Lecture 7: Photosynthesis
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
autotroph
organism that creates their own food from inorganic substances using light energy and converting that into food
chloroplast
organelle which photosynthesis takes place
mesophyll
structure in the lead where chloroplasts usually remain
2 cells thick
contain two layers the palisade (upper), and the spongy (lower)
stomata
the opening between a pair of guard cells in the epidermis of a plant leaf
vascular bundles
plant tissue that contains the phloem and xylem which helps transport water, minerals, and food throughout the plant
intermembrane space
region located between the outer and inner membranes of the chloroplast envelope
holding area for proteins being transported into/out of the chloroplast
thylakoid space
internal compartment within each thylakoid
thylakoid
membrane-bound compartment within each chloroplast
space why light reactions occur
stroma
a part of the chloroplast which is the fluid within the compartment formed by the inner membrane of the chloroplast
grana
stacks of thylakoid
electromagnetism
the absorption of visible light by pigment molecules to excite electrons
photon
“particle like” quantum of light energy
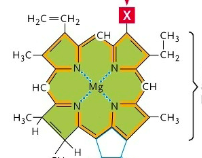
Porphyrin ring
ring structure in chloroplast where there is Mg++ ion in the middle
light reactions
the first stage of photosynthesis where radiant energy is absorbed and converted to chemical energy → ATP & NADH
occurs in the thylakoid membrane
NADP+
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate acts as an essential electron carrier during the light-dependent reactions
Calvin cycle
light independent reaction where CO2 is being converted to sugars using ATP and NADPH produced from the light-dependent reactions
three phases: carbon fixation, reduction and regeneration of CO2 acceptor
occurs in the stroma
1 cycle produces triose G3P
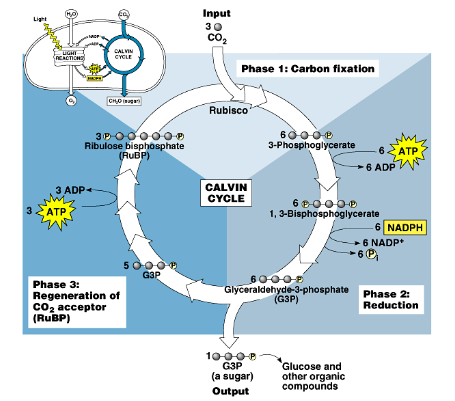
carbon fixation
process where autotrophic organisms convert inorganic carbon (CO2) to organic compounds
pigment
light absorbing molecules in photosynthesis
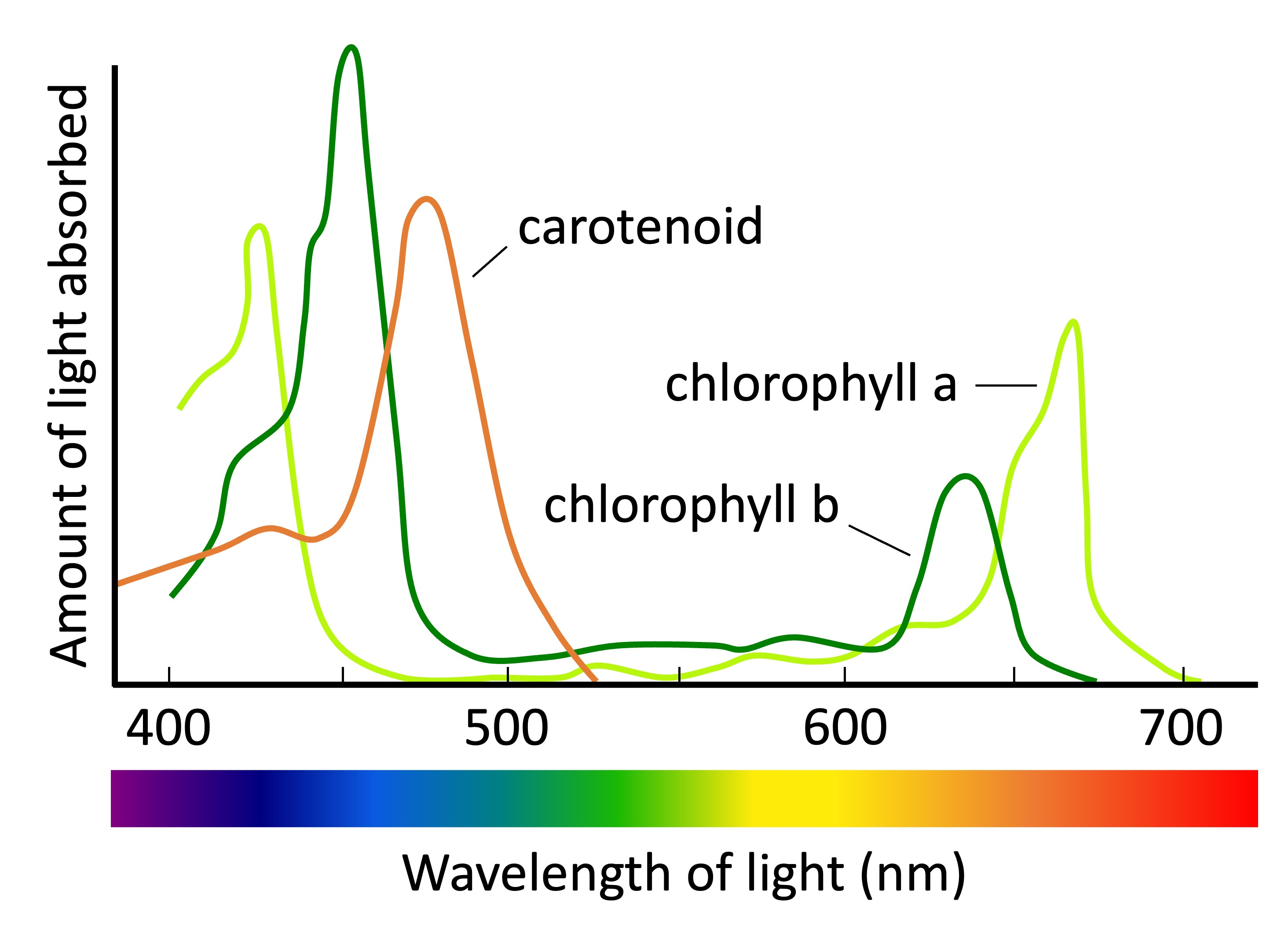
chlorophyll
type of pigment in plants where there are two different kinds a and b
green pigment
xanthophylls
red, yellow color produced → chlorophylls are broken which represents a leaf color change
protect carotenoid pigments from light damage
carotenoids
yellow-orange pigment by which light is absorbed in photosynthesis
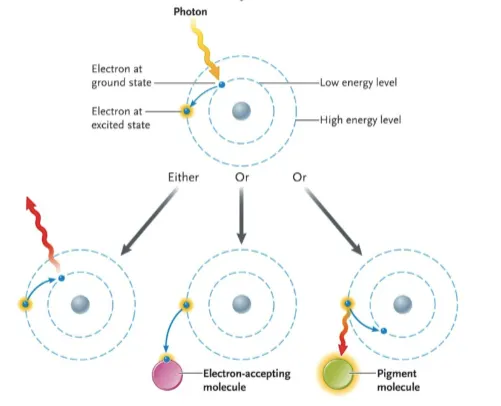
photoexcitation
when a photon is absorbed by an exited electron going from an area of low energy to high energy
three scenarios can happen
energy gets lost as flourescence or heat
energy gets absorbed by a pigment as it returned to its ground state
an electron hungry molecule accepts the high energy electron
action spectrum
shows the rate of photosynthesis at different wavelengths of light
photosystem
large complex where light-absorbing pigments for photosynthesis are organized with proteins and other molecules
antenna complex
sites where light is absorbed and converted to chemical E; contain several hundred chlorophyll a,b and carotenoids
role → harvest E and take it to the reaction center
reaction center
apart of PS1 and PS2 in the chloroplast which will receive light energy absorbed by antenna complex in the same photosystem
reaction center chlorophyll
contains 2 chlorophyll a → transfer excited e- to ETC
a pair of chlorphylls
primary e- acceptor
receives an excited electron from the reaction center chlorophyll during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, initiating the electron's journey down the electron transport chain
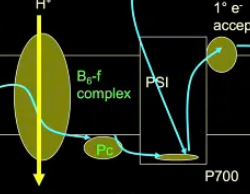
Pc
plastocyanin which passes e- to oxidized chlorophyll molecules in PS 1
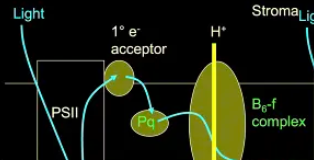
Pq
plastoquinone; crucial electron and hydrogen carrier in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, moving electrons from Photosystem II to the cytochrome b6f complex
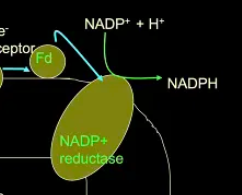
ferrodoxin
mobile carrier that transfers high E e- from PSI to NADP+ reductase
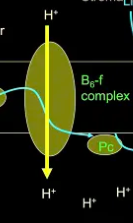
B6-F complex
protein complex that linked PSII and PSI in ETC during photosynthesis; containing cytochromes
creates electrochemical gradient for ATP synthase
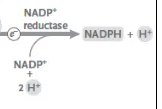
NADP+ reductase
an enzyme that catalyzes the reduction of NADP+ to NADPH
photophosphorylation
synthesis of ATP coupled to the transfer of electrons energized by photons of light
analogous to oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria
ribulose bisphosphate
a five-carbon organic molecule that acts as the primary CO₂ acceptor in photosynthesis
the starting and ending substrate of the Calvin cycle
rubisco
An enzyme that catalyzes the key reaction of the Calvin cycle, carbon fixation, in which combines with RuBP (ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate) to form 3-phosphoglycerate
glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate
the ending produce of phase 2 of the calvin cycle (reduction)
a direct product of the Calvin cycle, a three-carbon sugar used to synthesize glucose and other carbohydrates, as well as to regenerate ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) for carbon fixation