Unit B: Electrochemistry
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Reduction - Oxidation reactions
Chemical reactions in which there is a transfer of electrons
Do you need both oxidation and reduction?
There must be both oxidation and reduction happening for the reaction to occur
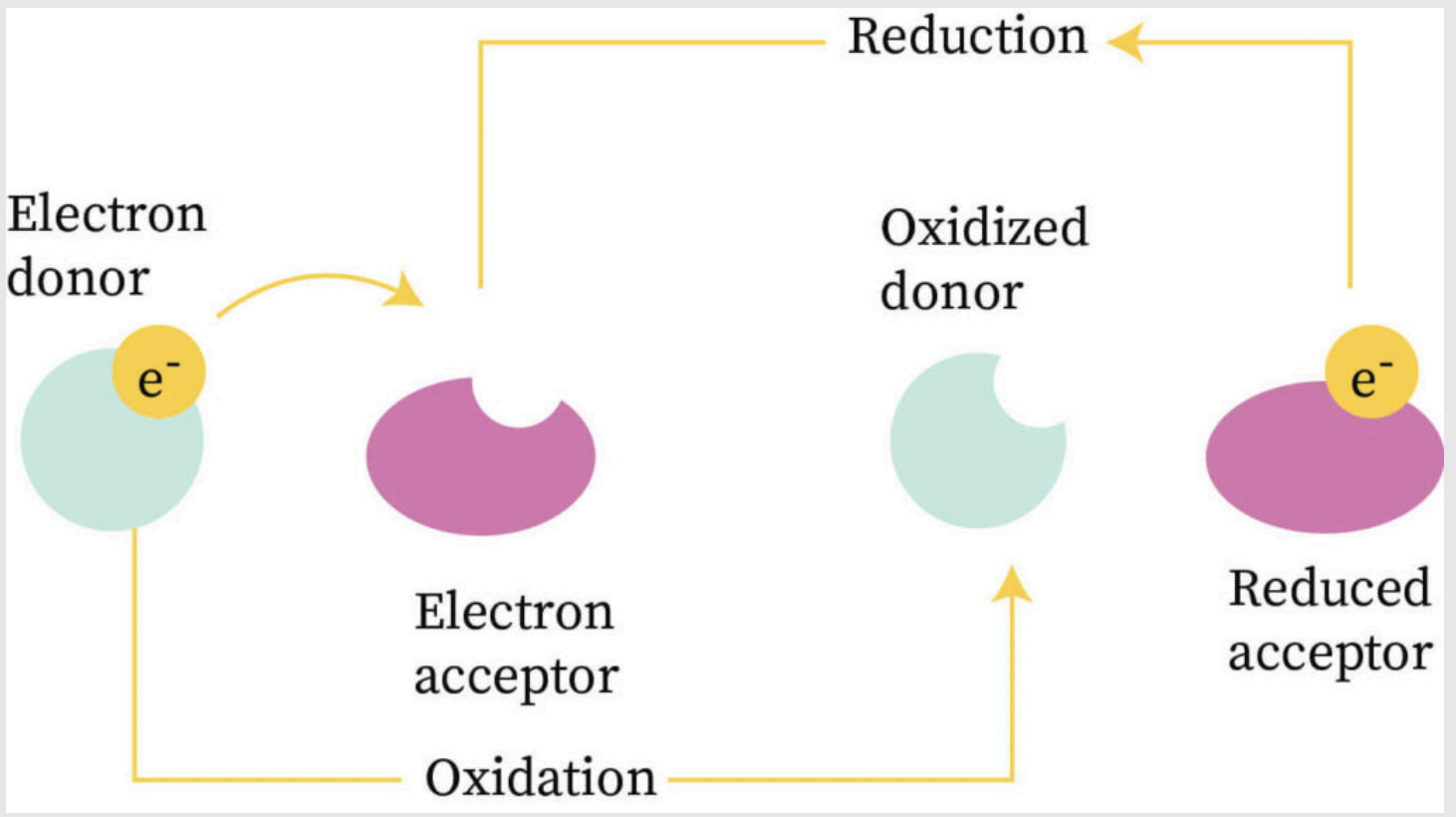
Reduction
A process in which electrons are gained by an entity
Oxidation
A process in which electrons are lost by an entity
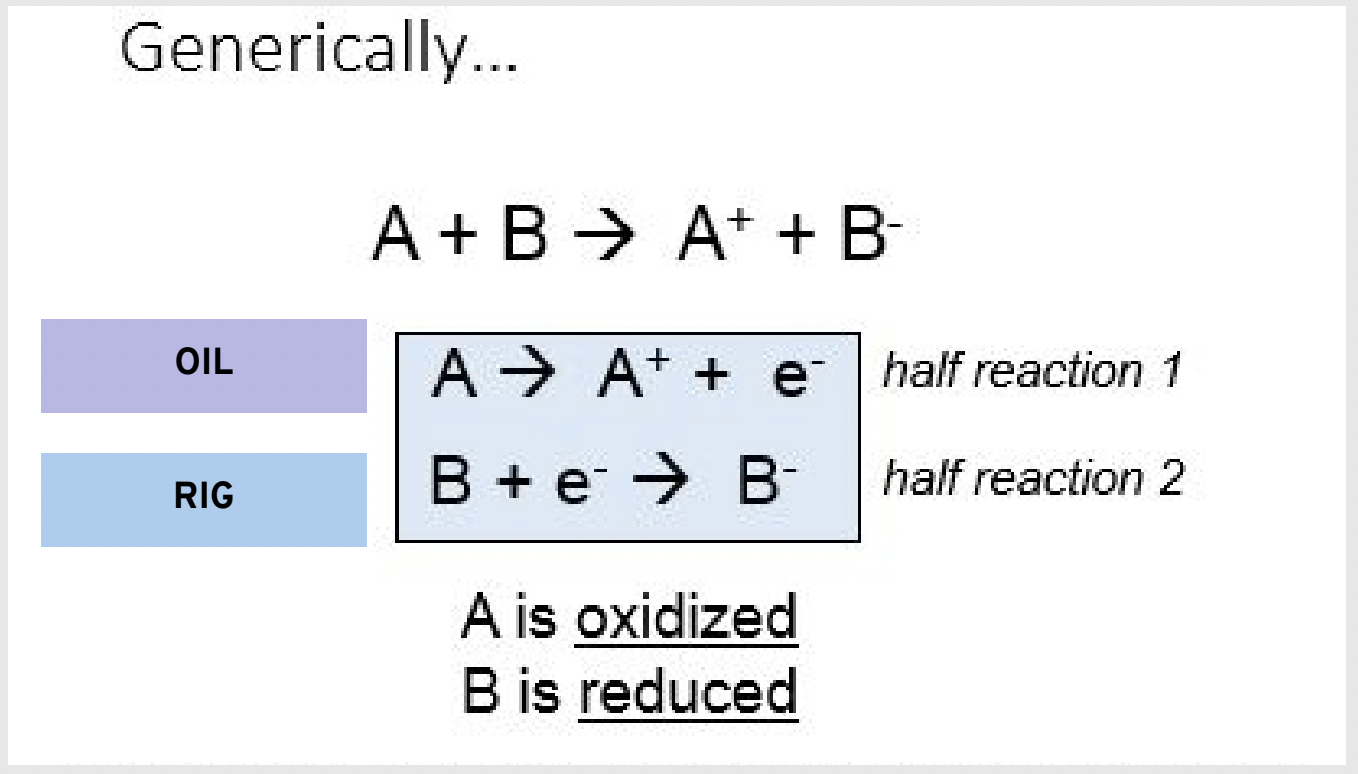
OIL RIG
Oxidation is Losing electrons
Reduction is Gaining electrons
Examples of REDOX
Formation, decomposition, combustion, single replacement, cellular respiration, photosynthesis
Wich reaction are NOT REDOX reactions?
Double replacement
Half reactions
A half reaction represents what is happening to one reactant - it tells one part of the story
The other half is used to tell the other side of the story
When metal is placed into a HCl solution, gas bubbles form as the zinc slowly disappears.
Zn(s) + HCl(aq) ⟶ ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
What is happening to the Zn and the H? -
Zn(s) ⟶ Zn 2+ (aq) + 2e
2H (aq) + 2e - ⟶ H (g)
How are half reactions balanced?
By mass (number of atoms) and by charge
Show the generic outline of the half reactions for oxidation and reduction:
Name background of reduction
Historically the formation of a metal from it “ore” (or oxide)
Recap of reduction
A gain of electrons occurs (so they become more negative)
Electrons are shown as the reactant in the half reaction
Name background of oxidation
Historically, reactions with oxygen
Recap of oxidation
A loss of electrons occurs (so the entity becomes more positive)
Electrons are shown as the product in the half-reaction
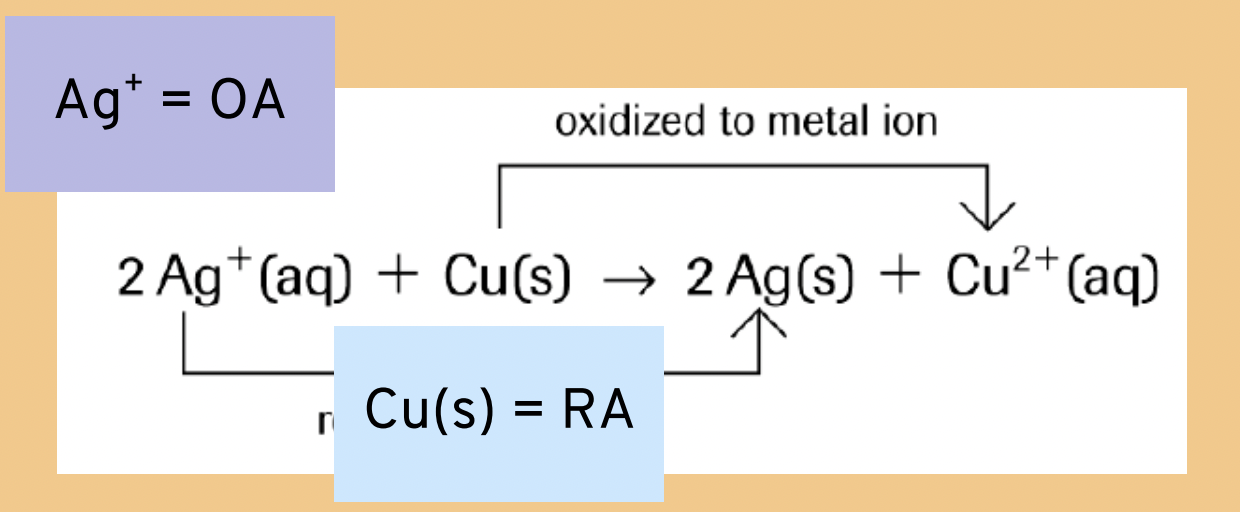
Oxidizing Agent (OA)
Causes oxidation by removing e
Reducing Agent (RA)
Causes reduction by donating e
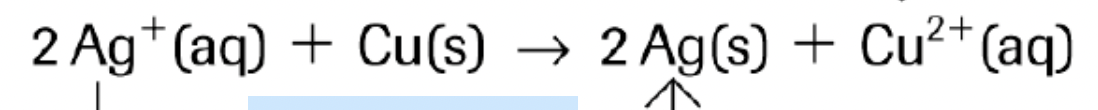
WHICH IS THE RA AND OA IN THIS EXAMPLE?
If a substance is a very strong oxidizing agent, what does this mean in terms of electrons?
The substance has a very strong attraction for electrons.
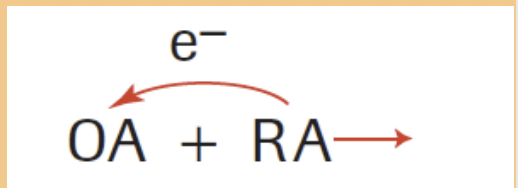
If a substance is a very strong reducing agent, what does this mean in terms of electrons?
The substance has a weak attraction for its electrons, and they can be easily removed
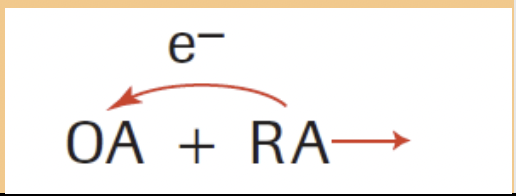
If the Oxidation Agent is stronger than the reducing agent the reaction can happen
Spontaneously

So far we have been using examples where the oxidizing agents are metal ions and the reducing agents are metal atoms. What else can gain or lose electrons?
Non-metal atoms i.e., Cl2 + 2e- ⟶ 2 Cl (g)-
Non-metal ions i.e., 2Br-(aq) ⟶ Br2(l)+ 2e-
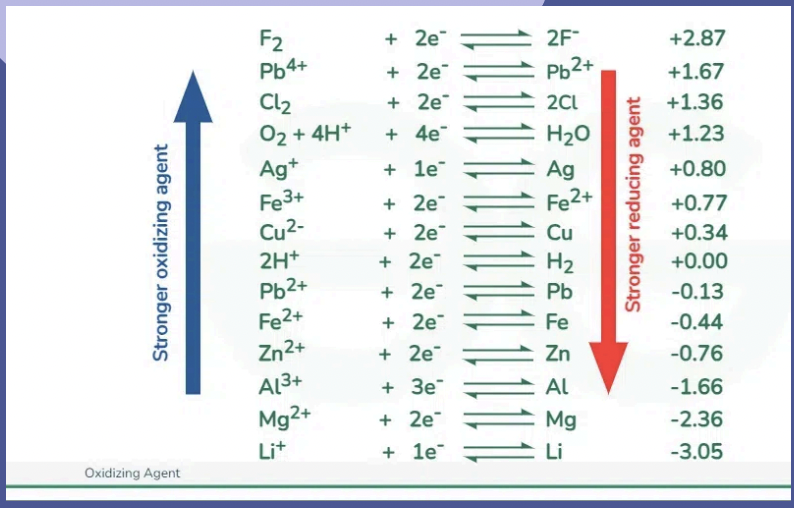
Redox Table Trend
OAs tend to be metal ions and non-metal atoms Ras tend to be metal atoms and non-metal ions
Multivalent metals
Entities that can act as BOTH RAs and OAs
example IRON can be Fe or Fe

Hints for listing and labeling entities

Steps to create balanced redox reaction equations
Step 1 - determine all the entities that are present. *remember in solutions, molecules and ions behave independently of each other.
Step 2 - determine all the possible OA’s and RA’s
Step 3 - Identify the Strongest oxidizing agent (SOA) and the strongest reducing agent (SRA)
Step 4 - show the 1⁄2 reactions
Step 5 - balance the 1⁄2 reactions and combine
Step 6 - Predict if the reaction is spontaneous or not
Disproportionation
A reaction in which the SAME species is both oxidized and reduced at the same time
What is disproportionation also called?
Sometimes called autooxidation or self oxidation-reduction
Occurs when a substance can act as either an OA or and RA

What is substance can always be considered either and OA or RA?
Water
Electric cell
Converts chemical energy into electrical energy
Alessando Volta
Invented the first electric cell but got his inspiration from Luigi Galvani.
Galvani
Crucial observation was that two different metals could make the muscles of a frog’s legs twitch. Unfortunately, Galvani thought this was due to some mysterious “animal electricity”. It was Volta who recognized this experiment’s potential.
Battery
Two or more electric cells connected in series to produce a steady flow of current
Volta’s first battery
Consisted of several bowls of brine (NaCl ) connected by metals that dipped from one bowl to another

Volta’s revised design
Consisted of a sandwich of two metals separated by paper soaked in salt water.
Alessandro Volta’s invention was an immediate technological success because it?
Produced electric current more simply and reliably than methods that depended on static electricity.
Also produced a steady electric current –something no other device could do.
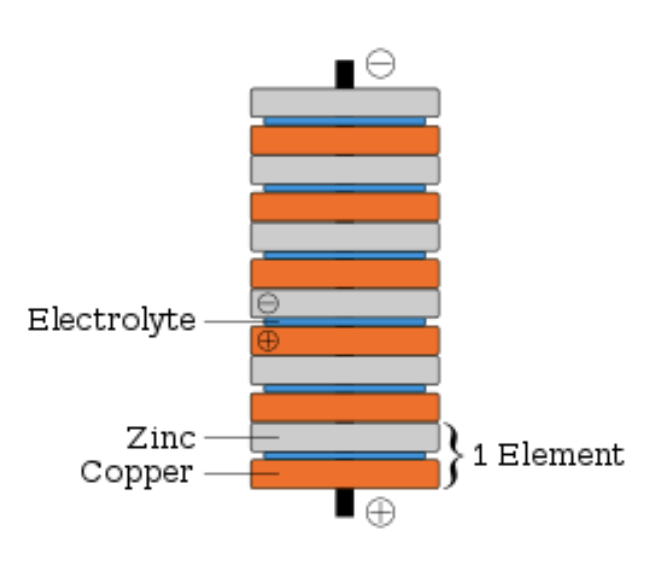
Electric cells are composed of?
Two electrodes and at least one electrolyte (aqueous electrical conductor).
Electrodes