Myelography - Contrast Radiography of the Spinal Cord
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Myelography
Indication to identify spinal lesions that are unable to be identified on a plain radiograph
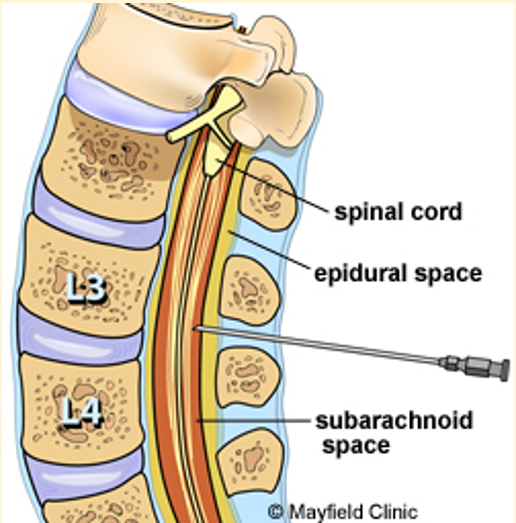
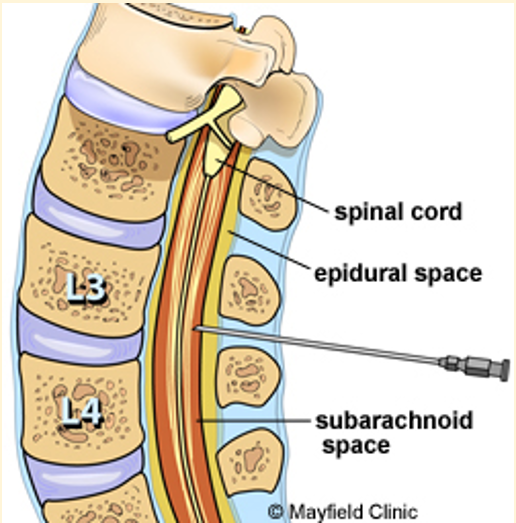
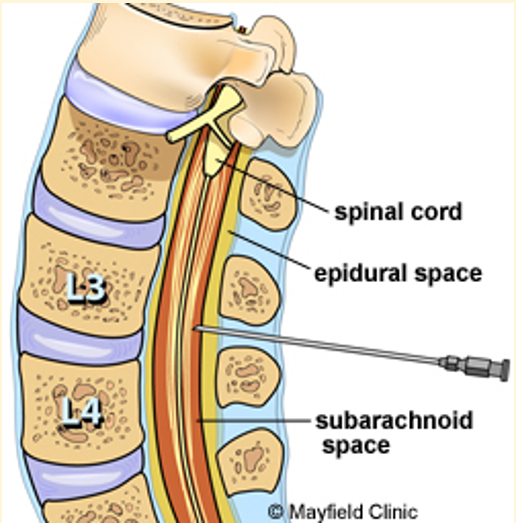
Myelography involves ..
An injection of a contrast agent into the subarachnoid space to highlight the spinal cord
General anaesthesia is required
Myelography - Indications for use
Paresis or paralysis
Ataxia
Spinal pain
Myelography may be used to identify compression of the spinal cord, inflammation and CSF obstruction. Also helps to identify whether lesions are extradural, intradural or intramedullary. Potential complications include ..
Seizures post anaesthesia recovery
Spinal cord damage if the needle is placed incorrectly
Septic meningitis
A worsening of the neurological signs for which the patient initially presented
What type of contrast medica is used for these studies?
A low osmolar, non-ionic, water soluble iodine-based contrast agent
Where can it be injected?
Site for cisternal puncture
Site for Lumbar puncture
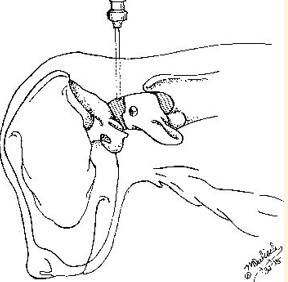
Site for cisternal puncture
The cisternal magna at the base of the skull
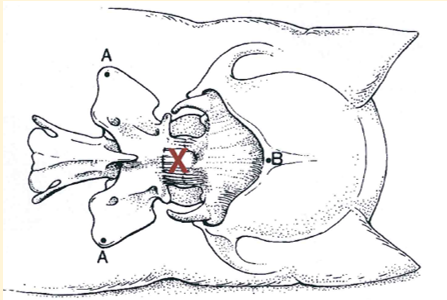
Cisterna Megna Preparation
Aseptic preparation
Lateral recumbency
Flex head to 90° and hold in place
Elevate nose to medial plane (30 to 45° angle)
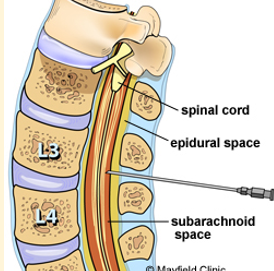
Site for lumbar puncture
Lumbar spinal canal, usually at L3-4 or L4-5
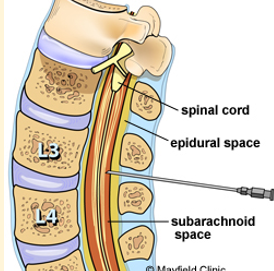
Lumbar puncture patient preparation
Position patient in lateral recumbency and flex the spine and hips
Why is it often easier to inject contrast media into the cisternal magna?
CSF flows more readily from this site
Care must be taken when injecting into the cisterns magna as the contrast media is under gravity. Excessive pressure during administration may cause ..
A backflow towards the brain → seizures
This is particularity important if obstructed lesions are suspected
Speed is essential during myelography as the contrast media is ..
Rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream, for this reason, automatic or digital processing should be available
Nursing care post myelography - patients head
Keep the patients head elevated above the body to prevent the contrast medial flowing back towards the brain and causing seizures. This should be continued until the patients has fully recovered.
Nursing care post myelography
Close monitoring during recovery and record observations
Inform the Veterinary Surgeons immediately if fitting occurs
These patients should be under constant supervision and would be within a high-dependency/intensive care setting if in a referral hospital
Why should myelography only be performed if the outcome will influence how the case is managed and benefit the patient?
This imaging technique involves many risks to the patient
Myelography is no longer commonly performed in practice due to ..
CT/MRI
Other contrast studies
Arthrography
Angiography
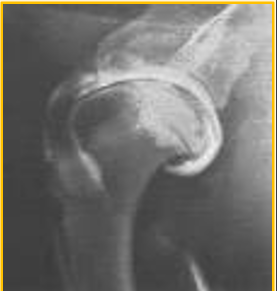
Arthrography - used for ..
Elevate peripheral joints, in particular, the shoulder
Osteochondrosis
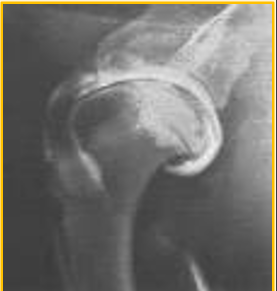
Arthrography - preferred contrast
Positive contrast arthrogram preferred
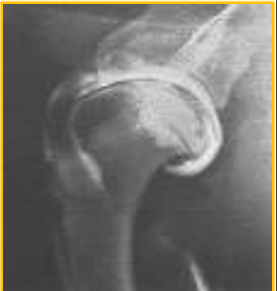
Arthrography - Contrast studies
Negative and double contrast studies may cause air bubbles to mix with the synovial fluid in the joint space interpretation difficult
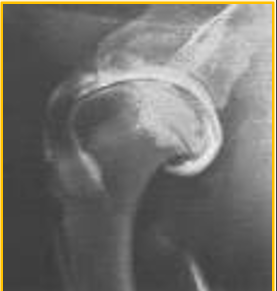
Arthrography
Not a routine procedure → Performed most commonly in orthopaedic referrals. CT and MRI often used instead of this imaging technique
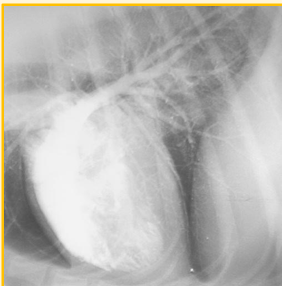
Angiography - used for ..
To visualise and evaluate blood filled structures
Congenital defects and cardiac malformations
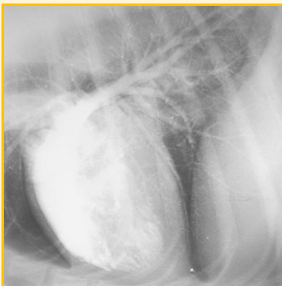
Angiography - Contrast media used
Positive contrast used (WSIB - Water soluble iodine based)
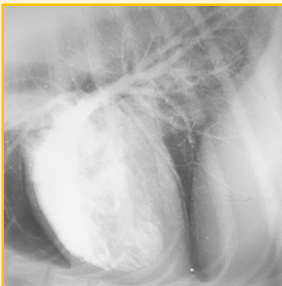
What blood filled structures does Angiography visualise and evaluate?
Arteries
Veins
Heart chambers
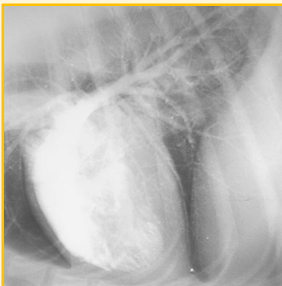
Angiography
Not a routine procedure → Performed most commonly in referral practice