Cognitive Theories and Models
1/9
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
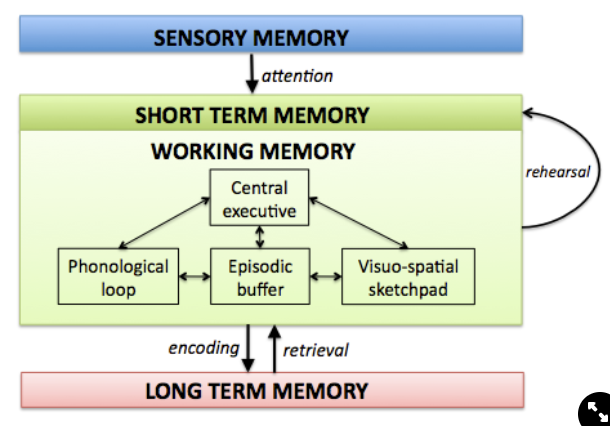
Working Memory Model
Focuses on short term memory. Divides STM into 4 components:
central executive
phonological loop
visuo-spatial sketchpad
episodic buffer
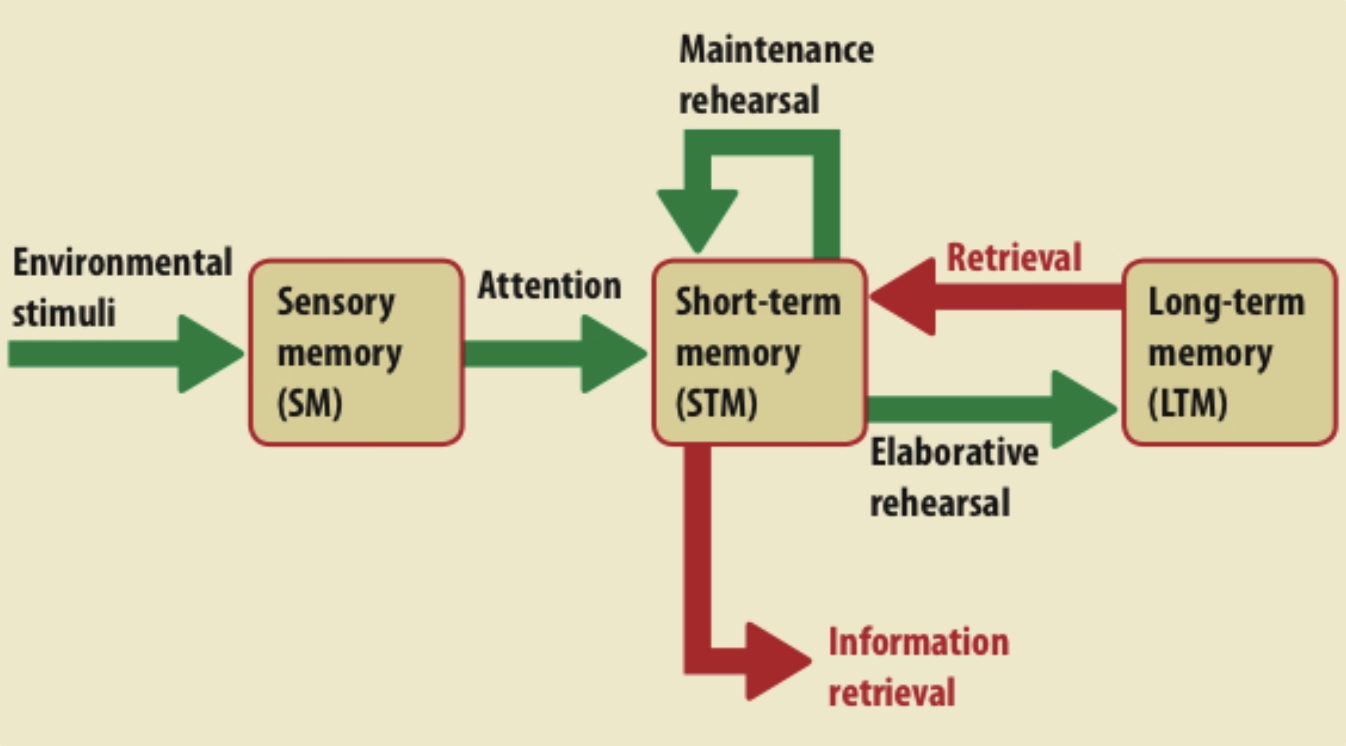
Multi-Store Model
Describes memory processing in a linear way through multiple independent stores:
Sensory memory, short term memory and long term memory
Reconstructive Memory
Human beings are active processors, not passive
Schemas can determine what individuals pay attention to
Memories are constructed and then reconstructed throughout the memory process based on schematic influence
proactive interference
When schematic processing influences memory encoding
When schematic processing influences memory recall
retroactive interference
Anchoring Bias
the tendency to use an initial piece of information for future subsequent judgements and decisions
Adjust thinking from the anchor
Can even occur when the anchor (initial piece of information) is random or arbitrary
Very difficult to avoid even when people understand the bias and are motivated to avoid it
Anchoring as Adjustment
Anchor is set
Individuals use the anchor as the base to adjust away from (anchor is understood as invalid)
But....they are lazy and so insufficiently adjust and stop at the boundary of an acceptable range
This is within cognitive awareness
Selective Accessibility
Anchor is set
Individual uses anchor as a plausible suitable decision and thus judges its attributes as valid (anchor is understood as valid)
When proposing new decision, it is judged with regard to valid aspects of anchor
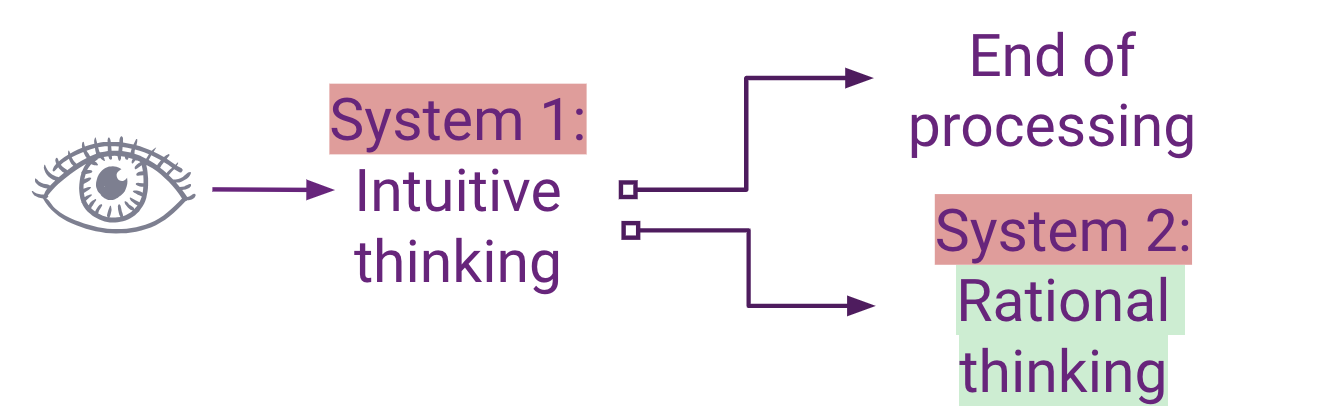
Dual Processing Theory
System 1= Unconscious, implicit thinking. Fast but error prone.
System 2= explicit, conscious reasoned thought. Requires more cognitive effort and time. Leads to more accurate decision making.
Flashbulb memory
A clear and vivid long-term memory of an especially emotional, surprising and meaningful event.
Theorised to be highly detailed and accurate episodic memory due to triggering of biological processing, dubbed the 'print now' mechanism. Potentially evolutionarily advantageous.