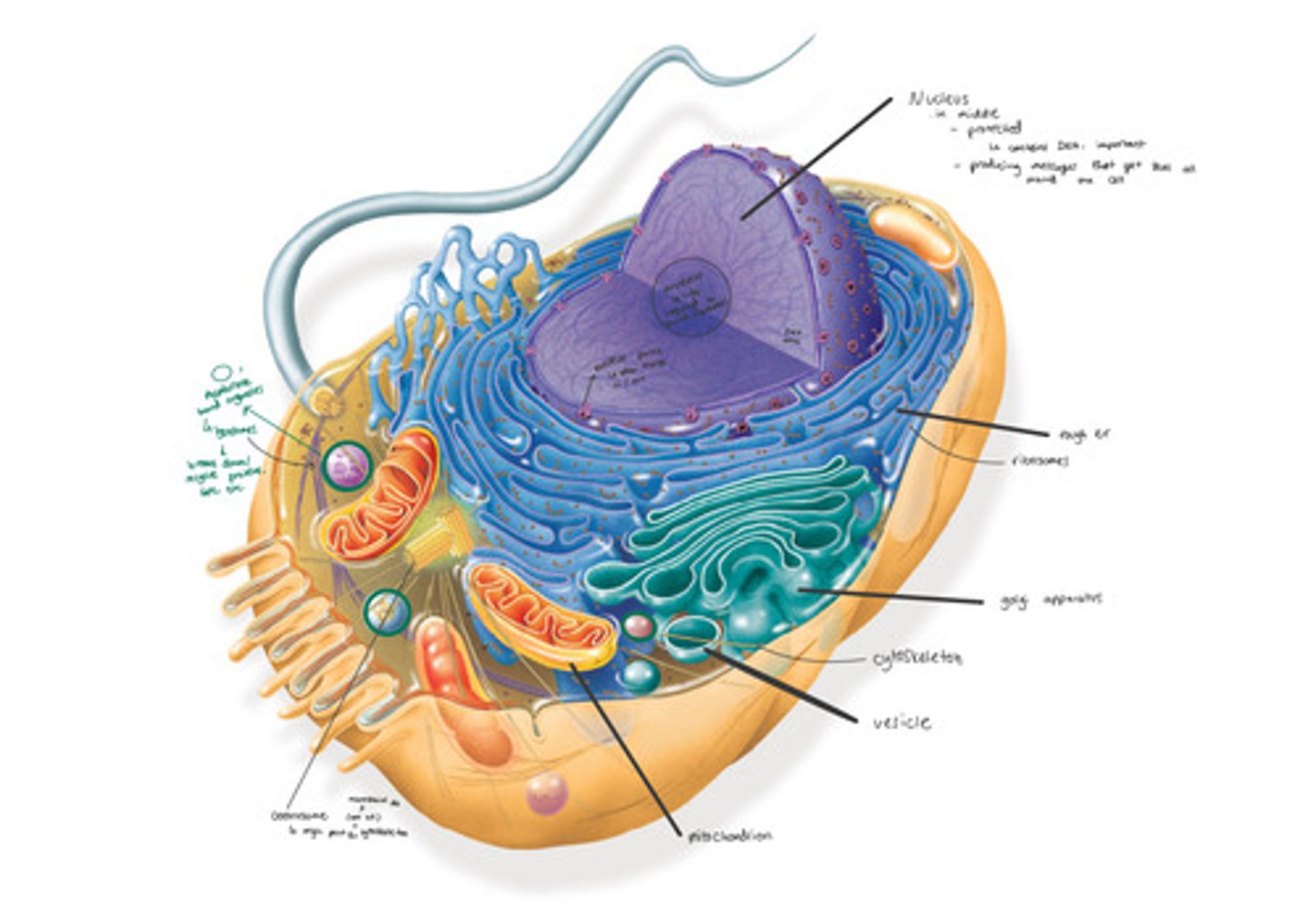
tour of the cell (cell vocab)
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is the cell theory? Cells are...
1. smallest living unit in all organisms
2. all living things made of cells (unicellular or multicellular)
3. all cells come from other pre-existing cells
What is a prokaryote?
A cell without a nucleus or any membrane bound organelles. (Bacteria, archaea)
What is a eukaryote?
A cell with a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. (Protists, plants, fungi, animals)
What do prokaryotes and eukaryotes have in common?
Genetic material (DNA), cytoplasm, ribosomes, cell membranes
What is the plasma membrane / cell membrane?
"Wall" of cell, semi-permeable
What does semi-permeable mean?
Only select molecules can get in or out, keeping cell stable
What is the cytoplasm?
Jelly like material around internal cell structures
What is an organelle?
Any of a number of organized or specialized structures within a cell
What is the cytoskeleton?
Collection of fibers that provide support for the cell and its organelles, can play major role in cell movement, very complex. Organized differently in different cells.
What are ribosomes?
Small organelles that make protein. Not membrane bound. Can be free in cytoplasm or attached to another organelle. Very important because so much genetic material (DNA) codes for protein.
What does membrane-bound mean?
Surrounded by a membrane
What is the nucleus?
Holds the genetic material and controls the cells activities
What is the nucleolus?
Inside nucleus, where ribosomes components are produced
What is the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)?
A highly folded membrane network extending off the nuclear envelope (rough and smooth). Does much processing of molecules for the cell (ex protein folding), highly involved in transporting molecules around
What is the rough ER?
Has ribosomes attached to it, protein producing and transporting
What is the smooth ER?
No ribosomes, many roles (ex detoxification, makes some types of lipids)
What are vesicles?
Membranous sacs that are used to transport materials in the cell. What molecules that leave the ER are sent away in (small sac that pinches off the ER)
What is the golgi apparatus?
"Ultimate packaging center." Receives items from transport vesicles. Enzymes that modify and sort molecules it receives determine where to send molecules (potential for secretion out of cell)
What is the mitochondria?
Powerhouse of the cell. Produces ATP energy to power the cell through cellular respiration fueled by glucose and oxygen.
What is chloroplast?
In plant cells (big diff between animal and plant cells is this - plant cells have mitochondria too still). Makes glucose through photosynthesis, tends to look green.
What is a vacuole?
In plant cells - one big central one with many different functions, primarily storage of material (including water)
In animal cells - smaller ones also with many different functions, primarily storage of material (including water)
What is the cell wall?
Additional protection and shape layer in plant cells.
Cell parts as city functions
Label cell