3.4.3 Monopolistic competition
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION- EXAMPLES
hairdressers
estate agents
restaurants
MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION- CHARACTERISTICS
imperfect competition
non-homogenous goods
large no. of buyers and sellers
no barriers to entry and exit
price makers
IMPERFECT COMPETITION
firms are SR profit maximisers
both buyers and sellers have imperfect info
NON-HOMOGENOUS GOODS
due to branding- product differentiation
but there are a lot of close substitutes
makes XED of g and s sold high
LARGE NO. OF BUYERS AND SELLERS
each seller has the same degree of market power as other sellers
but market power is relatively weak
PRICE MAKERS
can raise prices without losing all of their customers
NO BARRIERS TO ENTRY AND EXIT
allows new firms to enter when SNP are being made and some to leave in the case of losses
so only normal profits can be made in LR
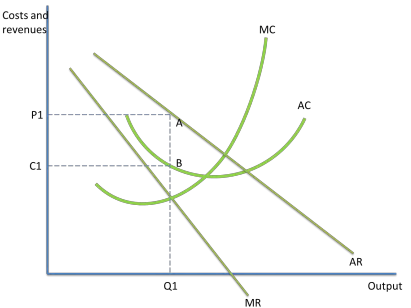
PROFIT MAXIMISING EQUILIBRIUM- SHORT RUN
firms profit maximise at the point MC = MR
area P1C1AB represents SNP that firms in a monopolistically competitive market earn
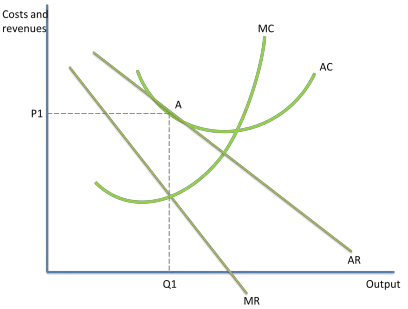
PROFIT MAXIMISING EQUILIBRIUM- LONG RUN
new firms enter market- incentivised by SNP
makes demand for existing firms’ products more price elastic which shifts AR curve left
so only normal profits can be made
equilibrium point is P1Q1
firms can try and stay in short run by differentiating their products and innovating
if question asks u to show change include the OG AR curve
ADVANTAGES OF MONOPOLISTICALLY COMPETITIVE MARKETS
consumers get a wide variety of choice and firms may be able to enjoy some degree of EoS
likely to be dynamically efficient- differentiated products and so know that innovative products will give them an edge over their competitors and enable them to make SNP in the short run
DISADVANTAGES OF MONOPOLISTICALLY COMPETITIVE MARKETS
LR- dynamic efficiency might be limited due to the lack of SNP
not be allocatively or productively efficient
firms have x-inefficiency, since they have little incentive to minimise their costs