Bio Ch. 11
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/46
Earn XP
Last updated 11:52 PM on 5/29/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
1
New cards
Define surface area
SA^cube(l x w x b) amount "covering" an object
2
New cards
Define volume
V^cube(l x w x h) amount of space inside object; how much space it takes up
3
New cards
What cells have the largest surface area to volume ratio?
Smaller cells
4
New cards
What cells have the smallest surface area to volume ratio?
Larger cells
5
New cards
Define information crisis
Too many demands placed on DNA
6
New cards
Define traffic problems
When the volume of a cell grows too fast relative to surface area, material exchange is insufficient
7
New cards
Describe cell division
Produces two daughter cells, cells must replicate DNA before division, diving to make more so smaller cells keep surface area to volume ratio high, can be either sexual or asexual
8
New cards
Describe asexual reproduction
A single parent produces genetically identical offspring, produces many offspring in short period, in stable environments genetically identical offspring thrive but if conditions change offsping not well adapted
9
New cards
Describe sexual reproduction
Involves fusion of two different parent cells, offspring inherit genetic information from each parent, relatively fewer offspring, growth takes more time, need to find a mate, in changing environments genetic diversity can be beneficial, offspring ma be less well adapted in current conditions
10
New cards
What has to occur before cell division?
Genetic material must be duplicated
11
New cards
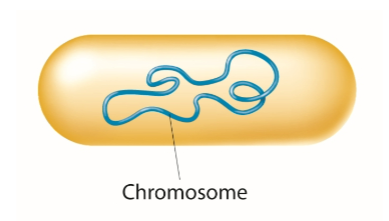
What happens before cell division in prokaryotic cells?
DNA is packaged into a single, circular chromosome
12
New cards
What happens before cell division in eukaryotic cells?
DNA is packaged into multiple chromosomes, DNA wound around proteins called histones is called chromatin, precisely separated into two daughter cells during cell division
13
New cards
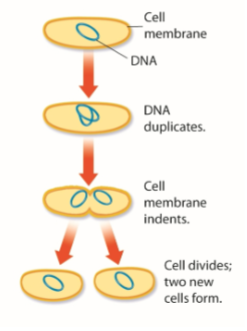
Describe the prokaryotic cell cycle
Undergo binary fission; cell duplicates, cell membrane indents, cell divides and two new cells form
14
New cards
Summarize the eukaryotic cell cycle
Cell grows, prepares for division, then divides to form two daughter cells
15
New cards
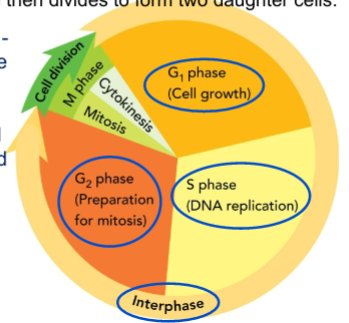
Describe interphase
Time in-between divisions, divided into G1 (cell growth), S (DNA replication), and G2 (preperation for mitosis) phases
16
New cards
Describe the M phase
Cell division occurs during M phase, includes prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase
17
New cards
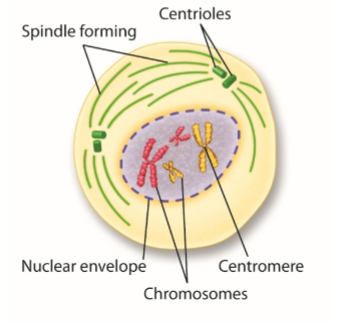
Describe prophase
Nucelus condenses and chromosomes become visible, spindle begins to form
18
New cards
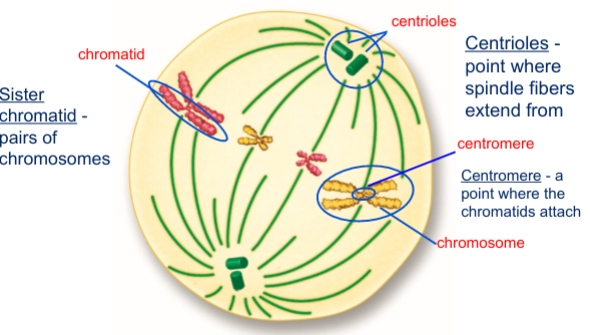
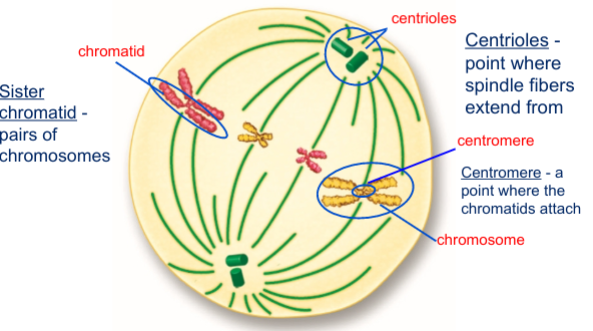
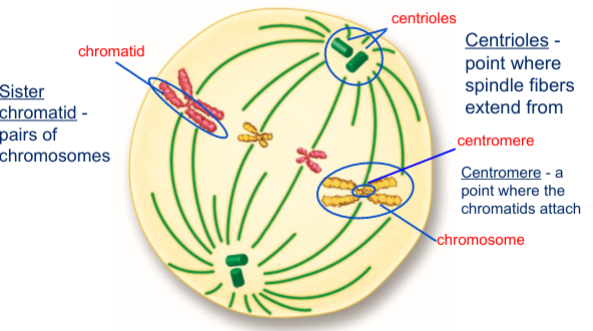
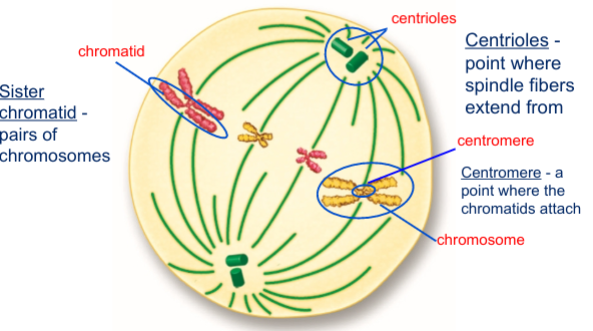
Describe metaphase
Chromosomes line up at the center of the cell
19
New cards
Define sister chromatid
Pairs of chromosomes
20
New cards
Define centioles
Point where spindle fibers extend from
21
New cards
Define centomere
a point where the chromatids attach
22
New cards
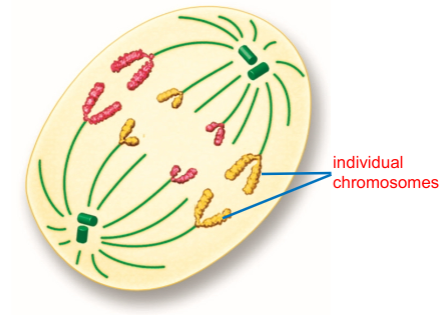
Describe anaphase
Chromosomes move toward oppisite poles
23
New cards
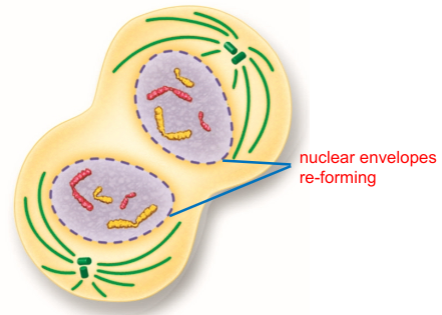
Define Telophase
Cell begins to divide into daughter cells
24
New cards
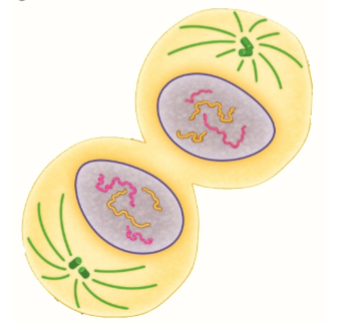
Cytokinesis
In animal cells, cell membrane pinches in the center to form two daughter cells
25
New cards
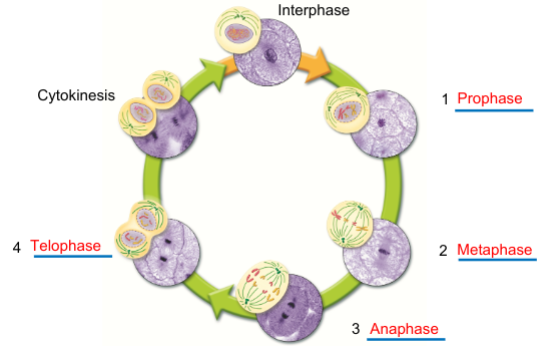
List and describe the phases of mitosis
Interphase (includes G1- cell growth, S- DNA replication, G2- preparation for mitosis) which occurs in-between cell divisions, and M phase, which cell division occurs in (prophase- nucleus condences and chromosomes become visible, spindle begins to form, metaphase- chromosomes line up in center, anaphase- chromosomes move torwards oppisite poles, telophase- cell begins to divide into daughter cells, and cytokinesis (animal cells)- cell membrane pinches in center to form two daughter cells)
26
New cards
How does cell division relate to healing a bone
Cells at the edge of an injury are stimulated to divide rapidly, as an injury heals, the rate of cell division slows
27
New cards
Define cyclins
Proteins that regulate the cell cycle, the signal that controls the cell cycle, what tells a cell when to divide, when to duplicate chromosomes, when to enter another cell cycle stage
28
New cards
Describe how cyclins were discovered
Scientists found a protein in a cell undergoing mitosis, injecting protein into non dividing cell, mitotic spindle started to form
29
New cards
What are the two types of regulatory proteins
Internal and External regulators
30
New cards
Describe Internal regulators
Respond to events inside the cell
Let cell cycle proceed only when certain steps have already happened
Let cell cycle proceed only when certain steps have already happened
31
New cards
Describe external regulators
Respond to events outside the cell
Direct cells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle
Direct cells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle
32
New cards
Define and describe apoptosis (me rn)
Process of programmed cell death, important role in structuring tissues during growth and development, cell undergoes series of controlled steps for self destruction
33
New cards
Describe cancer cells
Don’t respond to normal regulatory signals and in turn cell cycle is disrupted and cells grow and divide uncontrollably
34
New cards
Describe cancer formation
A cell begins to divide abnormally, produce a tumor and start to displace normal cells and tissues, cancer cells move to other parts of the body
35
New cards
What causes cancer?
A defect in genes that controll cell growth and division, in all cancers control over the cell cycle
36
New cards
37
New cards
38
New cards
Define differentiation
The process by which a cell becomes specialized, determines cell’s ultimate identity
39
New cards
Define stem cells
Specialized cells from which differentiated cells develop
40
New cards
Define totipotent cells
Cells that can develop into any type of cell in the body
41
New cards
Define pluripotent cells
Cells that are capable of developing into most but not all cell types
42
New cards
A human embryo forms into a blastocyst
A duck walks into a bar (idk but it seemed important so i put it)
43
New cards
Define multipotent
Limited potential to develop into many different types of differentiated cells
44
New cards
Describe adult stem cells
Multipotent, mainly found in bone marrow, hair follicles, also some in brain, heart, and skeletal muscle
45
New cards
Describe a bone marrow transplant (regenerative medicine)
Stem cells filtered from bone marrow removed from a patient’s hip, stem cells are injected into heart’s damaged area, environment of the heart stimulates injected stem cells to differentiate into new heart muscle cells
46
New cards
Describe the ethical issues in stem cells
Human adult stem cell research is rarely controversial because of willing donors. However, embryonic stem cells is controversial because arguments for and against involve ethical issues of life and death
47
New cards
Describe induced pluripotent stem cells
Breakthrough in 2007, human fibroblasts could be converted into cells that closely resembled embryonic stem cells, now widely used in research
Genes are added to adult cells, display properties similar to embryonic stem cells, now have capacity to develop into number of specialized cell types
Genes are added to adult cells, display properties similar to embryonic stem cells, now have capacity to develop into number of specialized cell types