Biological Membranes
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
lipid
Membranes are complex _______- based structures that form pliable sheets
it's surroundings
All cell membranes separate the cell from ?
organelles
Eukaryotic cells have various internal membranes that divide the internal space into compartments known as...
1. define boundaries of the cell
2. allow for import and export of selective nutrients and waste
3. retain metabolites and ions within the cell
4. Sense external signal and transmit information into the cell
5. provide compartmentalization within the cell (seperate energy producing reactions from energy consuming ones)
6. produce and transmit nerve signals
7. store energy as a proton gradient
8. support synthesis of ATP
What are the 8 functions of membranes?
1. micelles
2. bilayers
3. liposomes
Lipids will aggregate into structures in water. What are three major structures that are observed?
1. type of lipid
2. concentration
The structure of the lipid formed in water depend on what two traits?
amphipathic
Micelle is formed in the solution of __________ molecules.
fatty acids and sodium dodecyl sulfate
Micelles have larger more polar heads than tails. What are the tails made of?
a few dozen to a few thousand
How many lipid molecules are micelles composed of?
two leaflets of lipid monolayers
The membrane bilayer consists of
phospholipid and sphingolipids
What two molecules will cause the spontaneous organization of a lipid bilayer?
spherical; concentration
Liposomes (vesicles) are small bilayers that will spontaneously seal into a ____________ vesicles in a ______________ dependent manner
These vesicles can be made in vitro and the central aqueous cavity can dissolve drugs or viruses which will allow it to go through the lipid membrane. The vesicle can then fuse with the membrane.
Why are micelles used as artificial carriers?
bimolecular sheets
Is bimolecular sheets or micelles favored in the formation of a lipid bilayer?
no they are asymmetric
Are membranes symmetric?
1. enzymes
2. gates
3. pumps
4. energy transducers
5. receptors
Membrane proteins serve as what 5 things?
Sphingolipids
Cholesterol
Phosphatidylcholine (PC)
What are the three main components of a membrane?
Phosphatidylcholine (PC)
What molecule is in promident amounts in different membrane types?
the amount of Phosphatidylcholine (PC) to cholesterol
The structure and fluidity of a membrane is mainly determined by ...
non-covalent
The interaction between lipids and proteins are
glycerol + two fatty acids + phosphorylated alcohol
What is a phosphoglyceride?
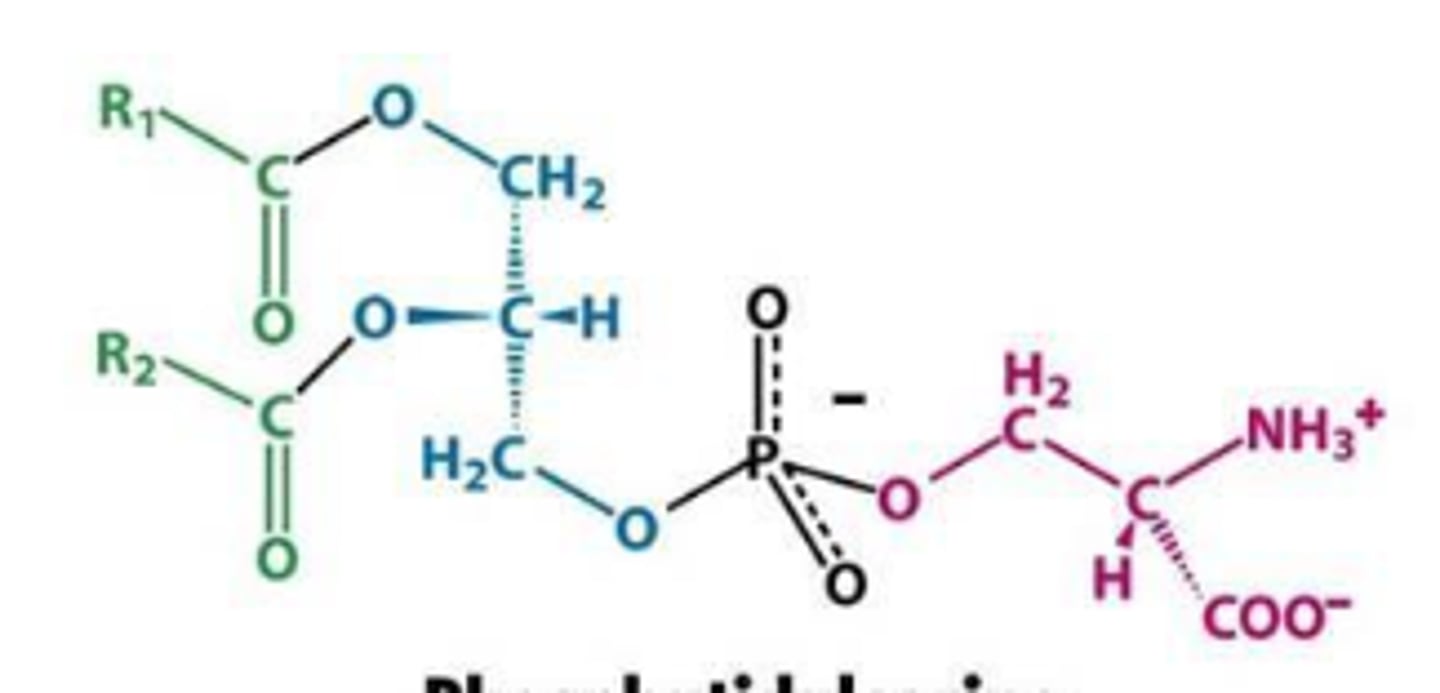
Phosphatidylserine
What is this phosphoglyceride?
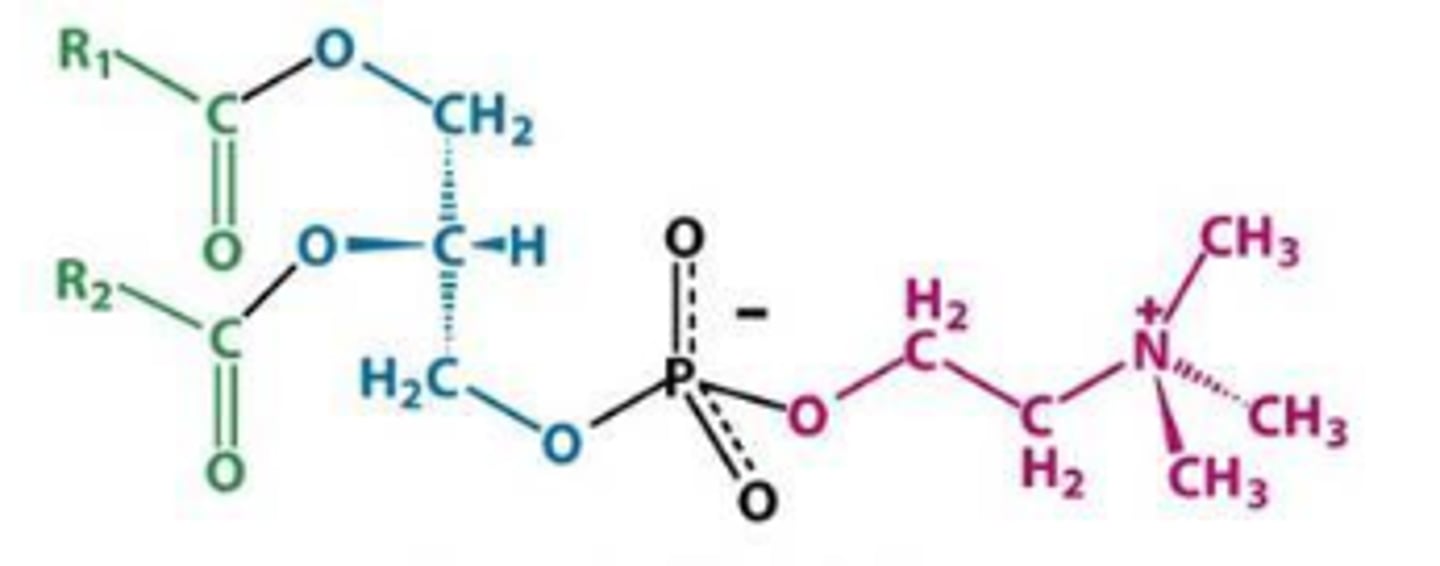
Phosphatidylcholine
What is this phosphoglyceride?
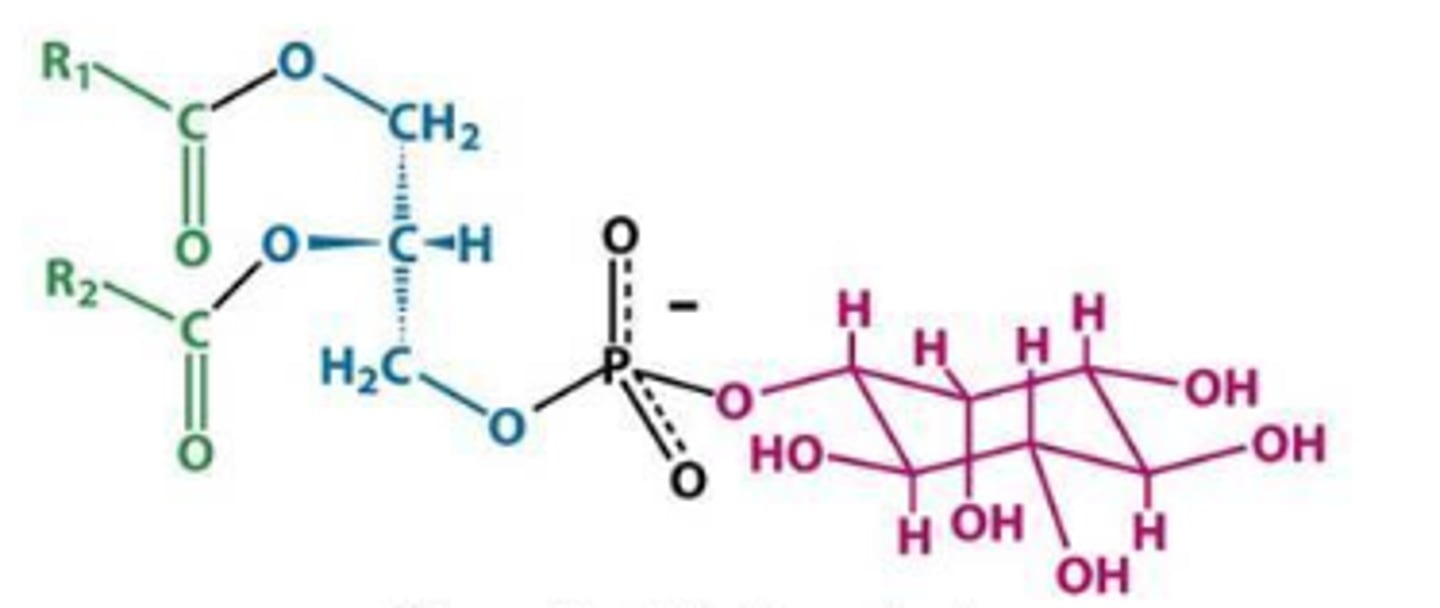
Phosphotidylinositol
What is this phosphoglyceride?
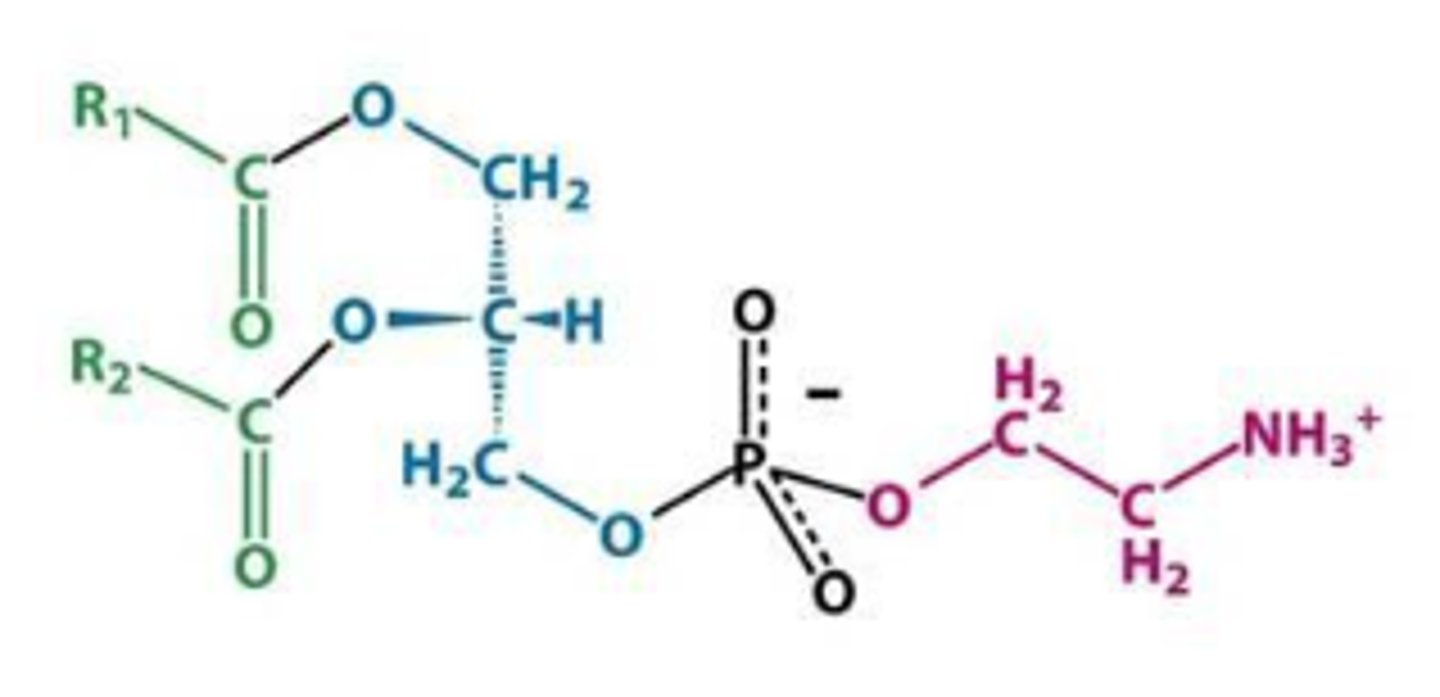
Phosphatidylethanolamine
What is this phosphoglyceride?
Sphingosine
What is sphingomyelin derived from?
triacylglycerol (no hydrophilic component)
What are the only neutral lipids?
ether bonds are more resistant to cleavage
What is the significance of ether bonds in lipids?
7
Up to how many sugars can be attached to glycolipids?
Sphingosine
Glycolipids are derived from?
covalently
Are glycolipids covalently bound or non-covalently bound to sugars?
The more fluid a membrane is the more cholesterol it has
the more rigid a membrane is the less cholesterol it has
How does cholesterol related to membrane fluidity?
ridig
when cholesterol is decreased it can cause muscles to become more
integral are firmly associated
peripheral are loosely associated
Describe the association to the membrane between integral proteins and peripheral protein
on the extracellular component
Where are carbohydrates located on the membrane?
yes via chemical treatment by piercing the membrane
Can permeability be increased?
yes - butter is a example of how membranes can undergo phase transitions
Can membranes exist in various phases and undergo phase transition?
ions ( K+, Na+, Cl-)
What molecules would need a channel to get through the membrane?
large uncharged polar molecules
What molecules would need a transporter to get through the membrane?
hydrophobic molecules
small uncharges polar molecules
What molecules can go through the membrane via simple diffusion?
SDS-PAGE electrophoresis
What technique can be used to analyze membrane proteins?
free- energy barrier
What prevents membrane proteins from rotating?
non-GPI linked can be dissociated from the membrane fairly easily during changes in ionic strength
GPI- linked proteins are linked to the membrane during specific regulatory events and can be reversibly removed
What is the difference between a non-GPI linked and GPI- linked peripheral protein?
in the presence of strong detergents
How would integral proteins be removed?
removed by disrupting ionic interactions either with high salt or pH changes
How are peripheral proteins removed?
any lipids
If the protein is purified then it is no longer associated with
amphitropic
GPI - linked proteins are also called
covalent
Amphitropic proteins are attached by what kinds of interactions with lipids/ carbohydrates?
attachment to, or cleavage from lipids
The biological regulation of amphitropic proteins result in
no different proteins for different domains
Are there all the same integral proteins throughout the membrane?
asymmetric ( like the membrane)
Are integral proteins symmetric or asymmetric?
phospholipids
Purified integral proteins still have ____________ attached.
how many times a protein spans the lipid bilayer
What does a hydropathy plot tell you?
~ 20 alpha helices
The transmembrane region consists of how many residues?
anion
___________ channels are formed by several transmembrane alpha- helices
Glycophorin high charge keep the RBC from adhering to the inside of the vessel wall and allow for it to move freely
Explain glycophorin's effect on red blood cells
120 days
What is the life span of RBC's?
outer:
phosphatidylcholine (PC), sphingomyelin (SM)
inner:
phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphoinositol (PI), phosphatidylserine (PS)
What are the components of the outer and inner membrane of RBC's?
bind extracellular matrix proteins to microfilaments of the cytoskeleton via intracellular attachment proteins
What do transmembrane linker proteins do?
diversity that aids in cell to cell interactions and cell-specific properties
The diversity of integrin heterodimers contribute to
extracellular divalent cations
What does the ligand binding to integrin depend on?
integrin to actin microfilaments
Binding sites of cytosolic intergin tail interacts with intracellular attachment proteins to link
secrete less fibronectin and increased migration and proliferation
What does cancer like cell secrete less of and how do they behave differently?
liquid ordered: gel phase- individual molecules do not move around
liquid disordered: fluid phase- individual molecules move around
Depending on the temperature and composition the membrane can be in a gel phase or fluid phase.
What is the difference between the liquid- ordered stage and liquid disordered stage?
fluid- like
Under physiological conditions what phase does the membrane favor?
fatty acid composition and melting point
Membrane fluidity is mainly determined by
more
Membranes that have shorter and more unsaturated fatty acids will be __________ fluid.
decreases
Melting point __________ as double bonds are added.
saturated
At higher temperature cells need longer more ____________ fatty acids.
unsaturated
At lower temperature cells need more ___________ fatty acids