Heredity
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
What phenomenon is defined as the genetic passing characteristics from one generation to another?
heredity
What is genetic material on a chromosome for encoding a trait?
gene
What is the location on chromosome where a gene is found?
locus
What are alternative forms of a gene that allow for differences such as different hair or fur colors?
alleles
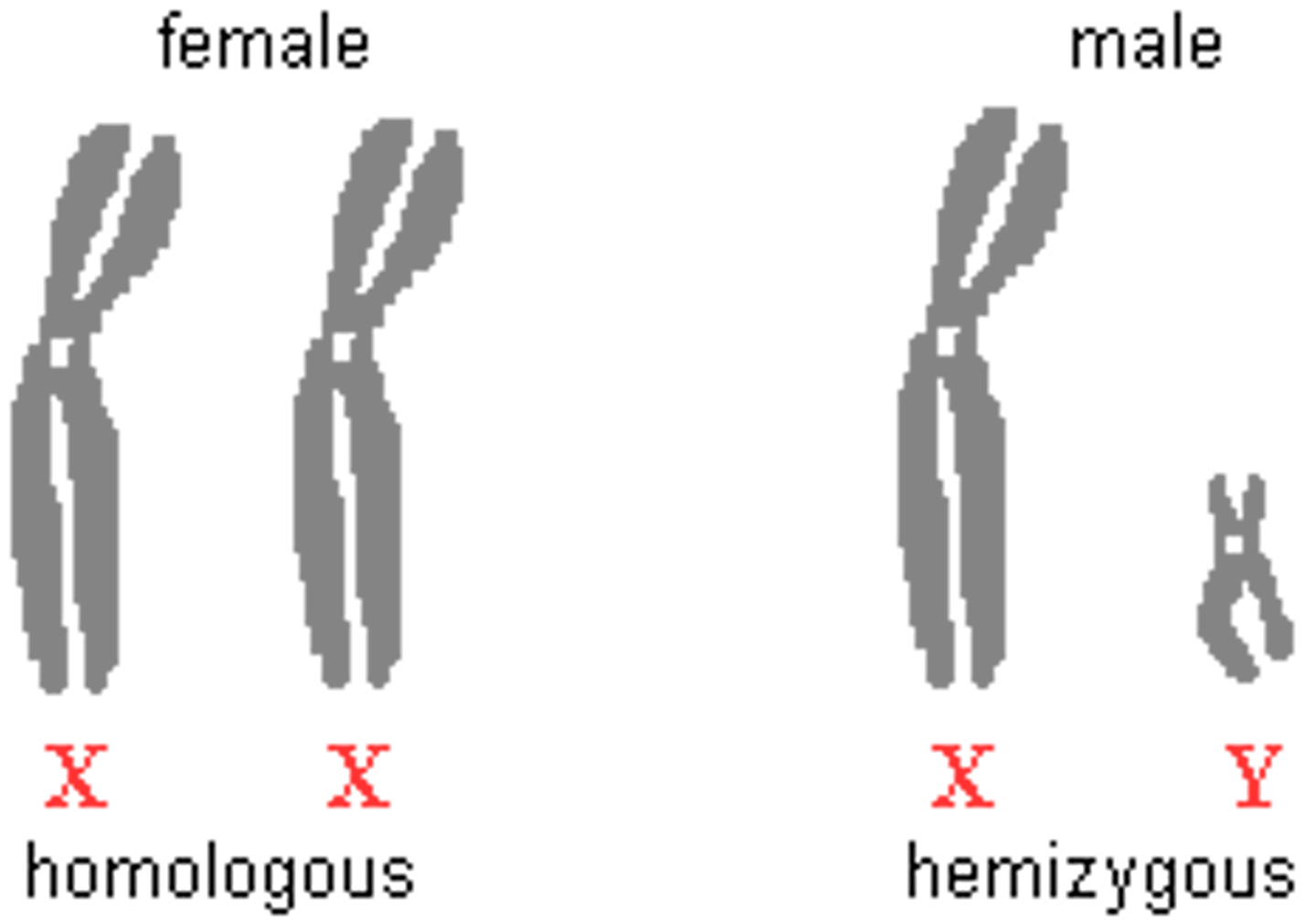
What are pairs of chromosomes that contain the same genetic material?
homologous chromosomes
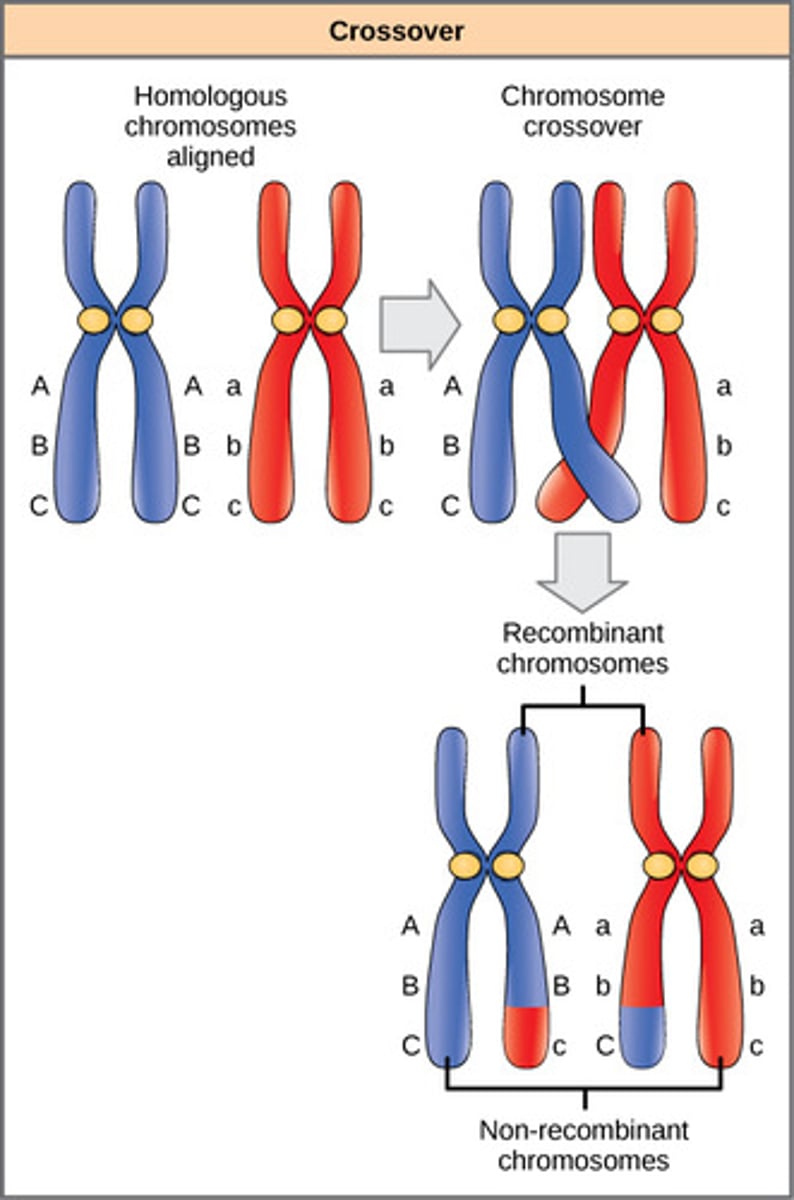
What chromosomes contribute to the homologous chromosome pair?
each parent contributes one of the chromosomes
(Note: allows different alleles to be present for each gene)
What is the cell division process that accounts for genetic diversity?
meiosis
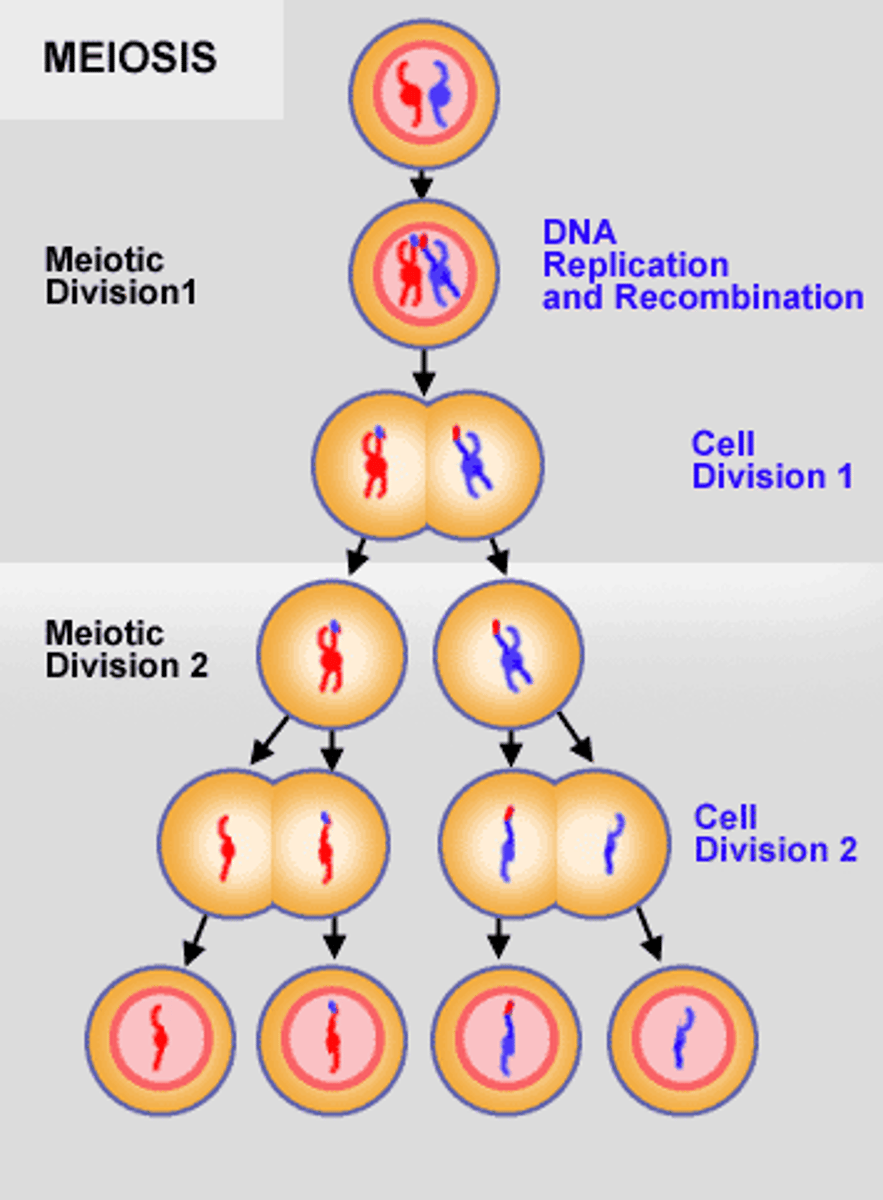
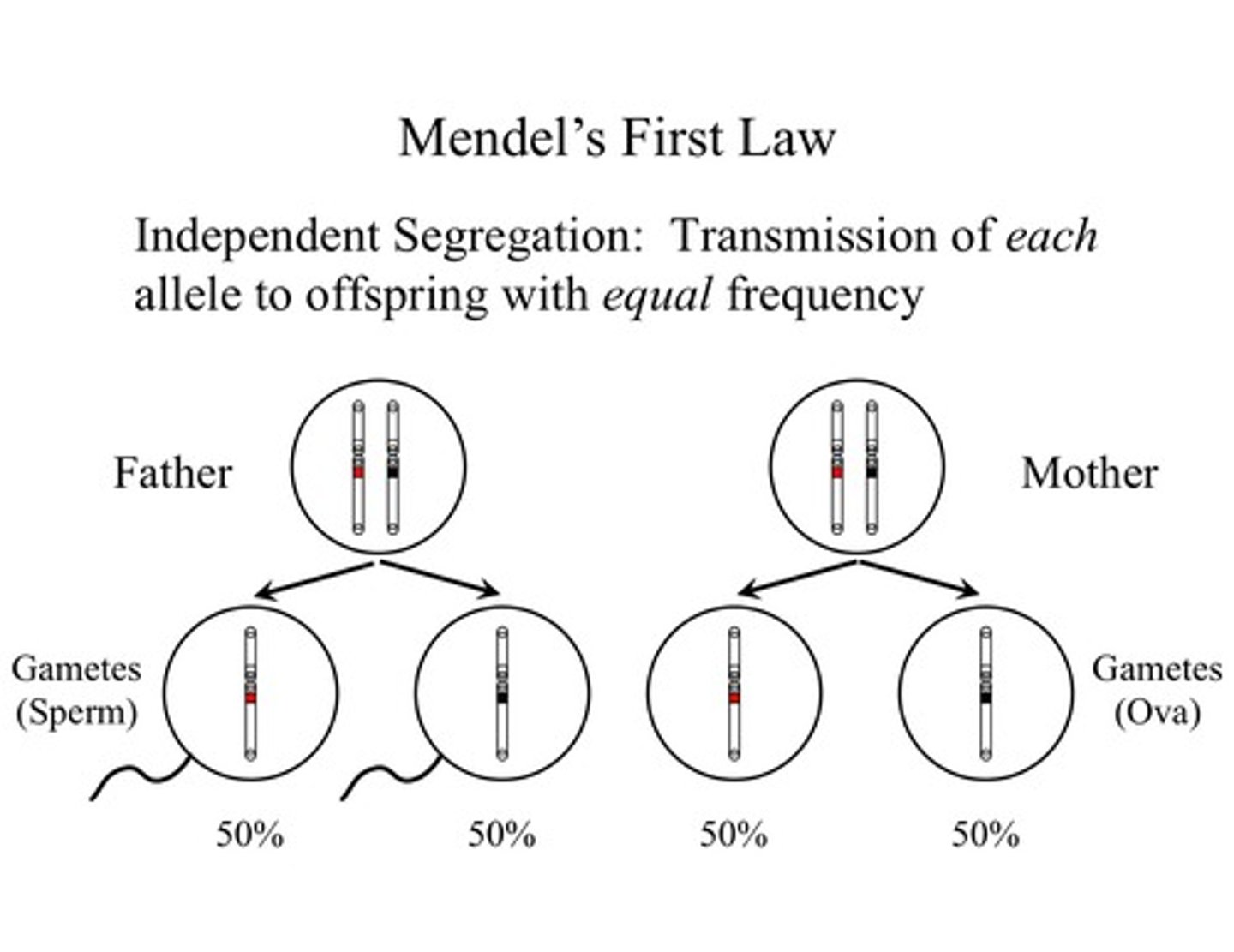
Which law of meiosis states that one member of each chromosome pair migrates to an opposite pole in anaphase I, resulting in haploid gametes?
law of segregation
Which law of meiosis states that the migration of homologues within one pair of homologous chromosomes does not influence the migration of homologues of other homologous pairs?
law of independent assortment
(Note: RANDOM separation)
Which law of meiosis is displayed in dihybrid crosses of peas where there are different phenotype combinations?
law of independent assortment
(Note: genes for different traits form different combinations - assort independently)
Which scientist discovered the basic principles of hereditary through extensive experiments with pea plants?
Gregor Mendel

What are the experiments where two organisms exchange genetic information to give rise to a new generation?
crosses
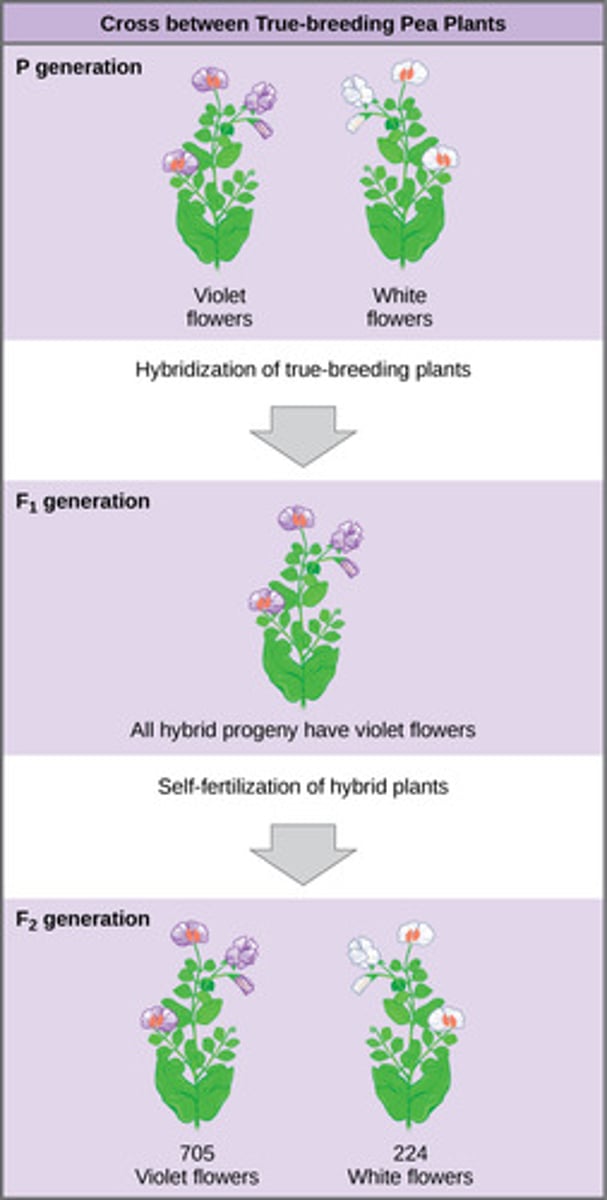
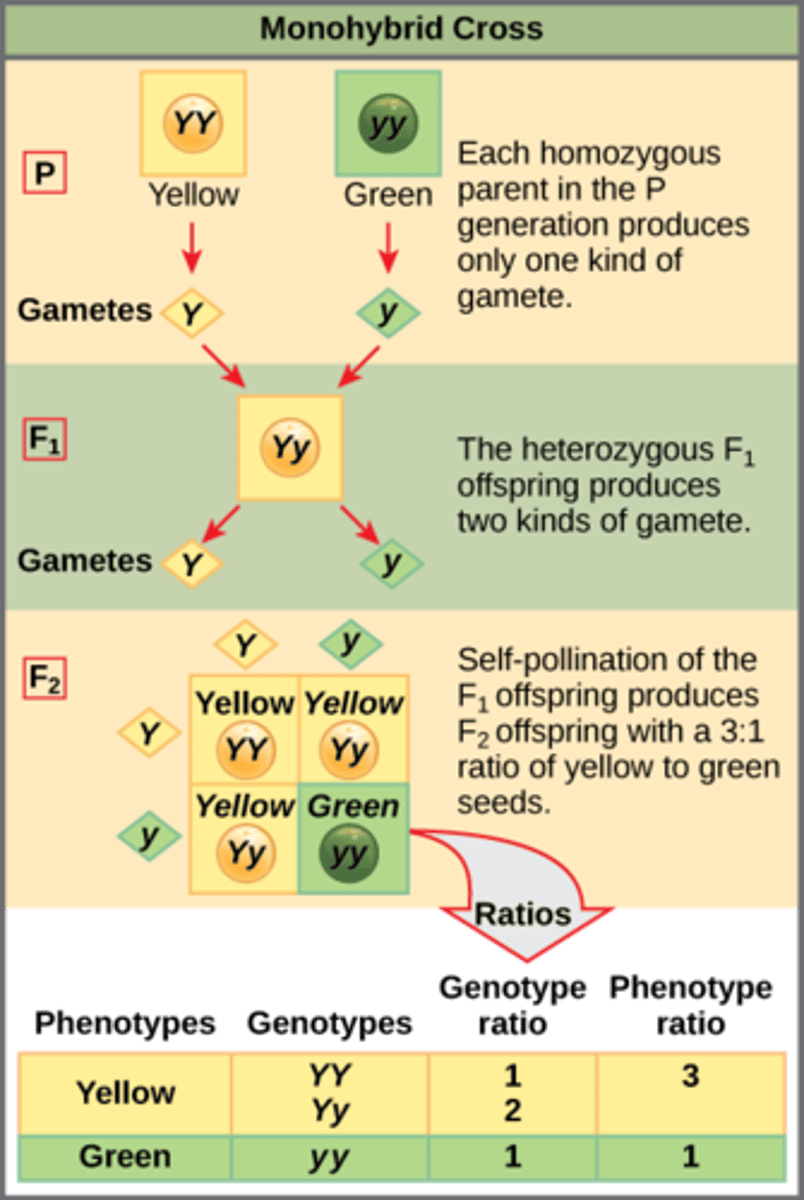
Which type of cross occurs when two organisms with variations at one gene of interest are crossed?
monohybrid cross
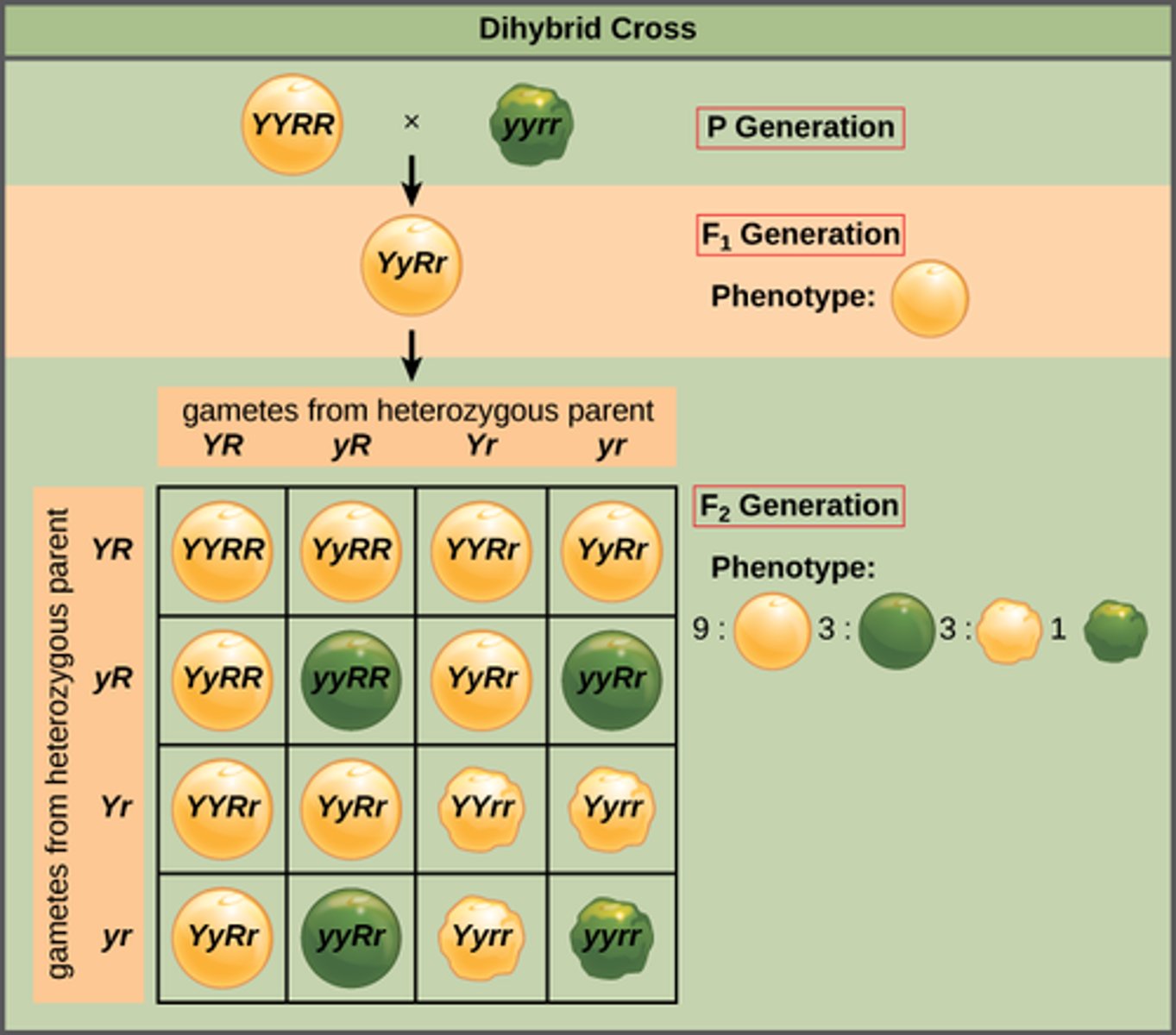
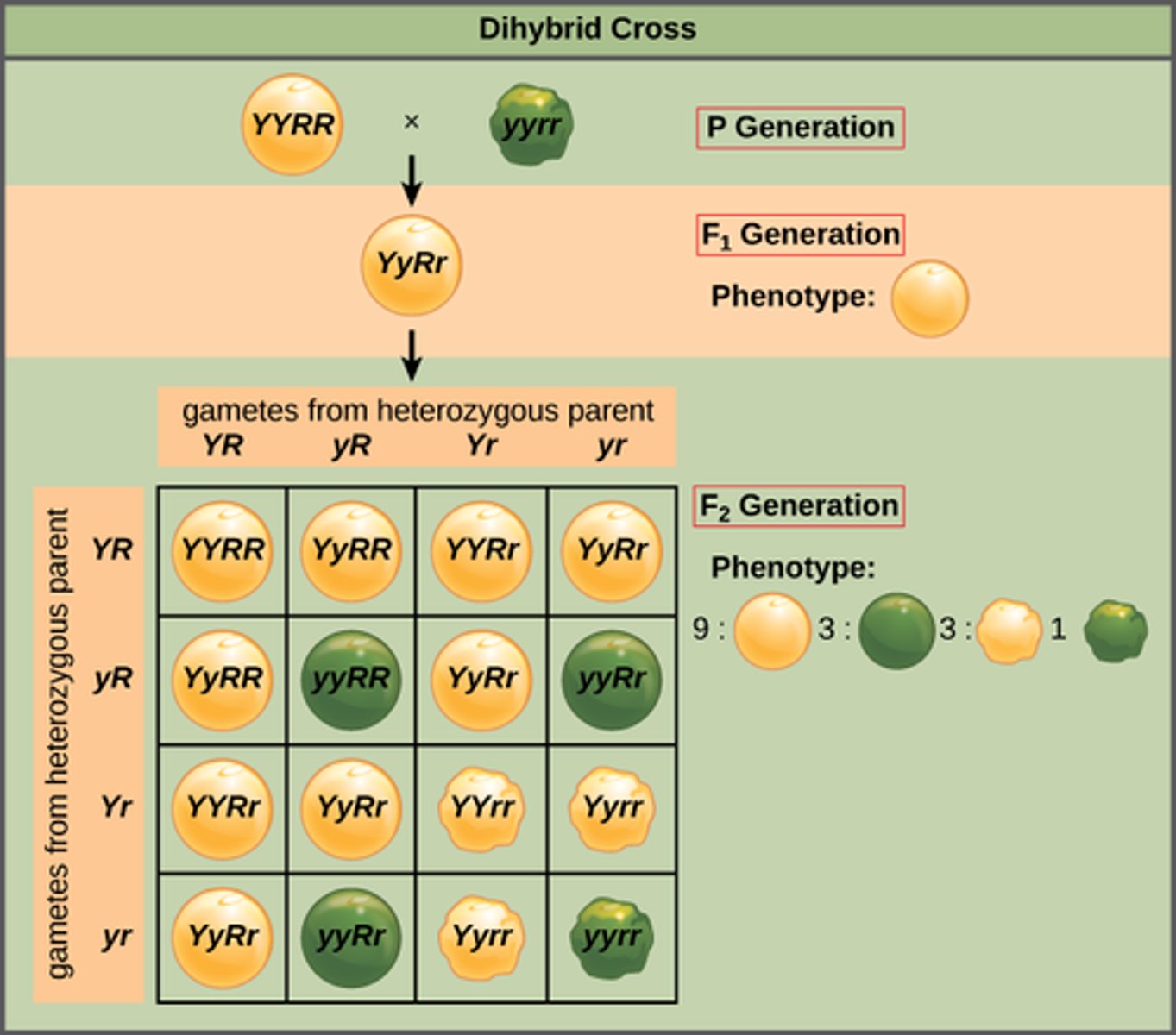
Which type of cross occurs when two organisms with variations are two genes of interest on different chromosomes are crossed?
dihybrid cross
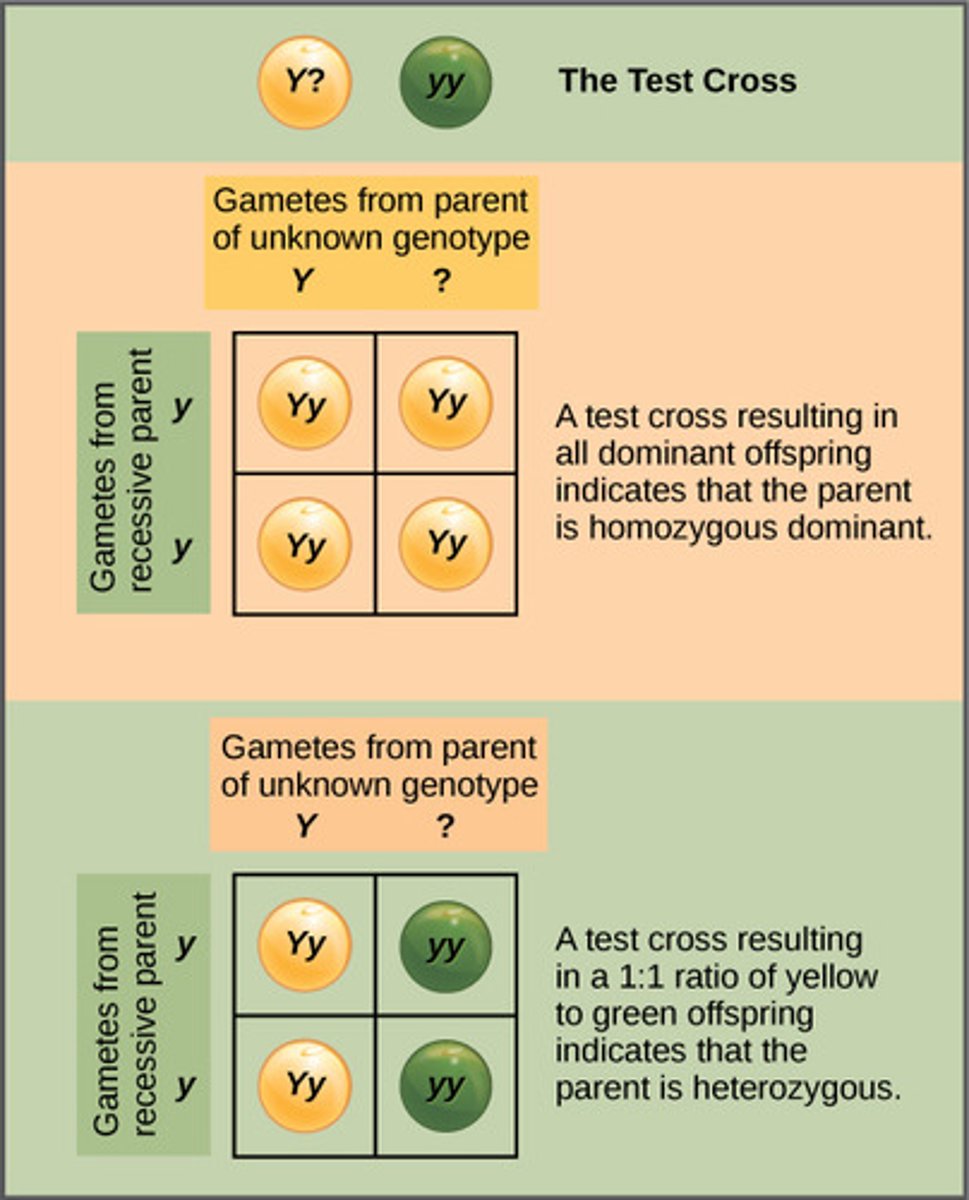
Which type of cross occurs when an unknown organism is crossed with a homozygous recessive organism to determine if the unknown is homozygous dominant, or heterozygous dominant?
test cross
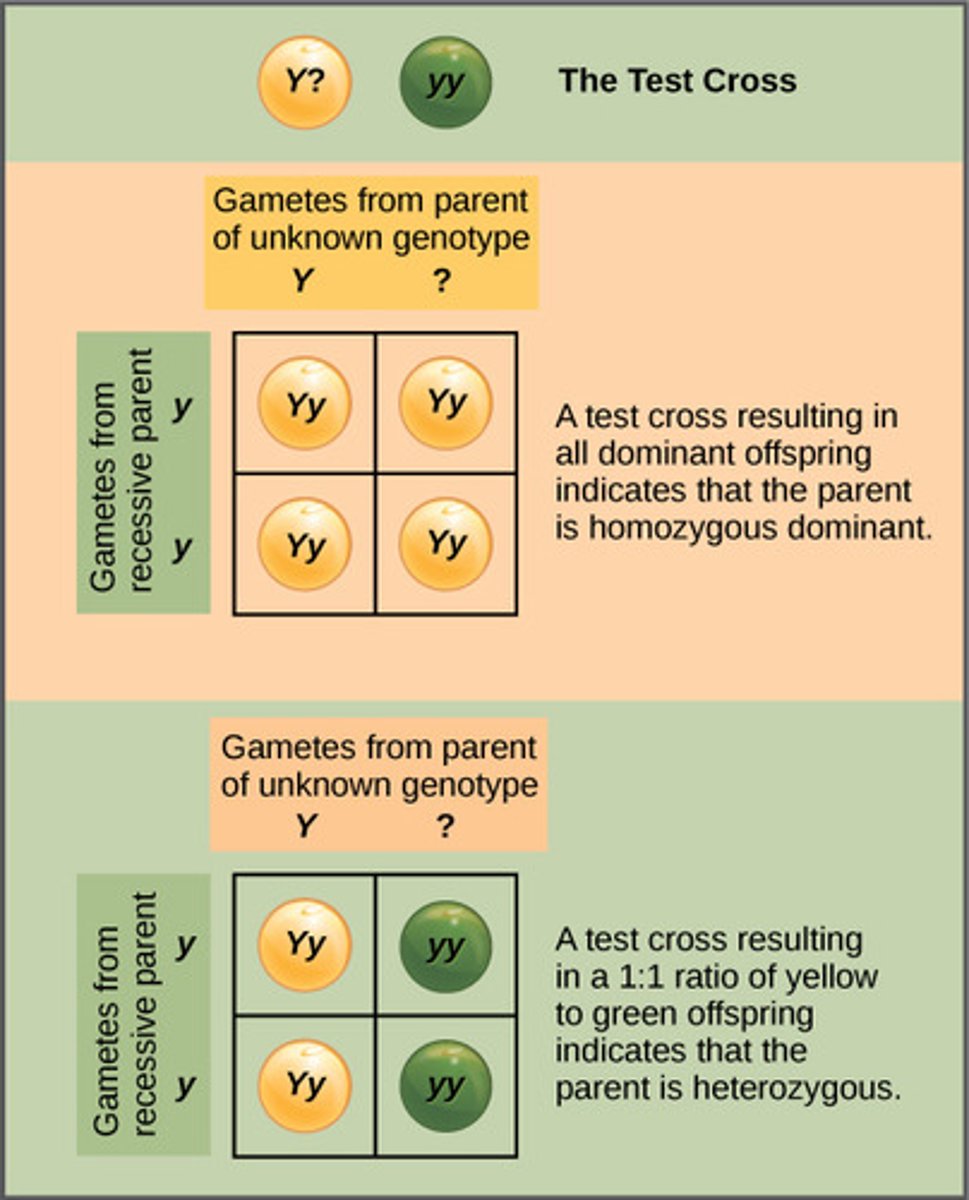
What are the conditions required for attempting a test cross?
the genotype of an organism expressing the dominant phenotype is unknown
What is a technique that uses probability rules to determine the outcomes of either monohybrid or dihybrid crosses?
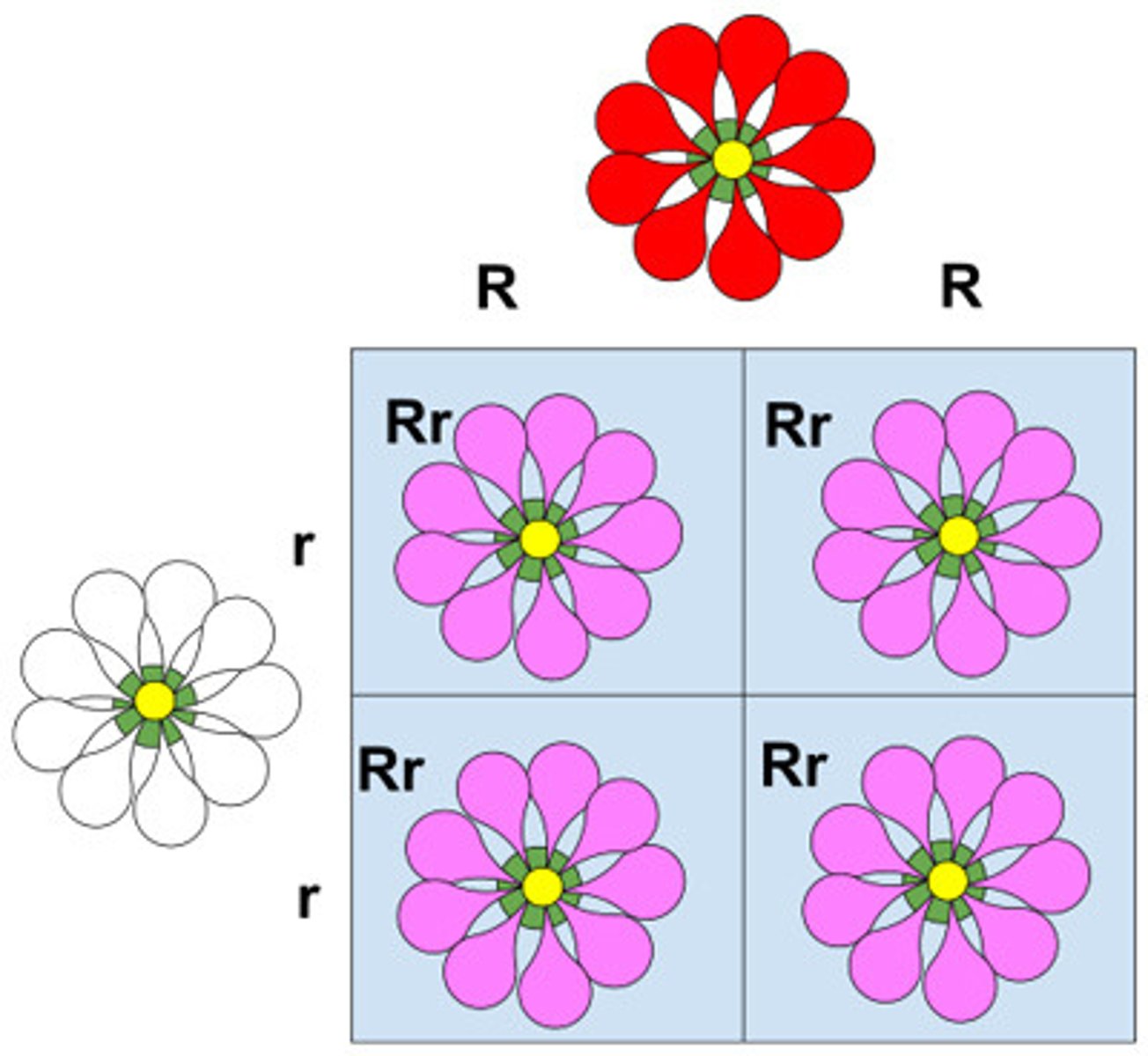
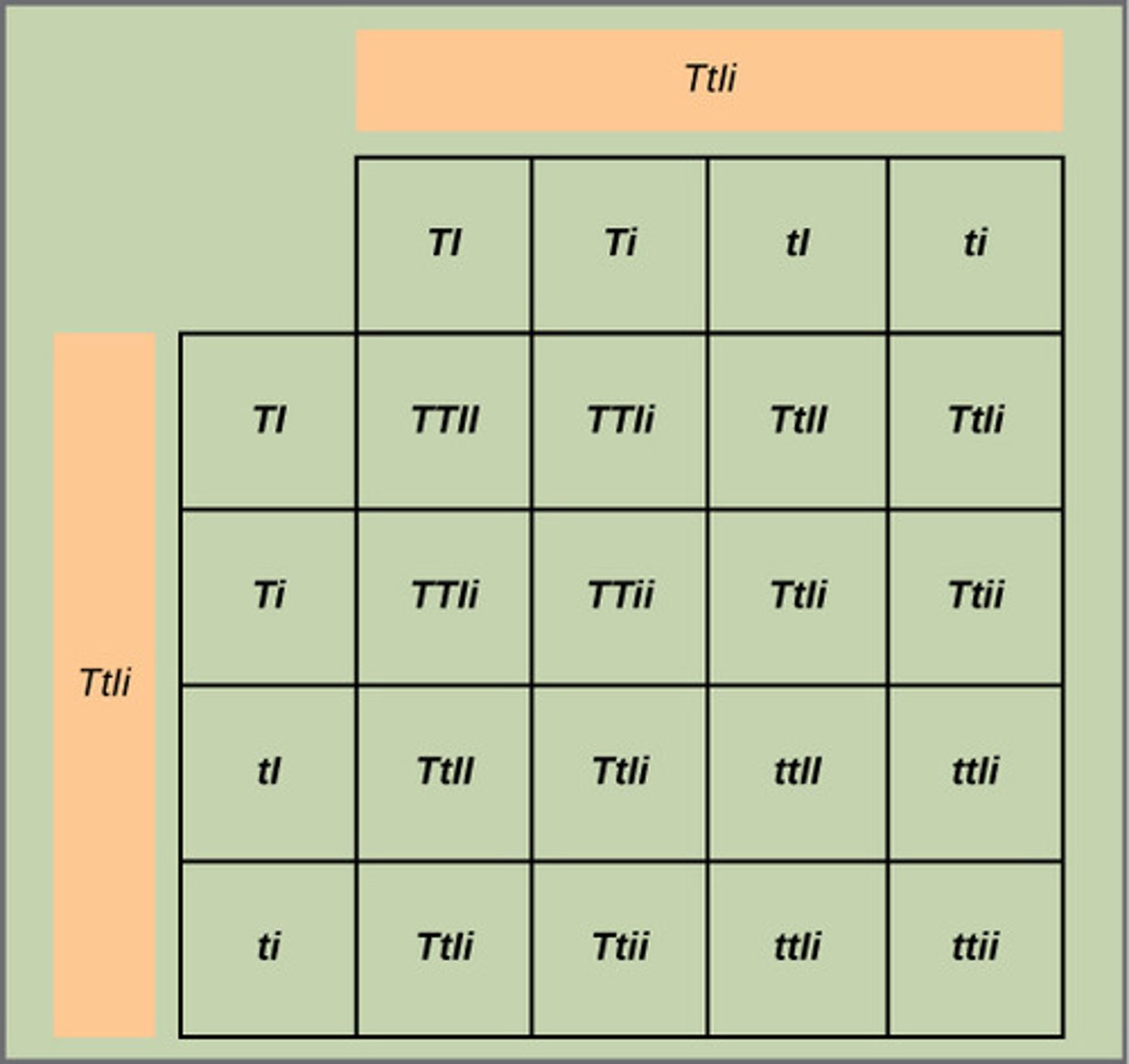
punnet squares
(Note: predicts the subsequent expected frequencies)
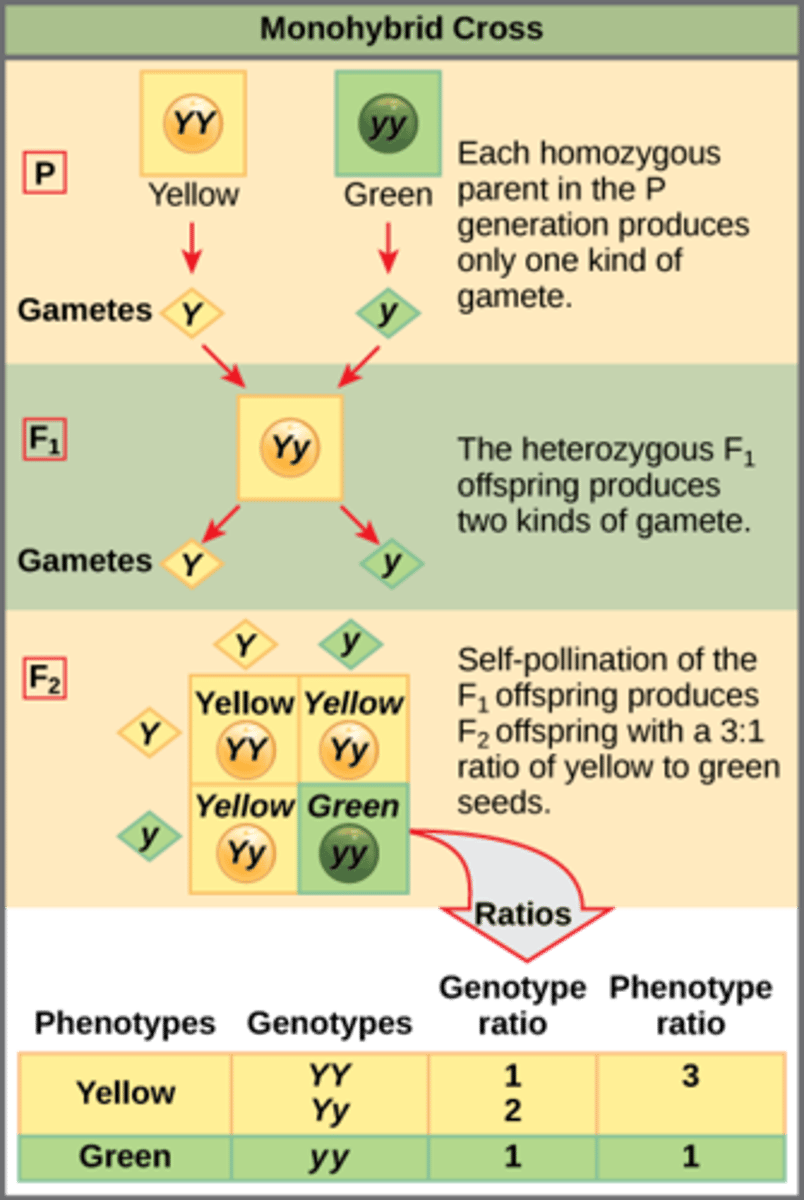
Which genotypes are listed outside the punnet square box?
genotypes of both parents
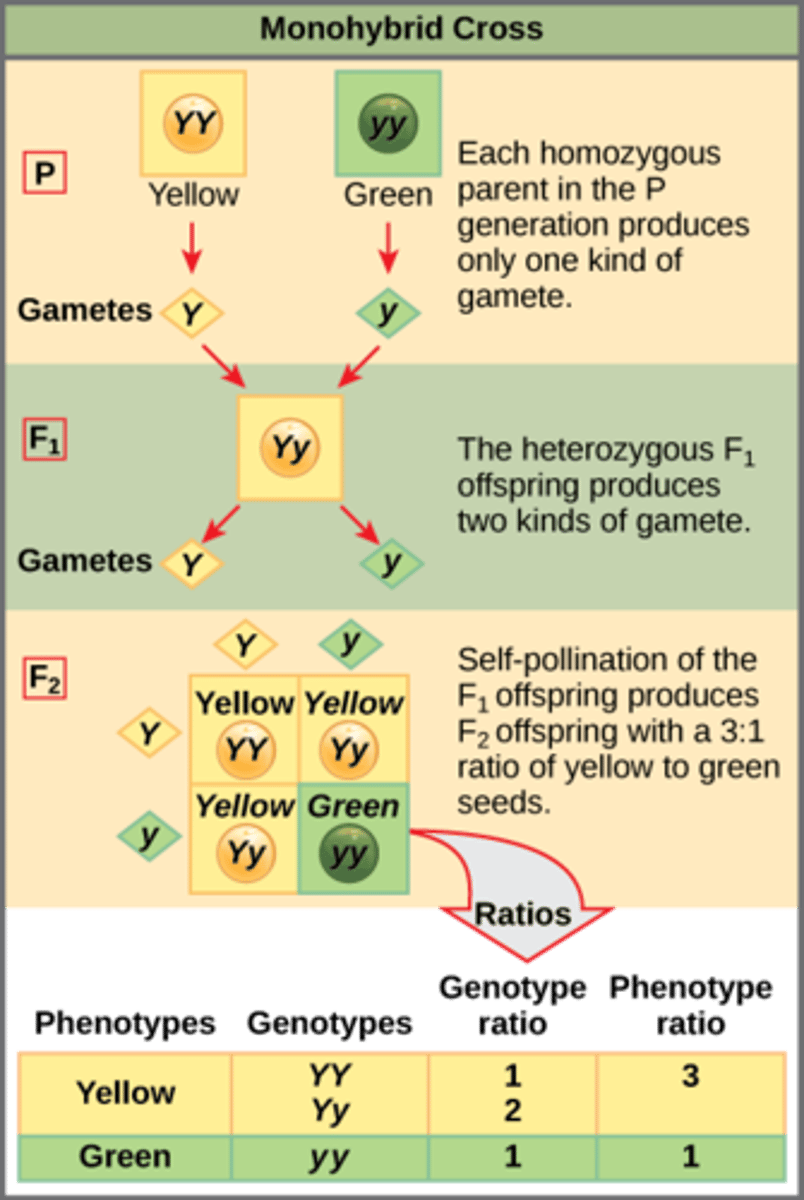
Which genotypes are written inside the punnet square box?
resultant combinations of offspring
Which type of inheritance demonstrates the blending allele expressions?
incomplete dominance
Which type of inheritance demonstrates the expression of both inherited alleles?
codominance

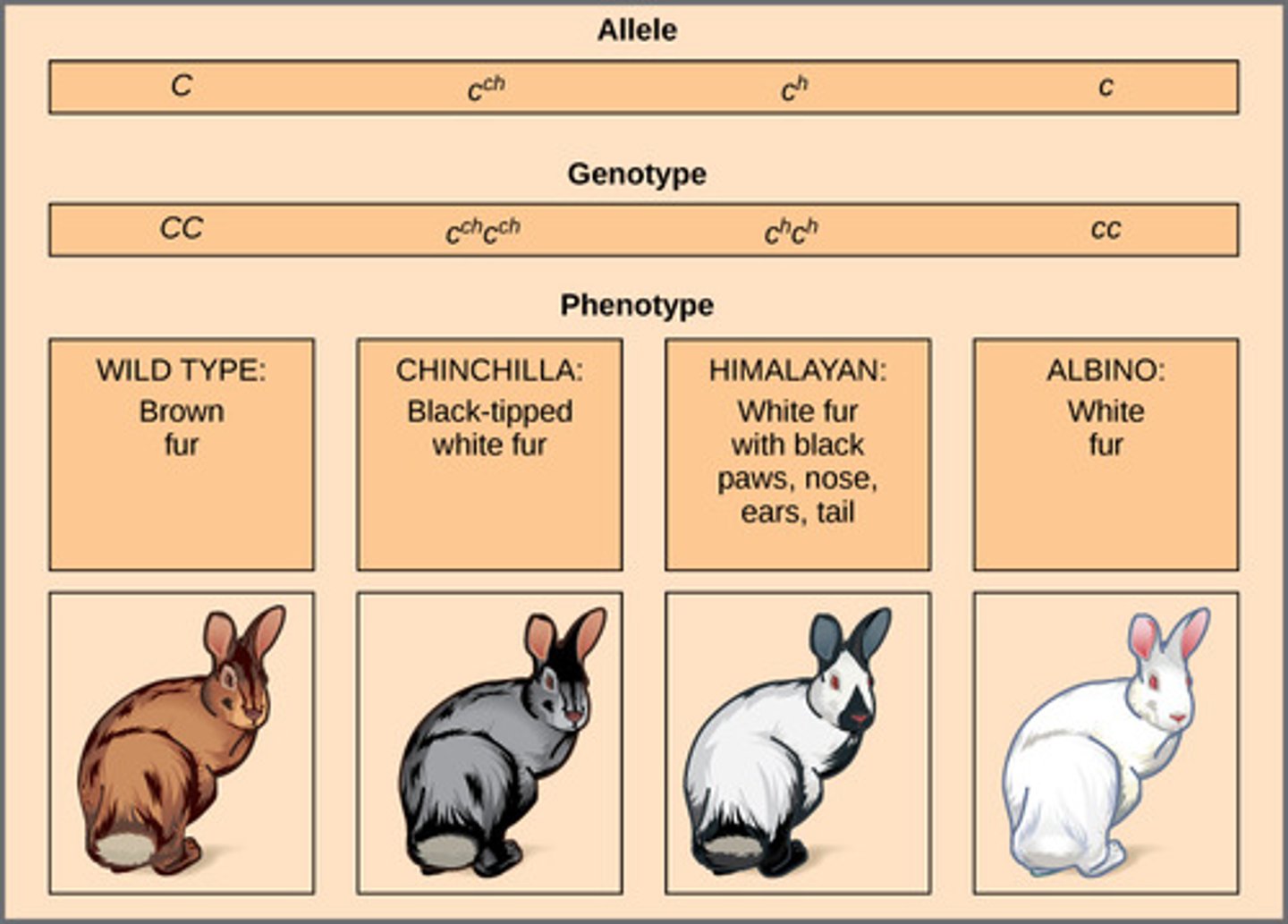
Which type of inheritance occurs when a trait has three or more distinct alleles?
multiple alleles
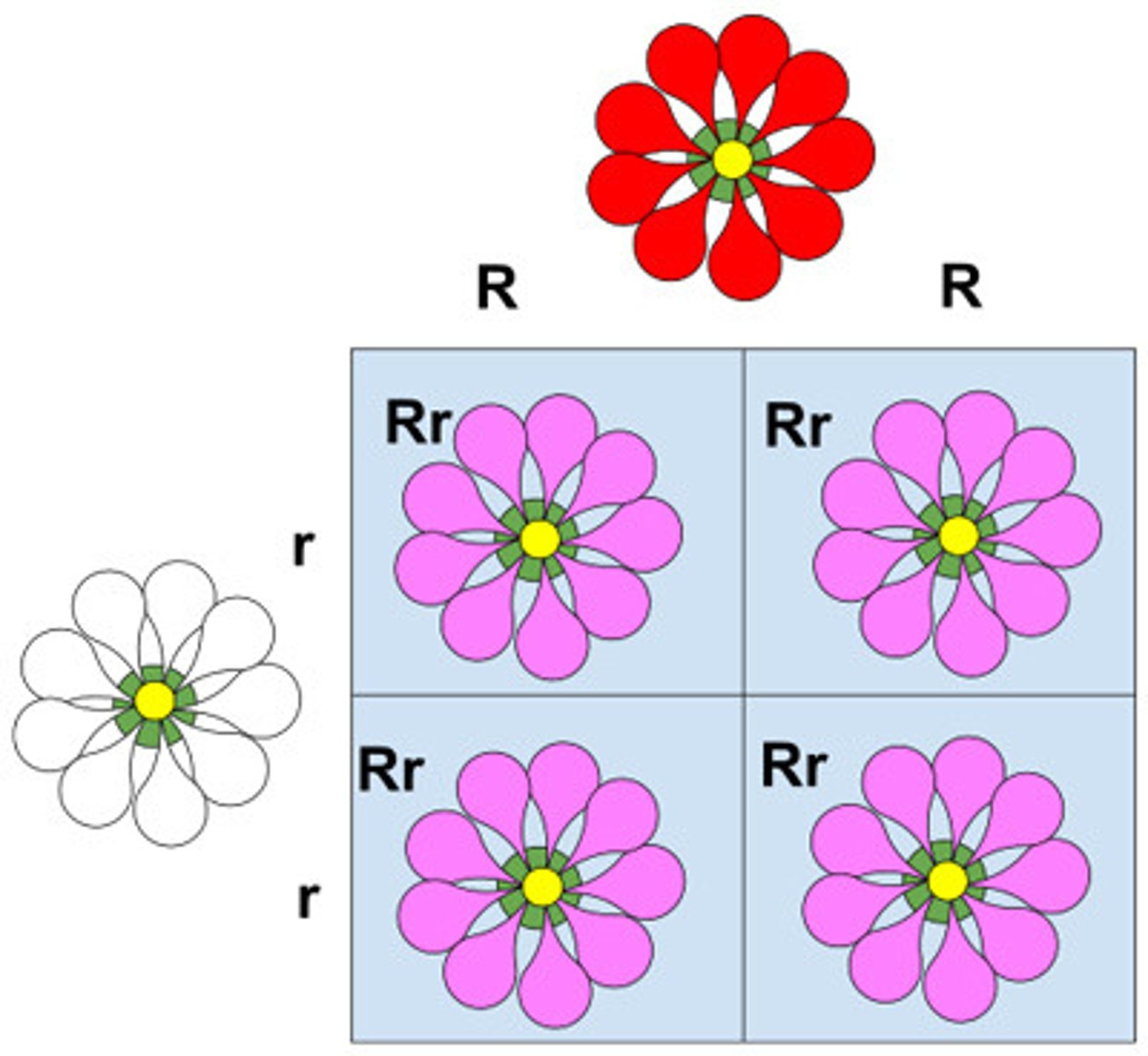
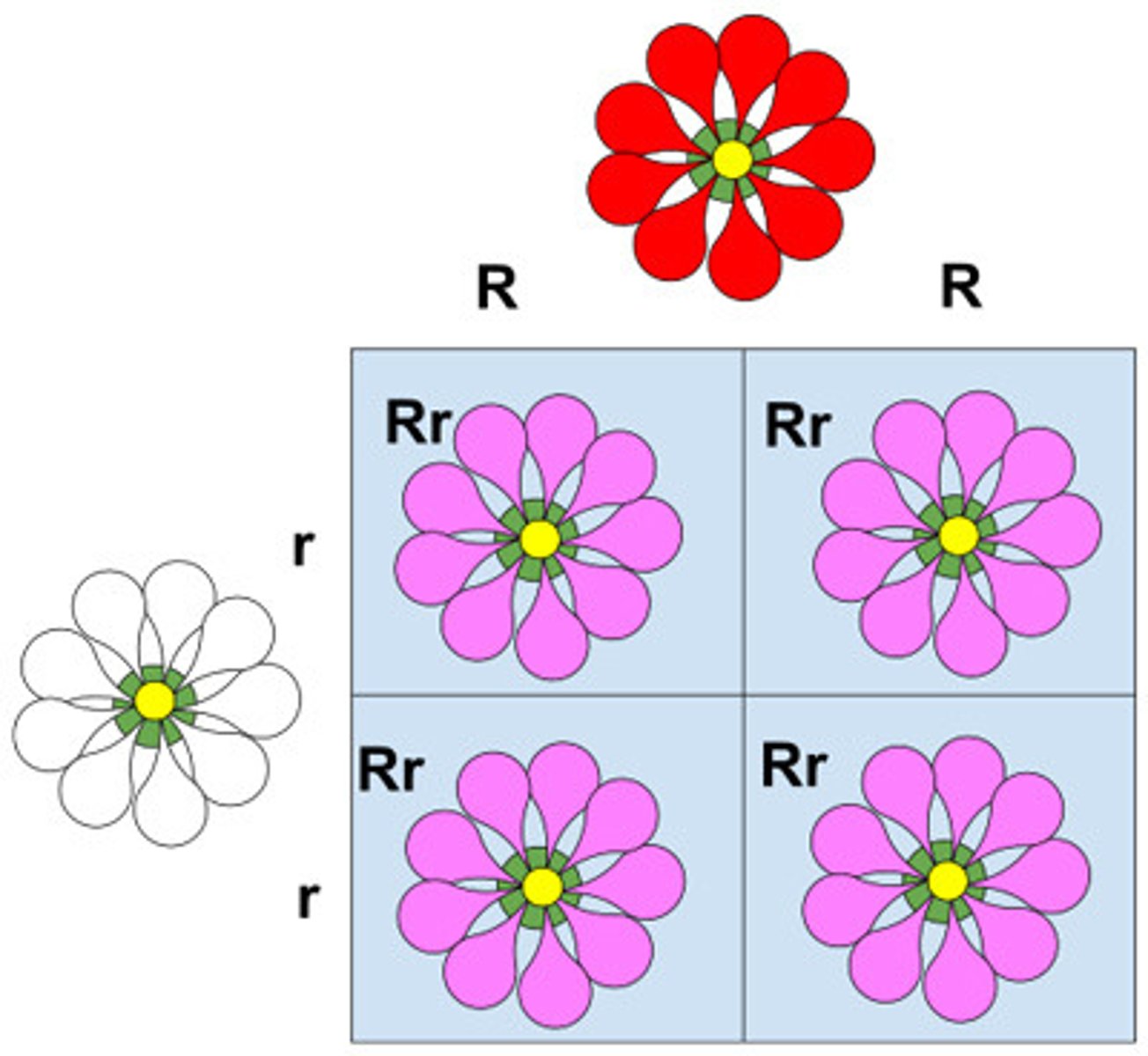
A red and white flower producing a pink offspring is an example of which inheritance?
incomplete dominance
A brown cow and a white cow producing a brown and white spotted cow is an example of which inheritance?
codominance

Blood groups having four possible genotypes and phenotypes arising from the alleles A, B, and O is an example of which inheritance?
multiple alleles
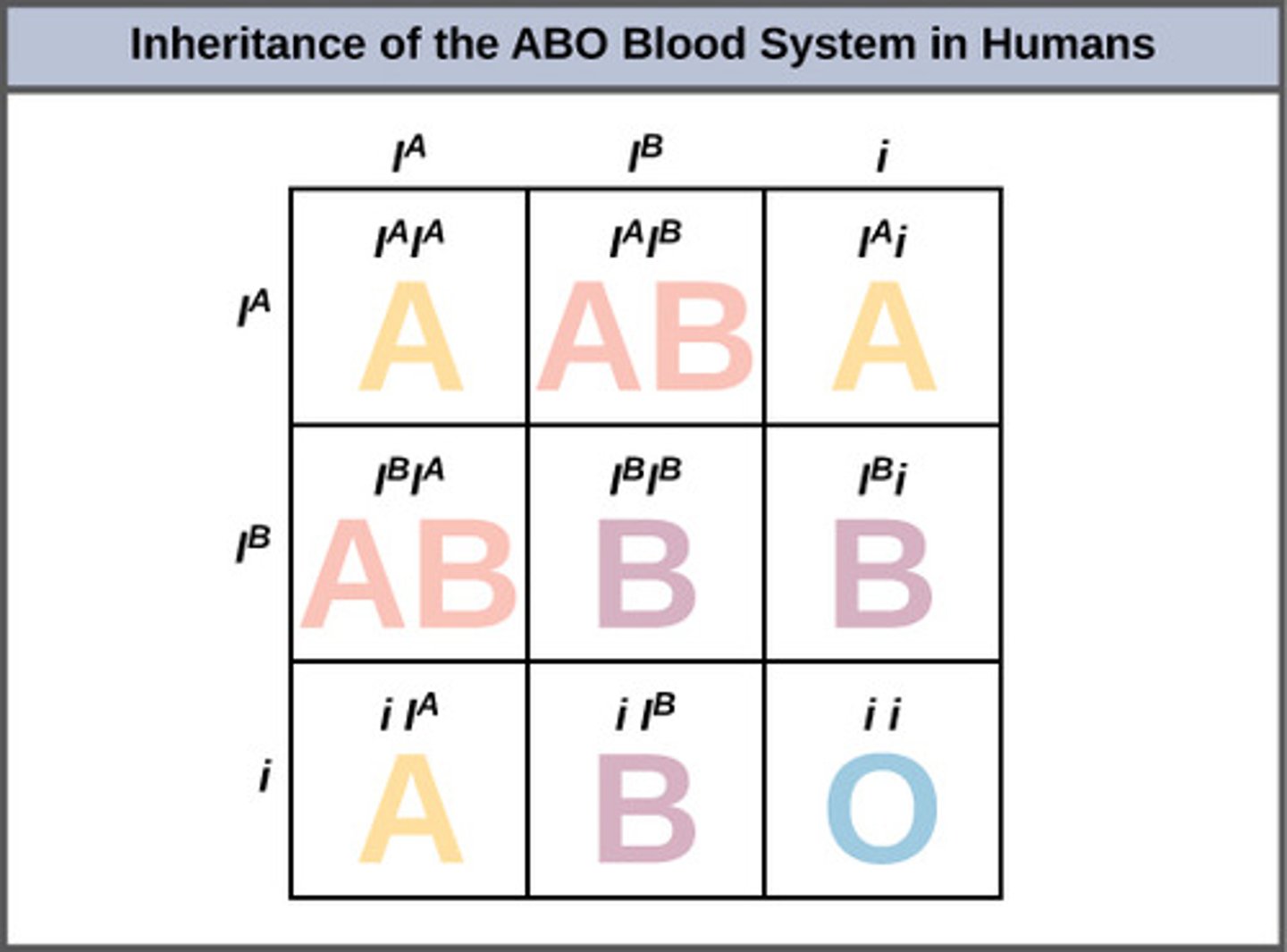
Genes have complex interactions which produces what result?
observed phenotype
What is the purpose for genes interacting with each other?
fine control
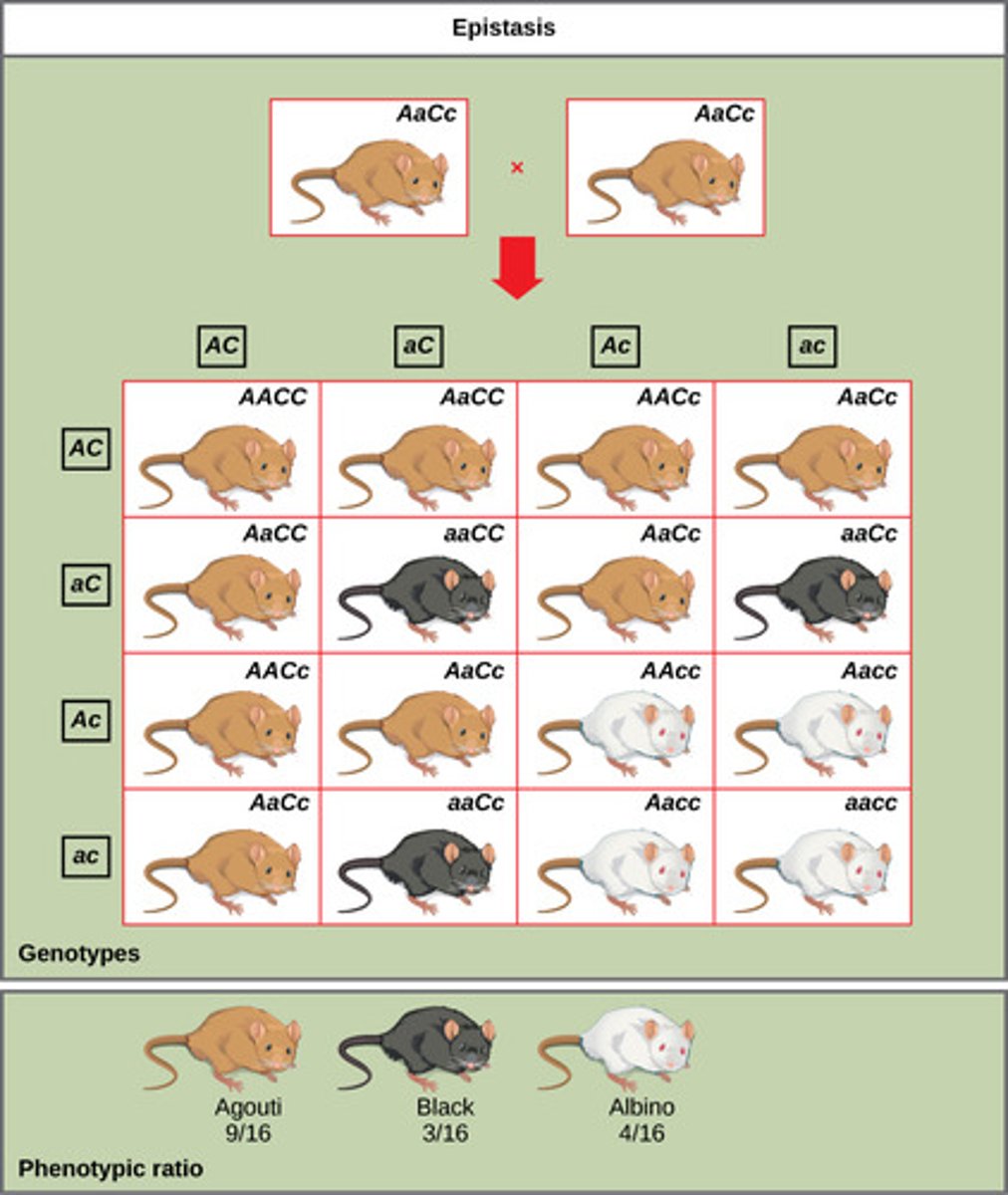
What gene interaction occurs when one gene affects the phenotypic expression of a second gene?
epistasis
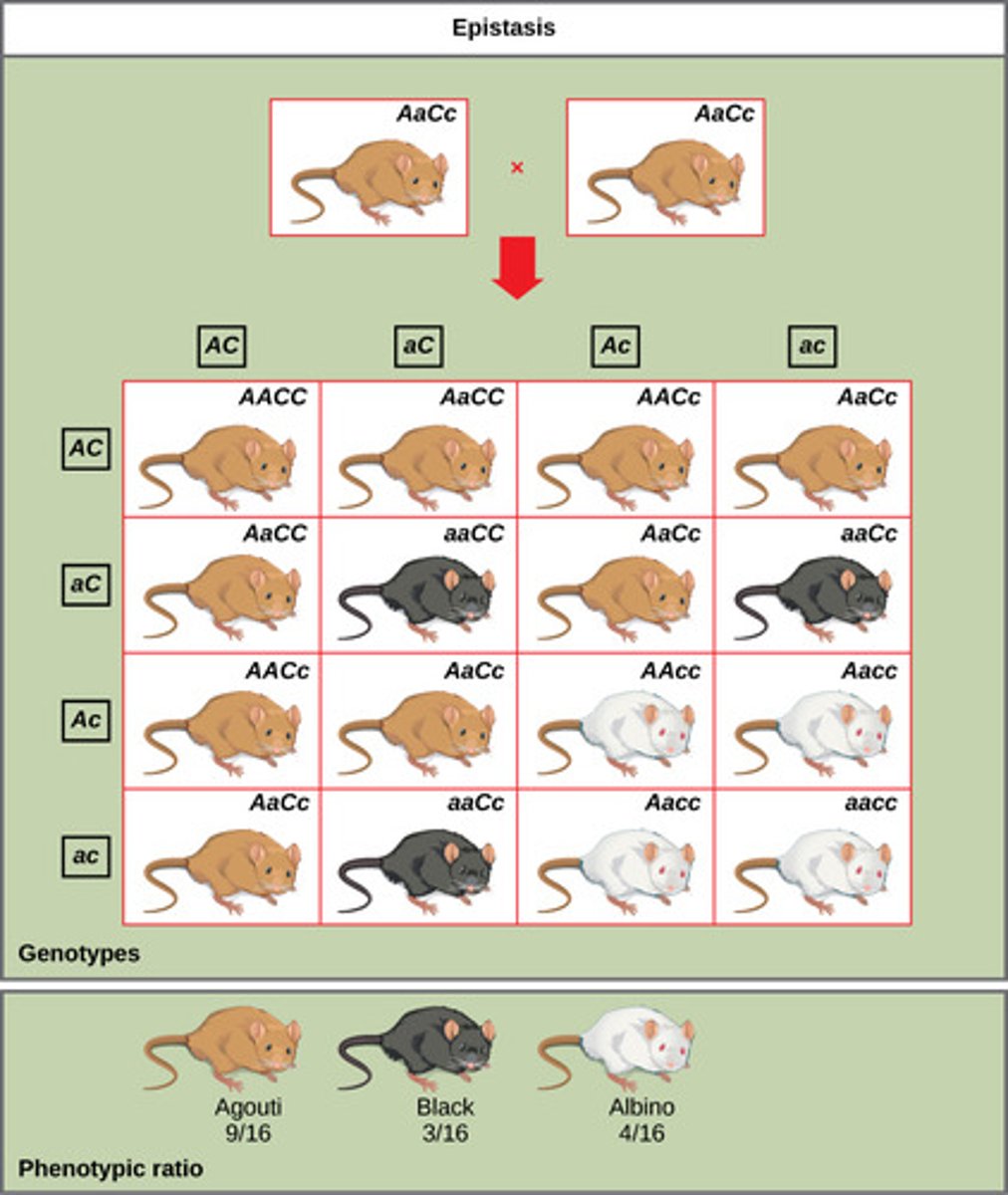
In mice, one gene controls the production of pigment by either turning on or turning off and the second gene controls the color or amount of color deposited in the fur. This is an example of what gene interaction?
epistasis
(Note: if the first gene codes for no pigment, then the second gene has no effect)
What gene interaction occurs when a single gene has more than one phenotypic expression?
pleiotropy
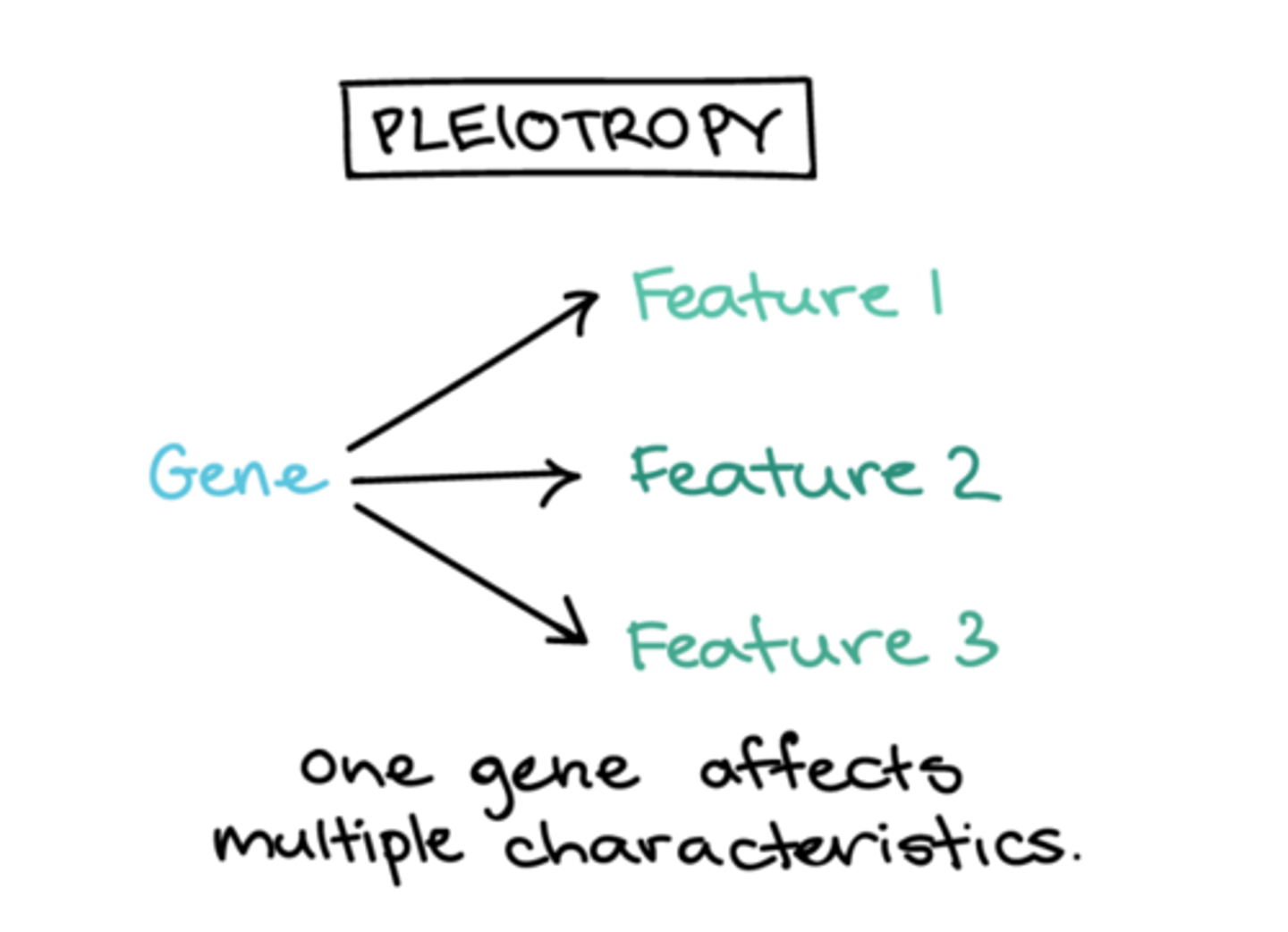
In pea plants, a gene expresses seed texture but also influences starch metabolism and water uptake. This is an example of what gene interaction?
pleiotropy
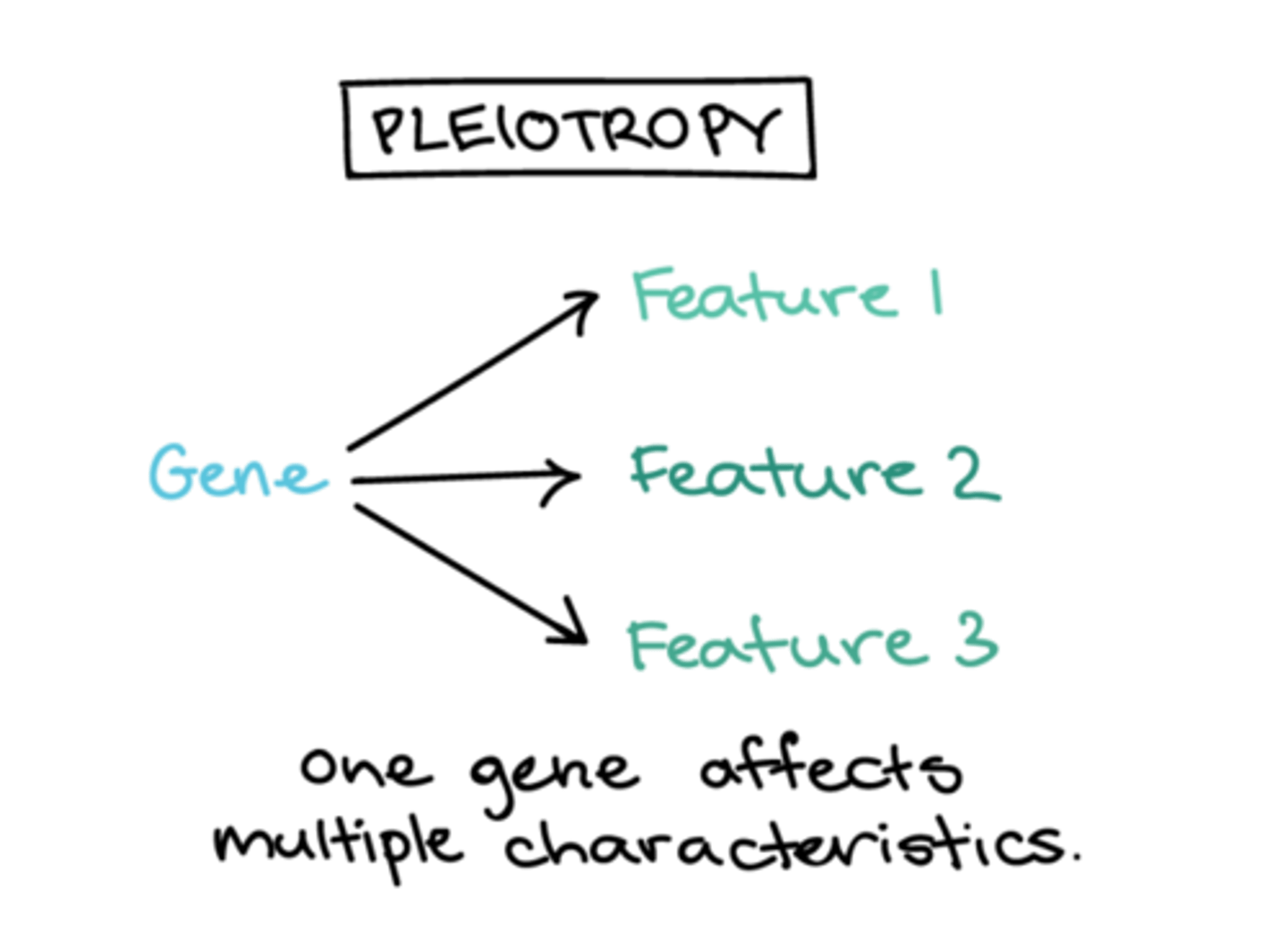
Sickle cell anemia affecting other health conditions is an example of what gene interaction?
pleiotropy
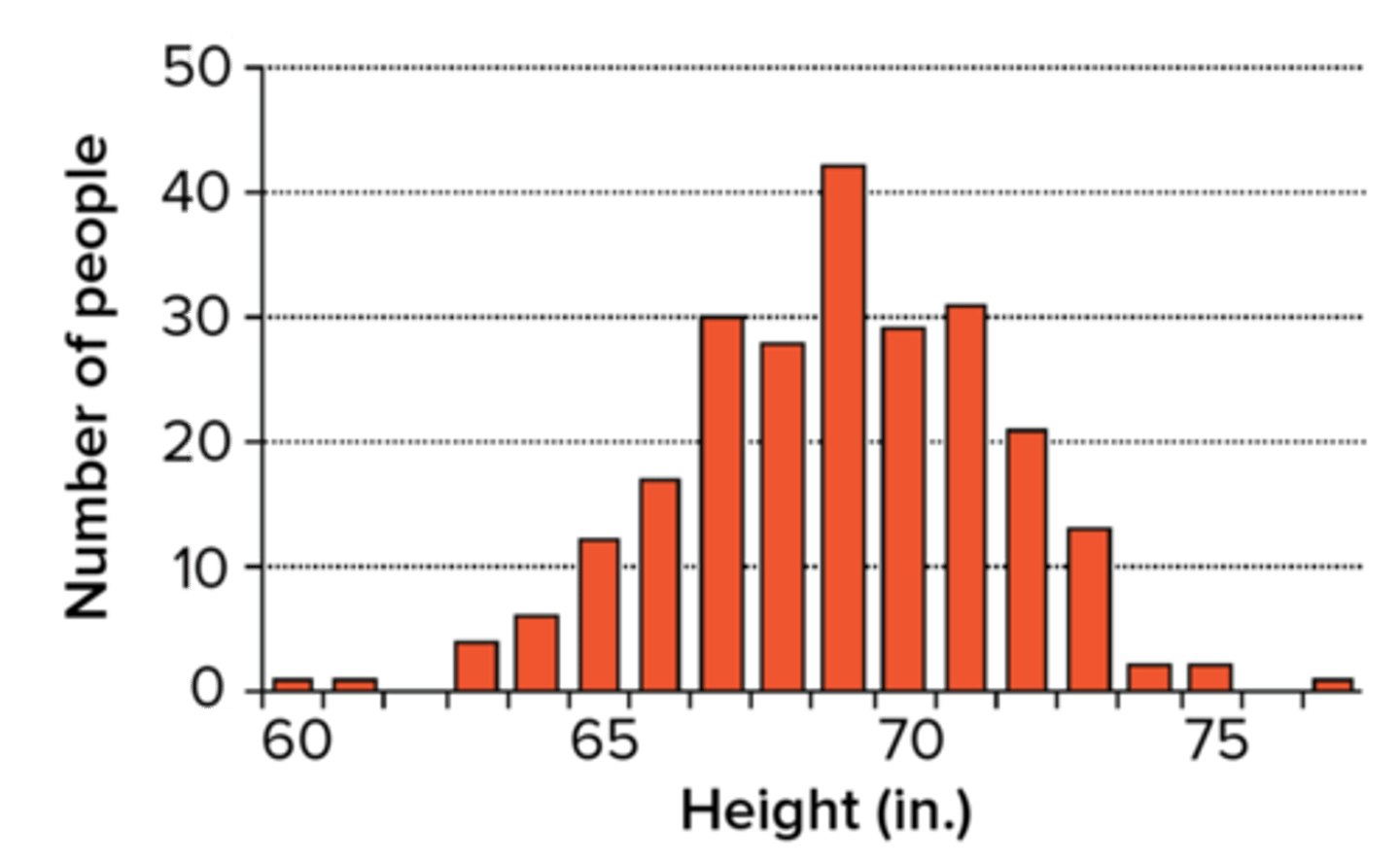
What gene interaction occurs when many genes shape a single phenotype with continuous variation?
polygenic inheritance
What is a helpful way to relate pleiotropy and polygenic inheritance?
think of them as opposites - pleiotropy is when a single gene affects many phenotypes while polygenic inheritance is when many genes affect a single phenotype
Variance in height, skin color, or hair color are controlled by which gene interaction?
polygenic inheritance
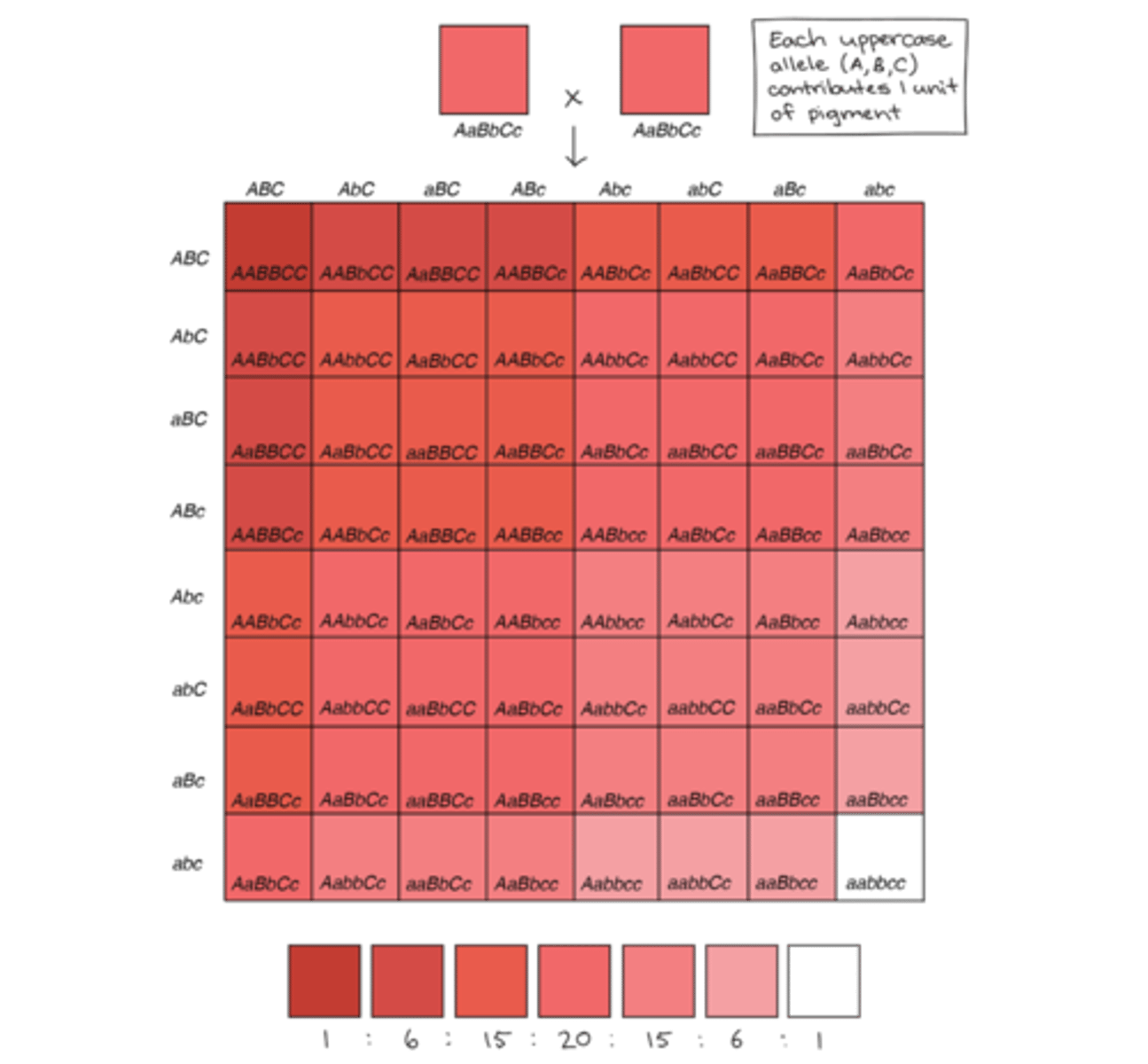
What gene interaction occurs when two or more genes reside physically close to one another on the same chromosome and are inherited together?
linked genes
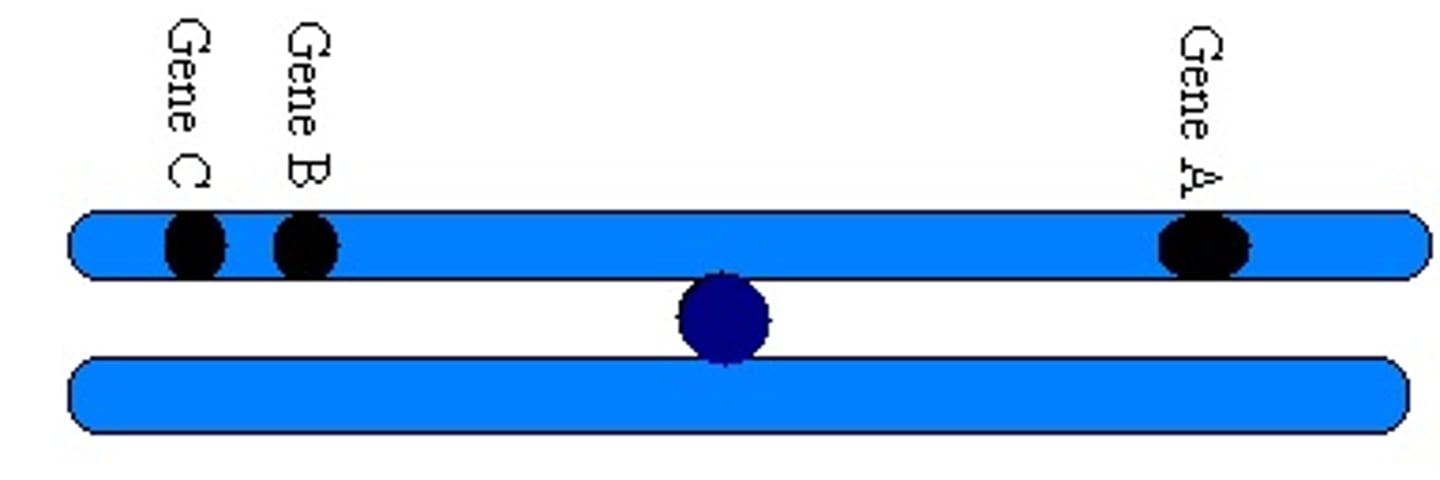
How does physical proximity of genes affect genetic recombination?
the closer two genes are on a chromosome, the less likely they are to be separated by genetic recombination
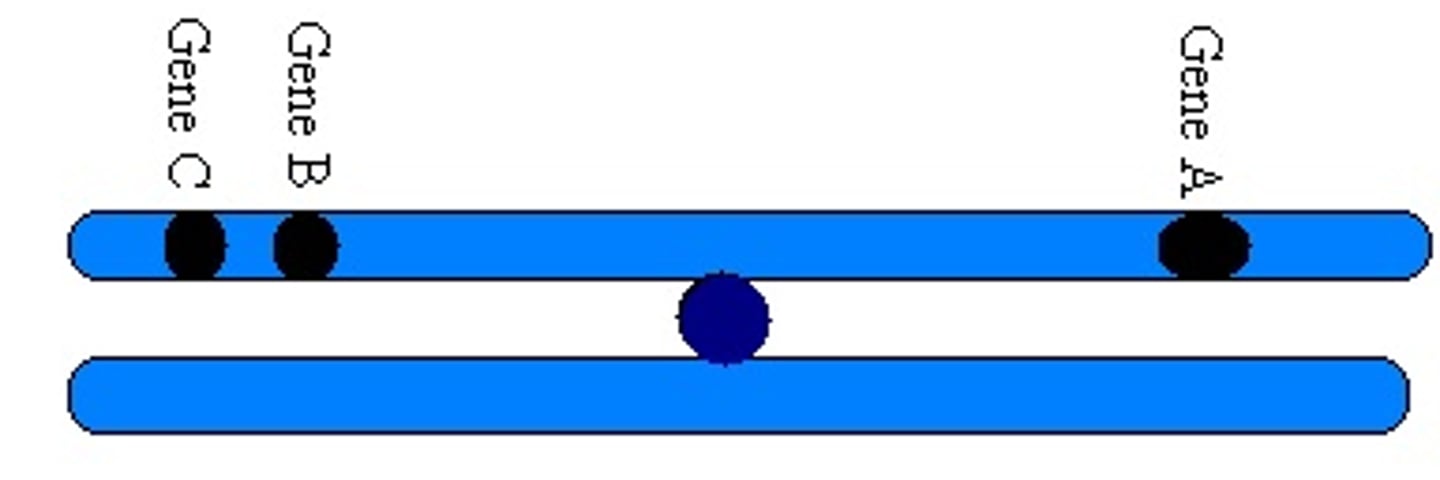
Genes that are unlinked have what percentage chance of recombination?
50%
(Note: lower probability indicate physical proximity)
What images can be generated to visualize recombination frequency in linked genes?
linkage maps
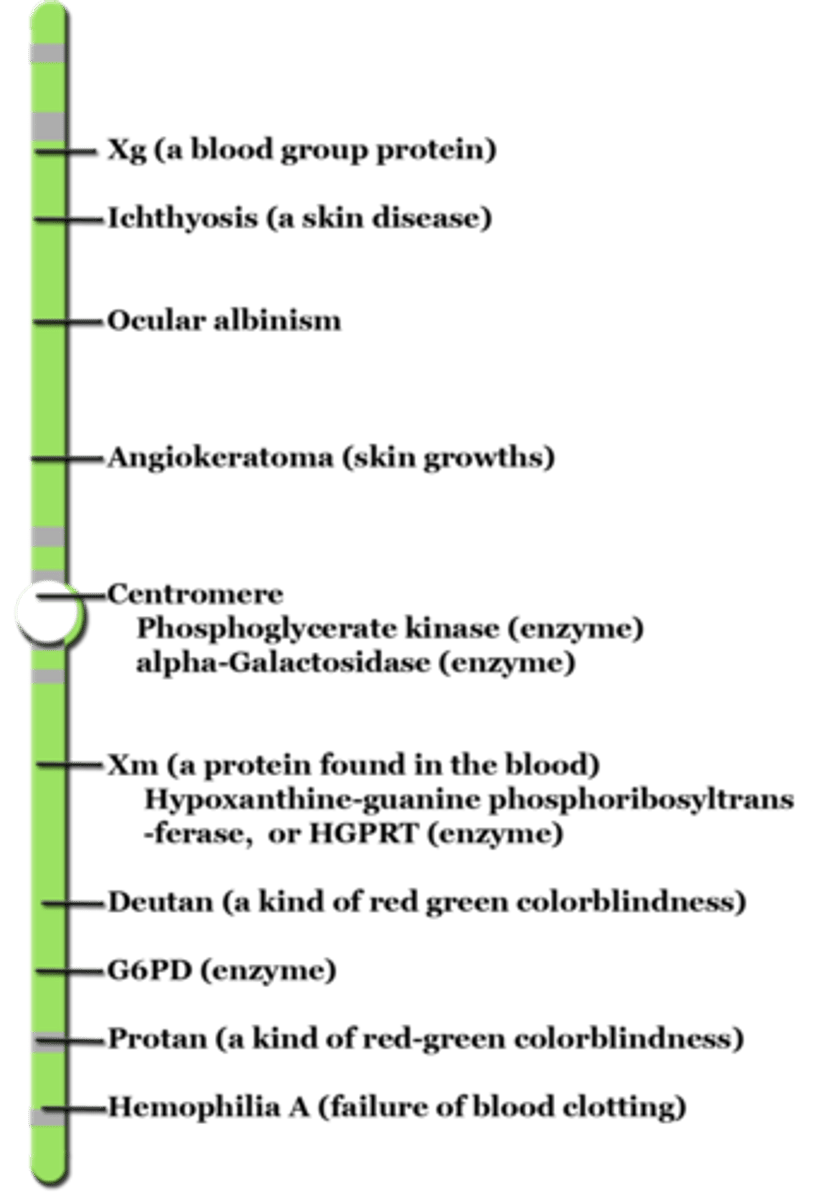
What is a type of linked gene that resides on a sex chromosome that is inherited differently in males and females?
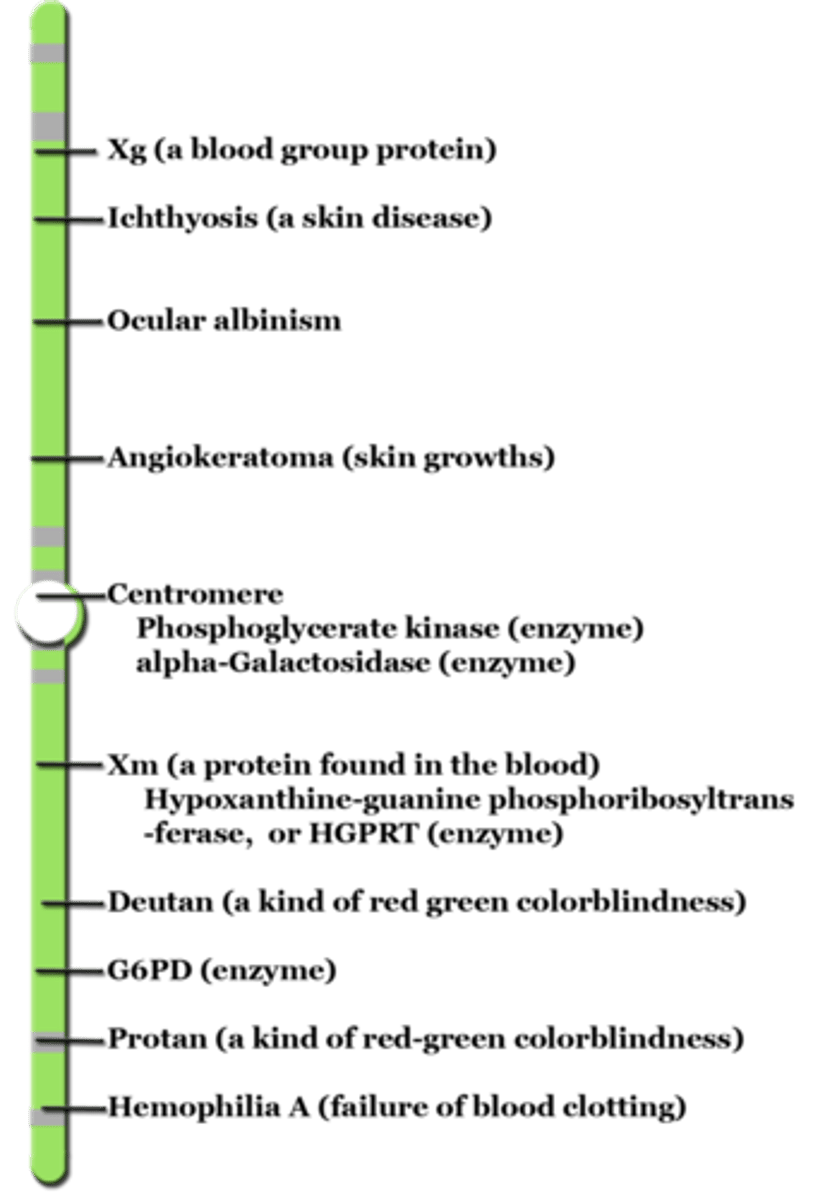
sex-linked gene
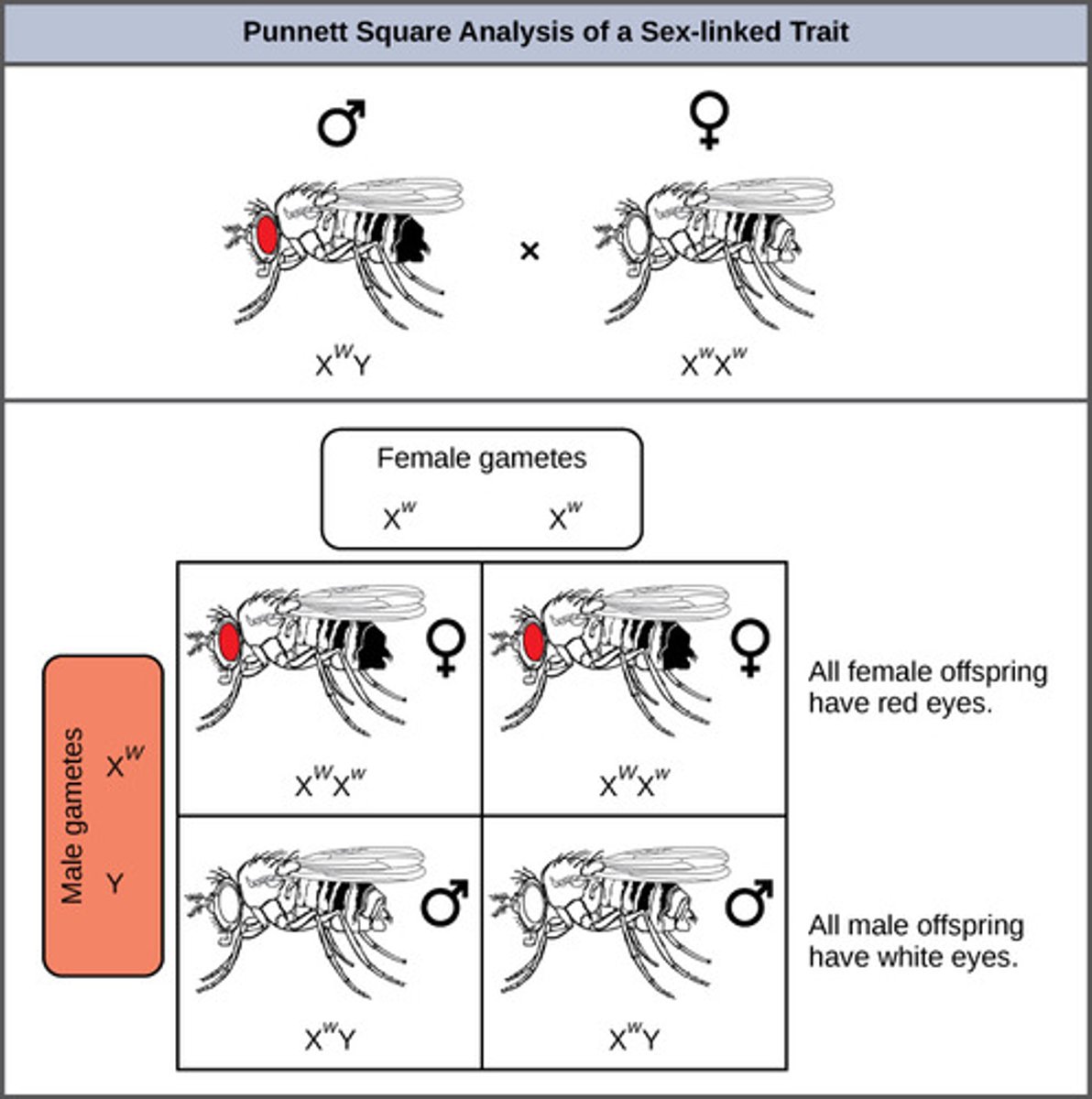
What is a type of gene that influences gene expression based on the sex of the individual carrying the trait?
sex-influenced gene
What gene expression occurs when one allele, either paternal or maternal, is not expressed in the offspring?
genomic imprinting
(Note: can also be seen in autosomal chromosomes)
What concept describes the probability an organism with a specific genotype will express a particular phenotype?
penetrance
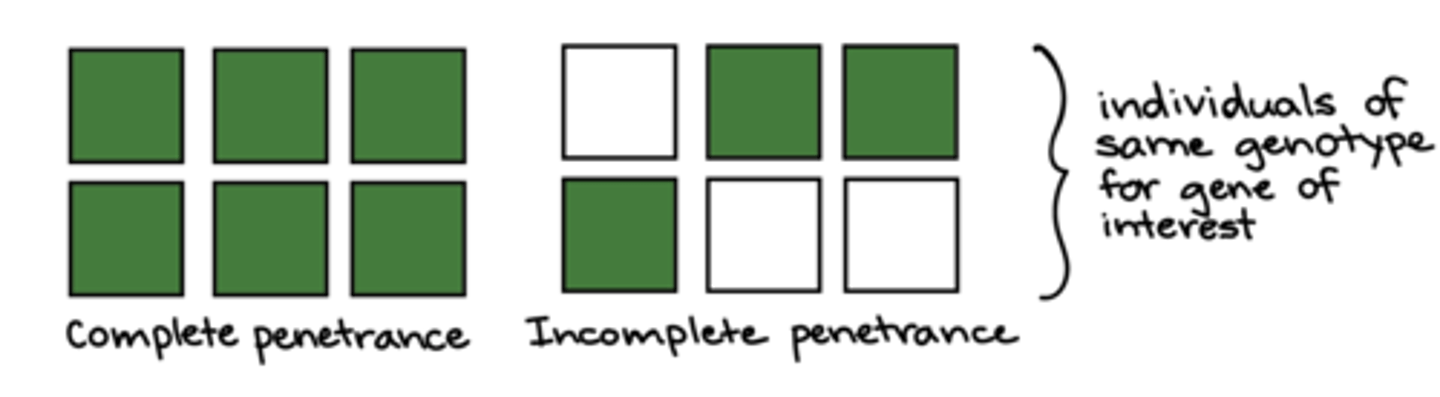
What type of penetrance involves genes for a trait being expressed in all of the population who have the gene?
complete penetrance
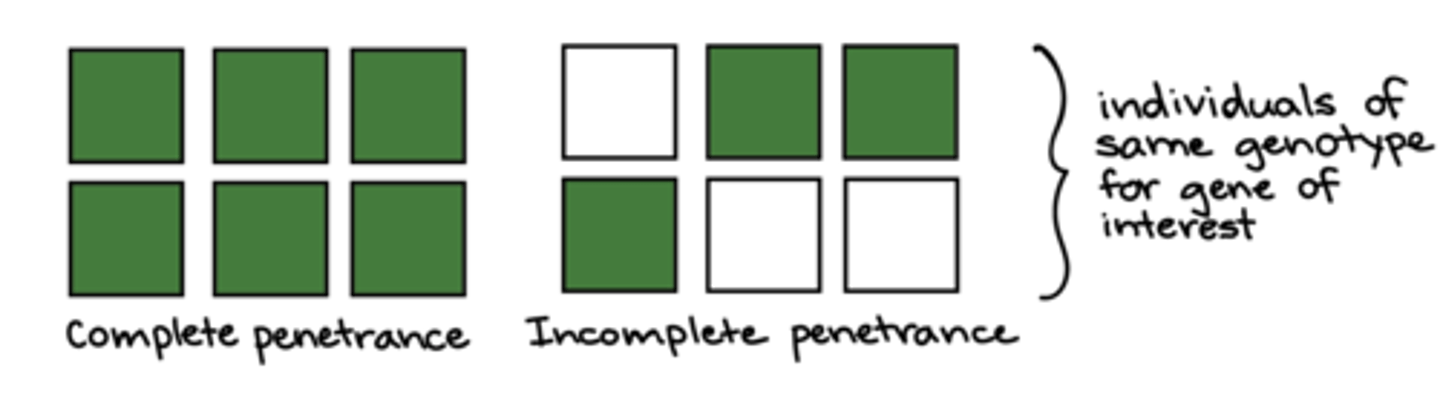
What type of penetrance involves genes for a trait being expressed in a percentage of the population?
incomplete penetrance
What term describes the variation or range of phenotypes for a specific genotypes?
variable expressivity

Red hair exists on a spectrum. What phenotypic expression does this represent?
variable expressivity

What genetic change describes when female mammals express one inherited X chromosome and do not express the other?
X-inactivation
(Note: either chromosome can be inactivated)
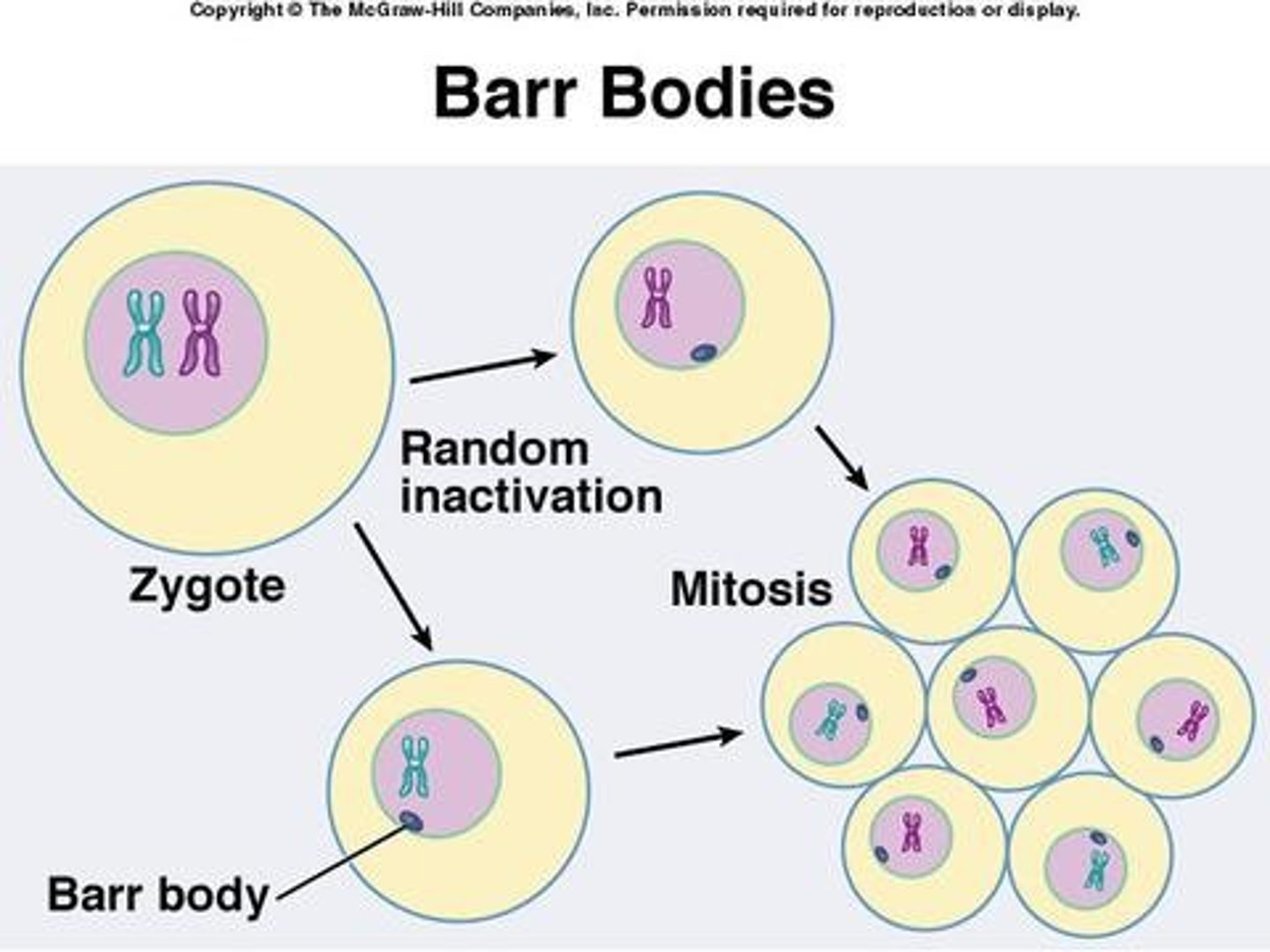
In X-inactivation, what is the unexpressed X chromosome called?
Barr body
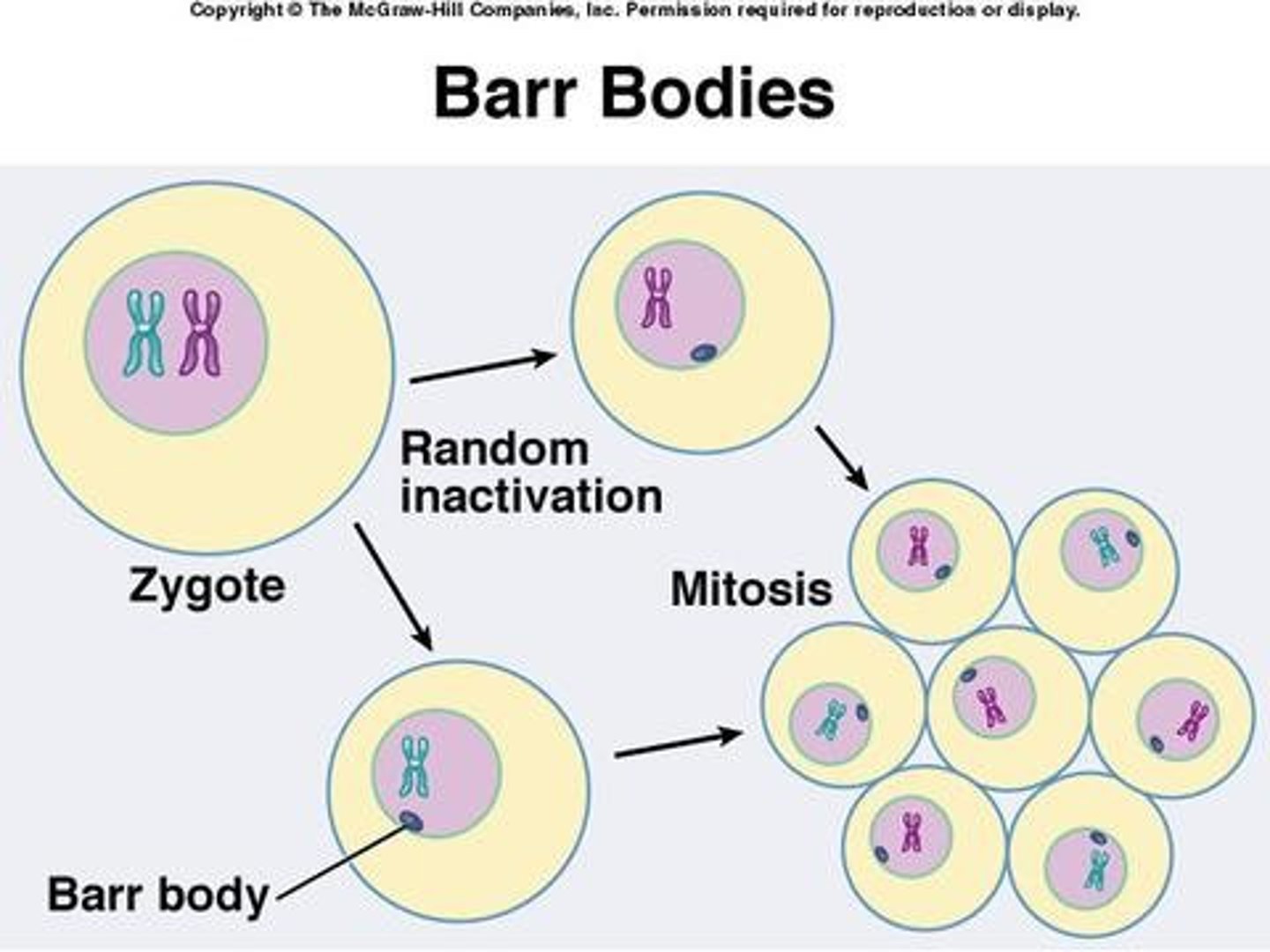
Hemophilia is a genetic disease which results from what type of genetic change?
X-inactivation
(Note: XHXh = normal carrier, XH gets inactivated, results in Xh expressed which results in disease)
Which genetic change describes when one or more chromosome pairs or chromatids fail to separate during mitosis?
nondisjunction
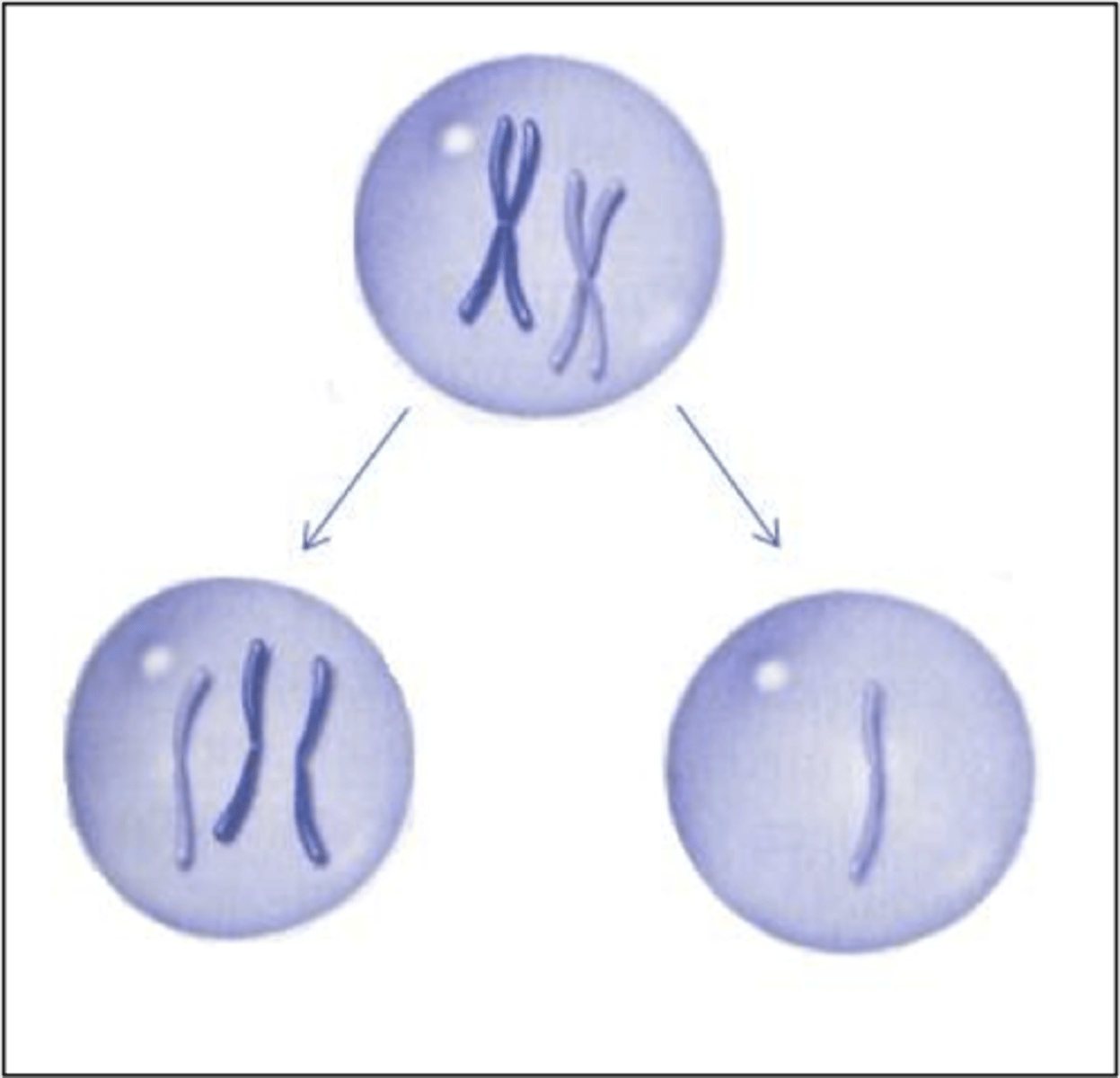
During which scenarios does nondisjunction commonly occur?
1. anaphase of mitosis
2. when two chromatids of a single chromosome fail to separate
3. anaphase of meiosis
What type of nondisjunction results in a fraction of body cells have extra or missing chromosomes?
mosaicism
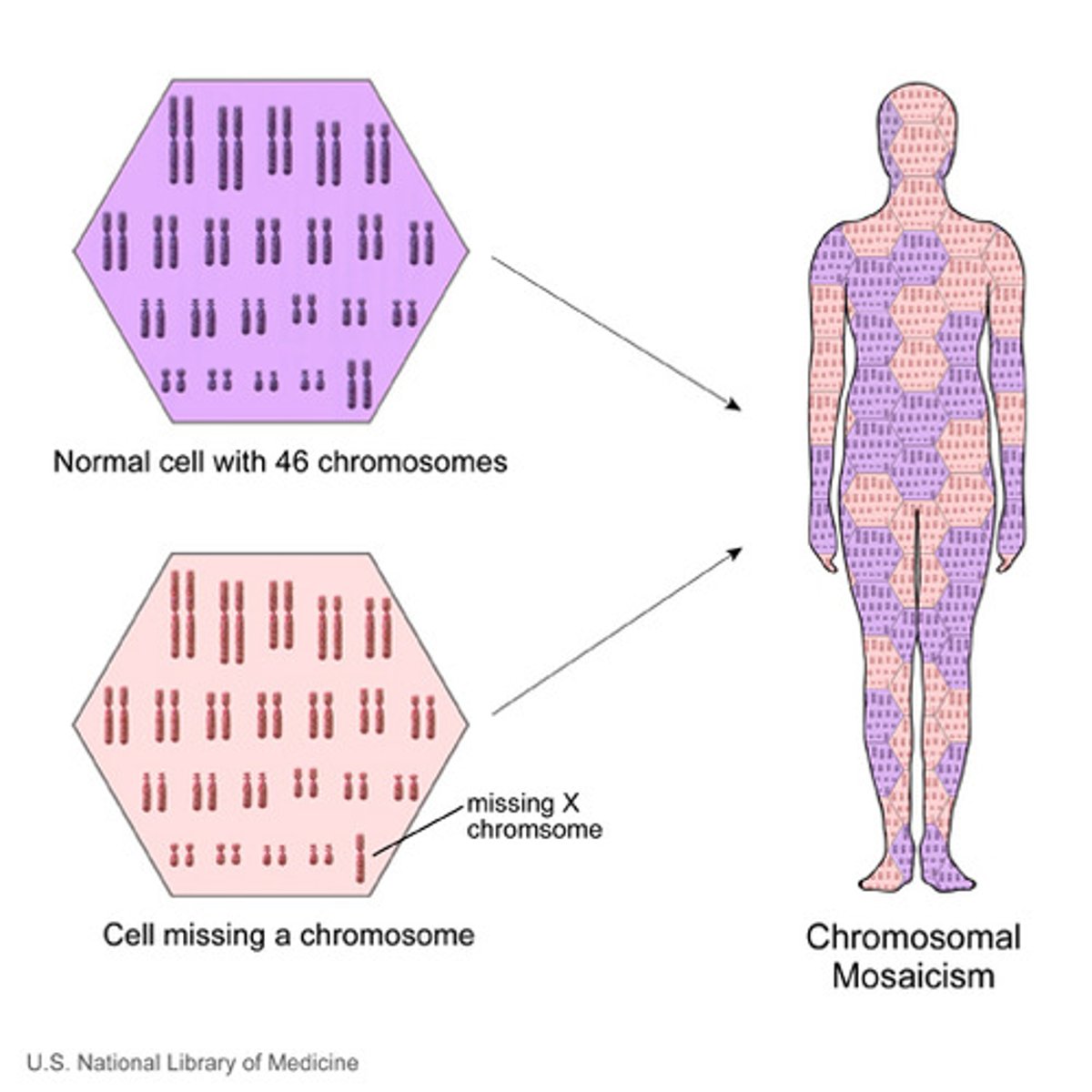
When does mosaicism occur in humans?
meiosis during embryonic development
What is the chromosomal result of mosaicism
fraction of body cells have extra or missing chromosomes
What type of nondisjunction occurs when all chromosomes undergo meiotic nondisjunction and produce gametes with twice the number of chromosomes?
polyploidy
In which organisms is polyploidy common?
plants
Which genetic defect involves a single nucleotide change causing either substitution, insertion, or deletion?
point mutation
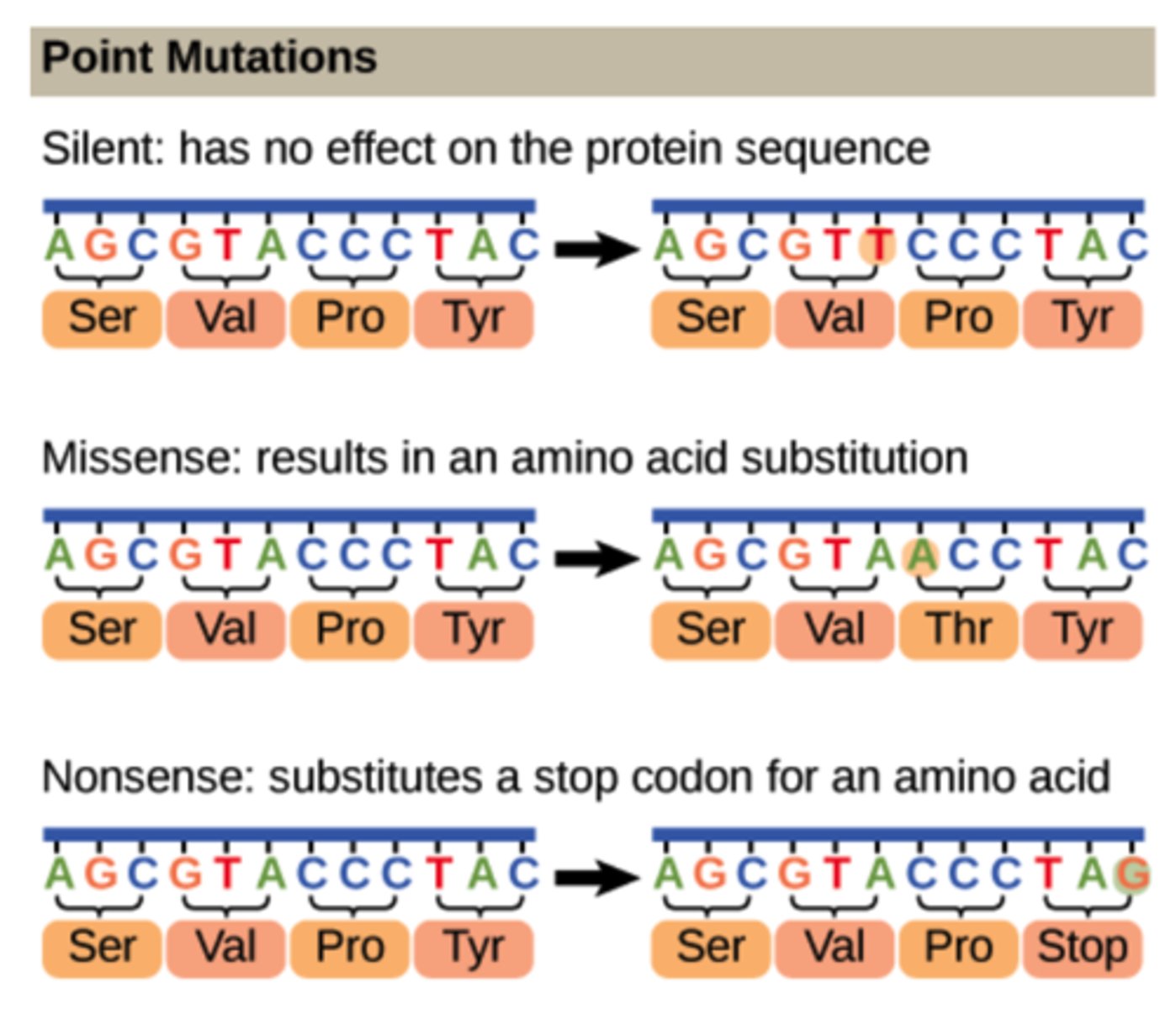
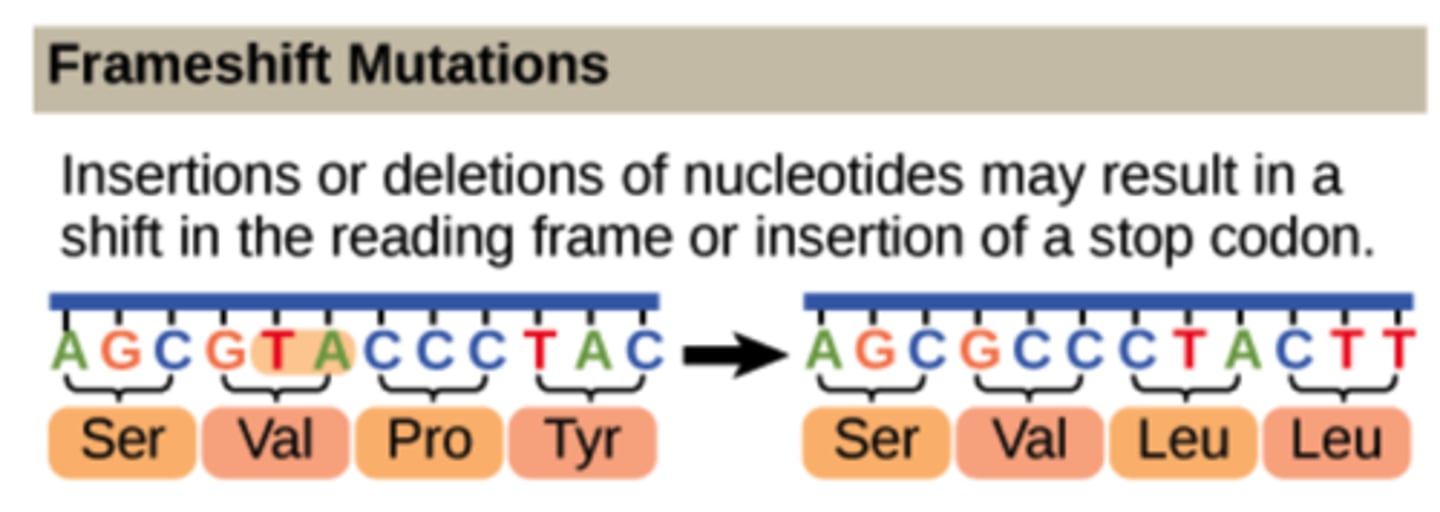
Which genetic defect can cause a frameshift mutation?
insertion and deletion
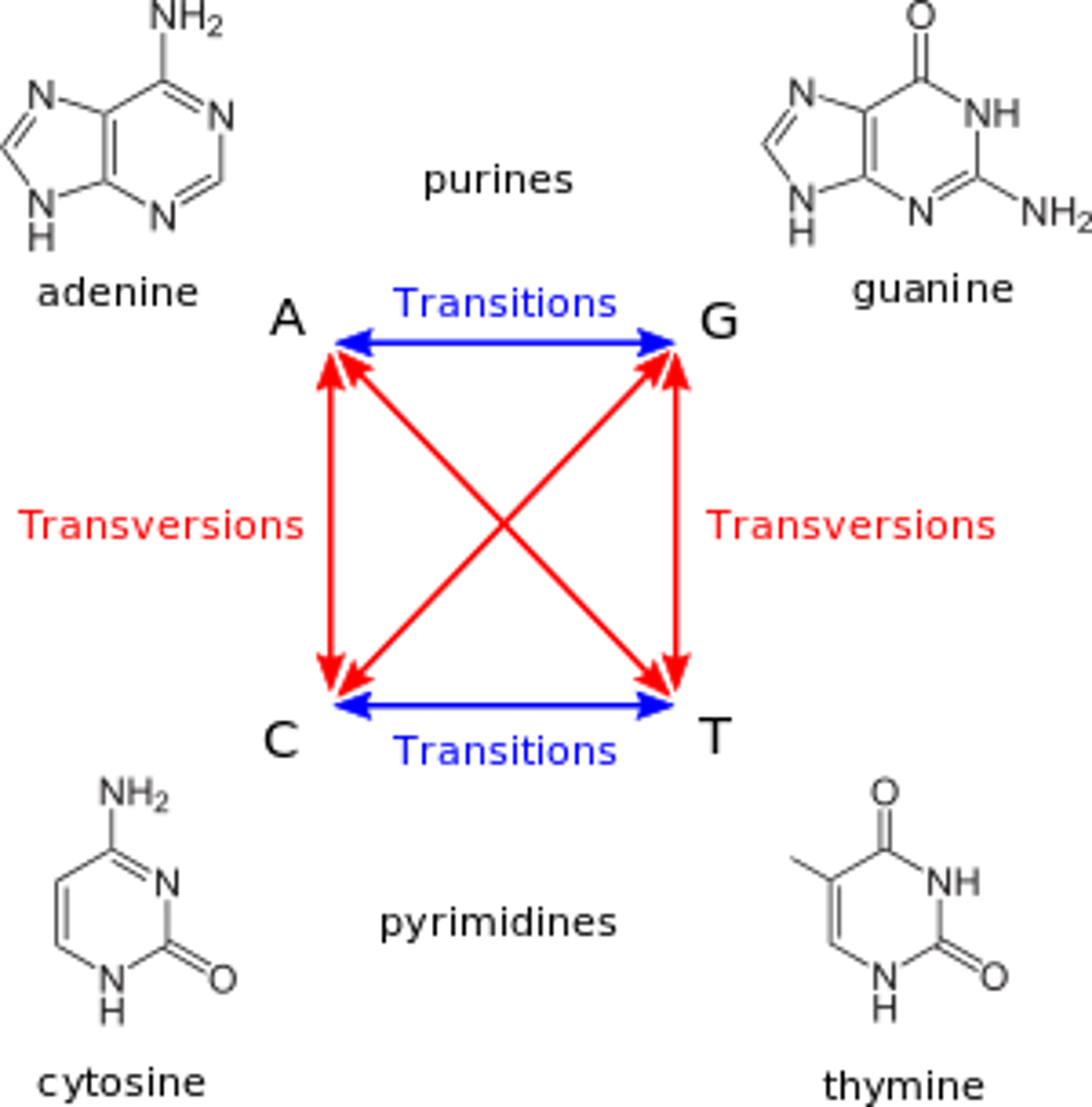
What point mutation involves the conversion of a purine to purine or pyrimidine to pyrimidine?
transition mutation
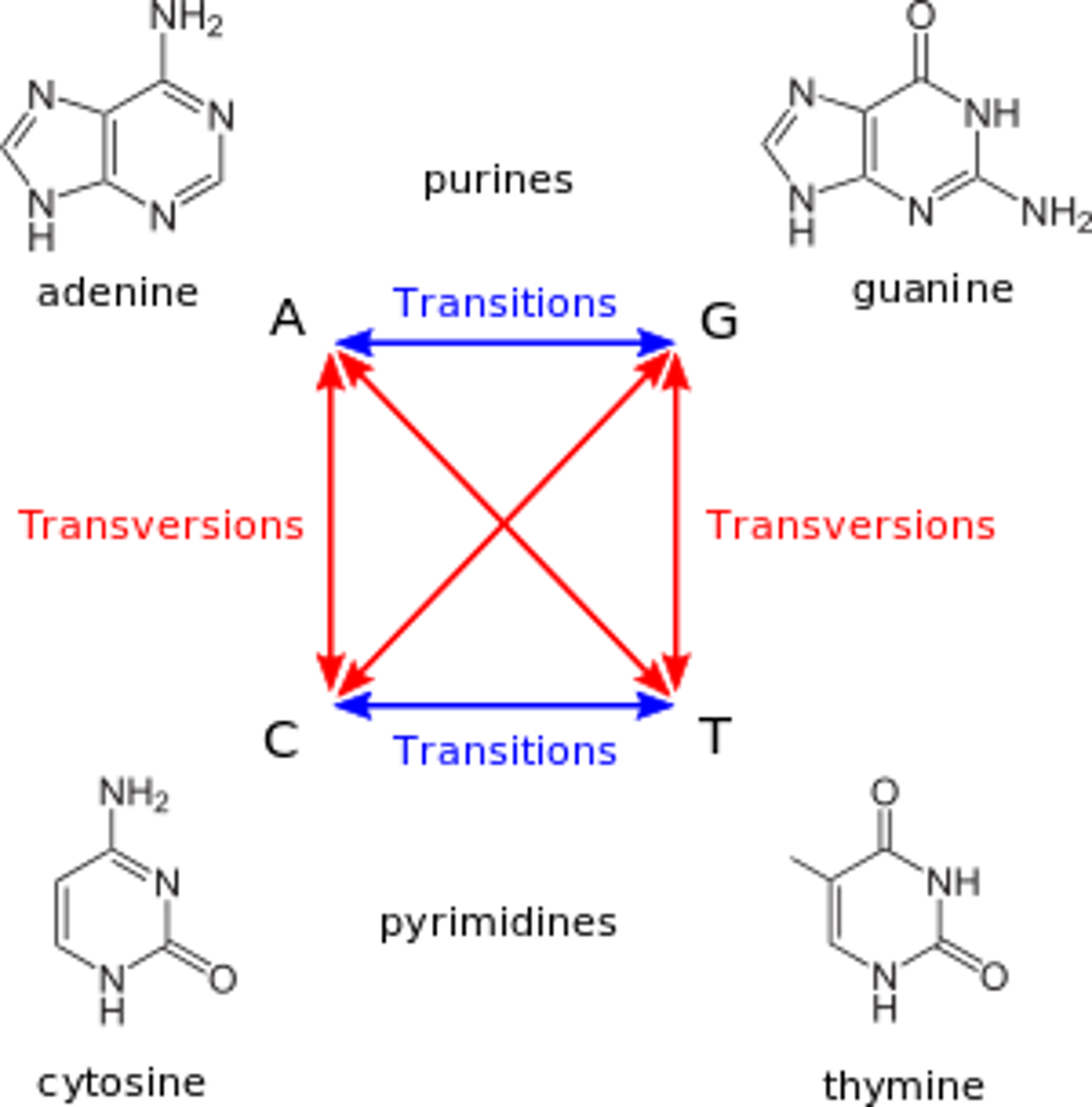
What point mutation involves the conversion of a purine to pyrimidine or vice versa?
transversion mutation
Which genetic defect involves a genome with extra or missing chromosomes, often caused by nondisjunction?
aneuploidy
Down syndrome is an example of which genetic defect?
aneuploidy
(Note: trisomy of chromosome 21)
What is the genetic condition in which a female is either completely missing or partly missing, an X chromosome?
Turner syndrome
(Note: leads to genotype XO)
What genetic change causes turner syndrome?
nondisjunction
What is the main physical defect caused by turner syndrome?
physical abnormalities
What genetic condition occurs when a male is born with an extra X chromosome (XXY)?
Klinefelter's Syndrome
What problems occur when chromosome segments are changed?
chromosomal aberrations
Which chromosomal aberrations involve chromosome
segments that are repeated on the same chromosome?
duplications
What causes duplications?
unequal crossing over
Which chromosomal aberrations involve chromosome segments that are rearranged in reverse orientation?
inversions
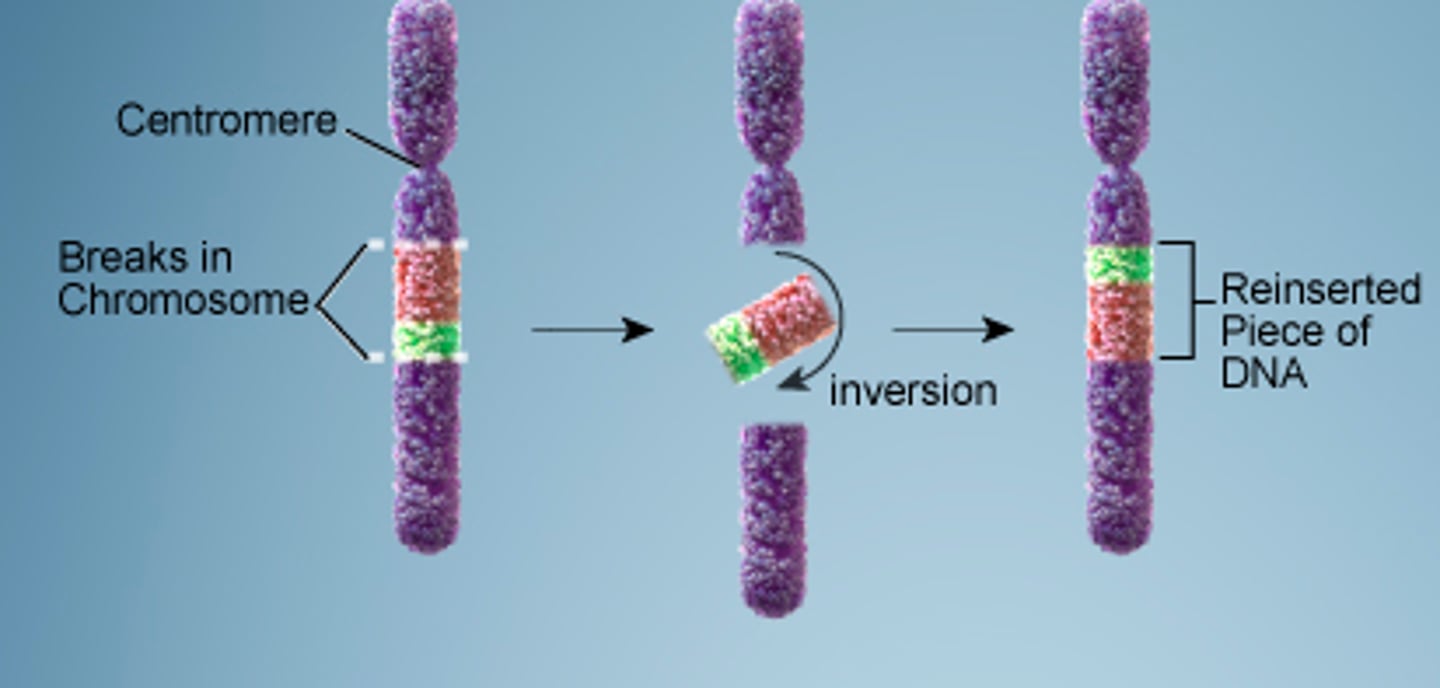
Which chromosomal aberrations involve one segment of a chromosome that is moved to another chromosome?
translocations
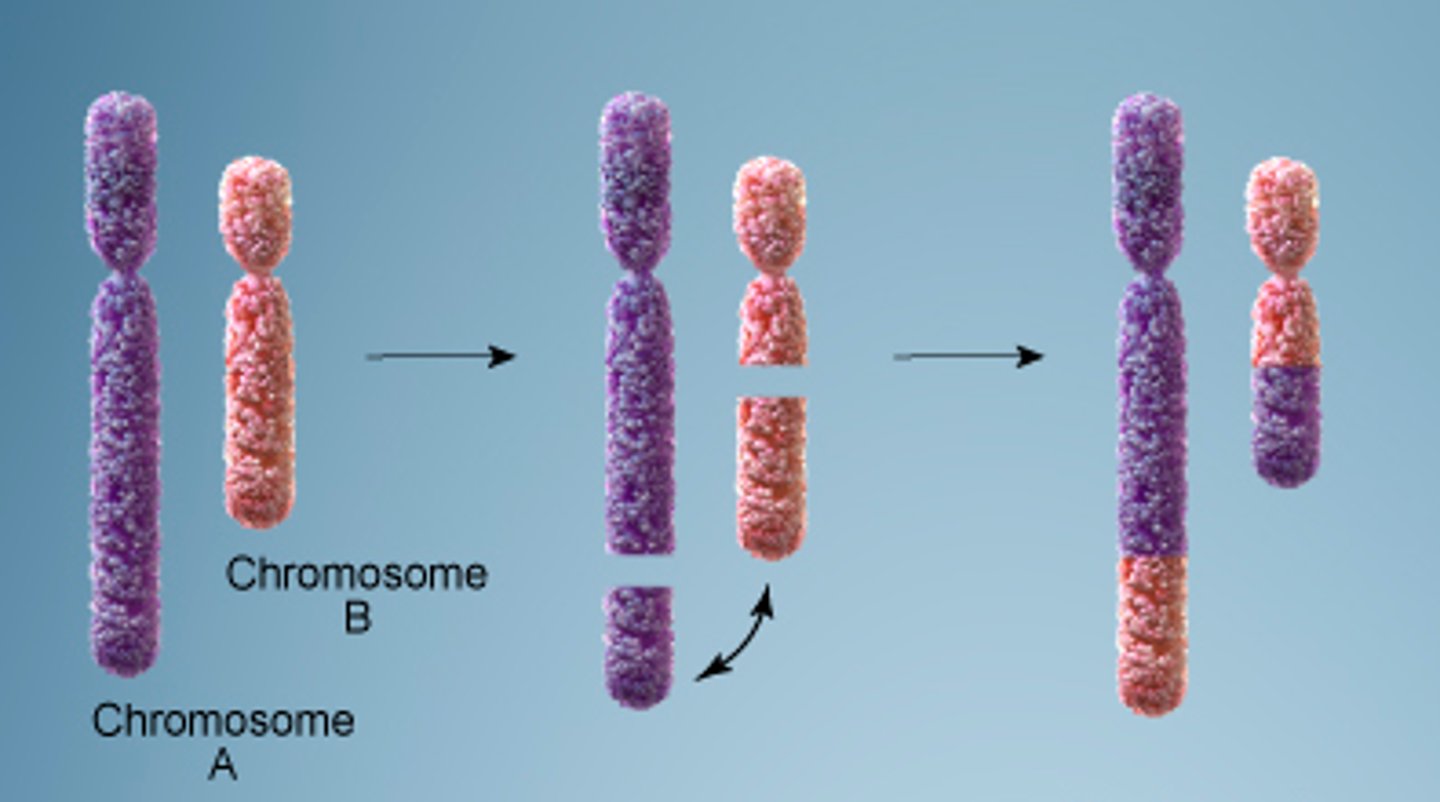
Which translocation occurs when two non-homologous chromosomes swap segments?
reciprocal translocation
Which translocation occurs when one chromosome from a homologous pair becomes attached to another chromosome from a different pair?
Robertsonian translocation
Which translocation involves the loss of genetic information?
Robertsonian
(Note: reciprocal does not lose genetic information)
Which genetic defect involves the spontaneous or induced breakage of a chromosomal segment via mutagenic agents or X-rays?
chromosomal breakage
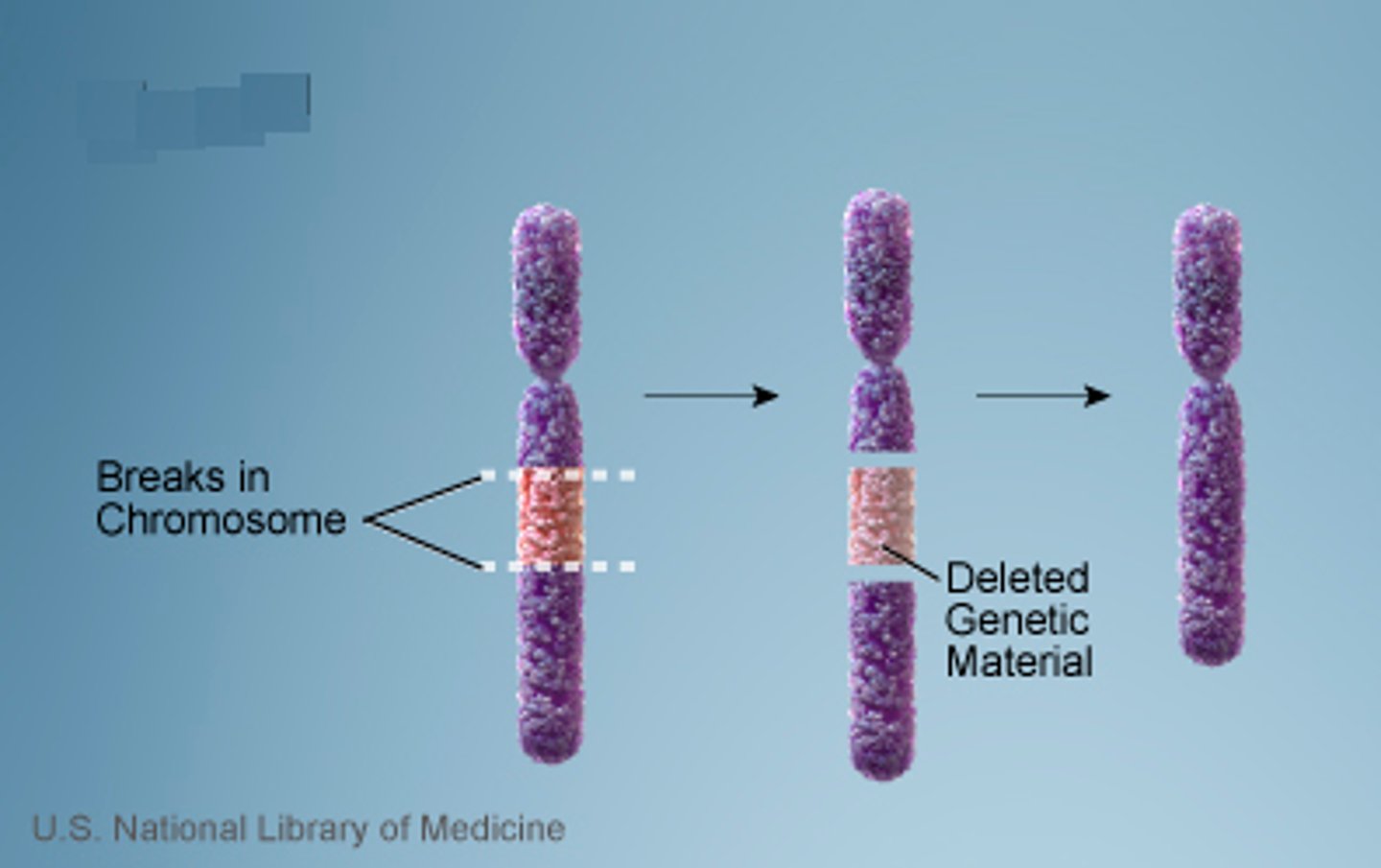
Cosmic rays, X-rays, UV rays, radioactivity, and various chemical compounds are what type of agents?
mutagenic agents
Mutagenic agents can cause what changes in a genome?
genetic mutations
(Note: mutagenic agents are generally also carcinogenic)
Colchicine inhibits spindle formation, which can cause what type of nondisjunction?
polyploidy
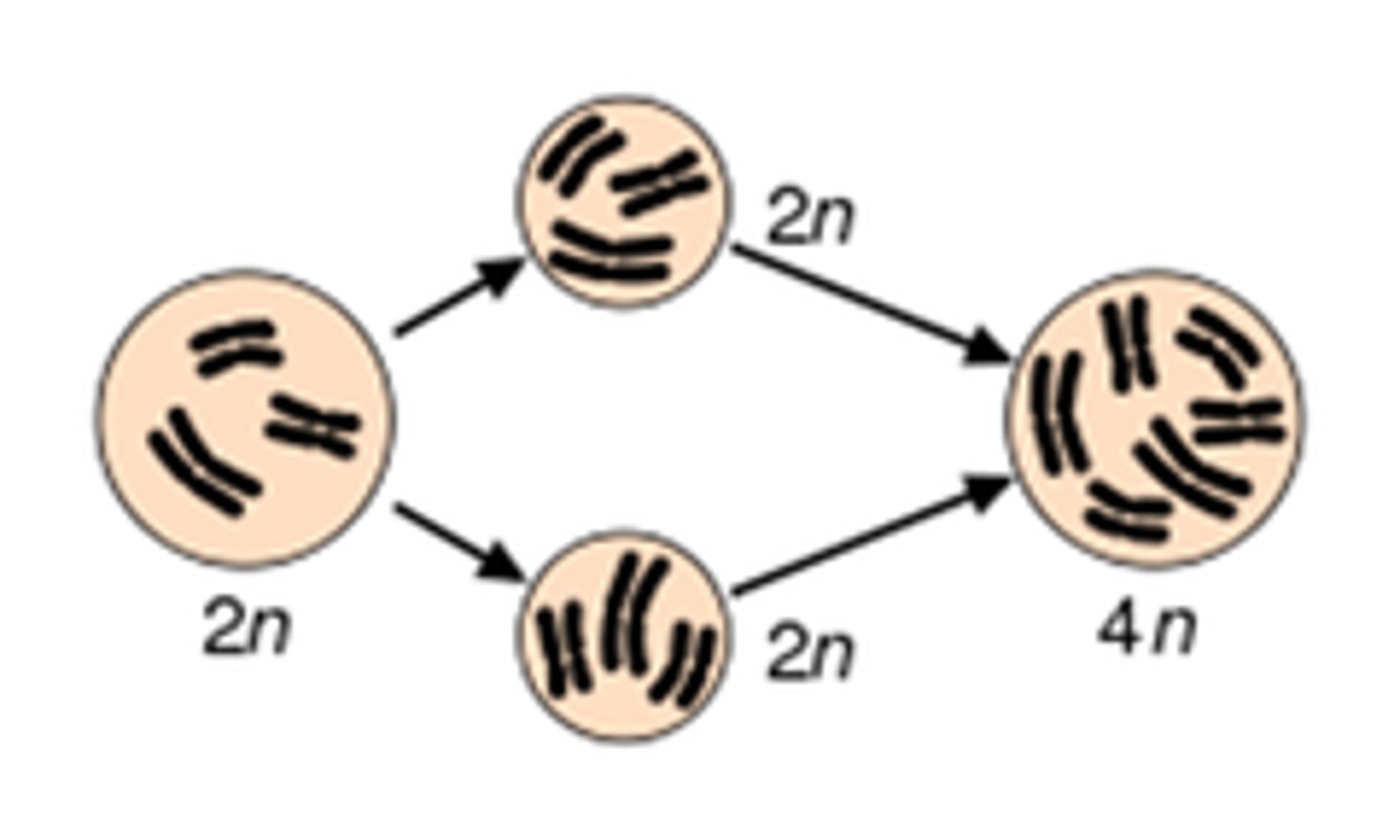
What autosomal recessive condition involves the inability to produce the proper enzyme for phenylalanine breakdown?
phenylketonuria
(Note: causes the degradation product phenylpyruvic acid to accumulate)
What autosomal recessive condition involves fluid buildup in respiratory tracts?
cystic fibrosis
What autosomal recessive condition involves a lysosome defect in which cells can’t breakdown lipids for normal brain function?
Tay-Sachs
What autosomal dominant condition involves nervous system degeneration?
Huntington's disease
Which autosomal dominant condition causes dwarfism?
achondroplasia
Which autosomal dominant condition involves excess cholesterol in the blood that progresses into heart disease?
hypercholesterolemia
Which sex-linked recessive condition causes abnormal blood clotting?
hemophilia
What kind of genetic condition is colorblindness?
sex-linked recessive
(Note: mostly in males)
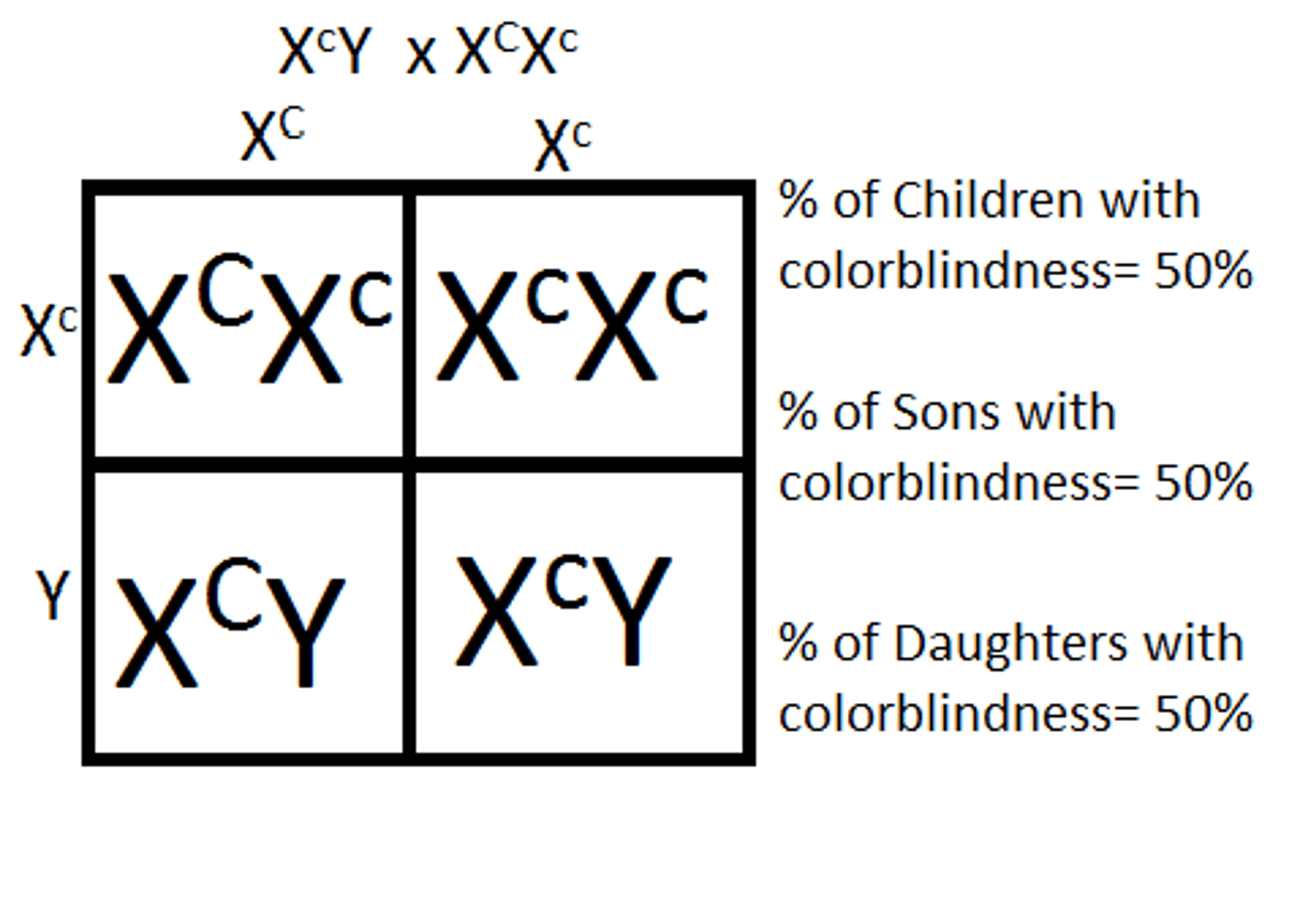
Which sex-linked recessive condition involves the progressive loss of muscle?
Duchenne's muscular dystrophy
Which genetic disorders change the number or structure of chromosomes?
chromosomal disorders
Which chromosomal disorder is a trisomy of 21?
Down's syndrome
Which chromosomal disorder involves the deletion of an X chromosome, resulting in an XO genotype?
Turner's syndrome
Which chromosomal disorder involves the presence of an extra X chromosome, resulting in an XXY genotype?
Klinefelter's syndrome
Which chromosomal disorder involves the deletion of chromosome 5?
Cri du Chat
How can a fetus be tested for genetic disorders?
1. amniocentesis
2. chorionic villus sampling (CVS)
extranuclear genes are found in mitochondria and chloroplasts, which leads to what type of inheritance?
extranuclear inheritance
Defects in which organelle's DNA can reduce a cell's ATP production?
mitochondrion
Why are all mitochondrial defects/ diseases inherited?
they come only from the mother
(Note: mitochondrial DNA is also an exception to the universality of the genetic code)
What does homozygous refer to regarding alleles?
two copies of the same allele (AA or aa) are inherited
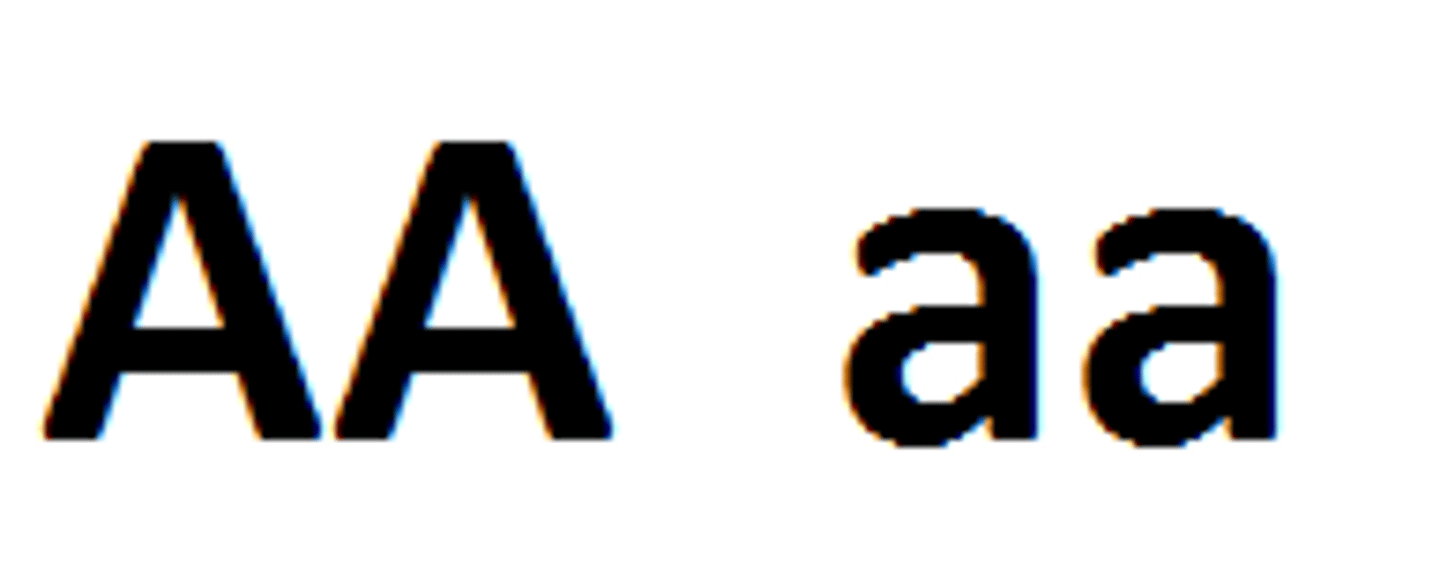
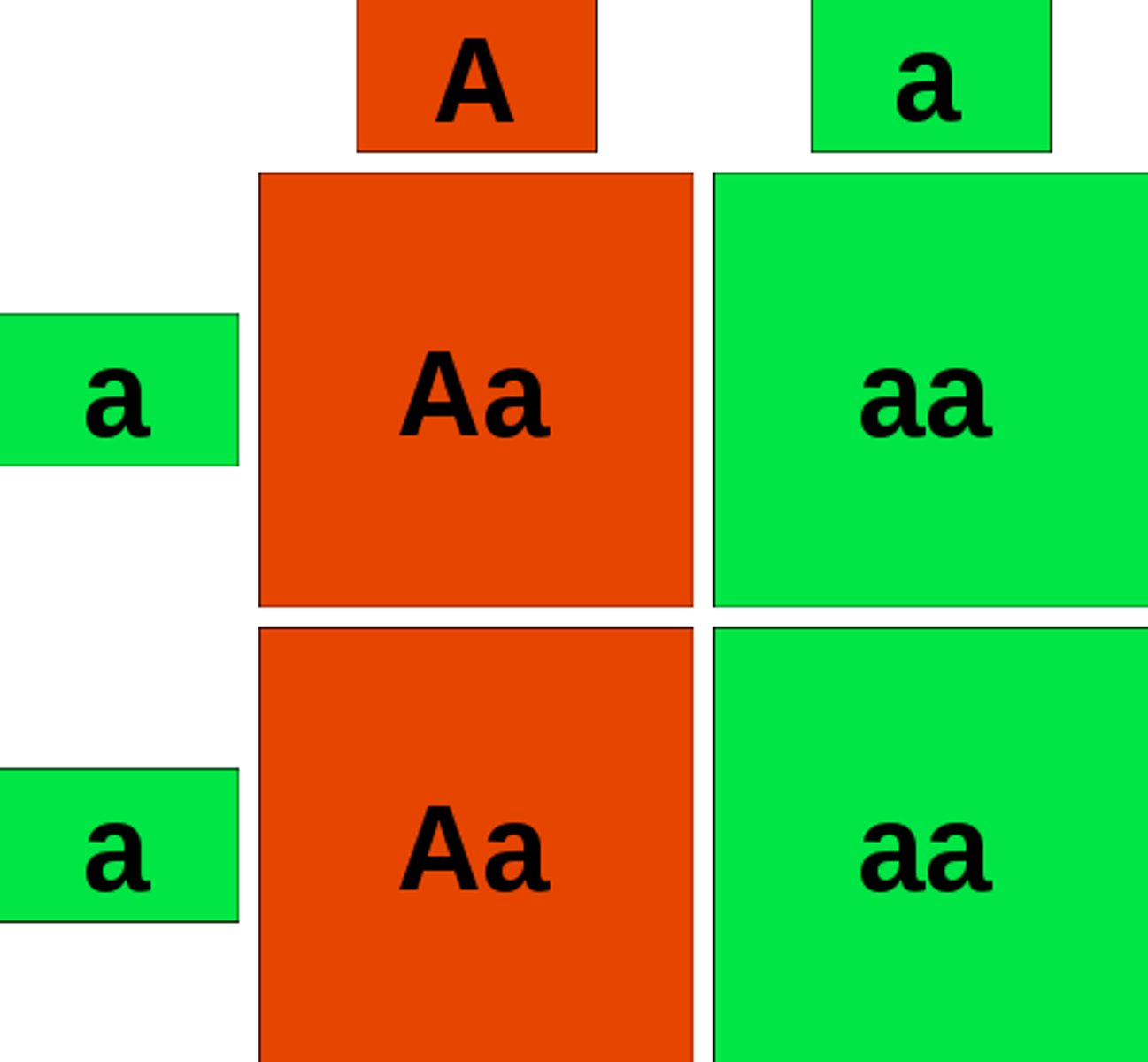
What does heterozygous refer to regarding alleles?
different alleles of the same gene (Aa) are inherited
What does hemizygous refer to regarding alleles
single copy of a gene is inherited instead of two
(Note: males having XY chromosomes is a good example of hemizygous genotype)