3.2.4 Properties of Period 3 elements and their oxides
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is the equation for the reaction between Na and water? What is observed?
2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
Na fizzes on the surface of water and burns with a yellow flame
What is the reaction between Mg and water?
What is the observation?
Mg(s) + H2O(l) → Mg(OH)2(s) + H2(g)
Reacts very slowly with water forming a few bubbles
What is the reaction between Mg and steam?
What is the observation?
Mg(s) + H2O(g) → MgO(s) + H2(g)
Burns with white flame to form white powder
Why do metal oxides have ionic bonding?
Large difference in electronegativity
What is the reaction between Na and oxygen?
What is observed?
Explain the melting point of the product
4Na(s) +O2(g) → 2Na2O(s)
Na burns with a yellow flame to give a white solid
Na2O has a high MP because it has an ionic lattice structure and a large amount of energy is required to break the strong electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a lattice
What is the reaction between Mg and oxygen?
What is observed?
Explain the melting point of the product
2Mg(s) +O2(g) → 2MgO(s)
Burns with bright white flame giving white fumes and a white solid
MgO has a high MP because it has an ionic lattice structure and a large amount of energy is required to break the strong electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a lattice
Why does MgO have a higher melting point than Na2O?
Mg2+ ions are smaller and have a greater charge than Na+ therefore Mg2+ has a larger charge density, attracting the O2- ion more strongly
What is the reaction between Al and oxygen?
What is observed?
Explain the melting point of the product
2Al(s) + 1.5O2(g) → Al2O3(s)
Burns with white flame to give a white solid
High MP because it is ionic with covalent character and a large amount of energy is required to break the strong electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a lattice
Why do non-metal oxides have covalent bonding?
Small difference in electronegativity
What is the reaction between Si and oxygen?
What is observed?
Explain the melting point of the product
Si(s) + O2(g) → SiO2(s)
Burns with white flame to give a white solid
High MP because it has a giant covalent structure and a large amount of energy is required to break the many strong covalent bonds that hold the lattice together
What is the reaction between P and oxygen?
What is observed?
Explain the melting point of the product
P4(s) + 5O2(g) → P4O10(s)
Burns with white flame to give a white solid (white phosphorous spontaneously ignites in air)
Low MP because it has a simple molecular structure and little energy is required to break weak Van der Waals forces of attraction between the molecules
Why does P4O10 have a higher melting point than SO2 and SO3?
P4O10 is larger and has more electrons than SO2 and SO3 therefore has stronger Van der Waals forces between the molecules
What is the reaction between S and oxygen?
What is observed?
Explain the melting points of the products (which is higher than the other and why?)
1/8S8(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g) burns with blue flame giving a pungent gas
or 1/8S8(s) + 1.5O2(g) → SO3(l)
Low MPs because they have simple molecular structures and little energy is required to break the weak Van der Waals forces of attraction between the molecules
SO3 has a higher MP than SO2 because it is larger so has more electrons therefore stronger VdW forces between the molecules
Why are metal oxides basic?
They contain the oxide ion O2-
Reaction with water: O2-(aq) + H2O(l) → 2OH-(aq)
Reaction with an acid: O2-(aq) + H+(aq) → OH-(aq)
What is the reaction between Na2O and water?
What is observed?
What is the pH of the solution formed?
Na2O(s) + H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq)
White solid dissolves in a highly exothermic reaction, giving a colourless solution
14 (strong base which fully dissociates NaOH(aq) → Na+(aq) + OH-(aq))
What is the reaction between MgO and water?
What is observed?
What is the pH of the solution formed?
MgO(s) + H2O(l) ⇌ Mg(OH)2(s)
MgO is a sparingly soluble white solid
9 (weak base which partially dissociates Mg(OH)2 (aq) ⇌ Mg2+ (aq) + 2OH- (aq))
Why is Al2O3 insoluble in water?
What is the pH of the solution formed?
Lattice enthalpy is much greater than the hydration enthalpy (due to polarising nature of Al3+ ions, Al2O3 has covalent character in addition to its ionic attraction) therefore enthalpy of solution is very positive and water cannot supply enough energy to break the ionic lattice
7
Are non-metal oxides acidic or basic?
Acidic
Why is SiO2 insoluble in water?
What is the pH of the solution formed?
It has a giant covalent structure so atoms in the lattice are linked by many strong covalent bonds. Bond enthalpy is much greater than the hydration enthalpy therefore enthalpy of solution is very positive and water cannot supply enough energy to break the covalent bonds
7
What is the reaction between P4O10 and water? inc. ionic equation
What is observed?
What is the pH of the solution formed?
What is the structure of the acid and the anion formed?
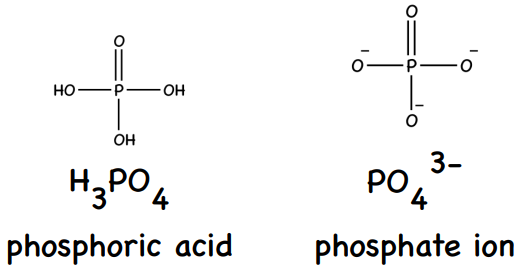
P4O10(s) + 6H2O(l) --> 4H3PO4(aq)
P4O10(s) + 6H2O(l) → 12H+(aq) + 4PO43-(aq)
White solid dissolves in a highly exothermic reaction to give a colourless solution
0 (strong acid which fully dissociates H3PO4(aq) --> 3H+(aq) + PO43-(aq))
What is the reaction between SO2 and water? inc. ionic equation
What is observed?
What is the pH of the solution formed?
What is the structure of the acid and the anion formed?
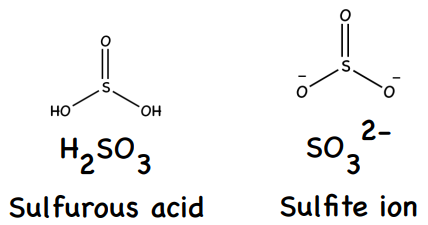
SO2(g) + H2O(l) → H2SO3(aq)
SO2(g) + H2O(l) → 2H+ + SO32-(aq)
Colourless gas dissolves and reacts to give a colourless solution
3 (weak acid which partially dissociates H2SO3(aq) ⇌ 2H+(aq) + SO32-(aq))
What is the reaction between SO3 and water? inc. ionic equation
What is observed?
What is the pH of the solution formed?
What is the structure of the acid and the anion formed?
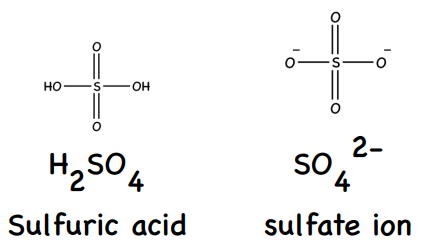
SO3(l) + H2O(l) → H2SO4(aq)
SO3(l) + H2O(l) → 2H+(aq) + SO42-(aq)
Colourless liquid dissolves and reacts vigorously to give a colourless solution
0 (strong acid which fully dissociates H2SO4(aq) → 2H+(aq) + SO42-(aq))
Why is H2SO3 a weaker acid than H2SO4?
SO32- is not as stable as SO42- so the equilibrium lies further to the LHS, therefore higher pH (fewer H+ ions)
How does a salt form between an acid and base?
Base produces the positive ion and acid produces the negative ion
How do the basic oxides react with acids?
Metal oxides
Na2O produces Na+
MgO produces Mg2+
Al2O3 produces Al3+ (amphoteric- reacts with both acids and bases)
How do the acidic oxides react with bases?
Non-metal oxides
Al2O3 produces [Al(OH)4]- (amphoteric- reacts with both acids and bases)
SiO2 produces SiO32-
P4O10 produces PO43-
SO2 produces SO32-
SO3 produces SO42-