4.1.1.6 Culturing microorganisms
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/44
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards
equipment
• a nutrient agar plate
• a Bunsen burner
• a heatproof mat
• a disposable plastic pipette
• a culture of bacteria (Bacillus subtilis)
• a glass spreader
• filter paper discs
• three antiseptics (such as mouthwash, TCP, and antiseptic cream)
• disinfectant bench spray
• a ‘discard beaker’ of disinfectant
• a small beaker of ethanol
• forceps
• tape
• hand wash
• a marking pen
• access to an incubator.
2
New cards
Disinfectants
- used to kill bacteria in environment but are toxic to people
3
New cards
method
1. clean bench with disinfectant solution-kills microorganisms that could conatminate our culture
2. sterilise an inoculating loop by passing it through a bunsen burner flame
3. open a sterile agar gel plate near a bunsen burner flame. the flame kills bacteria in the air
4. use loop to spread chosen bacteria evenly over the plate
5 . place sterile filter paper discs containing antibiotic onto the plate
6. incubate plat at 25 degree celcius
7. The more effective the antibiotic is against the bacteria the larger the inhibition zone will be
\
4
New cards
Aim
To investigate the effect of antiseptics or antibiotics on bacterial growth using agar plates and measuring zones of inhibition
5
New cards
Antiseptics
disinfectants that kill bacteria and are safe to use on human skin
6
New cards
Antibiotics
chemicals that can be used inside body to kill bacteria or prevent them from growing
7
New cards
Aseptic
free from contamination caused by harmful bacteria, viruses, or other microorganisms
`surgically sterile or sterilized.
`surgically sterile or sterilized.
8
New cards
Sterile
- free from bacteria or other living microorganisms; totally clean
9
New cards
List the precautions that were taken to avoid contamination of your nutrient agar culture medium when it was prepared in the petri dishes by the technician.
petri dishes were sterilized
nutrient agar culture medium sterilized
agar petri dish sealed
sealed agar petri dish stored upside down ( to reduce risk of airbone particles setting on them and to prevent the accumulation of any water condensation)
nutrient agar culture medium sterilized
agar petri dish sealed
sealed agar petri dish stored upside down ( to reduce risk of airbone particles setting on them and to prevent the accumulation of any water condensation)
10
New cards
How did you make sure that the lawn of Bacillus subtilis was spread using aseptic techniques?
uncontaminated disposable pipettes used
spreader dipped in ethanol
flamed lid of petri dish raised near bunsen burner for as little time as possible
spreader dipped in ethanol
flamed lid of petri dish raised near bunsen burner for as little time as possible
11
New cards
Once the petri dishes had been prepared with Bacillus subtilis & antiseptic discs, why were they only sealed with two small pieces of tape?
to allow air into bacillus subtillis so they respire aerobically
to prevent anaerobic respiration- these are not wanted as they may promote the growth of pathogenic strains of bacteria
to prevent anaerobic respiration- these are not wanted as they may promote the growth of pathogenic strains of bacteria
12
New cards
The Bacillus subtilis will multiply. What is this simple cell division called?
binary fission
13
New cards
The agar is the culture medium. What is in the culture medium that allows the Bacillus subtilis to grow? Why is it there?
glucose:
minerals including nitrates: for protein synthesis
additional proteins and vitamins may be present to promote binary fission
minerals including nitrates: for protein synthesis
additional proteins and vitamins may be present to promote binary fission
14
New cards
In school laboratories, why is maximum temperature for incubation of cultures set at 25°C?
reduces chances of growing harmful bacteria/pathogens
15
New cards
Why are higher temperatures used under controlled conditions in industry & hospital
microoraginsms divide more rapidly- more binary fission
16
New cards
why do you take the mean value of the clear zone
clear zones are not always perfectly circular so you will need to measure the diameter twice (at 90 to each other) and calculate a mean diameter for each clear zone
17
New cards
define what is meant by aseptic technique and why it is important
to prevent cultures from being contaminated.
To investigate effects of Chemical such as disinfectants and antibiotic
To investigate effects of Chemical such as disinfectants and antibiotic
18
New cards
List 3 possible ways of contamination when preparing a culture of micro organisms
skin, eyes,air, water, work area
19
New cards
What is meant by the term inoculate
Transfer of microorganisms into a
culture medium
culture medium
20
New cards
why was the inoculating loop put in a flame
to kill unwanted pathogens/ bacteria
21
New cards
why did you seal the petri-dish after the practical
to avoid contamination, stop bacteria getting into petri dish as this may affect the result
22
New cards
why did you need to allow the inoculating wire to cool before placing it into your bacteria culture
it will kill/cure bacteria
23
New cards
why do schools inoculate at maximum of 25 degrees celcius
to prevent the growth of unwanted pathogens
24
New cards
why was the petri dish and nutrient agar sterilised before using
kills unwanted microorganisms prevents contamination
25
New cards
why did you store the petri dish upside down
stops moisture from dripping down onto the bacteria and disrupting colonies
26
New cards
list all aseptic techniques used in the practical disinfection
sterilise all petri dishes, agar, bacterial nutrient broth and agar (by heating at a high temperature) kills unwanted microorganisms prevents contamination
sterilise inoculating loop by passing it through a flame ie bunsen burner attach petri dish
using adhesive tap-stops lid falling off and unwanted microorganisms entering or air getting in
Petri dish stored upside down- to stop drops of condesation falling into the agar surface
sterilise inoculating loop by passing it through a flame ie bunsen burner attach petri dish
using adhesive tap-stops lid falling off and unwanted microorganisms entering or air getting in
Petri dish stored upside down- to stop drops of condesation falling into the agar surface
27
New cards
how to culture bacteria
use agar gel plate
contains nutrients
which has been set in a jelly
poored into a petri dish and allowed to set
in agar gel plate bacteria is grown in visible colonies
contains nutrients
which has been set in a jelly
poored into a petri dish and allowed to set
in agar gel plate bacteria is grown in visible colonies
28
New cards
zone of inhibition
region where the bacteria have not grown
29
New cards
calculate area of zone of inhabitation
πr²
30
New cards
Binary Fission
Bacteria multiply by a type of simple cell division known as binary fission
In the right conditions, a bacterial cell prepares to divide by replicating its genetic material before it increases in size
A copy of each piece of circular DNA moves to each end of the cell before the cytoplasm divides, and new cell walls form around each daughter cell
In the right conditions, a bacterial cell prepares to divide by replicating its genetic material before it increases in size
A copy of each piece of circular DNA moves to each end of the cell before the cytoplasm divides, and new cell walls form around each daughter cell
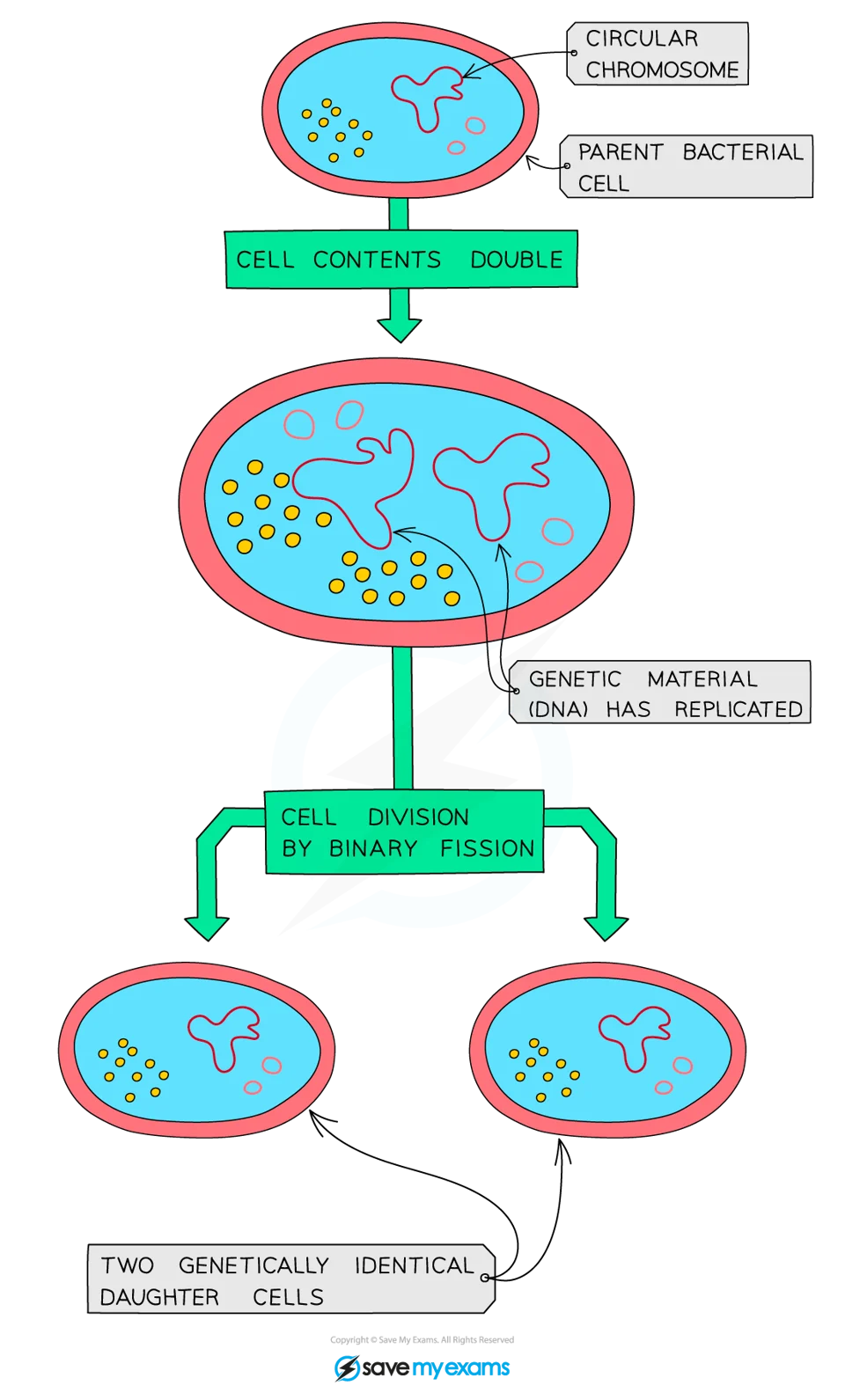
31
New cards
what increases bacteria multiplication
In the right conditions, some species of bacteria (such as coli) can multiply as much as once every 20 minutes. This is ideal as large cultures of bacteria for study can be grown in relatively short periods of time
32
New cards
Warmer temperatures
promote faster growth, but in a school lab the maximum allowed temperature for growth is 25°C
Above this temperature, more harmful pathogens are likely to grow
Above this temperature, more harmful pathogens are likely to grow
33
New cards
There are two ways to grow microorganisms in the lab:
. In nutrient broth solution- involves making a suspension of bacteria to be grown
and mixing with sterile nutrient broth (the culture medium), stoppering the flask
with cotton wool to prevent air from contaminating it and shaking regularly to
provide oxygen for the growing bacteria.
2. On an agar gel plate- the agar acts as the culture medium, and bacteria grown on
it form colonies on the surface.
Making the plate:
● Hot sterilised agar jelly is poured into a sterilised Petri dish, which is left to
cool and set
● Wire loops called inoculating loops are dipped in a solution of the
microorganism and spread over the agar evenly
● A lid is taped on and the plate is incubated for a few days so the
microorganisms can grow (stored upside down)
and mixing with sterile nutrient broth (the culture medium), stoppering the flask
with cotton wool to prevent air from contaminating it and shaking regularly to
provide oxygen for the growing bacteria.
2. On an agar gel plate- the agar acts as the culture medium, and bacteria grown on
it form colonies on the surface.
Making the plate:
● Hot sterilised agar jelly is poured into a sterilised Petri dish, which is left to
cool and set
● Wire loops called inoculating loops are dipped in a solution of the
microorganism and spread over the agar evenly
● A lid is taped on and the plate is incubated for a few days so the
microorganisms can grow (stored upside down)
34
New cards
bacteria at end=
bacteria at beginning x 2 ^number of divisions =
35
New cards
Petri dishes and culture media
must be sterilised before use, often
done by an autoclave (an oven) or
UV light.
must be sterilised before use, often
done by an autoclave (an oven) or
UV light.
If this step does not take place, they are likely to be contaminated with other microorganisms. These could be harmless but will compete with the
desired bacteria for nutrients and space, or they could be harmful (for example through a mutation taking place), potentially producing a new pathogen
desired bacteria for nutrients and space, or they could be harmful (for example through a mutation taking place), potentially producing a new pathogen
36
New cards
Inoculating loops must be sterilised
by passing them through a flame.
by passing them through a flame.
This kills unwanted microorganisms, which is needed for reasons above.
37
New cards
The lid of the Petri dish should be
sealed (but not completely) with
tape.
sealed (but not completely) with
tape.
Sealing stops airborne microorganisms from contaminating the culture, but it should not be sealed all the way around as this would result in harmful anaerobic bacteria growing (due to no
oxygen entering).
oxygen entering).
38
New cards
The Petri dish should be stored
upside down.
upside down.
This is to prevent condensation from the lid landing on the agar surface and disrupting growth.
39
New cards
The culture should be incubated at
25 degrees.
25 degrees.
If it were incubated at a higher temperature, nearer 37 degrees (human body temperature), it would be
more likely that bacteria that could be harmful to humans would be able to grow as this is their optimum temperature. At lower temperatures,
colonies of such bacteria would not be able to grow.
more likely that bacteria that could be harmful to humans would be able to grow as this is their optimum temperature. At lower temperatures,
colonies of such bacteria would not be able to grow.
40
New cards
To calculate the zone inhibition
R^2
41
New cards
Binary fission
The process by which prokaryotic organism, like bacteria divide and reproduce
42
New cards
Which **two** things must a bacterial cell do before it can divide?The
Grow
Replicate its genetic material
Replicate its genetic material
43
New cards
Once a bacterial cell has grown and replicated its genetic material, it is ready to divide by binary fission.
\
Describe the stages of this process.
\
Describe the stages of this process.
The circular DNA and plasmids replicate
They sell gets bigger and The two circular strands of DNA move to opposite sides of the cell
A new cell wall from down the middle of the cell
The two halves pull apart to form two cells
The plasmids are randomly arranged, so there are often more plasmids in one cell that the other.
They sell gets bigger and The two circular strands of DNA move to opposite sides of the cell
A new cell wall from down the middle of the cell
The two halves pull apart to form two cells
The plasmids are randomly arranged, so there are often more plasmids in one cell that the other.
44
New cards
What is the mean division time?
The mean (average) time it takes for a bacterial cell to divide
45
New cards
Condition for rapid division
Warm
Damp
Lots of nutrients
If conditions become unfavourable they stop dividing eventually die
Damp
Lots of nutrients
If conditions become unfavourable they stop dividing eventually die