eyelids 1
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
the grey line is the junction of
skin and conjuctival mucous membrane
anterior vs posterior eye anatomy
anterior
-orbicularis muscle
-skin
posterior
-conjuctiva
-meibomian gland
-mucocutaneous junction
gray line is also known as
muscle of riolan
main vs minor retractor
main: levator
innervation: CN 3
elevated by 15mm
minor: mullers
innervation: sympathetic nervous system
elevated by 3mm
what muscle aids in drainage of aqueous humor
horner’s
surrounds canaliculi
inferior retractors
analogous to levator: inferior tarsals aponeurosis
analogous to muller: inferior tarsal muscle
orbicularis oculi is innervated by which nerve?
CN 7
palpebral fissure distances
vertical 9-10 mm
horizontal 25-30mm
what is MRD?
marginal reflex distance
>measure from middle of pupil superior and inferior
ranges:
MRD1 (superior): 4mm
MRD2 (inferior): 5mm
palpebral fissure (addition of both): 9mm
epicanthic fold
upper or lower eye lid → medial canthi
tx:
V-Y or Z-plasty
most common type of epicanthal fold
palpebralis
*most common in cacucasians
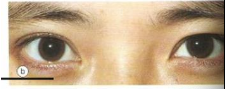
fold in the upper eyelid is known as _________ and is most common in which ethnicities
tarsalis
orientals
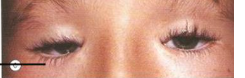
fold in the lower lid is known as
inversus
*may be associated with syndromes
& blepharophimosis

what type of fold arise above the brown and extend downward?
superciliaris
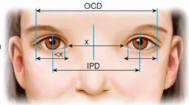
what is this an example of ? (hypertelorism or telecanthus) and how do you know?
hypertelorism
due to smaller outer canthal distance
due to wide bony separation of the orbits
rare AD inherited syndrome
palpebral fissure 20-22mm (normal is 25-30mm)
poor levator muscle function
whats the dz?
BPES
which disorder presents vertical lashes?
epiplepharon
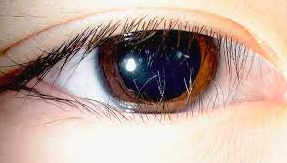
microphthalmos may cause ________ __________
congenital entropion
patients with this disease also have low ears
due to ______________
teacher collins syndrome
due to mandibulofacial dysostosis
what syndrome has syndactyly and what is it?
fraser syndrome
fusion of fingers or toes
eyelids that appear unusually wide or stretched are caused by which disease?
euryblepharon
this disease may present fish-like mouth & do not have eyelids
ablepharon
which disease presents a filament of skin that doesn’t open completely
Ankyloblepharon filiforme adnatum
districhiasis congenital vs acquired
congenital: dark and thick
acquired: thin and light
misdirection of growth
FBS
irritation
tearing
redness
trichiasis
aberrant lashes (lashes are where they shouldn’t be)
^appear in the grey line
districhiasis
excessive eyelash growth
trichomegaly
madarosis vs trichotillomania
madarosis: loss of lashes
trichotillomania: pt pulls out hair
*can tell due to new growth, which madarosis does not have
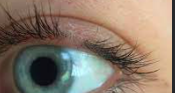
what disorder does this patient have?
trichotillomania

T/F poliosis is associated with uveitis
true