AMINO ACIDS, PROTEINS AND DNA
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
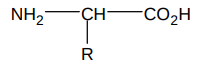
What is the general structure of an a amino acid?
R group determines the amino acid
a means both NH2 and COOH groups are joined to the same C
What is the simplest amino acid?
glycine
R is H
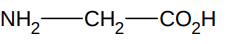
What is the optical activity of all amino acids?
theyre chiral as there are 4 different groups around the C
rotate plane polarised light
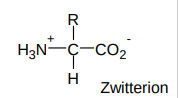
What is a zwitterion?
amino acids are always charged
exist as dipolar zwitterions
What causes the relatively high melting points of amino acids?
amino acids are often solids, and there is an ionic interaction between zwitterions which is stronger than the hydrogen bonding found in the no charge form
What is basic on an amino acid?
amine group
What is acidic on an amino acid?
carboxylic acid group
What can amino acids act as?
weak buffers and will only gradually change pH if small amounts of acid or alkali are added to the amino acid
What happens to an amino acid at high pH (in alkaline solution)?
the carboxylic end looses its H to become COO-
What happens to an amino acid at low pH (in acidic solution)?
the amine end gains a H to form NH3+
What’re dipeptides?
simple combination molecules of 2 amino acids with one amide link
there are 2 possible combinations of the amino acids in the dipeptide
What reactions can the carboxylic acid group and the amine group undergo?
esterification in the presence of a strong acid catalyst
How’re dipeptides hydrolysed?
heated with concentrated HCl or concentrated strong alkalis (NaOH)
split back into constituent amino acids
What is the method for thin-layer chromatography?
wearing gloves, draw a pencil line 1 cm above the bottom of the TLC plate and mark spots for each sample equally spaced along the line
use a capillary tube and add a tiny drop of each solution to a different spot and allow the plate to air dry
add solvent to a chamber with a lid so its less than 1cm in depth
place the TLC plate in, making sure the level of the solvent is below the pencil line and add the lid
when the level of the solvent reaches 1cm from the top of the plate, remove the plate and allow it to dry in a fume cupboard
spray with ninhydrin and put in oven
calculate the Rf values of the observed spots
Why should you wear gloves during thin-layer chromatography?
prevents contamination from the hands to the plate
Why should you draw a pencil line during thin-layer chromatography?
will not dissolve in the solvent
Why should you use a tiny drop of the amino acid solutions during thin-layer chromatography?
too big of a drop will cause different spots to merge
Why should you only use 1cm depth of the solvent during thin-layer chromatography?
if the solvent is too deep it will dissolve the sample spots from the plate
Why should you use a lid during thin-layer chromatography?
prevents evaporation of the toxic solvent and allows evaporation in the chamber to create a concentrated solution to increase the speed of moving up the paper
Why should you allow the solvent to rise to 1cm from the top of the paper during thin-layer chromatography?
will get more accurate reesults
Why should you allow the plate to dry in a fume cupboard during thin-layer chromatography?
the solvent is toxic
Why should you use ninhydrin during thin-layer chromatography?
shows up as blue dots, allowing the amino acids to be seen
How do you calculate the Rf value?
distance moved by amino acid/ distance moved by the solvent
What’re proteins?
polymers made from combinations of amino acids linked by peptide links
What is the primary structure of a protein?
the sequence of the 20 different naturally occurring amino acids joined together by condensation reactions with peptide links
What is the secondary structure of a protein?
alpha helix is the 3D corkscrew shape arrangement of amino acids which is held in place by hydrogen bonds between the H of N-H and the O of C=O of the 4th amino acid along the chain, causing the R groups to be pointed outside of the helix
beta pleated is the protein chain folding into parallel strands side by side, with hydrogen bonds between the H of N-H and the O of C=O
What is the tertiary structure of a protein?
the folding of the secondary structure into more complex shapes, held by hydrogen bonding, disulfide bonds and ionic interactions
How’re hydrogen bonds established in the tertiary structure?
form between 2 serine side chains in different parts of the folded chain
How are ionic interactions established in the tertiary structure?
form between acidic amino acids and basic amino acids, causing a transfer of a hydrogen ion from the -COOH to the -NH2 to form zwitterions
How are sulfur bridges established in the tertiary structure?
2 cysteine side chains will react to form a sulfur bridge
What’re enzymes?
proteins
active site is hollow where the substrate molecule can bond to the amino acid side chains through hydrogen bonding, van der waals, permanent dipole dipole forces and ionic interactions
What feature must the interactions be between enzymes and substrates?
must be strong enough to hold the substrate for long enough for the catalysed reaction to occur but weak enough for the product to be released
What is an enzyme substrate complex?
when the enzyme bonds to the active site
Whats the lock and key hypothesis?
only substrate molecules with the right shape and correct positions of function groups will fit and bind to the active-site
How can drugs act as enzyme inhibitors?
they block the active site by binding to it
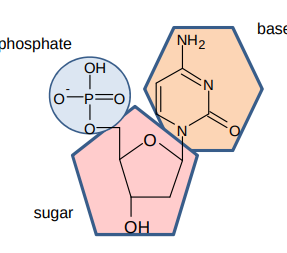
What’re nucleotides made from?
a phosphate ion bonded to 2-deoxyribose which is bonded to a base
What does a nucleotide look like?
How is a sugar-phosphate-sugar phosphate polymer chain made?
a condensation reaction occurs between nucleotides
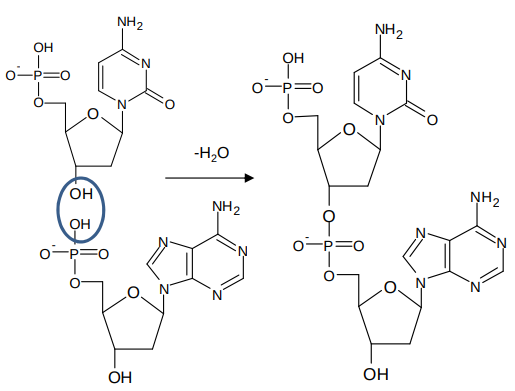
What does DNA exist as?
2 complimentary strands of sugar phosphate polymer chain arranged in the form of a double helix
complementary means 2 strands have base sequences which match (A-T, G-C)
hydrogen bonds between base pairs leads to 2 complementary strands of DNA
What is the structure of cisplatin?
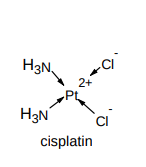
What is cisplatin used for?
as a cancer drug
How does cisplatin work?
2 chloride ions are displaced and the molecule joins onto the DNA, stopping the replication of cancerous cells
this is due to a ligand replacement reaction with DNA where a dative covalent bond is formed between nitrogen atom on guanine
What is a diagram of the function of cisplatin?

What’re negatives of using cisplatin as a cancer drug?
prevents replication of healthy cells by bonding onto healthy DNA, leading to unwanted side effects
unwanted side effects are minimised by small doses