Digeneans, Monogeneans, Platyhelminthes,
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
Platyhelminthes, broken into Platy + helminthes = ___
flat worm
all Platyhelminthes are ___
dorso-ventrally flattened acoelomates, triploblastic, and bilaterally symmetrical
Why don’t Platyhelminthes have a fossil record? Because __
they have soft bodies
Acoelomate - space between digestive system and integument is ____
filled with mesodermally derived tissue = parenchyma
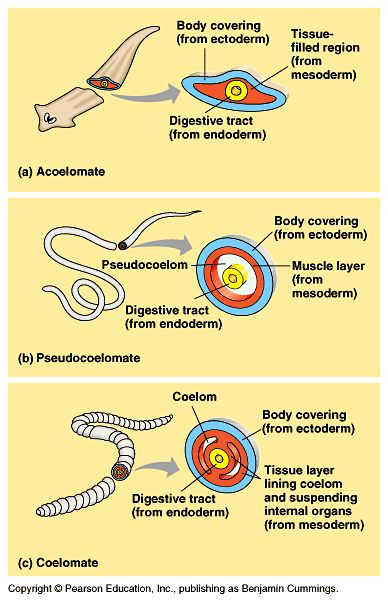
Pseudocoloemate -
inside surface of integument is bounded by mesoderm
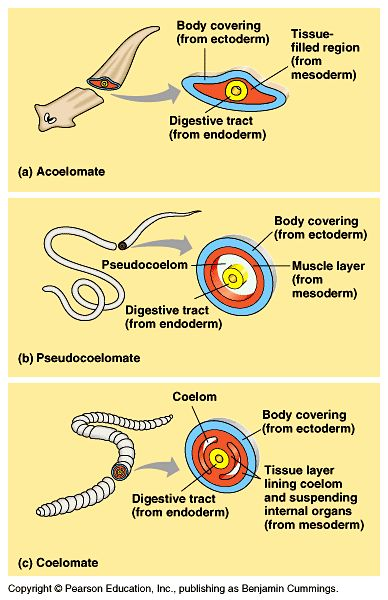
Coelomate -
Entire cavity is bounded by mesoderm
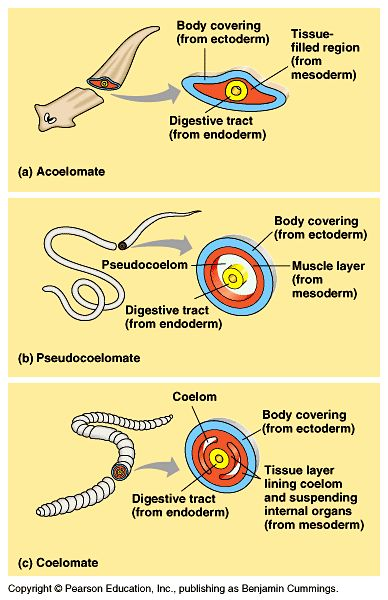
Triploblastic refers to ___
derivation of all adult organs and tissues from 3 embryonic layers
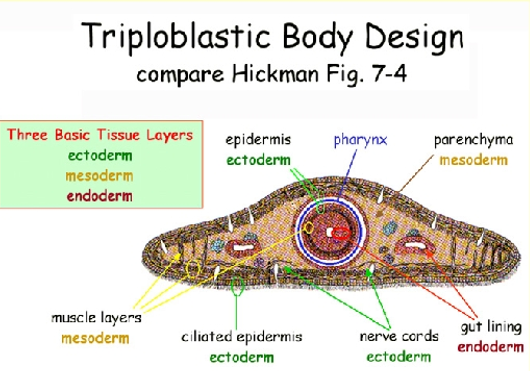
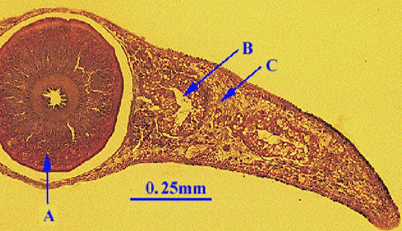
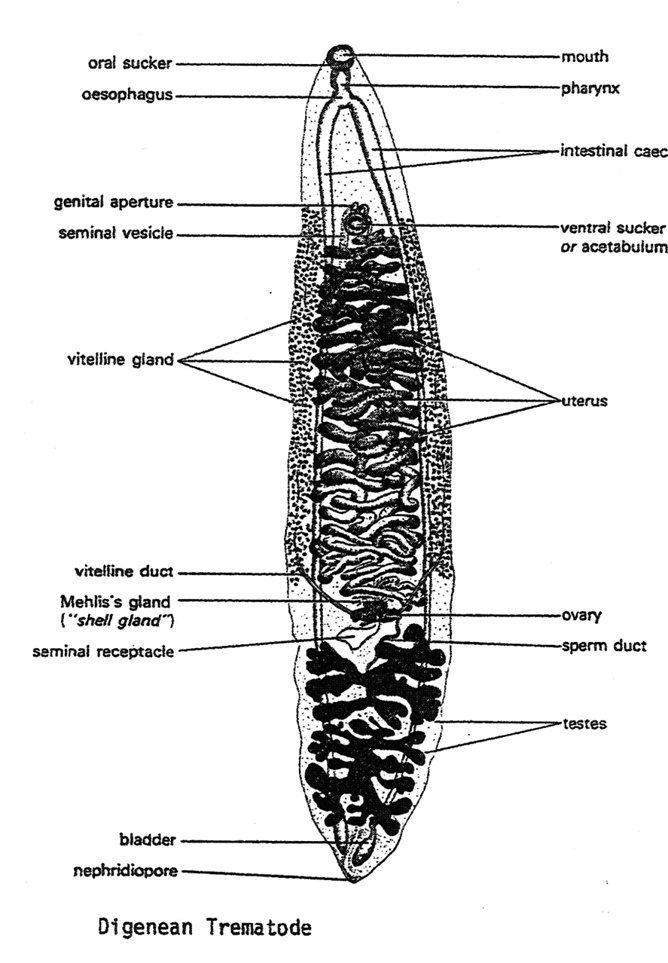
What does A point to?
pharynx
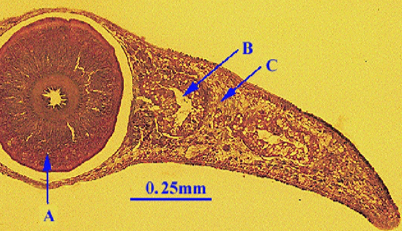
What does B point to?
gut

What does C point to?
parenchyma
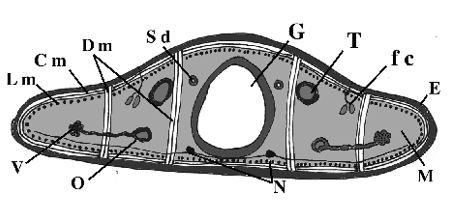
What does G point to? (white portion)
Gut

What does M point to? (light gray portion)
mesoderm
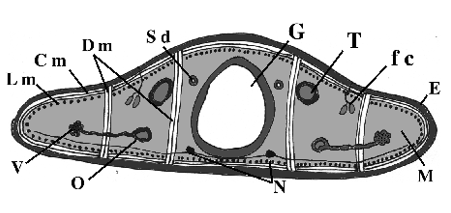
What does fc point to? (small dots)
flame cells
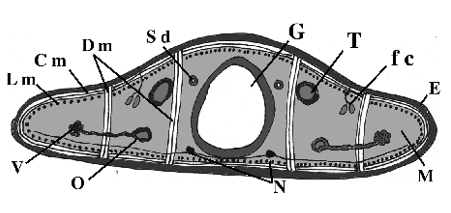
What does N point to? (black dots under gut)
Nerve cords
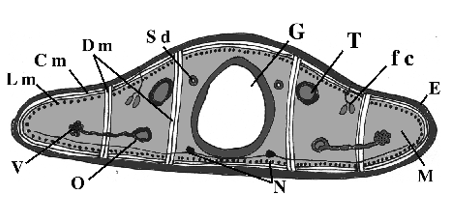
What does T point to?
testes

What does O point to?
oviduct
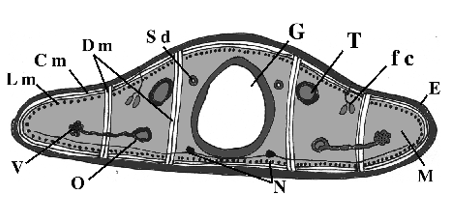
What does V point to?
Vitellaria
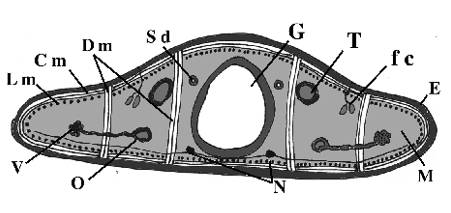
What does Sd point to?
Sperm duct
What are the groups of Platyhelminthes? (older classification)
Turbellaria, Cestoda, Monogenea, Trematoda, Aspidogastrea
What group of platyhelminthes is described as free-living?
Turbellaria
We humans are ___ (body cavities)
Coelomates
Nematodes are ___ (body cavities)
Pseudocoelomates
Platyhelminthes are ___ (body cavities)
Acoelomates
The parenchyma is a “packing-material” which has various cell types for various functions, like ___
secretory, waste/food storage, energy production
The parenchyma of platyhelminthes is __
regenerative
What muscle type(s) do platyhelminthes have?
longitudinal, circular
The tegument is the ___
outer surface
What does it mean if the tegument is syncytial? It means that ___
the outer covering is one continuous layer of cytoplasm with many nuclei and no separate cell membranes
The tegument is ___ in adults
syncytial
What type of nervous system do platyhelminthes have?
Orthogon type (ladder type)
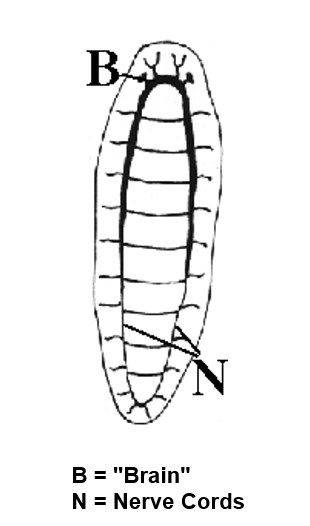
In platyhelminthes, the commissures __
connect the longitudinal nerve cords, forming a ladder-like nervous system.

In the platyhelminthes nervous system, longitudinal nerve trunks ___
run posteriorly (the length of the body)
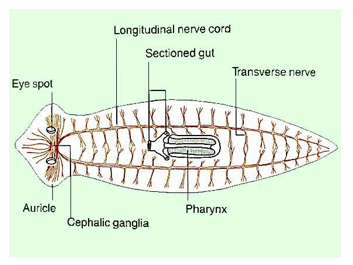
In the Platyhelminthes nervous system, where do nerves run in relation to sensory or holdfast organs?
Nerves run anterior (in front) of the sensory or holdfast organs
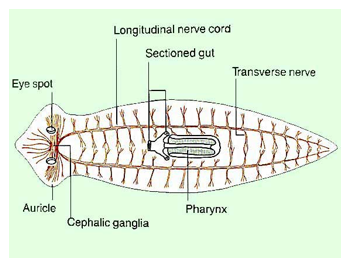
The digestive system of platyhelminthes is a __
blind sac (mouth and anus = same hole)
Which group does NOT have a digestive system?
Cestodes
Platyhelminthes have a ___, from simple to highly branched
great variety in digestive systems

Platyhelminths are endowed with ___ for excretion of metabolic wastes
protonephridia
Platyhelminths excretory system is mainly to regulate ___
osmotic pressure (if too much water they can get rid of it)
Platyhelminths excretory system is composed of ___
flame cells
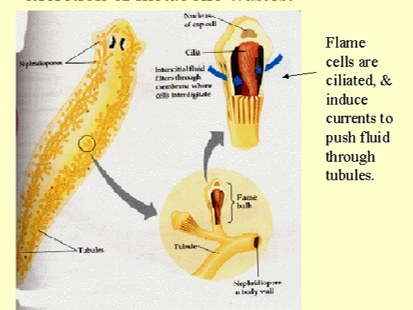
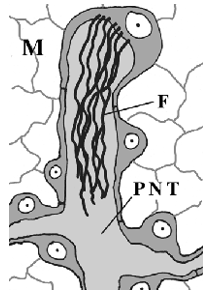
Excretory system; what’s PNT?
protonephridial tubule
Which Platyhelminths system is primarily osmoregulatory?
excretory system
The vast majority of flatworm species are ___
simultaneous hermaphrodites
simultaneous hermaphrodites means
male and female in the same body
Self-fertilization is rare in flatworms, but does occur among __
cestodes (tapeworms)
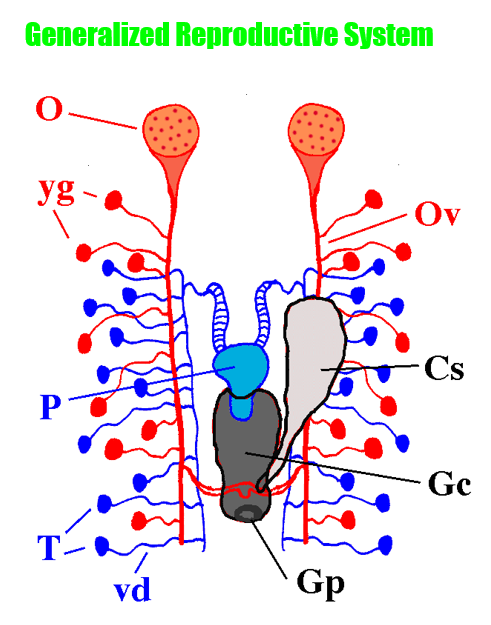
Reproductive System: what’s the tiny red/female sacs
yolk (vitelline) glands
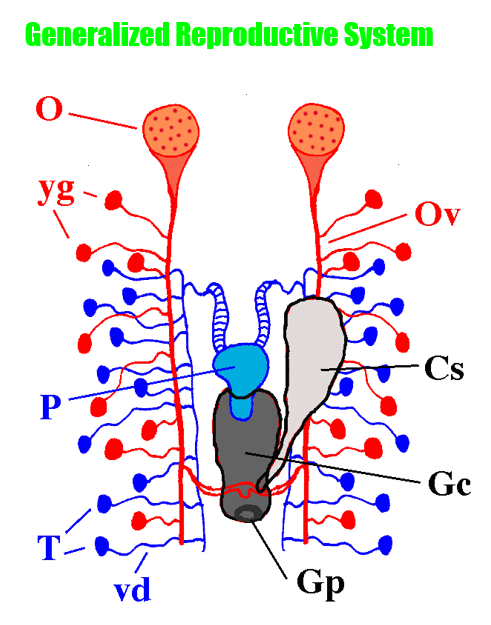
Reproductive System: what’s the hole on the genital chamber?
genital pore
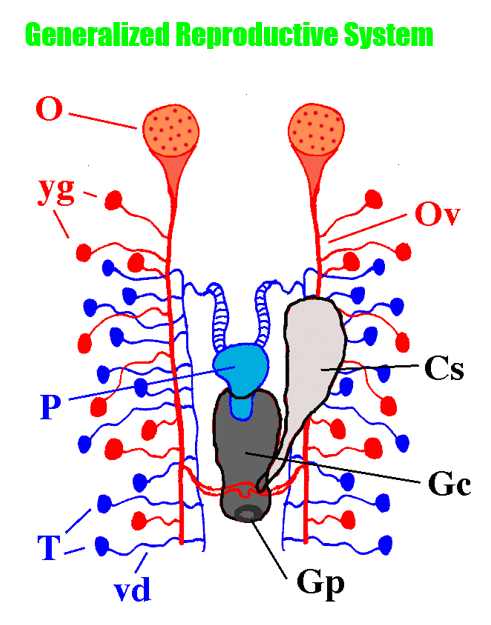
Reproductive System: what’s the big gray sac below the penis
genital chamber
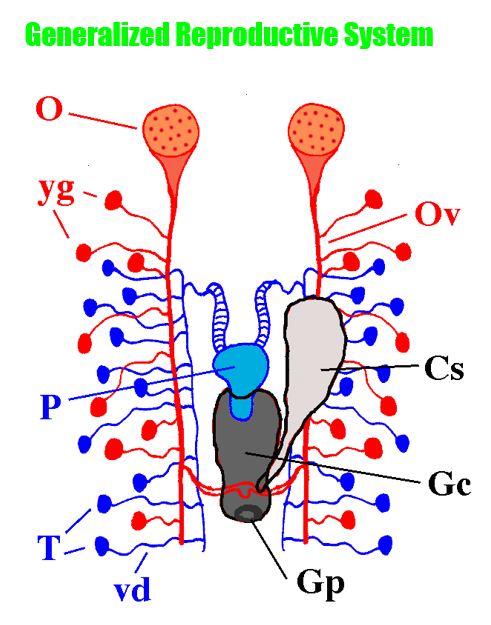
Reproductive System: what’s the big gray sac hanging off the genital chamber
copulatory sac
____ contains subclass Aspidobothrea and subclass Digenea (new classification)
class Trematoda
____ contains subclass Eucestoda (new classification)
class Cestoidea

A sample platyhelminth is called ___, it’s a free-living flatworm – “turbellarian”
Dugesia spp.
“Turbellarians”
mostly free-living predators but some symbionts
“Turbellarians” are ALL __
hermaphroditic
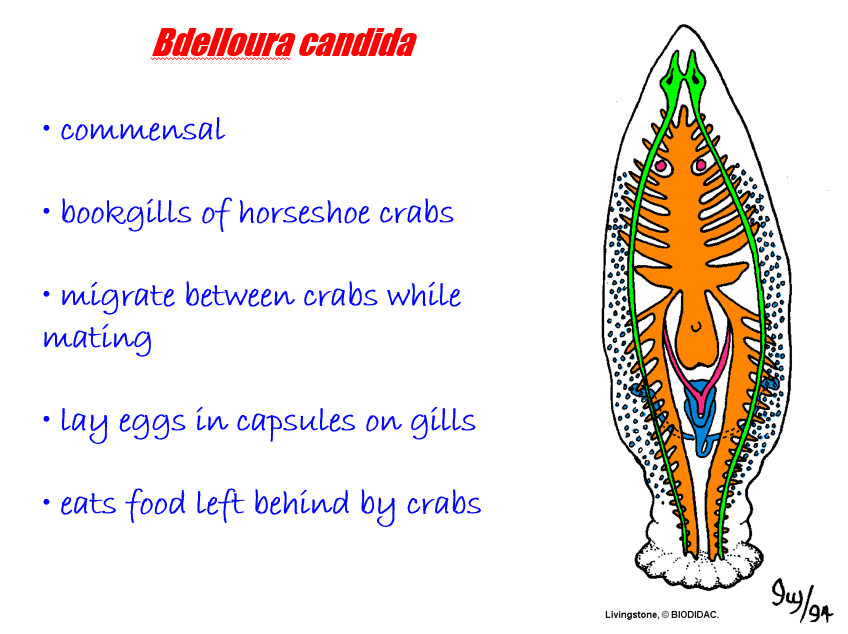
Bdelloura candida is a ___
commensal living in the gills of horseshoe crabs
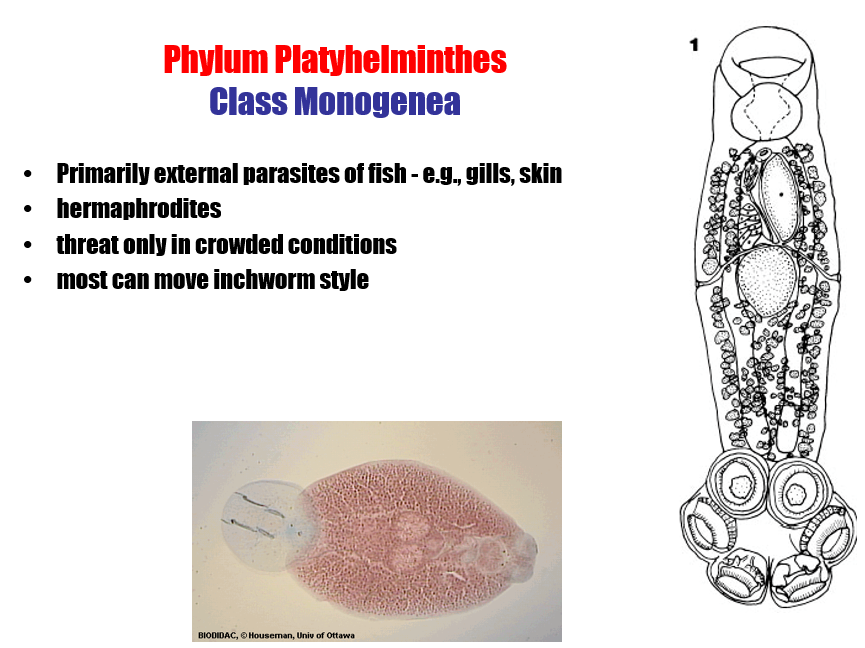
Of phylum platyhelminthes, ___ are primarily external parasites of fish
class monogenea
class monogenea has 1 form in mammals:
Oculotrema hippopotami
Oculotrema hippopotami lives in ___
hippo eyes
class monogenea has high ___
host and site specificity
body plan of class monogenea includes these main body parts:
cephalic region, trunk, penduncle (in some, not all), and haptor
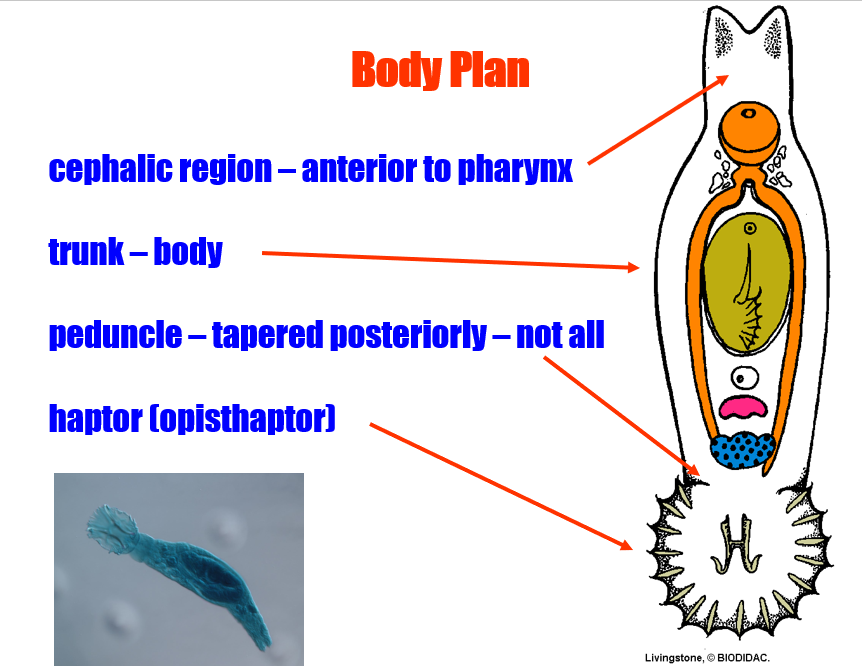
defining characteristic of clsas monogene is __
haptor (or opisthaptor)
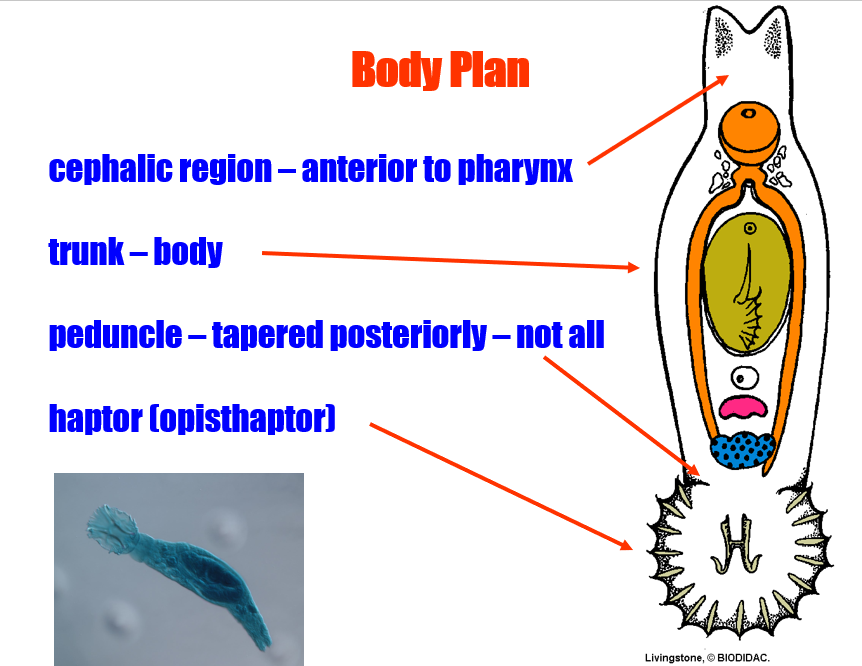
Class monogenea: Prohaptor =
anterior attachment organ
in class monogenea, there are 2 types of prohaptor
glandular (secretes adhesives) or oral sucker
Class monogenea: Haptor/opisthaptor =
posterior attachment organ
What does the haptor do?
Allows parasite to attach to host
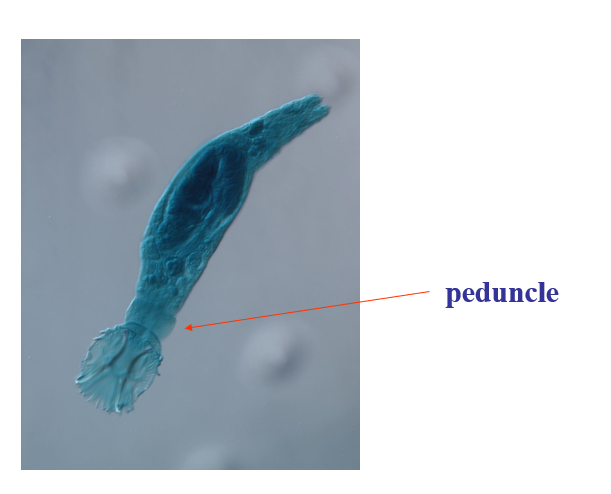
what does the peduncle do?
separates haptor from the body
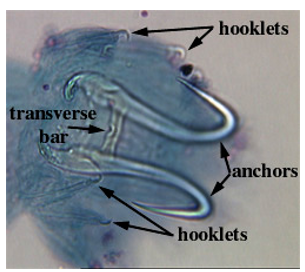
Class monogenea: Haptor morphology: anchors (hammuli)
large hooks
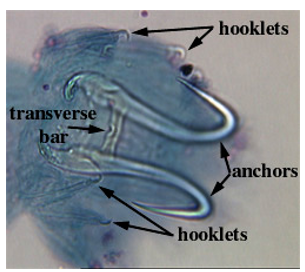
Class monogenea: Haptor morphology: hooklets
small hooks
Class monogenea: Haptor morphology: clamps
muscular pinching organ
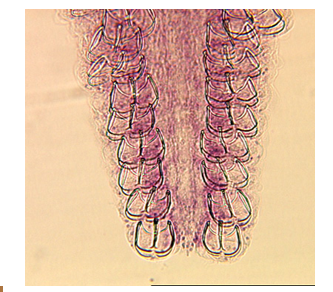
Platyhelminthes: Class monogenea: feeding
pharynx secretes protease
Platyhelminthes: Class monogenea: intestine ___
divides into 2 crura
Platyhelminthes: Class monogenea: has a ___
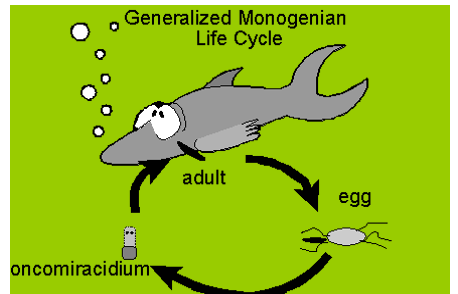
direct life cycle
Platyhelminthes: Class monogenea: life cycle
egg-> onchomiracidium -> adult
Dactylogyrus spp will interfere with __
fish respiration (bc it infects gills)
What is the small fish monogene that infects fish gills
Dactylogyrus spp
What is the small fish monogene that infects fish skin
Gyrodactylus spp.
Gyrodactylus spp. will spread by
contact
Gyrodactylus reproduction
viviparous and sequential polyembryony
sequential polyembryony generates __ from 1 zygote
up to 4 offspring
viviparous
produces live offspring, rather than eggs
[…] is a monogene parasite that infects frogs
Polystoma intergerrimum
Polystoma intergerrimum is ___, which is rare for monogeneans
Endoparasitic
When the Polystoma intergerrimum oncomiracidium attaches external gills, it’s called ___
neotenic larva
[…] is a monogene parasite that infects European freshwater cyprinid fish gills
Diplozoon paradoxum
When a Diplozoon paradoxum adds 2 more clamps, ventral sucker & dorsal papillae, it is called a ___
diporpa
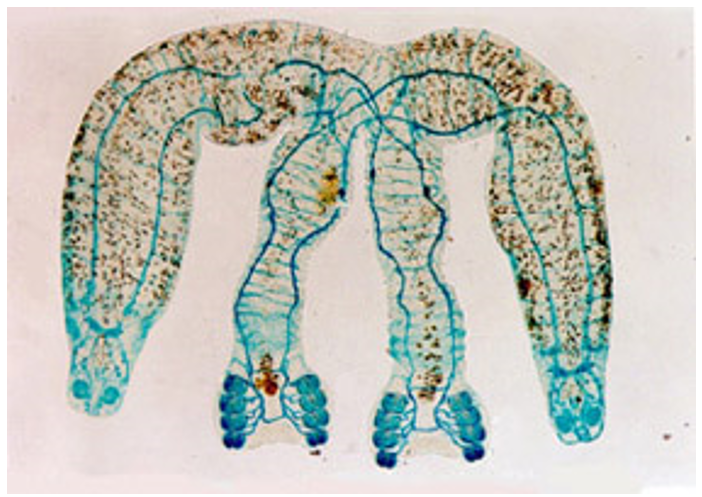
Which parasite has no development unless 2 diporpa larvae meet
Diplozoon paradoxum
Which parasites are also called flukes?
Digenean Trematodes
Digenean Trematodes have a ___
minimum of 2 hosts, first is always a mollusc
Digenean Trematodes are all parasitic, and infect __
all vertebrate classes (esp fish)
Digenean Trematodes will alternate __,which is why they’re called digenetic
asexual and sexual reproductive phases
Digenean Trematodes bodies are highly variable, but they’re always __
dorsal ventrally flattened
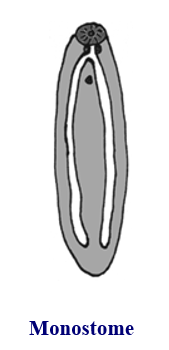
Digenean suckers: monostome
oral sucker only
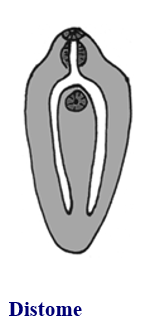
Digenean suckers: distome
oral and ventral suckers
Digenean suckers: gasterostome
single ventral sucker
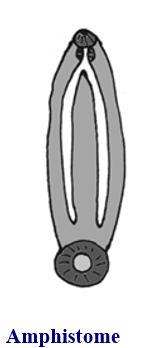
Digenean suckers: amphistome
oral and posterior ventral suckers
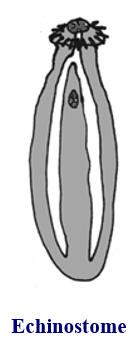
Digenean suckers: echinostome
oral sucker with collar of spines and ventral sucker
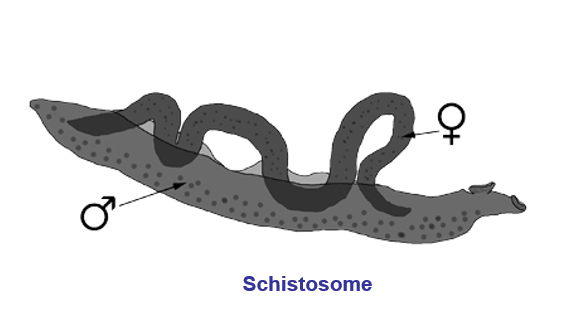
Digenean suckers: schistostome
oral & ventral sucker, male has split body
Digenean suckers: strigeid
2 suckers; split into fore & hind body (with gonads)
The Digenean tegument is a complex structure containing ___
distal cytoplasm, cytons, and spines
What are internuncial processes
connect cyton and cytoplasm in the Digenean tegument
The excretory system of digeneans is mainly for __
osmoregulation