Chapter 5- Electrons and Bonding
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
what is the maximum number of electrons that can fill the first four shells?
2, 8, 18, 32
what is an atomic orbital?
a region around the nucleus that can hold up to 2 electrons with opposite spins
what are the different types of orbitals?
s
p
d
f
how many electrons can an s-subshell hold?
2 electrons
how many electrons can a p-subshell hold?
6 electrons
how many electrons can a d-subshell hold?
10 electrons
shape of the different orbitals?
s orbital- spherical (one occurs in every principal energy level)
p orbital- dumb bell ( 3 ocur in energy levels except the first)
d orbital- various ( 5 occur in energy levels except the first and second)
f orbital- various
how does the energy of the orbitals increase?
it increases from s to p to d
meaning the orbitals are filled in this order
what are the three rules for writing out electron configurations?
the lowest energy orbital is filled first
for orbitals with the same energy, electrons occupy orbitals singly with the same spin before pairing begins
no single orbital holds more than 2 electrons
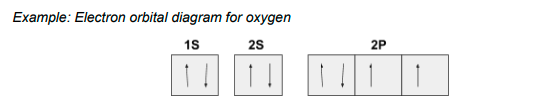
within an orbital, how do electrons pair up?
they pair up with the opposite spin so that the atom is as stable as possible
electrons in the same orbital must have opposite spins
the spins are represented by opposite arrows
number of orbitals that s,p and d subshells contain?
s subshell- 1 orbital
p subshell- 3 orbitals
d subshell- 5 orbitals
order of orbitals?
1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 4d, 4f
how to determine what block an element is is?
by what orbital receives its valence electrons
why is electron configuration an example of a periodic trend?
elements in the same group have the same number of electrons in their outer shell or subshell
same pattern or trend of filling the subshells is repeated in other periods
what is ionic bonding?
the electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions
how is a giant ionic lattice formed?
repeating pattern of oppositely charged ions
what is the relationship between charge of ion and strength of ionic bond formed?
ions with a greater charge will have a greater attraction to the other ions, resulting in stronger forces of attraction and therefore, stronger ionic bonding
do larger ions with a greater ionic radius have a weaker or stronger attraction to the oppositely charged ion?
weaker attraction because the attractive forces have to act over a greater distance
phsycial properties of ionic compounds?
high melting and boiling points because the electrostatic forces holding the ionic lattice together are strong and require a lot of energy to overcome
only conduct electricity in molten or aqueous solution because the ions separate and are no longer held in a lattice. the ions are free to move and carry a flow of charge
they are brittle materials- when the layers of alternating charges are distorted, like charges repel, breaking apart the lattice into fragments
tend to dissolve in polar solvents such as water
why do ionic compounds dissolve in polar solvents such as water?
the polar water molecules break down the lattice and surround each ion in solution
however, in a compound made of ions with large charges, the ionic attraction may be too strong for water to be able to break down the lattice structure
this causes the compound to not be very soluble
what two main processes does solubility require?
the ionic lattice must be broken down
water molecule must attract and surround the ions
what is covalent bonding?
the electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of electrons and 2 positive nuclei.
a covalent bond is the overlap of atomic orbitals, each containing one electron, to give a shared pair of electrons
what is a dative covalent bond?
a covalent bond in which the shared pair of electrons has been supplied by one of the bonding atoms only.
example of this is NH4
what is average bond enthalpy?
a measurement of covalent bond strength
the larger the value of the average bond enthalpy, the stronger the covalent bond
compare the bond enthalpies of single and triple covalent bonds?
single covalent bonds involve less shared electrons, and therefore have a weaker electrostatic attraction between the nuclei, as to why they have the weakest bond
why are triple bonds shorter than single bonds?
they have a greater number of shared electrons, meaning greater electrostatic pull between nuclei. this stronger pull causes nuclei to come closer together, making the bond shorter, but stronger