Ch. 10 - The Foreign Exchange Market
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Foreign Exchange Market
Market for converting the currency of one country into that of another country
Exchange rate
the rate at which one currency is converted into another
2 functions of the Foreign Exchange Market
Enables conversion of the currency of one country into the currency of another.
Provides some insurance against foreign exchange risk
Foreign Exchange Risk
the adverse consequences of unpredictable changes in exchange rates
Currency Conversion is used to:
convert export receipts, income received from foreign investments or income received from licensing agreements.
To pay a foreign company for products or services.
To invest spare cash for short terms in money markets
Currency Speculation
short-term movement of funds from one currency to another in hopes of profiting from shifts in exchange rates
Carry Trade
borrows one currency where interest rates are low and invests these in another currency where interest rates are high
Hedging
A firm that protects itself against foreign exchange risk
What are ways the market performs hedging
Spot exchange rates.
Forward exchange rates.
Currency swaps.
Spot Exchange Rates
Rate at which a foreign exchange dealer converts one currency into another currency on a particular day
How are spot exchange rates determined?
by the interaction between supply and demand
Forward exchange rates
two parties agree to exchange currency and execute the deal at some specific date in the future (usually quoted 30, 90, or 180 days)
Currency Swap
Simultaneous purchase and sale of a given amount of foreign exchange for two different value dates
When are currency swaps used?
when it is desirable to move out of one currency into another for a limited period without incurring foreign exchange rate risk
Arbitrage
process of buying a currency low and selling it high
What are Important Factors Impacting Future Exchange Rate Movements?
A country’s price inflation.
A country’s interest rate.
Market psychology.
Law of One Price
identical products sold in different countries must sell for the same price when the price is in the same currency
what does Purchasing Power Parity do in efficient markets?
predicts that changes in relative prices result in changes in exchange rates
efficient markets
markets in which few impediments to international trade and investment exist—the price of a “basket of goods” should be roughly equivalent in each country
If we can predict inflation rates
we can predict how a currency’s value might change
Growth of a country’s money supply determines
its likely future inflation rate
inflation occurs
When the growth in the money supply is greater than the growth in output
Empirical Tests of P P P Theory
Indicates it is not completely accurate in estimating exchange rate changes in the short run but relatively accurate in the long run
The purchasing power parity puzzle
Assumes away transportation costs and barriers to trade.
Governments routinely intervene in trade and foreign exchange market.
Investor psychology plays a role on exchange rate movements
Fisher effect
a country’s nominal interest rate (i) is the sum of the required real rate of interest (r) and the expected rate of inflation over the period for which the funds are to be lent (I)
International Fisher effect (IFE)
for any two countries, the spot exchange rate should change in an equal amount but in the opposite direction to the difference in nominal interest rates between the two countries.
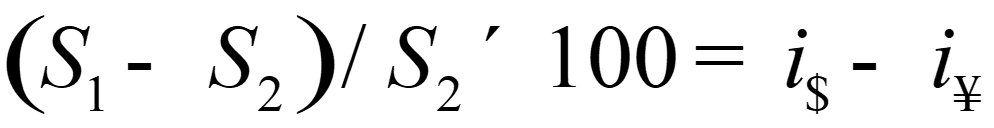
Bandwagon effect
occurs when expectations on the part of traders turn into self-fulfilling prophecies, and traders join the bandwagon and move exchange rates based on group expectations. gov can intervene
The Efficient Market School
prices reflect all available information.
Forward exchange rates are the best predictors of future spot exchange rates.
Investing in forecasting services is a waste of money
The Inefficient Market School
prices do not reflect all available information.
Forward exchange rates are not the best predictors of future spot exchange rates.
Companies should invest in forecasting services.
Approaches to Forecasting
Fundamental and Technical Analysis
Fundamental analysis
Draws upon economic factors like interest rates, monetary policy, inflation rates, or balance of payments information to predict exchange rates
Technical analysis
Uses price and volume data to determine past trends that are expected to continue
Freely convertible
both residents and nonresidents can purchase unlimited amounts of foreign currency with the domestic currency
Externally convertible
only nonresidents can convert their holdings of domestic currency into a foreign currency
Nonconvertible
both residents and nonresidents are prohibited from converting their holdings of domestic currency into a foreign currency
capital flight
when residents and nonresidents rush to convert their holdings of domestic currency into a foreign currency.
countertrade
barter-like agreements by which goods and services can be traded for other goods and services—to facilitate international trade
Transaction exposure
extent to which the income from individual transactions is affected by fluctuations in foreign exchange values
Translation exposure
impact of currency exchange rate changes on the reported financial statements of a company
Economic exposure
extent to which a firm’s future international earning power is affected by changes in exchange rates.
Lead strategy
collecting foreign currency receivables early when a foreign currency is expected to depreciate and paying foreign currency payables before they are due when a currency is expected to appreciate
Lag strategy
delaying collecting foreign currency receivables if the currency is expected to appreciate and delaying payables if the currency is expected to depreciate