Micrometrics SAQ 1
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Why is particle size measurement of pharmaceutical powders important?
Can affect final formulation performance, appearance, stability and processability of powders such as flowability, mixing, compression and compactions
Why are the solubility characteristics of a material important to know in terms of choosing an appropriate method for particle size analysis?
Solubility determines whether a wet or dry method should be used – i.e. whether a powder can be run in suspension or dry, which directly affects method suitability and accuracy
What type of a distribution do you get from a microscopy analysis?
Number distribution
What is Martin’s diameter?
The length of the line which bisects the particle image. The lines may be drawn in any direction which must be maintained constant for all image
Why will coin-shaped particles lead to a bias in the measured distribution?
They tend to lead to a bias as they have a tendency to fall with their maximum surface area in contact with the slide, affecting apparent measured size.
What is an eyepiece reticle/graticule?
A manual measurement method which allows us to compare particles to globes and circles of different sizes. Dark particles are compared to globes whilst light/transparent particles are compared to circles
How does electron microscopy differ from optical microscopy?
Electron microscopy uses electrons instead of light allowing visualization of sub-micron particles, optical microscopy is limited by diffraction and depth of focus
What type of a distribution do you get from a sieve analysis?
weight distribution
What is the aperture size of a sieve? What is the mesh size?
Aperture size: the minimum square opening through which a particle can pass
Mesh size: the number of wires per liner inch
Why might you want to undertake a wet sieve analysis, rather than a dry sieve analysis?
Wet sieving is used when powders are cohesive, contain fine particles or when agglomeration prevents efficient passage through the sieve during dry sieving
Describe air-jet sieving
Air jet sieving uses a jet of air to disperse particles and clear sieve apertures improving separation of fine particles
1. Material placed on mesh of sieve
2. Underneath screens a scale rotates
3. Compressed air comes up through nossel
4. Material is fluidized on screen
5. Vacuum suction under screen pull fluidized small material through screen
6. Fractions powder into two portions
Why will rod-shaped particles give you an overestimation of under-size in a sieve analysis?
They can pass through sieve apertures in their smallest dimension
What is the basis principle of particle size analysis by laser diffraction?
Particles scatter light at angles inversely related to particle size as they pass through a laser beam: the scattered light intensity pattern is analysed to obtain particle size distribution
What type of a distribution do you get from a laser diffraction analysis?
volume distribution
In laser diffraction analysis, the d50 is a frequently reported parameter. What is the d50?
The median particle size: 50% of the particles are smaller and 50% are larger than this size
What is the basic principle of particle size analysis by dynamic light scattering (DLS)?
DLS measures time-dependent fluctuations in scattered light intensity caused by Brownian motion of particles: smaller particles move faster than larger ones
In DLS analysis, what is the autocorrelation function?
It is the mathematical comparison of the scattered light signal with itself over time use to relate the rate of decay to particle size
What type of diameter is measured by DLS?
They hydrodynamic diameter – the diameter of a sphere that diffuses at the same rate as the particle
Light scattering phenomena and (analyses based thereon) light scattering can be classified as: time-averaged scattering or time-dependent scattering. Which relates to laser diffraction and which to DLS?
Laser diffraction: time averaged scattering
DLS: time dependent scattering
What is the specific surface area of a powder?
The total surface area per unit mass expressed as m^2/g
Describe how the process of gas adsorption onto a solid surface can be used to determine the surface area of the solid.
The amount of gas needed to form a monolayer on the solid surface is measured. Knowing cross sectional area of gas molecules allows calculation of the solids surface area (BET method)
In particle sizing, why do we refer to equivalent sphere diameters?
Because many techniques assume particles behave like spheres allowing comparison between different methods even when particles are irregular in shape
Draw an example of a frequency distribution curve.
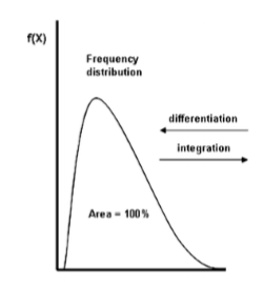
Draw an example of a cumulative distribution curve
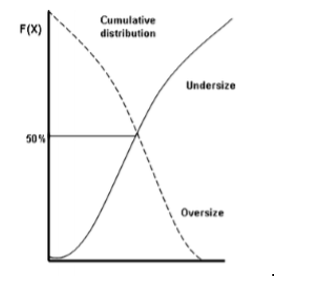
What is the median of a particle size distribution?
The particle size at which 50% of particles are smaller and 50% are larger
What is the mode of a particle size distribution?
The most frequent particle size corresponding to the peak of the frequency curve
What is meant by the term a “skewed distribution”?
A distribution that is asymmetric with a longer tail on one side of the curve
What is a log-normal distribution?
A distribution that becomes symmetrical when particle size is plotted on a logarithmic scale