Topic 9 - Fundamentals of Communication and Networking
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Define Baud rate
The number of signal changes in a communication medium per second
A communication medium uses 8 bits per signal and has a Baud rate of 128Bd. What is the medium’s bit rate?
1024 bps (8 × 128 = 1024)
In which method of data transmission is used for transmitting data over medium to long distances?
Serial data transmission
What unit is used for bandwidth?
Hertz (Hz)
Define bandwidth
The range of frequencies that a communication medium is capable of transmitting
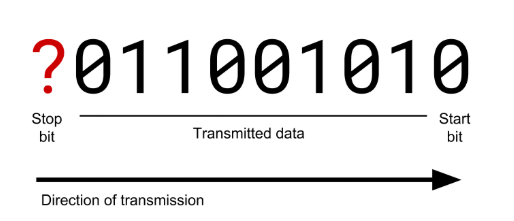
What should be the value of the stop bit in the diagram?
1
Define latency
The difference in time between an action being initiated and its effect being noticed
Define protocol
A set of rules relating to communication between devices
Which method of data transmission is suitable for transmitting information in real-time systems?
Synchronous data transmission
In which method of data transmission is data sent one bit at a time over a single communication line?
Serial data transmission
In which method of data transmission do the sender and receiver synchronise their clocks only for the duration of data transmission?
Asynchronous data transmission
In which method of data transmission do numerous parallel communication lines send multiple bits between components simultaneously?
Parallel data transmission
What problem is caused by signals from tightly packed communication lines leaking into others?
Crosstalk
In which method of data transmission is a clock signal shared between the sender and receiver?
Synchronous data transmission
In which method of data transmission is used over short distances?
Parallel data transmission
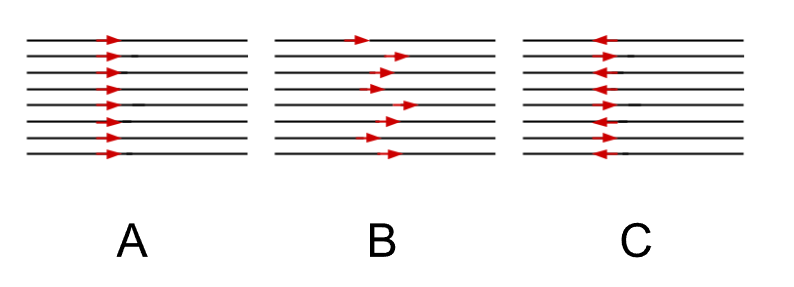
Which diagram represents skew?
B
Which communication method is more reliable: serial or parallel?
Serial
Which method of data transmission uses start and stop bits?
Asynchronous data transmission
In which physical network topology does the failure of one cable not affect the performance of the rest of the network?
Star
What name is given to a device communicating on a network that cannot be “seen” by another device that wants to transmit over the network?
Hidden node
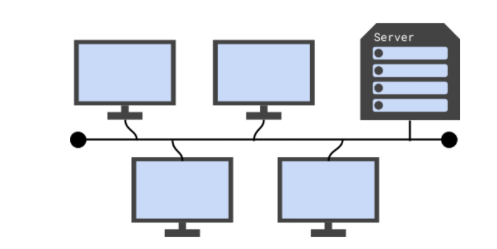
Which physical topology is shown in the diagram?
Bus
Which type of topology refers to the architecture of connections in a network: physical or logical?
Physical
In which physical network topology is there no central hub?
Bus
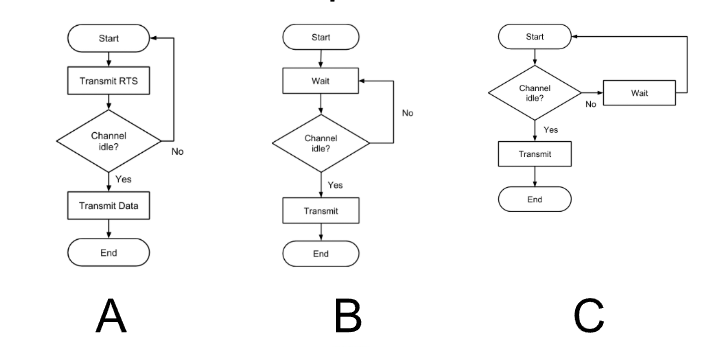
Which flowchart represents CSMA/CA?
C
What name is given to a wireless local area network that is based on international standards?
WiFi
Which type of topology refers to the flow of data packets in a network: physical or logical?
Logical
What name is given to the cable which connects all of the clients in a physical bus network?
Backbone
What can be used to make a physical star network behave as a logical bus?
A bus protocol
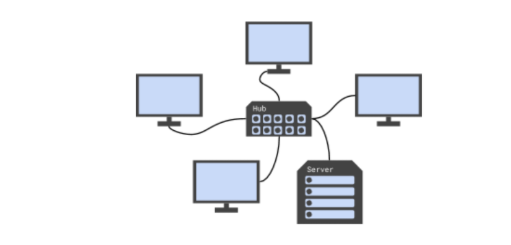
Which physical topology is shown in the diagram?
Star
In which type of networking between hosts do clients have equal status: client-server or peer-to-peer?
Peer-to-peer
In which physical topology does each client have its own direct connection to a central hub?
Star
Which type of networking between hosts is used by large file-sharing networks and multimedia providers to provide high-performance services without the requirement for a server?
Peer-to-peer
Which two pieces of hardware are required in order to set up and use a wireless network?
Wireless access point 2. Wireless network adapter
What is an SSID
and what do the letters stand for?
Which physical network topology is expensive to install thanks to the amount of cable required?
Star
For what do the letters RTS/CTS stand?
Ready to send
What do the letters MAC stand for in MAC address?
Media access control
Define the Internet
A network of interconnected computer networks which uses an end-to-end communication protocol
Which type of malware requires a host file: worms
Trojans or viruses?
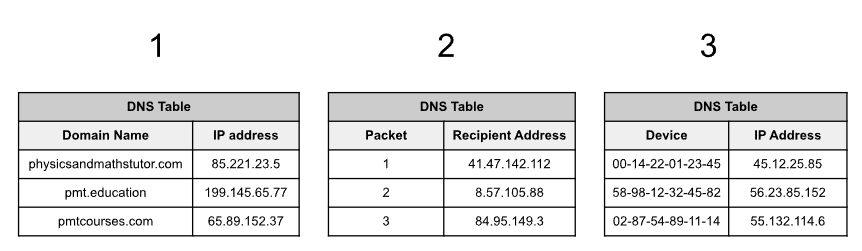
Which of the tables could be a DNS table?
1
What is an internet service provider?
A company that provides its customers with access to the Internet
For what do the letters TTL stand?
Time to live
What name is given to the process of a packet moving from one router to another?
Hop
Name three of the primary components of a packet
Sender’s address
What device is used between networks that use different protocols?
Gateways
In what type of packet control is the content of a packet examined by a firewall: packet filtering or stateful inspection?
Stateful inspection
For what do the letters URL stand?
Uniform resource locator
List two benefits that digital signatures bring to asymmetric encryption
Verifies sender authenticity
Verifies message integrity
Which type of malware is disguised as a benign file: worms
Trojans or viruses?
For what do the letters TLD stand?
Top-level domain
In what type of encryption do the sender and receiver share the same private key?
Symmetric encryption
How are different continents connected to the Internet?
By underwater cables
For what do the letters FQDN stand?
Fully qualified domain name
Which organisations are responsible for the allocation of IP addresses?
Internet registries
What name is given to servers that sit between a public network and a private network?
Proxy servers
Using asymmetric encryption
a message is encrypted using the recipient’s public key. Which key can now decrypt the message?
Name three pieces of information contained in a digital certificate
Serial number
Owner’s name
Expiry date
Owner’s public key
Certificate authority’s signature
Which layer of the TCP/IP stack is responsible for establishing a virtual path between the sender and the receiver?
Transport
Name the four HTTP request methods used by REST
POST

Which is a socket address?
56.32.112.3:21
Which protocol uses port 80?
HTTP
A device has the IP address 192.168.12.44 and the subnet mask 255.255.0.0. What is the device’s network identifier?
192.168.0.0
Which layer of the TCP/IP stack is responsible for controlling physical connections between pieces of hardware in a network?
Link
Which type of IP address allows for more unique permutations: IPv4 or IPv6?
IPv6
What is FTP used for?
Sending files between devices
How many bits are assigned to each part of an IPv4 address?
Eight (one byte)
Which protocol uses port 995?
POP3
Which allows for greater centralised control of a network: thick- or thin-client?
Thin-client
Which protocol uses a pool of available IP addresses to allocate IP addresses?
DHCP
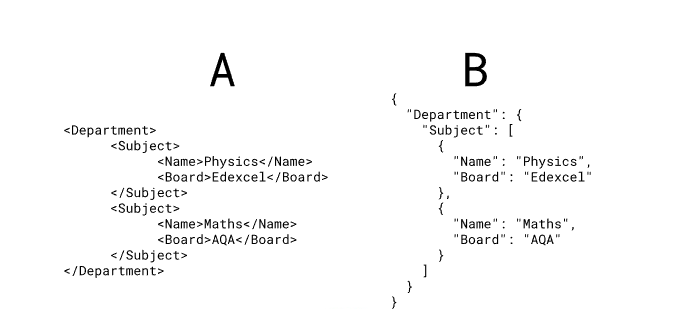
Which is JSON?
B
Which API allows for fast transmission of data by reducing the size of packet headers?
The WebSocket protocol
For what do the letters DHCP stand?
Dynamic host configuration protocol
Which protocol uses port 443?
HTTPS
What is REST an acronym for?
Representational state transfer
List the four layers of the TCP/IP stack in the correct order
Application
How long are IP addresses issued to a device by DHCP assigned for?
The duration of the device’s session
What name is given to the process of routers replacing private IP addresses on packets with their own routable IP address?
NAT (Network address translation)
Which layer of the TCP/IP stack is responsible for providing the correct IP addresses for each packet’s source and destination?
Network
Which type of IP address is globally unique: routable or non-routable?
Routable (public)
What is an application programming interface (API)?
A set of protocols relating to how different applications communicate with each other
What is used when a client needs to communicate with a server that is connected to a private network?
Port forwarding
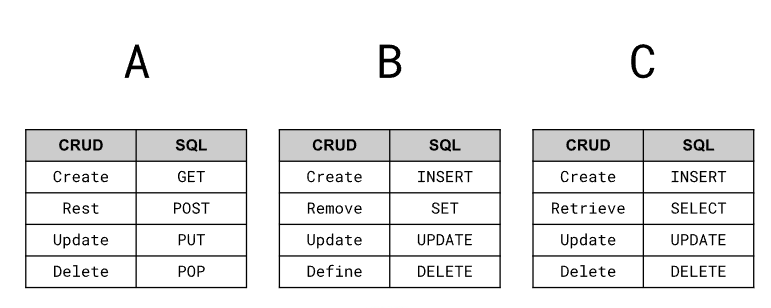
Which table is correct?
C