BIO5 - End of unit
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/147
Earn XP
Last updated 3:00 AM on 8/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
1
New cards
The Nervous System
* coordinates actions of complex organisms via transmission of electrochemical signals
* Transmitted by specialised cells called neurons (nerves)
* Transmitted by specialised cells called neurons (nerves)
2
New cards
Neurons + basic features of a neuron
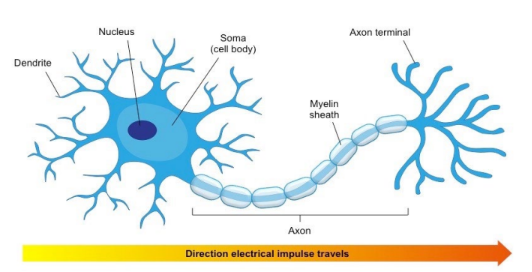
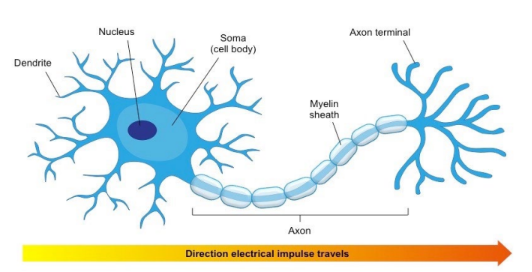
* Specialised cells that function to transmit electrical impulses within nervous system → convert sensory information to electrical impulse to rapidly detect + respond to stimuli
* Share some basic features
* **Dendrites** – Short-branched fibres that convert chemical information from other neurons or receptor cells into electrical signals
* **Axon** – An elongated fibre that transmits electrical signals to terminal regions for communication with other neurons or effectors
* **Soma** – A cell body containing the nucleus and organelles, where essential metabolic processes occur to maintain cell survival
* Share some basic features
* **Dendrites** – Short-branched fibres that convert chemical information from other neurons or receptor cells into electrical signals
* **Axon** – An elongated fibre that transmits electrical signals to terminal regions for communication with other neurons or effectors
* **Soma** – A cell body containing the nucleus and organelles, where essential metabolic processes occur to maintain cell survival
3
New cards
Myelin/ Myelin sheath
* Improves conduction speed of electrical impusles along axon → require more space + energy
4
New cards
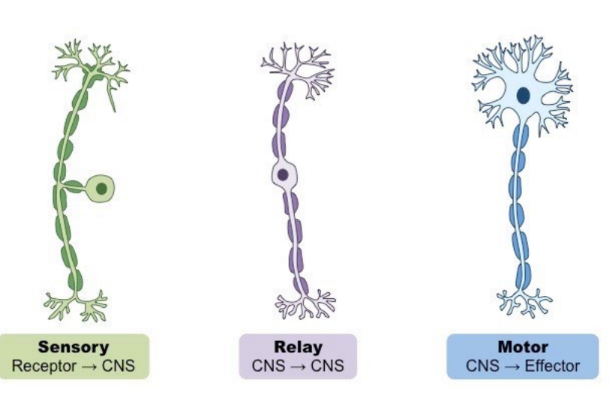
3 types of Neurons
* **Sensory neurons -** Transmit information from sensory receptors to central nervous system (CNS)
* **Relay neurons (interneurons)** - Transmit information within the CNS as part of the decision-making process
* **Motor neurons** transmit information from CNS to effectors (muscles / glands) to initiate response
* **Relay neurons (interneurons)** - Transmit information within the CNS as part of the decision-making process
* **Motor neurons** transmit information from CNS to effectors (muscles / glands) to initiate response
5
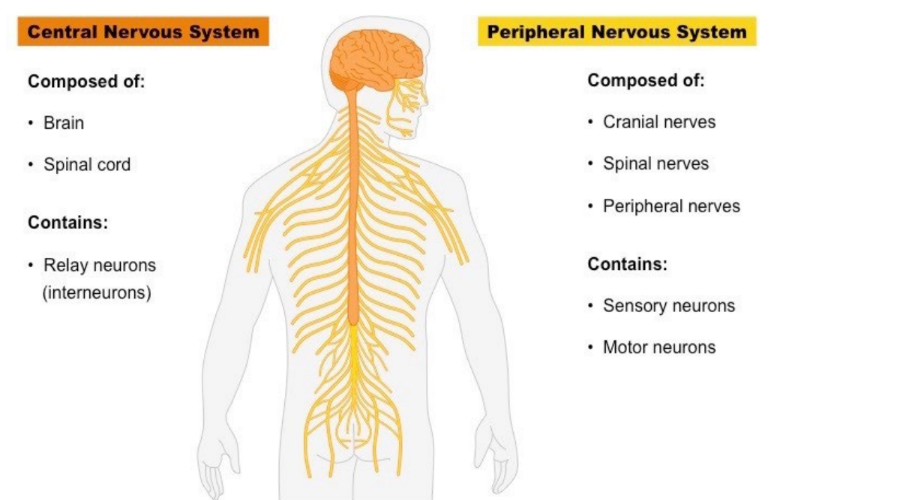
New cards
Components of the nervous system
6
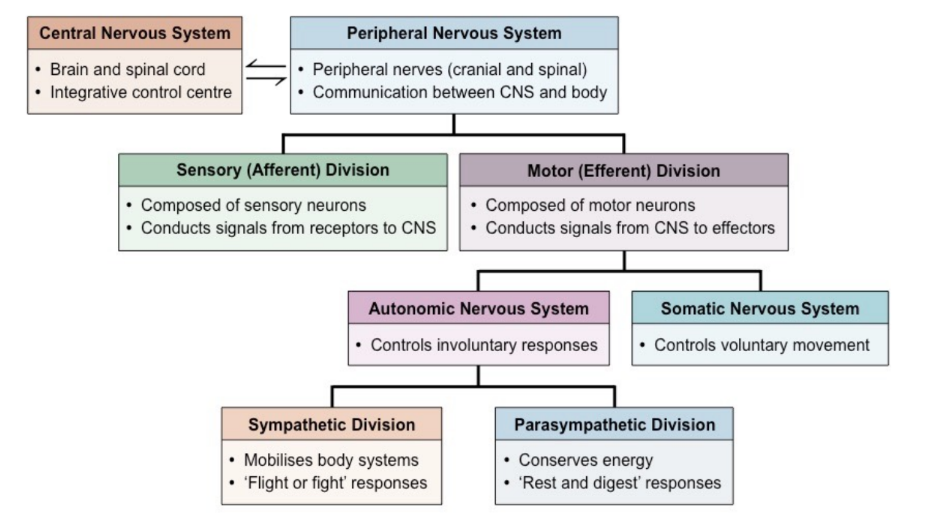
New cards
Divisions of the nervous system
7
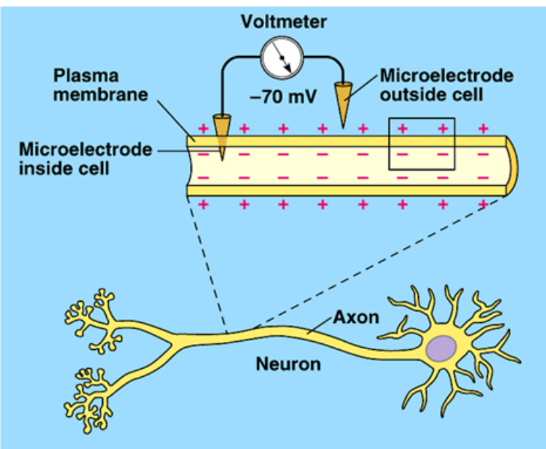
New cards
Nerve Impulses
◻ Neurons generate and conduct electrical signals by pumping positively charged ions (Na+ and K+) across their membrane
There is an unequal distribution of ions on each side of the membrane which creates a charge difference called a membrane potential
There is an unequal distribution of ions on each side of the membrane which creates a charge difference called a membrane potential
8
New cards
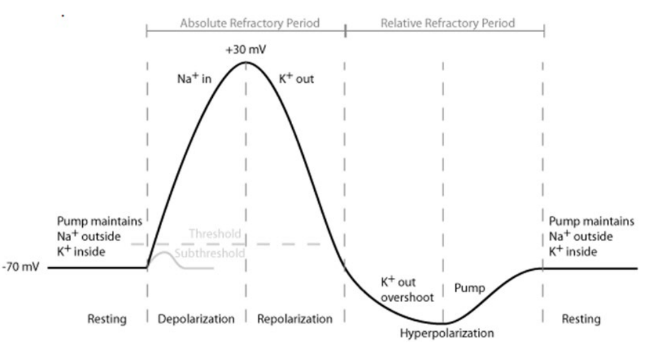
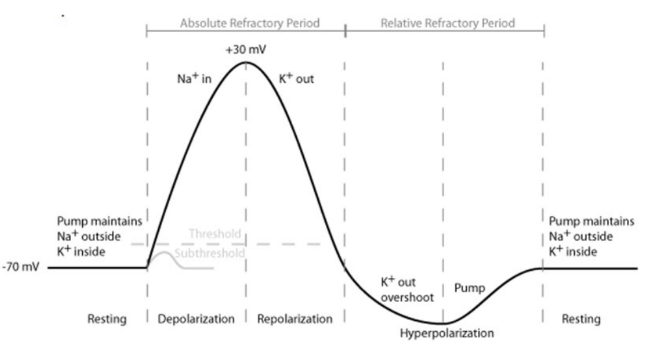
Action Potentials + Stages of action potential
Action potentials are the rapid localised change in membrane charge that occur in order to generate and propagate an electrical impulse along the neuron. Occurs in 3 stages
* Depolarisation
* Repolarisation
* Refractory Period
An action potential will only occur if the initial depolarisation exceeds a threshold potential of approximately –55 mV
* Depolarisation
* Repolarisation
* Refractory Period
An action potential will only occur if the initial depolarisation exceeds a threshold potential of approximately –55 mV
9
New cards
Depolarisation
As a stimulus reaches the membrane, sodium channels open allowing the Na+ to flow in, depolarizing the membrane and making it less negative.
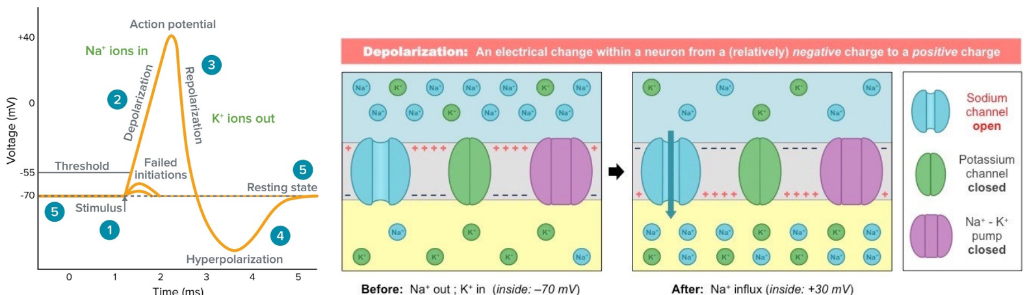
10
New cards
Repolarisation
The sodium channels then close and potassium channels open, allowing K+ ions to escape which causes the membrane potential to return to a more negative internal differential.
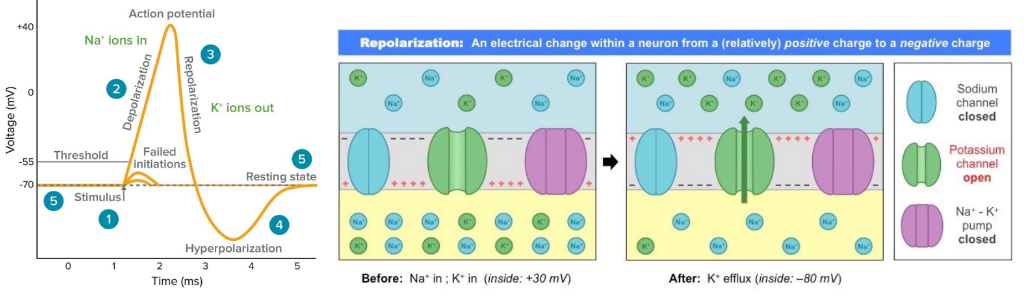
11
New cards
Refractory period
At this stage, the resting ionic distribution is largely reversed. The resting potential must be restored by the sodium-potassium pump. The nerve can’t fire again until the resting potential is restored.
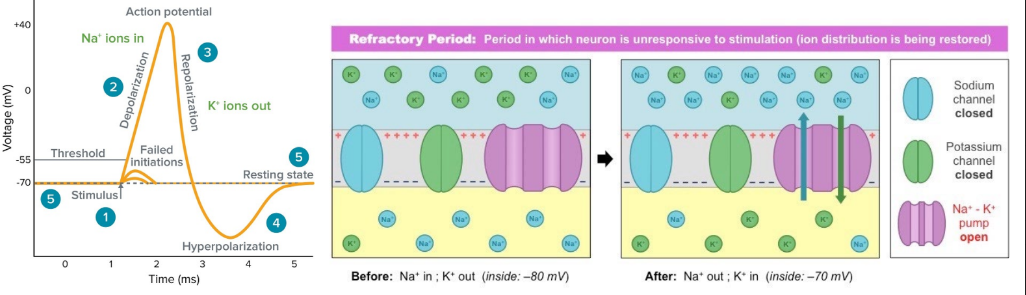
12
New cards
Propagation of the Action Potential
* Nerve impulses are action potentials that move along the length of an axon as a wave of depolarisation
* The ion channels that occupy the length of the axon are voltage- gated (they open in response to changes in membrane potential near them)
* Hence, depolarisation at one point of the axon triggers the opening of ion channels in the next segment of the axon
* It is an all-or-none situation:
* An action potential of the same magnitude will always occur provided the threshold potential (–55 mV) is reached If the threshold potential is not reached, an action potential cannot be generated and hence the neuron will not fire
* The ion channels that occupy the length of the axon are voltage- gated (they open in response to changes in membrane potential near them)
* Hence, depolarisation at one point of the axon triggers the opening of ion channels in the next segment of the axon
* It is an all-or-none situation:
* An action potential of the same magnitude will always occur provided the threshold potential (–55 mV) is reached If the threshold potential is not reached, an action potential cannot be generated and hence the neuron will not fire
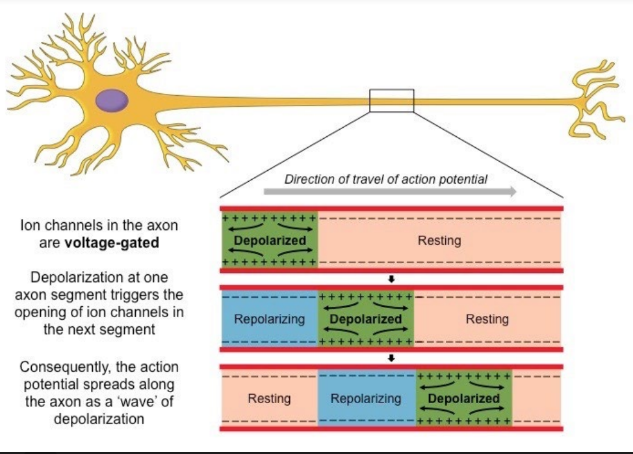
13
New cards
Oscilloscopes
Oscilloscopes measure and show the membrane potential changes at rest and during an action potential.
14
New cards
Myelination
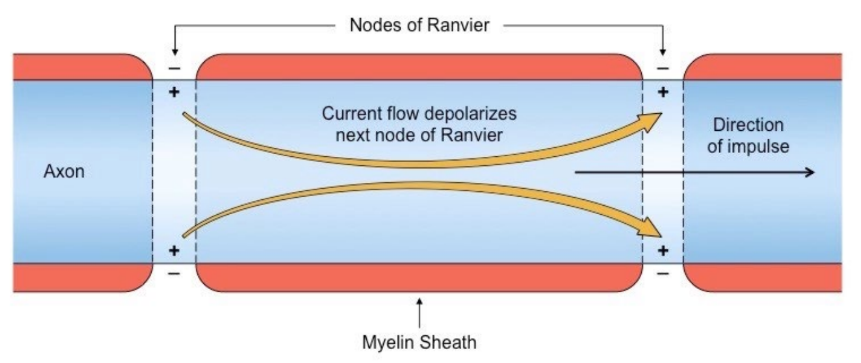
* Some neurons are covered in a fatty, white, insulating substance called myelin
* This layer increases the speed of nerve impulse transmission by saltatory conduction
* Along unmyelinated neurons, action potentials propagate sequentially along the axon in a continuous wave of depolarisation
* In myelinated neurons, the action potentials ‘hop' between the gaps in the myelin sheath called the nodes of Ranvier
* This results in an increase in the speed of electrical conduction by a factor of up to 100-fold
* This layer increases the speed of nerve impulse transmission by saltatory conduction
* Along unmyelinated neurons, action potentials propagate sequentially along the axon in a continuous wave of depolarisation
* In myelinated neurons, the action potentials ‘hop' between the gaps in the myelin sheath called the nodes of Ranvier
* This results in an increase in the speed of electrical conduction by a factor of up to 100-fold
15
New cards
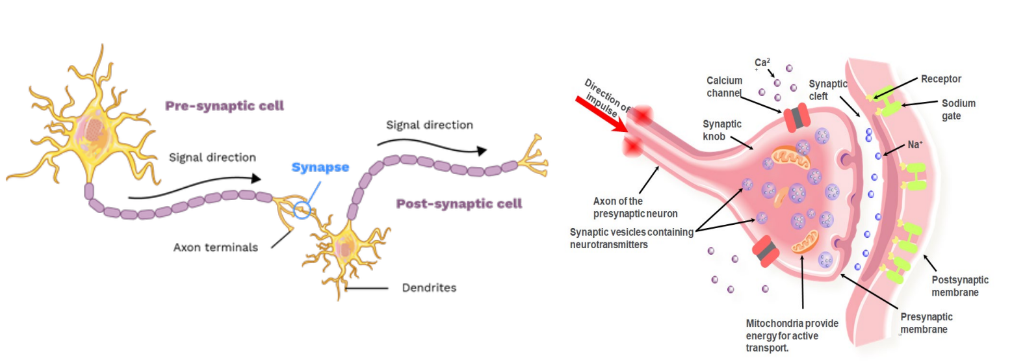
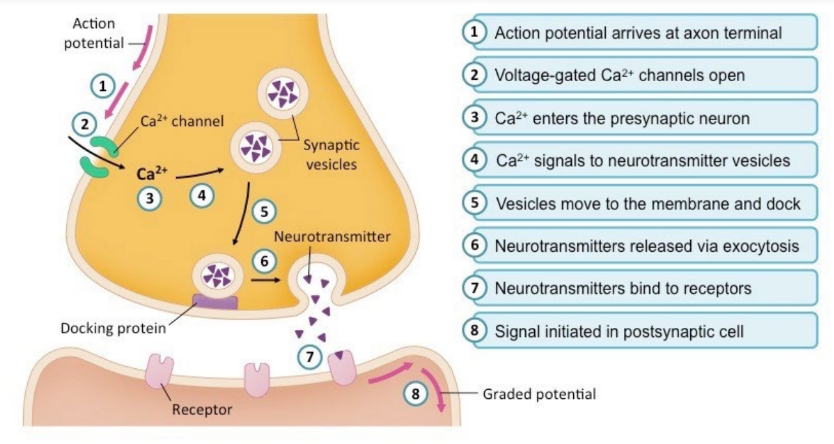
Synapses
Synapses are the junctions between two neurons
Action potentials are transmitted between neurons via the release of signalling molecules called neurotransmitters
When the neurotransmitter diffuses across the synapse, it interacts with the receiving membrane to cause depolarization that results in propagation of the nerve signal to the next neuron
Action potentials are transmitted between neurons via the release of signalling molecules called neurotransmitters
When the neurotransmitter diffuses across the synapse, it interacts with the receiving membrane to cause depolarization that results in propagation of the nerve signal to the next neuron
16
New cards
Transmission at a synapse: Step 1
Step 1: inse
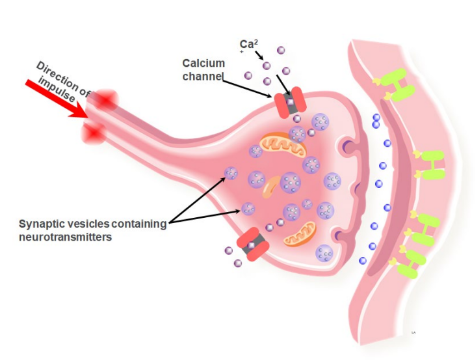
17
New cards
Transmission at a Synapse: Step 2 + 3
Step 2: The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane of a dendrite on another neuron. This delays the impulse transmission by about 0.5 ms.
Step 3: The neurotransmitter binds to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane.
Step 3: The neurotransmitter binds to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane.
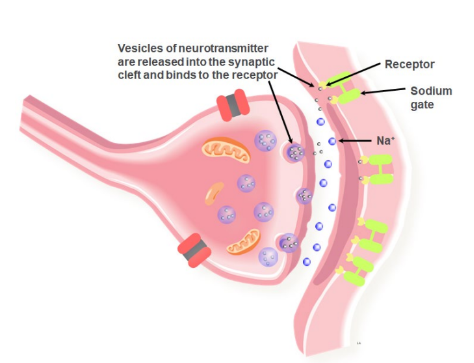
18
New cards
Transmission at a synapse: Step 4
Step 4: Ion channels in the post synaptic membrane open, causing an influx of Na+. This response may or may not reach the threshold (-55mV) required to generate a new action potential and nerve impulse
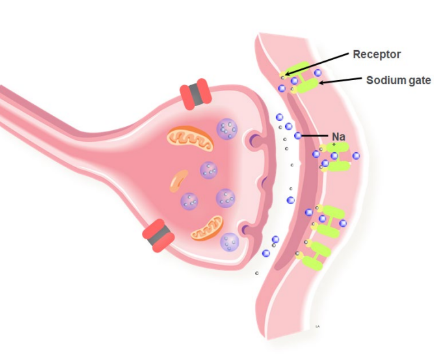
19
New cards
Transmission at a synapse: Step 5
Step 5: The neurotransmitter is deactivated by an enzyme (E.g. acetylcholinesterase) located on the membrane. Components of the neurotransmitter are actively reabsorbed back into the synaptic knob, recycled, and repackaged.
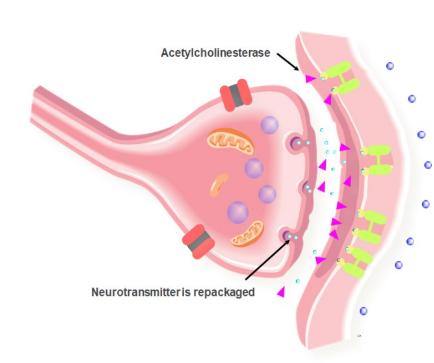
20
New cards
Synapse transmission summary
21
New cards
Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters maintain signals in the nervous system by binding to receptors on post-synaptic neurons and triggering electrical impulses
* They also activate responses by effector organs (such as contraction in muscles or hormone release from endocrine glands)
* Neurotransmitters may be either excitatory or inhibitory in their effect (some may be both depending on the receptor they bind to)
* Excitatory neurotransmitters trigger depolarisation, increasing the likelihood of a response
* Inhibitory neurotransmitters trigger hyperpolarisation, decreasing the likelihood of a response
* They also activate responses by effector organs (such as contraction in muscles or hormone release from endocrine glands)
* Neurotransmitters may be either excitatory or inhibitory in their effect (some may be both depending on the receptor they bind to)
* Excitatory neurotransmitters trigger depolarisation, increasing the likelihood of a response
* Inhibitory neurotransmitters trigger hyperpolarisation, decreasing the likelihood of a response
22
New cards
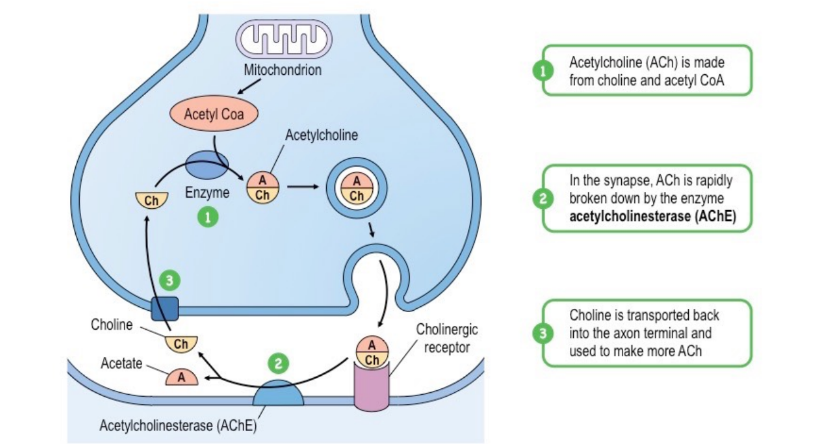
Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that activates a post-synaptic cell by binding to one of two classes of specific receptor (nicotinic or muscarinic)
* Acetylcholine must be continually removed from the synapse, as overstimulation can lead to fatal convulsions and paralysis
* Acetylcholine is broken down into its two component parts by the synaptic enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
* AChE is either released into the synapse from the presynaptic neuron or embedded on the membrane of the post-synaptic cell
* The liberated choline is returned to the presynaptic neuron where it reforms acetylcholine
* Acetylcholine must be continually removed from the synapse, as overstimulation can lead to fatal convulsions and paralysis
* Acetylcholine is broken down into its two component parts by the synaptic enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
* AChE is either released into the synapse from the presynaptic neuron or embedded on the membrane of the post-synaptic cell
* The liberated choline is returned to the presynaptic neuron where it reforms acetylcholine
23
New cards
Acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholine is broken down into its two component parts by the synaptic enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
24
New cards
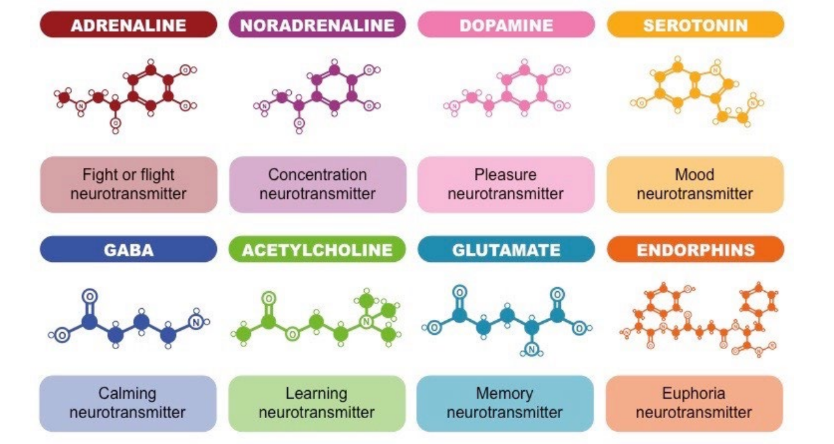
Other neurotransmitters -
**Adrenaline**
* Adrenaline is primarily a hormone released by the adrenal gland, but some neurons may secrete it as a neurotransmitter
* It increases heart rate and blood flow, leading to a physical boost and heightened awareness
* It is produced during stressful or exciting situations
**Noradrenaline**
* In contrast to adrenaline, noradrenaline is predominantly a neurotransmitter that is occasionally released as a hormone
* It contracts blood vessels and increases blood flow, improving attention and the speed at which responsive actions occur
**Dopamine**
* It is primarily responsible for feelings of pleasure, but is also involved in movement and motivation
* People tend to repeat behaviours that lead to dopamine release, leading to addictions
* Abnormal dopamine secretion is common in specific movement disorders, like Parkinson’s disease
**Serotonin**
* Contributes to feelings of well-being and happiness
* Is affected by exercise and light exposure, and plays a role in the sleep cycle and digestive system regulation
**GABA**
* Inhibits neuron firing in the CNS – high levels improve focus whereas low levels cause anxiety
* Also contributes to motor control and vision
**Acetylcholine**
* Involved in thought, learning and memory within the brain
* Activates muscle contraction in the body and is also associated with attention and awakening
**Glutamate**
* Most common brain neurotransmitter
* Regulates development and creation of new nerve pathways and hence is involved in learning and memory
**Endorphins**
* Release is associated with feelings of euphoria and a reduction in pain (body’s natural 'pain killers’) ◻ Released during exercise, excitement and sex
* Adrenaline is primarily a hormone released by the adrenal gland, but some neurons may secrete it as a neurotransmitter
* It increases heart rate and blood flow, leading to a physical boost and heightened awareness
* It is produced during stressful or exciting situations
**Noradrenaline**
* In contrast to adrenaline, noradrenaline is predominantly a neurotransmitter that is occasionally released as a hormone
* It contracts blood vessels and increases blood flow, improving attention and the speed at which responsive actions occur
**Dopamine**
* It is primarily responsible for feelings of pleasure, but is also involved in movement and motivation
* People tend to repeat behaviours that lead to dopamine release, leading to addictions
* Abnormal dopamine secretion is common in specific movement disorders, like Parkinson’s disease
**Serotonin**
* Contributes to feelings of well-being and happiness
* Is affected by exercise and light exposure, and plays a role in the sleep cycle and digestive system regulation
**GABA**
* Inhibits neuron firing in the CNS – high levels improve focus whereas low levels cause anxiety
* Also contributes to motor control and vision
**Acetylcholine**
* Involved in thought, learning and memory within the brain
* Activates muscle contraction in the body and is also associated with attention and awakening
**Glutamate**
* Most common brain neurotransmitter
* Regulates development and creation of new nerve pathways and hence is involved in learning and memory
**Endorphins**
* Release is associated with feelings of euphoria and a reduction in pain (body’s natural 'pain killers’) ◻ Released during exercise, excitement and sex
25
New cards
Insecticides
Neurotransmitters can be exploited by scientists for useful applications.
Most insecticides are based on excitatory neurotransmitters, e.g. neonicotinoids.
* Neonicotinoid insecticides are a group of insecticides which mimic the action of acetylcholine.
* They bind irreversibly to the postsynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptor causing overstimulation of the neuron, resulting the death of the insect.
Most insecticides are based on excitatory neurotransmitters, e.g. neonicotinoids.
* Neonicotinoid insecticides are a group of insecticides which mimic the action of acetylcholine.
* They bind irreversibly to the postsynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptor causing overstimulation of the neuron, resulting the death of the insect.
26
New cards
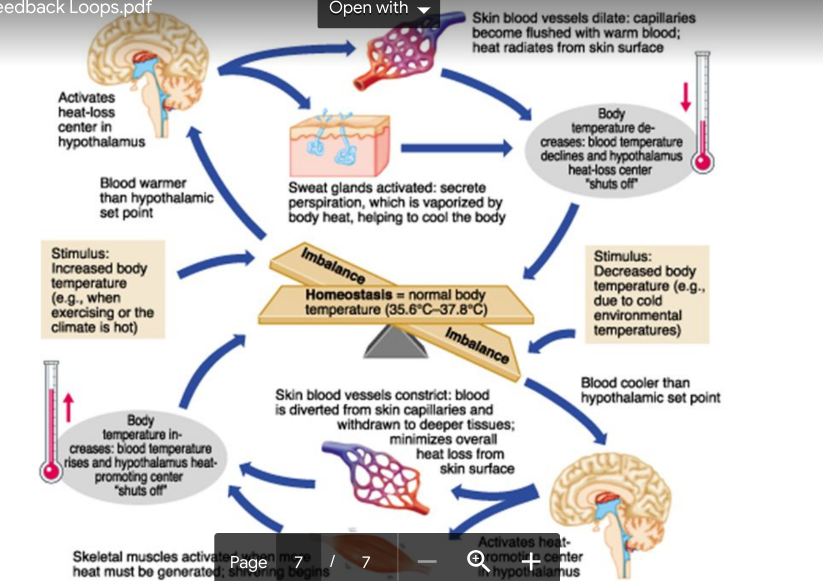
Homeostasis
* Maintenance of body conditions within certain parameters
* Homeostatic mechanisms operate via feedback loops that may involve either the nervous/ endocrine systems (or both!)
* Nerves respond very quickly, while longer term responses are controlled by the endocrine system (hormones)
* Some factors include
* Blood/Water volume, blood pressure
* O2/CO2
* Blood pH
* Temperature
* Blood glucose levels
* Levels of Ca^2+, Na^2+ K+ Cl- etc
* Homeostatic mechanisms operate via feedback loops that may involve either the nervous/ endocrine systems (or both!)
* Nerves respond very quickly, while longer term responses are controlled by the endocrine system (hormones)
* Some factors include
* Blood/Water volume, blood pressure
* O2/CO2
* Blood pH
* Temperature
* Blood glucose levels
* Levels of Ca^2+, Na^2+ K+ Cl- etc
27
New cards
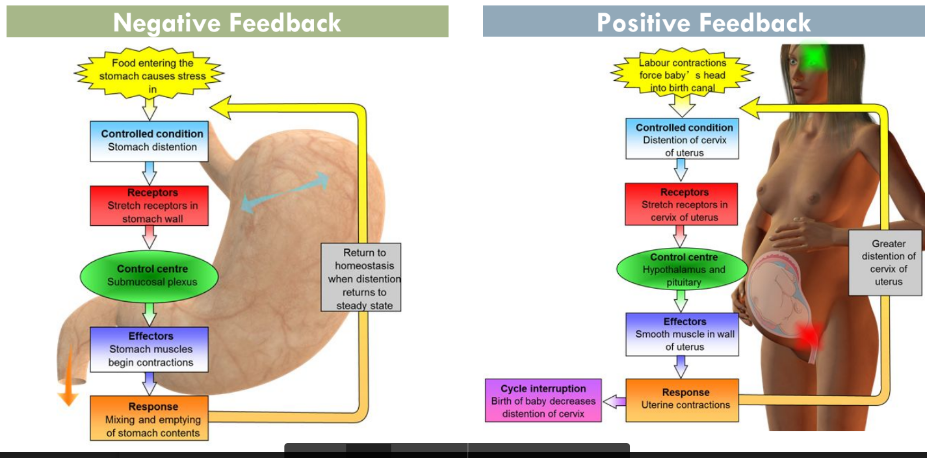
Feedback loops
Physiological processes are commonly moderated via 2 distinct feedback mechanisms: Positive + Negative feedback
* Homeostatic processes are controlled by negative feedback → these systems occur more commonly within the body to keep / return the body to a steady state
* Positive feedback usually involves departure from the steady state → increase in the change/ rate (think domino effect) (less common)
* Homeostatic processes are controlled by negative feedback → these systems occur more commonly within the body to keep / return the body to a steady state
* Positive feedback usually involves departure from the steady state → increase in the change/ rate (think domino effect) (less common)
28
New cards
Homeostasis components/ requirements
* Receptors: To detect changes
* Processing: To determine response
* Effectors: Return parameter to steady state
\
Ex: Body temp
* Human body temp maintained at about 37 degrees
* Receptors - temperature receptors (skin, blood)
* Processor - hypothalamus controls/ regulates body temperature
* Effectors - muscle contractions, sweat glands, blood vessels, metabolism
* Processing: To determine response
* Effectors: Return parameter to steady state
\
Ex: Body temp
* Human body temp maintained at about 37 degrees
* Receptors - temperature receptors (skin, blood)
* Processor - hypothalamus controls/ regulates body temperature
* Effectors - muscle contractions, sweat glands, blood vessels, metabolism
29
New cards
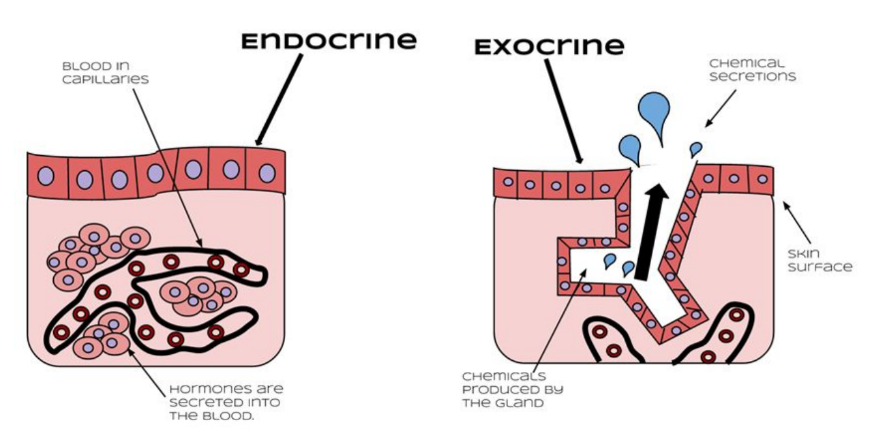
Endocrine vs Exocrine
* Endocrine glands release chemical substances directly into the bloodstream/ tissues of the body. Chemical substances released by the endocrine glands/ generally known as hormones
* Exocrine glands release chemical substances through ducts to outside the body/ onto another surface within the body
* Exocrine glands release chemical substances through ducts to outside the body/ onto another surface within the body
30
New cards
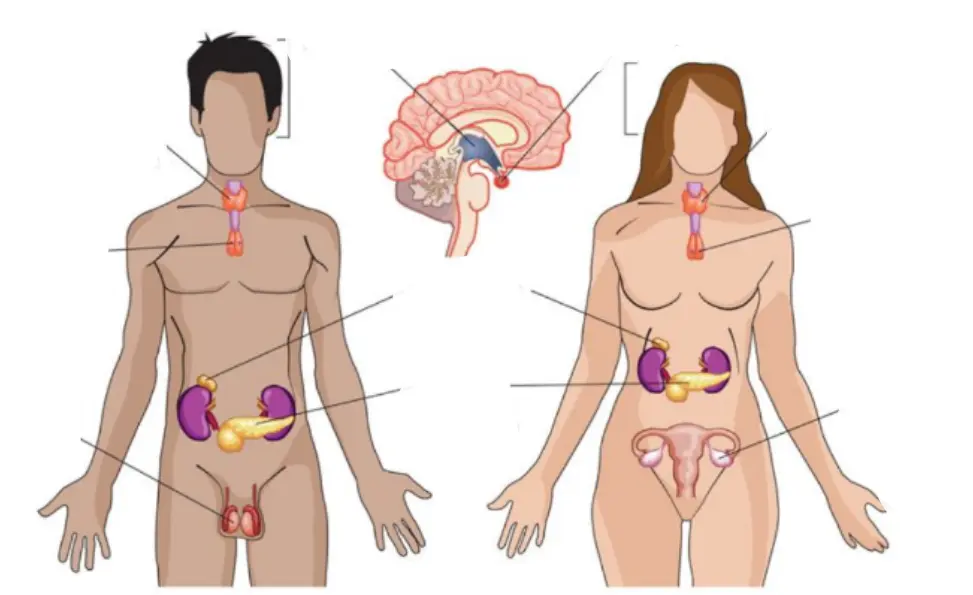
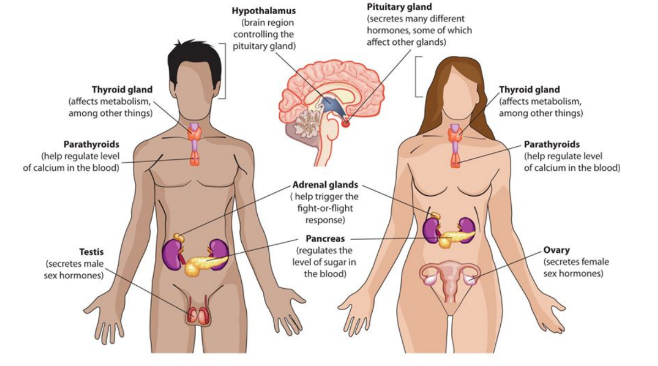
Endocrine system - Glands
**Thyroid gland**
* Affects metabolism/ other things
**Parathyroids**
* Regulate blood calcium levels
**Hypothalamus**
* Brain region controlling pituitary gland
**Adrenal glands**
* Help trigger fight/ flight response
**Pancreas**
* Regulate blood sugar levels
**Ovary**
* Secretes female sex hormones
**Testis**
* Secretes male sex hormones
* Affects metabolism/ other things
**Parathyroids**
* Regulate blood calcium levels
**Hypothalamus**
* Brain region controlling pituitary gland
**Adrenal glands**
* Help trigger fight/ flight response
**Pancreas**
* Regulate blood sugar levels
**Ovary**
* Secretes female sex hormones
**Testis**
* Secretes male sex hormones
31
New cards
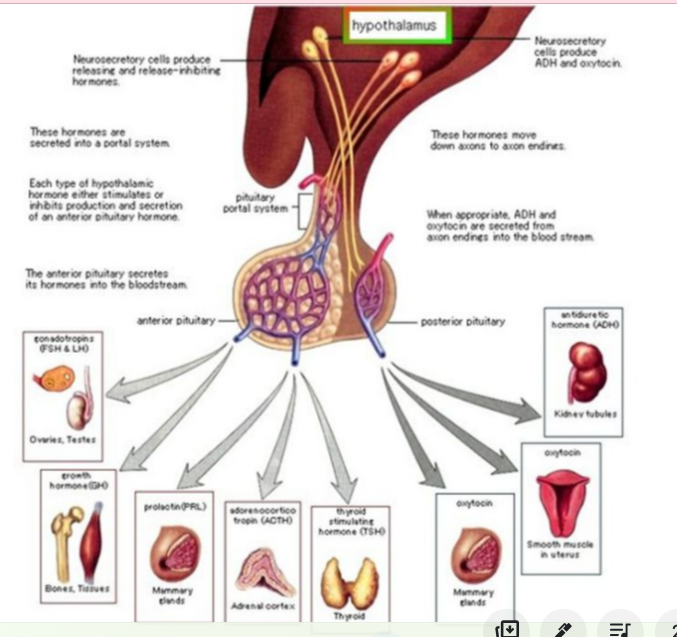
Name 4 different hormones made in the pituitary gland
po
* **Posterior pituitary**
* Antidiuretic hormone
* Oxytocin
* **Anterior pituitary**
* Growth hormone
* Thyroid stimulating hormone
* Follicle stimulating hormone
* Luteinising hormone
* **Posterior pituitary**
* Antidiuretic hormone
* Oxytocin
* **Anterior pituitary**
* Growth hormone
* Thyroid stimulating hormone
* Follicle stimulating hormone
* Luteinising hormone
32
New cards
Three types of hormones
steroid hormones, peptide hormones and amino acid derivatives.
33
New cards
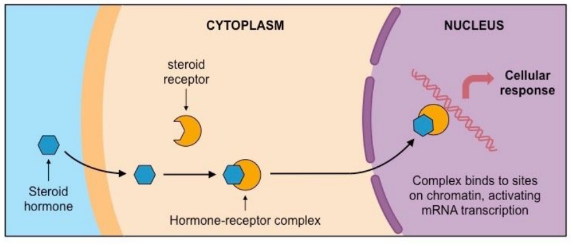
Steroid hormones
* Lipophilic → can freely diffuse across plasma membrane of a cell + Bind to receptors in either the cytoplasm/ nucleus of the target cell → form active receptor-hormone complex
* this activated complex will move to the nucleus + bind directly the DNA, acting as a transcription factor for gene expression
* Ex Gonads (estrogen, progesterone + testosterone)
* this activated complex will move to the nucleus + bind directly the DNA, acting as a transcription factor for gene expression
* Ex Gonads (estrogen, progesterone + testosterone)
34
New cards
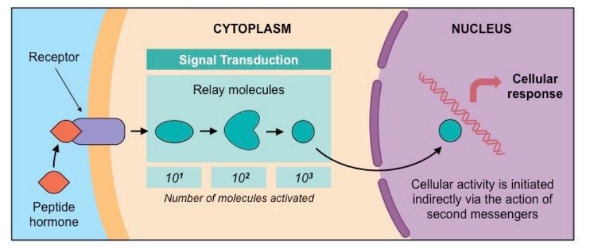
Peptide hormones
* Hydrophilic and lipophobic → cannot freely cross the plasma membrane so they bind to receptors on the surface of the cell
* Receptor complex activates a series of intracellular molecules → called second messengers which initiate cell activity + enable amplification of initial signal (more molecules are activated) → leads to alteration of cell activity
* Peptide hormones include insulin, glucagon, leptin, ADH and oxytocin
* Receptor complex activates a series of intracellular molecules → called second messengers which initiate cell activity + enable amplification of initial signal (more molecules are activated) → leads to alteration of cell activity
* Peptide hormones include insulin, glucagon, leptin, ADH and oxytocin
35
New cards
Hypothalamus
* Region at the base of the brain that links the nervous system to the endocrine systems thru its connection to the pituitary gland
* Helps control the release of hormones from other endocrine glands
* Helps regulate (among other functions):
* Body temperature
* Hunger
* Thirst
* Sleep
* Helps control the release of hormones from other endocrine glands
* Helps regulate (among other functions):
* Body temperature
* Hunger
* Thirst
* Sleep
36
New cards
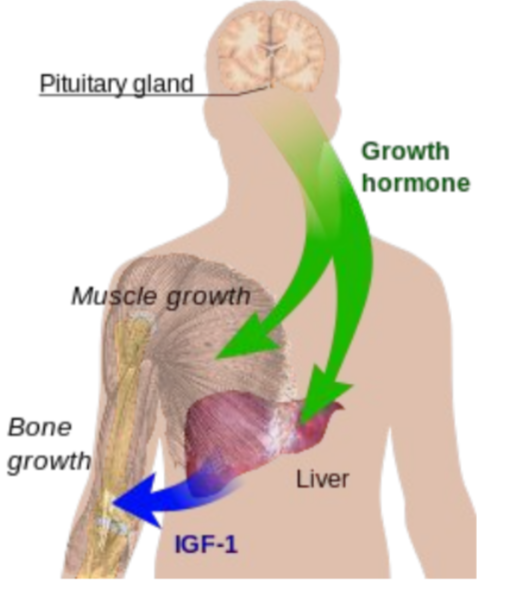
Growth hormone
* Peptide hormone released from the anterior pituitary gland
* Important for normal growth during childhood
* Stimulates cells to grow and divide
* Makes long bones increase in length
* Increases muscle mass
* GH released during deep sleep repair of body tissues
* Many secondary roles (glucose metabolism)
Note:
* Too much in kids - gigantism
* Too little - Pituitary dwarfism (proportional)
* Too much in adults - Acromegaly
* Important for normal growth during childhood
* Stimulates cells to grow and divide
* Makes long bones increase in length
* Increases muscle mass
* GH released during deep sleep repair of body tissues
* Many secondary roles (glucose metabolism)
Note:
* Too much in kids - gigantism
* Too little - Pituitary dwarfism (proportional)
* Too much in adults - Acromegaly
37
New cards
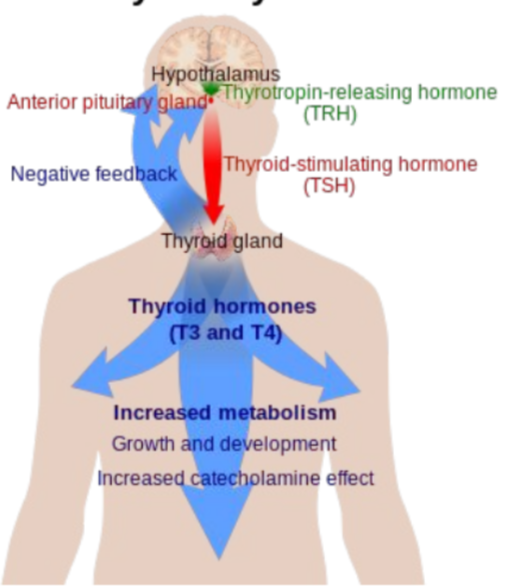
Thyroxin (Thyroid Hormone)
* Amine hormone released from thyroid gland → acts on nearly every tissue in the body and essential to the proper development and differentiation of cells
* Primary role is to increase the basal metabolic rate
* Achieved by stimulating carbohydrate + lipid metabolism through the oxidation of glucose _ fatty acids
* Can also increase the body’s sensitivity to catecholamines (such as adrenaline)
* Iodine is an important component of thyroxine
* Lack of soil iodine means not enough thyroid hormones
* Causes goiter (thyroid swelling)
* In children, causes cretinism → stunted growth + impaired brain development
* Primary role is to increase the basal metabolic rate
* Achieved by stimulating carbohydrate + lipid metabolism through the oxidation of glucose _ fatty acids
* Can also increase the body’s sensitivity to catecholamines (such as adrenaline)
* Iodine is an important component of thyroxine
* Lack of soil iodine means not enough thyroid hormones
* Causes goiter (thyroid swelling)
* In children, causes cretinism → stunted growth + impaired brain development
38
New cards
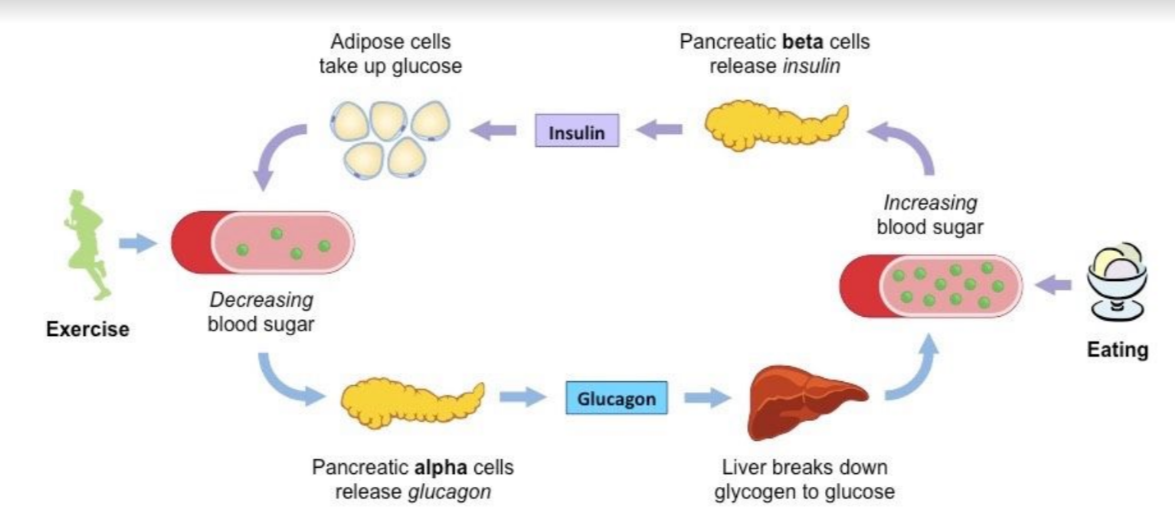
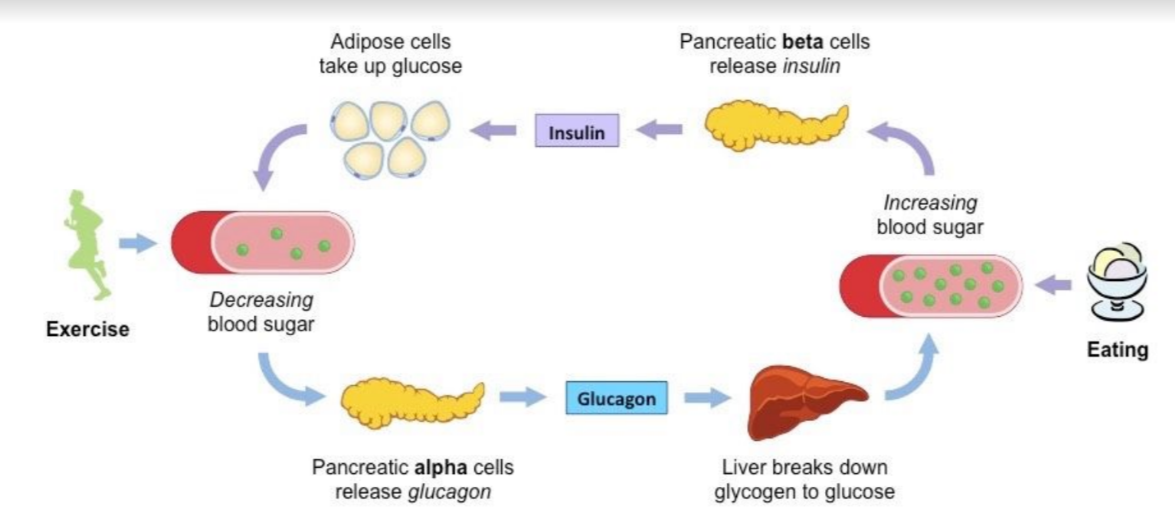
Insulin
Insulin is a peptide hormone released from beta (β) cells of the pancreas + causes decrease in blood glucose concentration
* Involves stimulating glycogen synthesis in the liver (glycogenesis), promoting glucose uptake by the liver + adipose tissue/ increasing the rate of glucose breakdown (inc cell respiration rates)
* Involves stimulating glycogen synthesis in the liver (glycogenesis), promoting glucose uptake by the liver + adipose tissue/ increasing the rate of glucose breakdown (inc cell respiration rates)
39
New cards
Glucagon
Peptide hormone released from alpha (α) cells of the pancreas + causes increase in blood glucose concentration
* Involves stimulating glycogen breakdown in the liver (glycogenesis) → promoting glucose release by the liver + adipose tissue/ decreasing the rate of glucose breakdown (by reducing cell respiration rates)
* Involves stimulating glycogen breakdown in the liver (glycogenesis) → promoting glucose release by the liver + adipose tissue/ decreasing the rate of glucose breakdown (by reducing cell respiration rates)
40
New cards
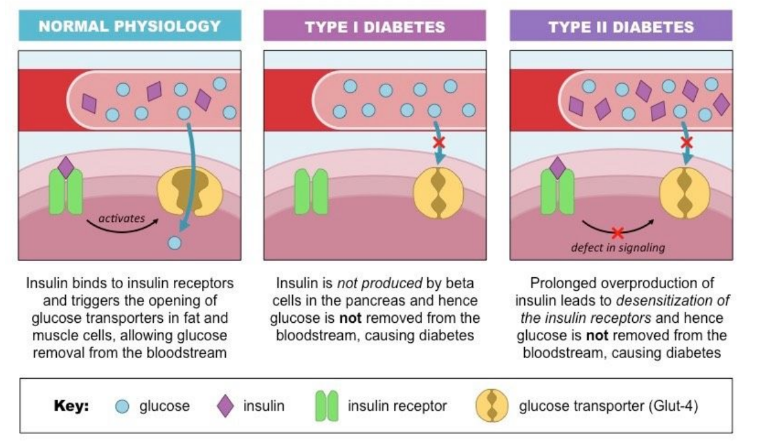
Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder that results from a high blood glucose concentration over a prolonged period
\
Type 1 (Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM)):
* Early onset
* Body does not produce sufficient insulin
* Caused by destruction of beta cells (autoimmune)
* Requires insulin injections to regulate blood glucose
\
Type 2 (Non Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM)):
* Late onset
* Body does not respond to insulin production
* Caused by down-regulation of insulin receptors
* Controlled by managing diet/ lifestyle
\
Type 1 (Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM)):
* Early onset
* Body does not produce sufficient insulin
* Caused by destruction of beta cells (autoimmune)
* Requires insulin injections to regulate blood glucose
\
Type 2 (Non Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM)):
* Late onset
* Body does not respond to insulin production
* Caused by down-regulation of insulin receptors
* Controlled by managing diet/ lifestyle
41
New cards
Melatonin
helps with the timing of your circadian rhythms (24-hour internal clock) and with sleep.
42
New cards
Leptin
Leptin helps inhibit (prevent) hunger and regulate energy balance so that your body doesn't trigger a hunger response when it doesn't need energy (calories).
43
New cards
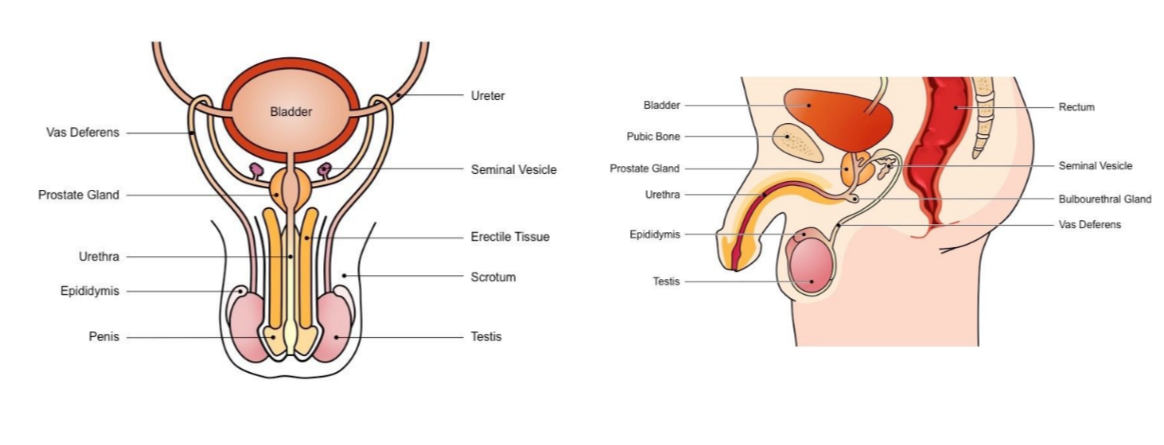
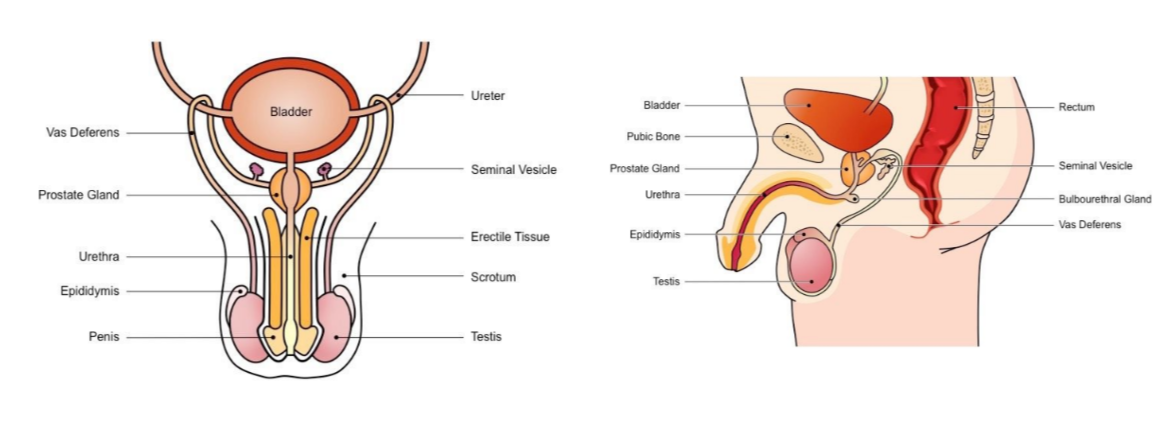
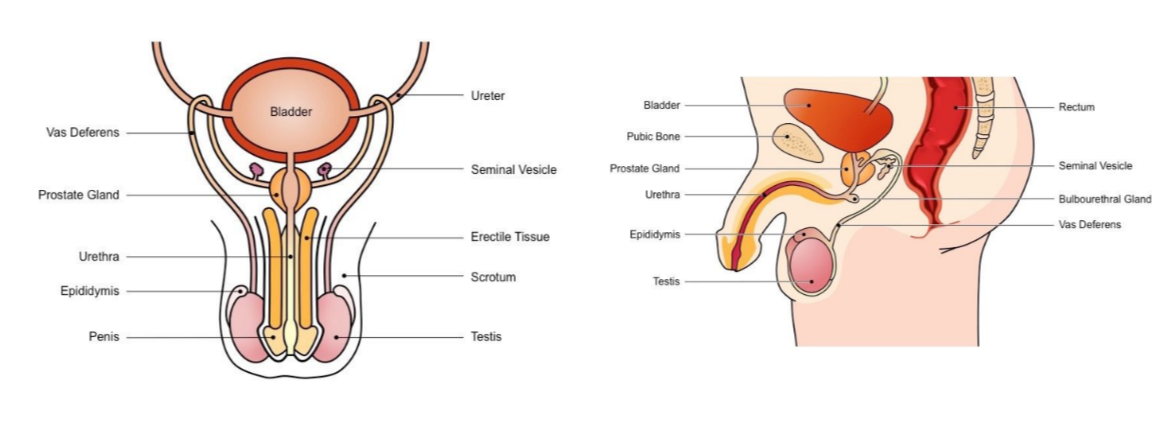
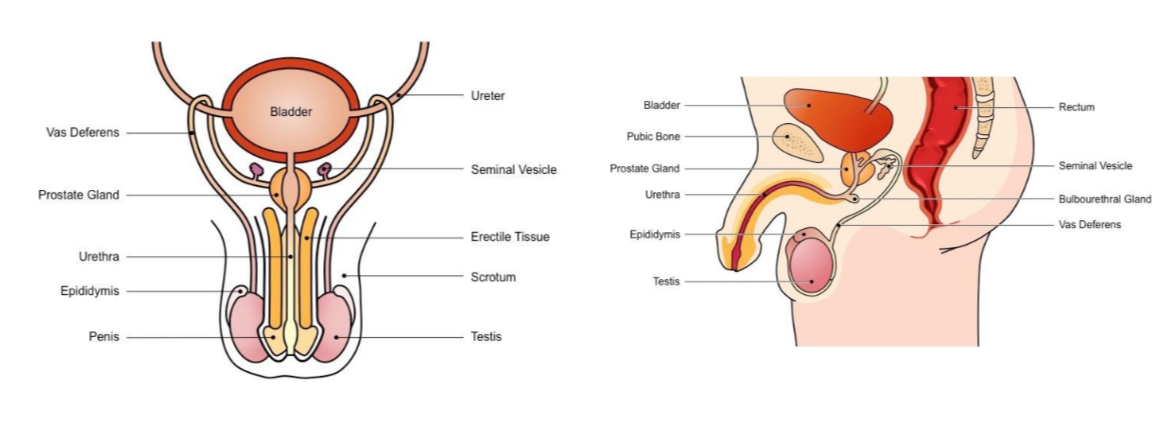
Male reproductive system
* Includes all the organs responsible for the production of sperm
* Also includes organs that synthesise semen in which the sperm is transported
* Also includes organs that synthesise semen in which the sperm is transported
44
New cards
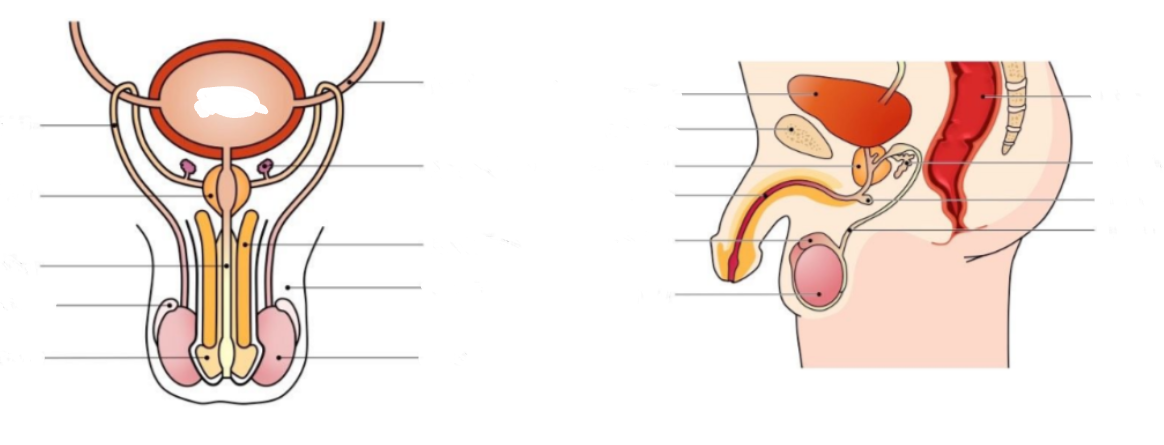
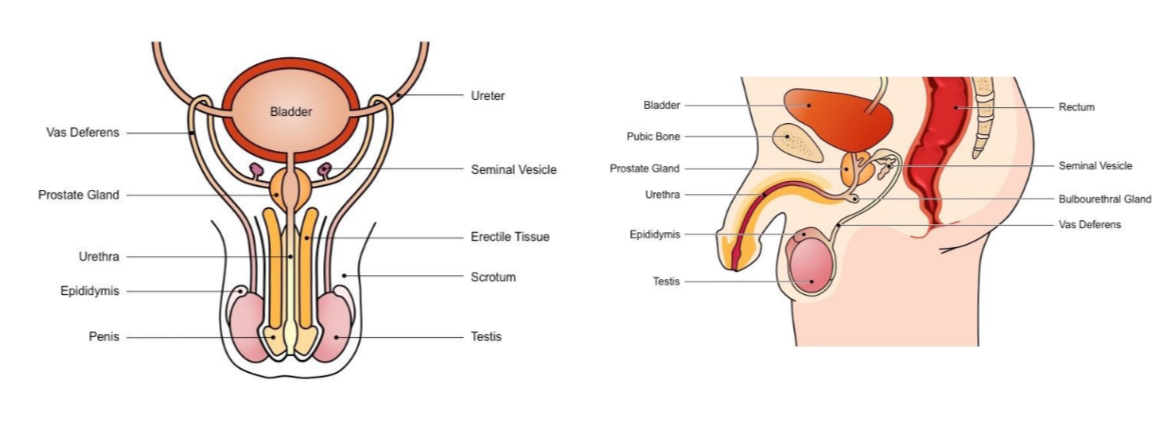
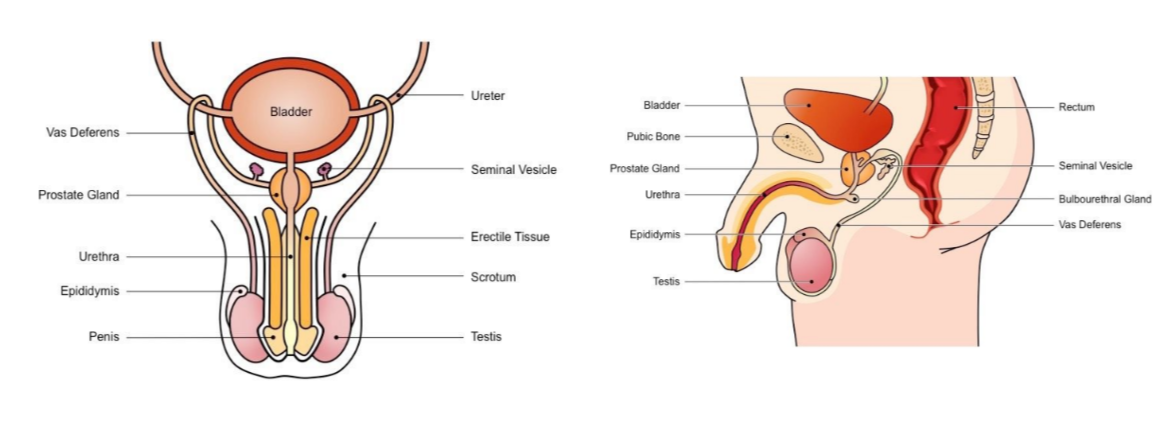
Label the following diagram
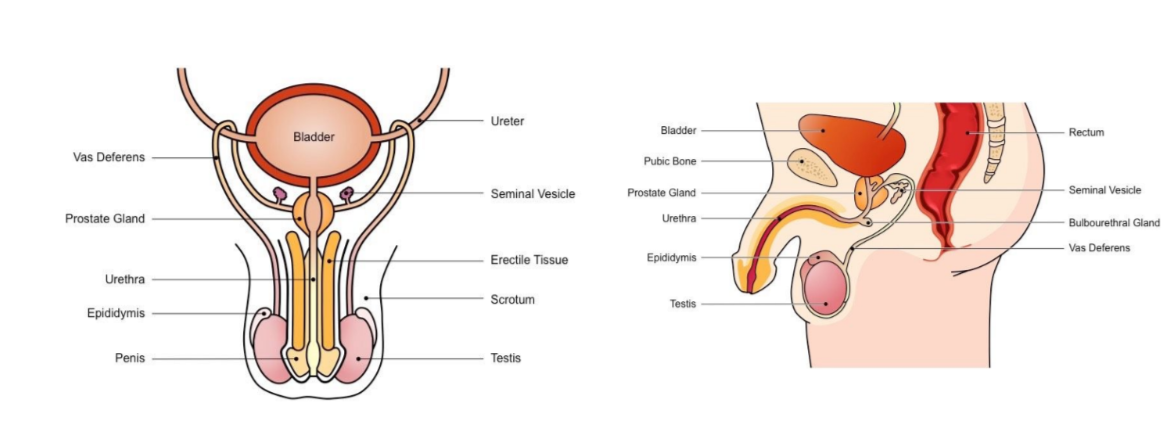
45
New cards
The male reproductive system
\
\
* Includes all responsible organs for sperm production (male gamete)
* includes organs involved in synthesising the semen in which sperm transported during intercourse
* includes organs involved in synthesising the semen in which sperm transported during intercourse
46
New cards
Male reproductive system - Testis
Responsible for production of sperm + testosterone
47
New cards
Epididymis
Site of sperm maturation and develops motility → mature sperm stored here until ejaculation
48
New cards
Vans Deferens
Long tube which conducts sperm from testes to the prostate gland (connects to urethra) during ejaculation
49
New cards
Seminal vesicle
Secretes fluids containing fructose (nourish sperm) mucus (protect sperm) and prostaglandin (triggers uterine contractions)
50
New cards
Prostate gland
\
\
Secretes alkaline fluid to neutralise vaginal acids (necessary to maintain sperm viability)
51
New cards
Urethra
Conducts sperm from the prostate gland to outside of the body via penis (also used to convey urine)
52
New cards
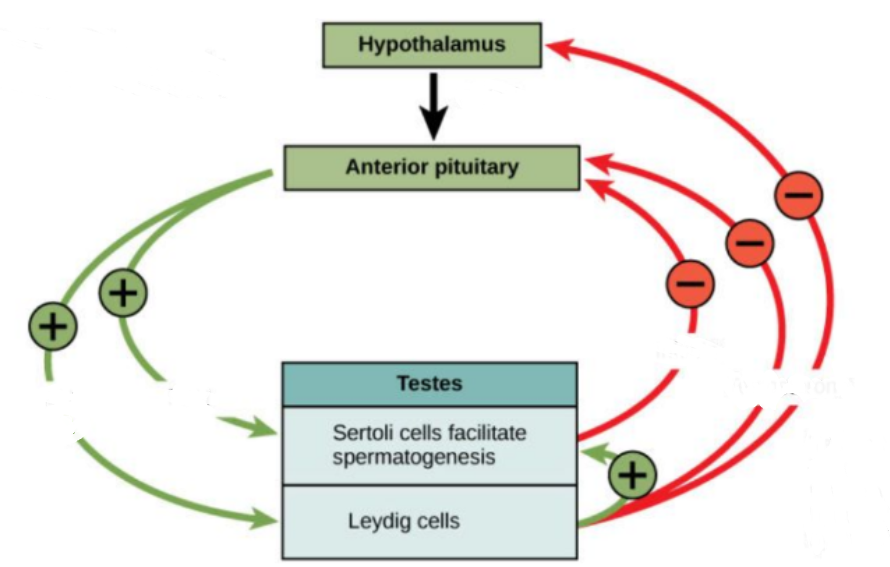
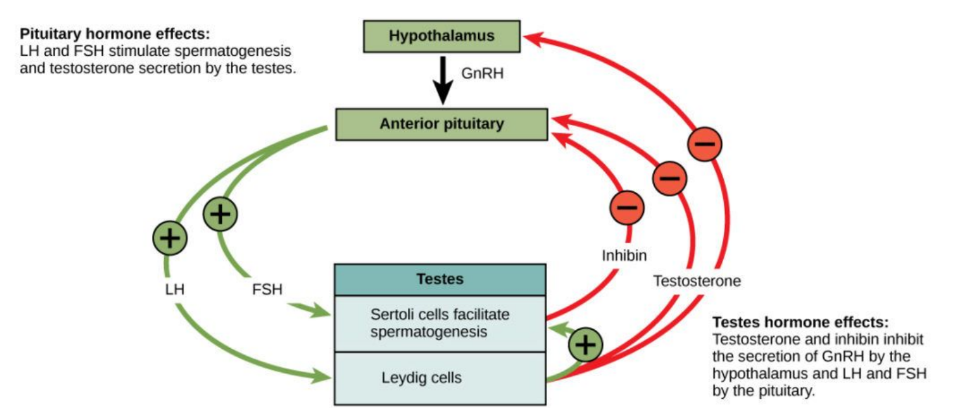
Male reproductive hormones - list and function
* Gonadotrophin releasing Hormone (GnRH)
* Produced by hypothalamus - stimulates anterior pituitary gland to release gonadotrophins that act on the gonads (testes)
* Lutenising hormone (LH)
* Stimulates Leydig Cells in the testes to produce testosterone
* Follicle stimulating Hormone (FSH)
* Gonadotrophin - Stimulates Sertoli cells to facilitate sperm production
* Testosterone
* Stimulates sperm production (+ development of secondary sexual characteristics at puberty)
* Produced by hypothalamus - stimulates anterior pituitary gland to release gonadotrophins that act on the gonads (testes)
* Lutenising hormone (LH)
* Stimulates Leydig Cells in the testes to produce testosterone
* Follicle stimulating Hormone (FSH)
* Gonadotrophin - Stimulates Sertoli cells to facilitate sperm production
* Testosterone
* Stimulates sperm production (+ development of secondary sexual characteristics at puberty)
53
New cards
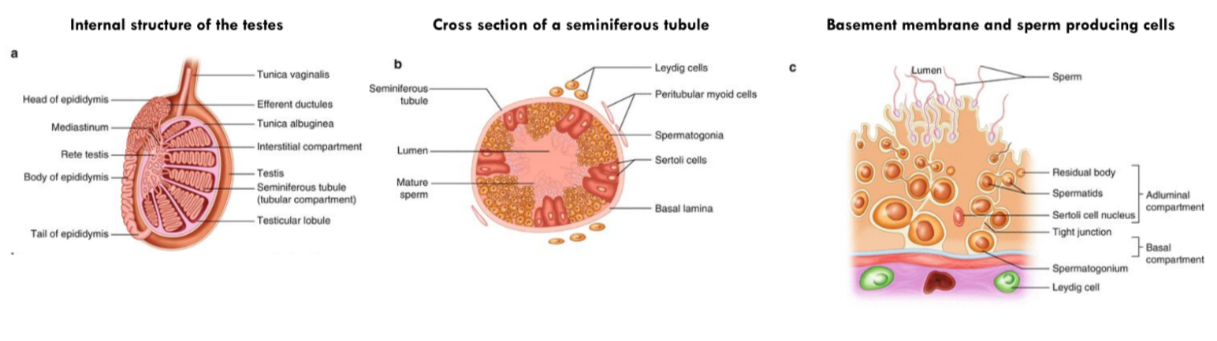
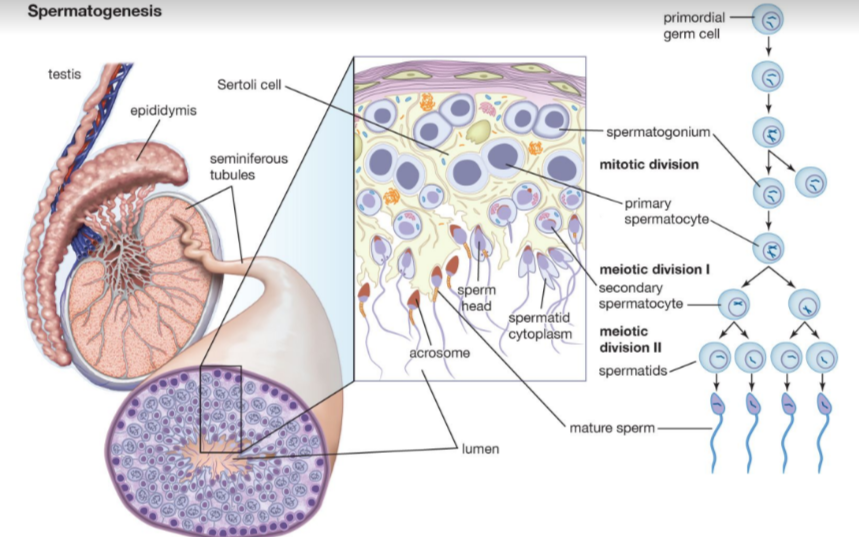
Spermatogenesis
* Occurs in the seminiferous tubules of the testes
* Basement of tubules lined by germline epithelium → at puberty divide by mitosis to make spermatogonia (which divide by meiosis to make spermatids)
* Spermatids differentiate into functional spermatozoa → released into tubule lumen
* Nourished by **Sertoli cells** (reside in the tubule lining)
* Outside of tubules are blood capillaries + interstitial cells (Leydig cells) → produce testosterone
* Basement of tubules lined by germline epithelium → at puberty divide by mitosis to make spermatogonia (which divide by meiosis to make spermatids)
* Spermatids differentiate into functional spermatozoa → released into tubule lumen
* Nourished by **Sertoli cells** (reside in the tubule lining)
* Outside of tubules are blood capillaries + interstitial cells (Leydig cells) → produce testosterone
54
New cards
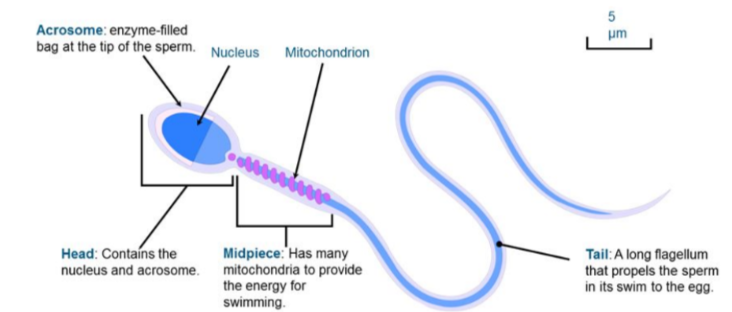
Sperm structure
* Simple as sole purpose is to deliver genetic material
* Composed of 3 main regions: Head, mid-piece + tail
* Composed of 3 main regions: Head, mid-piece + tail
55
New cards
Female reproductive system
* Includes organs responsible for production of oocyte (female gamete)
* Involves organs involved in initially developing/ maintaining embryo during early pregnancy stages
* Involves organs involved in initially developing/ maintaining embryo during early pregnancy stages
56
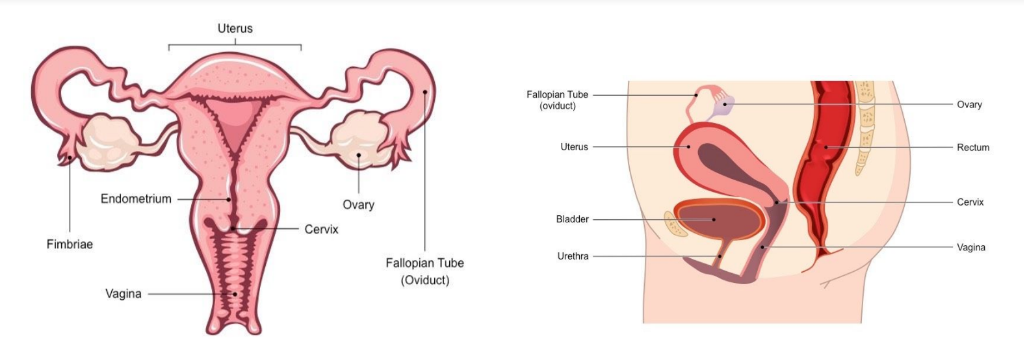
New cards
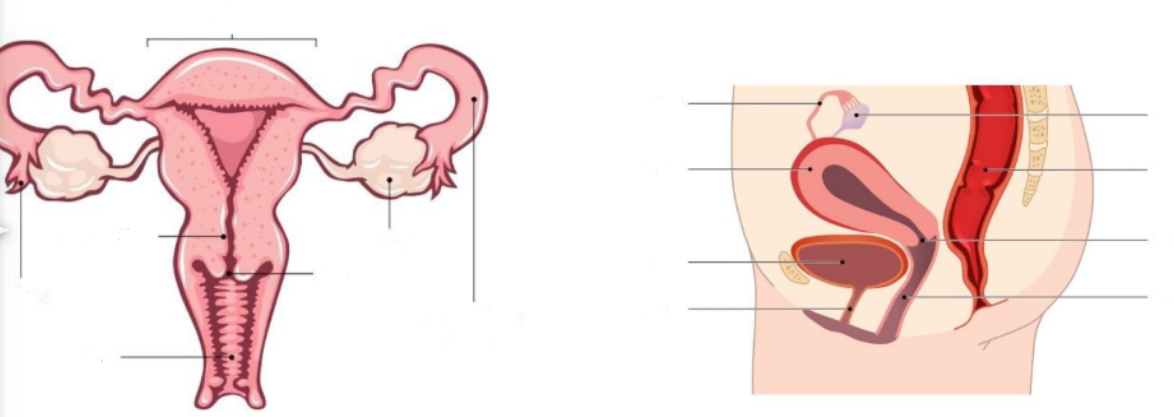
Label diagrams
57
New cards
Ovary
Where oocytes mature prior to release (ovulation) → also responsible for estrogen + progesterone secretion (female sex hormones)
58
New cards
Fimbria
Fringe of tissue adjacent to ovary that sweep an oocyte into the fallopian tube/ oviduct
59
New cards
Fallopian Tube/ Oviduct
Transports oocyte to the uterus → typically where fertilisation occurs
60
New cards
Uterus
Organ where a fertilised egg will implant + develop (becoming an embryo)
61
New cards
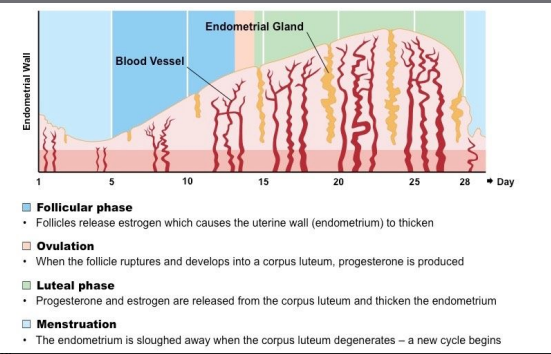
Endometrium
Mucous membrane lining of the uterus thickens in preparation for implantation or otherwise lost (via menstruation)
62
New cards
Vagina
Passage leading to the uterus where the penis can enter (uterus protected by muscular opening called the cervix)
63
New cards
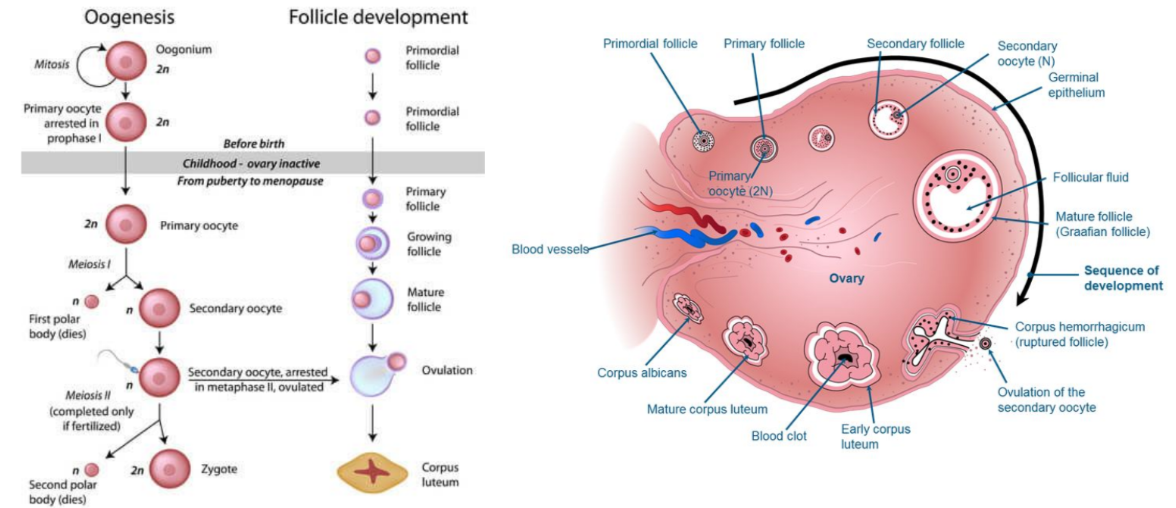
Oogenesis
1. Oogenesis (Egg production) occurs in the ovaries + begins during foetal development when a large number of primordial cells formed by mitosis
2. Cells (oogonia) undergo cell growth till theyre large enough to undergo meiosis (becoming primary oocytes)
3. Begin meiosis but arrested in prophase 1 when granulosa cells surround them to form follicles
4. Primary oocytes remain arrested till puberty, when menstruation begins
5. Monthly, Hormones (FSH) will trigger continued division to form 2 unequal cells
6. one cell retains cytoplasm to form secondary oocyte, other cell forms a polar body
7. Secondary oocyte begins second meiotic division but arrested in metaphase 2
8. Secondary oocyte released from ovary (ovulation) → enters the oviduct/ fallopian tube
9. Follicular cells surrounding oocyte form a corona radiata + function to nourish secondary oocyte
10. Follicular tissue in the ovary after ovulation forms the corpus luteum
11. if oocyte fertilised → chemical changes trigger completion of meiosis 2 + formation of another polar body (1st may also undergo a second division to form a 3rd polar body
12. Once Meiosis 2 finishes mature egg forms ovum before fusing nucleus to form a zygote
64
New cards
Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH)
Produced by the hypothalamus - stimulates the anterior pituitary gland to release gonadotropins that act on the gonads (ovaries)
65
New cards
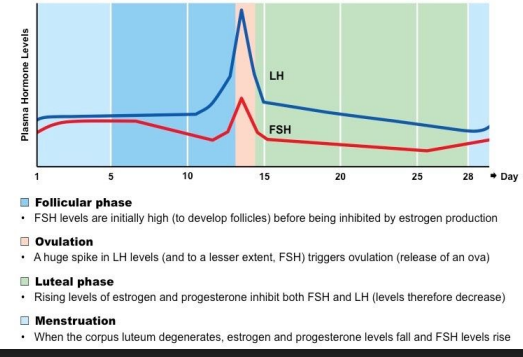
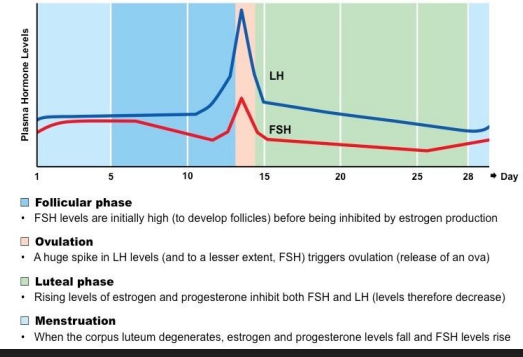
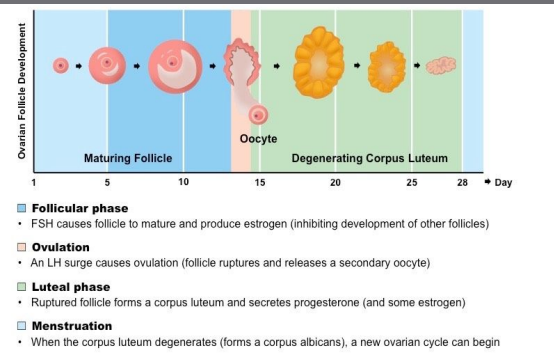
Luteinising Hormone (LH)
Gonadotropin - surge in release causes ovulation, results in the formation of the corpus luteum
66
New cards
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Gonadotropin - stimulates follicle growth, stimulates estrogen secretion (from developing follicles)
67
New cards
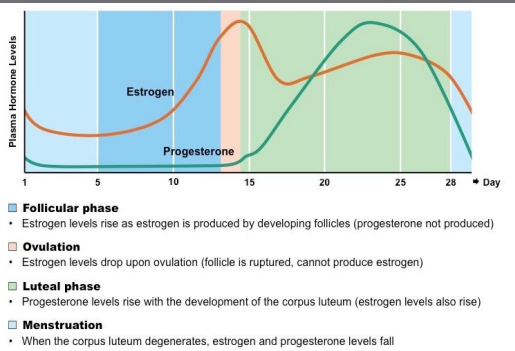
Estrogen
Produced by follicles - thickens endometrium, inhibits FSH and LH for most of the cycle, stimulates FSH and LH release pre-ovulation
68
New cards
Progesterone
Produced by corpus luteum - maintains the endometrium, inhibits FSH and LH
Also maintains pregnany and development of the mammary glands.
Also maintains pregnany and development of the mammary glands.
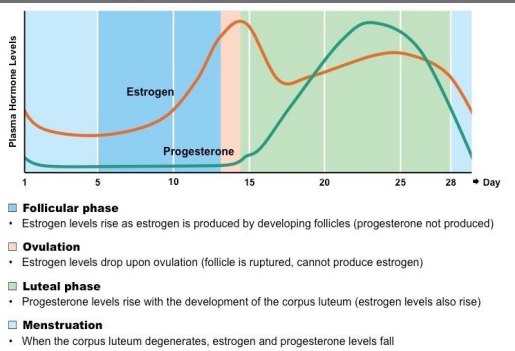
69
New cards
Ovarian cycle
70
New cards
Menstrual cycle
71
New cards
Ovarian and Menstrual Cycles
* Cyclic changes of the endometrium and the ovary
* Regulated by cyclic production of estrogens and progesterone
* FSH and LH regulate the production of estrogens and progesterone
* Both cycles are approximately 28 days in length
* Ovulation typically occurs midway through cycle (approximately day 14)
* The cycles are generally divided into three main components:
* The follicular phase
* Ovulation
* The luteal phase
* Regulated by cyclic production of estrogens and progesterone
* FSH and LH regulate the production of estrogens and progesterone
* Both cycles are approximately 28 days in length
* Ovulation typically occurs midway through cycle (approximately day 14)
* The cycles are generally divided into three main components:
* The follicular phase
* Ovulation
* The luteal phase
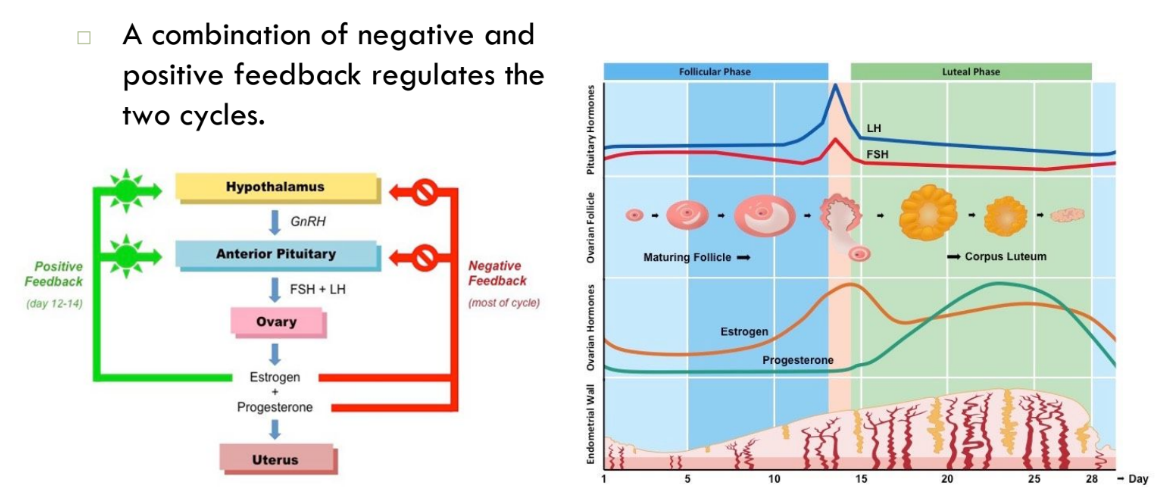
72
New cards
\
Fertilisation
Fertilisation
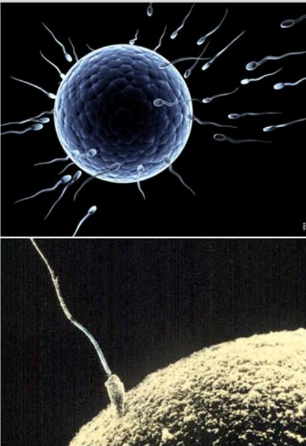
Fertilisation occurs when a single sperm penetrates an egg cell.
The sperm and egg unite to form a zygote.
Fertilisation has several stages (capacitation, acrosome reaction, fusion of sperm, cortical reaction, fusion of nuclei).
After fertilization, the zygote begins its development into a multicellular organism.
The sperm and egg unite to form a zygote.
Fertilisation has several stages (capacitation, acrosome reaction, fusion of sperm, cortical reaction, fusion of nuclei).
After fertilization, the zygote begins its development into a multicellular organism.
73
New cards
Capacitation
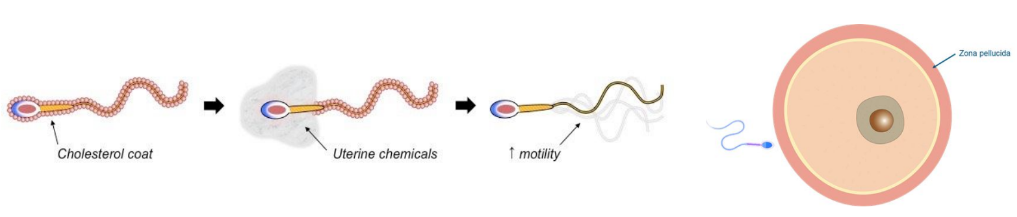
The surface of the sperm undergoes functional changes while in the female reproductive tract that allow it to fertilize the egg cell.
Its cholesterol coat is dissolved which improves motility, and the acrosome cap is destablised.
Its cholesterol coat is dissolved which improves motility, and the acrosome cap is destablised.
74
New cards
The Acrosome Reaction
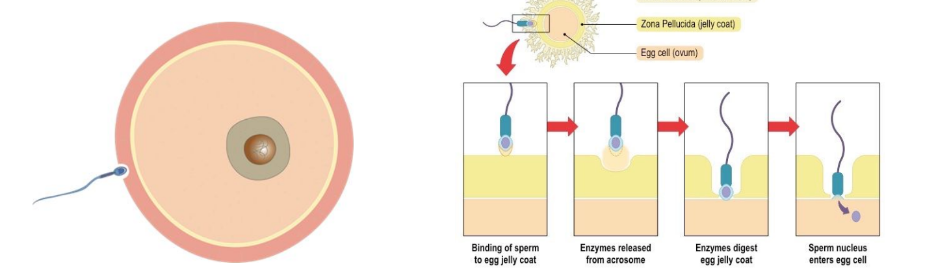
Enzymes from the acrosome are released and digest a pathway through the follicle cells and zona pellucida surrounding the secondary oocyte. The action of many sperm are required for just one to enter the egg cell.
\
\
75
New cards
Fusion
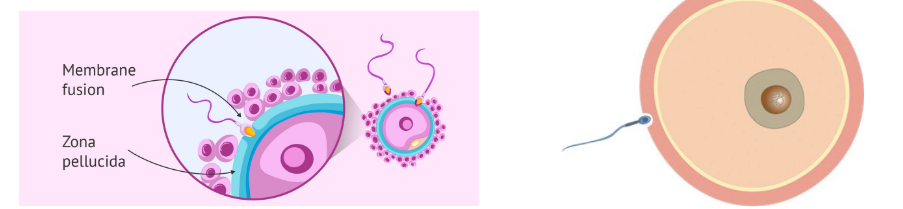
The membranes of the sperm and egg fuse, and the nucleus of the sperm enters the egg cytoplasm which causes a sudden membrane depolarization that acts as a fast block to further sperm entry. This also triggers the completion of meiosis II in the egg cell and induces the next stage of the fertilization sequence.
76
New cards
The Cortical Reaction
Cortical granules in the egg cytoplasm release their contents into the space between the plasma membrane and the vitelline layer.
* Substances released from the granules raise and harden the vitelline layer to form a fast (permanent) block to further sperm entry.
\
* Substances released from the granules raise and harden the vitelline layer to form a fast (permanent) block to further sperm entry.
\
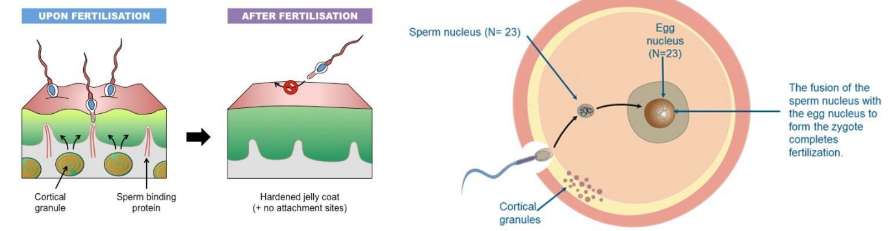
77
New cards
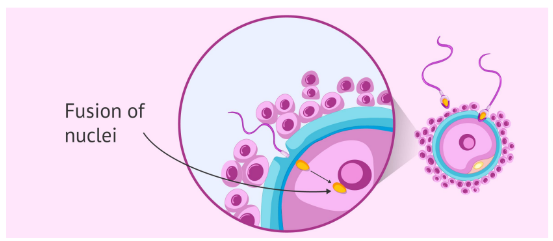
Fusion of Nuclei
* The membranes of both gametes disappear so that the chromosomes can fuse together, returning to a diploid state.
* The diploid fertilised egg is now referred to as a zygote.
* The diploid fertilised egg is now referred to as a zygote.
78
New cards
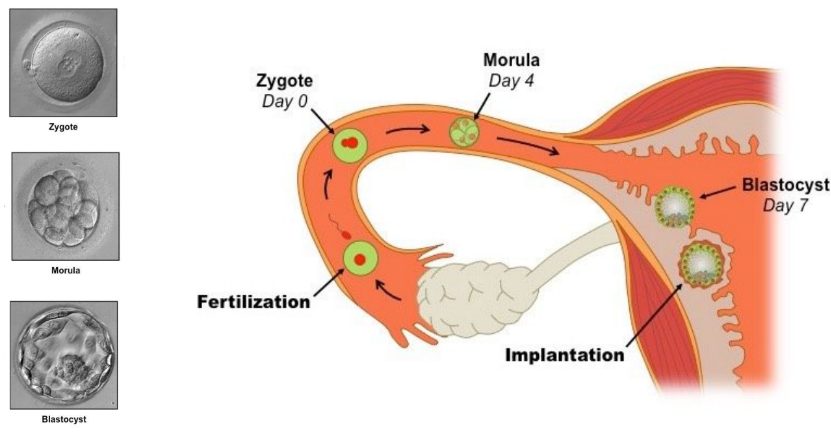
Cleavage and Morula
* Rapid cell division takes place Immediately after fertilization (cleavage), increasing the number of cells, but not the size of the zygote. The first cleavage is completed after 36 hours, and each succeeding division takes less time.
* After three days, successive cleavages have produced a solid mass of cells called a morula, which is still about the same size as the original zygote.
* After three days, successive cleavages have produced a solid mass of cells called a morula, which is still about the same size as the original zygote.
79
New cards
Blastocyst + implantation
After several days in the uterus, the morula develops into the blastocyst.
It makes contact with the uterine lining and pushes deeply into it, ensuring a close maternal-fetal contact.
The embryo produces HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), which prevents degeneration of the corpus luteum and signals that the woman is pregnant.
It makes contact with the uterine lining and pushes deeply into it, ensuring a close maternal-fetal contact.
The embryo produces HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), which prevents degeneration of the corpus luteum and signals that the woman is pregnant.
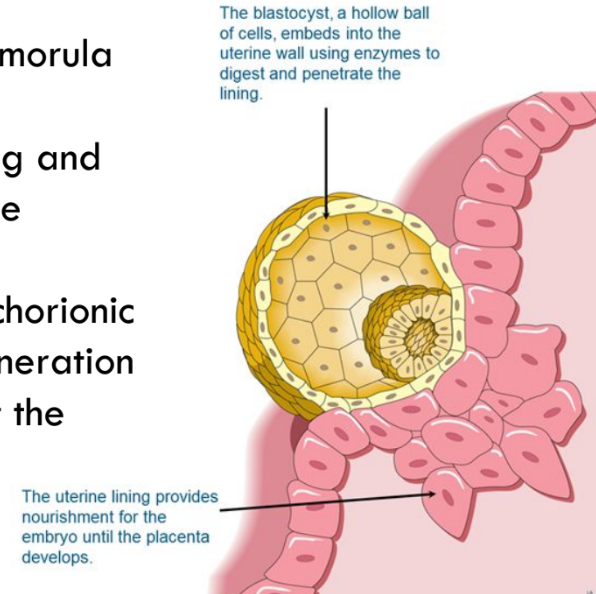
80
New cards
The Embryo
Five weeks after fertilization, the embryo is only 4-5 mm long, but already the central nervous system has developed and the heart is beating.
* The embryonic membranes have formed. The amnion encloses the embryo in a fluid-filled space, and the fetal membranes (allanto-chorion) form the fetal portion of the placenta.
* From two months the embryo is called a fetus.
* The embryonic membranes have formed. The amnion encloses the embryo in a fluid-filled space, and the fetal membranes (allanto-chorion) form the fetal portion of the placenta.
* From two months the embryo is called a fetus.
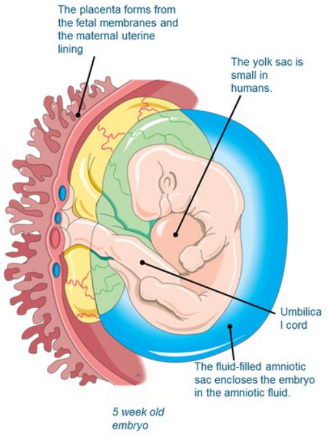
81
New cards
Sexual Development
The reproductive system develops from common tissue found in the developing embryo. The paired mesonephric ducts (Wolffian ducts) and paramesonephric ducts (Müllerian ducts) contribute the majority of male and female internal genital tract respectively.
* Development of this system commences in the embryo, continues through the foetal period then with key changes around birth, only completes functional development postnatally at puberty.
* The mesonephric/paramesonephric duct changes are one of the first male/female differences that occur in development, while external genitalia remain indeterminate in appearance for quite a while.
The Y chromosome includes a gene called the SRY gene (Sex Determining Region Y), which leads to male development The SRY gene codes for a testis-determining factor (TDF) that causes embryonic gonads to form into testes (male gonads) In the absence of the TDF protein (i.e. no Y chromosome), the embryonic gonads will develop into ovaries (female gonads)
* The male and female gametes produce different hormones to promote further development of sex characteristics: The testes produce testosterone to promote the further development of male sex characteristics The ovaries will produce estrogen and progesterone to promote the development of female sex characteristics
* Development of this system commences in the embryo, continues through the foetal period then with key changes around birth, only completes functional development postnatally at puberty.
* The mesonephric/paramesonephric duct changes are one of the first male/female differences that occur in development, while external genitalia remain indeterminate in appearance for quite a while.
The Y chromosome includes a gene called the SRY gene (Sex Determining Region Y), which leads to male development The SRY gene codes for a testis-determining factor (TDF) that causes embryonic gonads to form into testes (male gonads) In the absence of the TDF protein (i.e. no Y chromosome), the embryonic gonads will develop into ovaries (female gonads)
* The male and female gametes produce different hormones to promote further development of sex characteristics: The testes produce testosterone to promote the further development of male sex characteristics The ovaries will produce estrogen and progesterone to promote the development of female sex characteristics

82
New cards
The Fetus
* The early fetus is very small (30-40 mm long)
* The limbs are well formed and the bones are beginning to harden.
* The face has a flat, rather featureless appearance with the eyes far apart.
* Fetal movements have begun and brain development proceeds rapidly.
* The placenta is well developed, although not fully functional until 12 weeks.
* The umbilical cord, containing the fetal umbilical arteries and vein, connects the fetus and mother.
* The limbs are well formed and the bones are beginning to harden.
* The face has a flat, rather featureless appearance with the eyes far apart.
* Fetal movements have begun and brain development proceeds rapidly.
* The placenta is well developed, although not fully functional until 12 weeks.
* The umbilical cord, containing the fetal umbilical arteries and vein, connects the fetus and mother.
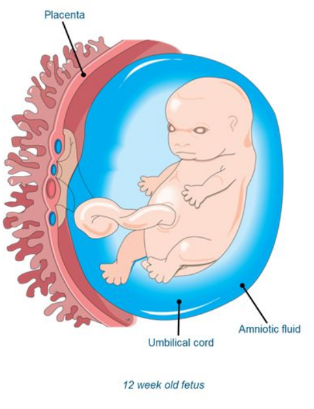
83
New cards
The Placenta
The placenta is the specialized organ that enables the exchange of nutrients from the mother to the fetus and wastes from the fetus to the mother.
* The placenta also has an endocrine role, producing hormones that enable the pregnancy to be maintained.
* It develops when finger-like projections of the fetal chorion (the chorionic villi) grow into the endometrium of the uterus containing the numerous capillaries connecting the fetal arteries and vein.
* The close proximity of the fetal and maternal blood vessels allows for the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and wastes between the maternal and fetal blood.
* The placenta also has an endocrine role, producing hormones that enable the pregnancy to be maintained.
* It develops when finger-like projections of the fetal chorion (the chorionic villi) grow into the endometrium of the uterus containing the numerous capillaries connecting the fetal arteries and vein.
* The close proximity of the fetal and maternal blood vessels allows for the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and wastes between the maternal and fetal blood.
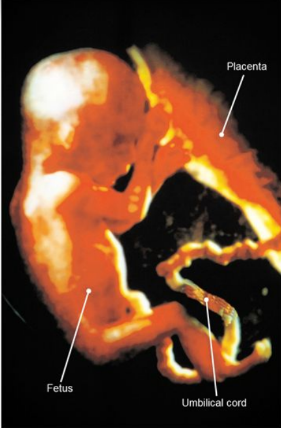
84
New cards
Hormones and pregnancy
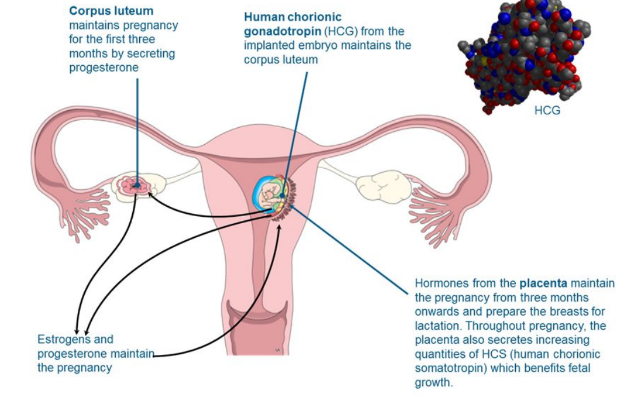
85
New cards
Progesterone changes
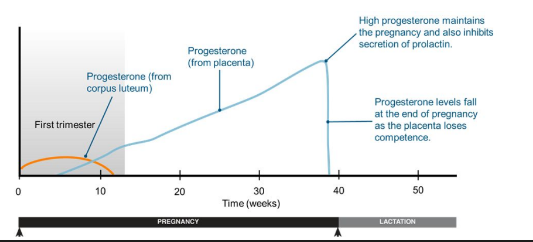
During the first 12 weeks of pregnancy, the corpus luteum secretes enough progesterone to maintain the uterine lining and sustain the developing embryo
* After this, the placenta takes over as the primary endocrine organ of pregnancy.
* It also prepares the mammary glands for lactation and inhibits
* After this, the placenta takes over as the primary endocrine organ of pregnancy.
* It also prepares the mammary glands for lactation and inhibits
86
New cards
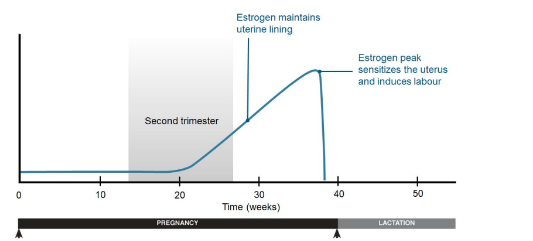
Estrogen changes
Estrogen levels increase to maintain the uterine lining and prepare the mammary glands for lactation.
* It also helps to induce labour at the end of pregnancy.
* It also helps to induce labour at the end of pregnancy.
87
New cards
Labour and Oxytocin
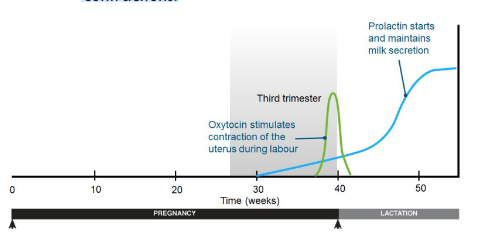
At the end of pregnancy, the placenta loses competency as a result of falling progesterone levels. High estrogen levels then trigger the onset of labour.
* A estrogen peak coincides with an increase in oxytocin, which stimulates uterine contractions.
* Labour progresses as a result of positive feedback. The increasing pressure on the cervix stimulates the release of more oxytocin, which increases the force of the contractions.
* After birth, the secretion of prolactin increases.
* Prolactin maintains lactation during the period of infant nursing.
* Prolactin secretion is inhibited by high progesterone during pregnancy.
* A estrogen peak coincides with an increase in oxytocin, which stimulates uterine contractions.
* Labour progresses as a result of positive feedback. The increasing pressure on the cervix stimulates the release of more oxytocin, which increases the force of the contractions.
* After birth, the secretion of prolactin increases.
* Prolactin maintains lactation during the period of infant nursing.
* Prolactin secretion is inhibited by high progesterone during pregnancy.
88
New cards
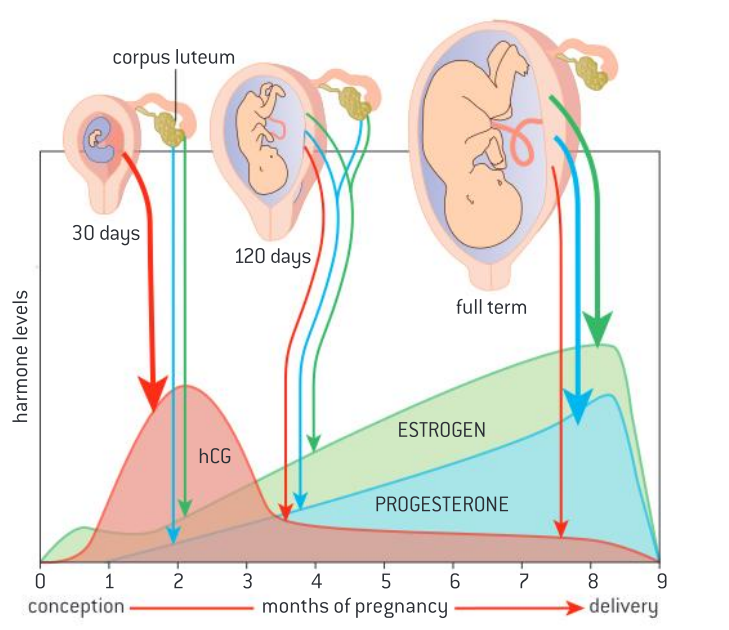
Explain the drop in hCG after 2 months
Human chorionic gonadotrophin → prevents degeneration of corpus luteum + signals woman is pregnant
\
However, once fetus moves to the placenta, the corpus luteum is no longer needed, so hCG lowers so it degenerates.
\
However, once fetus moves to the placenta, the corpus luteum is no longer needed, so hCG lowers so it degenerates.
89
New cards
Kidneys function
* The main organs of excretion are the kidneys, although the skin, gut, and lungs play important roles.
* As well as ridding the body of nitrogenous wastes, the kidneys excrete many unwanted poisons and drugs that are taken in from the environment. They also regulate water balance.
* Homeostasis
* Water and salt balance
* Produce the hormone that stimulates red blood cell production (erythropoietin/EPO)
* As well as ridding the body of nitrogenous wastes, the kidneys excrete many unwanted poisons and drugs that are taken in from the environment. They also regulate water balance.
* Homeostasis
* Water and salt balance
* Produce the hormone that stimulates red blood cell production (erythropoietin/EPO)
90
New cards
Excretion vs elimination
Excretion should not be confused with elimination or egestion of undigested and unabsorbed food material from the gut.
* Note that the breakdown products of hemoglobin (blood pigment) are excreted in bile and pass out with the faeces, but these waste products are not the result of digestion.
* Note that the breakdown products of hemoglobin (blood pigment) are excreted in bile and pass out with the faeces, but these waste products are not the result of digestion.
91
New cards
Osmoconformers
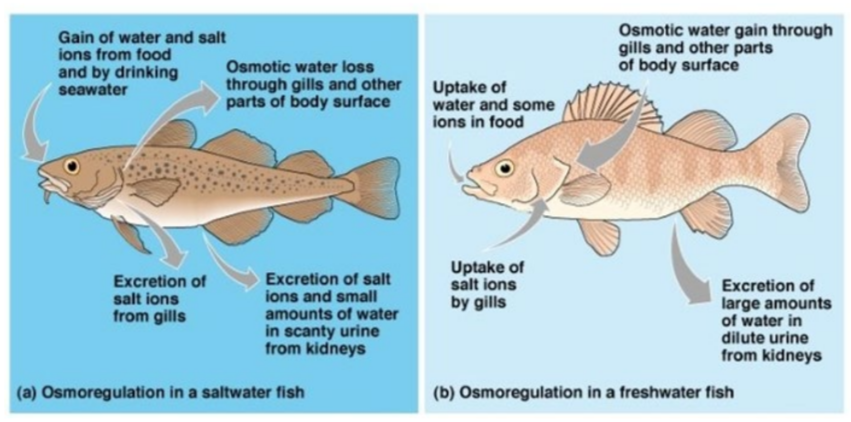
Osmoconformers cannot regulate their water and solute concentrations, their body fluids fluctuate with the changing solute concentration of their external environment.
92
New cards
Osmoregulators
Osmoregulators maintain (relatively) constant water and solute concentrations irrespective of the solute concentrations in their environment.

93
New cards
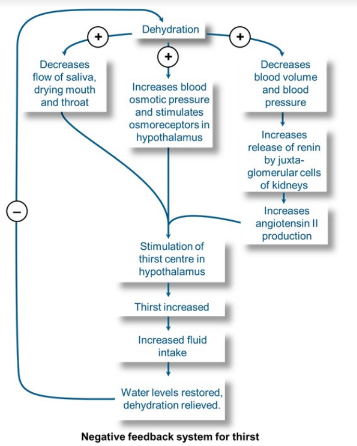
Thirst feedback loop
94
New cards
Nitrogenous waste
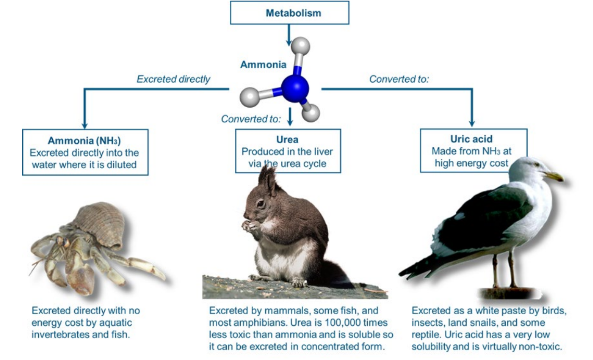
* Nitrogenous wastes are produced from the breakdown of amino acids.
* The simplest breakdown product is ammonia, a highly toxic molecule that cannot be retained in the body long.
* Some animals convert ammonia to a less toxic form (either urea or uric acid) that can remain in the body for a longer period of time.
* The simplest breakdown product is ammonia, a highly toxic molecule that cannot be retained in the body long.
* Some animals convert ammonia to a less toxic form (either urea or uric acid) that can remain in the body for a longer period of time.
95
New cards
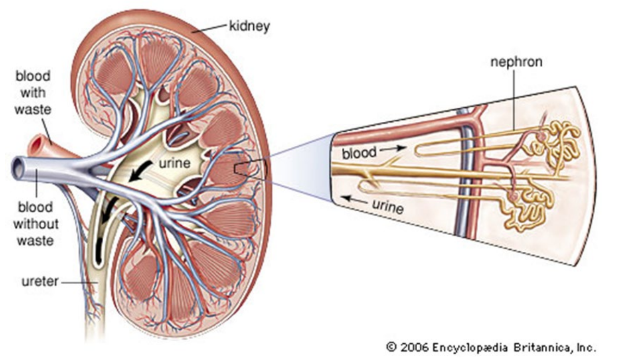
Internal kidney structure
The functional unit of the kidney is the nephron.
* The striated appearance of the kidney tissue is due to the alignment of the nephrons.
Each kidney contains more than 1 million nephrons.
* They are selective filters, which regulate blood composition and pH, and excrete wastes and toxins.
* The striated appearance of the kidney tissue is due to the alignment of the nephrons.
Each kidney contains more than 1 million nephrons.
* They are selective filters, which regulate blood composition and pH, and excrete wastes and toxins.
96
New cards
The nephron
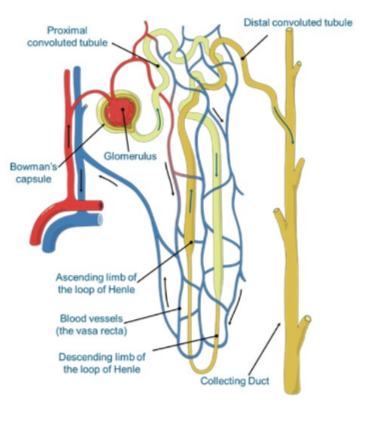
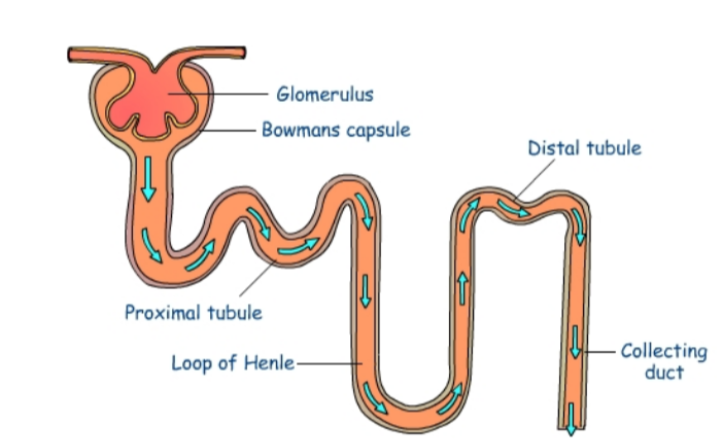
Filtrate flows from the glomerulus through the tubules that make up the rest of the nephron in this order:
* Proximal convoluted tubule
* Loop of Henle
* Distal convoluted tubule
* Collecting duct
Water and solutes are reabsorbed into surrounding blood vessels (vasa recta). The remaining filtrate flows into the collecting duct and leaves the kidney via the ureters.
* Proximal convoluted tubule
* Loop of Henle
* Distal convoluted tubule
* Collecting duct
Water and solutes are reabsorbed into surrounding blood vessels (vasa recta). The remaining filtrate flows into the collecting duct and leaves the kidney via the ureters.
97
New cards
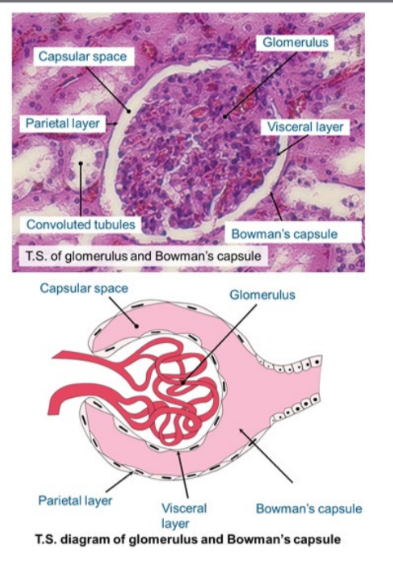
Bowman’s capsule + glomerulus
The Bowman’s capsule is a double- walled cup, lying in the cortex of the kidney and forms the start of the nephron.
* It encloses a capillary network called the glomerulus.
* It encloses a capillary network called the glomerulus.
98
New cards
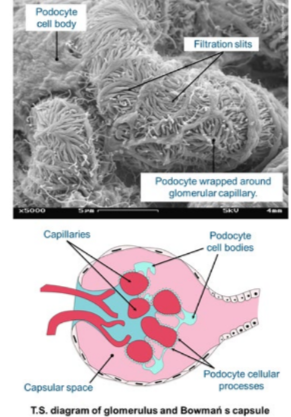
Podocytes
The Bowman’s capsule comprises specialized epithelial cells called podocytes.
The plasma filtrate passes through the filtration slits between them, but large molecules such as plasma proteins and blood cells remain in the capillaries.
The plasma filtrate passes through the filtration slits between them, but large molecules such as plasma proteins and blood cells remain in the capillaries.
99
New cards
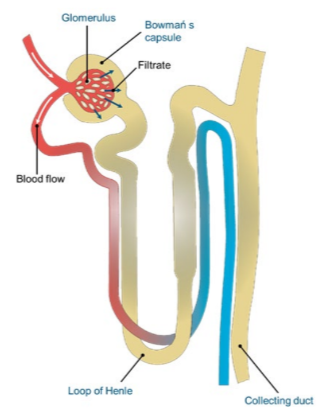
Filtration
The passage of water and solutes into the nephron and the formation of the glomerular filtrate depends on the pressure of the blood entering the afferent arteriole.
* This process is so precisely regulated that, in spite of fluctuations in arteriolar pressure, glomerular filtration rate per day stays constant.
* This process is so precisely regulated that, in spite of fluctuations in arteriolar pressure, glomerular filtration rate per day stays constant.
100
New cards
Proximal convoluted tubule
Water and bicarbonate is passively reabsorbed
Glucose, amino acids, Na+ and Cl- (NaCl) are actively reabsorbed
H+ is actively secreted into the tubule
K+ may be passively reabsorbed
Glucose, amino acids, Na+ and Cl- (NaCl) are actively reabsorbed
H+ is actively secreted into the tubule
K+ may be passively reabsorbed