Excretion
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Define osmoregulation and excretion. How are they related?
Osmoregulation: Control of water & solute balance. Excretion: Removal of metabolic wastes (e.g., nitrogen). They are related because excretion helps maintain water/solute balance (osmoregulation).
Examples of excretory products?
Nitrogenous wastes (ammonia, urea, uric acid), CO2, bile pigments, excess salts.
Examples of ions regulated within narrow limits?
Sodium (Na⁺), potassium (K⁺), calcium (Ca²⁺), chloride (Cl⁻).
Other functions of excretory systems besides removing toxins?
Osmoregulation (water/salt balance). 2. pH regulation of body fluids.
Review: solute, solvent, solution, tonicity.
Solute: Dissolved substance. Solvent: Liquid doing dissolving (e.g., water). Solution: Homogeneous mixture. Tonicity: Solution's effect on cell volume (osmotic pressure).
Distinguish diffusion and osmosis.
Diffusion: Movement of solutes down concentration gradient. Osmosis: Movement of water across membrane from high to low water concentration (low to high solute).
Define osmolarity. How does it determine osmosis?
Osmolarity: Total solute concentration (mol/L). Water moves from low osmolarity (hypoosmotic) to high osmolarity (hyperosmotic) solution.
Describe hypo-, hyper-, and isoosmotic solutions.
Hypoosmotic: Lower solute (higher water) concentration. Hyperosmotic: Higher solute (lower water) concentration. Isoosmotic: Equal solute concentration.
Osmoregulators vs. osmoconformers. Examples?
Osmoregulators: Actively maintain internal osmolarity different from environment (e.g., most fish, mammals). Osmoconformers: Internal osmolarity matches environment (e.g., marine invertebrates like sea stars).
Compare marine vs. freshwater fish: osmolarity of habitat.
Marine fish: Live in hyperosmotic seawater (lose water, gain salts). Freshwater fish: Live in hypoosmotic water (gain water, lose salts).
Compare marine vs. freshwater fish: passive movements & strategies.
Marine Fish: Lose water, gain salts passively. Strategies: Drink seawater, excrete salt via gills, produce little concentrated urine. Freshwater Fish: Gain water, lose salts passively. Strategies: Don't drink, absorb salts via gills, produce large dilute urine.
Osmoregulatory challenges for migrating salmon?
Move between fresh (hypoosmotic) and salt (hyperosmotic) water. They reverse osmoregulatory strategies by changing gill and kidney function.

How do sharks (chondrichthyans) differ from bony fish in osmoregulation?
Sharks retain urea & TMAO in blood to make tissues slightly hyperosmotic to seawater, reducing water loss. They do not drink seawater like marine bony fish.

Routes of water gain and loss in terrestrial animals?
Gain: Drinking, eating, metabolic water. Loss: Urine, feces, evaporation (skin/lungs).
Compare osmotic stress in aquatic, terrestrial, desert animals.
Aquatic: Water/salt balance in hypo/hyperosmotic medium. Terrestrial: Water conservation. Desert: Extreme water conservation (e.g., highly concentrated urine, nocturnal).
Compare ammonia, urea, uric acid.
Structure/Toxicity: Ammonia (simplest, most toxic). Urea (less toxic). Uric acid (most complex, least toxic). Solubility: Ammonia (very soluble). Urea (soluble). Uric acid (insoluble paste/crystals). Energy Cost: Ammonia (none). Urea (some). Uric acid (most).
How do habitat/lifestyle correlate with nitrogenous waste?
Ammonia: Aquatic animals (dilute with water). Urea: Mammals, amphibians (less water needed). Uric Acid: Birds, reptiles, insects (saves water; egg-laying).
How does a freshwater Paramecium osmoregulate?
Uses a contractile vacuole to actively pump out excess water that enters by osmosis.
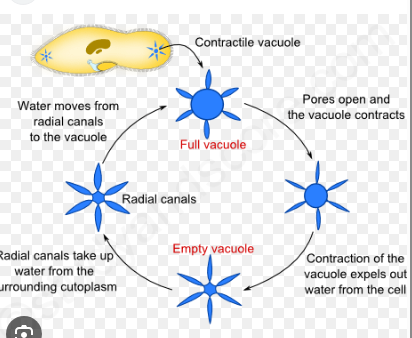
Do marine unicells need a contractile vacuole?
No. Their environment is iso- or hyperosmotic, so they do not constantly gain water by osmosis.
Describe filtration, reabsorption, secretion.
Filtration: Extract water & solutes from body fluid (blood/hemolymph). Reabsorption: Take back valuable solutes & water from filtrate. Secretion: Add toxins/unwanted solutes from body fluids into filtrate.
Excretion in a planarian?
Uses flame cells (protonephridia). Cilia create current to draw fluid into tubules; filtrate is processed and excreted via pores.
Excretion in an earthworm?
Uses metanephridia. Collect coelomic fluid via funnel (nephrostome), process it in tubule (reabsorbing solutes), excrete dilute urine via pore.
Excretion in an insect (grasshopper)?
Uses Malpighian tubules. Tubules secrete wastes & salts from hemolymph into gut; water & useful solutes reabsorbed in rectum; excrete dry uric acid.
Journey of a urea molecule from kidney to excretion.
Kidney (produced in urine) → Ureter (transports urine) → Urinary Bladder (stores urine) → Urethra (excretes urine from body).
Location, size, shape of human kidneys.
Paired, bean-shaped organs at back of abdominal cavity, each ~size of a fist.
Location of renal cortex and medulla?
Cortex: Outer region. Medulla: Inner region (striped), contains renal pyramids.
Location/function of renal pelvis?
Funnel-shaped cavity where kidney joins ureter. Collects urine from ducts and drains to ureter.
Is urea concentration higher in renal artery or vein? Why?
Higher in renal artery. Kidneys remove urea from blood to make urine, so blood leaving (renal vein) has less urea.
Components of a nephron.
1) Renal corpuscle (Bowman's capsule + glomerulus). 2) Proximal tubule. 3) Loop of Henle. 4) Distal tubule. 5) Collecting duct.
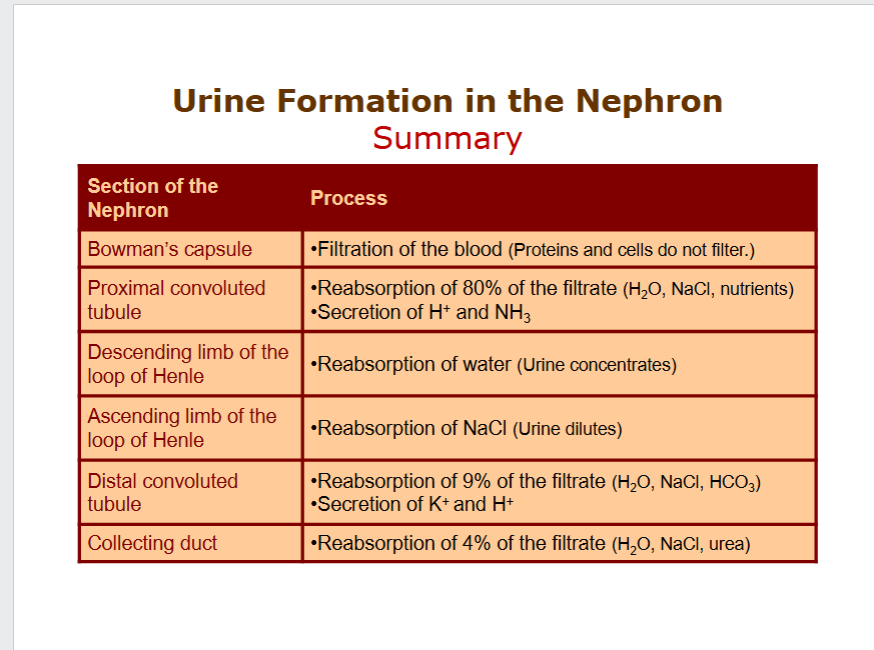
Location of vascular components relative to nephron.
Afferent arteriole: Feeds blood into glomerulus. Efferent arteriole: Carries blood away from glomerulus. Glomerulus: Ball of capillaries inside Bowman's capsule. Peritubular capillaries: Network around tubules (from efferent arteriole).
What is glomerular filtration? Driving force?
Blood pressure forces water & small solutes from glomerulus into Bowman's capsule. Driven by hydrostatic pressure.
What is tubular reabsorption? Examples?
Returning useful solutes & water from filtrate back to blood. Examples: Glucose, amino acids, Na⁺, water.
What is tubular secretion? Examples?
Adding wastes & excess ions from blood into filtrate. Examples: H⁺, K⁺, drugs, toxins.
How is glucose handled?
Completely reabsorbed in proximal tubule. Normally none in urine.
How is water handled?
Reabsorbed by osmosis throughout nephron, regulated by ADH in collecting duct.
How are K⁺ ions handled?
Reabsorbed in proximal tubule; excess is secreted in distal tubule/collecting duct (regulated by aldosterone).
How are H⁺ ions handled?
Secreted into filtrate (especially distal tubule) to regulate blood pH.
ADH & Aldosterone: production, stimulus, site of action.
ADH (Vasopressin): Produced: Hypothalamus/posterior pituitary. Stimulus: High blood osmolarity (dehydration). Site: Collecting duct. Aldosterone: Produced: Adrenal cortex. Stimulus: Low blood Na⁺/pressure, high K⁺. Site: Distal tubule/collecting duct.
Effects of ADH & aldosterone?
ADH: Increases water reabsorption → decreases urine volume, concentrates urine. Aldosterone: Increases Na⁺ reabsorption & K⁺ secretion → increases water reabsorption (follows Na⁺), decreases Na⁺ in urine.
How does eating salty food affect kidney function?
Increases blood osmolarity. Inhibits aldosterone, stimulates ADH. Kidneys excrete more Na⁺ (in urine) while reabsorbing more water to dilute blood.