Social Patterns and Trends
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 11:05 PM on 5/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
1
New cards
Demography
Study of human populations
2
New cards
Fertility Rate
Births per 1,000 Women (15-44)
3
New cards
Total Fertility Rate
Children a hypothetical women would have if she lived to 44
4
New cards
Replacement Level
The amount of fertility needed to keep the population the same from generation to generation
5
New cards
Replacement Rate
The number of births necessary to replace the loss of those who died during the year
6
New cards
Immigration Rate
People per 1,000 immigrating (coming into) a country
7
New cards
Emigration Rate
People per 1,000 emigrating (leaving) a country
8
New cards
Net Migration
The difference between immigration into and emigration out of a country
9
New cards
Mortality Rate
Deaths per 1,000
10
New cards
Internal migration
Migration within a country
11
New cards
Growth Rate
birth rate + death rate + migration
12
New cards
Constrictive Population Pyramid
Shows less young people and older people living longer, indicative of a rich country
13
New cards
Expansive Population Pyramid
Shows more young people and older people living shorter lives, indicative of a poor country
14
New cards
Cohorts
A group sharing a defining characteristic
15
New cards
Why research generational cohorts?
Looking at people by their place in life and by membership in a cohort born at the same time. Observes change over time, understanding how experiences impact/differences in attitudes
16
New cards
What are markers of the transition to adulthood?
* Finishing school
* Leaving home
* Full time work
* Conjugal union
* Children
* Leaving home
* Full time work
* Conjugal union
* Children
17
New cards
Why is the pace of transition to adulthood slower each decade?
* Women postponing childbearing to focus on careers
* Housing crisis/rising cost of living
* Less social pressure/desire to have a family/
* Emphasis on education (staying in school longer)/career growth
* Access to birth control/contraceptives
\
* Housing crisis/rising cost of living
* Less social pressure/desire to have a family/
* Emphasis on education (staying in school longer)/career growth
* Access to birth control/contraceptives
\
18
New cards
The Impact of Baby Boomers
* Adapting institutions to account for the size of the generation (schools, housing etc)
* Big voting block
* New, bigger target audience for products/media
* Effects on workforce/needed social institutions
* Social change: women’s/gay/civil rights
* Big voting block
* New, bigger target audience for products/media
* Effects on workforce/needed social institutions
* Social change: women’s/gay/civil rights
19
New cards
Dr. Spock
Behaviourist who published a parenting book valuing permissiveness, urging parents to respect their children and allow them to grow at their own pace. Critics say he created an egotistical and disrespectful generation.
20
New cards
How do demographics shape trends and patterns?
* More diversity
* Women in the workforce
* Voting habits
* Evolution of family
* Class divides
* Lack of religion
* Aging population
* More education
* Women in the workforce
* Voting habits
* Evolution of family
* Class divides
* Lack of religion
* Aging population
* More education
21
New cards
What is adolescence?
The transitional period between childhood and adulthood, from the onset of puberty to 18/24.
22
New cards
What was Stanley Hall’s theory on adolescence?
* Studied emotional development among teenagers
* Stated adolescent youth exhibit contradictory tendencies
* These divergences contributed to a period of “storm and stress” that marks adolescence
* Extreme swings of behaviour help determine personality and the ability to sort them out leads to stability of character/maturity
* Stated adolescent youth exhibit contradictory tendencies
* These divergences contributed to a period of “storm and stress” that marks adolescence
* Extreme swings of behaviour help determine personality and the ability to sort them out leads to stability of character/maturity
23
New cards
What was Margaret Mead’s theory on adolescence?
* Studied adolescent girls in Samoa (participant observation)
* Argued cultural factors, rather than biological ones caused emotional and psychological stress of adolescence
* Argued cultural factors, rather than biological ones caused emotional and psychological stress of adolescence
24
New cards
What defines Millennials?
* 1981-1996
* 9/11
* Wars in the Middle East
* Obama’s 2008 election
* Diversity
* Recession
* Internet
* 9/11
* Wars in the Middle East
* Obama’s 2008 election
* Diversity
* Recession
* Internet
25
New cards
What defines Gen X?
* 1965-1980
* “computer revolution”
* “computer revolution”
26
New cards
What defines Gen Z
* 1997 - 2012
* Internet/social media shifting behaviour/lifestyle
* Diversity - most diverse in U.S so far
* Internet/social media shifting behaviour/lifestyle
* Diversity - most diverse in U.S so far
27
New cards
What is Canada’s dependency load?
52\.1% - the number of dependants in relation to the total working population
28
New cards
What are the implications of Canada’s low fertility rate?
The population is decreasing. This is because of less importance placed on marriage, less desire for children, housing crisis/cost of living, staying in school longer, contraceptives/birth control/abortion etc. It indicates that Canada is a rich country.
29
New cards
Why is immigration important in Canada?
* Diversity
* Filling gaps in labour force
* Paying taxes/spending money
* Contributing to economy and social services (health care)
* Filling gaps in labour force
* Paying taxes/spending money
* Contributing to economy and social services (health care)
30
New cards
Is gentle parenting helpful or harmful to society?
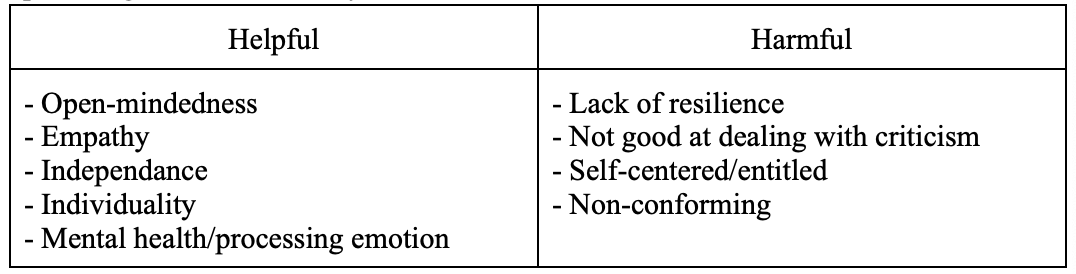
31
New cards
What is the slow start for Millennials and its impact?
* Life choices/earnings/entrance to adulthood was shaped by the recession, slowing the start to adulthood
* This created a lack of economic stability/homeownership, debt
* This created a lack of economic stability/homeownership, debt
32
New cards
Technological Determinism
Vebeln
The invention of a tool taking on a life of its own after its release, with the society reacting and adapting.
The invention of a tool taking on a life of its own after its release, with the society reacting and adapting.
33
New cards
What is technological lag?
Technology introduces change that temporarily destabilizes society and a period of transition occurs until society adapts
34
New cards
What is Anomie?
Loss of direction felt in society when the social control of individual behaviour has become ineffective. Norms are weak, conflicting or absent (Durkheim)
35
New cards
What is the Strain Theory?
Deviance is more likely to occur when a gap exists between cultural goals and the culturally approved means of achieving them (Merton)
Strain Typology includes Conformists, Ritualists, Innovators, Retreatists and Rebels
Strain Typology includes Conformists, Ritualists, Innovators, Retreatists and Rebels
36
New cards
Conformists
Strain Theory Typology: Accept the cultural goals of their society and the means by which to attain them
37
New cards
Ritualists
Strain Theory Typology: Accept the means or standards necessary to attain the end goals, but may not accept the cultural goal. They will work to provide for a certain lifestyle, but won’t strive to be industry leaders.
38
New cards
Innovators
Strain Theory Typology: Goals are in line with those of society, but will not accomplish them through acceptable/traditional means
39
New cards
Retreatists
Strain Theory Typology: Chose to disengage from mainstream culture altogether
40
New cards
Rebels
Strain Theory Typology: Openly reject cultural goals of society and the means by which to attain them. They attempt to change the society in which they live and their rebellions may be violent.
41
New cards
Control Theory
* Hirschi
* Conformity to social norms depends on the presence of strong bonds between individuals and society.
* If bonds are weak/broken, deviance occurs
* Social bonds control the behaviour of people
* Conformity to social norms depends on the presence of strong bonds between individuals and society.
* If bonds are weak/broken, deviance occurs
* Social bonds control the behaviour of people
42
New cards
Differential Association Theory
* Sutherland
* People learn the necessary techniques, motives, rationalizations and attitudes of deviant behaviour from people with whom they associate
* People have a greater tendency to deviate when associated with those who favour deviance
* People learn the necessary techniques, motives, rationalizations and attitudes of deviant behaviour from people with whom they associate
* People have a greater tendency to deviate when associated with those who favour deviance
43
New cards
Labeling Theory and Primary and Secondary Deviance
* Becker
* Deviants are people who have been successfully labeled as such by others
* Lemert
* Primary Deviance: norm or rule breaking behaviour one engages in
* Secondary Deviance: a reaction to having been labeled as deviant, with life and identity organized around deviance
* Deviants are people who have been successfully labeled as such by others
* Lemert
* Primary Deviance: norm or rule breaking behaviour one engages in
* Secondary Deviance: a reaction to having been labeled as deviant, with life and identity organized around deviance
44
New cards
Conflict Theory of Deviance
* The criminal justice system protects the power and privilege of the upper class
* System defines deviance differently based on class: activities of lower class are more likely to be labeled criminal/deviant
* System defines deviance differently based on class: activities of lower class are more likely to be labeled criminal/deviant
45
New cards
What is Ogburn’s stages of cultural lag?
1) Invention: material or social
2) Discovery: a new way of viewing reality
3) Diffusion: spread/acceptance
2) Discovery: a new way of viewing reality
3) Diffusion: spread/acceptance
46
New cards
What are McLuhan’s Four Laws of Media
1) any major medium enhances/accelerates a process/thing (ex money enhances trade)
2) new medium tends to render obsolete another thing (ex money made barter obsolete)
3) major medium retrieves some process/thing that had been previously obsolete (ex money retrieved conspicuous consumption)
4) major medium, when pushed to extreme, flips into something new (ex money to credit cards)
2) new medium tends to render obsolete another thing (ex money made barter obsolete)
3) major medium retrieves some process/thing that had been previously obsolete (ex money retrieved conspicuous consumption)
4) major medium, when pushed to extreme, flips into something new (ex money to credit cards)
47
New cards
What are the problems associated with a rise in hate crimes?
* Many officers are unclear on what constitutes a hate crimes
* Police have poor relationships with radicalized, religious and LGBTQ communities
* Police have poor relationships with radicalized, religious and LGBTQ communities
48
New cards
Why are police unsuccessful in securing prosecutions of hate crimes?
* There exists a difficulty in determining hate motivation
* There is a low priority placed on hate crimes
* Hate crimes have low margins of success and officers often face a high bar in securing approvals for prosecution
* There is a low priority placed on hate crimes
* Hate crimes have low margins of success and officers often face a high bar in securing approvals for prosecution
49
New cards
What measures of social control can be used to curb hate crimes?
* Legislation
* Establishment of trust
* Action in police/justice system : deterrence
* Establishment of trust
* Action in police/justice system : deterrence