GCSE Geography OCR B - Volcanoes
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
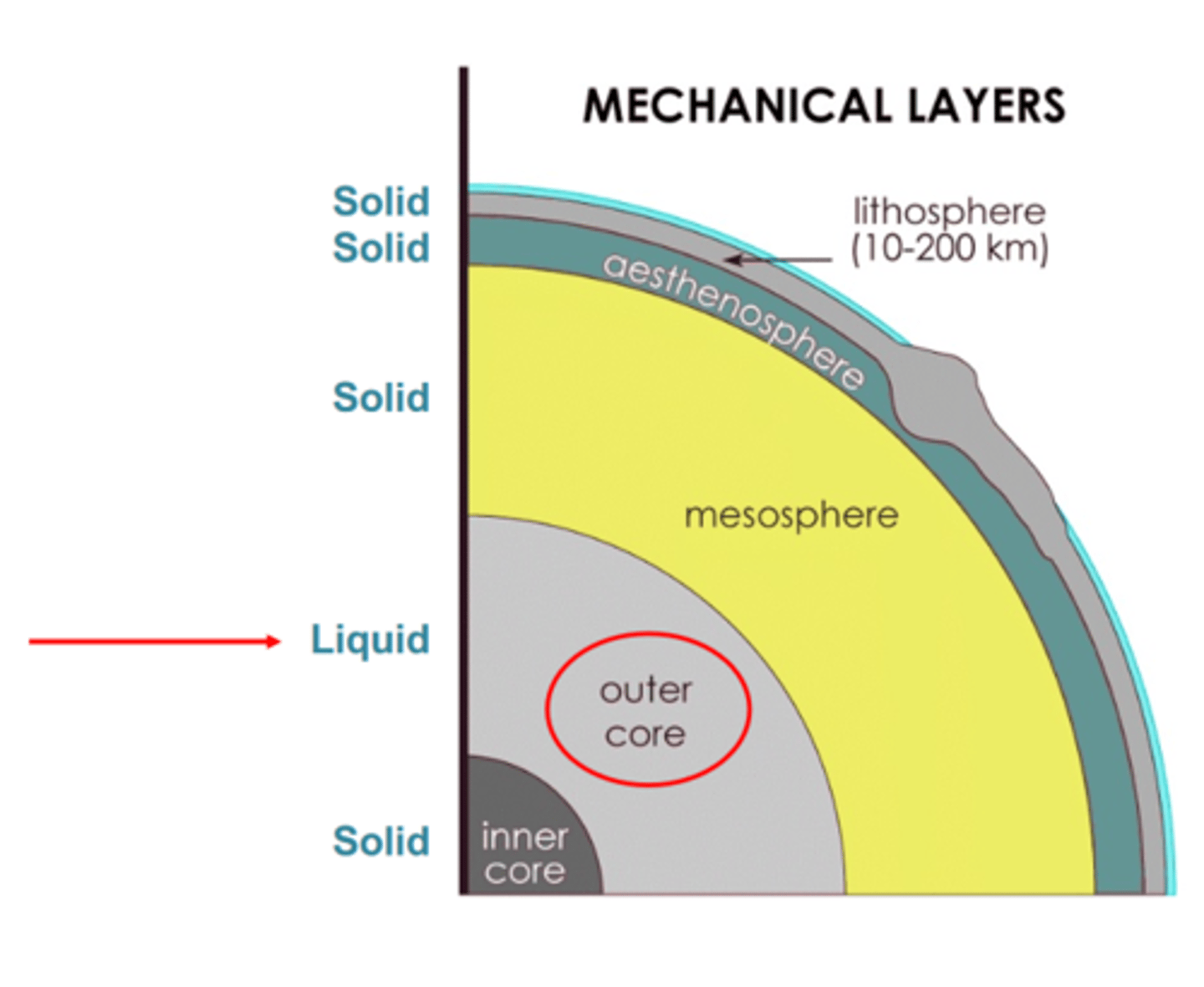
Mechanical layers of the Earth
Lithosphere - 0-100km, solid crust
Asthenosphere - 100-350km, not exactly solid
Mesosphere - 350-2900km, rigid
Outer Core - 2900-5100km, molten
Inner Core - 5100-6370km, solid, iron
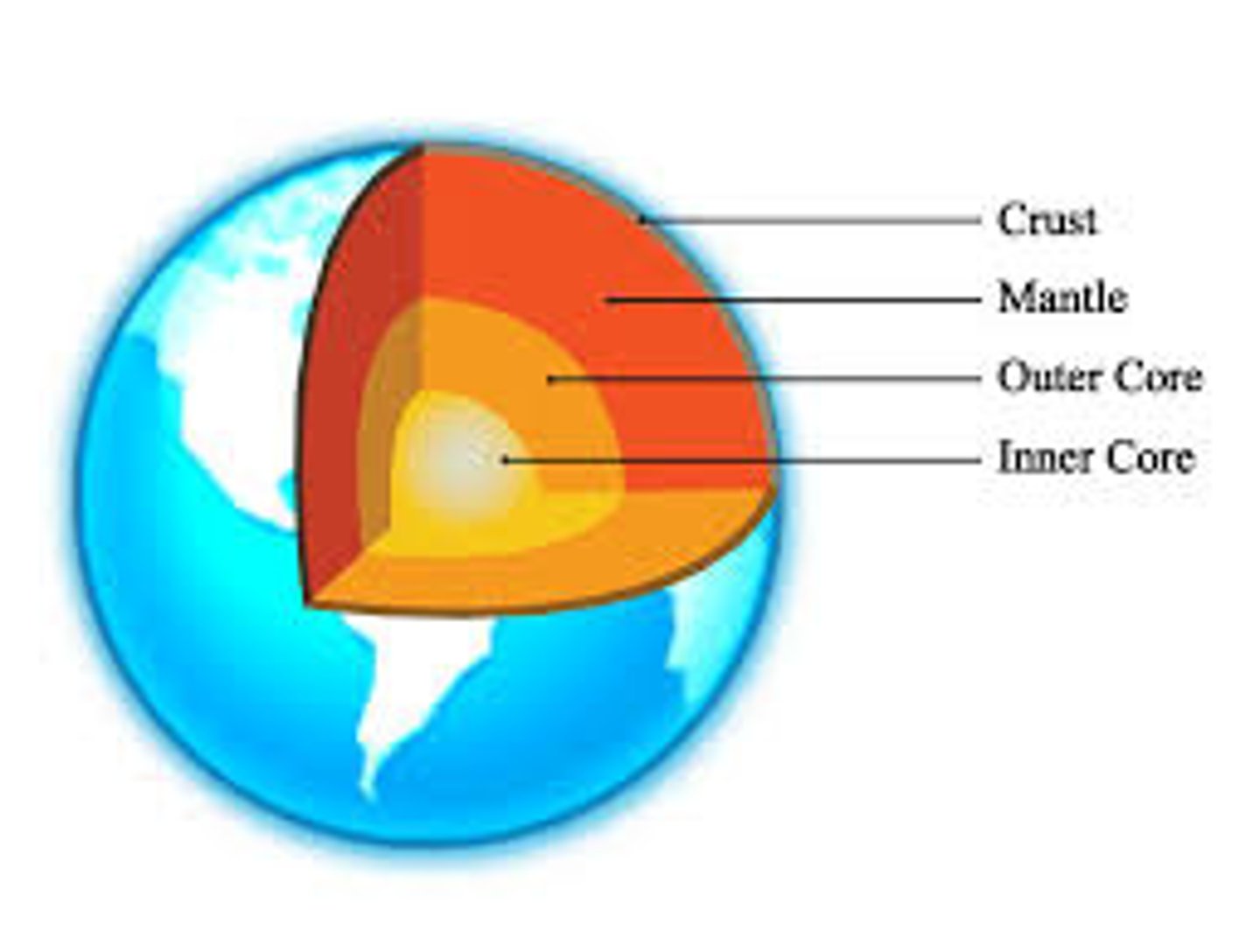
Structure of Earth
Crust - outer layer, 0-100km
Mantle - middle layer, 100-2900km
Outer Core - 2900-5100km, 5000°c
Inner Core - centre, 5100-6378km, 3000°c
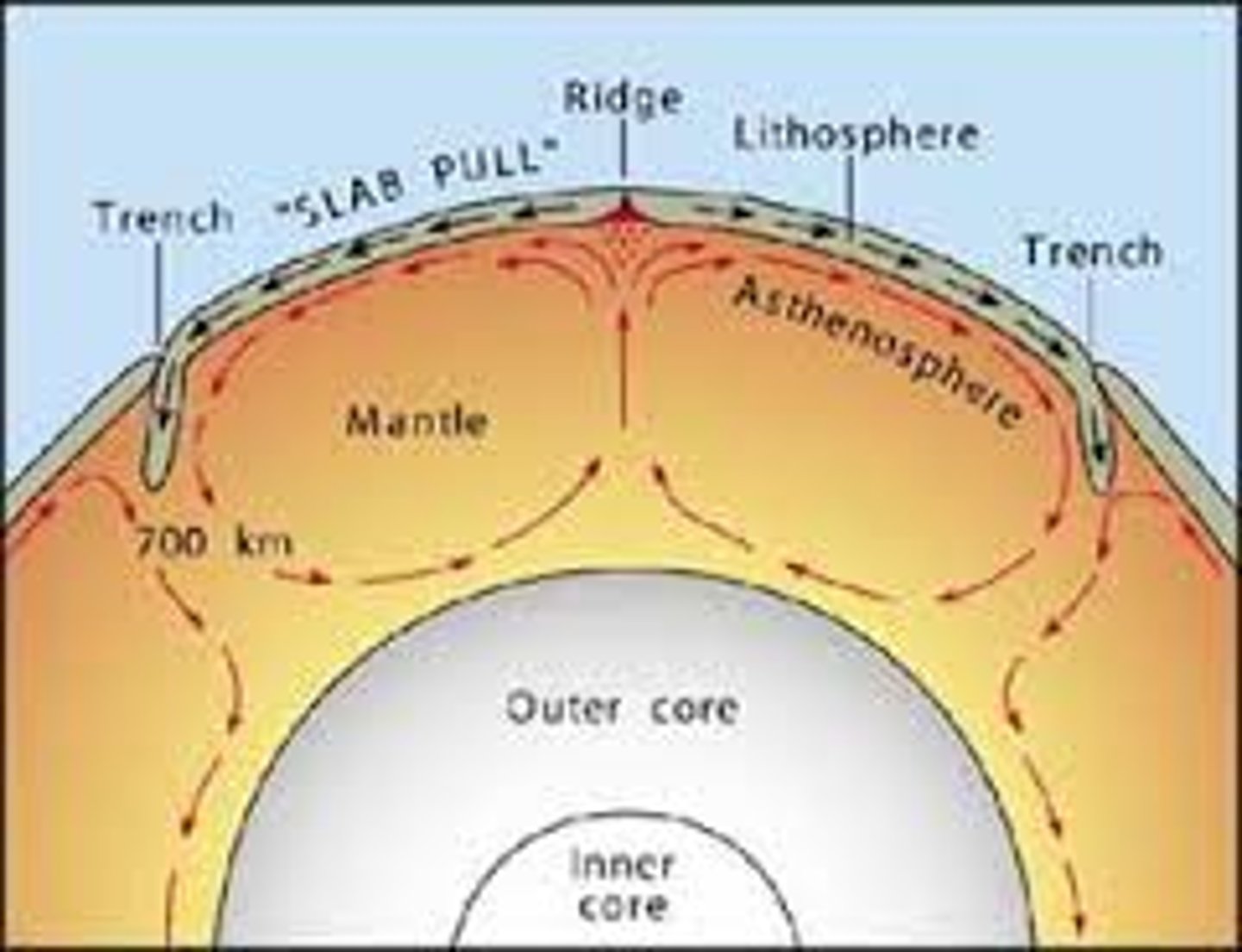
Convection Currents
Heat from the core rises to the top of the mantle
Magma heats up
Heated magma rises to the top of the mantle
Heated magma spreads to the sides
As magma cools down, it goes back through the mantle
Magma goes back down to the heat source
Crust moves in direction of magma
Oceanic Crust Vs Continental Crust
Oceanic Crust:
Heavier/Dense
Thin (6-10km)
Young (less than 200 million years)
Continental Crust:
Lighter/Less Dense
Thick (35-70km)
Old (over 1500 million years)

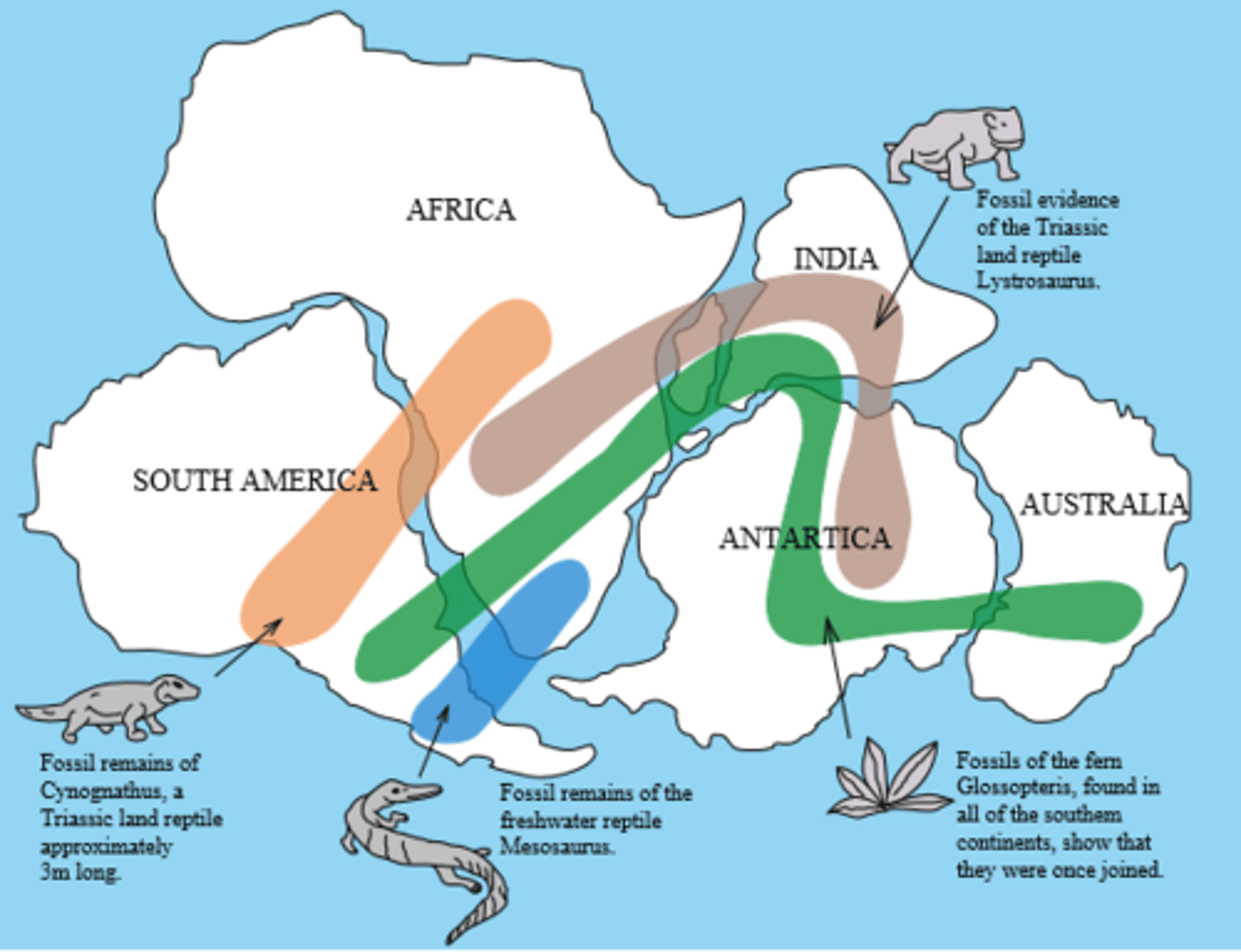
Proof of Continental Drift
Jigsaw Fit:
-Fossils and rocks of the same animal, found thousands of miles apart
-Continents look like they should fit together
-Rock types, layers and orders are the same, but thousands of miles apart
Palaeomagnetism:
-Magnetism of rocks will vary between north and south poles
-Changes magnetism every 250,000 years
-Strips of rock have different magnetisms
-New technology to find ridges on ocean floor
Seismic Waves:
-Monitoring stations monitor seismic waves bouncing off of things
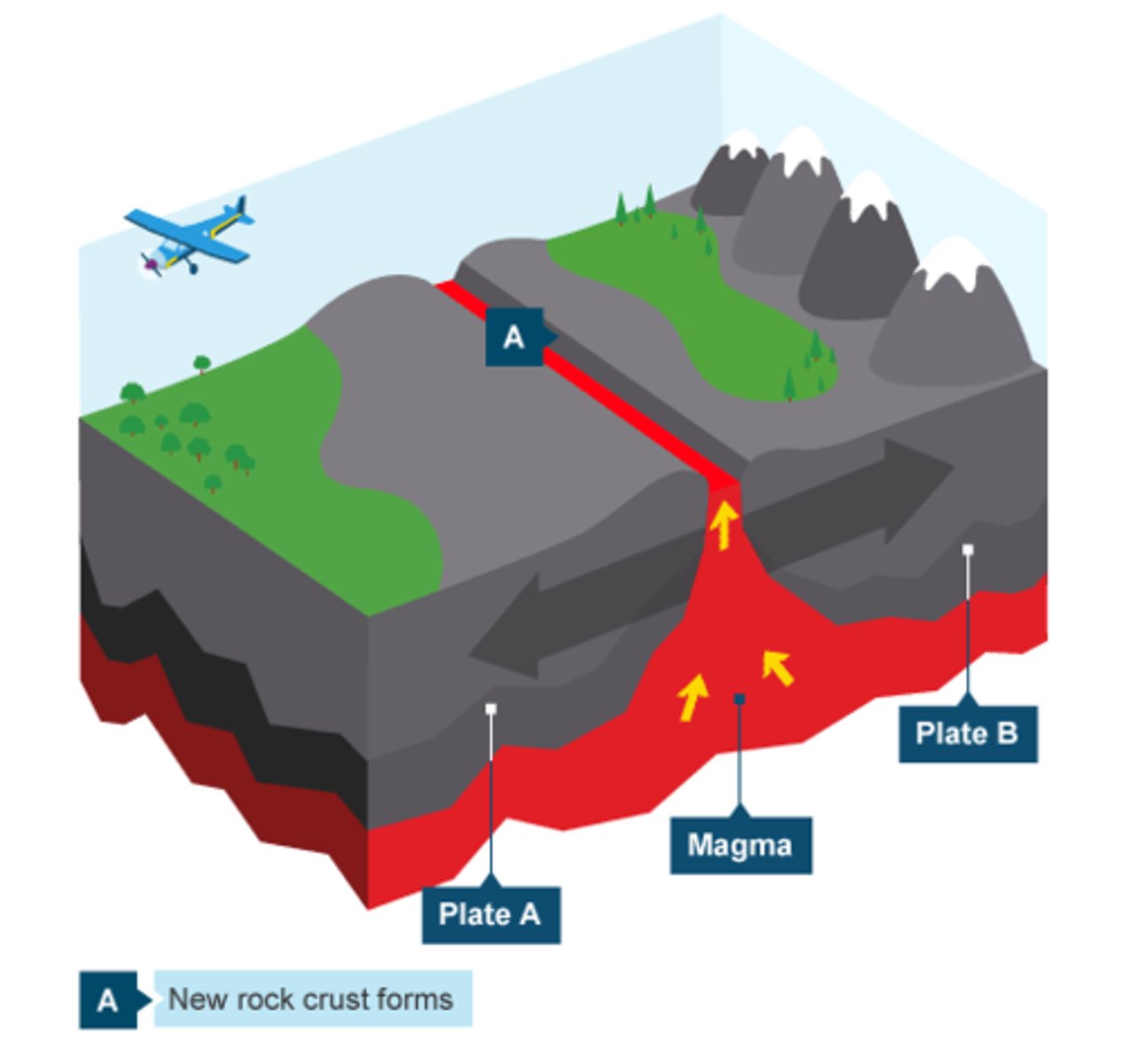
Constructive Plate Boundary
-Occurs when two plates move away from each other
-Earthquakes and volcanoes
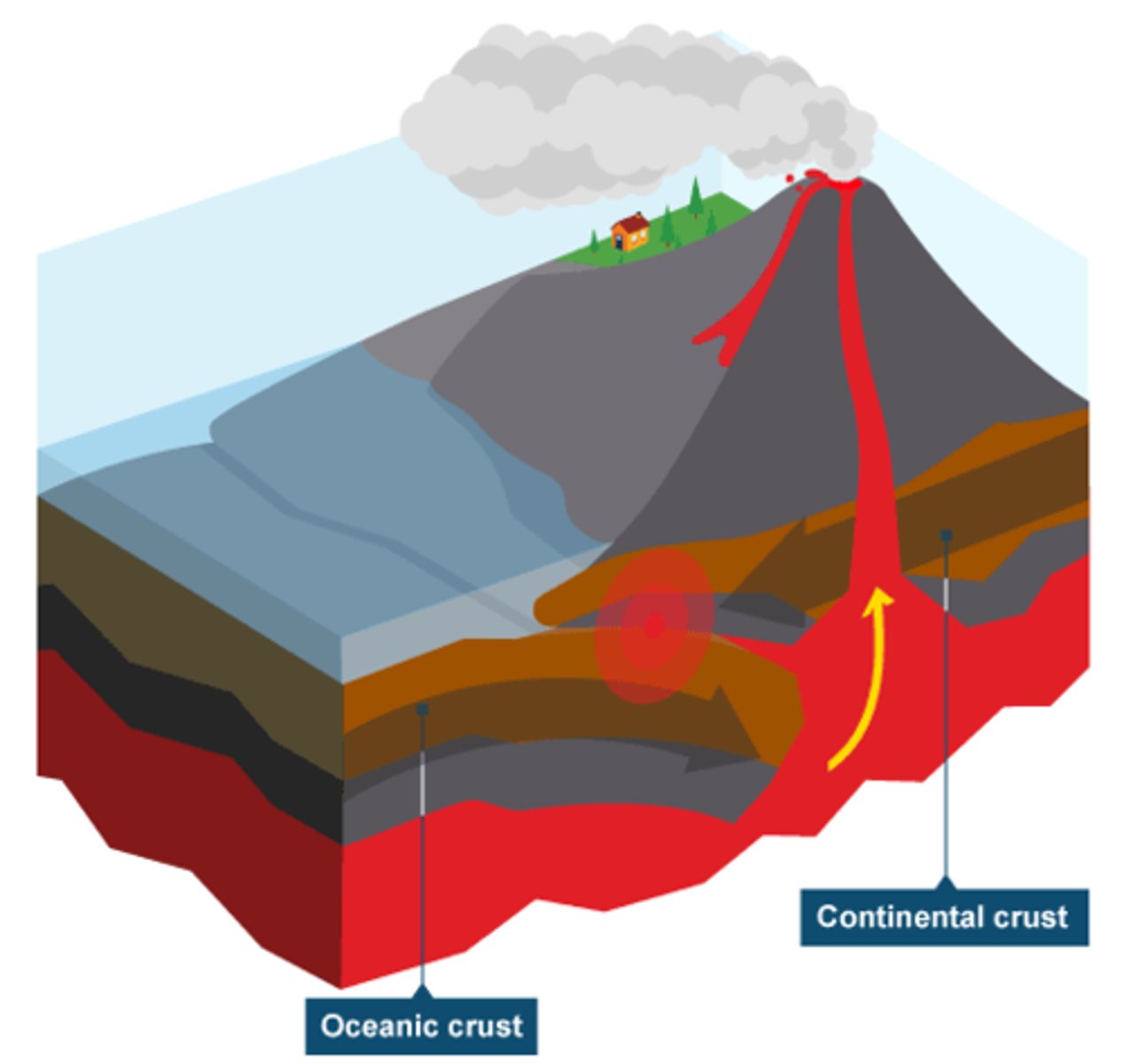
Destructive Plate Boundary
-Occurs when oceanic plate subducts the continental plate
-Earthquakes and Volcanoes
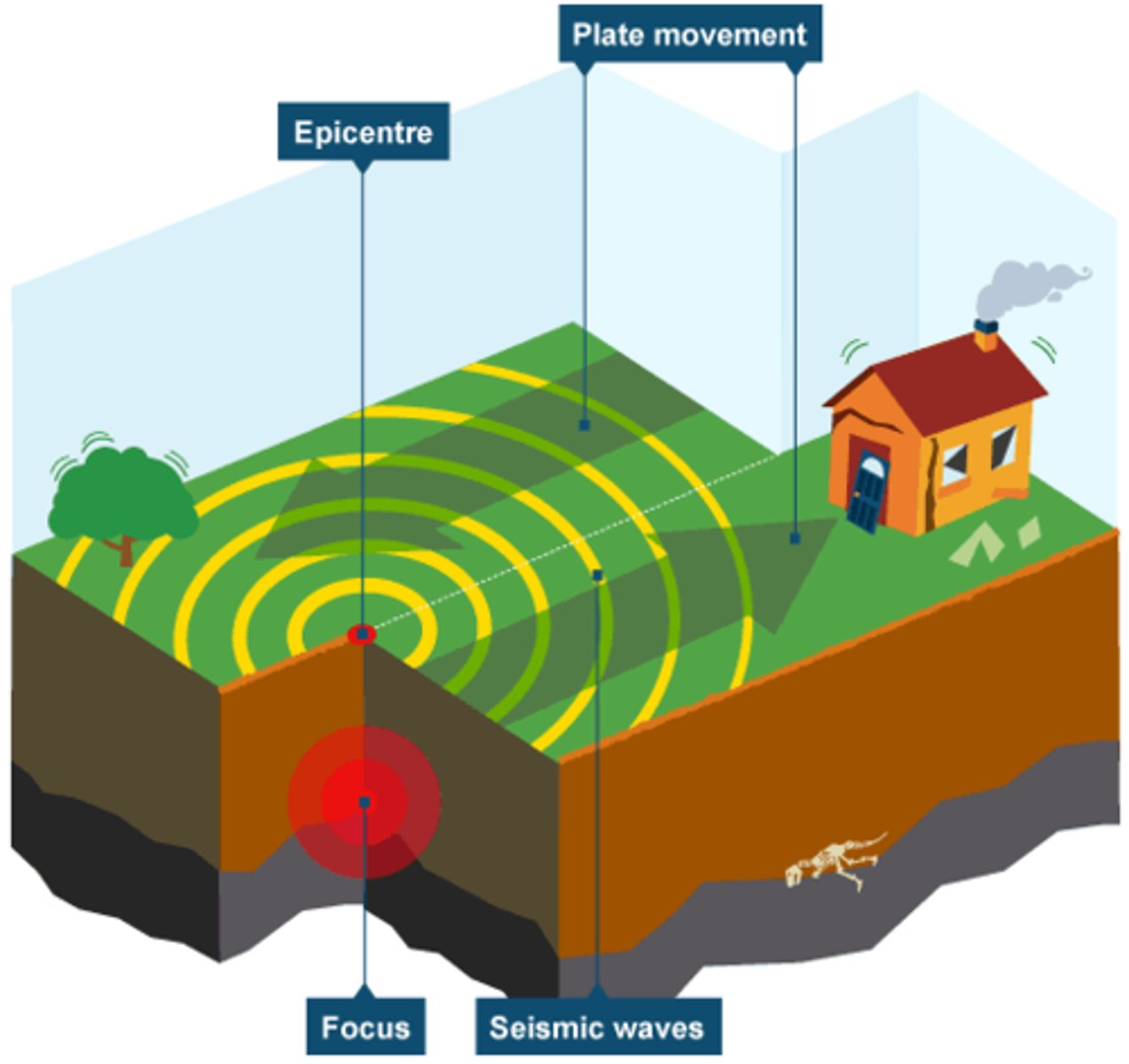
Conservative Plate Boundary
-Occurs when two plates slide past each other
-Earthquakes and Faulting
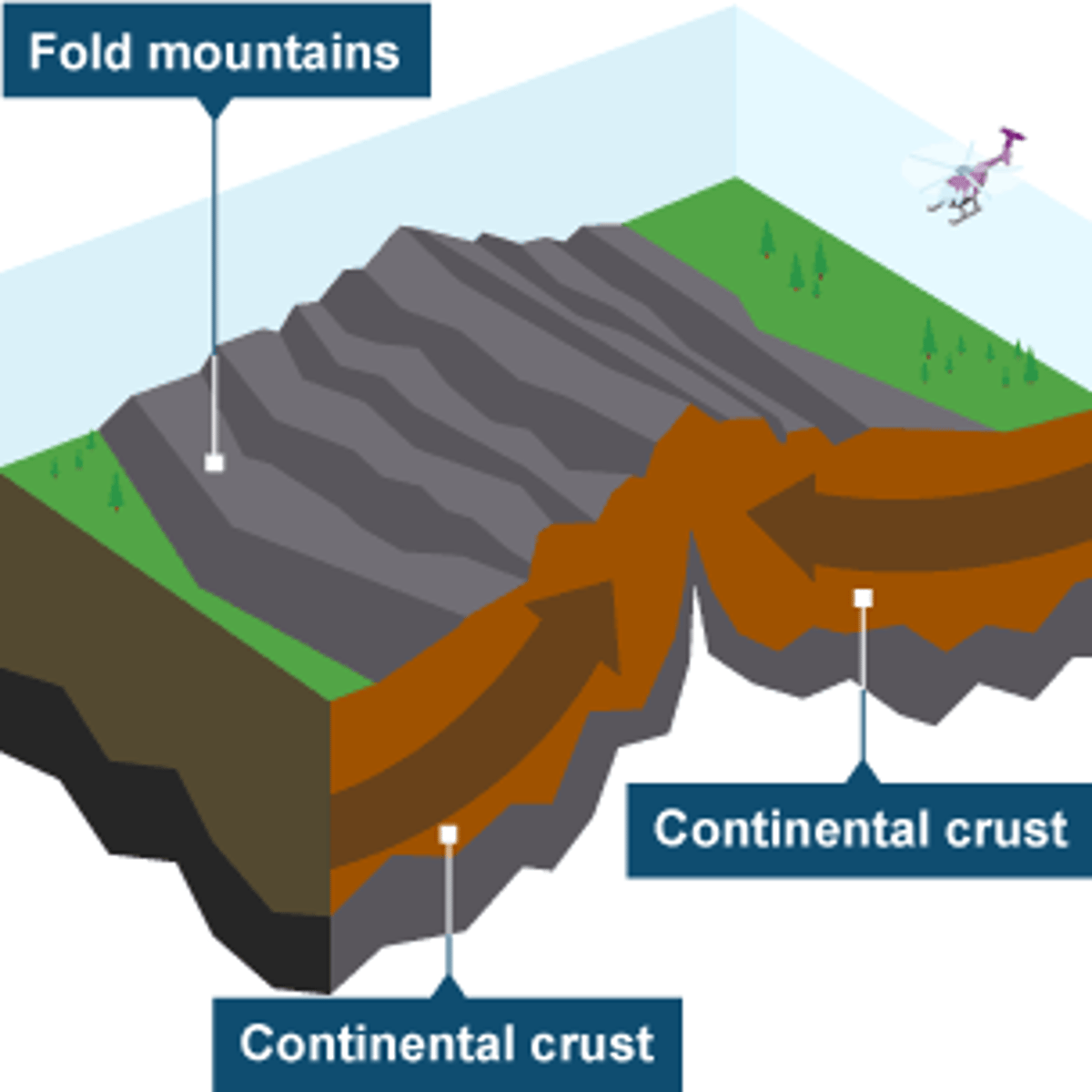
Collision Plate Boundary
-Occurs when two continental plates collide
-Earthquakes and Fold Mountains
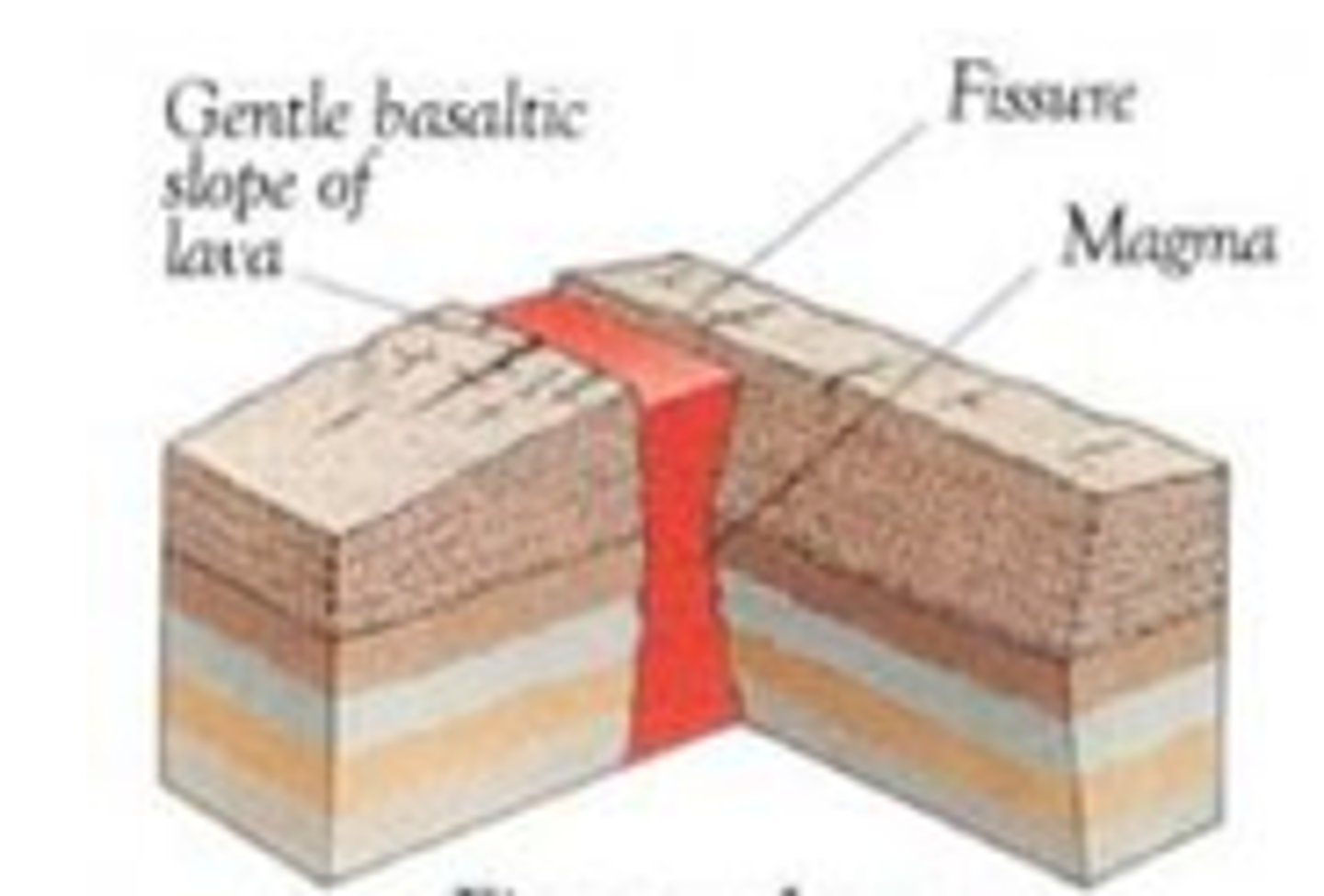
Fissure Volcano
-A long, narrow volcano that forms at cracks and weak points in the earth's crust
-Fluid, basaltic lava, "pahoehoe", effusive
-Found on Constructive plate boundaries
-Gentle and persistent eruptions
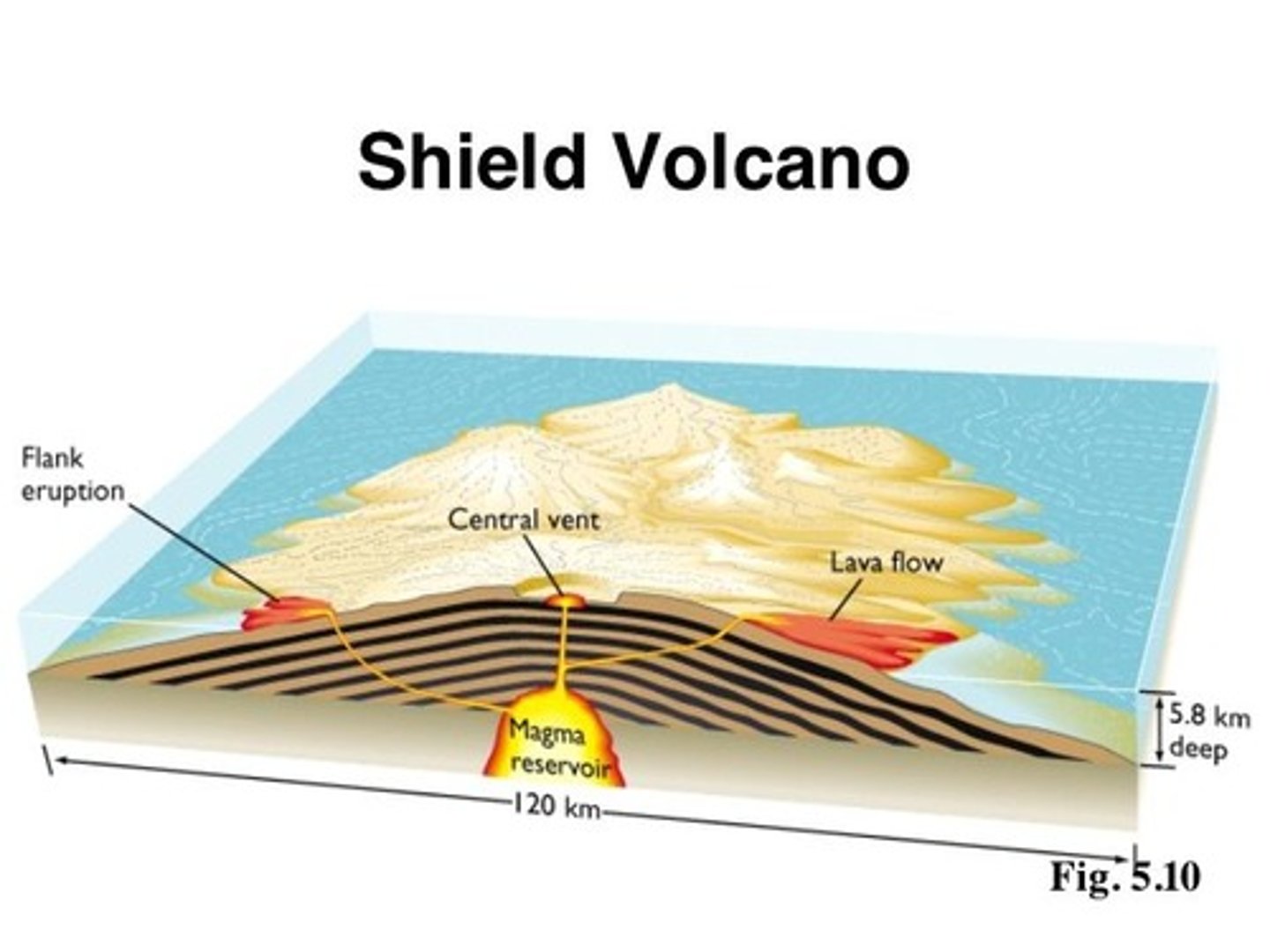
Shield Volcanoes
-Gentle, sloping sides. Low and flat
-Fluid, basaltic lava, "pahoehoe", effusive
-Found on Constructive plate boundaries or hotspots
-Gentle and predictable eruptions
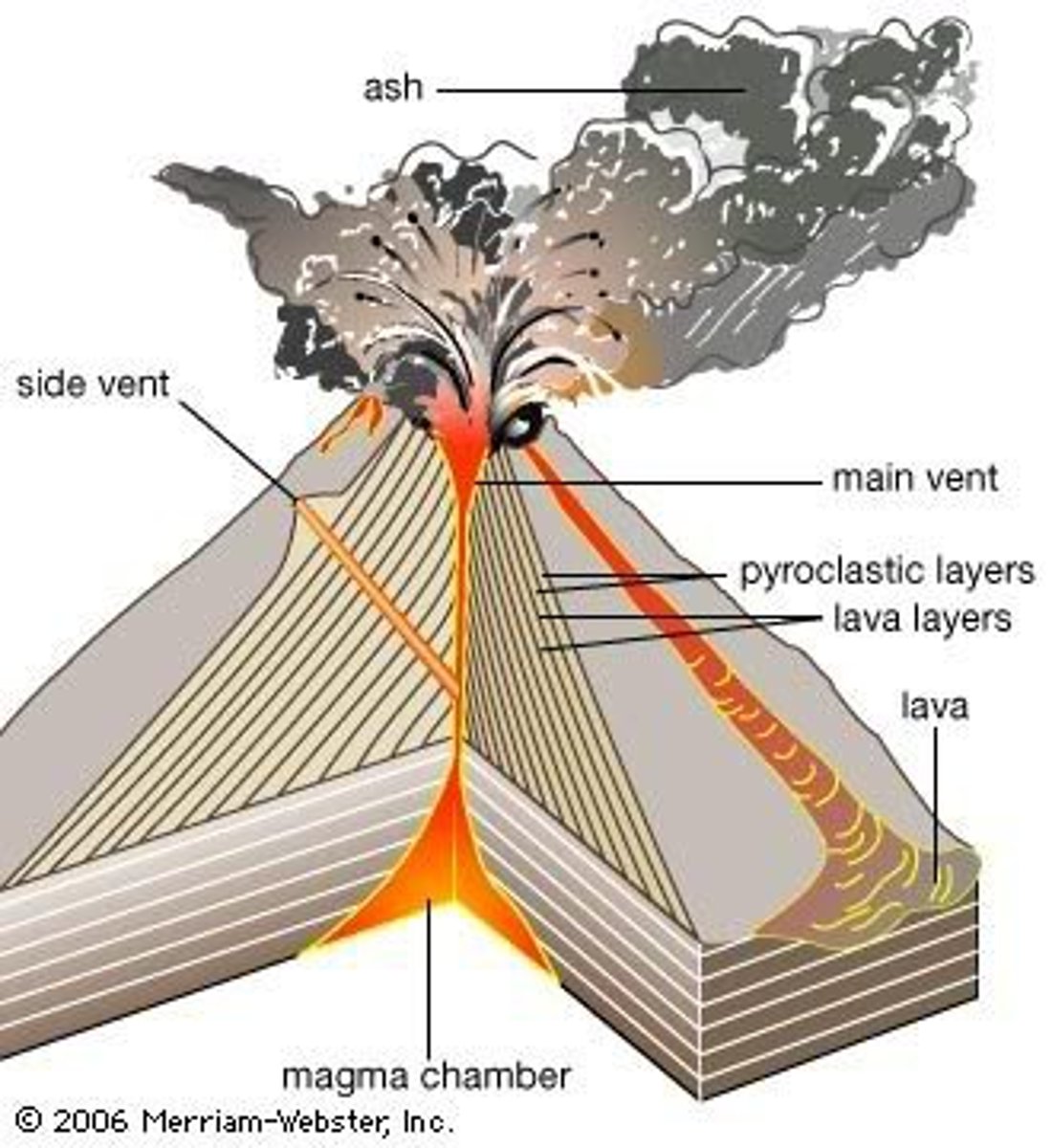
Composite Volcanoes
-A tall, cone-shaped mountain in which layers of lava alternate with layers of ash and other volcanic materials
-Viscous, sticky, high silica, lava, "aa", explosive
-Found on Destructive plate boundaries
-Explosive and unpredictable eruptions
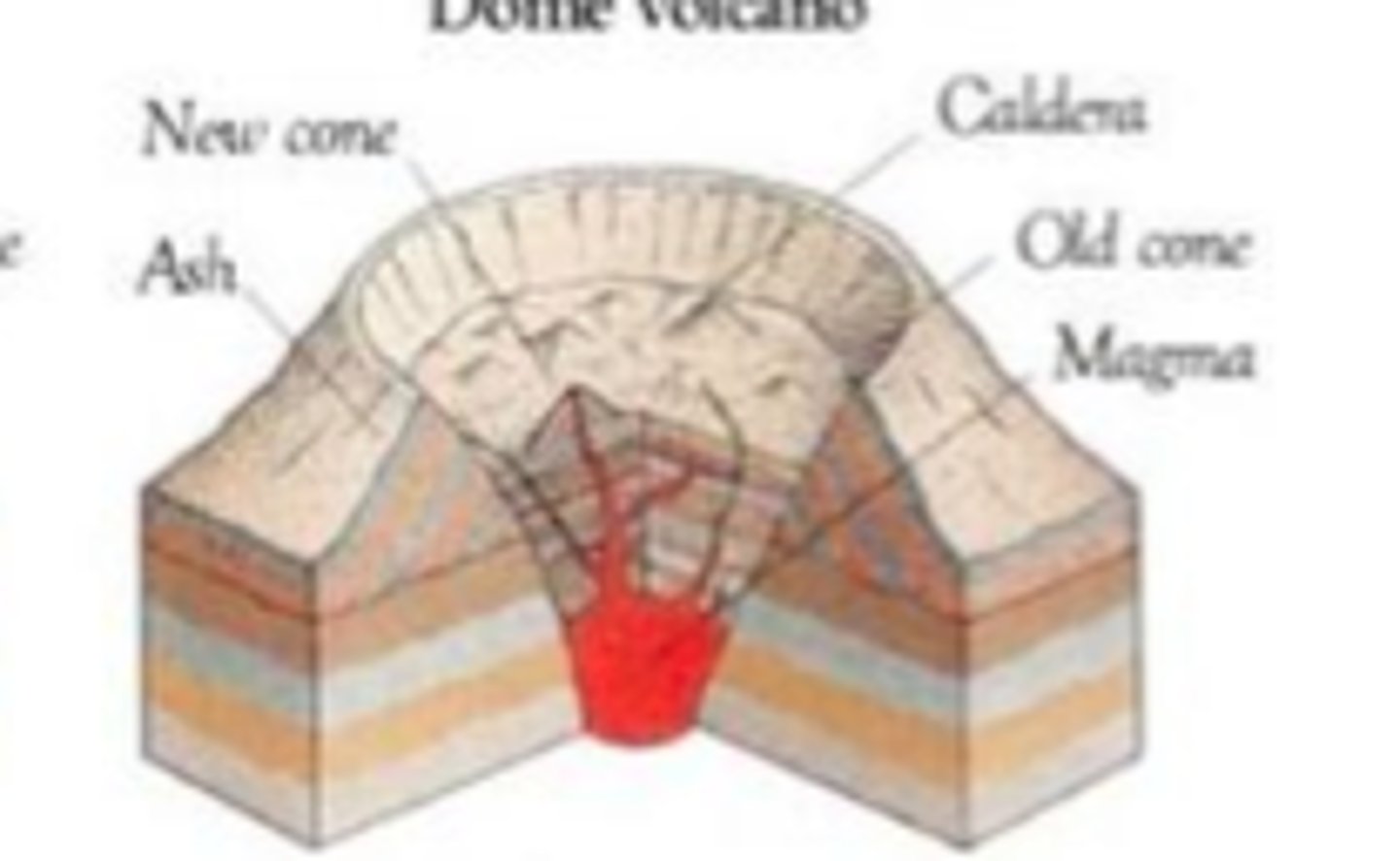
Caldera Volcanoes
-Gigantic volcanic depression, much larger than a crater; happens when magma chamber empties and the volcano collapses in
-Viscous, sticky, high silica, lava, "aa", explosive
-Found on Hotspots
-Very explosive and unpredictable
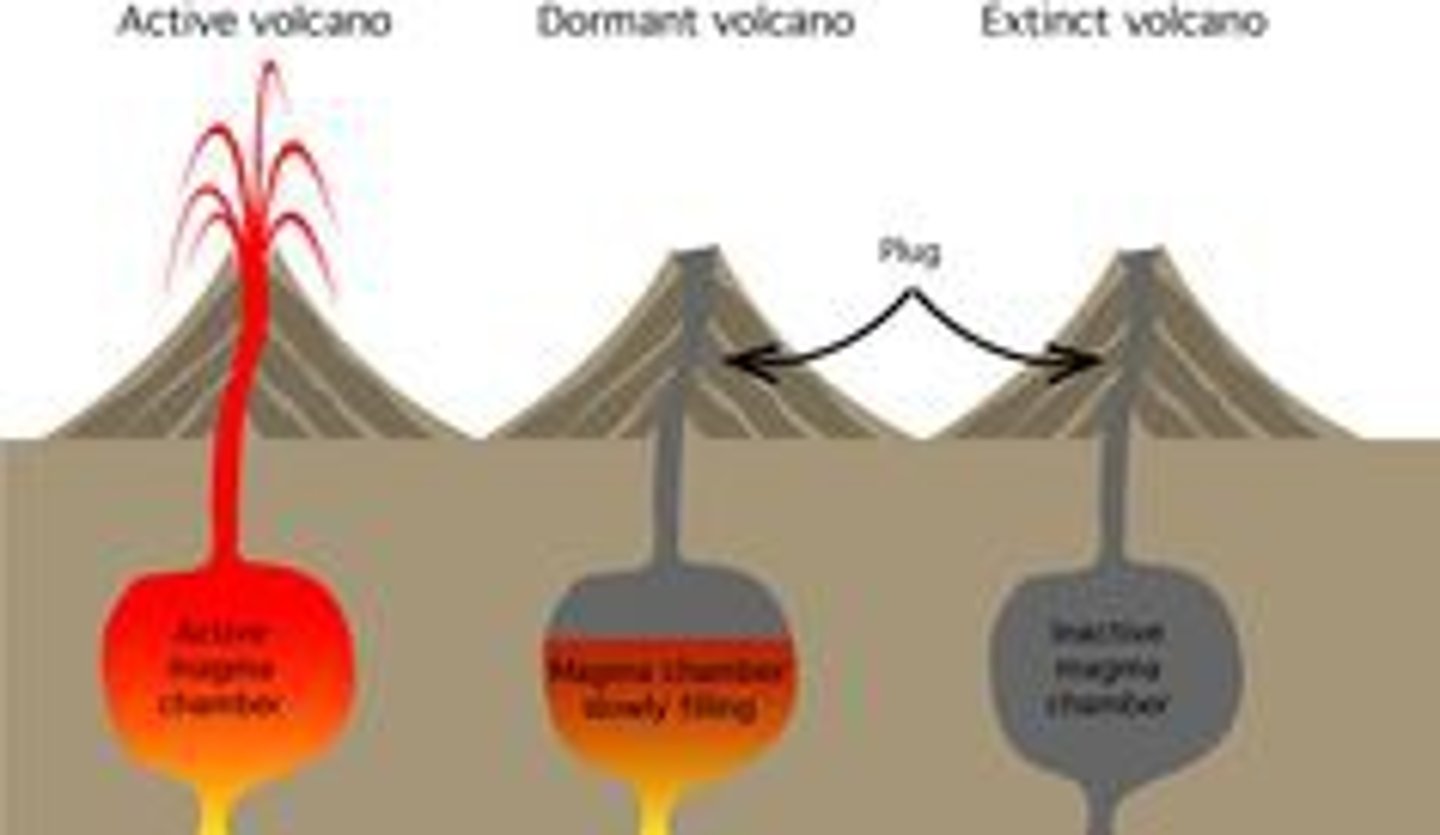
Volcano States
Extinct - never erupts again
Dormant - not erupted in 2000 years
Active - erupted recently, will erupt again
Why do people live near volcanoes?
Tourism
Precious Minerals
Geothermal Energy
Prediction/Monitoring Available
Tradition
Wealth
Good Soils

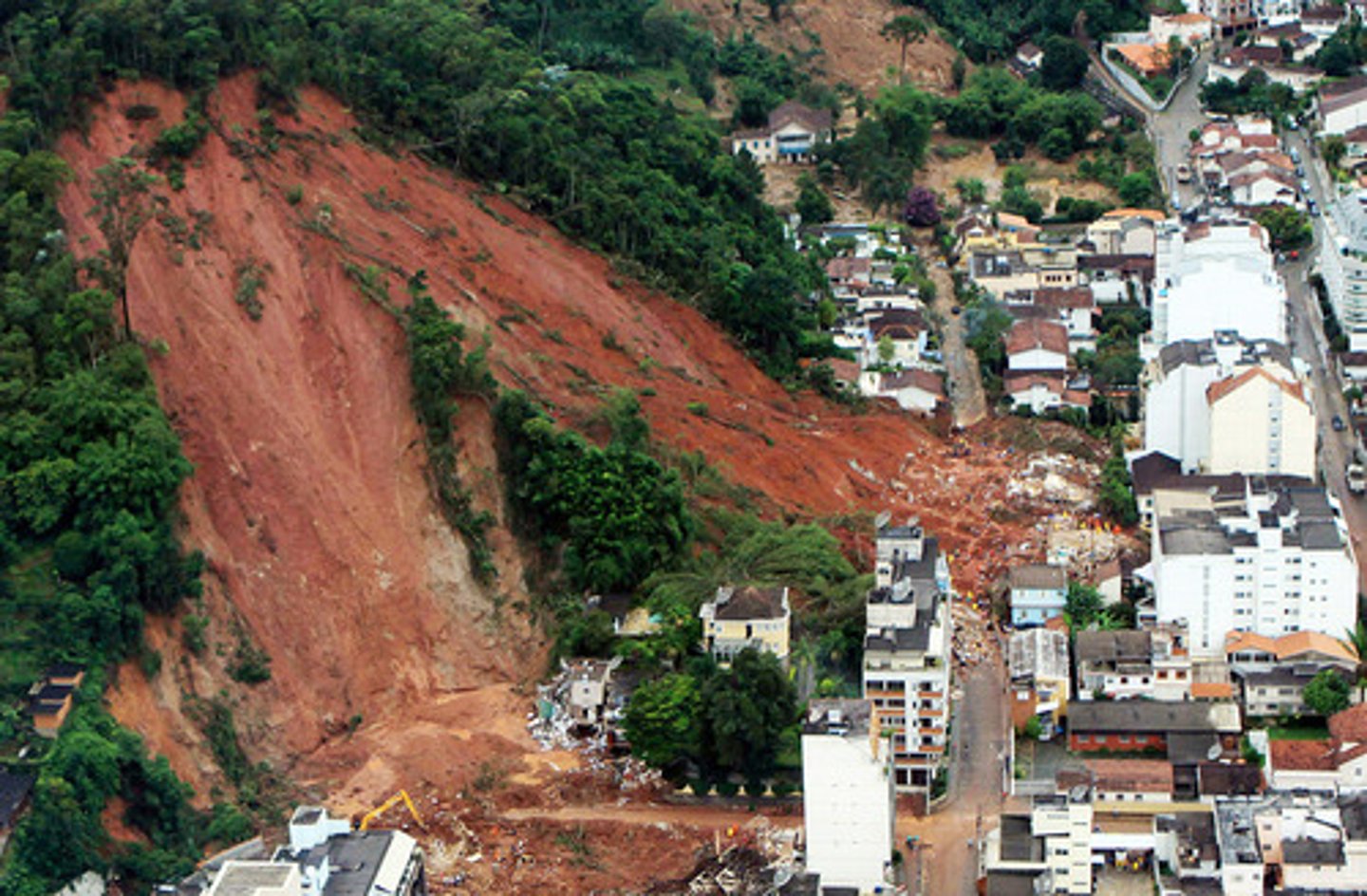
Primary Effects
-Blast, release of gasses, steam. sudden release of pressure
-Pyroclastic material, fragments of lava and rock
-Pyroclastic flows, incinerates everything in its path
-Lava flows
-Tsunami and earthquake
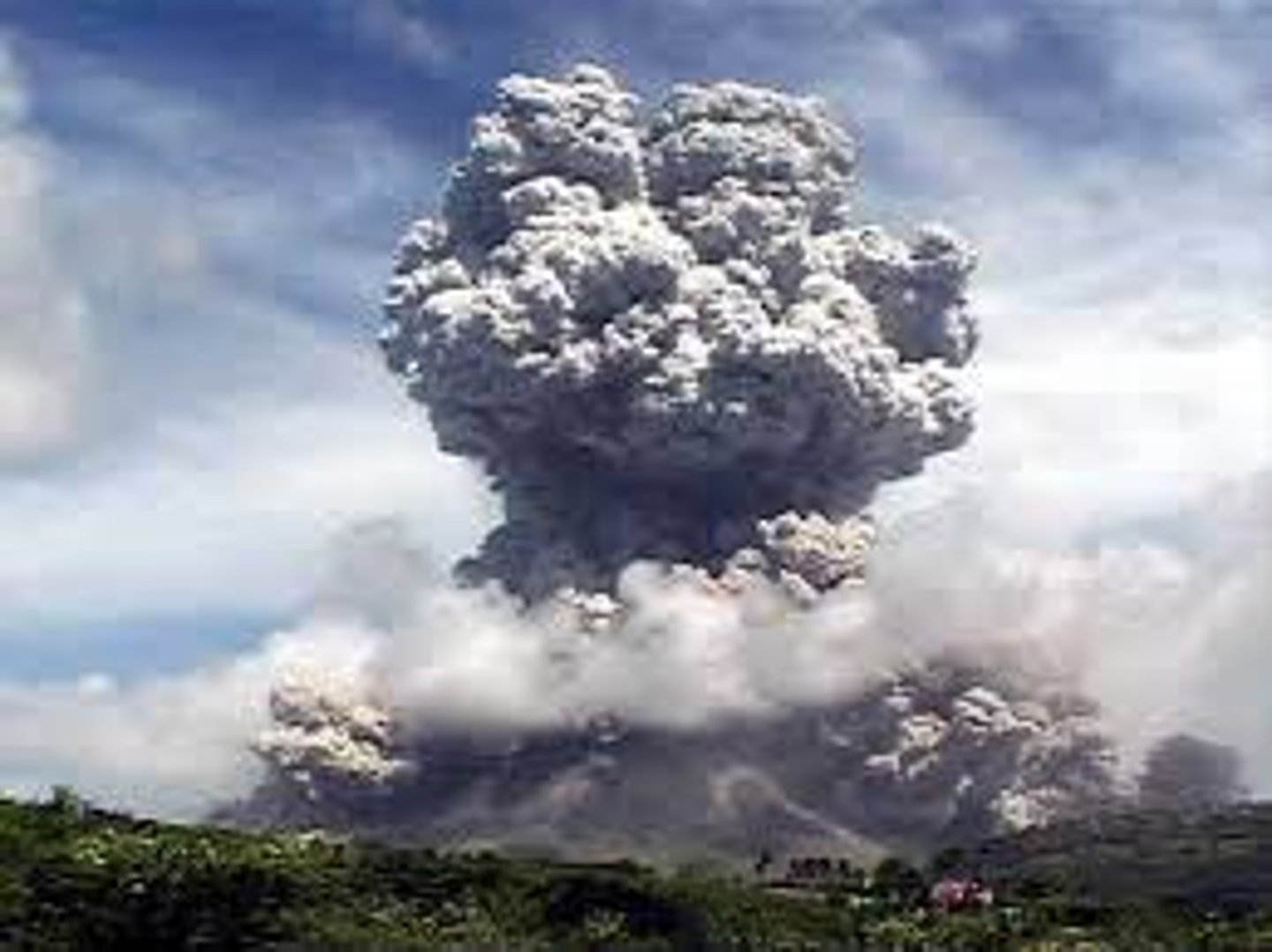

Secondary Effects
-Cloud formation, rainfall, thunderstorms
-Landslides, mudflows, lahars
-Melting ice caps
-Tsunami
