ANSC 240: Animal Production Exam #3
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
Pathogenic Organisms
Disease causing organism
Infection
Cell itself causes the illness
Intoxication
Toxins produced by bacteria causes the illness
Why are animal products high risk?
Due to a high expected microbial load
Why are muscle and milk from healthy animals considered sterile?
Skin, IS, and walls of GI tract providing protection
Contamination
Fecal, hide, hair, GI, and feather contamination
Harvest Procedures
Zero tolerance for hair, fecal, and milk; Antimicrobial washes
Temperature Control
Storage-refridgeration, perparation-cooking, hot holding, and cooling/reheating
Sanitation
Personal hygiene and equipment sanitation
Cross-contamination
The spreading of bacteria or other pathogens from one food to another
E. coli
Most strains are not pathogenic and common in animal GI tracts EHEC (STEC) and ETC are problem strains
-Symptoms: Bloody diarrhea, HUS, death
-Treatment: Not much, antiobiotics can cause a release of toxins
Shiga-toxins
Taken up by cells and inhibits protein production, linings of vessels breakdown=hemorrhaging, inability to reabsorb water
ETEC
Associated with beef products, colonizes rectum of cattle (no adverse affect on animal as it does not have shiga-toxin receptors), pathogenic but not as severe as ASTEC
ETEC Areas of Concern and Control
-Raw beef (ground beef), all other raw meat and milk are areas of concern
-Specific regulations like microbial testing required for beef carcasses and trim as well as proper sanitation and cooking
Salmonella
Found in GI tract, particularly of birds and has no real adverse impact on animals, is usually self limiting and extreme cases can result in hospitalization
Salmonella Areas of Concern and Control
-Raw meat, especially in poultry
-Proper sanitation and cooking
Listeria
L. monocytogenes and is a main concern and found in environment rather than species, grows at refrigerated temperatures, and dangerous for pregnant women and immuno-compromised people
Listeria Areas of Concern and Control
-Precooked items
-Proper sanitation, cooking, regulations for RTE, production testing, and interventions
Toxoplasma Gondii
Animal derived productions and contaminated drinking water, most immune systems keep in check (can stay in body for long period of time), dangerous for pregnant women and immuno-compromised people
Toxoplasma Gondii Areas of Concern and Control
-In raw animal products
-Proper cooking and sanitation
Campylobacter
Common foodborne pathogen in poultry and dairy, control usually involves sanitation and temperature control
USDA
-FSIS: Public health and meat/egg inspection
-APHIS: Animal welfare
-Food and Nutrition Service: Education and assistance with health

FDA
-Foods: Labeling, safety of food productions except meat and poultry
-Drugs: Human and vet
-Pesticides: Share with USDA and EPA
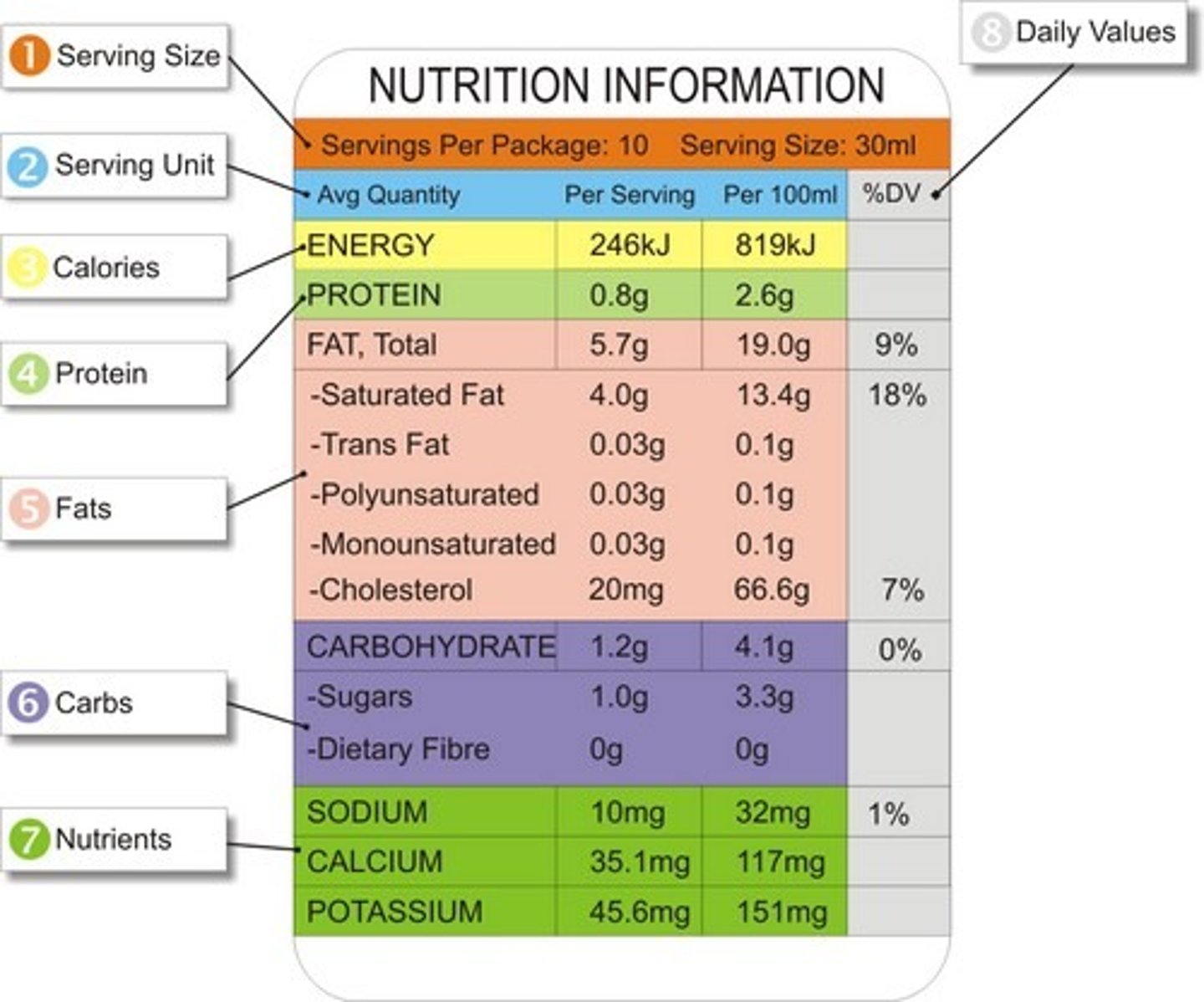
Inspection
Product dependent on animal health, processes, ingredients, etc. and also ensures products are as safe as possible for consumers before purchasing
Labelling
Clear communication to consumers and process verification (everyone follows the same "rules")
How do people influence process verification?
People are willing to pay for things that contain certain attributes (real or perceived) and guarantee is needed for consumers to have trust
What does process verification allow for?
Consistent interpretations, assurances to consumers, but does not speak to other implied attributes
National Foods Protection Act of 1990
Final rule published in 2000, and arguably most stringent process verification and focuses on animal origin, feed, housing, healthcare, and processing
Meat and Poultry Products (Organic)
Livestock fed 100% organically grown feed and forage with no synthetic hormones and vaccinations, no pesticides on pastures, no sewage sludge, and must be raised from birth to organic standards
Meat and Poultry Products (Organic) Labelled
100% organic and contains organic ingredients
Antibiotics in Livestock Production
Treatment of infections, prevention of infections and performance (low levels in feed improves feed efficiency-gut health and ADG increase)
What does increased antibiotic use lead to?
Increase in population of antibiotic resistant bacteria (impacts drug efficiency)
US Companies and Antibiotics
Have begun to phase out antibiotics (big push for this in 2015) and poultry industry is the main industry to capitalize on this and every major broiler producer has segment of business antibiotic free and currently more than without
Halal
Islamic food laws
Kosher
Jewish food laws
Slaughter Practices for Religious Dietary Constraints
Religious practitioner present or performing harvest, stunning not allowed although animals are restrained, addition carcass inspection to make sure it meets criteria on purity
Why are CFO/CAFO controversial to communities?
Concerns trace to manure: Environmental concerns, odor concerns, health concerns
Concerns with Manure Management
How much manure and storage, major concerns, manure managed to mitigate concerns, new tech/practices to prevent contamination and "odor events"
Operation and Manure Management
Must estimate how much manure is generated (EX: 1, 200 lb pig= about 75 square ft of manure per year)
Lagoon
Traditional method, still used in new, especially dairy, operations, basin to store waste, decomposes, 2x year applied to field as fertilizer

Deep Pit
Pit immediately under floor holding animals- slotted floor, periodically pumped as fertilizer

Challenges with Manure Storage
Cracks in liner, potential spills when pumping, open top leads to odor (lagoon)
Positives to Manure Fertilizer
N, P, K, organic matter (increases soil stability, decreased erosion and water holding)
Drawbacks to Manure Fertilizer
Must be managed (too much of a "good thing"- N and P can be bad), must apply based on soil needs, soil testing needed (what does soil have/need and what are nutrient capacities), excessive manure could have runoff into water
Organic P and Animals
Not readily digested by animals and passes into manure= more P than plants need, use manure to get N can overshoot P, too much P leads to algae blooms which can use up unavailable O so fish die
N in Manure
Very active and can escape so mineralization process of N is key (organic N to inorganic N), organic N is not always available to animals, inorganic is although volatile
N Cycle
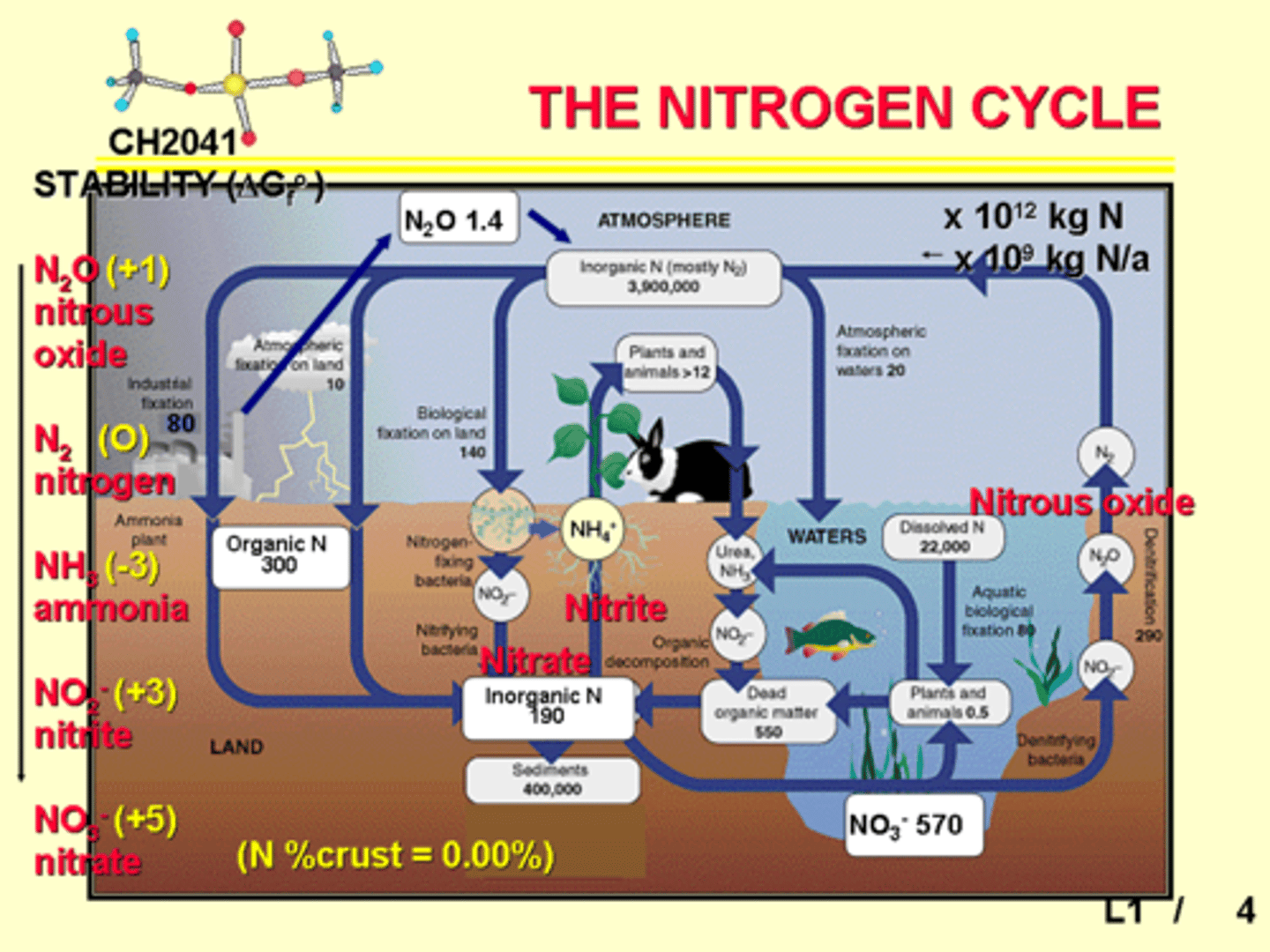
Challenge with N
As N loss increases, P concentration/issues increase
Retaining N
Microbes use organic N and N in AA in soil, then microbes will get N from wherever they can (inorganic N) impacts C in soil and ration to C is important (too little C= microbes trap inorganic N and make it unavailable to plants; too much C= volatility and odor increase)
N in Lagoons and Spraying Manure
-P and K will settle to bottom, increased N in top= more N loss, agitation can reduce this
-Surface= increased N loss, soil incorporation can reduce
IDEM Regulations
Confined feeding control law, confined feeding operation rules, concentrated animal feeding operations rule
-Focus is more on manure management to protect water
Define Setback (minimum distance structure can be from certain point)
-Water on surface: 100-300 ft
-Public water: 1000 ft
-On-site water supply: 100 ft
-Off-site residential or public building: 400 ft
Other Rules
Public notification, waste storage capacity, plot and farmstead map, nutrient management plant, soil and manure testing plan
Office of the Indiana State Chemists
Fertilizer use, distribution, and record keeping, focus is on protecting water, rules on how and where manure can be applied, must use licensed applicator (some special rules for CFO) and county level might have more regulations
County Level
More regulations like use of buffers, minimum lot sizes, odor standards, transportation standards, additional application standards, and distance solves most conflicts except odor
Modelling Odor Management
Can be modeled and determine distance (buffer) for neighbors but difficult to estimate
Odor Causes
Fresh manure (high concentration of intestinal bacteria which produce metabolites, gases, etc. decompose organic matter and other things), agitated manure (bacteria population change)
Main Gases
Methane (odorless and made by methagenic bacteria and knock out in high quantities), CO2 (odorless and asphyxiant), CO (odorless and poison), Amonium (pungent and irritant), H2S (pungent and poison), several trace metabolites
What affects odor?
Wind frequency, topography factor, orientation and shape factor, building odor emissions, animal #, odor emission factor, building design and management factor, manure removal frequency, manure dilution (swine), dry (poultry) or residue (dairy) factor, odor emission from outdoor storage, animal weight, abatement in and out of building
Methagens
Bacteria in manure that make methane that can survive in anerobic conditions and connects H to CO2 to make methane byproducts, found in rumen and microbes create energy and protein and digests fibrous feed, and some methane escapes via belches and the farts of monogastric animals
Methane
Major greenhouse gas related to animal agriculture and in 2006 UN stated livestock GHG emissions=18% (higher than transportation) although later many issues were found with this estimation like the math being off
Greenhouse Emissions in Developed Countries
-Energy: 31%
-Transportation: 26%
-Livestock/Food: 3.4% (cattle=1.4%)
GHG Research
Global warming potential (ability of gas to trap heat and methane is produced and used at different rates, and methane impact on the environment has been overestimated 4x), CO2 (stock gas stays in environment, CH4 is a flow gas that is produced and then destroyed), GWP* (new metric accounting for short livespan)
Reducing GHG
Using it with anerobic/methane digesters (decompose manure, microbes break down to biogas and digested solid), biogas (60% methane, 40% CO2, 0.3% Hydrogen Sulfide, 1/4 of the heating value of propane, highly corrosive, storage not practical)
Covered Anerobic Lagoons
Dairy and swine industry, needs impermiable flexible cover and manifold to collect gas, manure with less than 2% solids and needs warm climates with cold climates mainly using it for odor control
Complete Mix
Engineered tank above or below the ground, manure can be 3-10% solid, can operate in all climates
Plug Flow
Manure can be 11-13% solids and manure can operate in all climates, has not been used well in swine operations
Distillers Grains
From producing ethanol
Hooves and Horns
Adhesives, plastics, plant food, pet food, lamination, gelatin
Swine- Internal Organs
Insulin (pancreas), heart valves
Sheep- Lanolin
Cosmetic products (name brands), adhesives, printing ink
Poultry- Eggshells
Cleaning applications, soil amendments
Poultry- Feathers
Pillow stuffing, plastics, feather meal
Poultry- Comb and Shell Membrane
Hyaluronic acid (traps moisture)
All Livestock- Fat and Fatty Acids
Solvents, gum, paint, lubricants, cream and lotions
All Livestock- Skin/Hide
Leather, sports equipment, gelatin
All Livestock- Hair
Brushes, air filters
Blood
Cultural bacteria, glue, adhesives
Intestines
Sausage casings, instrument strings, sutures
Horizontal Integration
Each entity is owned by a different company (Price keeps going up- EX: beef)
Vertical Integration
Owned by 1 company (2 or more segments) and primarily used for poultry (meat and layers) and swine
Integrator
Owns multiple production portions (feed mill and transport)
Grower
Actually raises animals and contracts with integrator
Market Contract
Common in the swine industry, less farrow-to-finish and more grower/finisher operations, grower agrees to sell set # of animals at set time for set price (animals are owned by grower)
-Contract based on future market and assumption of prices
-Guarantees market timing and price is set and avoids market volatility (real price goes up or down... no change to payment)
Production Contract
Common for poultry industry, and grower agrees to raise animal and provide housing, equipment, labor/husbandry, and manure management according to standards set by integrator (think: renting service- animals owned by integrator)
-Producer provides everything but animals and feed
-Contract is usually base/guaranteed price but premiums are possible (total # of animals to market, F:G, competition between growers to meet metric)
-Pay out based on performance, contract, and # of buildings/animals you contract
Pros to Production Contracts
-Decrease some risk as it is spread out among entities
-Decrease initial investment and good for starting operations
Cons to Production Contracts
-Integrator has great deal of control (metrics, practices, expansion)
-Producers can't contract with 2 integrators at once
-Housing standards may= re-investments
-Imbalanced negotiations
Ovine
Refers to sheep family
FEC
Measurement of internal parasite burden in ruminant animals
Parasite Resistance
Ability of parasites to survive and reproduce despite exposure to anthelemintic treatments
Shearing
Act of cutting off wool
Genetic Component
Animal specific basis
Ewe
Female sheep any age
Broad Ewe
Female sheep of advanced age
Ram
Intact male sheep for breeding
Wether
Castrated male sheep
Lamb
Sheep of any sex under 1 year of age
Birth
Called lambing, 8-12 lb live weight, processed 2-5 days (introduced to flock), tail docked, castrated via hot knife, band, or surgical means
Weaning
Weaned at 60-90 days of age
Feed Lot
Finishing weight 120-140 lb