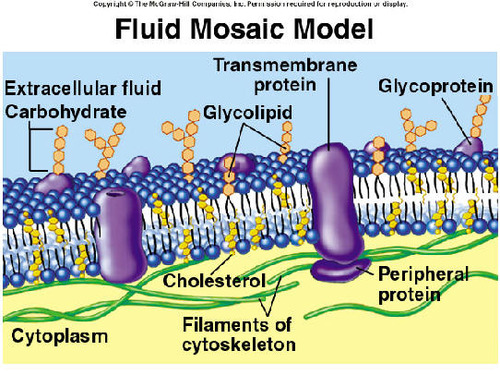
peripheral proteins
membrane proteins that are only inserted into one side of the lipid bilayer , its funtion is chemical signaling adhesion
hydrophobic tails
component of a phospholipid molecule that is non-polar
plasma membrane
cell structure that regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell
phospholipid bilayer
a two-layer structure of molecules that makes up the cell membrane
integral proteins
membrane proteins that extend through the lipid bilayer. transport mechanism
phospholipid fatty acid tail
hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail, the tail is hydrophobically composed of a fatty acid chain
membrane protein functions
transporters, anchors, receptors, enzymes
transporters
channels, carriers/pumps
receptors
e.g. hormones: helps with cell signaling/communication
The cell membrane is
very flexible
Cholesterol stabilizes the membrane by
preventing the fatty acid tails from sticking together, otherwise the membrane is too liquid
Cholesterol is located
wedged between fatty acid tails
carbohydrate chain function
communicate with other cells; cell to cell communication via signaling -identification tags (cell recognition tags that identifies cells to the body's immune system)
fluid
the phospholipid bilayer is the fluid portion of the membrane
3 types of passive transport
simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis
diffusion
the net transport of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration, no energy needed, the movement of a substance down it's gradient.
examples of simple diffusion
-diffusion of co2 and o2 into and out of lung alveoli
-diffusion of co2 and 02 into and out of eye cornea cells.
facilitated diffusion
transport proteins in the cell membrane allow larger molecules or charged particles to pass. H->L
facilitated diffusion is different than simple diffusion because
-molecules move through a channel protein in the membrane
-used for small charged molecules (ion) or larger molecules (glucose)
some molecules can't diffuse through the phospholipids and require
special protein channel to move through
channels (usually) or carrier proteins "help"
molecules across the membrane
osmosis
the movement of water by diffusion across a selectively permeable membrane to equalize solute concentrations
osmosis moves from
high to low concentration
Water is an excellent
solvent
solute
Particles dissolved in a liquid (solvent)
osmosis moves from an area of high concentration of water to an area of low concentration of water
this means that water moves from an area of low concentration of solutes to an area of high concentration of solutes.
osmosis depends on
the amount of solutes in solutions in relation to each other
hypotonic
a solution that has lower solute solute concentration and higher water concentration: water moves INTO the cell
isotonic
when two solutions have the same solute concentration, no net water movement
hypertonic
solution with higher solute concentration and a lower water concentration: water moves OUT of the cell
concentration gradient
variation between solute quantities of two different solutions
impermeable
a membrane that does not allow any substances to pass through
permeable
a membrane that allows substances to pass through by diffusion and osmosis
simple diffusion is when
small or uncharged particles cross the membrane through bilayer H to L
active transport requires
carrier proteins and ATP
2 types of active transport
protein pumps and bulk transport
bulk transport
endocytosis and exocytosis. larger molecules (proteins, starch) are transported in bulk by vesicles
protein pumps
transport small molecules and ions against their concentration gradients using ATP, from l to h against the gradient
endocytosis
vesicles move substances in. process by a cell which takes in large materials by infolding the cell membrane.
exocytosis
vesicles move substances out. is the process y a cell releasing large materials from inside the cell to outside the cell.
carrier proteins or pumps
found in the membrane move solutes from low to high concentration (with an input of energy) against it's gradient
sodium potassium pump
sodium na is transported out of the cell against its concentration gradient. potassium k is transported into the cell against it's concentration gradient
bulk transport vesicles
require energy input. bulk movement of large or charged particles into or out of cell requires a vesicle for transport.
vesicle
small membrane sacs that specialize in the transportation of particles
sodium-potassium pump
a carrier protein that uses ATP to actively transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into the cell
protein channels
proteins in the membrane whose role it is to pass molecules that cannot go through the membrane
functions of cell membrane
-to maintain homeostasis of a cell
-acts as a barrier between cell and external environment
-controls the movement of materials in and out of the cell
-allowing for communication between cells
-involved in recognition of cells to help with metabolic functions
active vs passive transport
passive: does not require energy, small molecules, oxygen, carbon dioxide, H to L, down gradient, requires
active: requires energy (atp), requires carrier proteins, against the gradient, L to H,
both: maintain homeostasis, method of cell transport, sugar, large charge particles
prefix that means outside
exo
prefix that means inside
endo
word that means "cell"
cyto
tonic means
water
Glycolipid
carbohydrate group is attach to the phospholipid, helps in cell recognition.
Glycoprotein
carbohydrate groups attached to proteins. cell markers and other function
phophosplipid head
phosphate head, composed of phosphate groups, charged or polar and hydrophillic
dynamic equilibrium
Result of diffusion where there is the continuous movement of particles but no overall change in concentration
Is the environment of this cell hypotonic , hypertonic, isotonic
Hypotonic and results in plants cells being turgid, more water and less solutes compared to the inside of the cells
Is the environment of this cell hypotonic , hypertonic, isotonic
isotonic, water is entering and leaving in the same rate. equal water inside and outside of the cell .
Is the environment of this cell hypotonic , hypertonic, isotonic
hypertonic environment, less water and more solutes compare to the inside of the cell
What organelle helps fresh water organism such as the paramecium to maintain water balance.
contractile vacuole
Identify the type of transport shown in the image
exocytosis
Identify the type of transport, the blue represents water
osmosis
Identify the type of cell transport
facilitated diffusion
Why is the cell membrane fluid
the tails of phospholipids can be bent, which makes them unsaturated, bent tails take up more space and are less dense and less rigid, which is ideal for colder conditions, they have a lower packing density that makes them more fluid, proteins interrupt packing and decrease the packing density in the phospholipids
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
What conditions is a plant cell turgid?
in an hypotonic environment (more water)
Turgor pressure in plant cells is
-A way to help the cell maintain its structure by pushing outward on the cell wall
-The force of water against the inside of the cell wall
-Necessary to keep plants from wilting
-A result of the walled cell being in a hypotonic environment