Lab 7 and 8: Plant Hormones: Gibberellins
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Hormone
a chemical released by a cell that sends messages that affect other cells
Auxin (IAA)
a plant hormone usually produced at the shoot apical meristems, young leaves, developing seeds, and fruits
Auxin (IAA) is responsible for
stimulating stem elongation, regulating fruit development, and promoting the formation of lateral roots
Ethylene
a gaseous plant hormone usually produced by most parts of the plant in high and low concentrations based on growth that
Ethylene is responsible for
promoting the ripening of many types of fruit, and promoting root and root hair formation
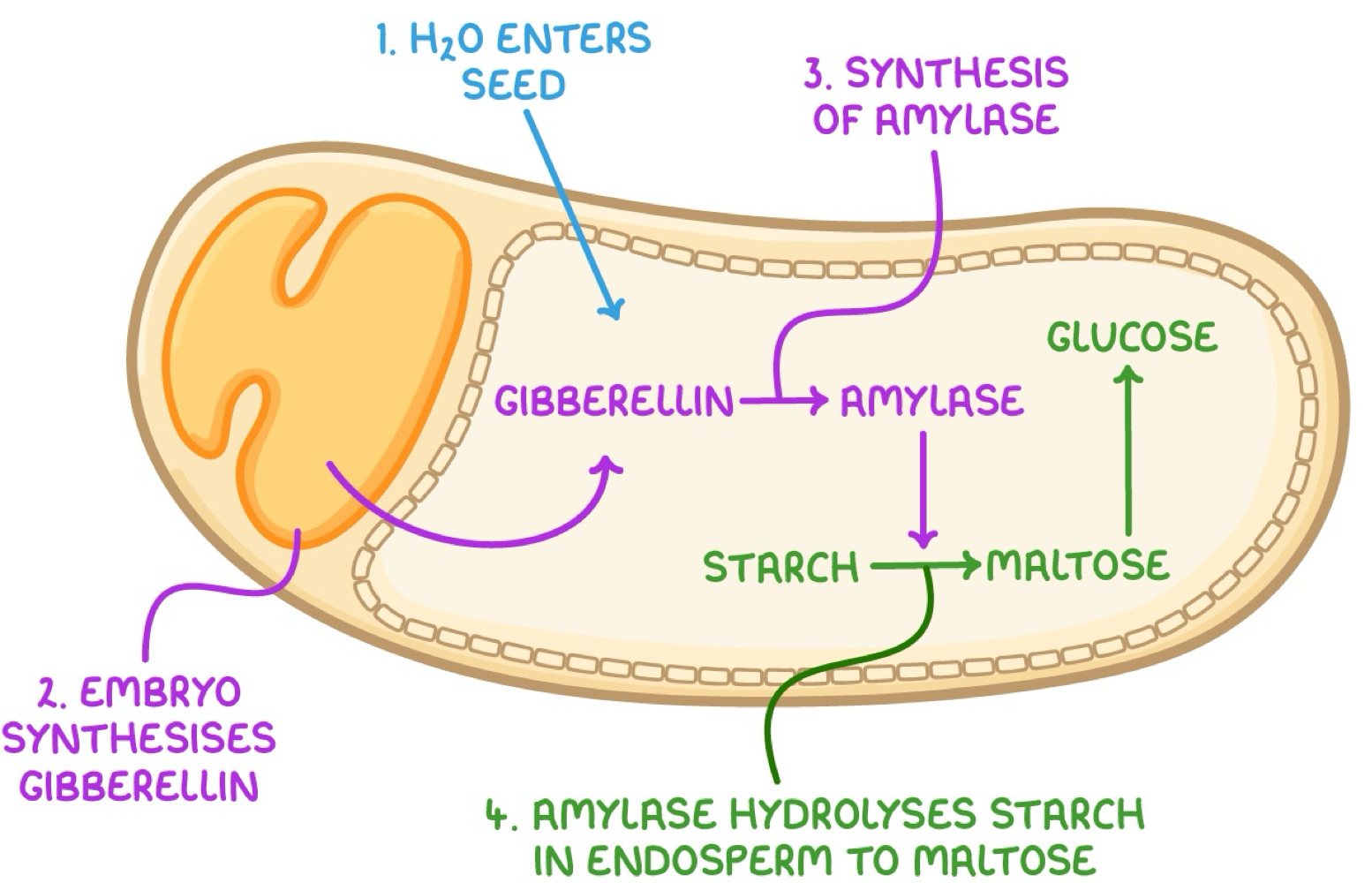
Gibberellins
a plant hormone produced by the apical bud meristem to stimulate stem elongation, and by developing seeds to initiate seed germination
Gibberellins is responsible for
stimulating stem elongation, and by developing seeds to initiate seed germination
P. Sativum
a species of angiosperms who produce pea pods as fruits
P. Sativum L. var Alaska
a normal variety of P. Sativum
P. Sativum L. var Little Marvel
a dwarf variety of P. Sativum that has a genetic mutation in the Giberellin-synthesizing gene
Taproot
the root coming directly form the stem
Lateral Roots
the roots branching out from the taproot that help absorb nutrients
Stem
the main structure above the ground that transports water from roots
Bud
undeveloped structure that develops into a flower, leaf, or shoot via meristem tissue
Lateral Bud
a bud that grows from the side of the stem, usually at the node, and can develop into a branch or flower
Apical Bud
a bud at the tip of the stem allowing the plant to grow taller or longer
Node
the point on the stem where leaves, branches, or buds grow
Meristematic Tissue
plant tissue that helps with growth
apical meristematic tissue
plant tissue that helps the plant grow taller
lateral meristematic tissue
plant tissue that helps the plant grow wider