AP Microeconomics-Unit 1:Teacher MCQ-6
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
At her current level of consumption, a consumer is willing to pay up to $1.50 for a bottle of water and up to $1,500 for a diamond ring because the
(A) total utility of diamond rings is greater than the total utility of water
(B) total utility of water is less than the marginal utility of a diamond ring
(C) marginal utility of a bottle of water is less than the marginal utility of a diamond ring
(D) marginal utility of a bottle of water is greater than the marginal utility of a diamond ring
(E) consumer is irrational and does not understand that water is more important than a diamond
answer C
Which of the following is true if consuming one unit of a good yields 100 utils and consuming the second unit of
the good increases satisfaction by 20 utils?
(A) The marginal utility of the first unit is 20.
(B) The marginal utility of the second unit is 80.
(C) The marginal utility of the second unit is 120.
(D) The total utility of consuming two units is 120.
(E) The total utility of consuming one unit is greater than the total utility of consuming two units.
answer D
Carlos has a van with 20 seats and charges $10 per person per ride to the airport from downtown. Carlos' cost of the trip is $140 for any number of passengers. On one trip, Carlos has 19 seats filled when a person offers him $5 for the last seat. Should Carlos accept the offer?
(A) No, since the $5 fare offered is below his average cost of $7.
(B) No, since the average variable cost is greater than $5.
(C) No, since it is illegal to charge different prices for the same service.
(D) Yes, since the marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost.
(E) Yes, since his total revenue exceeds his total cost by $5.
answer D
If a good is available free of charge, an individual will consume it until
(A) marginal utility is zero
(B) average utility is zero
(C) total utility is zero
(D) marginal utility equals average utility
(E) marginal utility equals total utility
answer A
Marginal analysis suggests that an individual will consume one additional unit of a good if the
(A) sunk cost can be recovered
(B) total benefit is less than the total cost
(C) total benefit is greater than the total cost
(D) additional benefit is less than the additional cost
(E) additional benefit is greater than the additional cost
answer E
Suppose that a consumer purchases two goods X and Y and that the marginal utility of X is MUx, the total utility of X is TUx, the marginal utility of Y is MUy, and the total utility of Y is TUy. If the prices of X and Y are Px and Py,
respectively, which of the following expressions defines consumer equilibrium?
(A) TUx = TUy
(B) MUx = MUy
(C) TUx/Px = TUy/Py
(D) MUx/Px = MUy/Py
(E) (MUx)(Px) + (MUy)(Py) = 1
answer D
To maximize utility, a consumer with a fixed budget will purchase quantites of goods so that the ratios of the
marginal utility of each good to its
(A) total utility are the greatest
(B) total utility are the same
(C) price are the greatest
(D) price are equal to one
(E) price are equal
answer E
Using cost-benefit analysis, a local government would decide to build a new bridge if
(A) The additional tax paid by an individual resident is greater than the additional benefit of building the
bridge for all residents.
(B) The toll paid by an individual resident crossing the bridge is less than the resident's benefit from
crossing the bridge.
(C) The total costs of building the bridge are less than the total benefits from building the bridge.
(D) The total costs of building the bridge are greater than the total benefits from building the bridge.
(E) Total costs are at a minimum and total benefits are at a maximum.
answer C
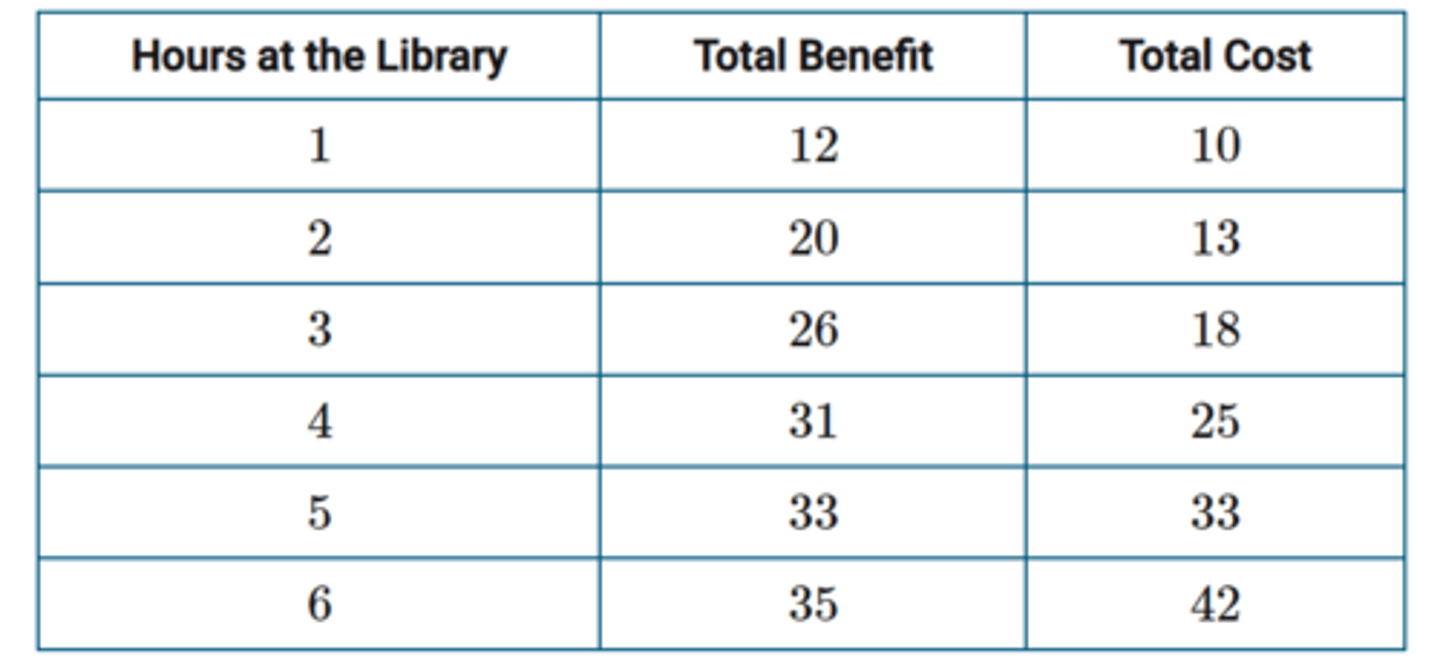
The table provided shows the total benefits and costs of studying at the library. If the student is rational, the optimal number of hours to spend at the library is
(A)2
(B)3
(C)4
(D)5
(E)6
answer B
The opportunity cost of owning a business is equal to which of the following?
I. The economic profits earned in the business
II. The accounting profits earned in the business
III. The profits that could be earned in another business using the same amount of resources
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I and III only
(E) I, II, and III
answer C
Which of the following best describes how a consumer maximizes total utility from the consumption of a bundle of goods and services?
(A) By choosing the quantity of each good such that the quantity demanded of each good is equal to the quantity supplied
(B) By choosing the quantity of each good such that the marginal utility from each good is equal to zero
(C) By choosing the quantity of each good such that the price is equal to the marginal revenue
(D) By choosing the level of output where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost
(E) By choosing the combination of goods such that the marginal utility per dollar spent on the last unit of
each good is equal
answer E
Which of the following best defines opportunity cost?
(A) It is the cost of producing those goods most desired by a given economy.
(B) It is the cost of the input mix that will lead to the greatest rate of growth for a given company.
(C) It is the amount of one product that must be given up in order to produce an additional unit of another
product.
(D) It is the use of the least-cost method of production.
(E) It is the cost of labor used in the production process.
answer C
In a given time period, a person consumes more and more of a good or service and, as a result, enjoys each
additional unit less and is willing to pay less for each additional unit. This behavior is consistent with the law of
(A) diminishing returns
(B) diminishing marginal product
(C) diminishing marginal utility
(D) increasing costs
(E) scarce resources
answer C
For a rational consumer with diminishing marginal utility, the consumption of an additional unit of a good will
result in which of the following?
(A) Total utility will increase until it equals marginal utility.
(B) Total utility will increase while marginal utility will be negative.
(C) Total utility will increase while marginal utility will decrease.
(D) Total utility will decrease while marginal utility will be positive.
(E) Total utility will decrease while marginal utility will increase.
answer C
Garcia is currently spending his entire lunch budget on 3 sodas and 4 hot dogs. At his current level of consumption, Garcia's marginal utility for sodas is 5 utils and his marginal utility for hot dogs is 10 utils. In order to maximize his total utility, Garcia should
(A) consume more sodas and fewer hot dogs regardless of the prices
(B) consume more hot dogs and fewer sodas regardless of the prices
(C) maintain his current level of consumption of sodas and hot dogs regardless of the prices
(D) maintain his current level of consumption if the price of a soda is $1 and the price of a hot dog is $2
(E) maintain his current level of consumption if the price of a soda is $2 and the price of a hot dog is $1
answer D
Assume a consumer is spending all her income on two goods: X and Y. At the current consumption combination of the two goods, if the marginal utility per dollar spent on the last unit of good X exceeds that of the marginal utility per dollar spent on the last unit of good Y, what should the consumer do to maximize utility?
(A) Purchase more units of X and more units of Y.
(B) Decrease the price of good X.
(C) Purchase more units of X and less units of Y.
(D) Increase income to buy more of both good Y and good X.
(E) Nothing; utility is maximized at current consumption bundles.
answer C
The table below shows the per-unit prices and marginal utility for the last unit of video games and comic books that Kyle purchased.
Kyle spent all of his allocated budget on video games and comic books. To maximize his utility, Kyle should have purchased
(A) more video games and fewer comic books
(B) fewer video games and more comic books
(C) fewer of both goods
(D) equal amounts of both goods
(E) more of both goods
answer B
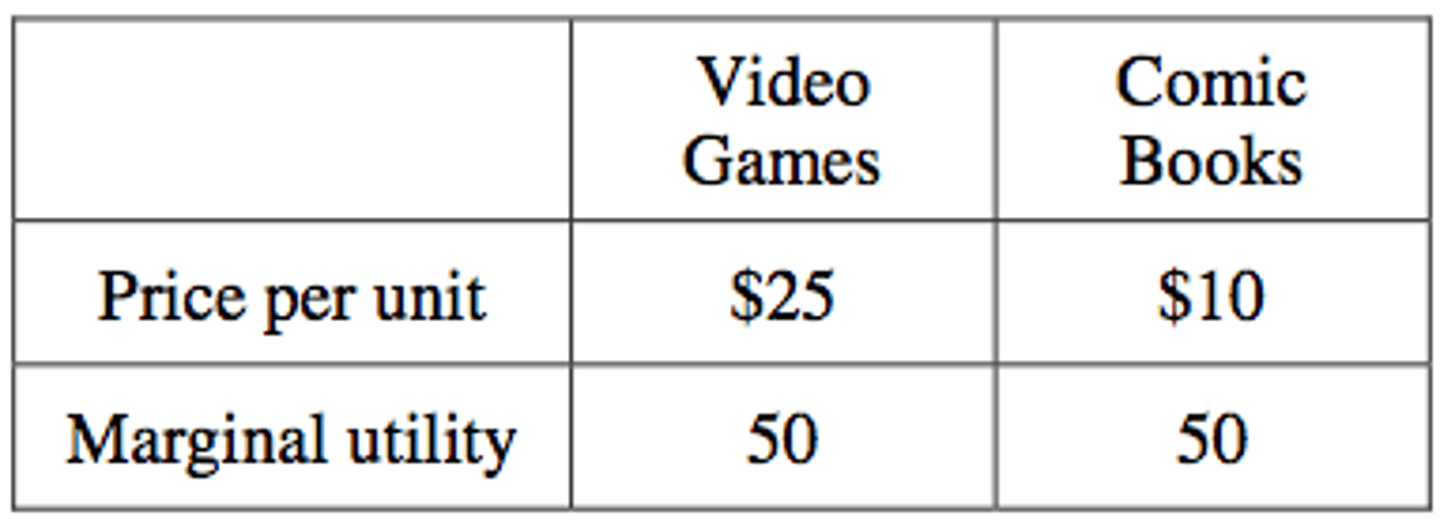
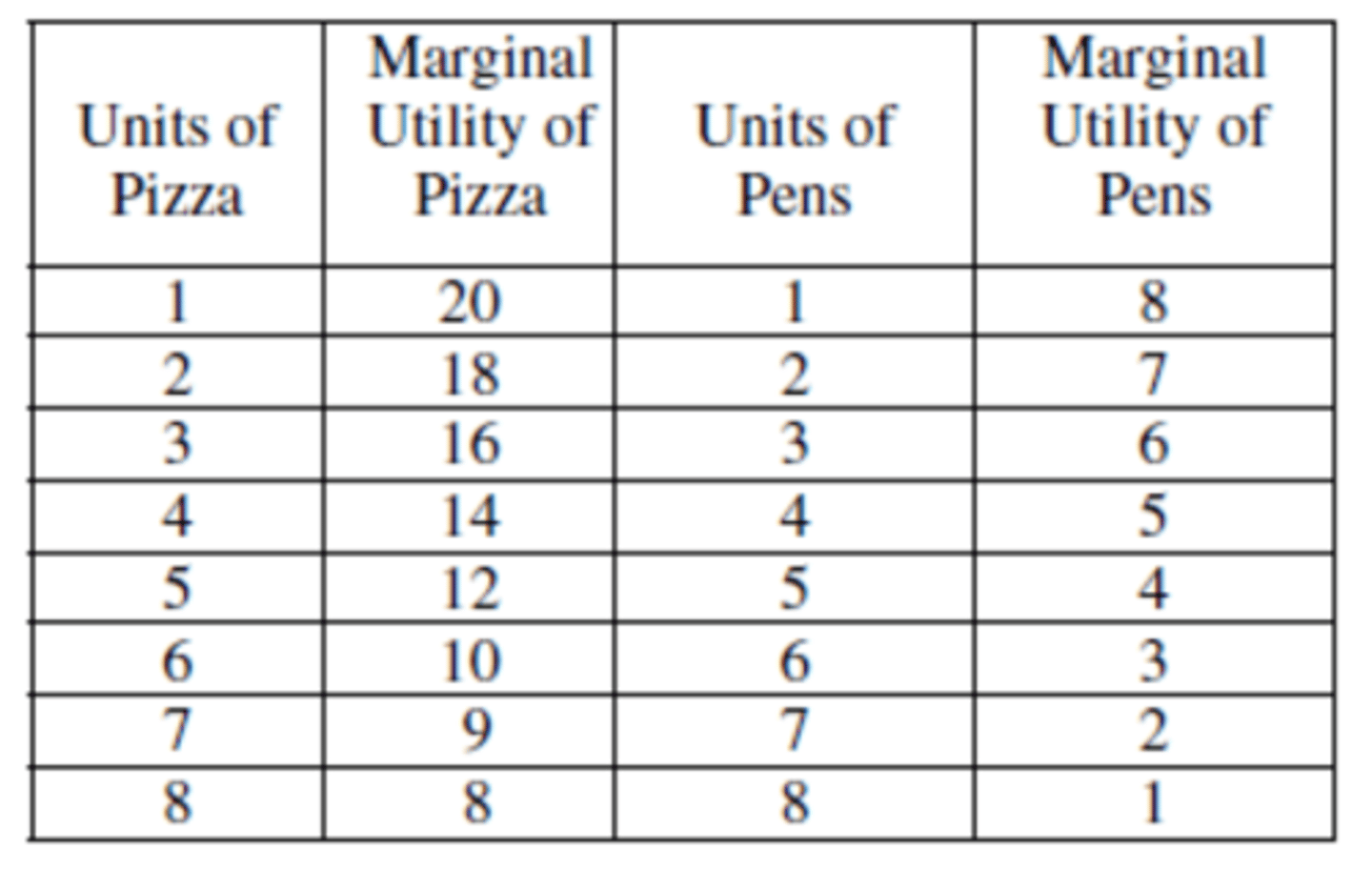
The information below shows the marginal utilities a student receives from the consumption of pizza and
pens. Assume that the marginal utility of each good is independent of the quantity of the other good
consumed.
If the student purchases 2 units of pizza and 2 units of pens, the student's total utility will be
(A) 4 utils
(B) 25 utils
(C) 28 utils
(D) 50 utils
(E) 53 utils
answer E
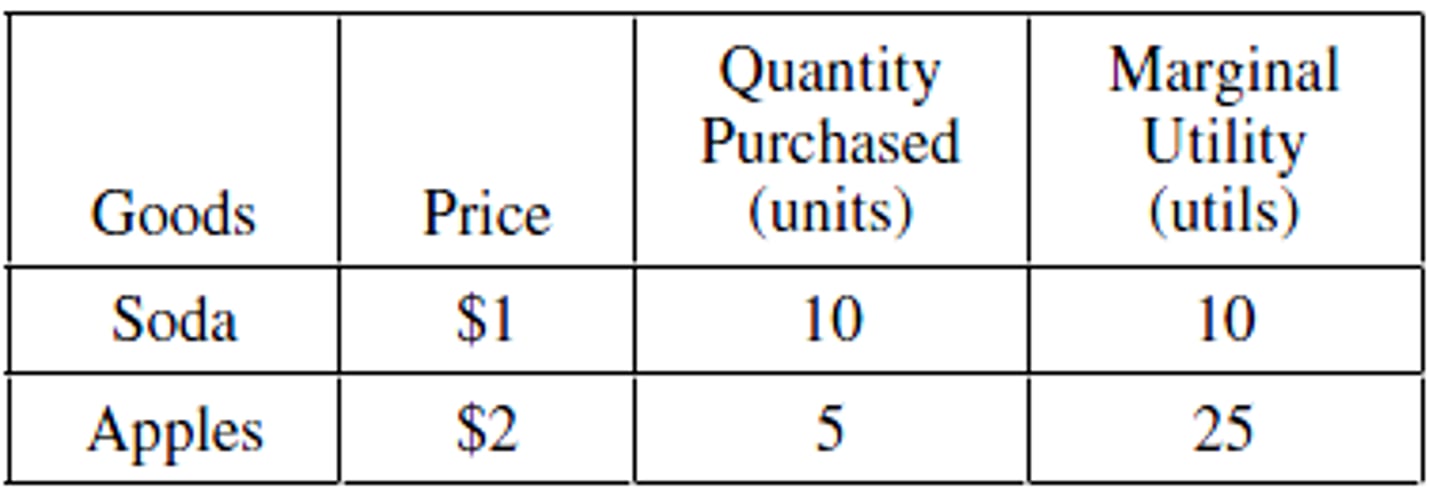
Jane spends all her weekly allowance to buy only two goods: soda and apples. According to the table above, if her preferences are characterized by the law of diminishing marginal utility, then which of the following statements is correct?
(A) Jane is maximizing her utility.
(B) Jane can buy more apples and less soda to maximize her utility.
(C) Jane can buy more soda and fewer apples to maximize her utility.
(D) Jane can buy more apples and the same amount of soda to maximize her utility.
(E) Jane can buy more soda and the same amount of apples to maximize her utility.
answer B
The following chart shows the total utility that Juan receives from consuming various amounts of chocolate candy bars each day.
Which of the following statements about Juan's marginal utility is correct?
(A) His marginal utility from the first candy bar is greater than his marginal utility from the second candy
bar.
(B) His marginal utility from the fourth candy bar is greater than his marginal utility from the third candy
bar.
(C) His marginal utility increases at a constant rate.
(D) He first experiences diminishing marginal utility with the consumption of the fifth candy bar.
(E) His greatest marginal utility comes from his consumption of the fourth candy bar.
answer A
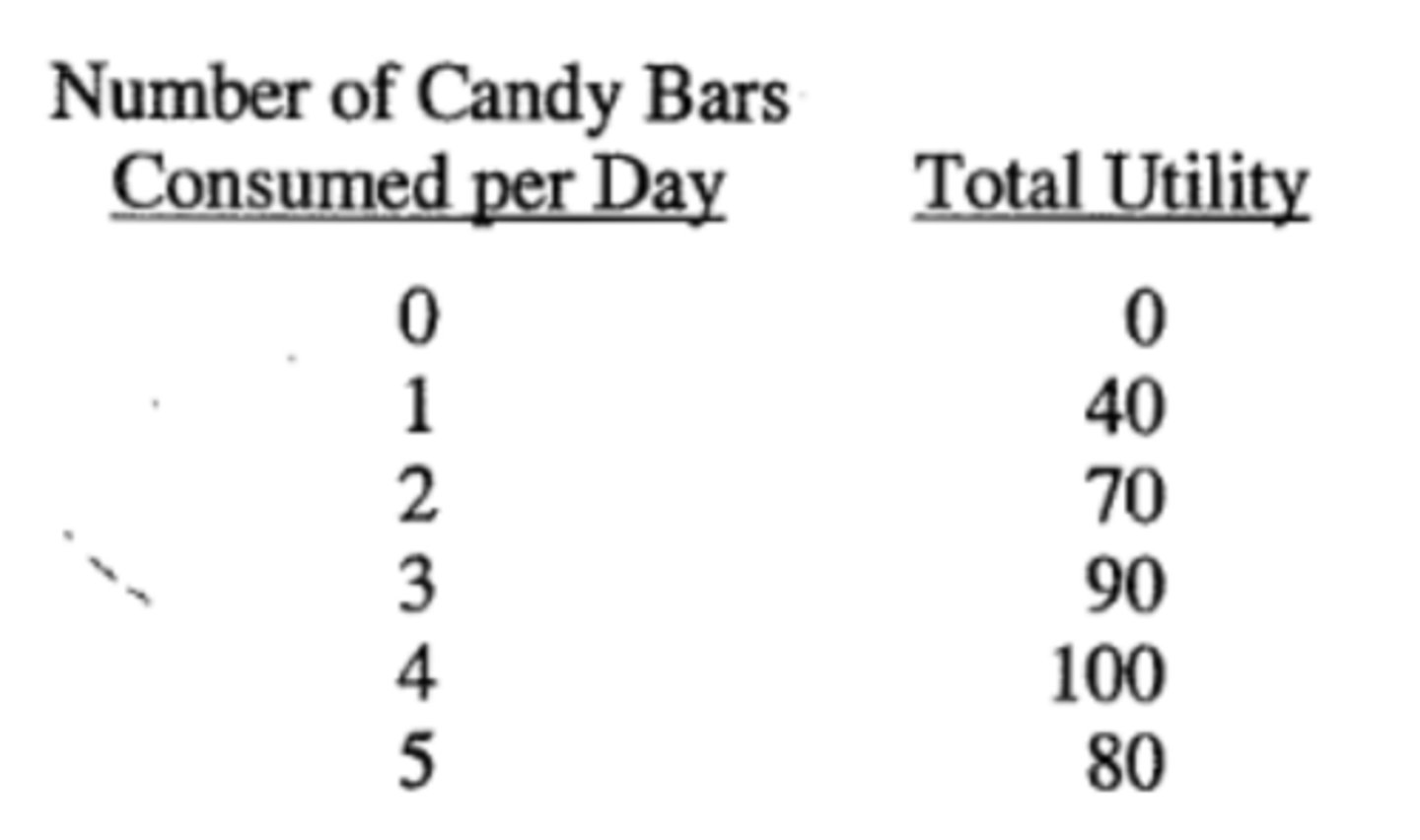
Karen works part-time at a local convenience store and earns $10 per hour. She wants to spend next Saturday
afternoon attending a music concert. The full price of a concert ticket is $75, but Karen was able to get a discounted price of $50 from a friend who purchased the ticket but has become unable to attend. If Karen took 4 hours off from her job to attend the concert, what was her opportunity cost of attending the concert?
(A) $40
(B) $50
(C) $75
(D) $90
(E) $115
answer D