L4 | Autonomic & Somatic Nervous System
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
The sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system exits from __________ and __________
thoracic & lumbar regions
The parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system exits from _________ and ____________
cranial and sacral areas
What determines if a nerve is sympathetic or pararsympathetic?
where the cell body of the preganglion comes from in the spine
Nerve fibers which only innervate striated skeletal muscle and have no ganglion are part of the ______________
somatic nervous system
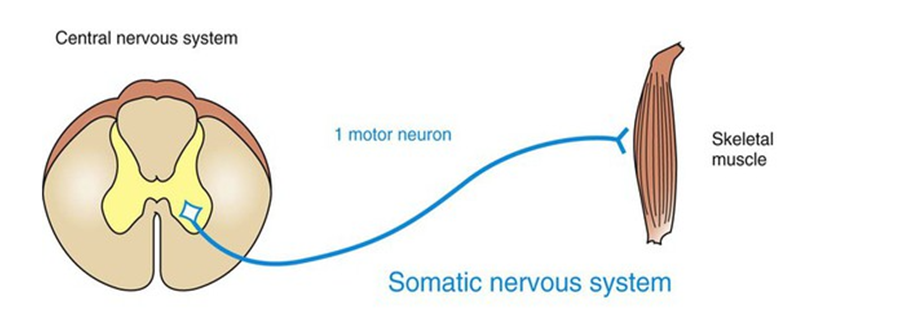
Nerve fibers which innervate smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands and has ganglion are part of the ______________
autonomic nervous system
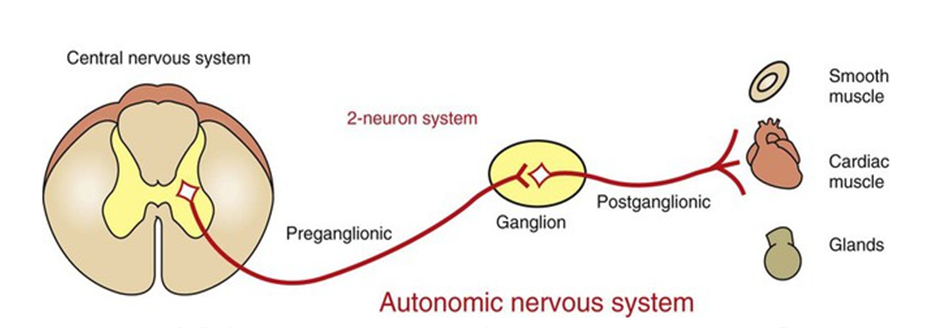
____________ and __________ are the neurotransmitters of the ANS
Acetylcholine (Ach) and Norepinephrine (NE)
Acetylcholine (Ach) has equal affinity for the two cholinergic receptors ___________ and _____________
Nicotinic (N) and Muscarinic (M)
Norepinephrine has affinity for the adrenergic receptors ___________, _________, and __________
Alpha-1, Alpha-2, and Beta-1
Norepinephrine will never bind to ___________
Beta-2
_____________ responses release epinephrine
Sympathetic
Epinephrine stimulates the adrenergic receptors _______________
Alpha-1, Alpha-2, Beta-1, Beta-2
Norepinephrine stimulates the adrenergic receptors ___________
Alpha-1, Alpha-2, and Beta-1
___________ innervates all organs/glands except skeletal muscle
Autonomic nerves
___________ innervates only skeletal muscle
Somatic nerves
Whar are some of the functions of the parasympathetic nervous system?
-conservation of energy
-bradycardia
-vasodilator predominance
-BP reduction
-renal blood flow increased
-urine output increased
-salivation increased
-respiration reduced
-GI motility and secretions increased
What are some of the functions of the sympathetic nervous system?
-expenditure of energy
-tachycardia
-vasoconstrictor predominance
-BP increased
-renal blood flow decreased
-urine output decreased
-salivation reduced
-respiration increased
-GI motility and secretions reduced
A nurse administers a medication that stimulates α₁-adrenergic receptors in the eye. Which assessment finding should the nurse expect?
Pupillary dilation (mydriasis)
α₁-adrenergic receptor stimulation activates the sympathetic nervous system
This causes contraction of the iris dilator muscle
The result is pupil dilation (mydriasis)
A nurse administers a medication that stimulates muscarinic (M) receptors in the eye. Which assessment finding should the nurse expect?
Pupillary constriction (miosis)
Muscarinic receptor stimulation activates the parasympathetic nervous system
This causes contraction of the iris sphincter muscle
The result is pupillary constriction (miosis)
ACh is predominantly metabolized by _______________
postsynaptic acetylocholinesterase (AChE)
A nurse is teaching a student about how acetylcholine (ACh) is inactivated after it binds to receptors at the synapse. Which process is primarily responsible for terminating the action of ACh?
A. Presynaptic reuptake of ACh into the nerve terminal
B. Metabolism of ACh by acetylcholinesterase (AChE) at the postsynaptic membrane
C. Diffusion of ACh away from the synaptic cleft
D. Binding of ACh to muscarinic and nicotinic receptors
B. Metabolism of ACh by acetylcholinesterase (AChE) at the postsynaptic membrane
A nurse is caring for a patient who is prescribed a medication that increases the concentration of acetylcholine (ACh) at the synapse. Which mechanism best explains how this medication increases ACh levels?
A. Blocking presynaptic reuptake of acetylcholine
B. Blocking acetylcholinesterase (AChE) to increase acetylcholine levels at the synapse
C. Stimulating α₁-adrenergic receptors
D. Increasing norepinephrine release from presynaptic neurons
B. Blocking acetylcholinesterase (AChE) to increase acetylcholine levels at the synapse
A nurse is reviewing how norepinephrine (NE) is removed from the synaptic cleft after receptor activation. Which mechanism is primarily responsible for terminating the action of NE at the synapse?
A. Breakdown of NE by acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in the synaptic cleft
B. Diffusion of NE away from the synaptic cleft
C. Presynaptic reuptake of NE via the norepinephrine transporter (NET)
D. Binding of NE to postsynaptic α- and β-adrenergic receptors
C. Presynaptic reuptake of NE via the norepinephrine transporter (NET)
What is the effect of stimulating nicotinic receptors at the postganglionic autonomic cell body?
generation of action potential
What is the effect of stimulating nicotinic receptors at the adrenal glands?
secretion of Epinephrine
What is the effect of stimulating nicotinic receptors at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ)?
contraction of skeletal muscle
What is the effect of stimulating muscarinic receptors at the heart?
bradycardia
What is the effect of stimulating muscarinic receptors on smooth muscle?
contraction
What is the effect of stimulating muscarinic receptors on vascular smooth muscle?
vasodilation
Stimulation of muscarinic receptors in the airways produces which effect?
bronchospasm
A patient exposed to an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (aka: muscarinic receptor) is showing signs of SLUDE. Which findings support this diagnosis? Select all that apply.
A. Increased sweating
B. Dry mouth
C. Increased tears
D. Vasodilation
E. Tachycardia
A, C, D
What is the effect of stimulating adrenegic receptors on the heart?
tachycardia (Beta-1)
What is the effect of stimulating adrenegic receptors on smooth muscle?
relaxation (Beta-2)
What is the effect of stimulating adrenegic receptors on vascular smooth muscle?
-Vasodilation (Beta-2)
-Vasoconstriction (Alpha-1, Alpha-2)
___________ of the iris radial dilator muscle causes mydriasis
constriction
_______________ is the regulation of an organ by both sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves, which typically exert opposite effects to maintain homeostasis.
dual innervation
What are the exceptions to dual innervations (which organs do not receive dual innervation)?
-blood vessels (sympathetic)
-sweat glands (sympathetic cholinergic)
-adrenal glands (sympathetic)
-bronchioles (parasympathetic)
Normally the predominant tone of dual innervation is __________________
parasympathetic
The exceptions to predominate tone are sites that do not have _____________
dual innervation