Medical Physics ALL MCQs; 1st year
1/406
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
407 Terms
1. Sound amplification in the outer ear (auditory canal)is affected by:
a. Sound speed
b. Sound pressure
c. Sound amplitude
b. Sound pressure
2. Prolonged exposure to loud noise can cause permanent damage to:
a. The air conductivity (of the ear)
b. The structure of the eardrum (tympanic membrane)
c. Inner ear
c. Inner ear
3. The loss of elasticity (stiffening) of the tympanic membrane will result in:
a. Increase of air conductivity
b. Decrease of hearing threshold
c. Decrease in the binaural effect
b. Decrease of hearing threshold
4. Sound intensity level (dB) and Loudness (phones) will have the same magnitude at the following frequency:
a. 20 Hz
b. 1000 Hz
c. 20 KHz
b. 1000 Hz
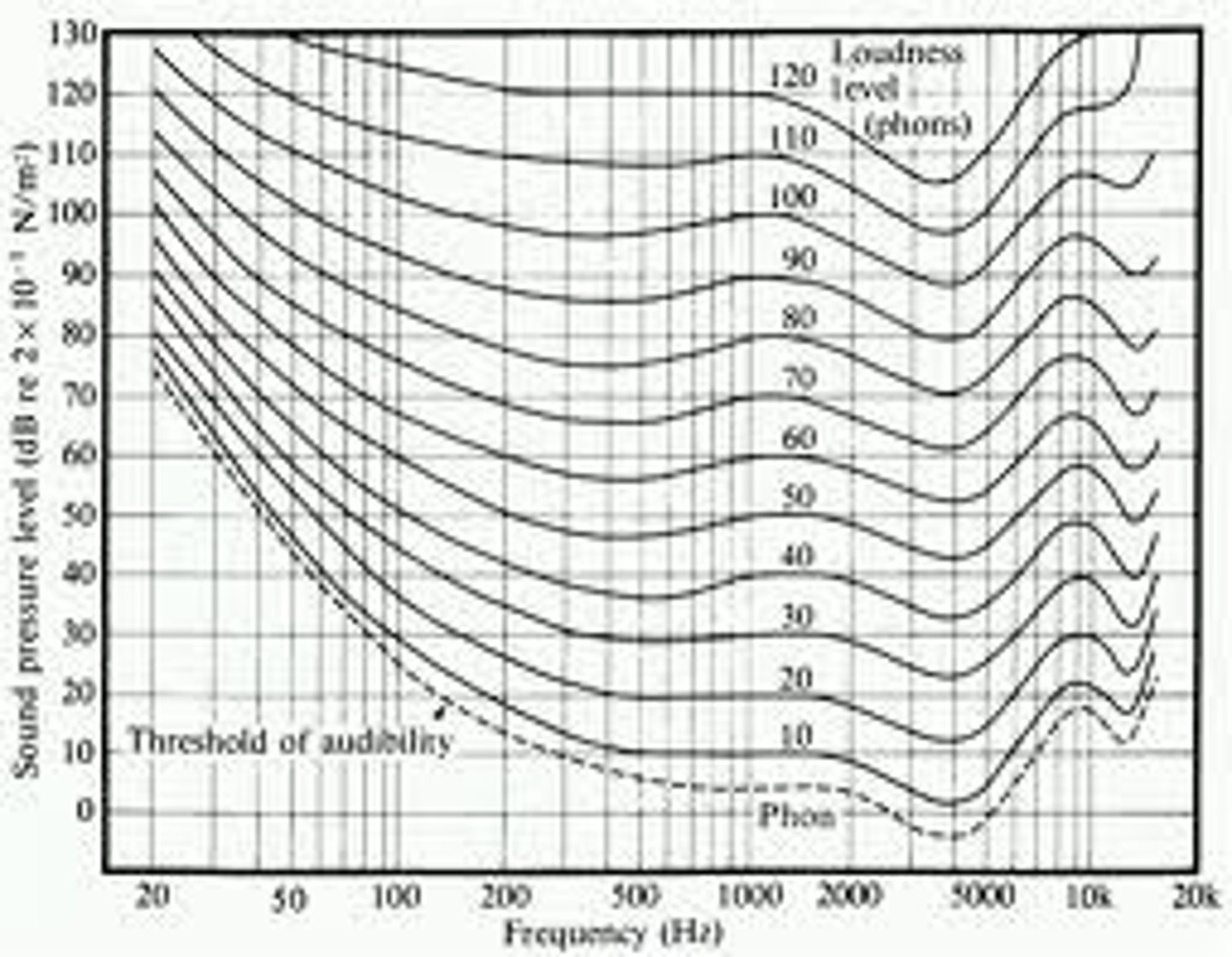
5. Refer to the equal-loudness curve above. At frequency of 4000 Hz the perceived sound is:
a. Louder than at 1000 Hz
b. The same as at 1000 Hz
c. Softer than at 1000 Hz
a. Louder than at 1000 Hz
6. Sound Intensity Level is proportional to the logarithm of the ratio of incoming to threshold intensity SIL = 10·Log (I/I0). If intensity is increased by a factor of 100, what is change in SIL?
a. Increase by a factor of 10 (10 times)
b. Double (2 times)
c. Increase with 20 dB (plus 20dB)
c. Increase with 20 dB (plus 20dB)
7. The sound intensity level in a room is 20 dB. A TV produces additional intensity level of 60 dB. What is the sound intensity in the room now?
a. 80 dB
b. 40 dB
c. 60 dB
c. 60 dB
8. Match the physical (objective) with the corresponding psychophysical (subjective) properties of the sound: (hint: multiple connections are possible)
a. Frequency
b. Intensity
c. Acoustic spectrum
1. Timbre
2. Pitch
3. Loudness
a. - 2.; b. - 3.; c. - 1.
9. Sound frequency is:
a. Psychophysical property (subjective)
b. Physical property (objective)
c. Sound is measured in wavelength, and light is measured in frequency
b. Physical property (objective)
10. The fundamental harmonic (frequency f0) in a complex sound is characterized by:
a. The lowest frequency and highest amplitude
b. The highest frequency and lowest amplitude
c. The highest frequency and highest amplitude
a. The lowest frequency and highest amplitude
11. The speed of sound is calculated by the Newton-Laplace formula √(K/ρ), where K is the stiffness coefficient, and ρ is the density of the material. If the density of the substance doubles, the speed of propagating sound wave will:
a. Increase
b. Decrease
c. Depends on the frequency
b. Decrease
12. What is the speed of sound in air?
a. 330 m/s
b. 900 m/s
c. 1550 m/s
a. 330 m/s
13. Does absorption of sound and the corresponding penetration depth depend on the wavelength?
a. No
b. It does. There is less absorption at longer wavelengths, and they propagate deeper
c. It does. There is less absorption at shorter wavelengths, and they propagate deeper
b. It does. There is less absorption at longer wavelengths, and they propagate deeper
14. Is it possible for internal organs to generate sounds that propagate to the skin, and are audible?
a. No
b. Yes, organs produce sounds that propagate through the tissues and are audible at the skin
c. No, organs generate sounds but the waves are absorbed by the tissues and are inaudible at the skin
b. Yes, organs produce sounds that propagate through the tissues and are audible at the skin
15. Noise can be defined as:
a. Intense sound with constant frequency
b. Directed sound waves with low intensity and changing modulation
c. Superposition of random sound vibrations, with frequency and amplitude constantly changing in time.
c. Superposition of random sound vibrations, with frequency and amplitude constantly changing in time.
16. Damping oscillations are:
a. Oscillations with increasing amplitude
b. Oscillations with decreasing amplitude
c. Not related to amplitude
b. Oscillations with decreasing amplitude
17. If the amplitude of a wave doubles (x2), what would happen to the period?
a. It will double
b. It will be halved
c. There will be no change
c. There will be no change
18. In which of the following mediums, sound waves cannot propagate?
a. Gases
b. Liquids
c. Vacuum
c. Vacuum
19. Which of the following waves are NOT mechanical?
a. Light
b. Water waves
c. Sound waves
a. Light
20. A propagating sound wave transfers:
a. Energy
b. Matter
c. Both, energy and matter
a. Energy
21. Which of the following factors has the most significant effect on the speed of propagation of sound waves?
a. Elastic properties of the medium
b. The size of the wave front
c. The pressure in gaseous environment
a. Elastic properties of the medium
22. Sound waves are:
a. Mechanical waves
b. Electromagnetic waves
c. Gravitational waves
a. Mechanical waves
23. The speed of sound (in non-dispersive medium):
a. Depends on the properties of the propagating medium
b. Is always constant, independent of the medium
c. Decreases as sound moves away from the its source
a. Depends on the properties of the propagating medium
24. Human ear is most sensitive to frequencies (refer to equal-loudness curve):
a. Below 1000 Hz
b. From 2000 Hz to 5000 Hz
c. Above 5000 Hz
b. From 2000 Hz to 5000 Hz
25. What is the meaning of 0 dB?
a. There is no sound
b. The sound is below hearing threshold level
c. The sound is at threshold reference level
c. The sound is at threshold reference level
26. Timbre is:
a. Physical (objective) property of sound
b. Psychophysical (subjective) sound property
c. Type of wood found in North America
b. Psychophysical (subjective) sound property
27. The pitch of sound depends mostly on:
a. Intensity of sound
b. Sound pressure
c. Sound frequency
c. Sound frequency
28. Which of the following does NOT have relevance to the reflection/transmission of sound waves?
a. The acoustic impedance of substances at the boundary
b. The colors of substances near the boundary area
c. The cross sectional area of the boundary surface
b. The colors of substances near the boundary area
29. Timbre is related to:
a. Harmonic overtones
b. Wooden instruments
c. Falling trees
a. Harmonic overtones
30. Weber-Fechner law (in psychophysics) describes a logarithmic relationship between the intensity of a sound wave and....:
a. Acoustic pressure
b. The sound pitch
c. The perception of loudness
c. The perception of loudness
31. Intensity is defined as:
a. Power per area
b. Power per time
c. Energy per time
a. Power per area
32. When sound wave travels across two materials with similar acoustic impedance, at the boundary surface there will be:
a. similar amounts of transmission and reflection
b. more transmission and less reflection
c. less transmission and more reflection
b. more transmission and less reflection
33. The acoustic impedance Z of a substance is defined as the product of:
a. The density and the atomic number of the element: ρZ
b. The density and the speed of sound: ρv
c. The temperature and the speed of sound: tv
b. The density and the speed of sound: ρv
34. Why can't we hear voices (speech) when submerged under water?
a. Most of the sound is reflected at the air/water boundary
b. Sound waves do not propagate under water
c. Ear canals are clogged with water
a. Most of the sound is reflected at the air/water boundary
35. What property of sound is measured in decibels (dB)?
a. Wavelength
b. Intensity level
c. Loudness
b. Intensity level
36. If the period of a wave is 0.02 s, what is its frequency? (Hint: how often does it vibrate in
one second?)
a. 200 Hz
b. 100 Hz
c. 50 Hz
c. 50 Hz
37. A person screams in the mountain and hears the echo after 2 seconds. How far was the cliff that caused the reflection of the sound (echo)?
a. 1020 m
b. 340m
c. 680m
b. 340m
38. Which of the following properties of sound is measured in Hertz (Hz)?
a. Power
b. Amplitude
c. Frequency
c. Frequency
39. When sound wave propagates between two media with similar impedance, there will be:
a. Equal amounts of transmission and reflection
b. Be more transmission and less reflection
c. Be more reflection and less transmission
b. Be more transmission and less reflection
40. The human ear is sensitive to frequencies in the range:
a. 20 Hz - 20 MHz
b. 200 Hz - 20 kHz
c. 20 Hz - 2000 Hz
c. 20 Hz - 2000 Hz
41. What are the SI units for loudness?
a. Sone
b. Phon
c. dB
b. Phon
42. The speed of sound in the human body is approximately:
a. 330 m/s
b. 1500 m/s
c. 6000 m/s
b. 1500 m/s
43. The audiogram is a method for hearing loss evaluation by measuring the threshold hearing intensity of sound for different:
a. Frequencies
b. Wavelengths
c. Amplitudes
a. Frequencies
44. Pure tone is characterized by:
a. Deviation from the equilibrium is proportional to the frequency
b. Constant velocity vector
c. Constant frequency
c. Constant frequency
45. When sound wave travels from air into the human body, what happens to its speed?
a. Increases, because tissue has higher acoustic impedance
b. Decreases, because tissue has lower acoustic impedance
c. It doesn't change because the speed of sound is constant
a. Increases, because tissue has higher acoustic impedance
46. Doppler shift applies to:
a. All wave phenomena
b. Ultrasound
c. Infrared EM waves
a. All wave phenomena
47. The contact gel used in ultrasonography (echography) is for:
a. Protection of the body from harmful ultrasound
b. Efficient transmission of sound waves into the tissue
c. Improvement of skin elasticity in the area of study
b. Efficient transmission of sound waves into the tissue
48. In medical imaging, Doppler echography is most appropriate for:
a. Deep body targets
b. Moving body targets
c. Surface targets
b. Moving body targets
49. Which of the following waves do cannot propagate in vacuum?
a. Radiowaves
b. X-rays
c. Ultrasound
c. Ultrasound
50. In what form is the information received with Doppler Echography displayed?
a. By sound
b. By one dimensional image
c. By two dimensional image with artificial coloring
c. By two dimensional image with artificial coloring
51. Doppler frequency (shift) is:
a. The infrared spectrum of light, studied by Doppler
b. The frequency generated by ultrasonic transducer
c. The difference between emitted and reflected (received) frequency between to objects in relative motion.
c. The difference between emitted and reflected (received) frequency between to objects in relative motion.
52. For which of the following numerical Doppler frequency shifts is the blood speed the
highest?
a. 1210 Hz
b. 800 Hz
c. 1530 Hz
c. 1530 Hz
53. Is it possible to tell the direction of motion of erythrocytes from the sign of the Doppler shift ∆f = f - f0?
a. Yes, when ∆f > 0 erythrocytes move towards the transducer
b. Yes, when ∆f > 0erythrocytes move away from the transducer
c. No, the sign of ∆f does not tell the direction of motion
a. Yes, when ∆f > 0 erythrocytes move towards the transducer
54. If shorter wavelengths of ultrasound are less penetrating in human tissue, then which of the following frequencies is most appropriate for DEEP tissue and organ imaging?
a. 8 MHz
b. 3 MHz
c. 20 MHz
b. 3 MHz
55. Doppler shift is defined as:
a. The frequency difference between emitted and received signals for observers at relative motion
b. The difference in acoustic impedance between two transmitting mediums
c. The intensity difference between emitted and reflected waves
a. The frequency difference between emitted and received signals for observers at relative motion
56. At what angle (Θ) to the surface of the body should the ultrasonic probe be applied in order to gain a maximum Doppler shift? Consider that Doppler shift is proportional to cos (Θ).
a. Θ = 45⁰ (cos 45 = 0.7)
b. Θ = 90⁰ (cos 90 = 0)
c. Θ = 60⁰ (cos 60 = 0.5)
a. Θ = 45⁰ (cos 45 = 0.7)
57. The speed of ultrasound in human tissue depends on:
a. The properties of the tissue
b. The properties of the apparatus
c. The speed of (ultra)sound does not depend on the tissue
a. The properties of the tissue
58. The so called "reverse piezoelectric effect" finds application in:
a. Ultrasound generation
b. X-ray tubes
c. Lasers
a. Ultrasound generation
59. Ultrasound can propagate through:
a. Vacuum
b. Matter
c. Everywhere where light propagates
b. Matter
60. Phonophoresis is:
a. Therapeutic application of ultrasound
b. Diagnostic application of ultrasound
c. Method for sterilization
a. Therapeutic application of ultrasound
61. Infrasound of certain frequency and intensity can:
a. Damage internal organs
b. Increase temperature of tissues
c. Rearrange water molecules
a. Damage internal organs
62. Infrasound CANNOT propagate through:
a. Soft tissue
b. Bones
c. Vacuum
c. Vacuum
63. Choose the correct statement:
a. Ultrasound is completely harmless for humans and animals
b. Sound reflection depends on the transparency of the medium
c. Sound impedance does not depend on frequency (for linear mediums)
c. Sound impedance does not depend on frequency (for linear mediums)
64. Choose the correct range:
a. Audible sound: 103 Hz—106 Hz
b. Infrasound: 3 Hz—10 Hz
c. Ultrasound: 10 kHz—10 kHz
b. Infrasound: 3 Hz—10 Hz
65. The resonant frequency of the vestibular system is in the range of:
a. Ultrasound
b. Infrasound
c. Ultraviolet
b. Infrasound
66. The direct piezoelectric effect is used for:
a. Ultrasound detectors
b. Ultrasound generators
c. Electrophoresis
a. Ultrasound detectors
67. Piezoelectric effect is defined as:
a. Electric polarization of solids under mechanical stress
b. Electro-mechanical coupling of objects falling off the tower of Pisa
c. Electric polarization in a solid due to temperature gradient.
a. Electric polarization of solids under mechanical stress
68. Does human tissue exhibit piezoelectric properties?
a. No, the human body exhibits only capacitive properties
b. No, piezoelectric properties are observed in inorganic crystals
c. Yes, tissue such a collagen has piezoelectric properties
c. Yes, tissue such a collagen has piezoelectric properties
69. Which statement is correct?
a. The size of the ultrasonic equipment (echograph) influences the acoustic density of imaged tissue.
b. The precision of the ultrasonic instrument does not have an effect on the quality of received images
c. The ultrasonic image, displayed on the monitor, represents the acoustic density of studied tissues.
c. The ultrasonic image, displayed on the monitor, represents the acoustic density of studied tissues.
70. Mechanical waves with frequency above 20 kHz are called:
a. Infrasound
b. Ultrasound
c. P-waves
b. Ultrasound
71. Infrasound is:
a. Electromagnetic waves with frequency under 20 Hz
b. Mechanical waves with frequency above 20 Hz
c. None of the above
c. None of the above
72. If Δf is the change in frequency between emitted and received ultrasound signals due to Doppler effect during measurement of the linear speed of blood, then:
a. The speed of blood relative to the stationary transducer (emitter and receiver) is as much great as Δf is greater
b. Blood motion does not affect Δf
c. The speed of blood relative to the stationary transducer is greater when Δf is smaller.
a. The speed of blood relative to the stationary transducer (emitter and receiver) is as much great as Δf is greater
73. Which natural science studies infrasound?
a. Pediatrics
b. Seismology
c. Dental medicine
b. Seismology
74. Mechanical waves used for destruction of kidney stones, in procedure called "lithotripsy", cause minimal damage to surrounding tissues because:
a. Mechanical waves do not propagate through the surrounding tissue
b. Acoustic pressure in the surrounding tissue is greatly reduced compared tothe pressure induced in the kidney stones
c. Mechanical waves do not have negative effect on soft tissue
b. Acoustic pressure in the surrounding tissue is greatly reduced compared tothe pressure induced in the kidney stones
75. Ultrasound waves propagate through human tissue as:
a. Longitudinal waves
b. Transverse waves
c. Both, longitudinal and transverse modes
a. Longitudinal waves
76. Can humans sense infrasound waves?
a. Only when the intensity of the wave is sufficiently high for the ear to detect
b. No, that's why they are called infra-sound
c. They can be sensed as vibrations by the tactile receptors of the skin
c. They can be sensed as vibrations by the tactile receptors of the skin
77. The resonant frequency of the internal organs is in the range of:
a. 10 MHz
b. Infrasound
c. Ultrasound
b. Infrasound
78. Which of the following is used in Doppler echography?
a. Magnetic resonance
b. Vacuum tubes
c. Piezoelectric effect
c. Piezoelectric effect
79. What units are used to measure blood pressure with aneroid manometer?
a. mmHg, kPa
b. mmHg, atm
c. N.m^-2, Torr
b. mmHg, atm
80. What is the predominant type of blood follow in the arteries of a healthy person?
a. Turbulent
b. Laminar
c. Transitional
b. Laminar
81. Blood pressure on the walls of blood vessels is compensated (counterbalanced) by the elasticity of blood vessels, and by the air pressure. If the reading of the sphygmomanometer during a systole is 120 mmHg and air pressure is 760 mmHg, what is the actual pressure that blood exerts on the walls of arteries?
a. 90 mmHg
b. 640 mmHg
c. 880 mmHg
c. 880 mmHg
82. Pulse pressure is defined as:
a. The difference between systolic and diastolic pressures
b. The difference between systolic and atmospheric pressures
c. The average of diastolic and systolic pressures
a. The difference between systolic and diastolic pressures
83. What is the most precise definition of blood pressure?
a. The pressure in the cardio-vascular system
b. The pressure exerted by blood on the walls of blood vessels
c. The pressure in the arteries
b. The pressure exerted by blood on the walls of blood vessels
84. When blood pressure is measured with a stethoscope, at what point is the systolic pressure detected?
a. At the loudest sound
b. At the first sound
c. When the sound disappears
b. At the first sound
85. When blood pressure is measured with a stethoscope, at what point is the diastolic pressure detected?
a. At the loudest sound
b. At the first sound
c. When sounds disappear
c. When sounds disappear
86. What is the variation of blood pressure across the cardio-vascular system:
a. It decrease linearly from arteries to veins
b. It oscillates between diastolic and systolic but stays mostly the same
c. It decreases non-linearly with the greatest drop at the capillaries
c. It decreases non-linearly with the greatest drop at the capillaries
87. What property of blood is characterized by the Reynolds number?
a. Blood viscosity
b. Blood speed
c. Type of blood flow: laminar or turbulent
c. Type of blood flow: laminar or turbulent
88. Cardiac resonant frequency in the range of:
a. Infrasound
b. Ultrasound
c. Infrared
a. Infrasound
89. What causes the Korotkoff sounds?
a. High blood pressure
b. Turbulent flow of blood around constrictions
c. High pulse rate
b. Turbulent flow of blood around constrictions
90. The speed of arterial pulse wave depends mostly on:
a. The hematocrit
b. The elasticity of blood vessels
c. The cross section of blood vessels
b. The elasticity of blood vessels
91. Gas embolism (clogging of blood vessel) can be explained with:
a. Reynolds number (Re)
b. Dynamic viscosity of blood (η)
c. Laplace pressure (Δp)
c. Laplace pressure (Δp)
92. Ideal liquids are defined as:
a. Lacking internal friction
b. Molecular cohesive forces
c. Surface tension and activity
a. Lacking internal friction
93. What quantity is transferred when there is internal friction?
a. Mass
b. Impulse
c. Charge
b. Impulse
94. Which of the following parameters is the most informative for the blood supply of a given organ?
a. Arterial pressure
b. The speed of blood
c. Blood flow
c. Blood flow
95. A necessary condition for internal friction (viscous force) in fluid dynamics is:
a. Concentration gradient
b. Velocity gradient
c. Electric charge gradient (potential difference)
b. Velocity gradient
96. Laplace pressure Δр does NOT depend on:
a. The radius of the surface
b. Atmospheric pressure
c. The coefficient of surface tension σ
b. Atmospheric pressure
97. Which of the following parameters of the vascular system have the greatest effect on blood flow resistance?
a. Viscosity of blood
b. Volumetric flow rate
c. Radius of vessels lumen
c. Radius of vessels lumen
98. Ideal (perfect) fluid is defined as:
a. Incompressible and without viscosity
b. High liquidity and low density
c. Constant velocity and surface tension
a. Incompressible and without viscosity
99. Where in the cardiovascular system is the blood pressure at minimum?
a. In the capillaries
b. In the veins
c. In the aorta
b. In the veins
100. The volumetric flow rate Q =dV/dt of blood in the cardiovascular system is:
a. Constant at any given time
b. Greater in the pulmonary circuit
c. Variable: it decreases from arteries to capillaries to veins
a. Constant at any given time