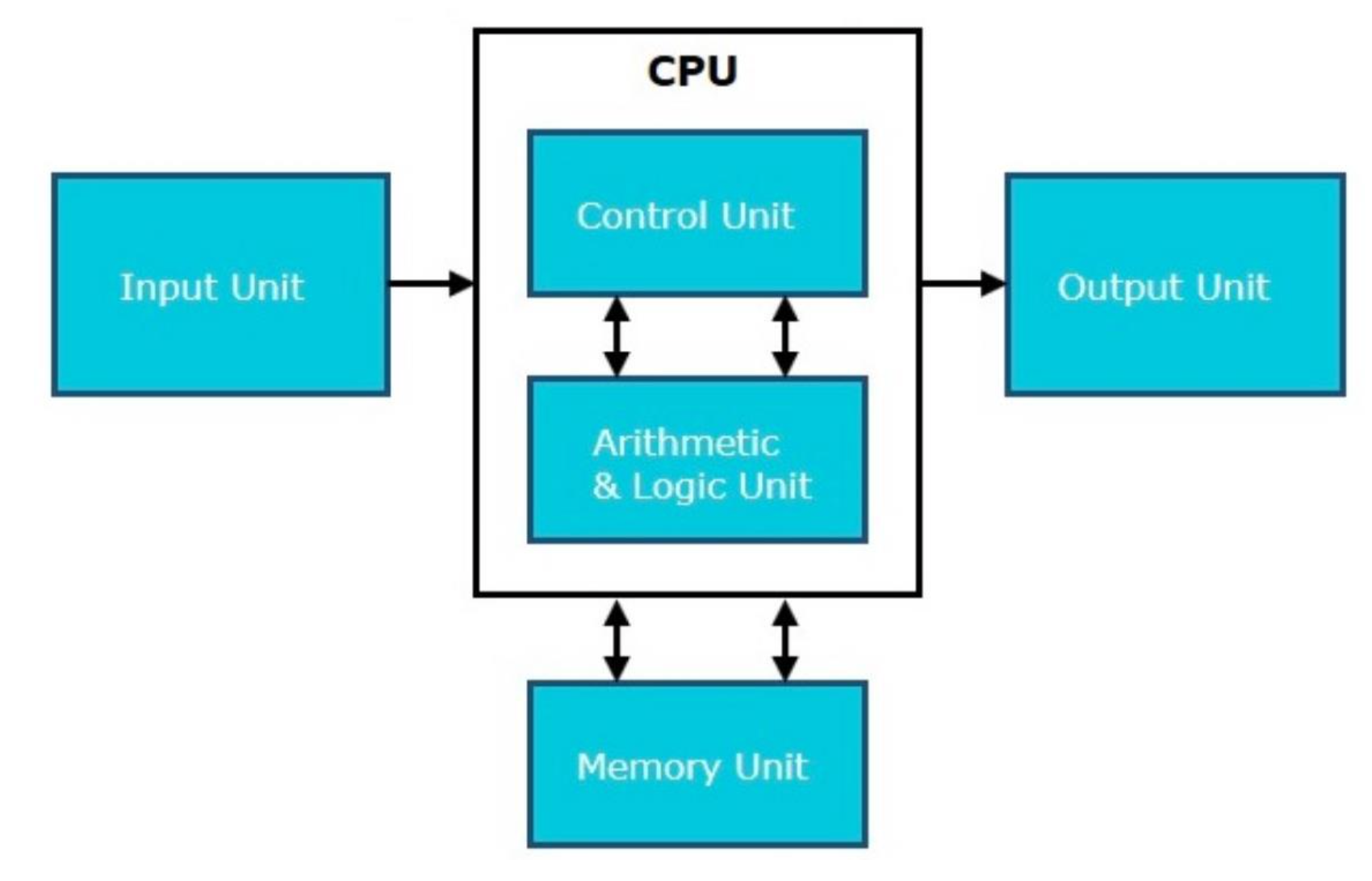
CPU
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CPU + Functions for Leaving Cert Higher Level Computer Science
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
CPU
The main processor of a computer that carries out most processing and computing tasks

Motherboard
The main circuit board that holds the CPU and connects it to other components
Functions of the CPU
Executes instructions from memory,
performs arithmetic and logic operations,
controls input and output
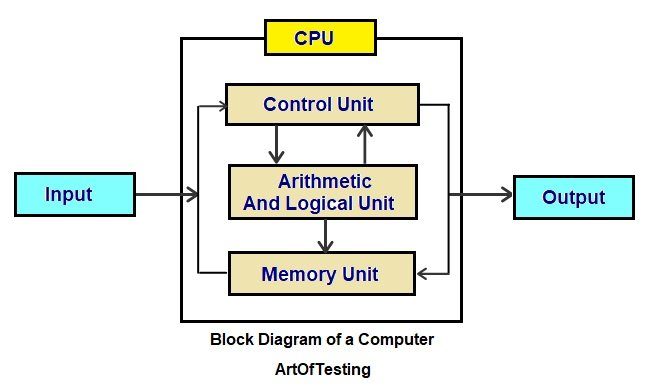
ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit)
Part of the CPU that performs arithmetic operations and logical comparisons
Control Unit (CU)
Part of the CPU that fetches decodes and executes instructions by coordinating other components
Cache
Small high-speed memory that stores frequently used data and instructions for quick CPU access
Registers
Small temporary storage locations inside the CPU holding data and instructions currently being processed
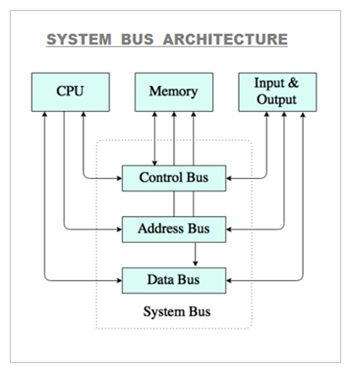
Bus
Set of pathways that allow data signals and power to travel between the CPU and other components
Clock
Component that provides timing signals to synchronize CPU and system operations
Fetch-Execute Cycle
The repeated process the CPU uses to run programs by fetching decoding and executing instructions
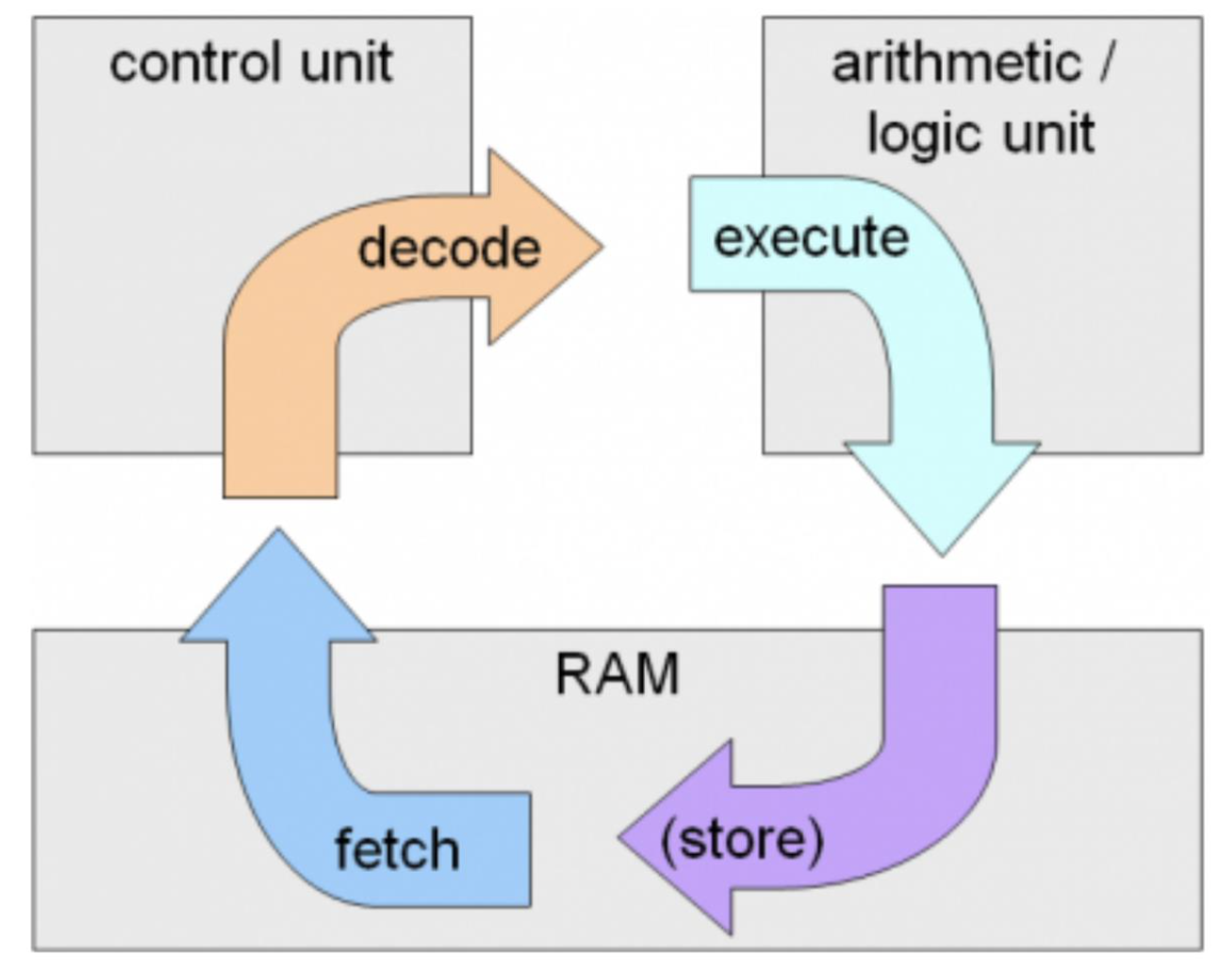
Fetch Stage
CPU retrieves an instruction from memory using the address stored in the program counter
Execute Stage
CPU decodes the instruction and performs the required operation
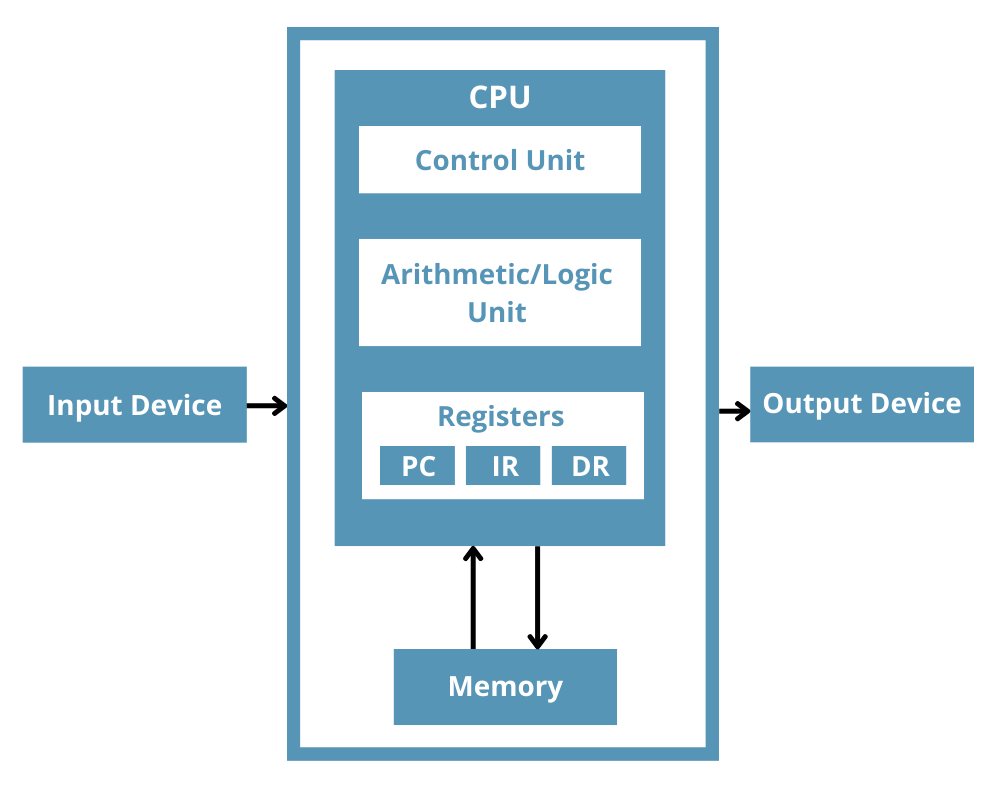
Program Counter (PC)
Register that stores the memory address of the next instruction to be executed
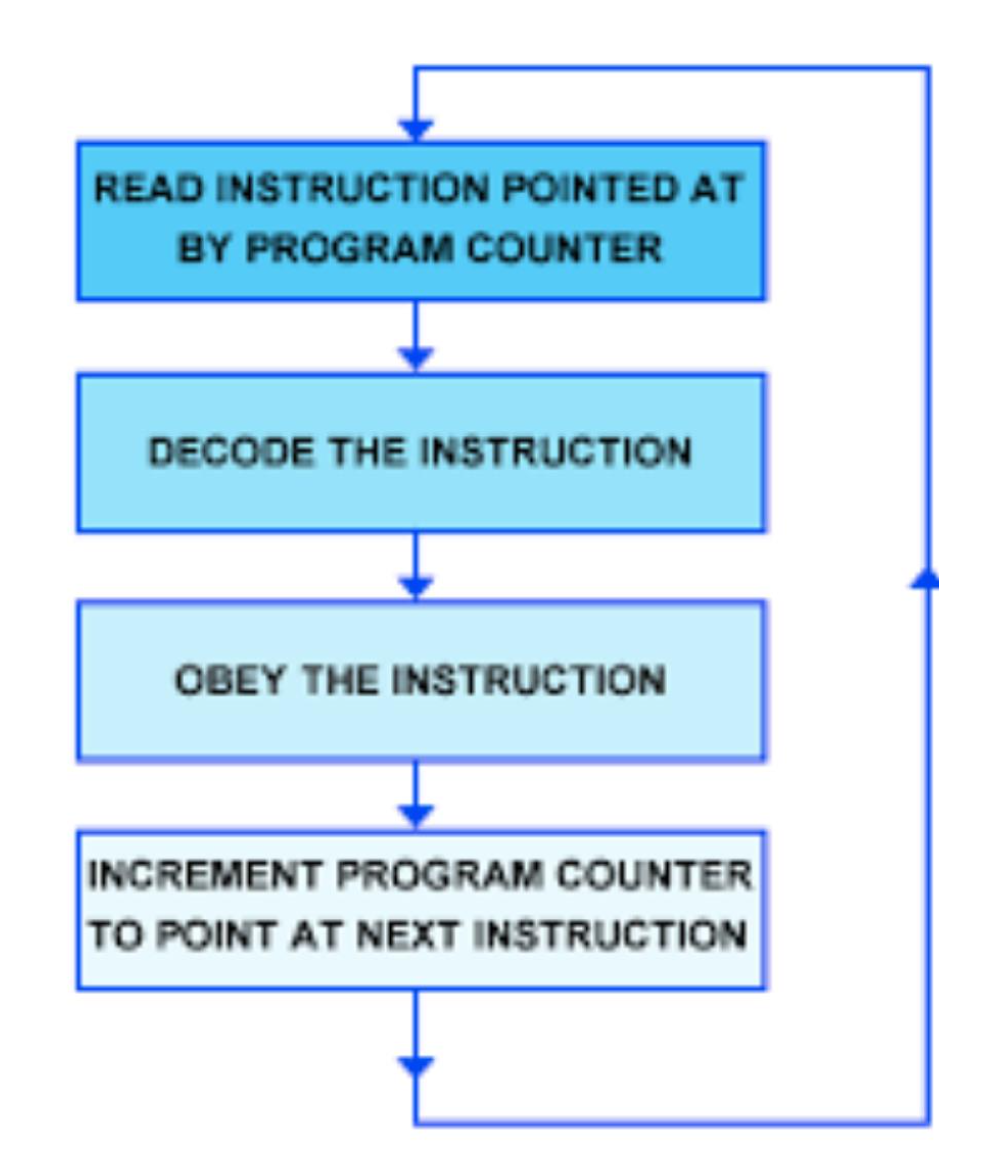
Memory Address Register (MAR)
Register that holds the memory address of data the CPU wants to access or modify
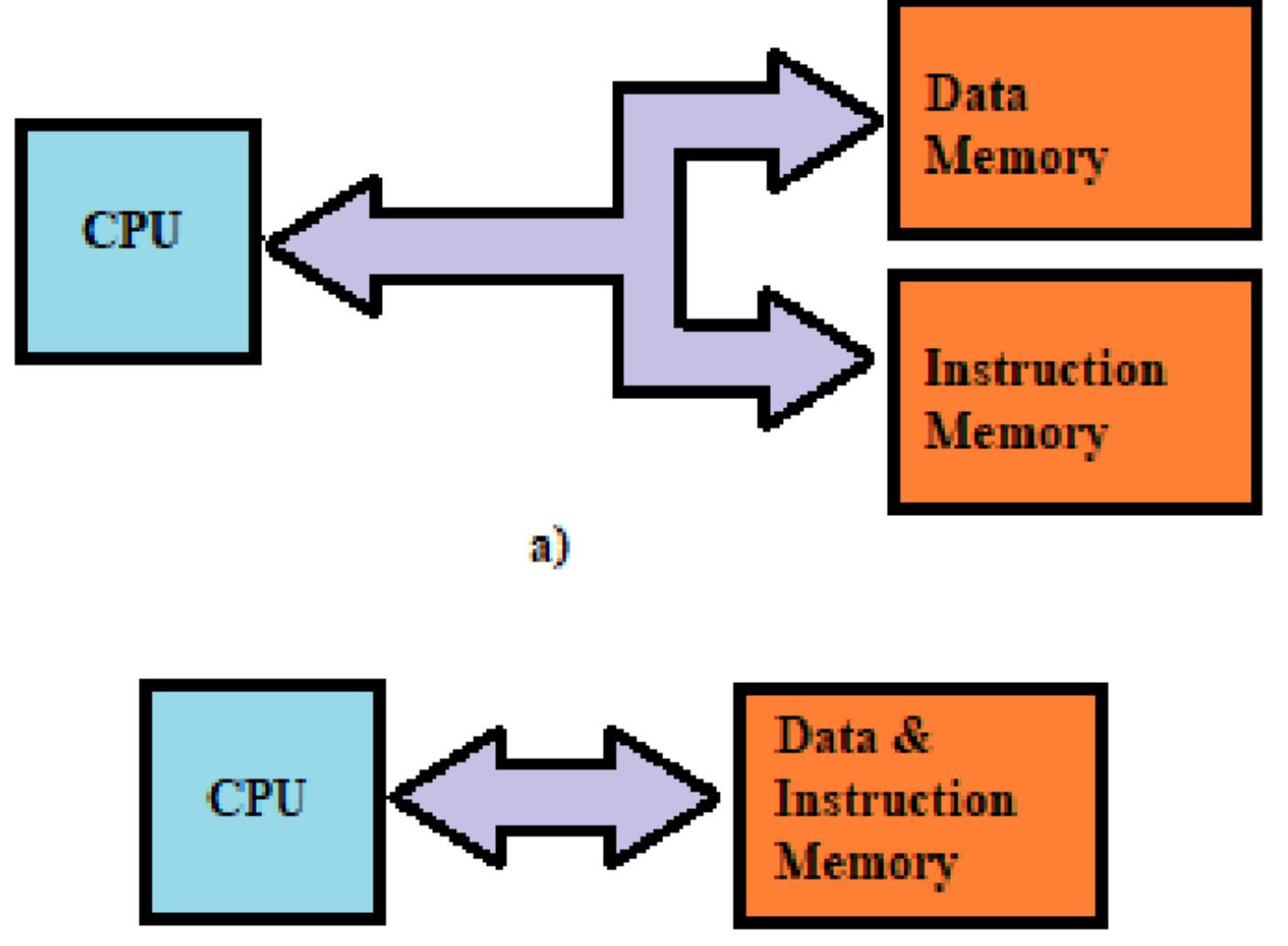
Von Neumann Architecture
Computer architecture where instructions and data share the same memory and bus
Harvard Architecture
Computer architecture where instructions and data use separate memories and buses
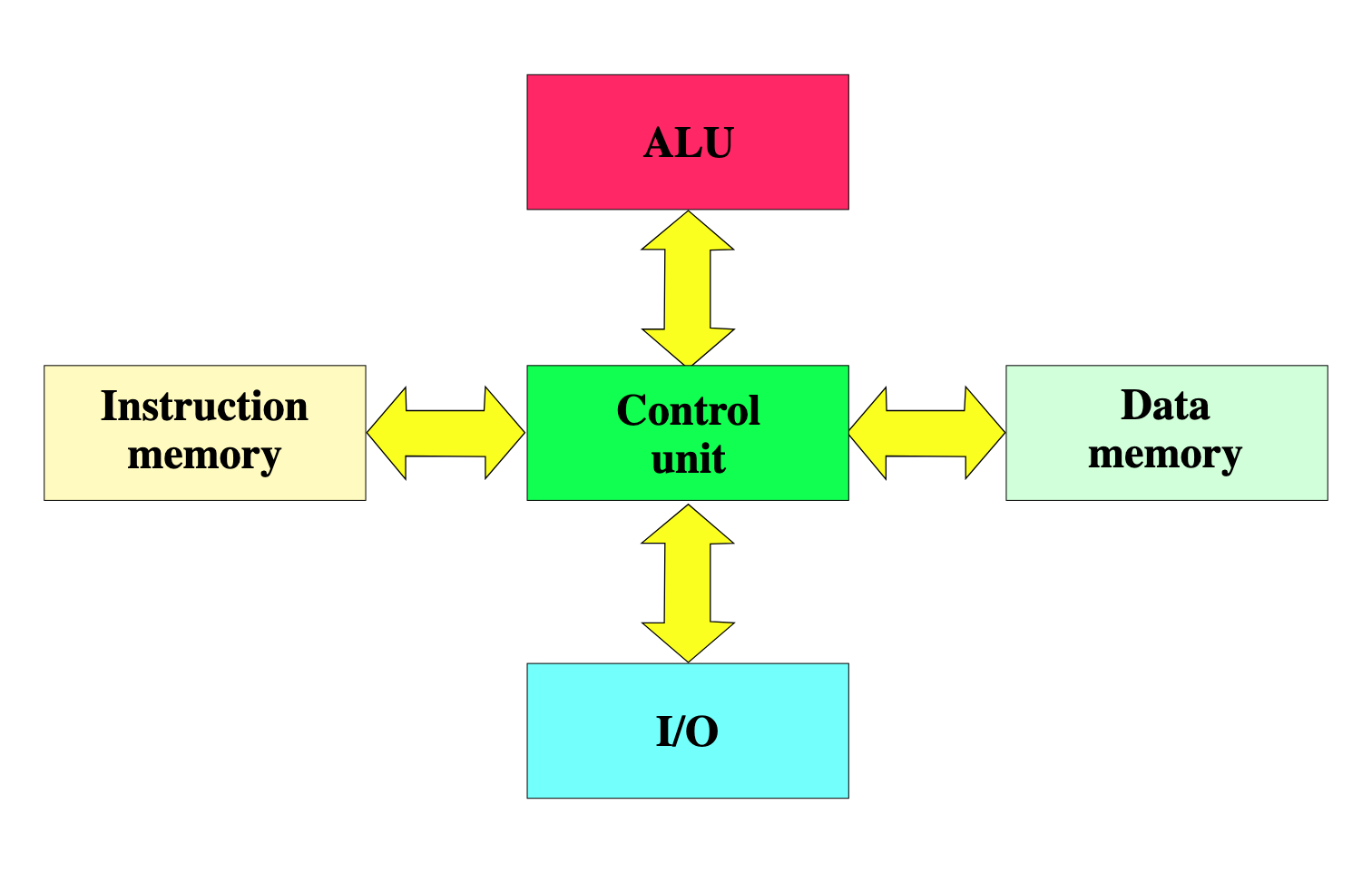
Von Neumann vs Harvard Architecture
Harvard uses separate instruction and data memories(Above)
Von Neumann uses shared memory(below)