Locomotion
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Aquatic Locomotion
Earliest form of locomotion in vertebrates
Aquatic Locomotion- Forces to generated & reduce/counteract what?
• Two forces to be generated:
– Lift: counteracts effects of gravity (vertical plane)
– Thrust: forward/backward motion (horizontal plane)
• Must also reduce drag (resistance)
• And counteract instability
Providing Lift
• Swim Bladder
– Fish regulate amount of air inside body
(via gases in blood, or through connections to
esophagus)
– Increasing/decreasing buoyancy
• Low density body structures
– Density of organs less than water
thanks to oil storage
(e.g., oily flesh, liver, etc.)
– Provides buoyancy
• Fins
– Heterocercal caudal fin particularly
good at generating lift in addition to thrust.
Providing Thrust
– Swimming locomotion done by undulations (waves), or oscillations (back-and-forth)
– Thrust is typically created by caudal region, but other regions also utilized (e.g., pectoral or anal fins)
Swimming Types can be classified according to ?
body regions used, and type of movement
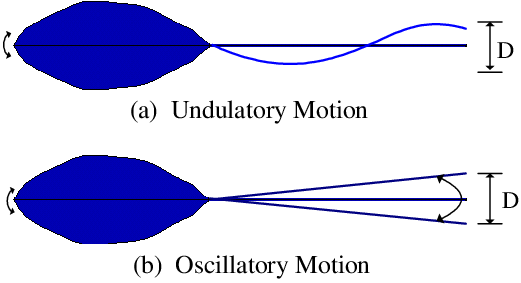
Undulation
waves motion
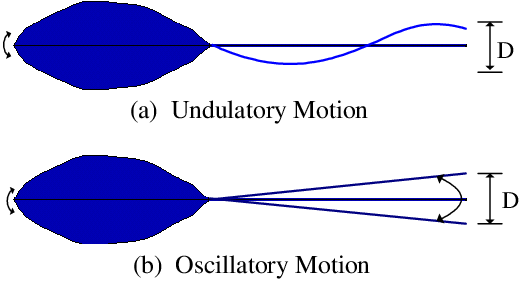
Oscillation
back and fourth motion
Thrust/Swimming: Movement Types
Anguilliform, Carangiform, Ostraciiform, Appendicular Locomotion
Instability
Rotation about the three axes
Instability- Roll
along longitudinal axis, tendency to move side to side
– Controlled by dorsal and anal fins
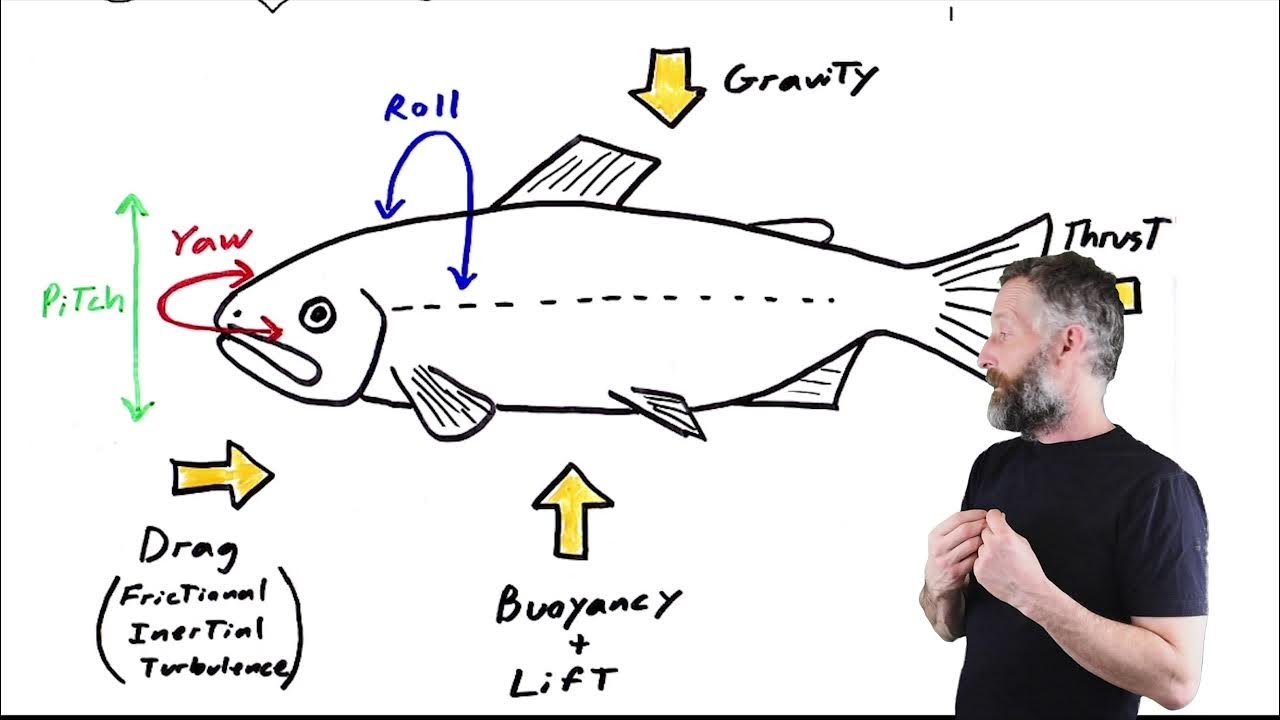
Instability- Pitch
along transverse axis, up & down movement, esp. at the front of the bodythe
– Controlled by pectoral fins; pelvic fins in
advanced fish
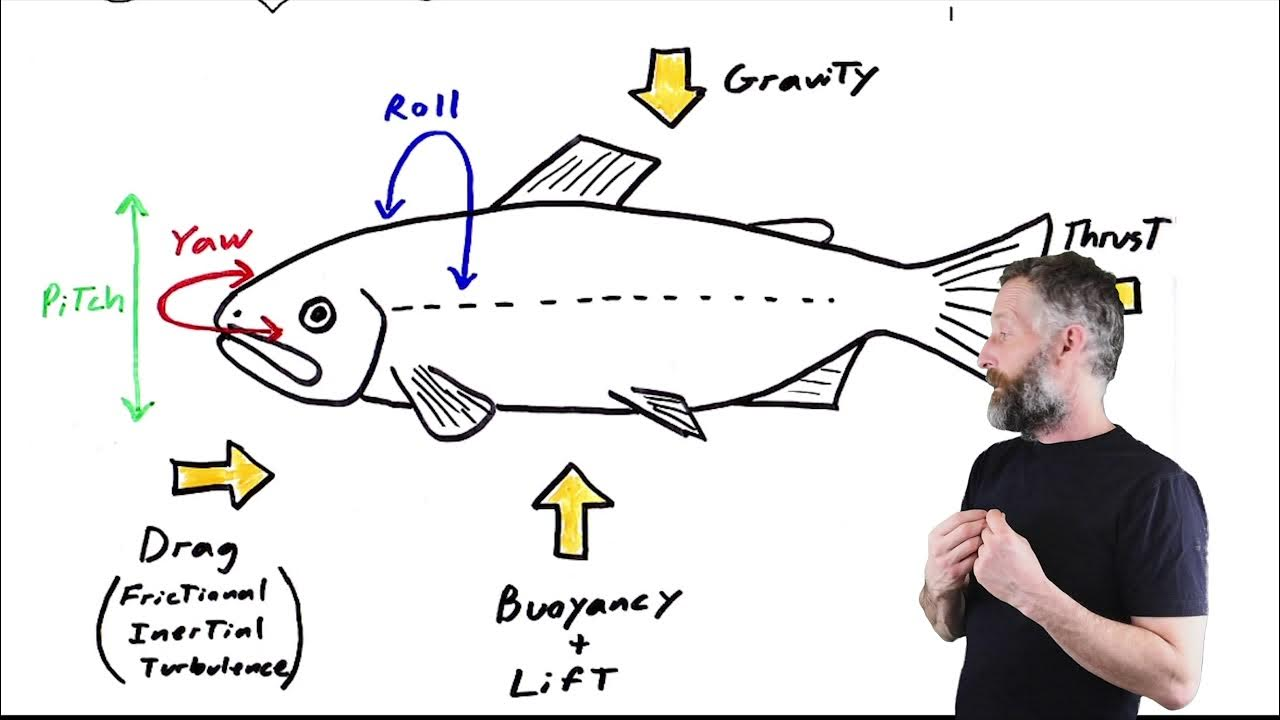
Instability- Yaw
along sagittal axis, tendency to go right or left
– Controlled by fins at back with vertical orientation, e.g. caudal fin
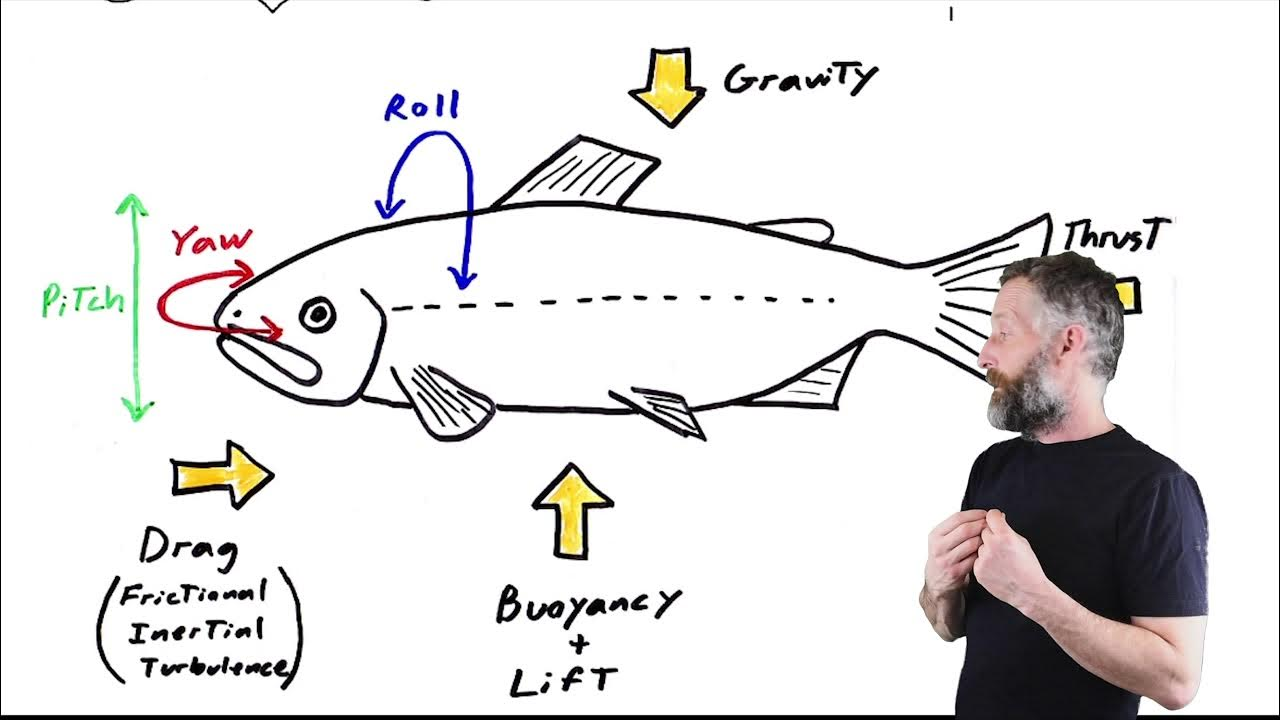
Counteracting Instability
Counteracted by fins:
Pitch (pectoral fin, pelvic fin)
Roll (dorsal fin, anal fin)
Yaw (tail fin (caudal fin))
Drag
Force that counteracts thrust
Causes of Drag
– Friction between body and water (viscous drag)
– Turbulence as fish moves and displaces water (inertial drag)
Reducing Drag
• Body Covering:
– smooth skin reduces viscous drag (no scales or many small ones)
– mucous/slime over scales reduces viscous drag by as much as 60%
• Body Shape: streamlined body reduces inertial drag, thin body = more viscous drag, but less turbulence
Fish Speeds
• Anguilliform: bursts 2-3 body lengths/second (bl/sec)
• Carangiform: bursts 10 bl/sec
Fish Muscle Types
• White: up to 90% of muscle
– Few mitochondria, poorer blood supply
– Good for bursts, but fatigue quickly
• Red: endurance, little force
– More mitochondria, good blood supply
– Used for cruising; show little fatigue
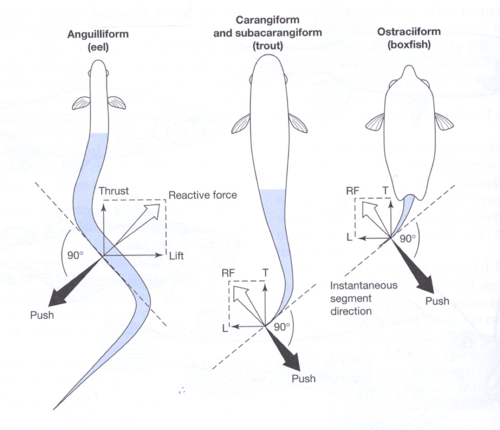
Anguilliform Swimming
Most of body used to produce thrust
• Muscles contract on one side,
relax on other; wave of contractions
• Examples: eels, shark (dogfish)
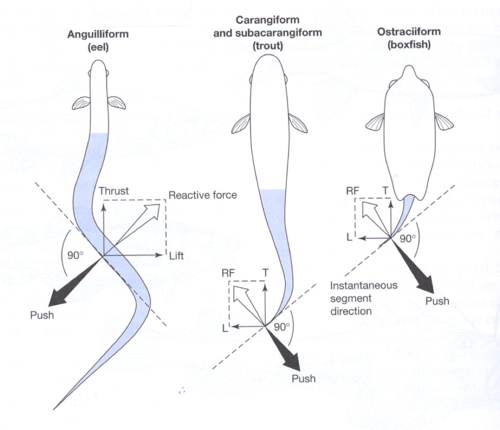
Carangiform Swimming
Front half body rigid, back half produces waves and contractions
• Examples: jack, trout, horse mackerel
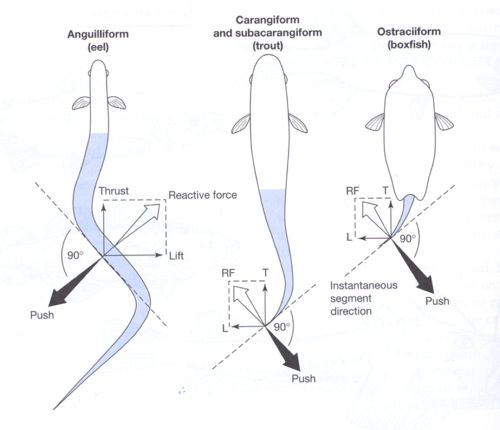
Ostraciiform
Only caudal fin involved in thrust (wig-wag motion)
• Example: boxfish (trunkfish)
4) Appendicular Swimming
Use appendages for swimming
Undulatory:use fin undulations
Dorsal and/or anal fins: e.g., bowfin, knife-fish
Pectoral fins:e.g., rays, skates, pufferfish
Oscillatory: use back / forth movement of appendages
– Use limbs like oars — frog, duck, otter
– Use fins like wings — turtle, penguin, seal