Musculoskeletal Quick Cram Cards (Smarty PANCE)
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
A positive Apley indicates what diagnosis?
Meniscal tear - Pt prone, knee to 90 degrees, axial load with rotation causes pain with meniscal pathology
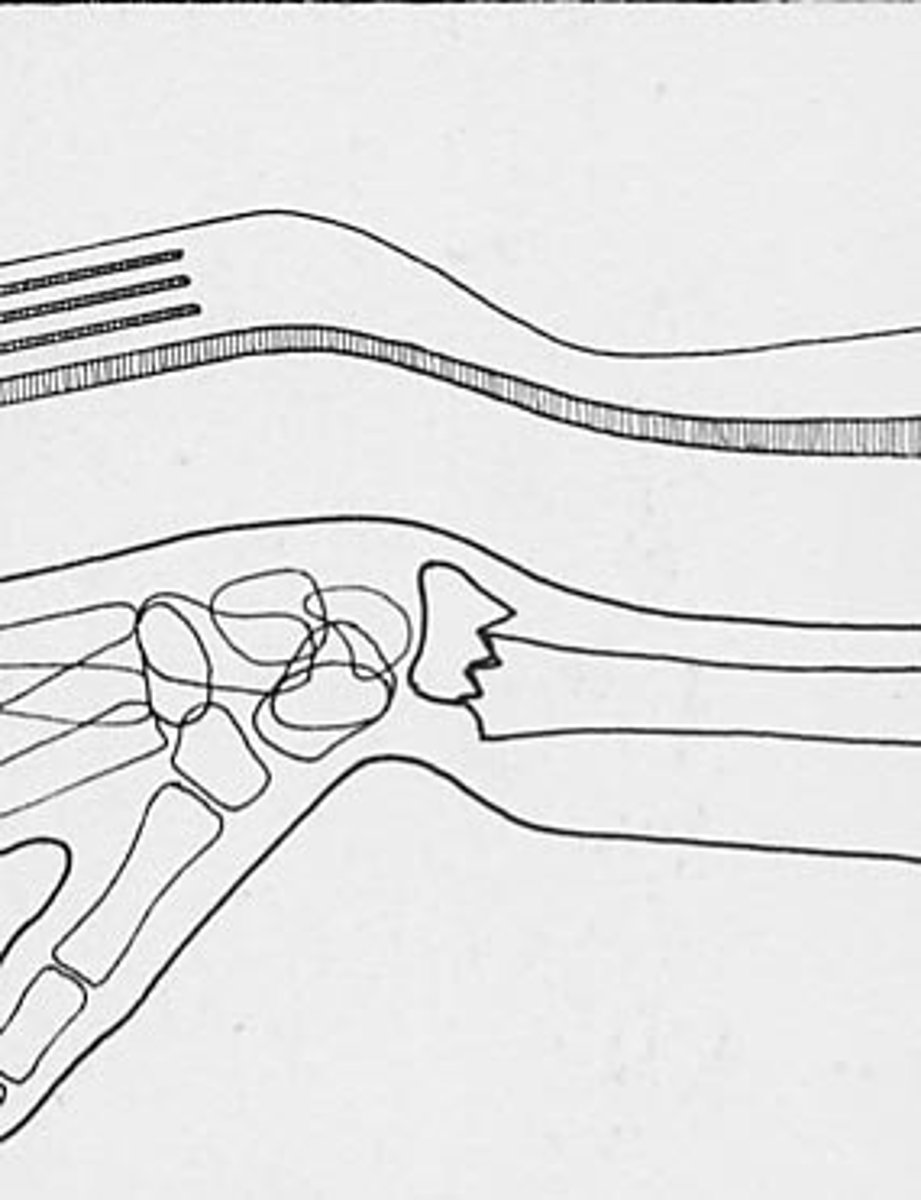
Silver-fork deformity on x-ray
Colles fracture - The distal radius compresses and displaces backward, producing the typical appearance of a "silver fork deformity
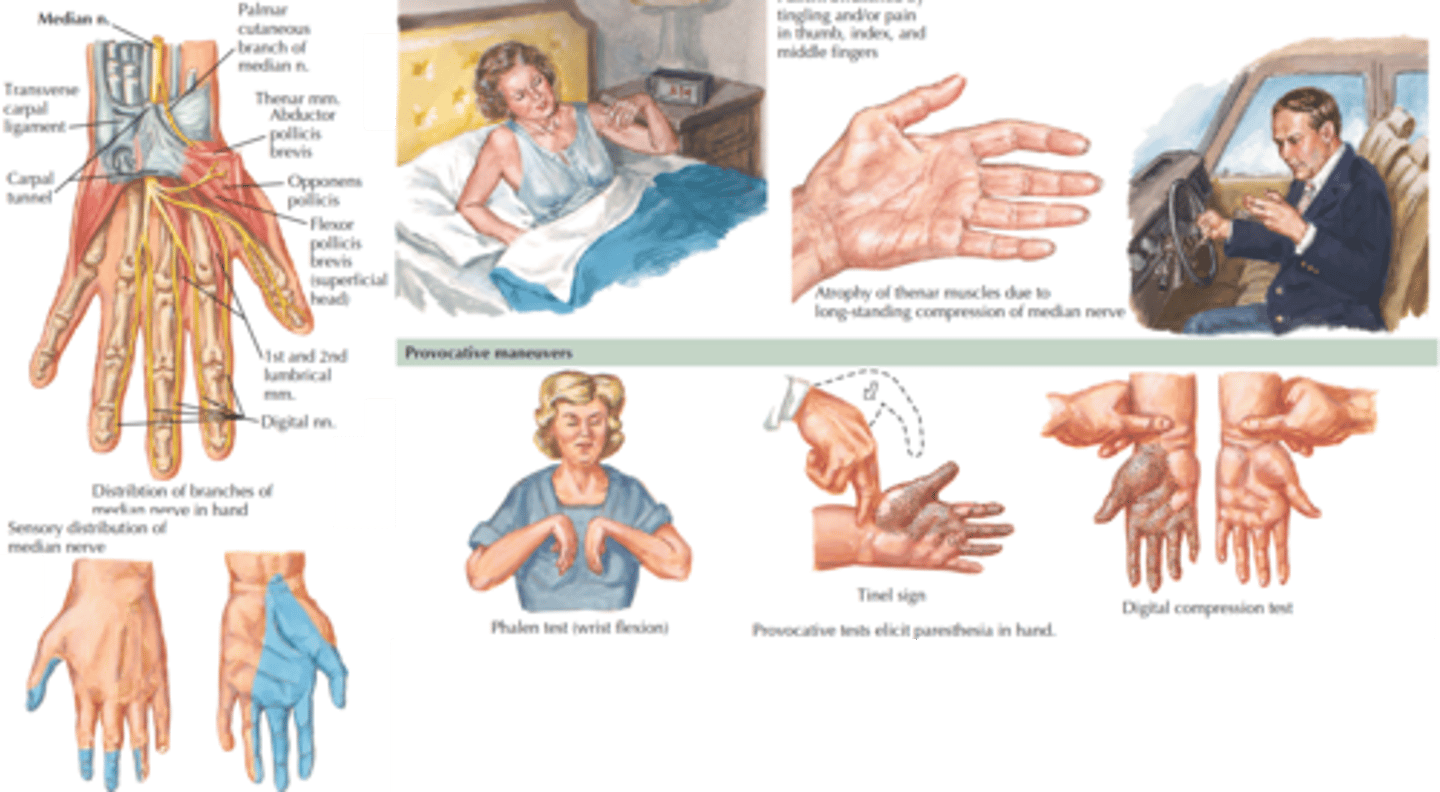
Carpal tunnel affects what nerve and what parts of the hand?
Median nerve. Thumb, pointer, and ring fingers. Thenar wasting is a sign of advanced disease.
An African American female presents with pain and stiffness, malar rash, and a positive double-stranded DNA antibody. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Lupus
A positive straight leg test indicates what diagnosis?
Herniated disc
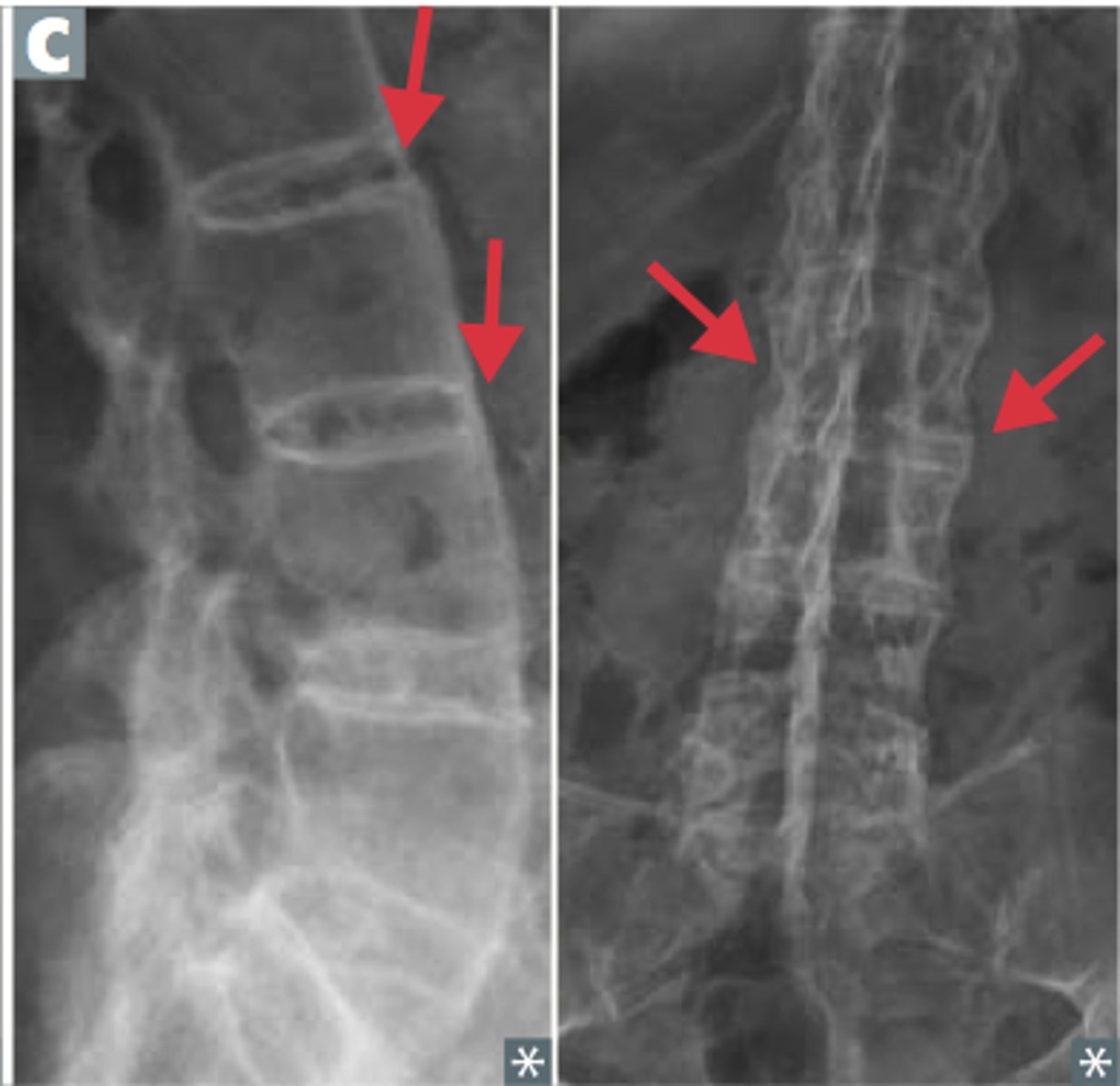
A bamboo spine indicates what diagnosis?
Ankylosing spondylitis
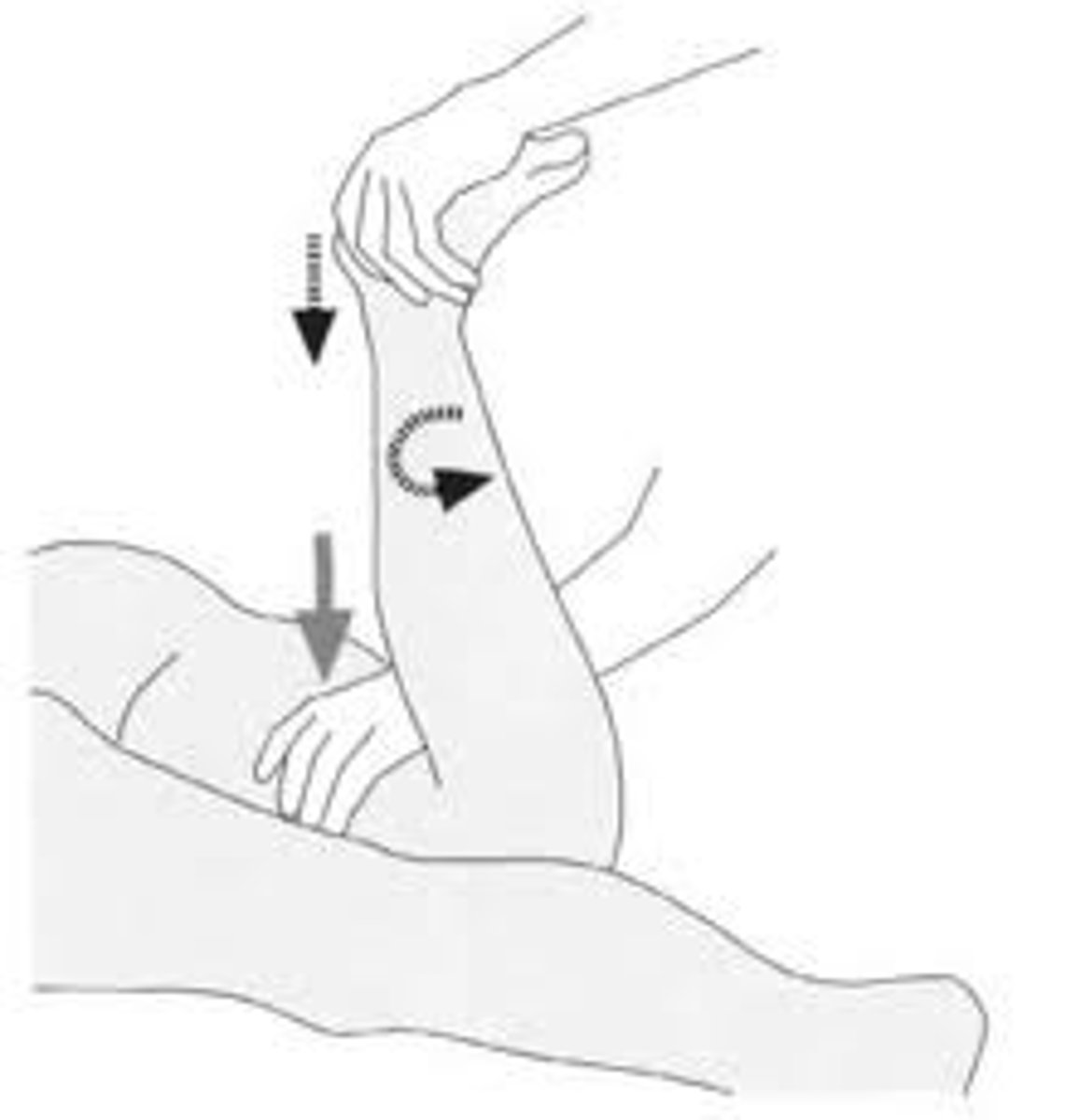
A positive Phalen and Tinel's sign indicates what
diagnosis?
Carpal tunnel
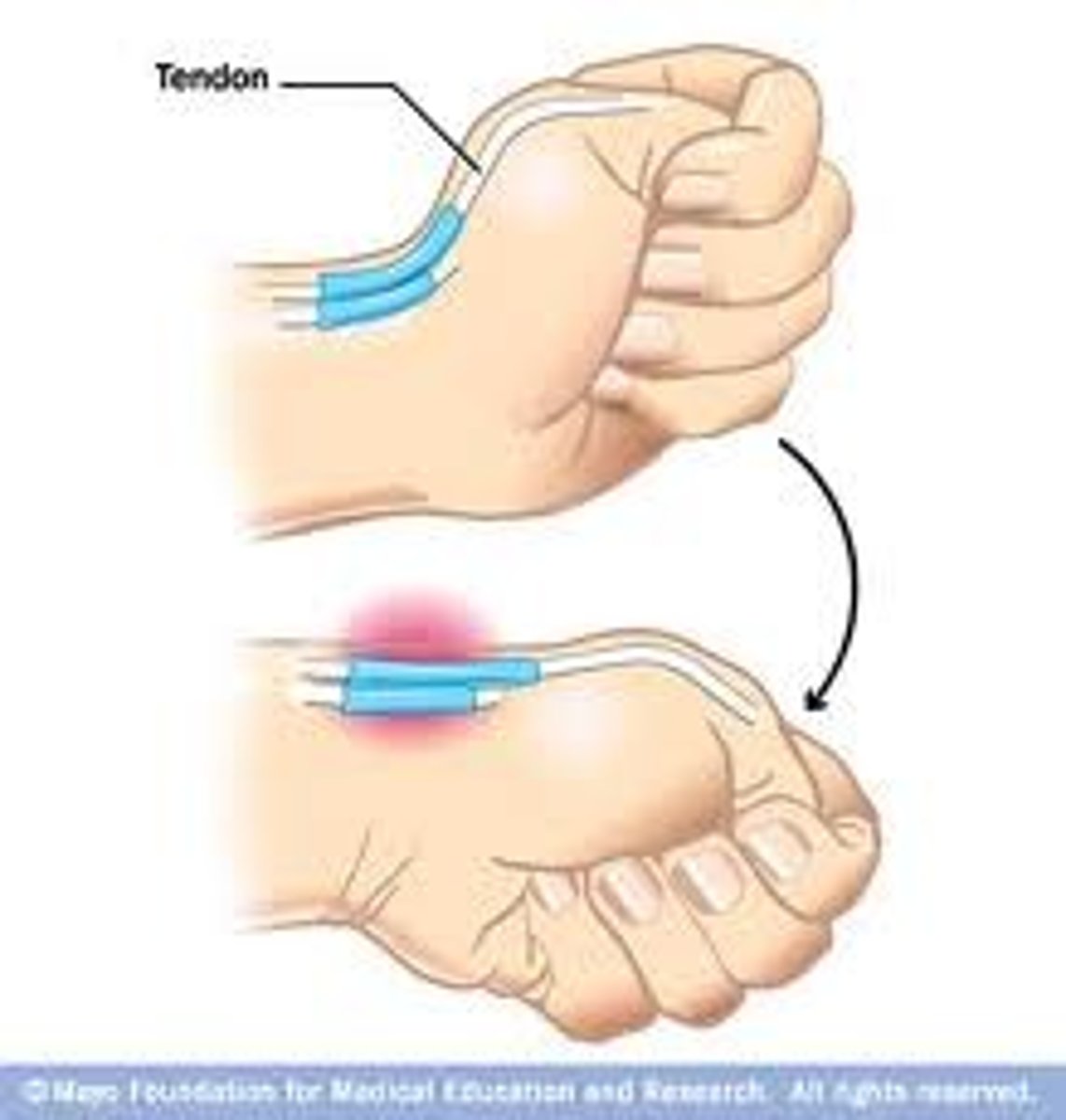
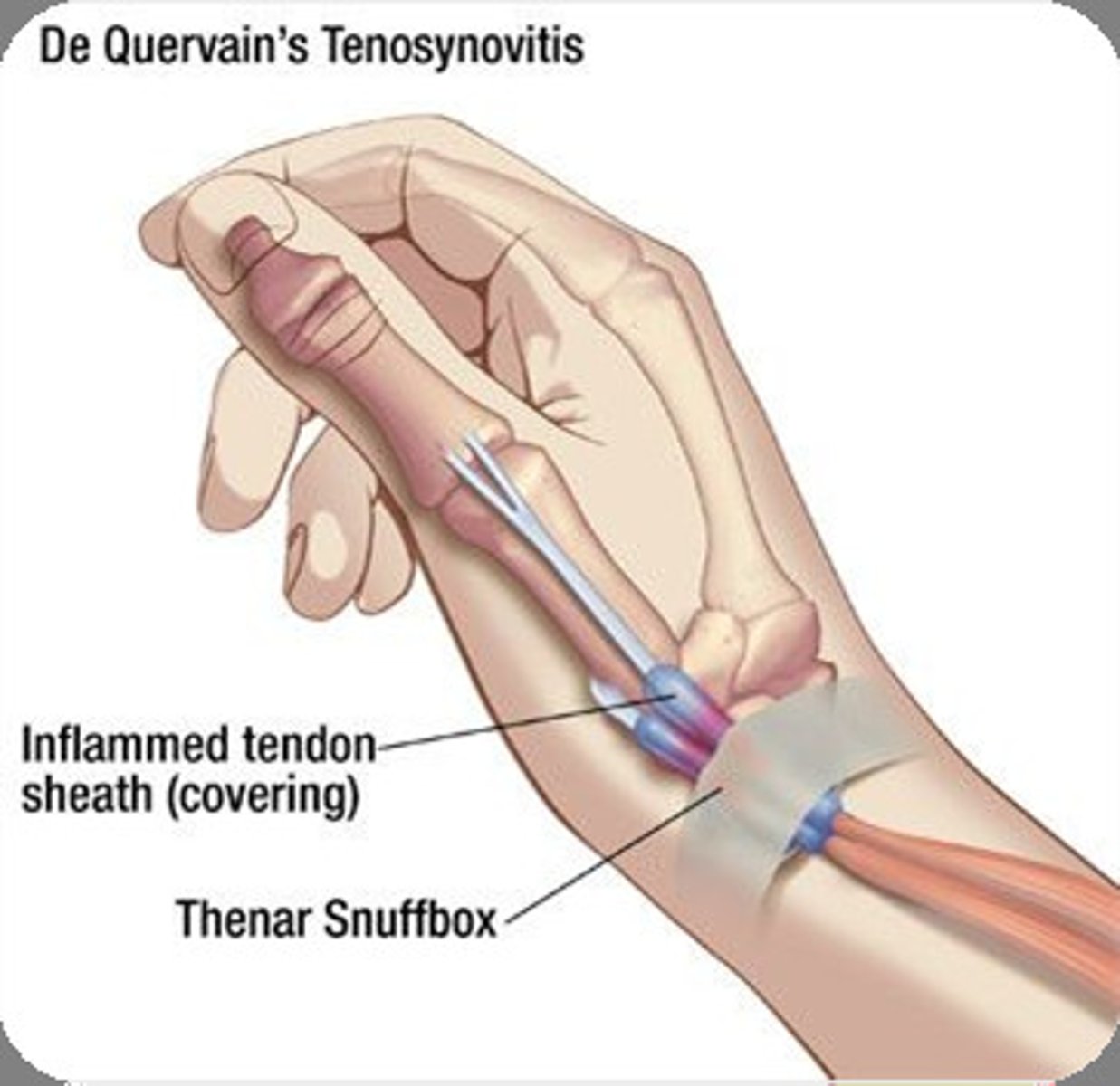
A positive Finkelstein's test indicates what diagnosis?
de Quervain's tenosynovitis
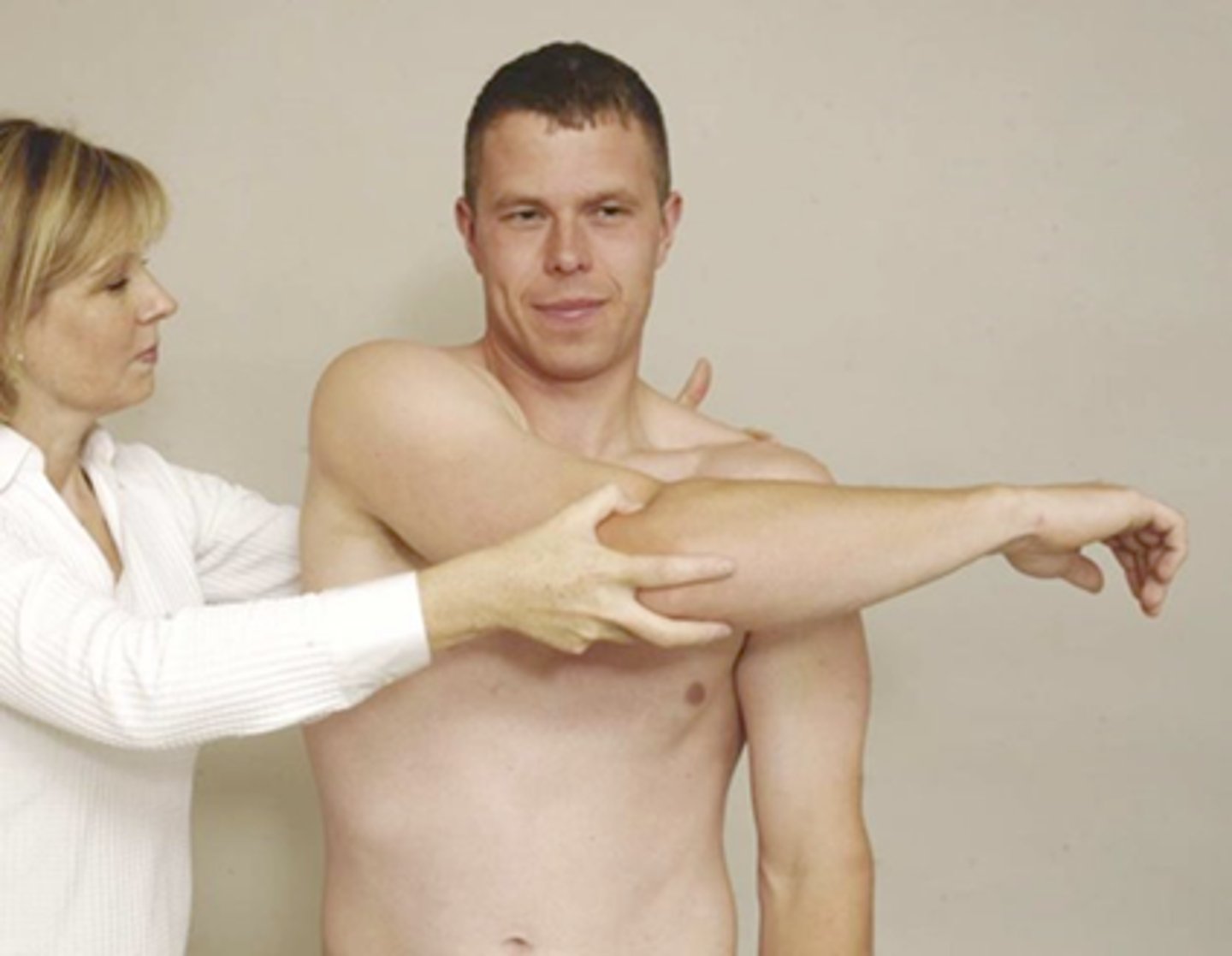
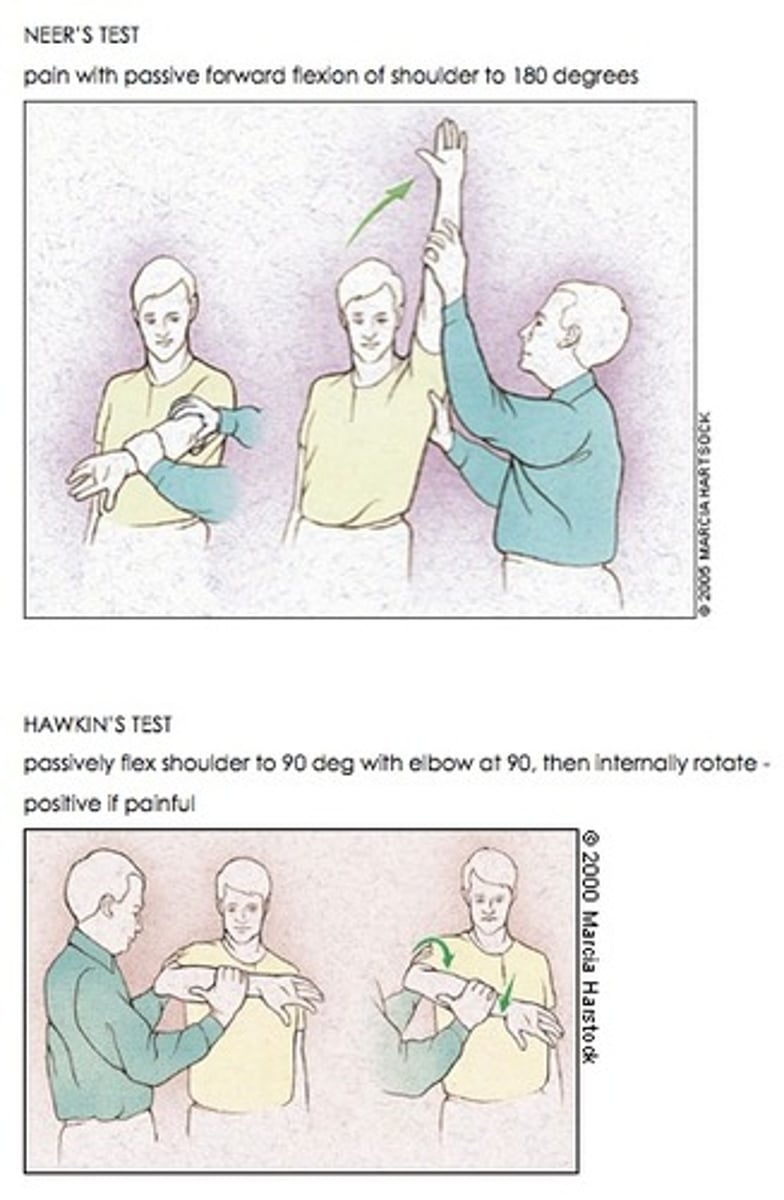
A positive Hawkins test indicates what diagnosis?
Rotator cuff impingement - The examiner places the patient's arm shoulder in 90 degrees of shoulder flexion with the elbow flexed to 90 degrees and then internally rotates the arm.
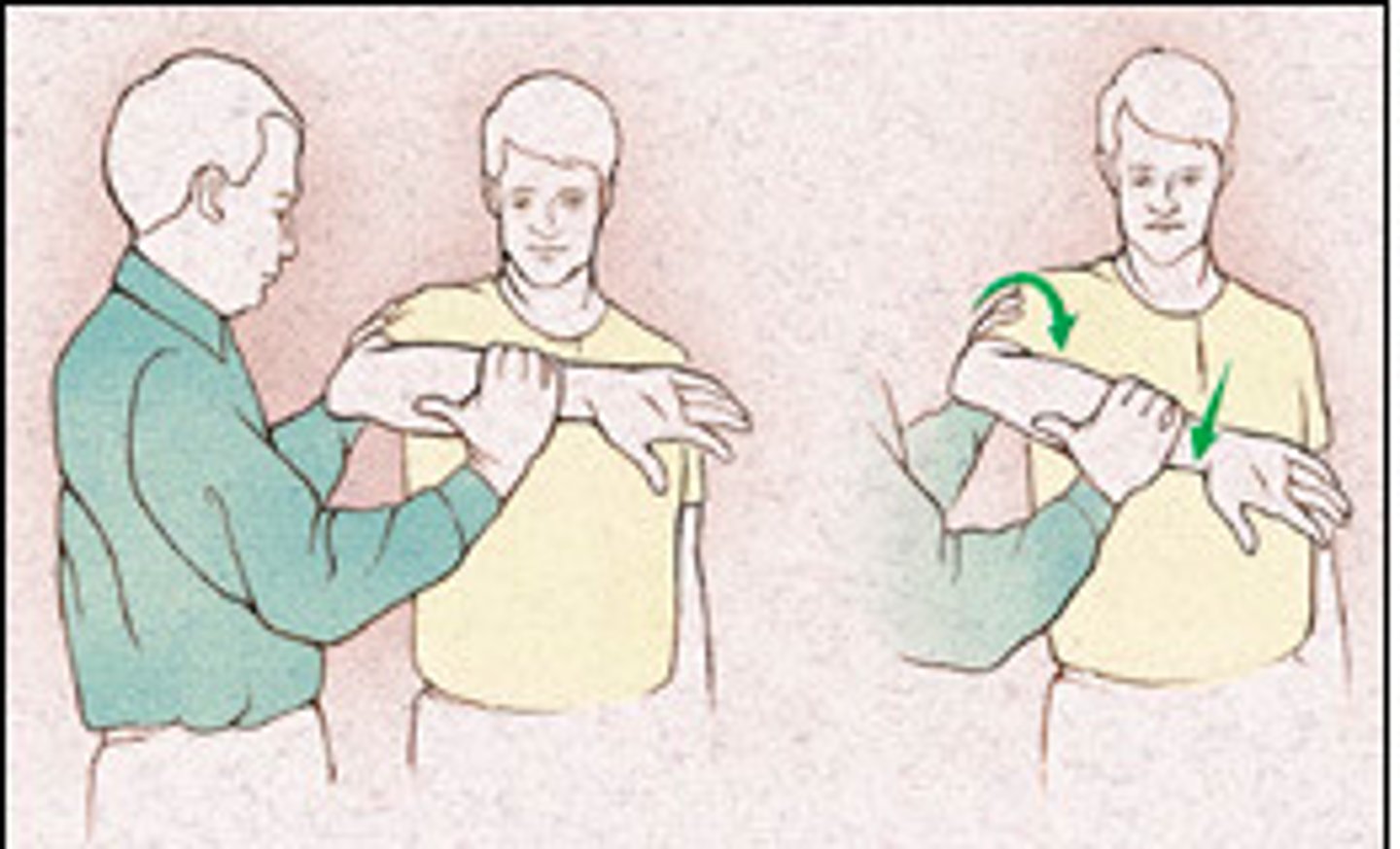
A positive crossover test indicates what diagnosis?
Acromioclavicular joint injury (AC joint) - Place one hand on the posterior aspect of the patient's shoulder and the other on the patient's elbow. Stabilize the patient's trunk and then passively and maximally horizontally adduct the test shoulder. A positive test is anterior, superior, or posterior shoulder pain
Anti-Jo-1 antibodies should make you think of what diagnosis?
Polymyositis
A 46-year-old male comes into ER limping a little on the right side. He states that it felt like he was kicked in the back of the leg during a soccer game, but clearly, no one was behind him. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Achilles tendon rupture
A patient presents with conjunctivitis, urethritis, arthritis, and oral lesions. What is the most likely diagnosis? What other lab might you expect to be positive?
Reactive arthritis, HLA B-27
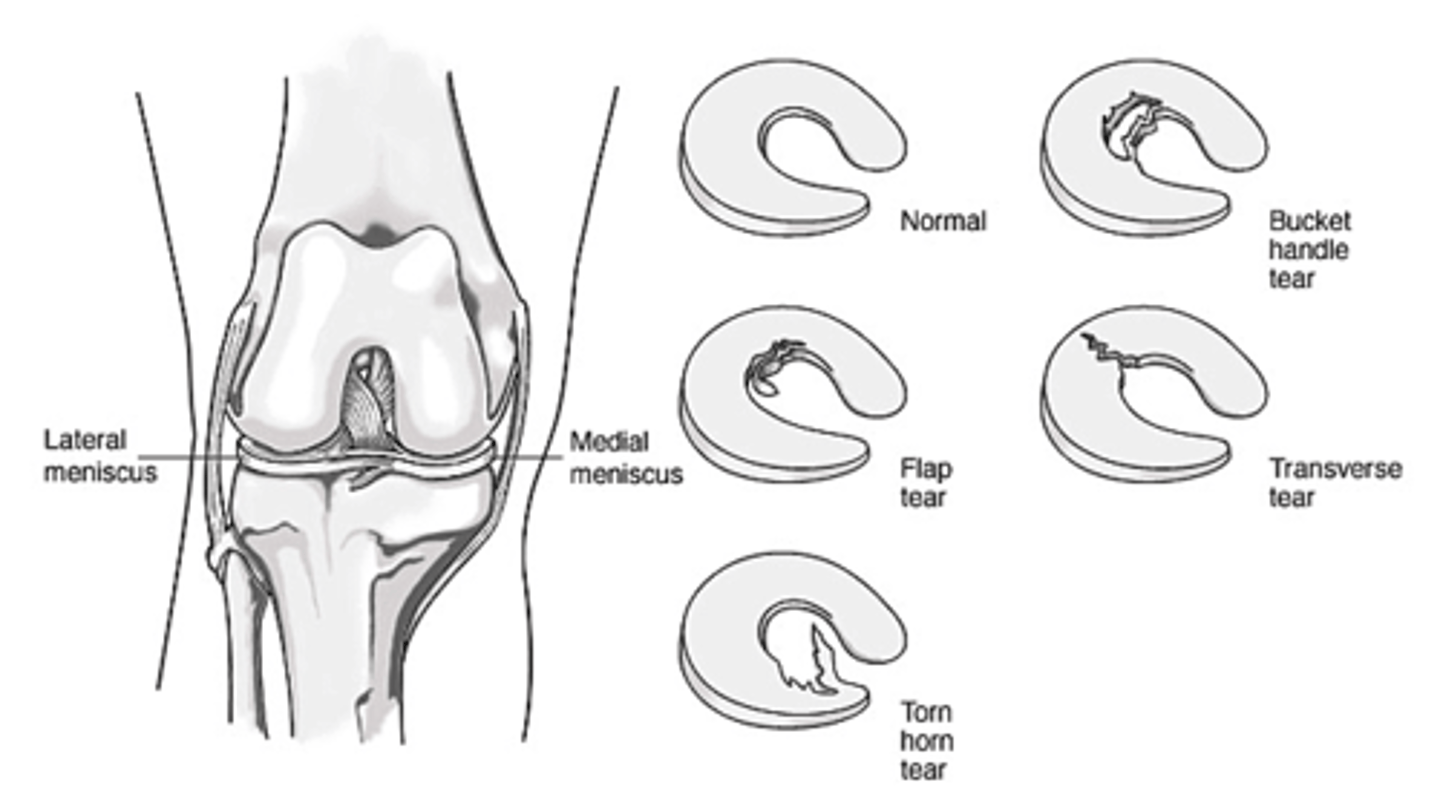
A patient presents with knee pain following a soccer game two days ago. He has joint line tenderness medially and feels a locking in the knee from time to time. What two physical exam tests should you do?
This is probably a medial meniscal tear. McMurry and Apley tests would be appropriate.
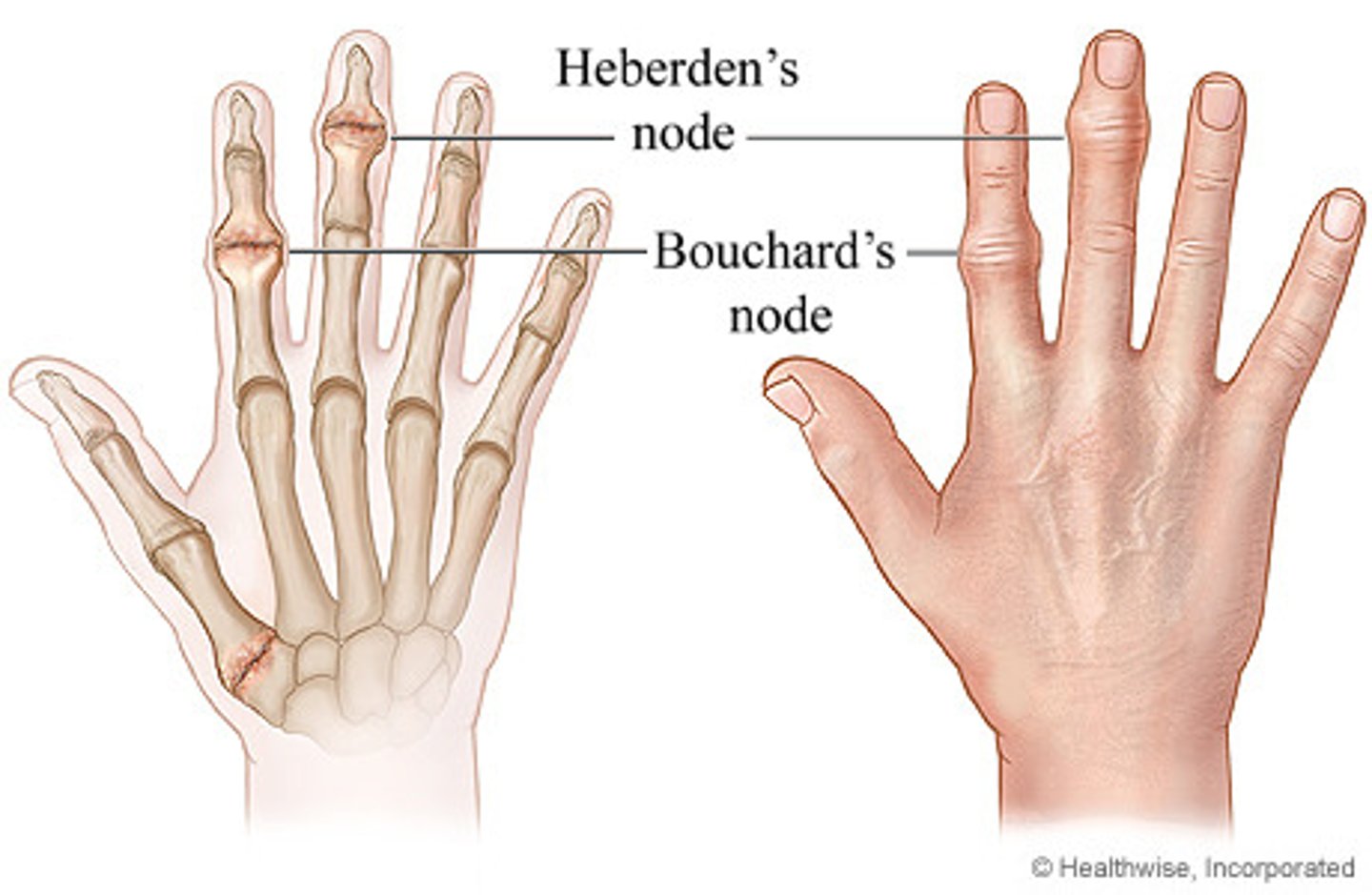
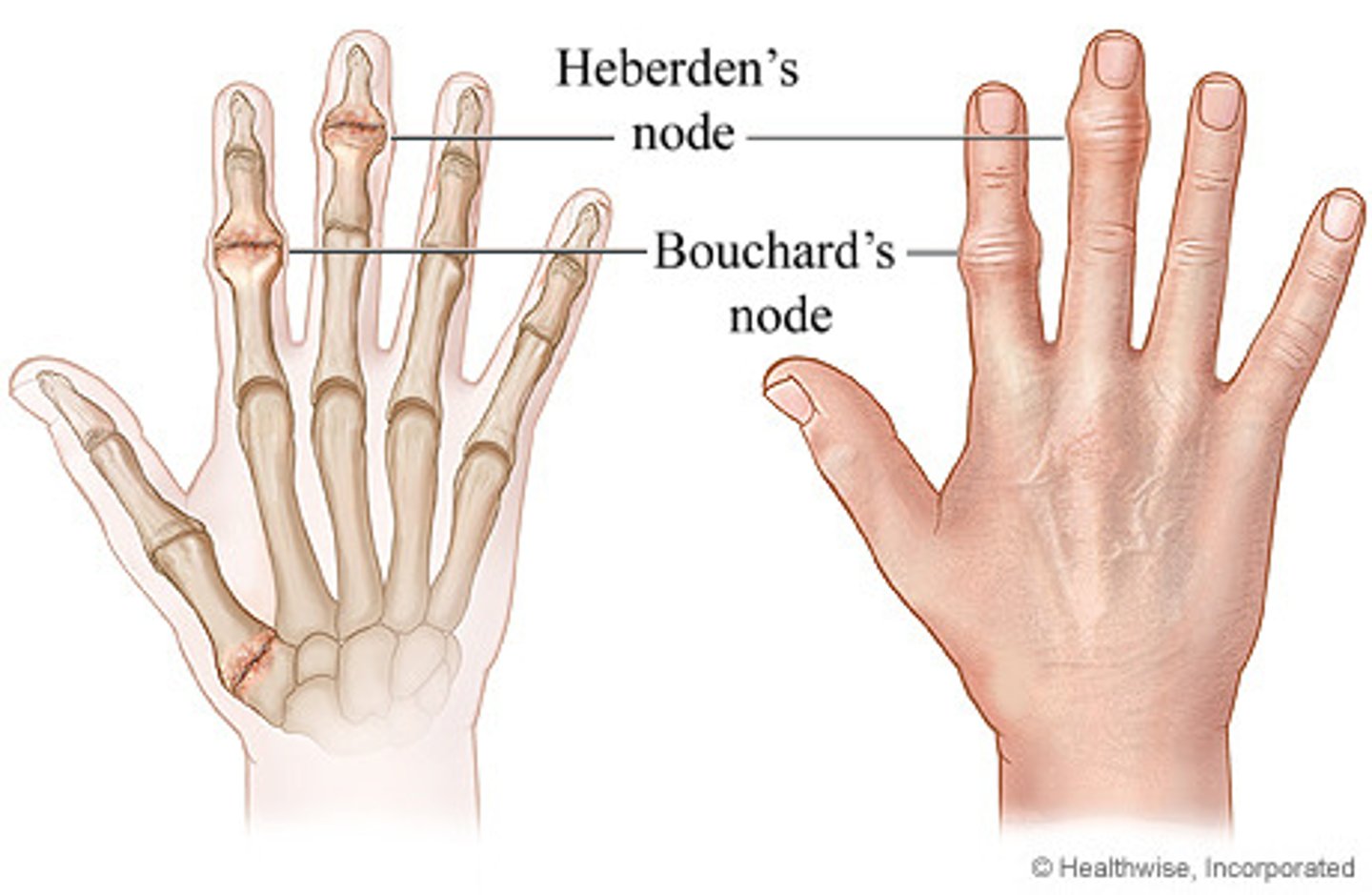
Where are Heberden's nodes found?
Distal interphalangeal joint (DIP)
● Heberden- Distal interphalangeal joint (H-D) (High Definition)
● Bouchard- Proximal interphalangeal joint (B-P) (Blue Picture)
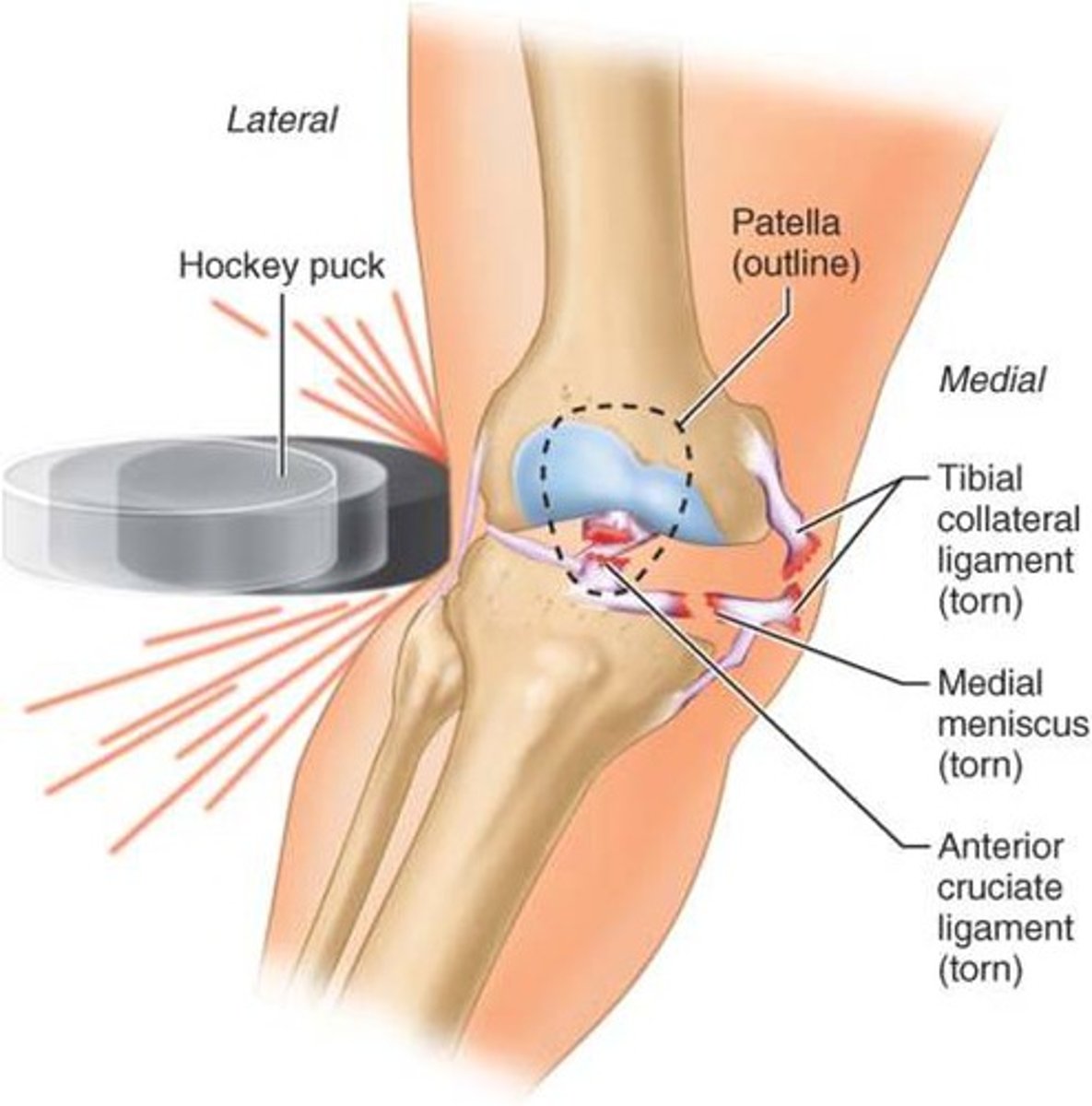
What is the most common knee injury?
Medial meniscal tear
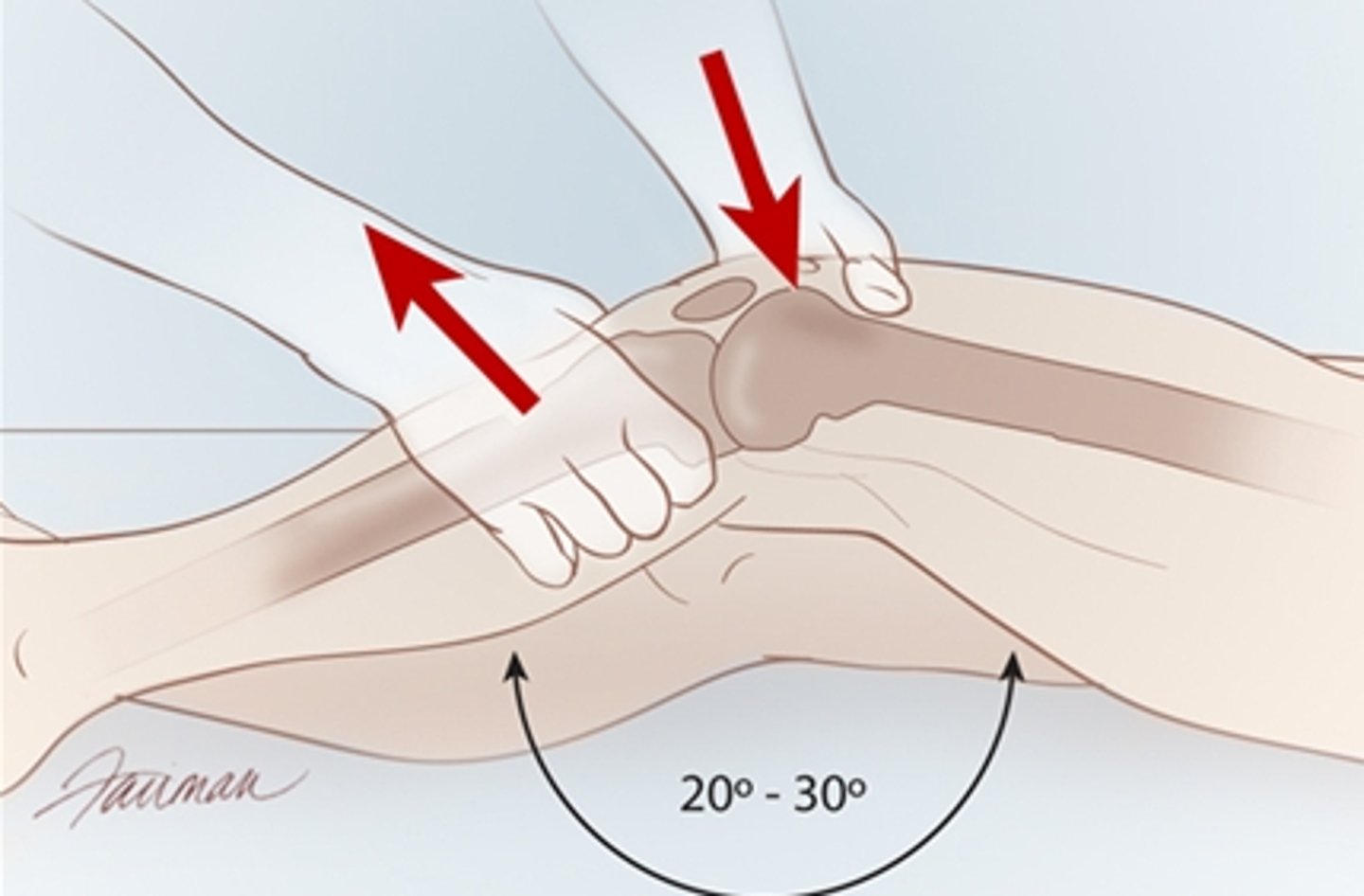
The most useful physical exam test for diagnosing an ACL tear?
Lachman's, followed by anterior drawer
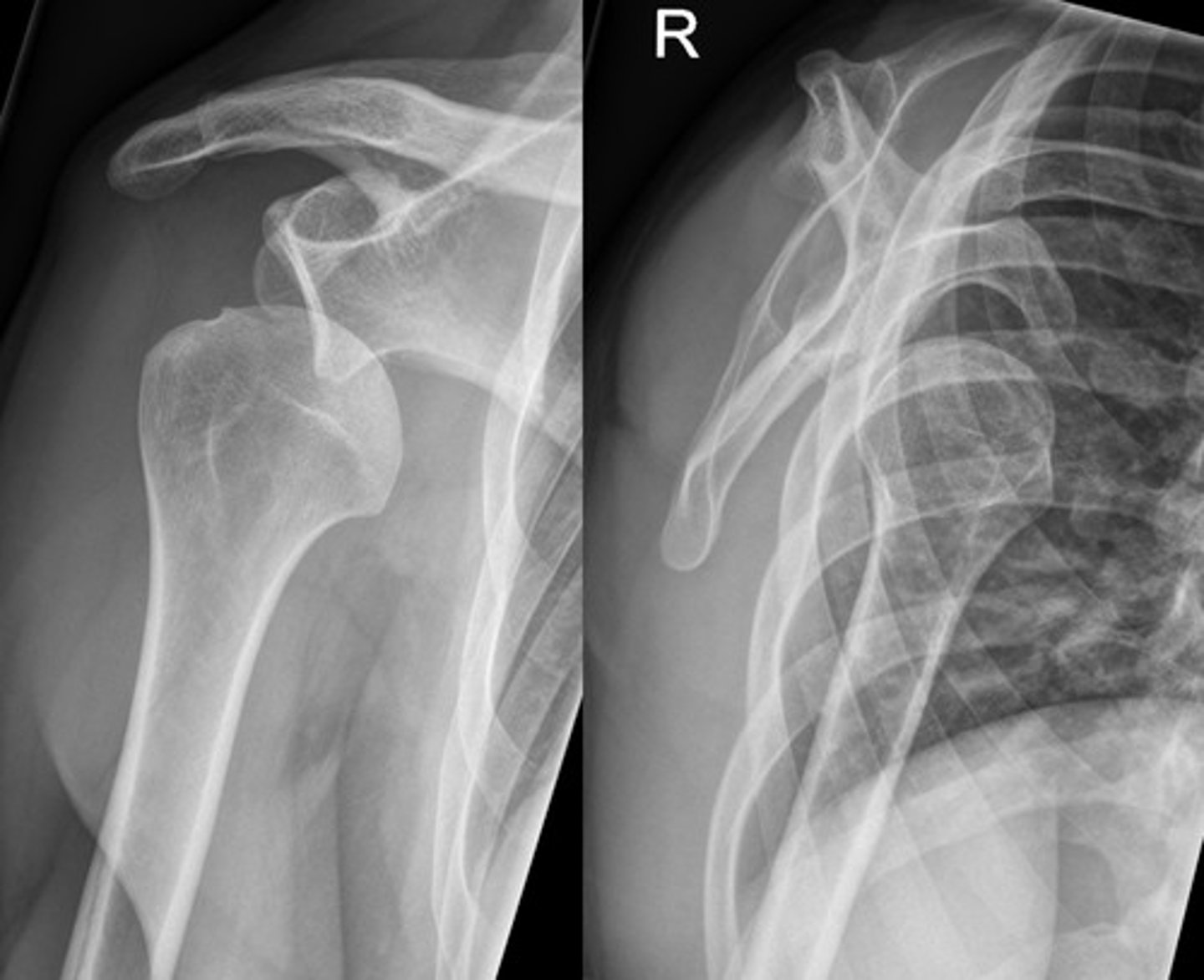
Are most shoulder dislocations anterior or posterior?
Anterior
Are most hip dislocations anterior or posterior?
Posterior
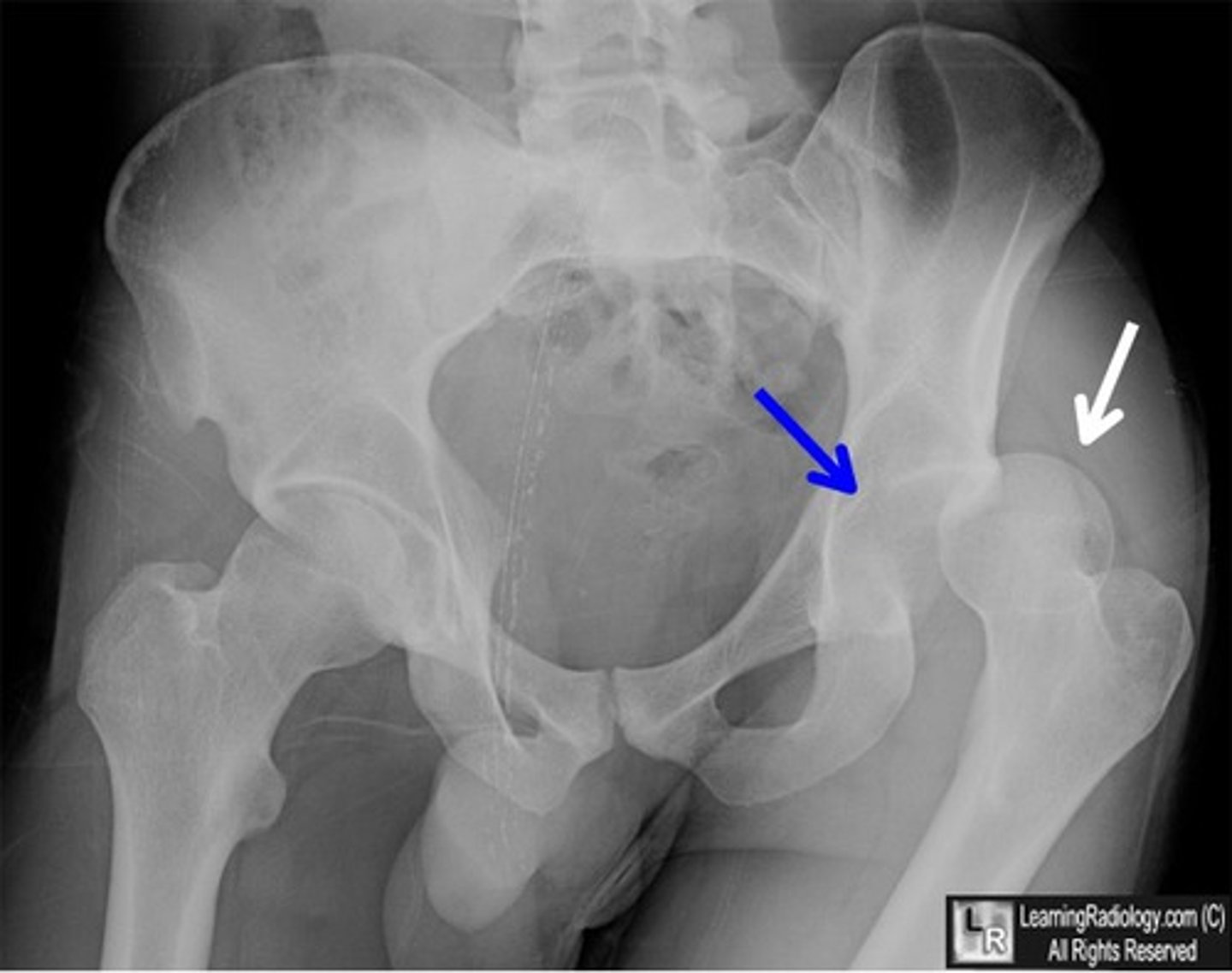
A patient presents to the ER after taking a baseball bat to the knee. He is unable to actively extend his knee. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Patella fracture
First line treatment for rheumatoid arthritis?
Methotrexate (Rheumatrex) - Methotrexate is considered the first-line DMARD agent for most patients with RA
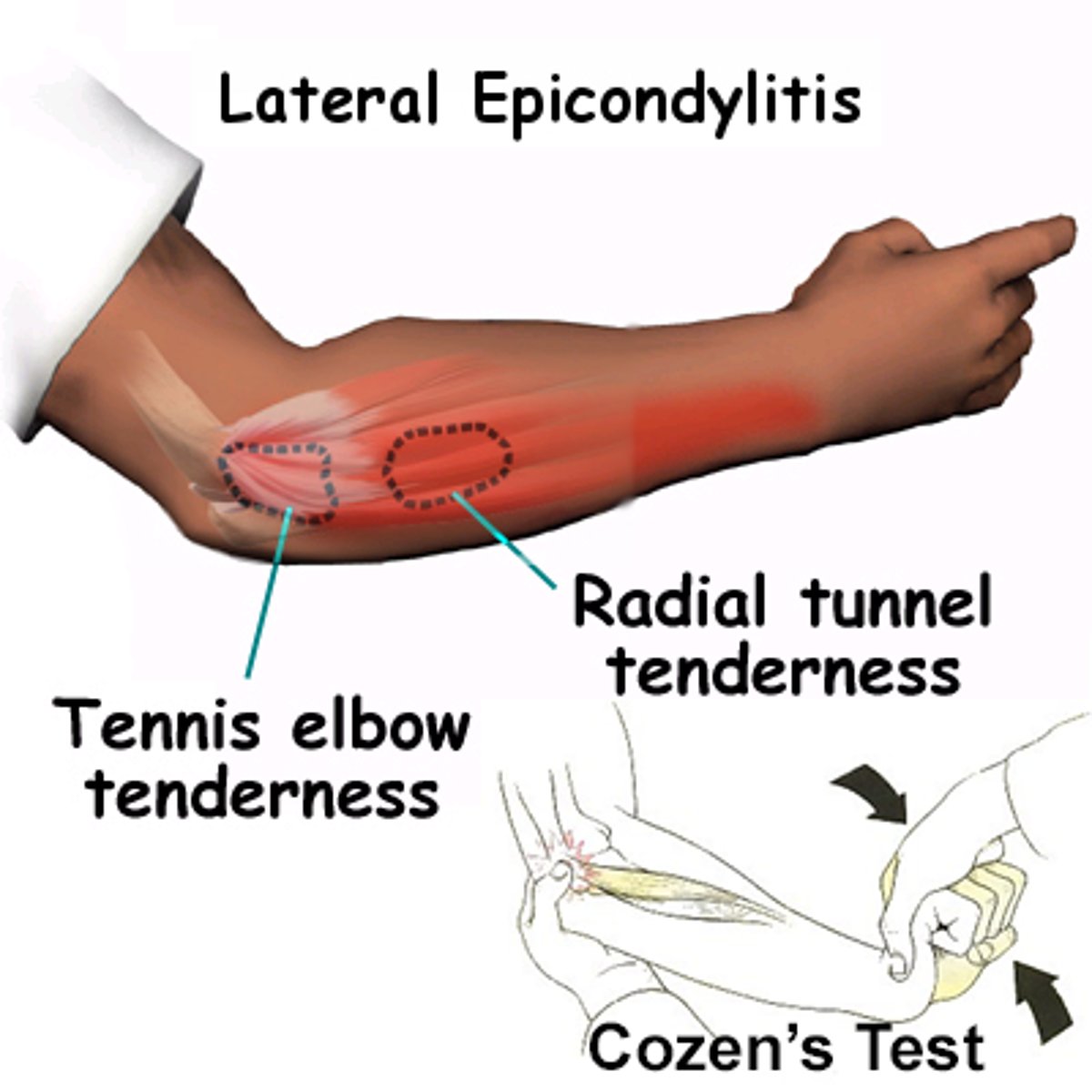
The medical term for tennis elbow?
Lateral epicondylitis
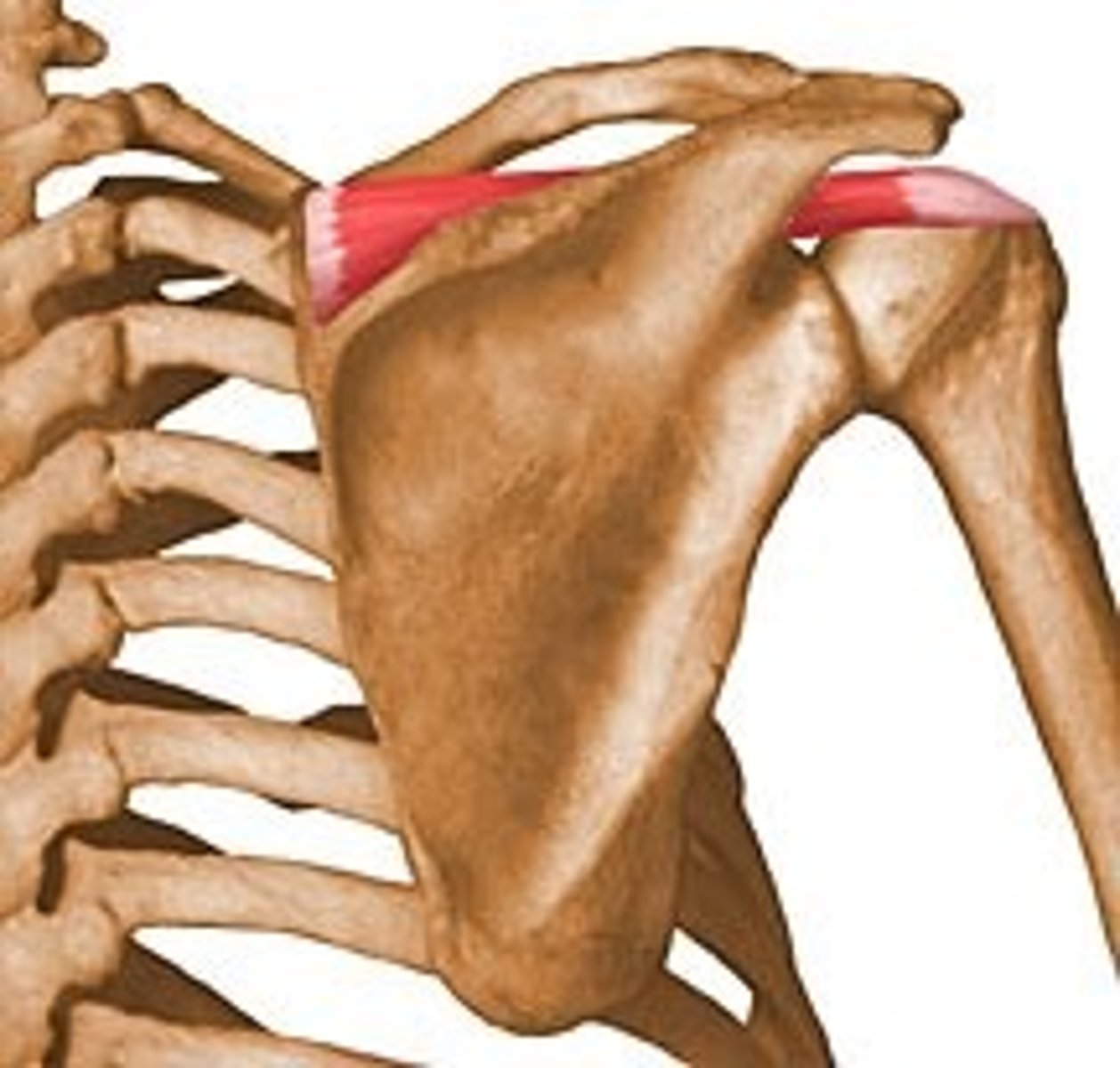
Which of the four rotator cuff muscles is most commonly injured?
Supraspinatus
You recommend bisphosphonates for a patient with osteoporosis. What instruction do you give her for immediately after taking the medication?
Remain upright for 30 minutes
A 95-year-old female presents to ER after a fall in her home. Her left leg is shortened and externally rotated. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Hip fracture
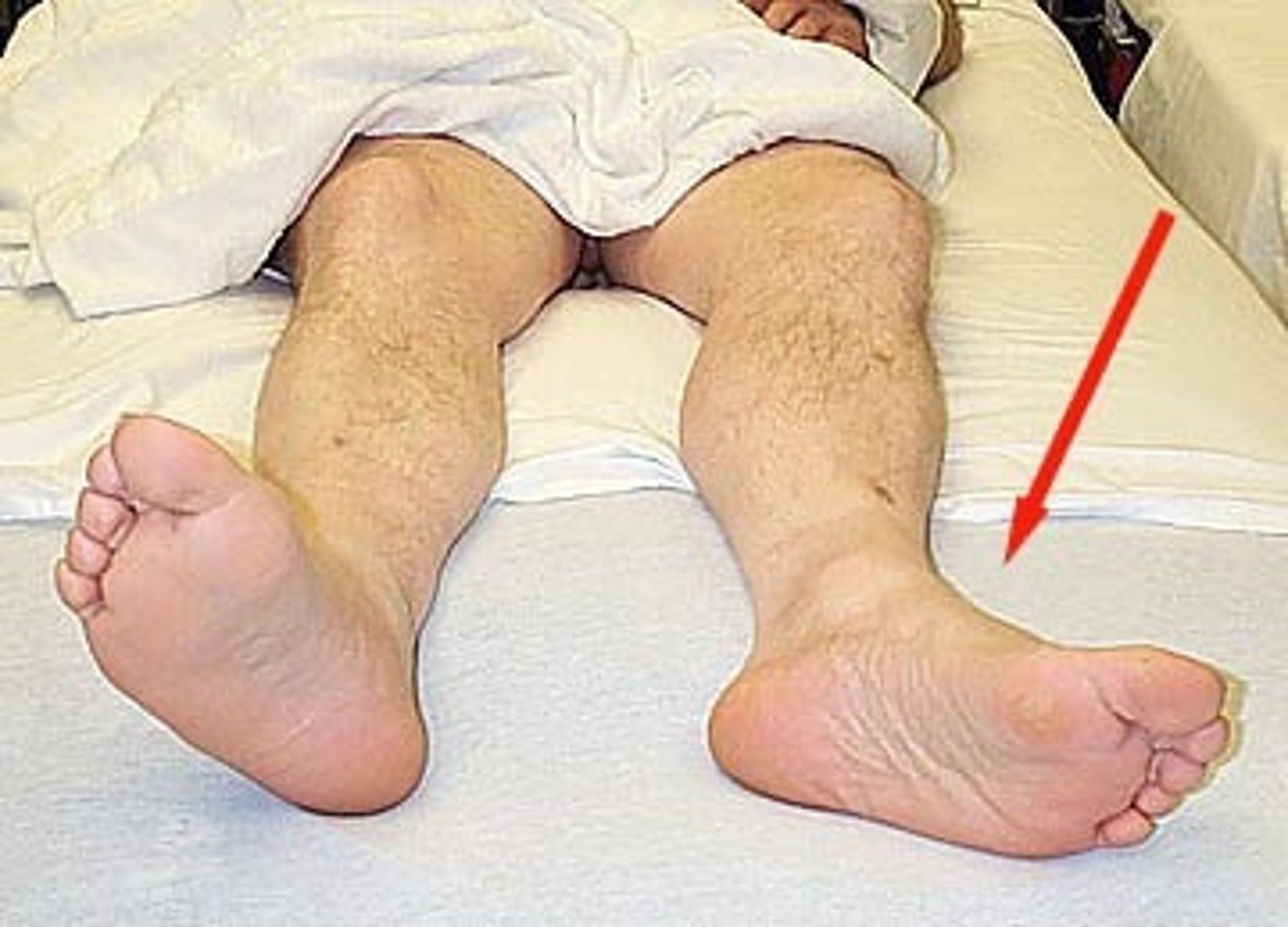
A patient with HIV presents with severe groin pain. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Antiretroviral medications put patients at an increased risk of AVN.
A patient presents to the ER with saddle anesthesia and loss of bowel and bladder function. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Cauda equina
What is another term for podagra?
Gout
What is the medical term for hunchback?
Kyphosis
The most common cause of C-spine fractures?
Motor vehicle accidents
What is the first line treatment for carpal tunnel?
Night splint
A positive McMurray indicates what diagnosis?
Meniscal tear - The patient is supine, knee flexed and externally (medial meniscus) or internally (lateral meniscus) extended - pain indicates a tear
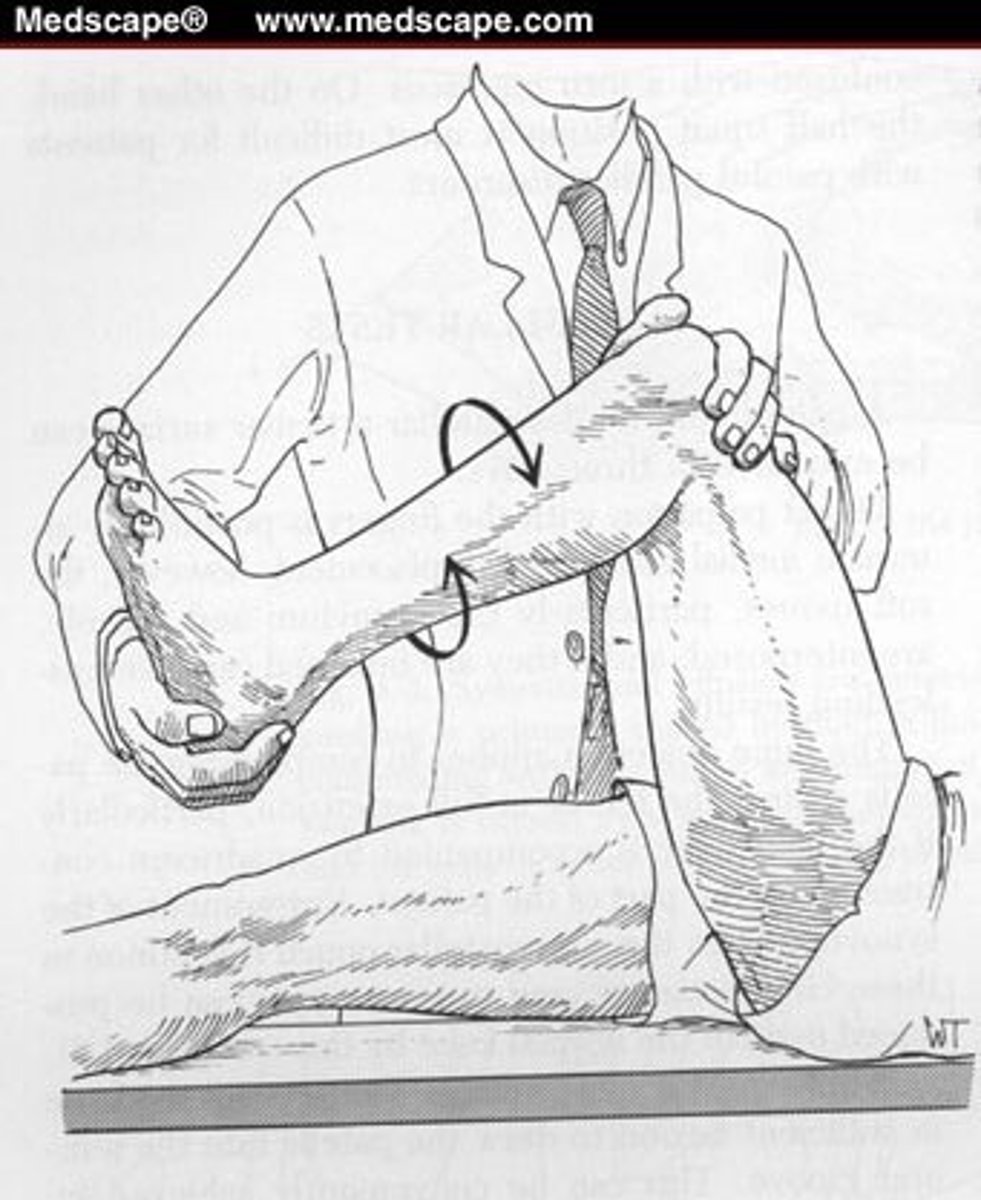
A new mother presents with pain over the radial wrist. She has a positive Finkelstein's test. What is the most likely diagnosis?
de Quervain's tenosynovitis
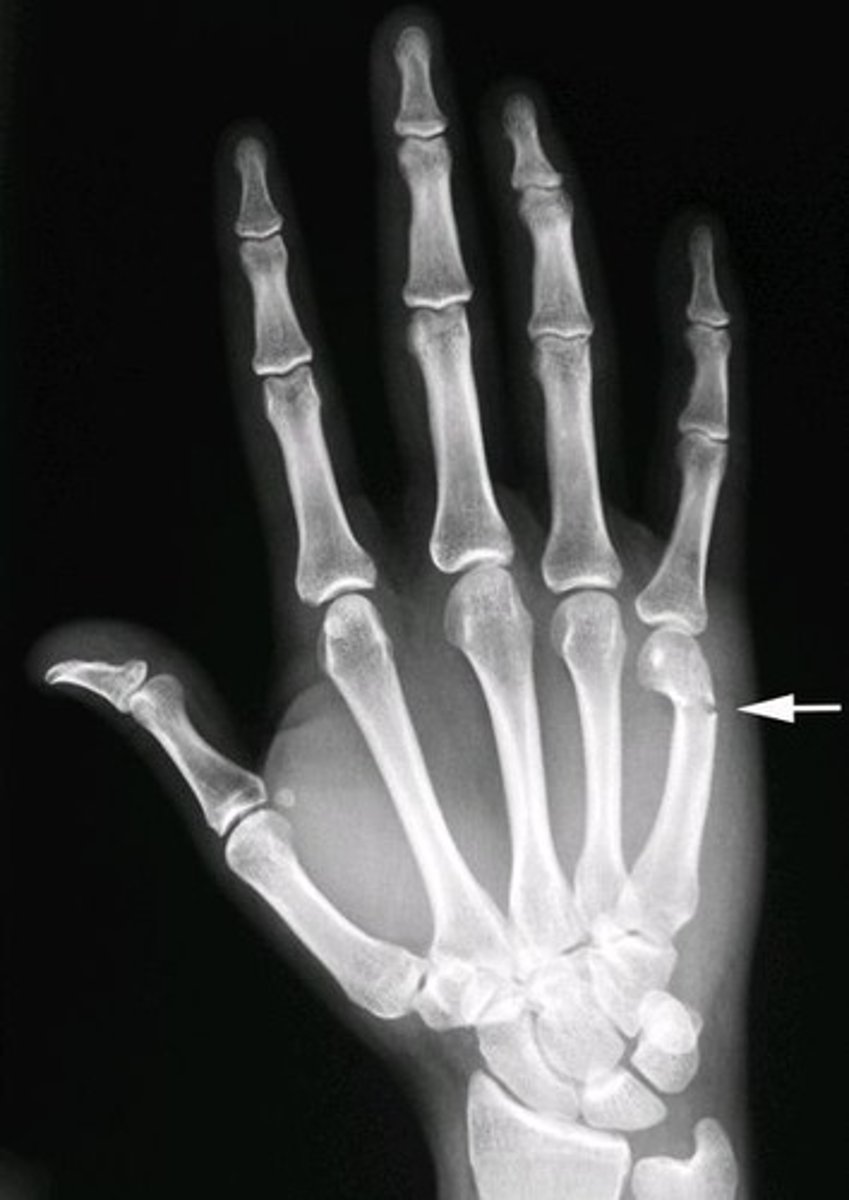
4th and 5th metacarpal fractures that often result from throwing a punch
Boxer's fracture
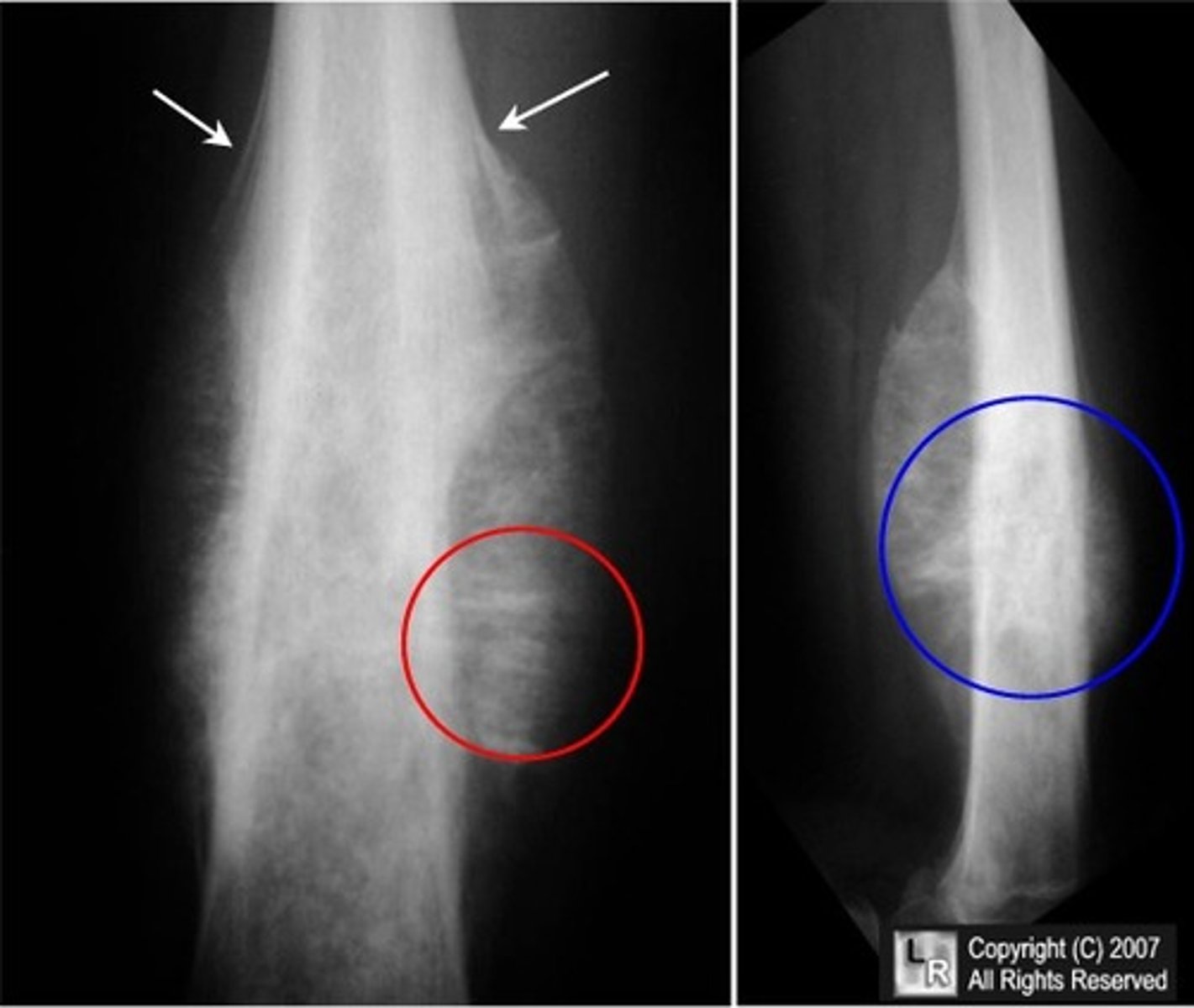
A 15-year-old boy presents complaining of night pain in the pelvis. You order an x-ray. The report comes back with a description of a mass with an onion skin appearance. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Ewing sarcoma
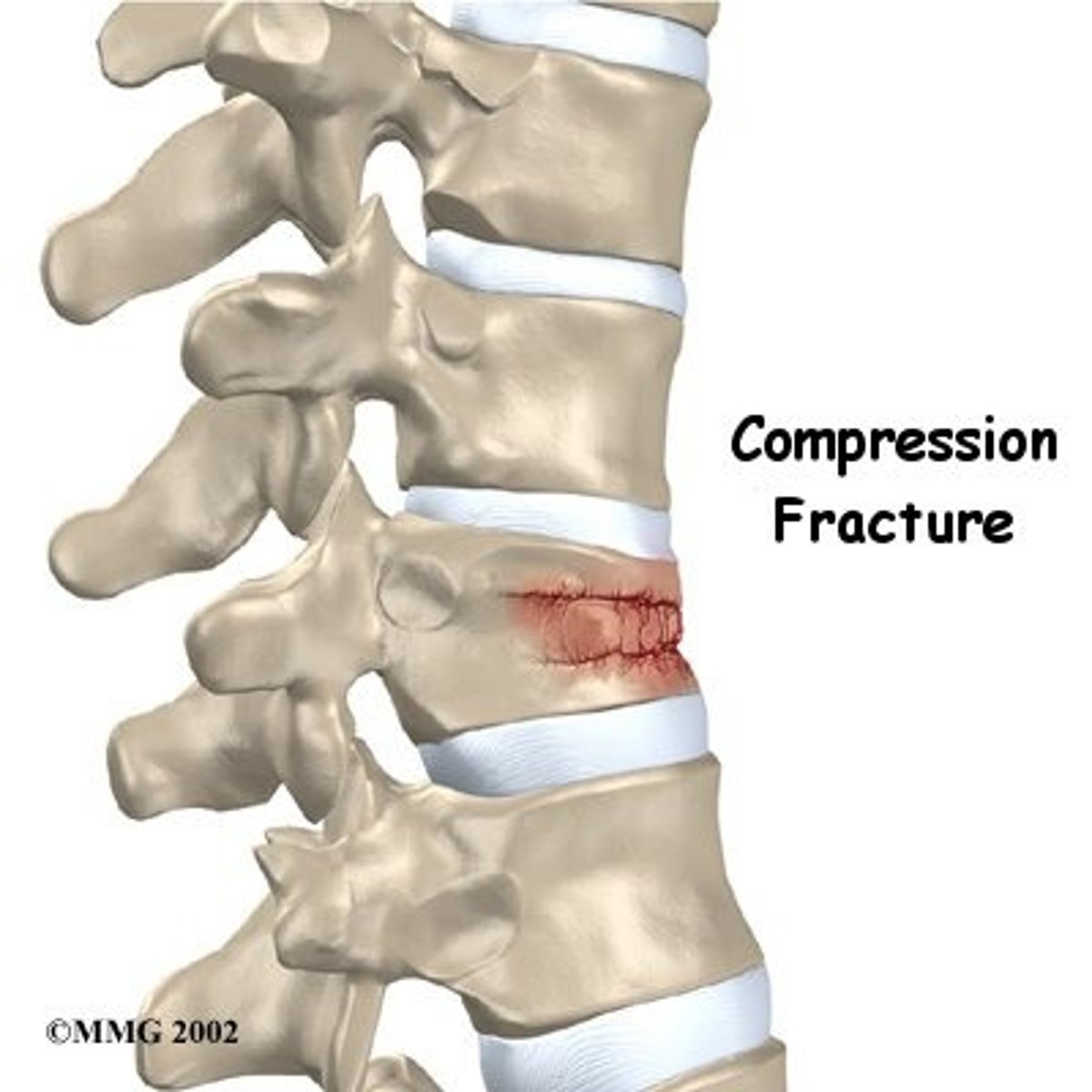
What is the most common fracture in a patient with osteoporosis?
A compression fracture of a vertebral body followed by hip fractures
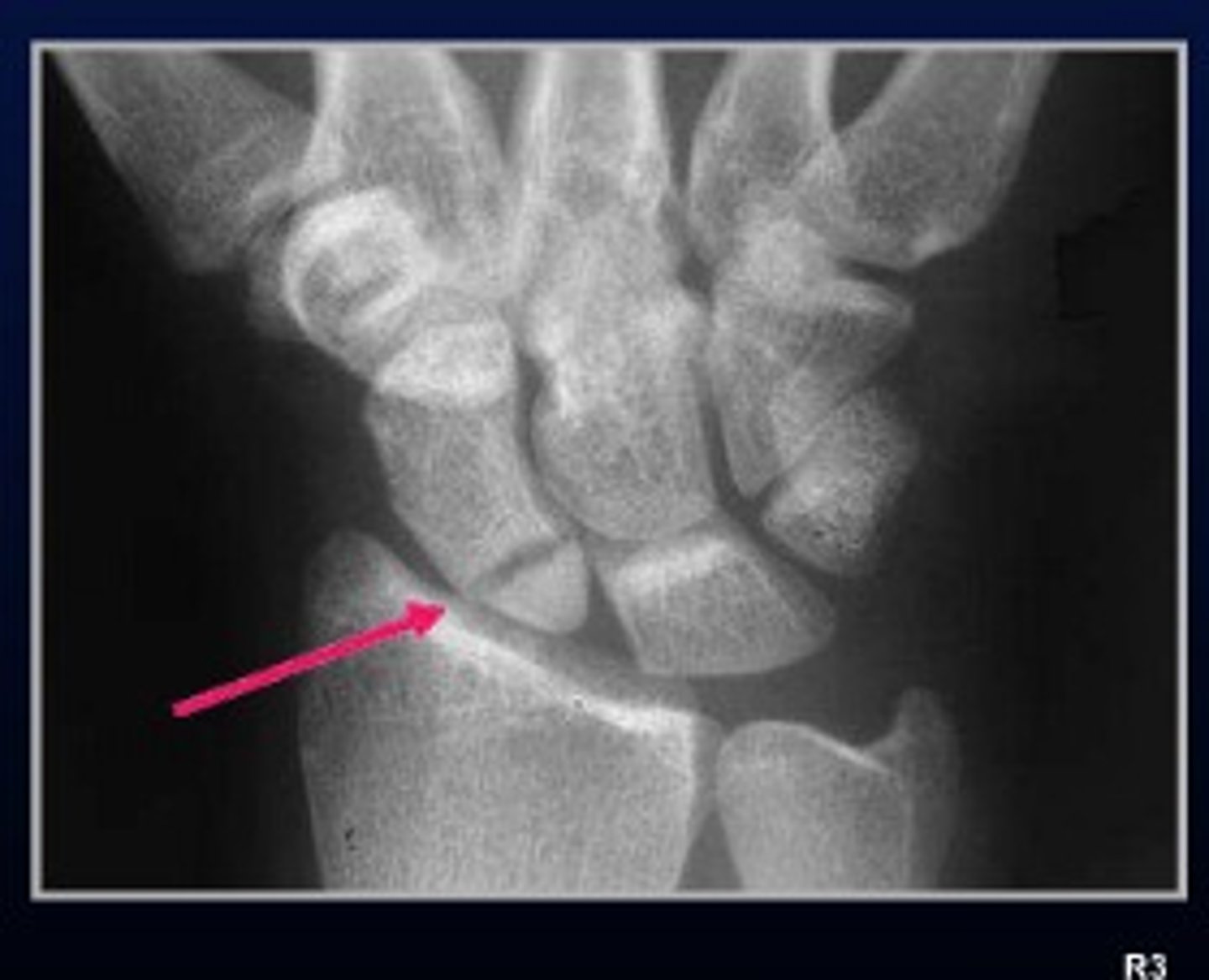
Tenderness over the anatomical snuffbox is indicative of what fracture?
Scaphoid
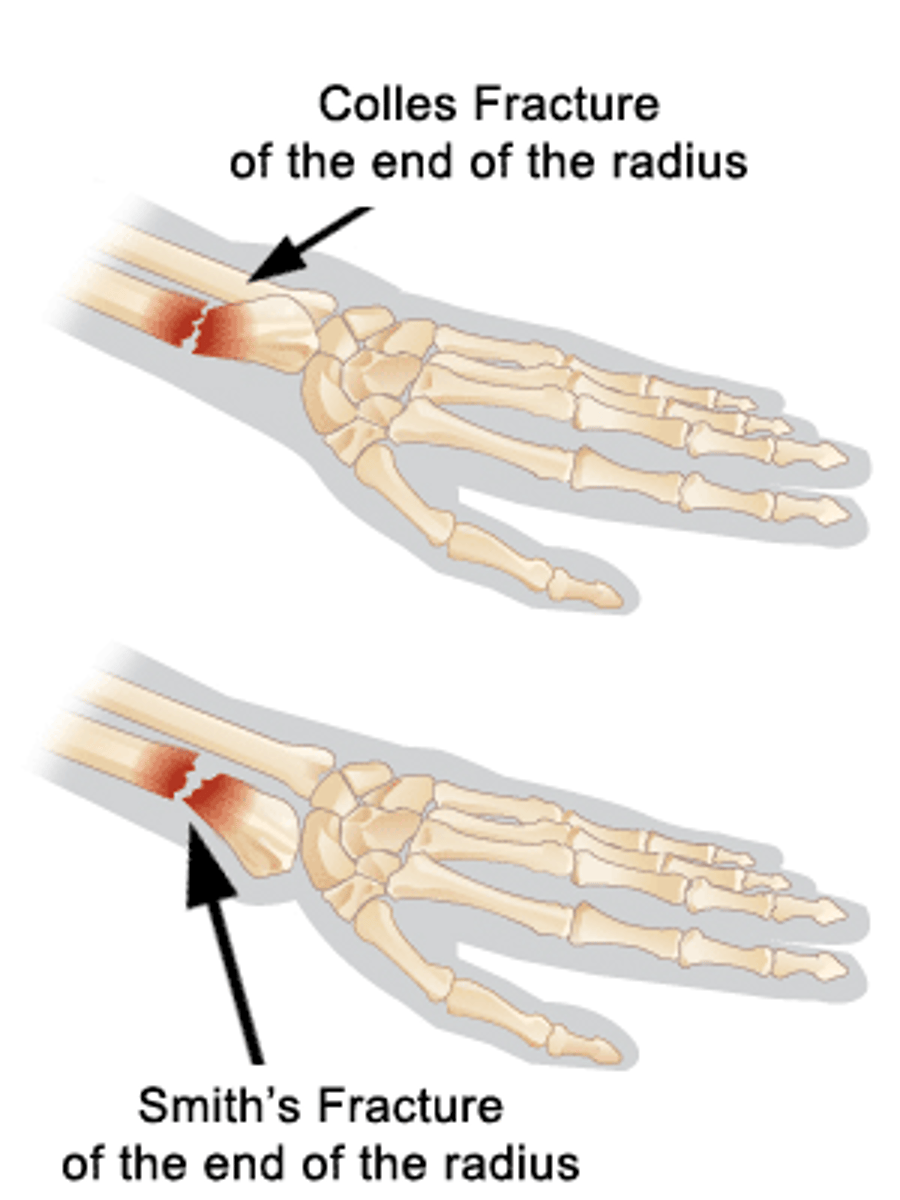
Which way does a Colles fracture angulate: dorsal or volar? What about a Smith fracture?
Colles = Dorsal, Smith = Volar
A patient presents with progressive neck and proximal muscle weakness. On physical exam, you see a reddish-purple maculopapular rash. Her lab work shows anti-Jo-1 antibodies. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Polymyositis
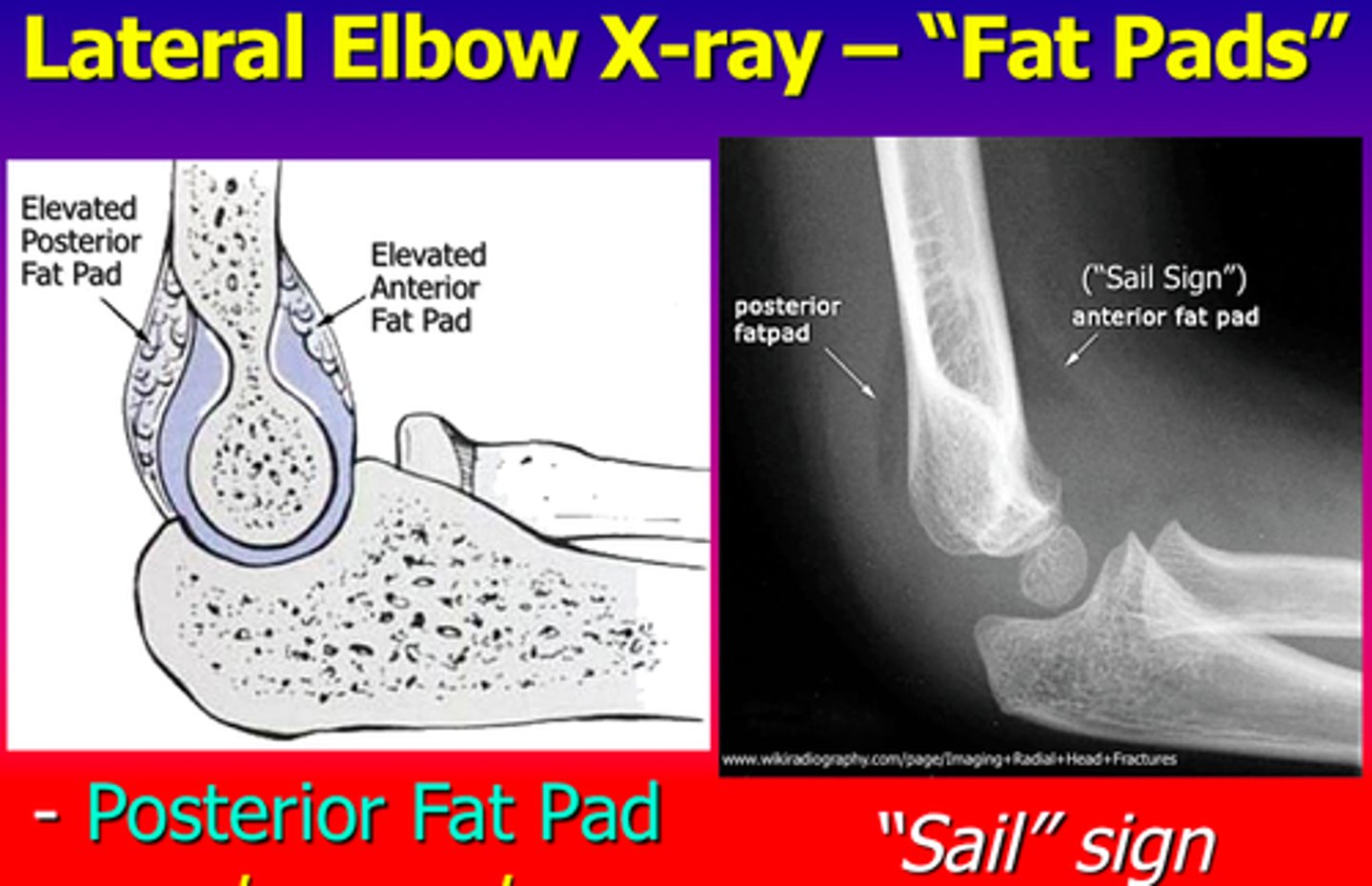
A fat pad sign on a lateral x-ray of the elbow has what significance?
It is blood in the joint indicating a fracture even if the fracture line cannot be seen.
What is the most common fracture in children?
Clavicle
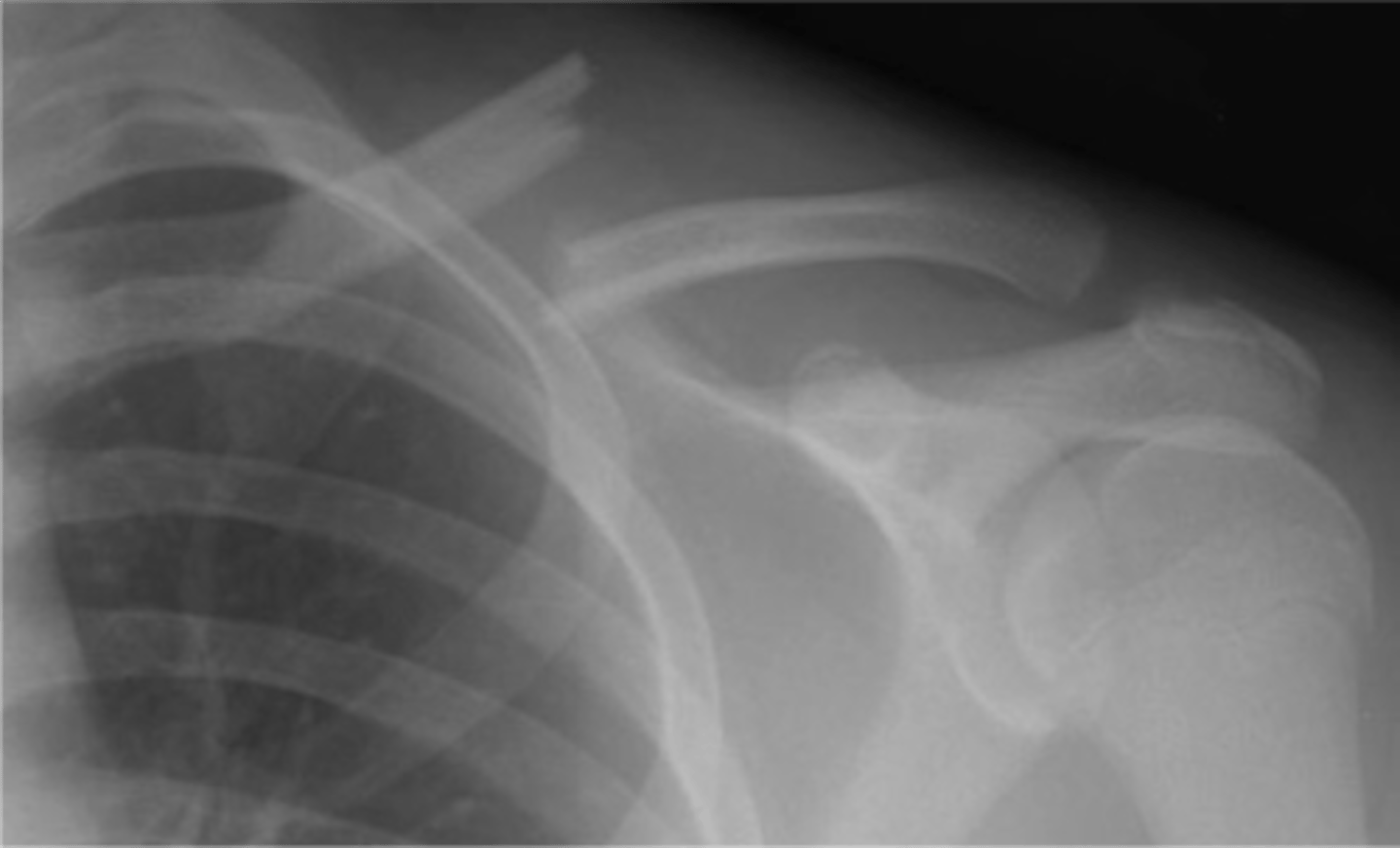
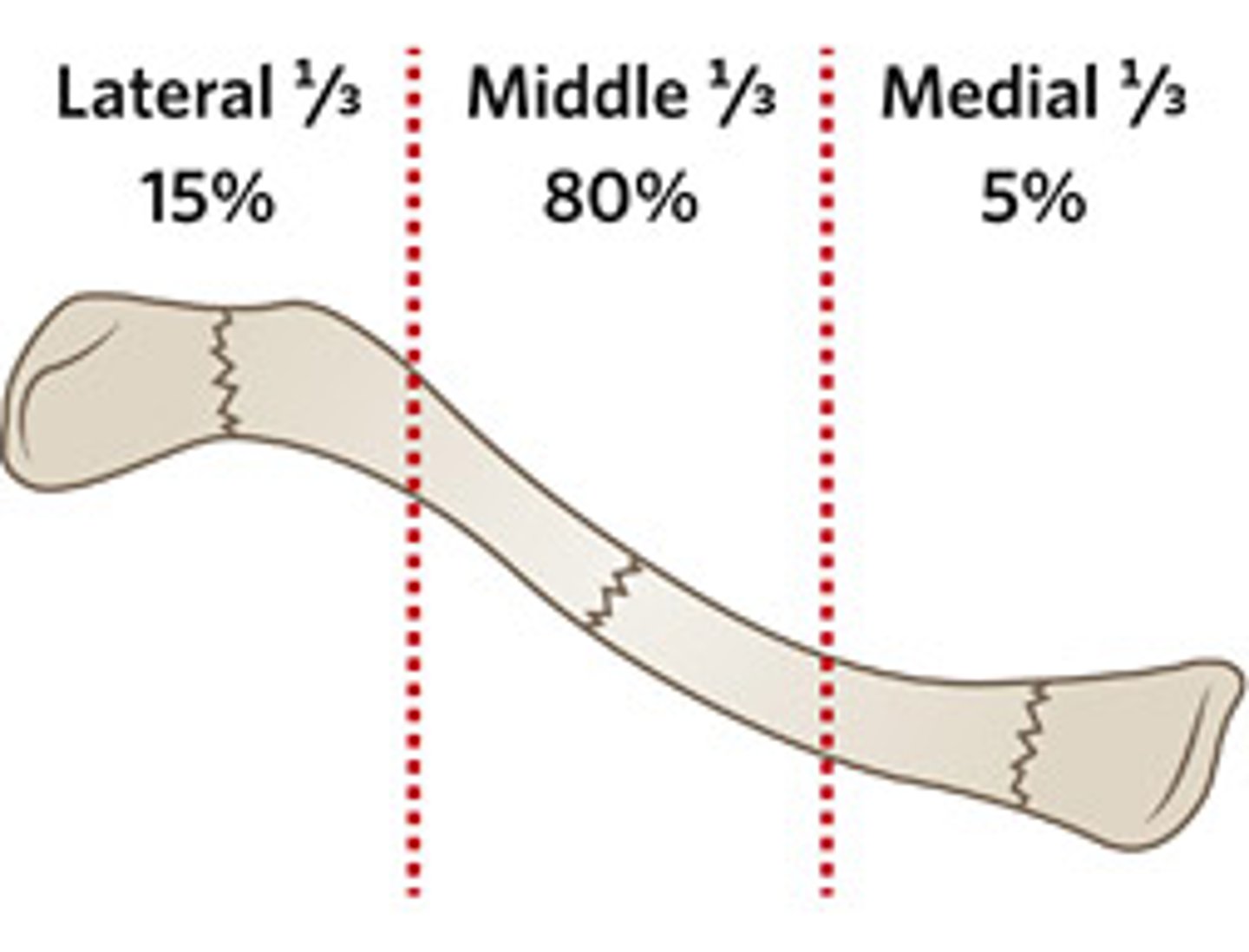
Anatomically where are 80% of clavicle fractures located?
Middle third
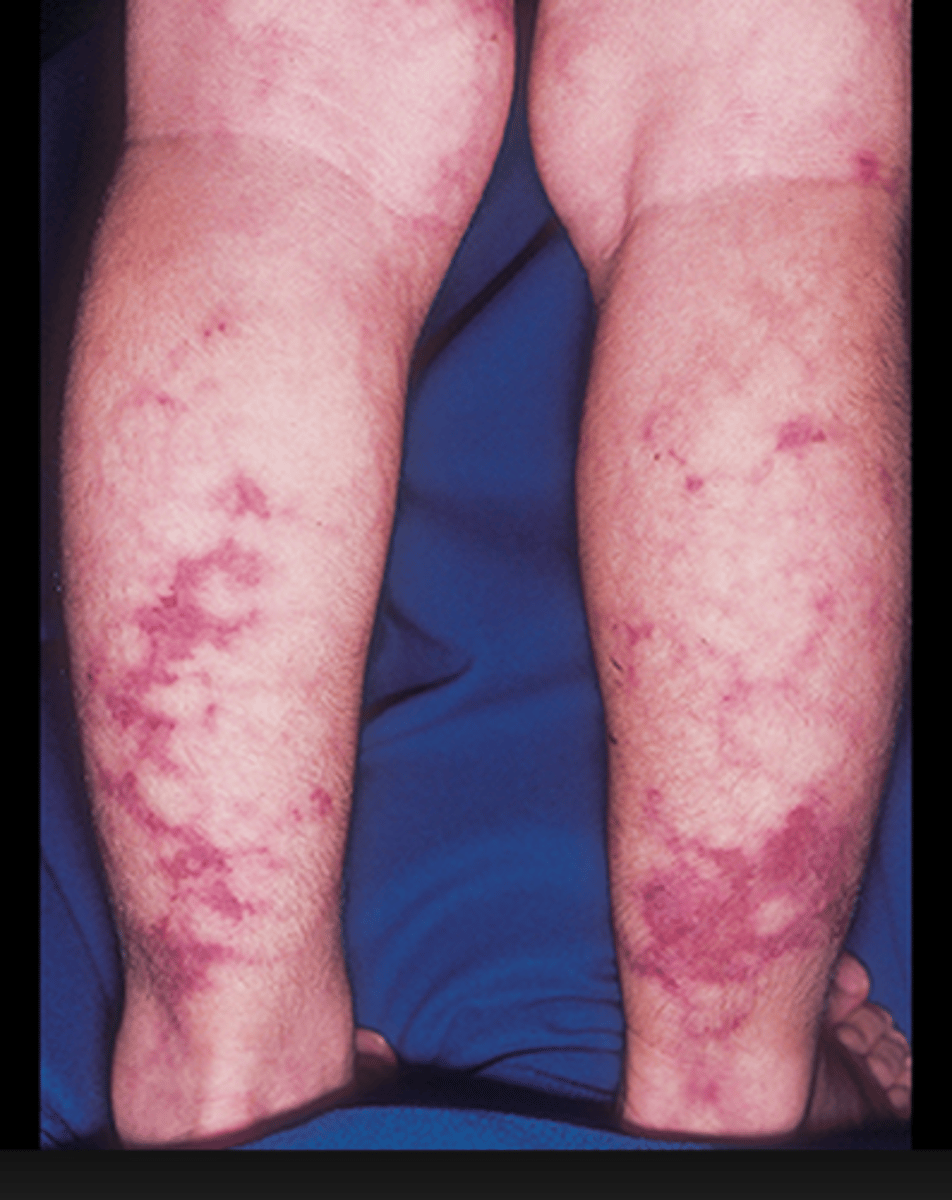
Vasculitis with a hepatitis B history should make you think of what diagnosis?
Polyarteritis nodosa
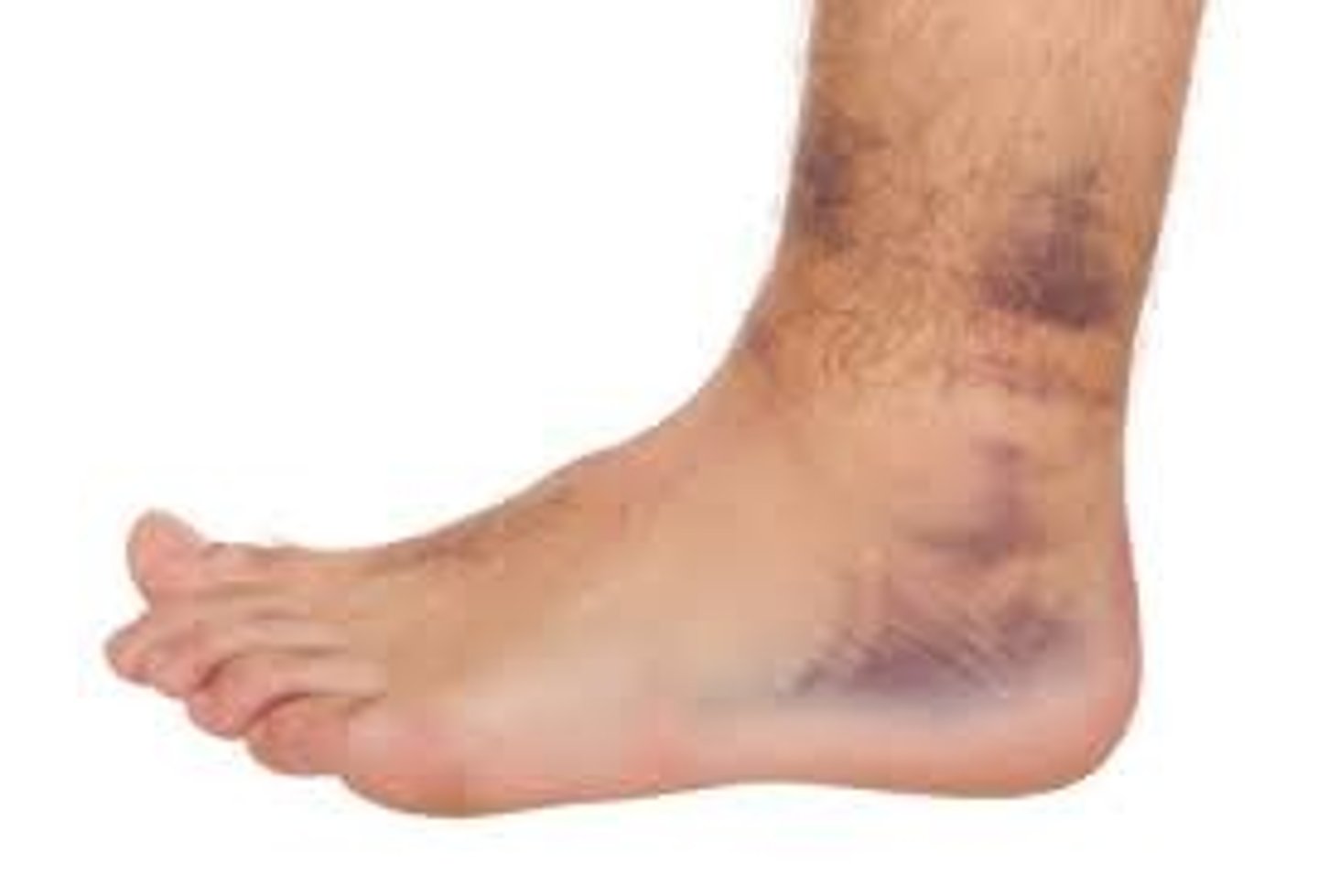
What ligament is most commonly injured in an ankle sprain?
Anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL)
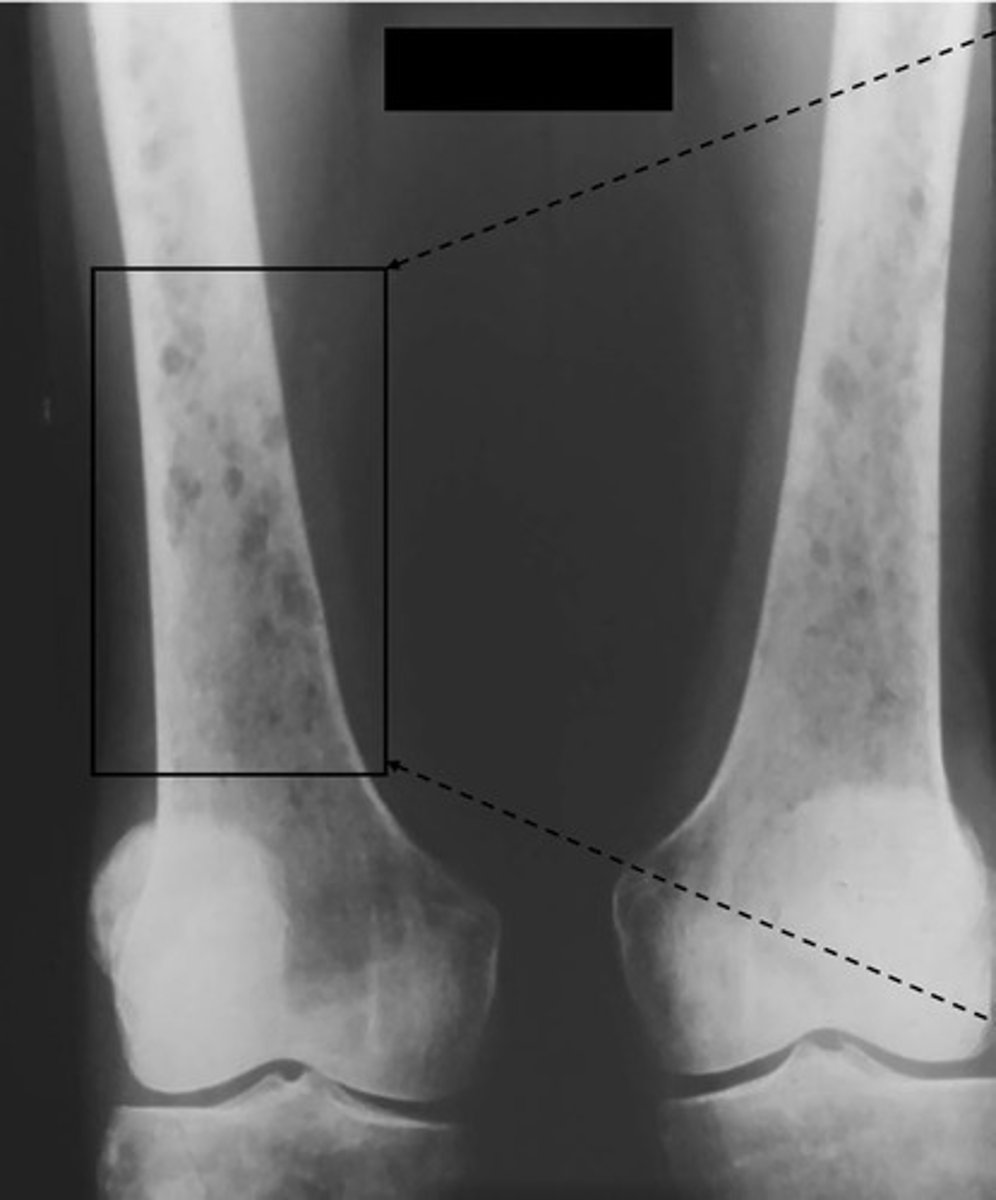
Describe the characteristics of a lytic lesion on x-ray.
Spiculated, elevated periosteum, bone destruction (think bad, very bad things)
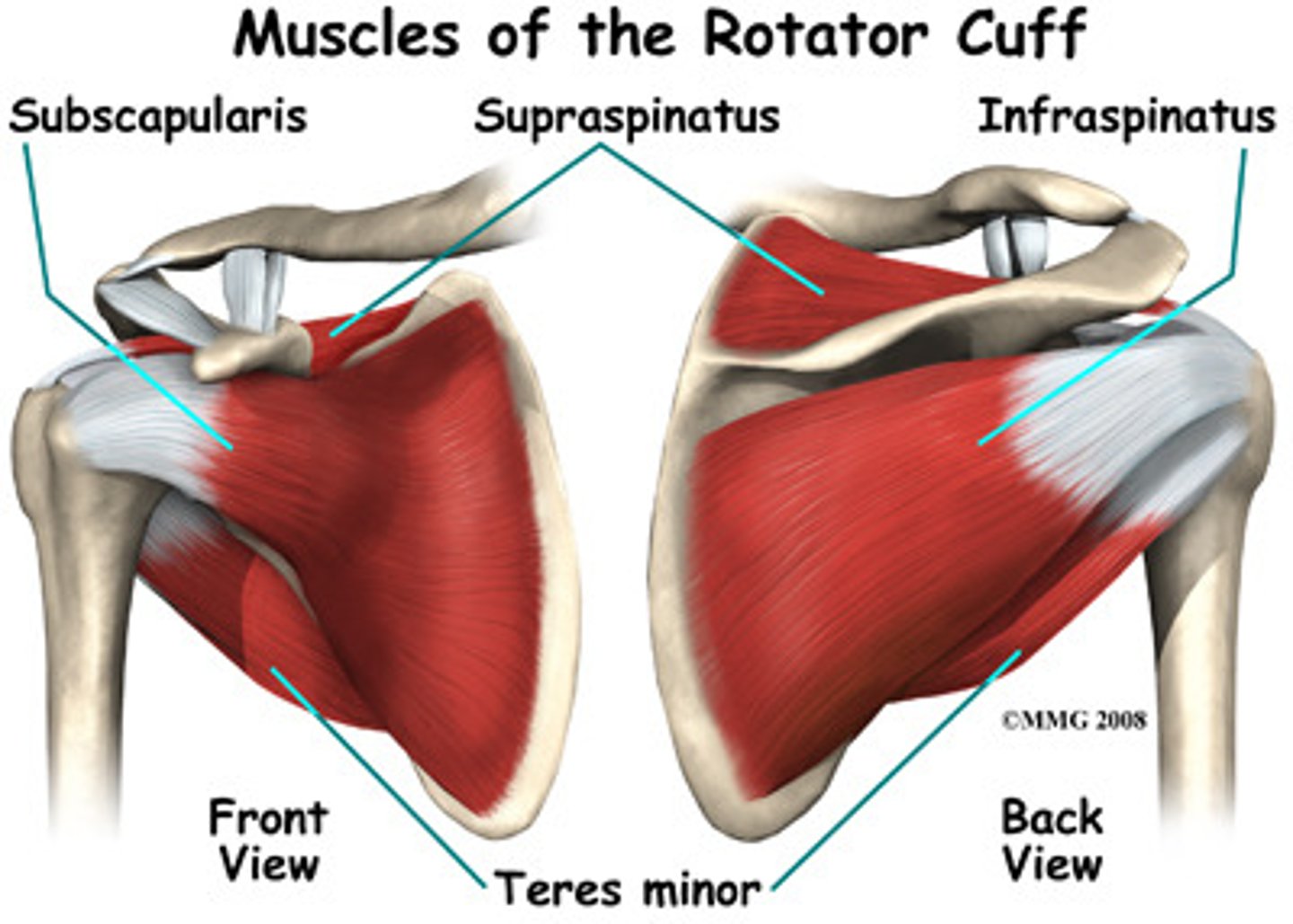
What are the four muscles of the rotator cuff?
Commonly referred to as the SITS muscles, they are Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres minor, and Subscapularis.
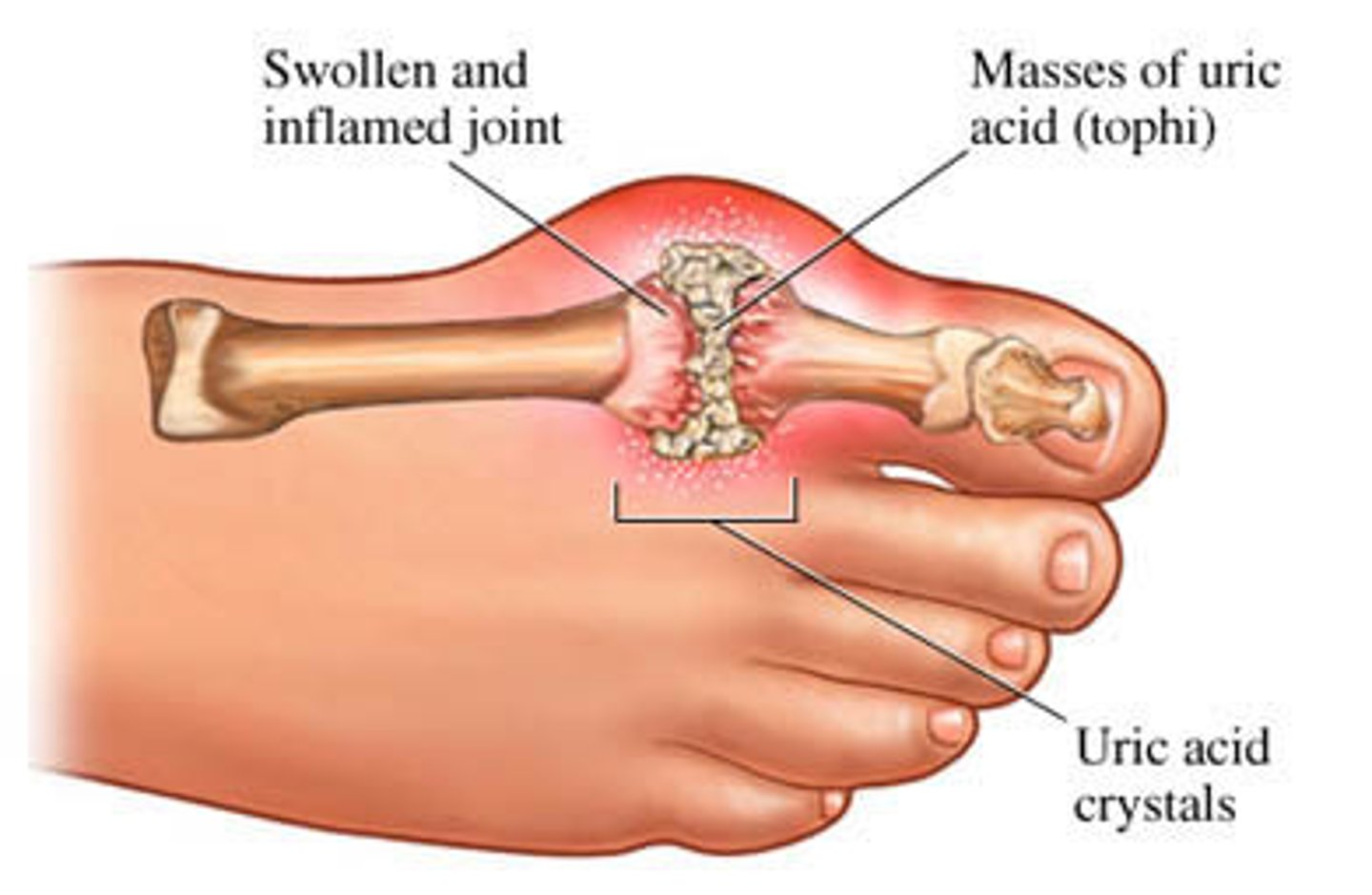
A pathology report comes back showing negatively birefringent crystals. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Gout
Remember - Pseudogout = Positively birefringent
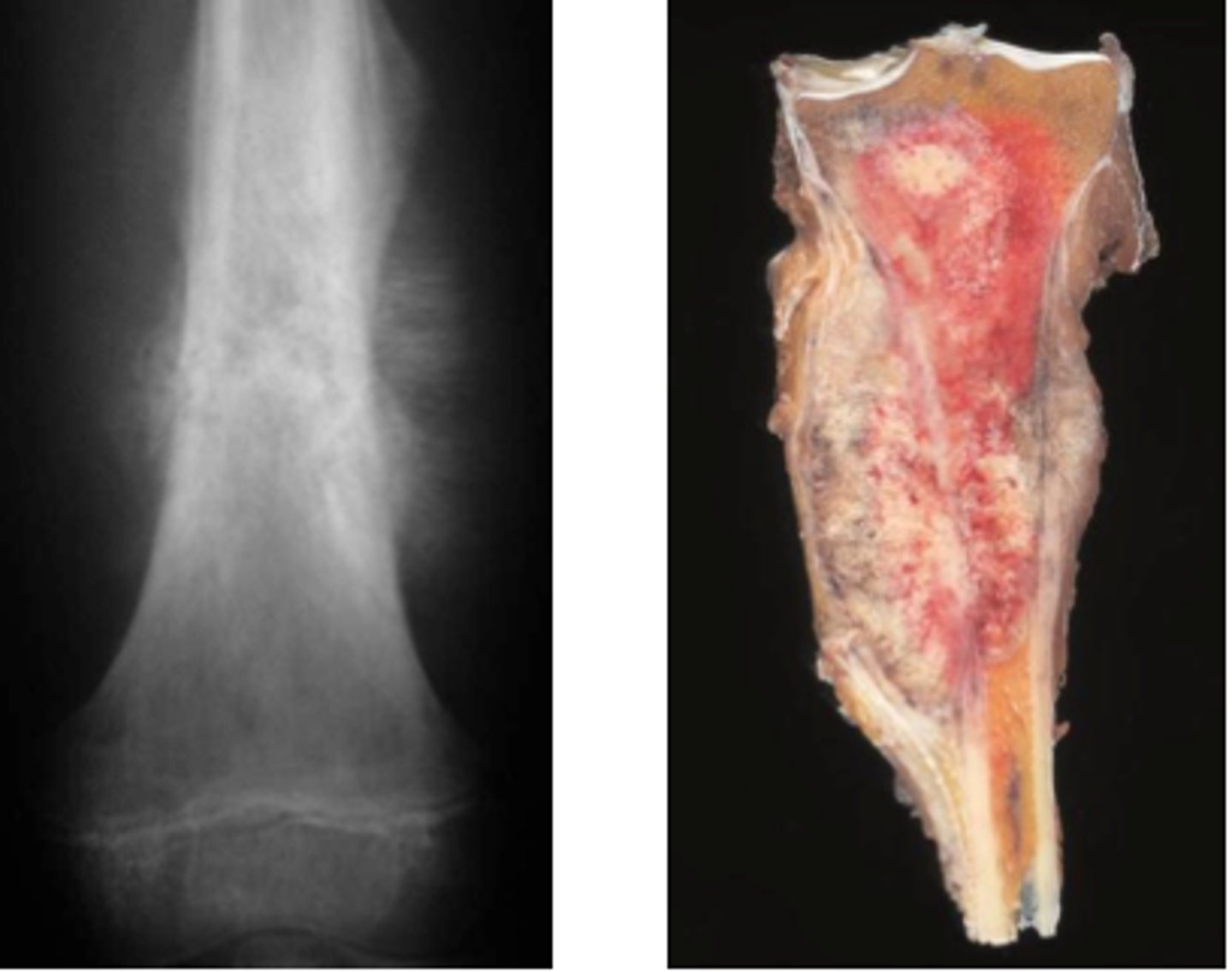
There is a sunburst appearance on x-ray. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Osteosarcoma
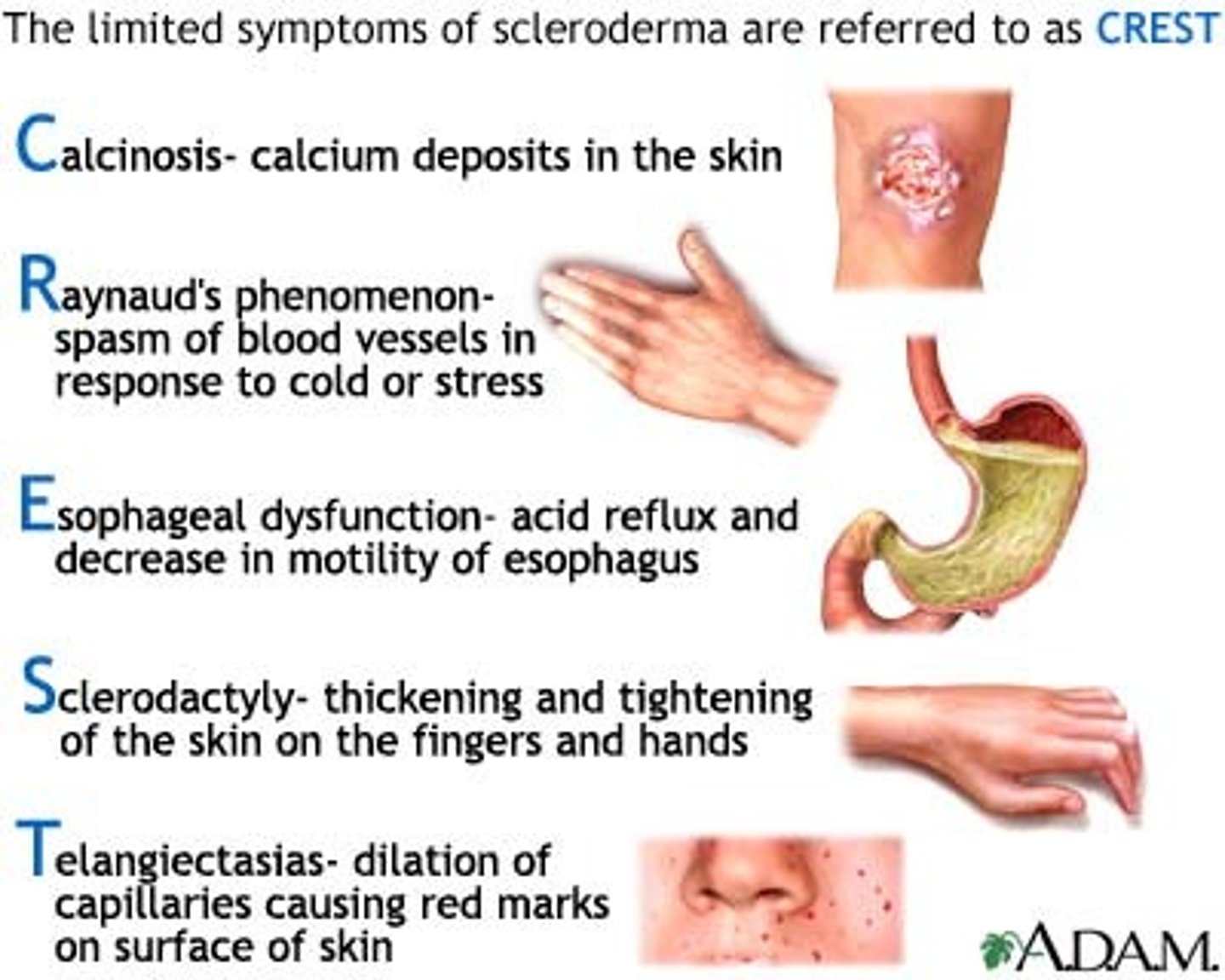
Scleroderma limited version has five main characteristics for which the CREST acronym is often used. What are those five things?
Calcinosis, Raynaud's, Esophageal dysmotility, Sclerodactyly, Telangiectasia
What medication is used for patients with lupus?
Systemic steroids
Which carpal bone has a high rate of nonunion and occult fracture?
Scaphoid
A patient with rheumatoid arthritis is heading to the OR for open reduction and internal fixation of the ankle. In addition to ankle films, what other x-rays should you get?
C-spine, anesthesia will want them due to concerns about instability of C1 & C2.
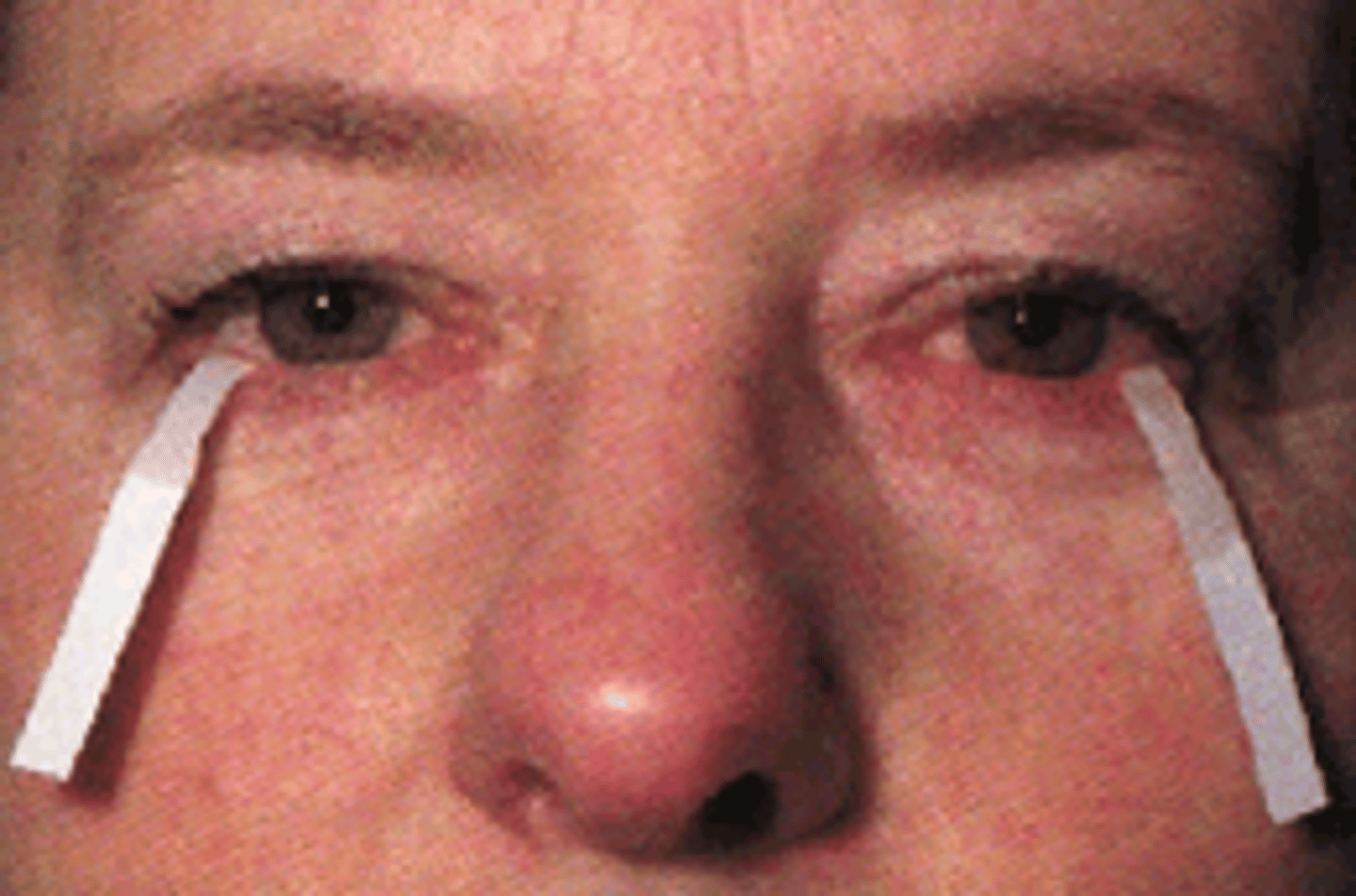
What test do you do for Sjogren's syndrome?
Schirmer test is used to determine whether the eye produces enough tears to keep it moist. The test is performed by placing filter paper inside the eye's lower lid. After 5 minutes, the paper is removed and tested for its moisture
List three medication that may cause lupus
Procainamide, isoniazid, and Quinidine
A positive Neer's test indicates what diagnosis?
Rotator cuff impingement - The examiner stabilizes the patient's scapula with one hand, passively flexing the arm while it is internally rotated. If the patient reports pain in this position, then the result of the test is considered to be positive.
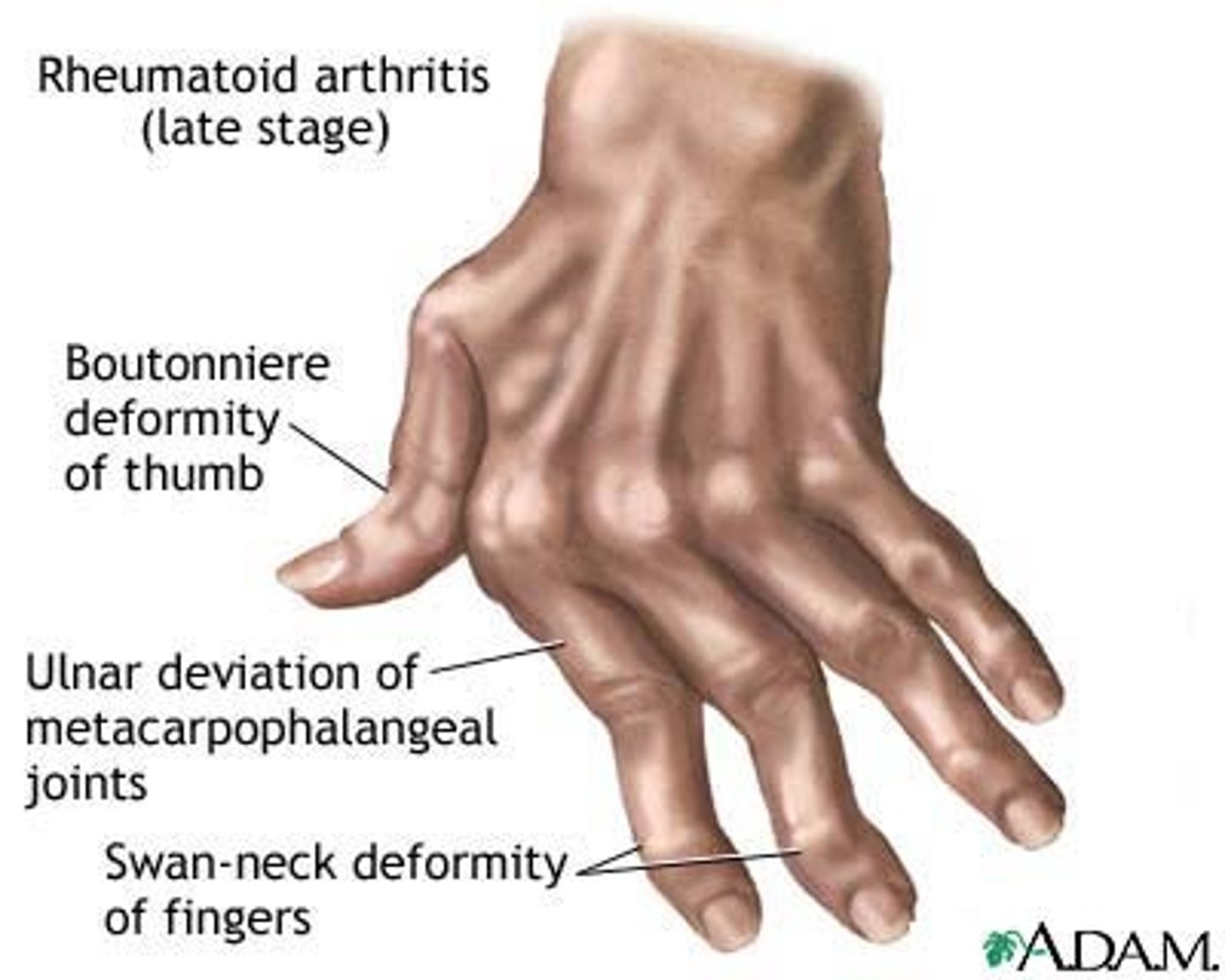
On physical exam, you notice ulnar deviations and swan neck deformities. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Rheumatoid arthritis
You suspect a patient has polyarteritis nodosa. What is the test for a definitive diagnosis, and what is the treatment?
Biopsy, high dose steroids
A patient with a history of hepatitis B presents complaining of bilateral knee pain, fever, and weight loss. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Polyarteritis nodosa
A pathology report comes back with positive birefringent crystals. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Pseudogout - Remember - Pseudogout = Positively birefringent
What is the medical treatment for gout?
Allopurinol, colchicine
What uric acid level helps to confirm a diagnosis of gout?
>7.5
Clicking or locking of the knee indicates what diagnosis?
Meniscal tear
You think a patient may have an osteoid osteoma due to his complaints of severe night pain. You set him up for an x-ray, but what medication do you start him on in the meantime?
If it is truly an osteoid osteoma ibuprofen will resolve his pain
● An osteoid osteoma is a benign (noncancerous) bone tumor that usually develops in the long bones of the body, such as the femur (thighbone) and tibia (shinbone). Although osteoid osteomas can cause pain and discomfort, they do not spread throughout the body.
What is the age range for osteosarcoma? Where are they most typically found in the body?
Osteosarcoma usually occurs in 15-25-year-old males and is most commonly found around the knee
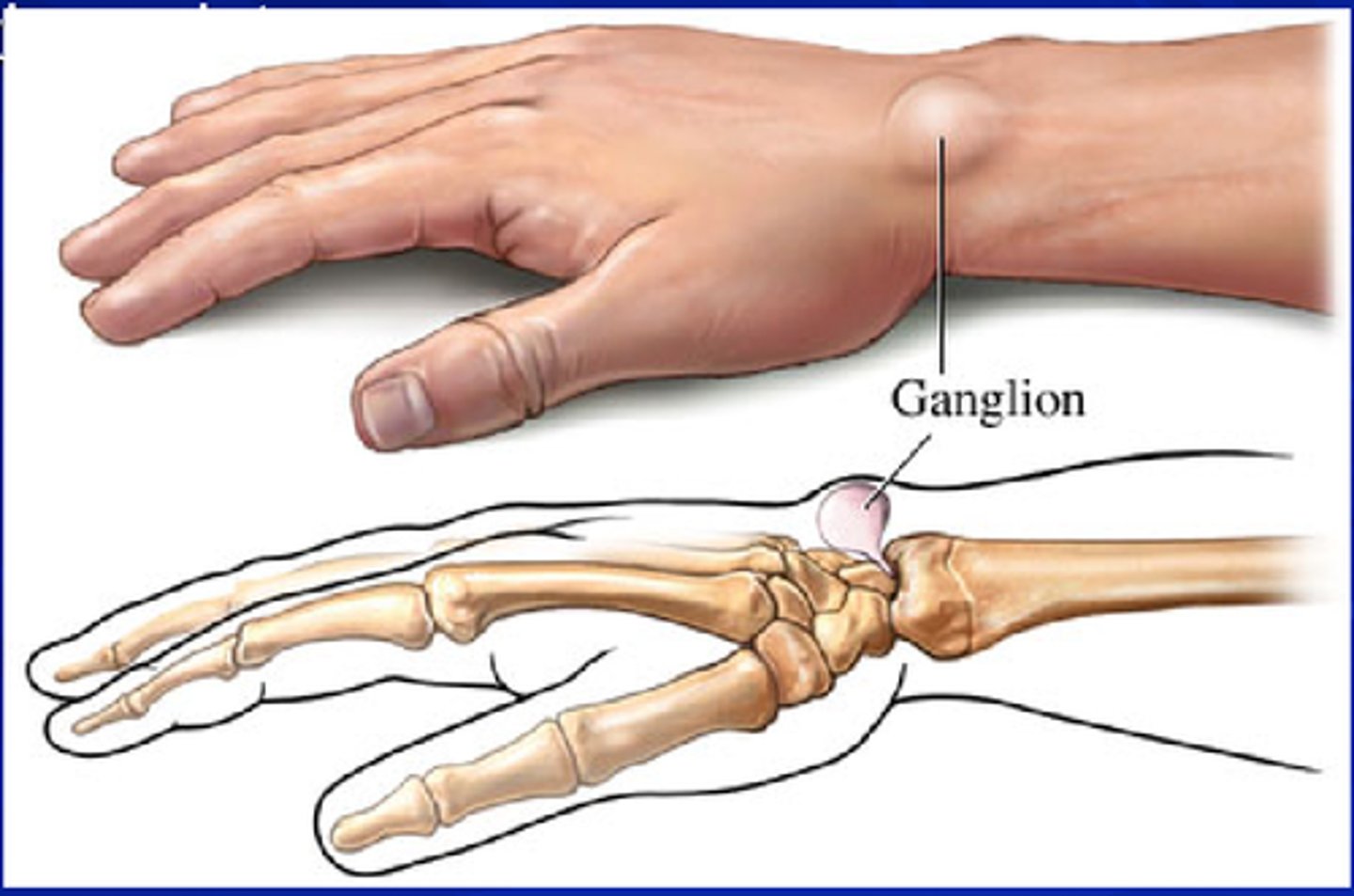
A patient presents with a painless mass in her right wrist. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Ganglion cyst
What would you expect the WBC count to be in the joint fluid of an infected knee?
>50,000 at a minimum and probably much higher.
A 22-year-old male patient presents with what is clearly a septic knee. You also notice lesions on his hands and feet. What is the most likely pathogen?
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
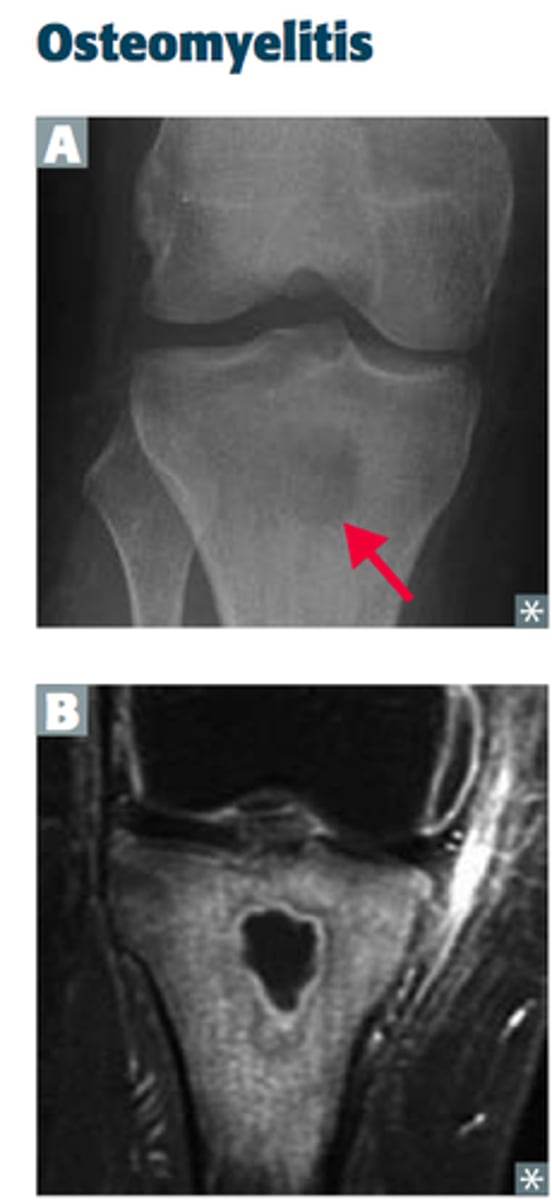
What is the best imaging to diagnose osteomyelitis?
Either a bone scan or an MRI will provide the diagnosis.
What will an x-ray show in acute osteomyelitis?
Nothing, it will show classic X-ray triad of demineralization, periosteal reaction, and bone destruction in chronic osteomyelitis
Where are Bouchard's nodes found?
Proximal interphalangeal joint (PIP)
A patient's lab work shows positive Smith antibody and positive double-stranded DNA antibodies. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Lupus
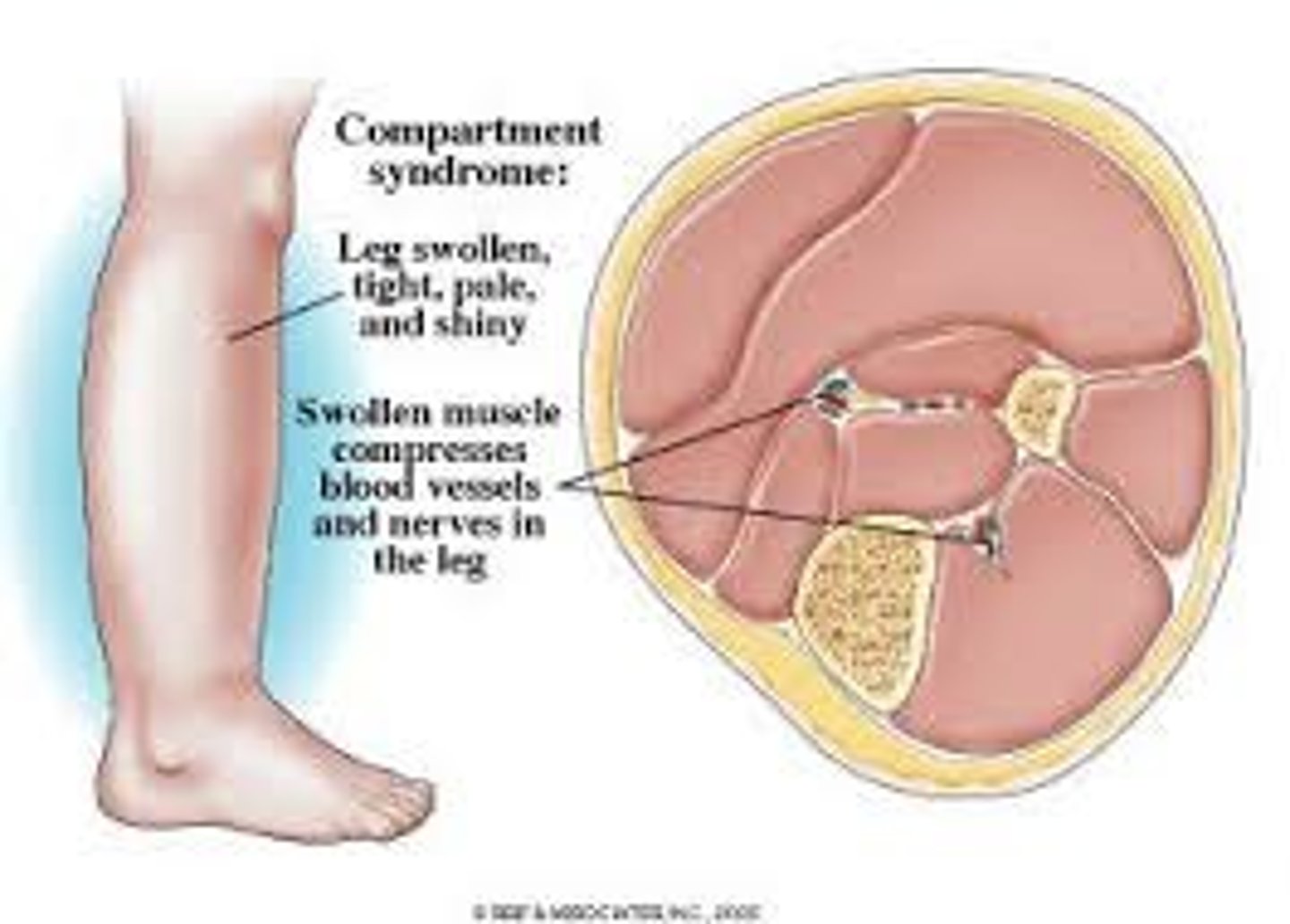
What fracture is the #1 cause of compartment syndrome?
Tibial shaft fracture
Give the DEXA score for osteopenia and osteoporosis.
Osteopenia = 1 to 2.4 standard deviations, osteoporosis = 2.5 standard deviations or greater
At what age should you begin ordering DEXA scans for male patients? What about female patients?
70 for males, 65 for females