EESA06 Topic 6: Earth Materials and Geologic Time
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
define strata
layers of rock, particulary sedimentary, that form in basins
i.e., sediments layered on top of each other
define stratigraphy
identifying which layers of sedimentary are layered and what they tell us about Earth’s history

what is the “basement” of the Grand Canyon made of?
Precambrian metamorphic and igneous rock
what does brittle failure of rock form?
faults
what are some types of faults?
normal
reversed
strike slip
what does plastic deformation of rocks form?
folds
what are dome types of folds?
synclines
anticline
what is a parent isotope? give an example.
unstable radioactive isotope that undergoes radioactive decay and transforms into a more stable isotope called a daughter isotope
e.g., U238 → Pb
what is subsidence?
when land depresses/goes down
contrasts with uplift
what is uplift?
when land goes up
contrasts with subsidence
how does subsidence relate to the formation of strata?
basins accommodate strate when they deepen (i.e., when subsidence of crust occcurs
what is conformable succession of strata?
constant subsidence → constant settling of sediment
best opportunity to track Earth’s history
how long does conformable succession occur?
as long as the surface stays below the base level of erosion (usually sea level)
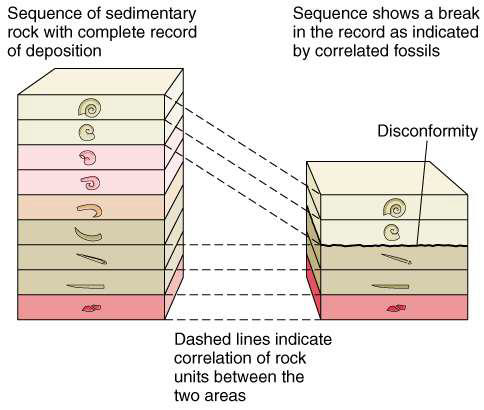
what are disconformities?
pauses in sedimentation within an otherwise conformable succession of strata
what are unconformities?
marks of longer episodes of uplift, erosion, and non-deposition
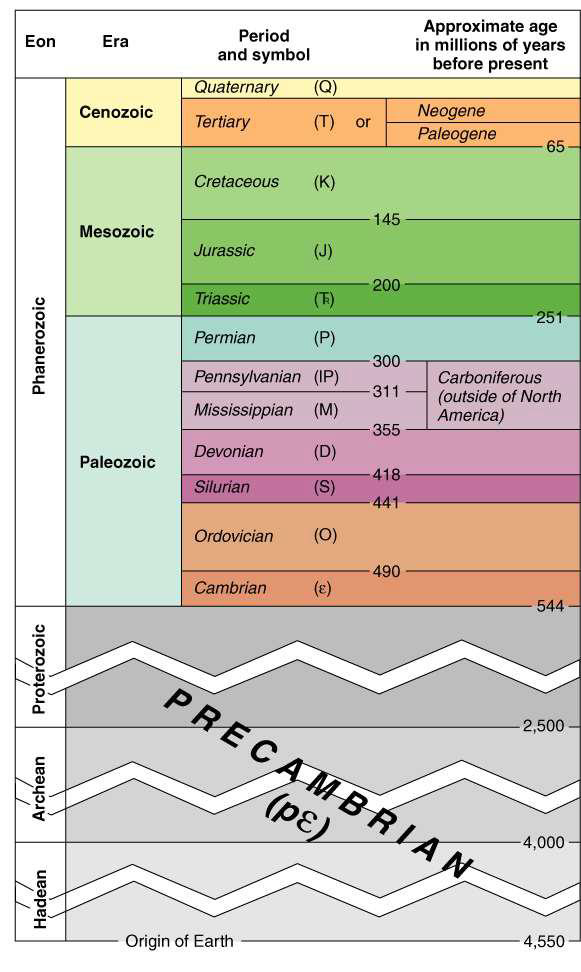
what is the law of superposition and what does it tell us about the Earth?
oldest rocks are at the bottom; strata gets younger as you move upwards
tells the relative age of strata
what are index fossils?
fossils of organisms that exist at very specific points in Earth’s history
describe index fossils
short lived - went extinct at the same time
evolve rapidly - i.e., species indicate specific time
what are examples of index fossils?
trilobite
ammonites
crinoid
why are index fossils useful?
evolve rapidly
widespread
i.e., they’ll clearly indicate what period they’re from
how can disconformities be identified?
index fossils
correlative layers (e.g., ash)
what do correlative layers (e.g., ash) allow us to do?
correlate across long distances and gaps
what methods can be used to do correlation?
biostratigraphy
lithostratigraphy
chronostratigraphy
describe biostratigraphy
using fossils to establish the relative ages of rocks and correlate successions of sedimentary rocks
describe lithostratigraphy
mapping rock types
classification of rock bodies based on their observable lithological properties and their relative stratigraphic positions
what are examples of lithological properties?
rock type
texture
color
describe chronostratigraphy
the branch of stratigraphy that studies the ages of rock strata in relation to time
what are fossil assemblages?
a collection of fossils found in a geological setting
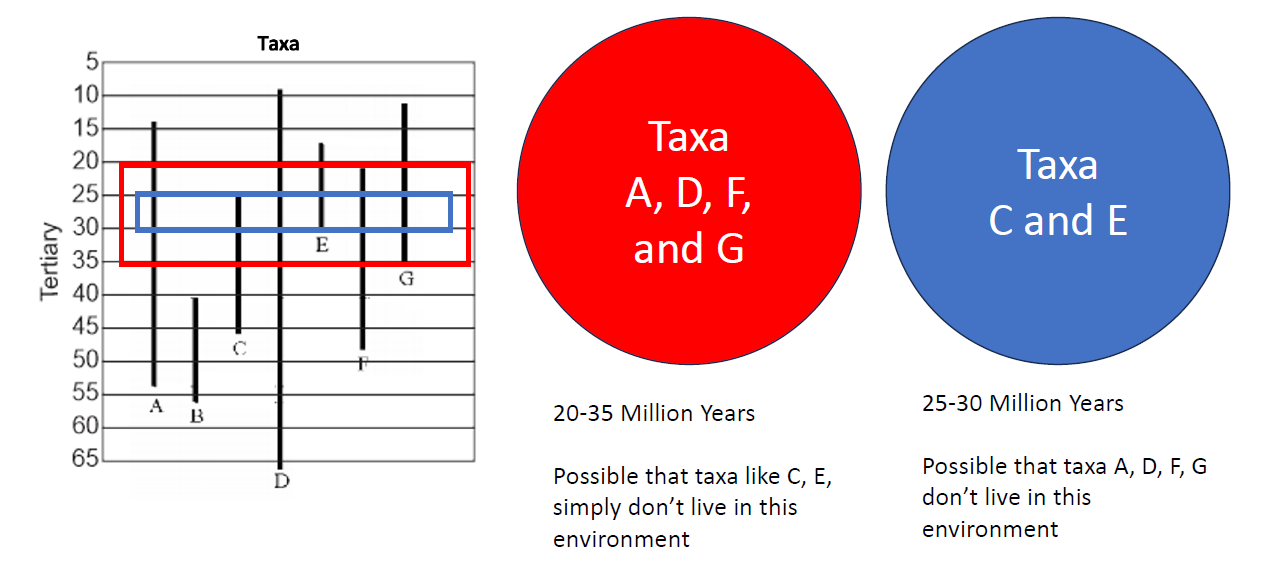
how can we narrow an age range of samples (e.g., strata)?
index fossils
fossil assemblages
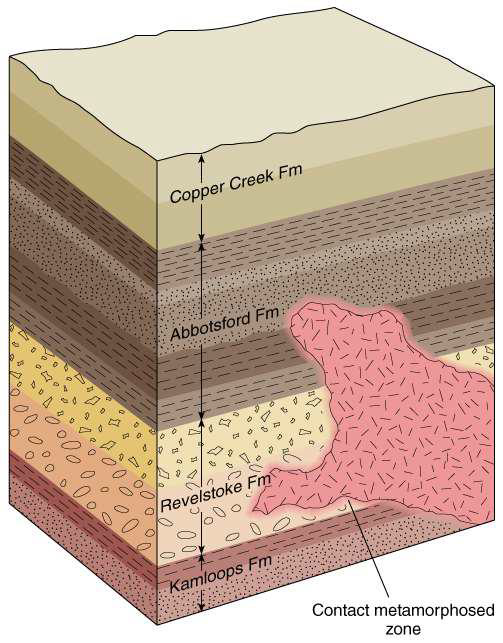
describe the law of cruss-cutting relations
if A cuts across B, then B must have existed before A
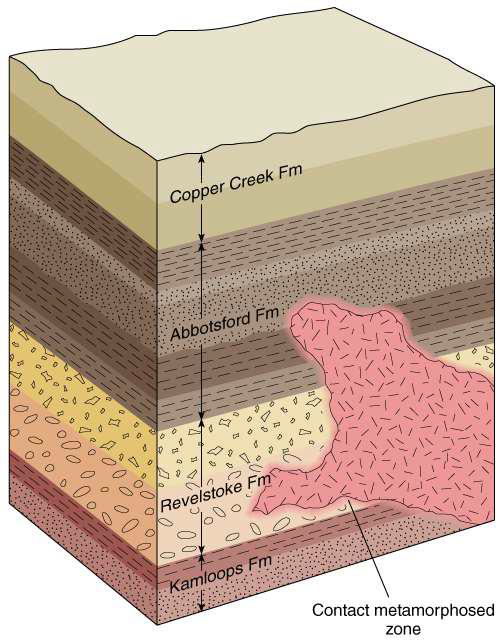
describe the law of intrusions
you can tell if A has intruded into B, therefore A must succeed B
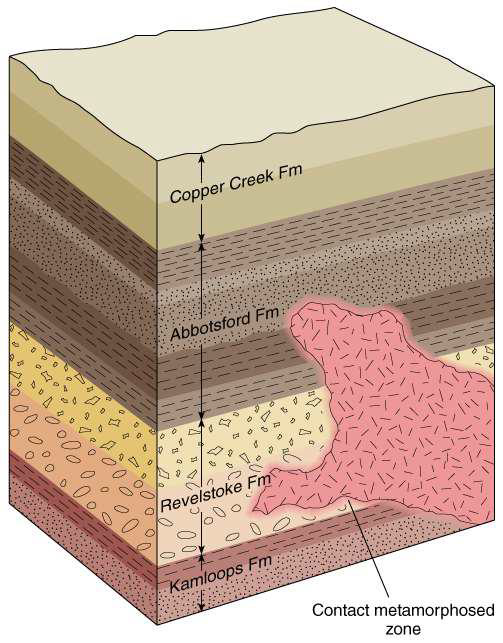
what could granitic plutons tell us about the tectonic environment?
granite plutons are common in orogenic zones and magmatic arcs
granite plutons indicate that the rock formation was in these tectonic situations
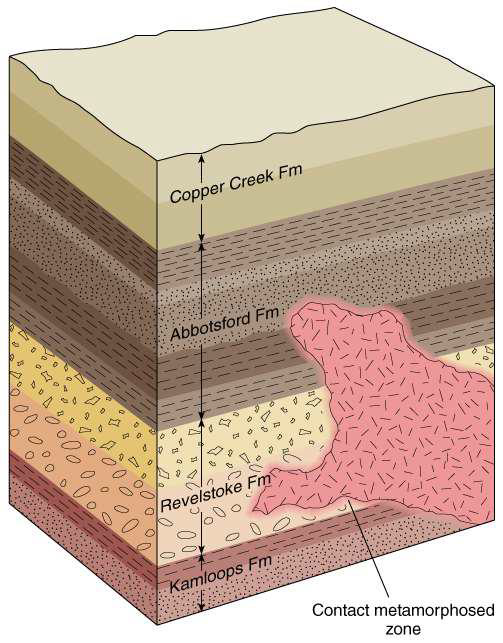
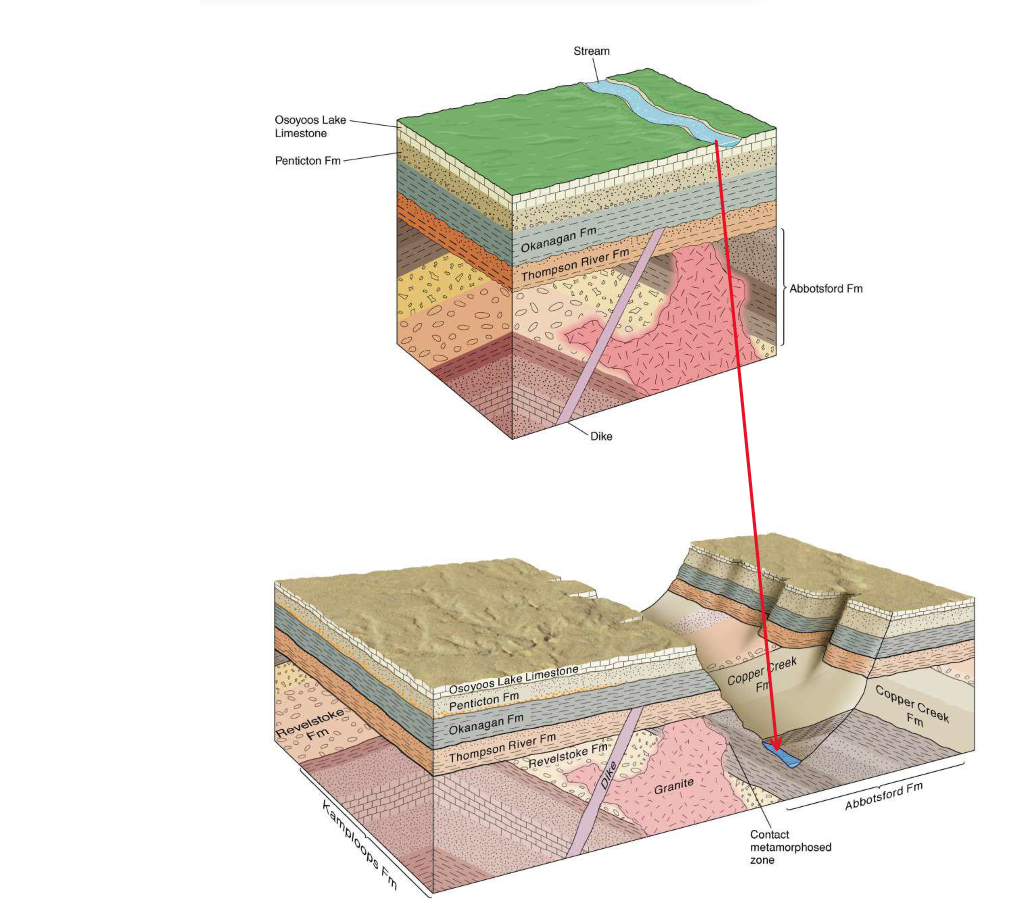
what is the contact metamophosed zone?
the area immediately adjacent to igneous intrusions
what is the law of original horizontality?
strata are originally horizontal
deviations like tilting are due to later structural changes
what are some deviations of the law of original horizontality?
folding
faulting
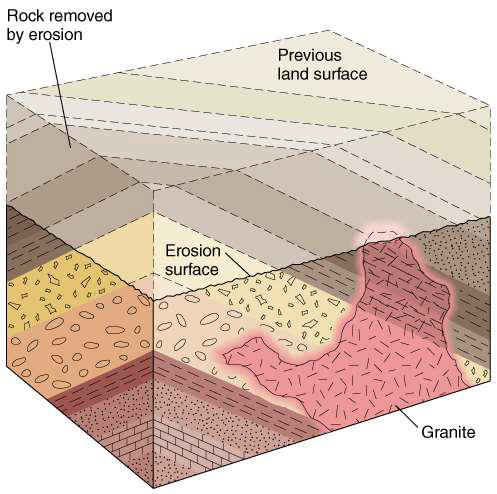
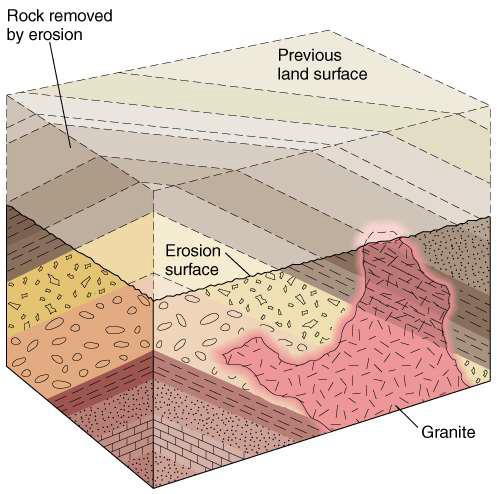
what does the presence of erosion surface indicate?
indicates that the rock formation has been uplifed
what do the presence of tilting, uplifting, and erosion indicate?
tectonic collisions
what do tectonic collisions lead to?
unconformities
i.e., not disconformities
describe the law of lateral continuity
strata originally continued laterally until the edge of the basin
if strata are interrupted laterally, some event has to have cause that
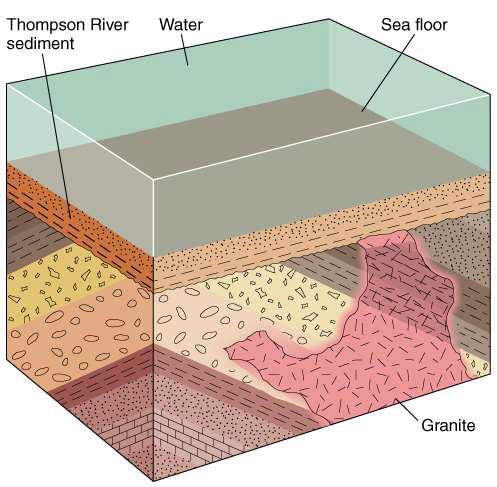
what might lead to deviations in the law of lateral continuity?
erosion
faulting
intrusion
etc.
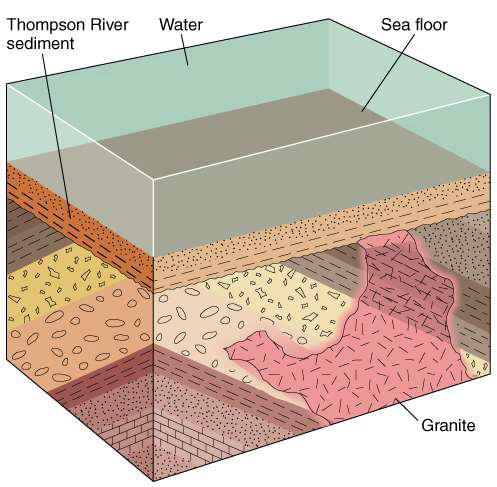
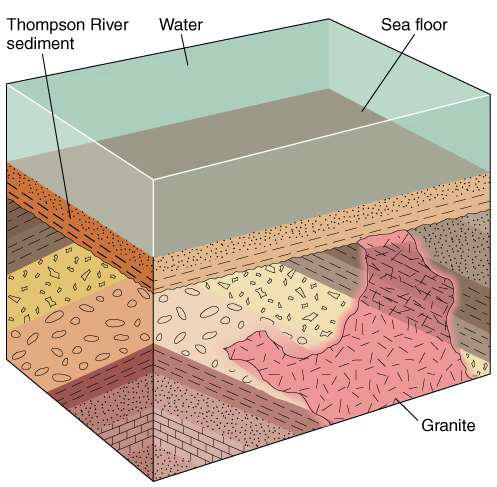
what does the presence of lateral layers above diagonal layers in this diagram indicate?
indicates subsidence and deposition of of new layers
describe the law of cross cutting relations (i.e., the law of intrusions)
something that cuts across some other feature is younger
e.g., the dike is the youngest
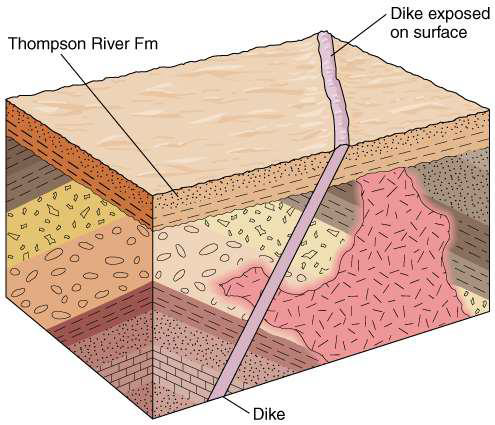
describe the law of inclusions
any rock fragments that are included in a rock must be older than the rock in which they are included
how can cross cutting relationships and the law of inclusions help establish a chronology?
you can use relative dating to determine which materials are older than others based on what the intrusion goes through
conglomerates must have formed after intrusions in order for the intrusion to be included in the conglomerate
how is a canyon created?
uplift of a stream
stream will continue to “carve” downwards until it meets the erosion erosion surface
what is structural geology interested in?
how rocks are…
folded
faulted
fractured
oriented
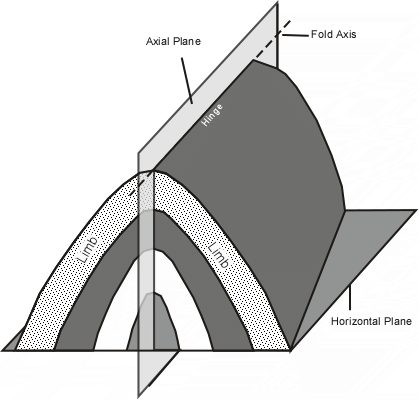
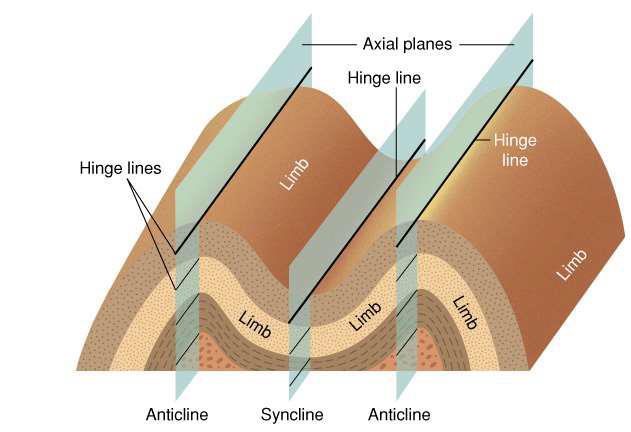
what are folds?
ductile wrinkling of rock layers
what are faults?
brittle breaks across which rock slides
what are fractures?
cracks or breaks in rocks where there has been little to no movement
i.e., faults with no movement
what are anticlines?
folding upwards
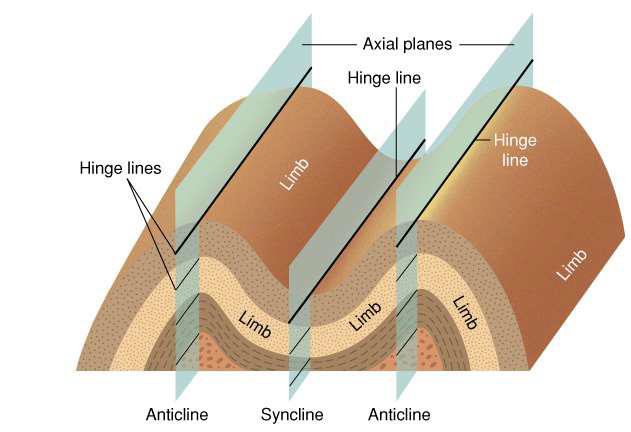
what are synclines?
folding downwards
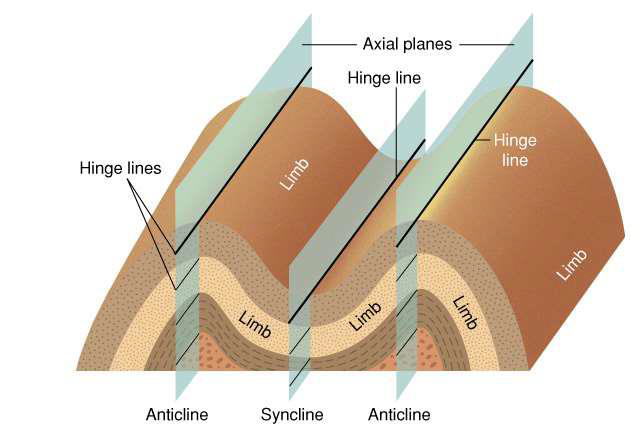
why are anticlines useful?
trap lightweight migrating fluids squeezed from rocks (e.g., hydrocarbons)
often sought when looking for oil
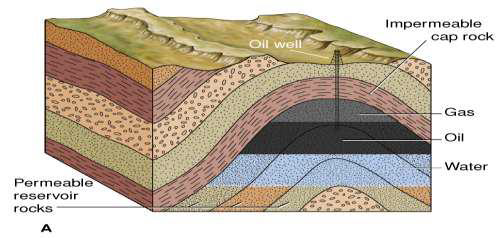
where does folding happen and why?
mostly 10+ km below ground
rock is more ductile
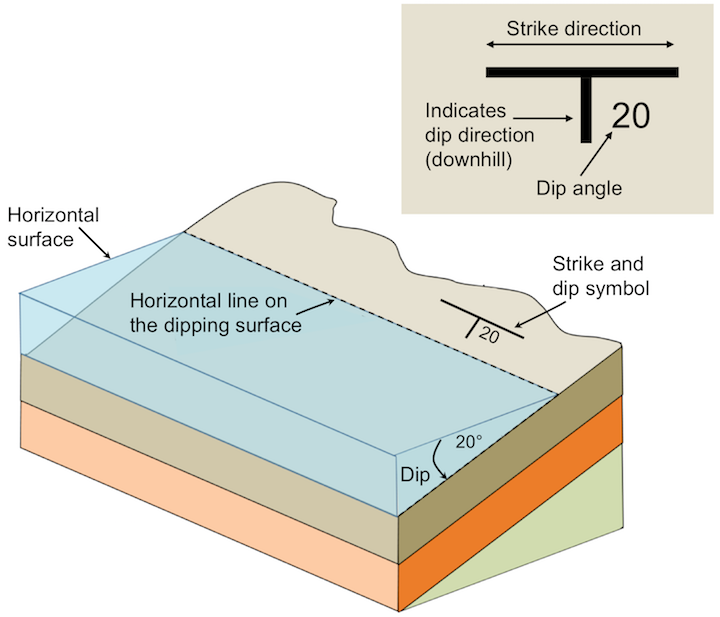
what is the dip of a layer?
how “far away” from flat
i.e., tilt
doesn’t tell much about orientation
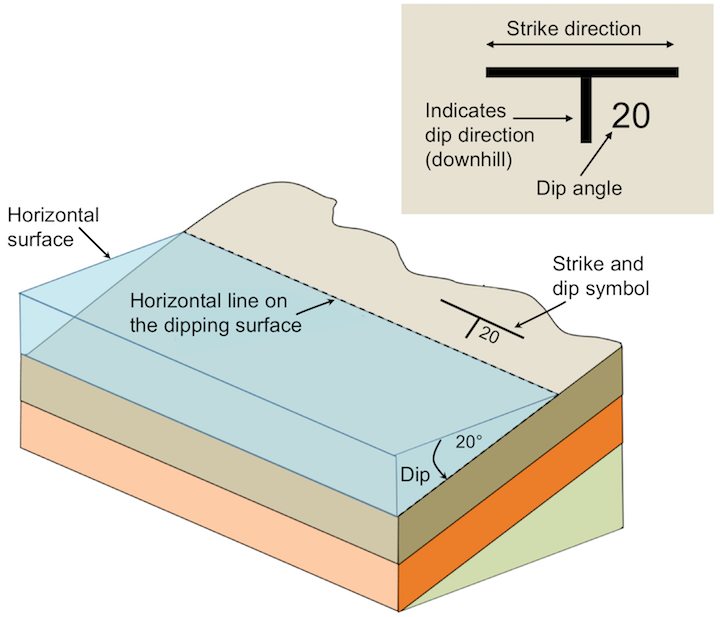
what is the strike of a layer?
measures orientation
the intersection of a horizontal plane and an inclined surface
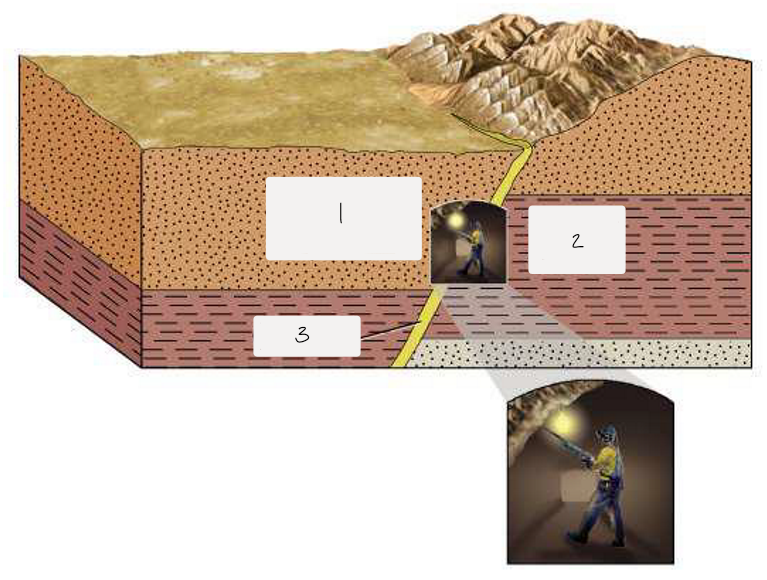
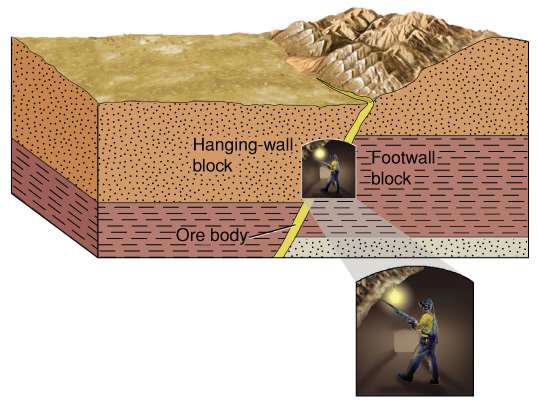
what are the elements of this diagram? describe each.
hanging-wall block - block of rock above the fault plane
moves down relative to footwall in normal fault
moves up relative to footwall in reverse fault
footwall block - block of rock below the fault plane
where miners are positioned
ore body - ore deposits
often form along faults because the fractures create pathways for mineral-rich fluids
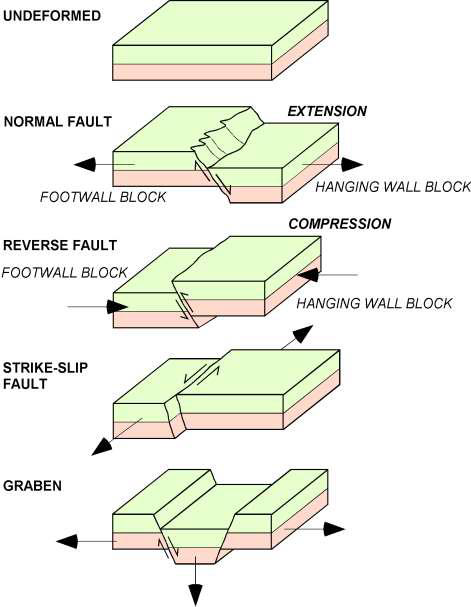
list the different types of faults
normal fault
reverse fault
strike-slip fault
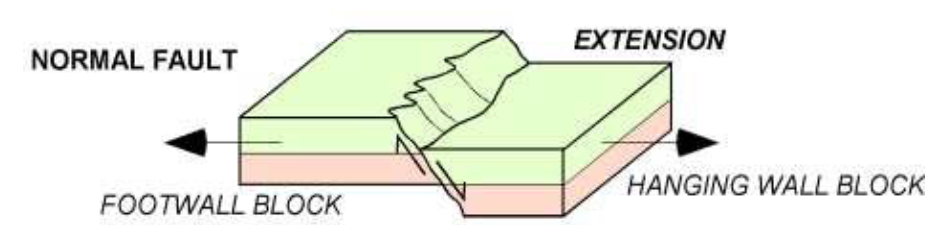
describe a normal fault
slippage involving extension
footwall block moves up
hanging wall moves down
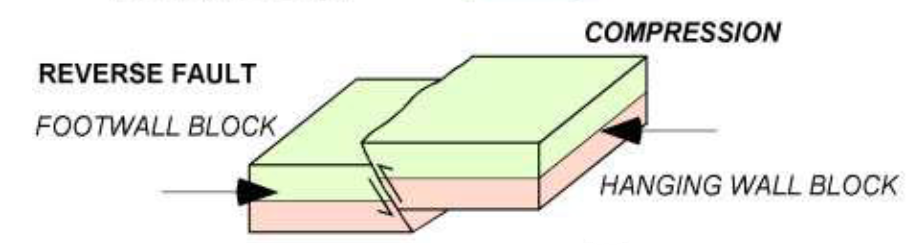
describe a reverse fault
“thrust fault”
hanging wall block pushed up relative to footwall block
compression of 2 blocks
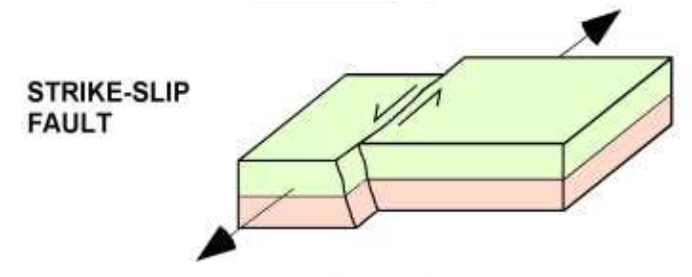
what is an example of strike-slip faults
transform margins
e.g., San Andreas Fault
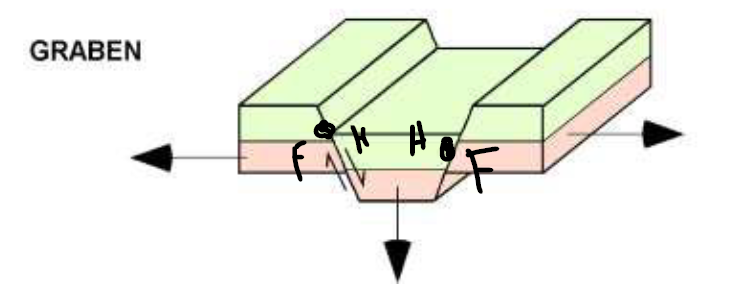
describe grabens
the hanging wall block drops down between 2 footwall blocks
what is the oldest know geological map?
Ancient Engyptian
looked for quartz veins to find gold
for Ramesses IV

what role did the Industrial Revolution (1790-1820) have in mineral extraction?
increased demand for
resources - e.g., coal
geologists
describe the No Coal Problem
1840 - Province of Canada
there was a growing domestic market based on manufacturing
no coal to power it
who was William Logan?
provincial geologist
first director of the Geologic Survey of Canada (GSC)

what resource was rich in the Province of Canada? was this resource useful?
oil shale (Georgian Bay)
poor substitute for coal
describe the significance of Petrolia’s resources
first “oil boom” in North America (1861)
free-flowing oil
how old did Archbishop Usher (1581-1656) suggest Earth was? on what did he base this calculation?
~ 6000 years
Earth formed at 9am on OCt 26, 4004 BC
based on counting generations in the Bible
what was James Hutton’s (1726-1797) contribution to modern geology?
proposed uniformatarianism
i.e., past is key to present
believed there was not point to aging the Earth
recognized
unconformities within rock layers
igneous origin of granite
what ideas/people did James Hutton (1726-1797) come in conflict with?
Diluvialism
Catastrophism
i.e., with people like Abram Werner
define diluvialism
specific surface features provided evidence of a worldwide flood which had followed earlier geological eras
define catastrophism
changes in the earth's crust during geological history have resulted chiefly from sudden violent and unusual events
define creationism
belief that the universe, Earth, life, and humans originated through supernatural acts of divine creation
define uniformatatianism
theory that changes in the earth's crust during geological history have resulted from the action of continuous and uniform processes
define evolution
the process by which living organisms change over time through changes in the genome
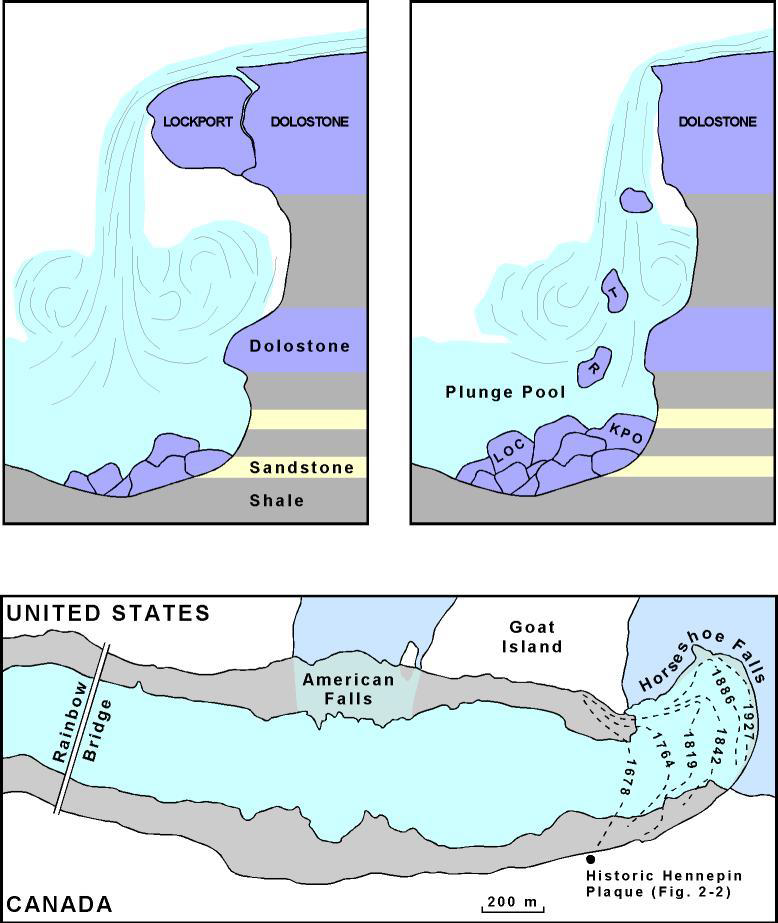
how many years did Charles Lyell (1830) estimate was needed to carve the Niagara Gorge? why?
at least 12 000
total erosion: 12 km
rate of erosion: 1m/year (before stabilization measures)
how old did William Tohmson, Lord Kelvin (1824-1907) suggest Earth was? on what did he base this calculation?
24-40 million years
based on: cooling rate of molten Earth through
conduction
radiation
NOTE: he didn’t know about the structure of the Earth, mantle convection, and radiation of minerals

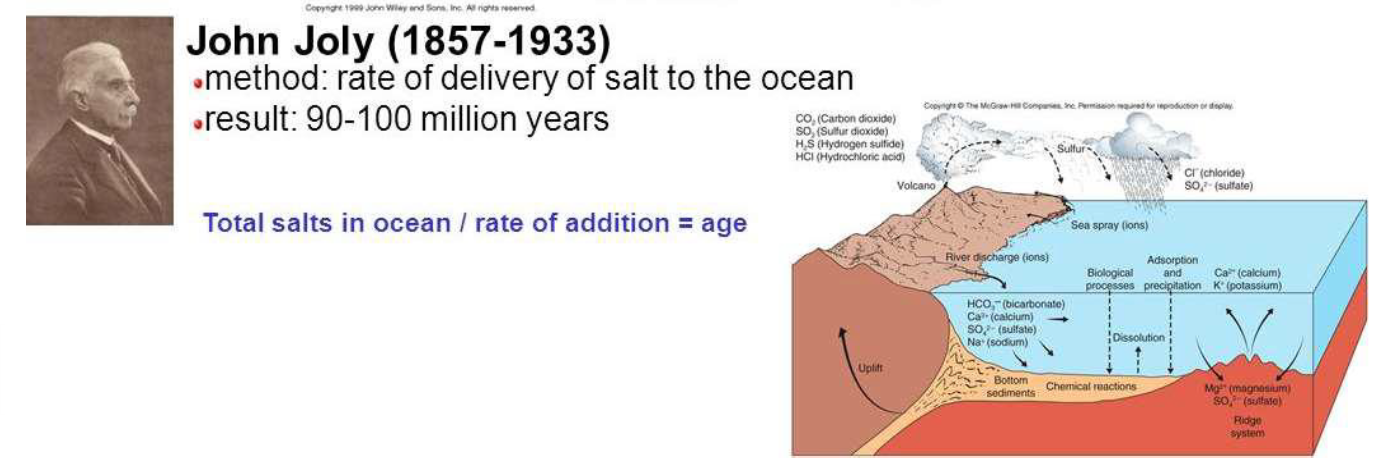
how old did John Joly (1857-1933) suggest Earth was? on what did he base this calculation?
90-100 million years
based on: rate of delivery of salt to the ocean
total salts in ocean / rate of addition = age
how did Arthur Holmes (1890-1965) contribute to contribute to calculating Earth’s age?
pioneered absolute dating/radiometric dating
published The Age of the Earth (1913)
what is an isotope?
different versions of an element having
same number of protons
different number of neutrons
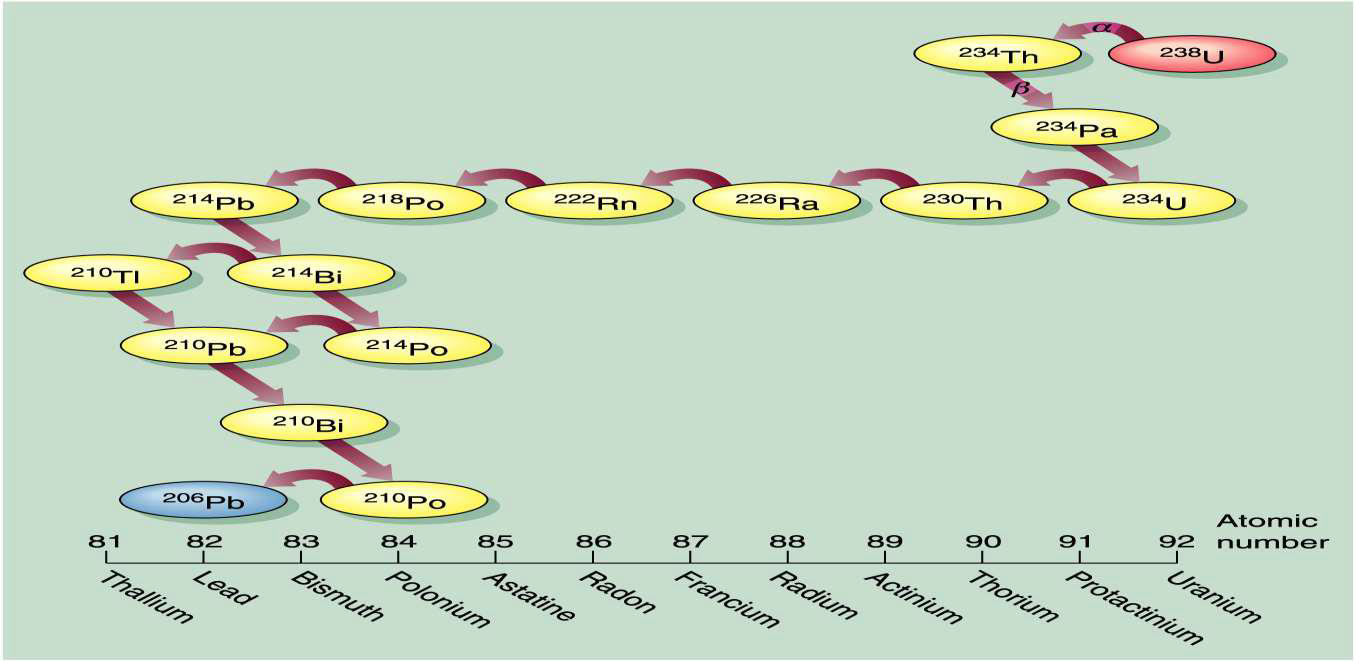
describe radioactive decay
unstable isotopes breakdown in various ways
e.g., losing protons and neutrons
produces daughter products with different atomic numbers
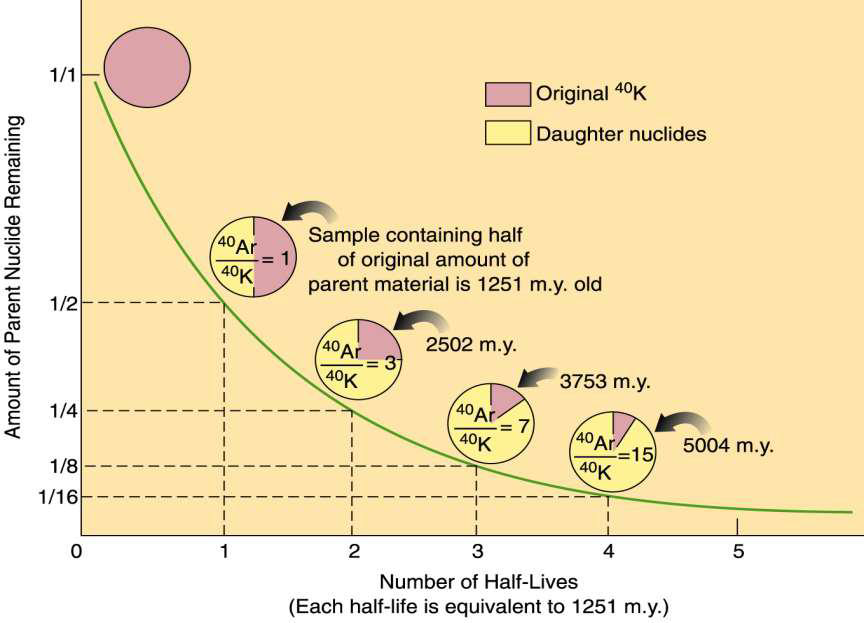
define half-life
time needed to reduce the original amount of a radioactive isotope by half
result of radioactive decay
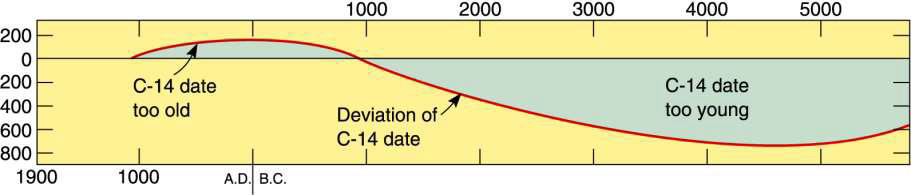
describe radiocarbon age dating
used to date organic material 75 000 years/75 ka
corrections needed for
changing solar flux
amount of C-14 in the atmosphere
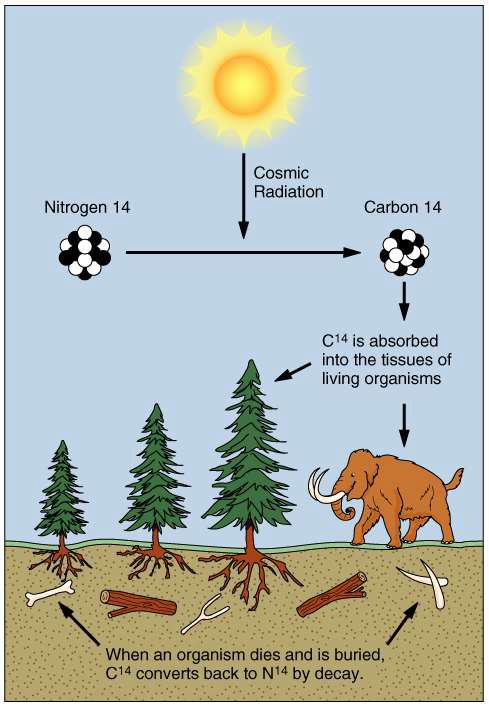
why is there a limit to radiocarbon age dating?
75 ka limit
because C-14 has a relatively short half-life
what is the oldest rock in Canada?
Acasta gneiss from NW Territories
4 billion years
what is the purpose of relative dating over radiometric dating?
not all rocks lend themselves to radiometric dating
what is the geologic column?
diagram that represents the sequence of rock formations and their relationship to geologic time
oldest rocks at the bottom and youngest at the top
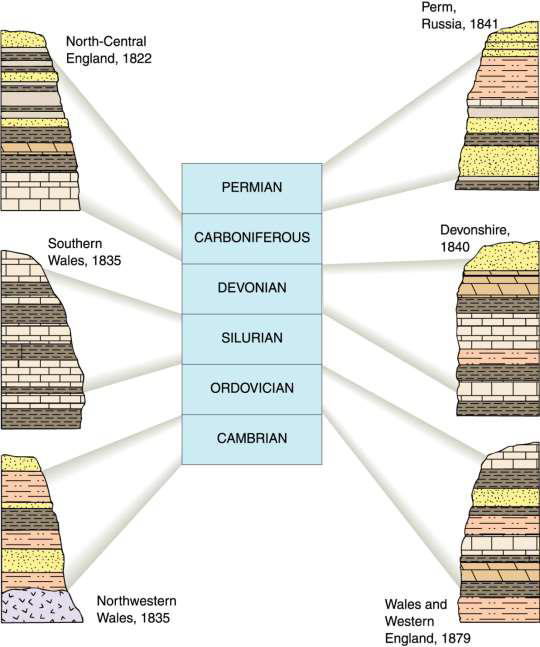
how was the geologic column put together?
from sites around the world
based on relative ages established from fossils
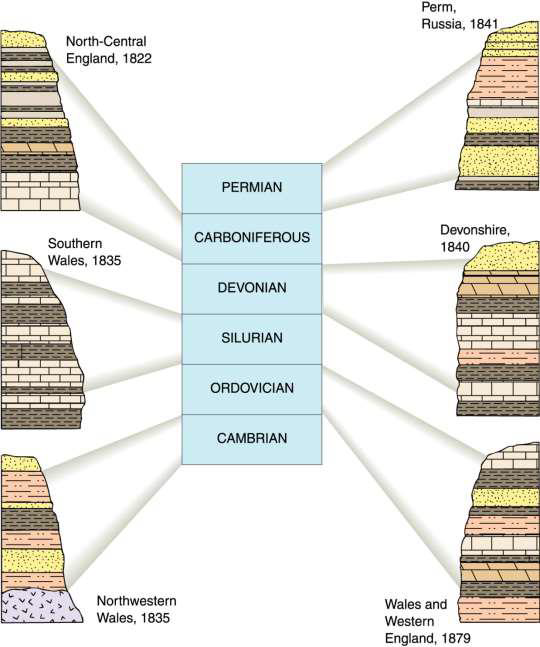
what are golden spike?
places that mark an agreed upon age boundary

what is the proportion of Precambrian and Phanerozoic time on the Geologic Time Scale?
87% Precambrain
13% Phanerozoic